A Comprehensive Study on EMI Shielding Performance of Carbon Nanomaterials-Embedded CFRP or GFRP Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. EMI Shielding Performance Test
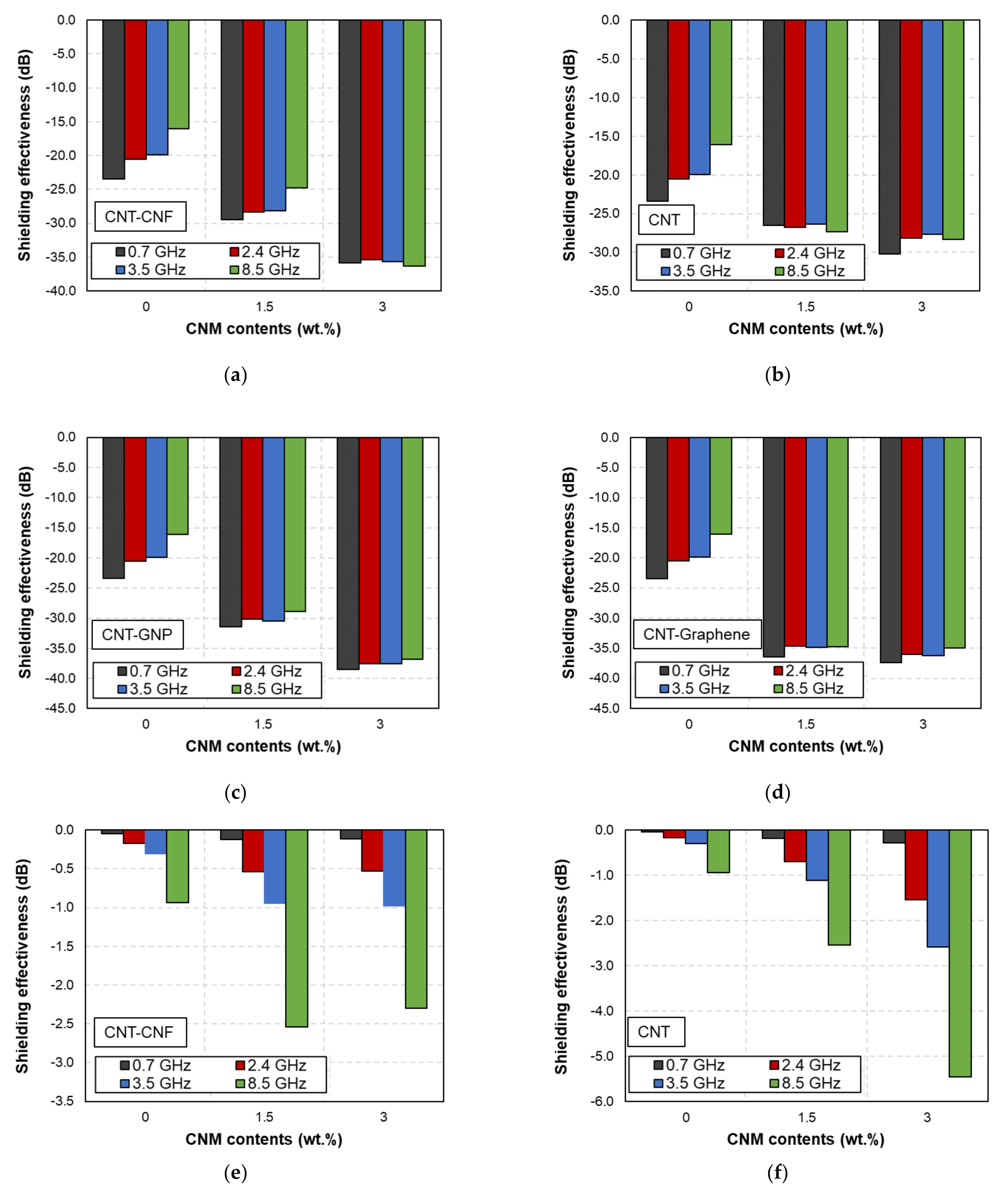
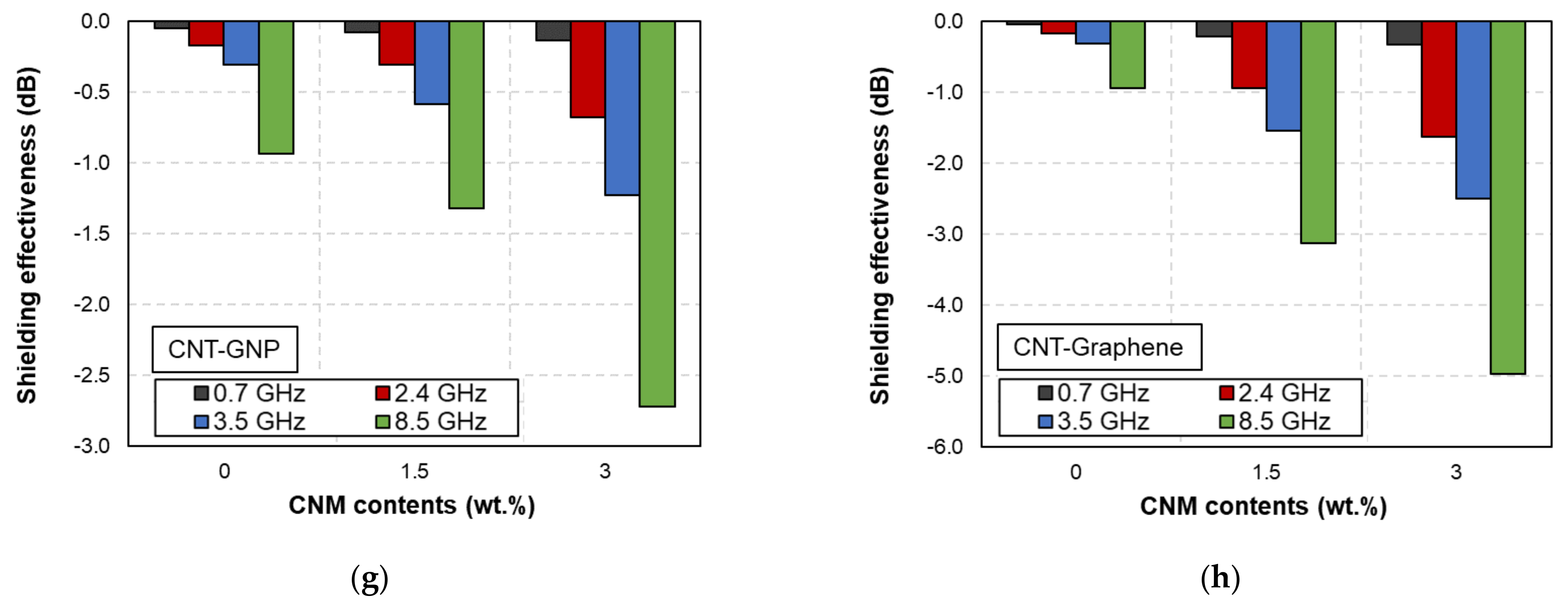
3. Results and Discussion
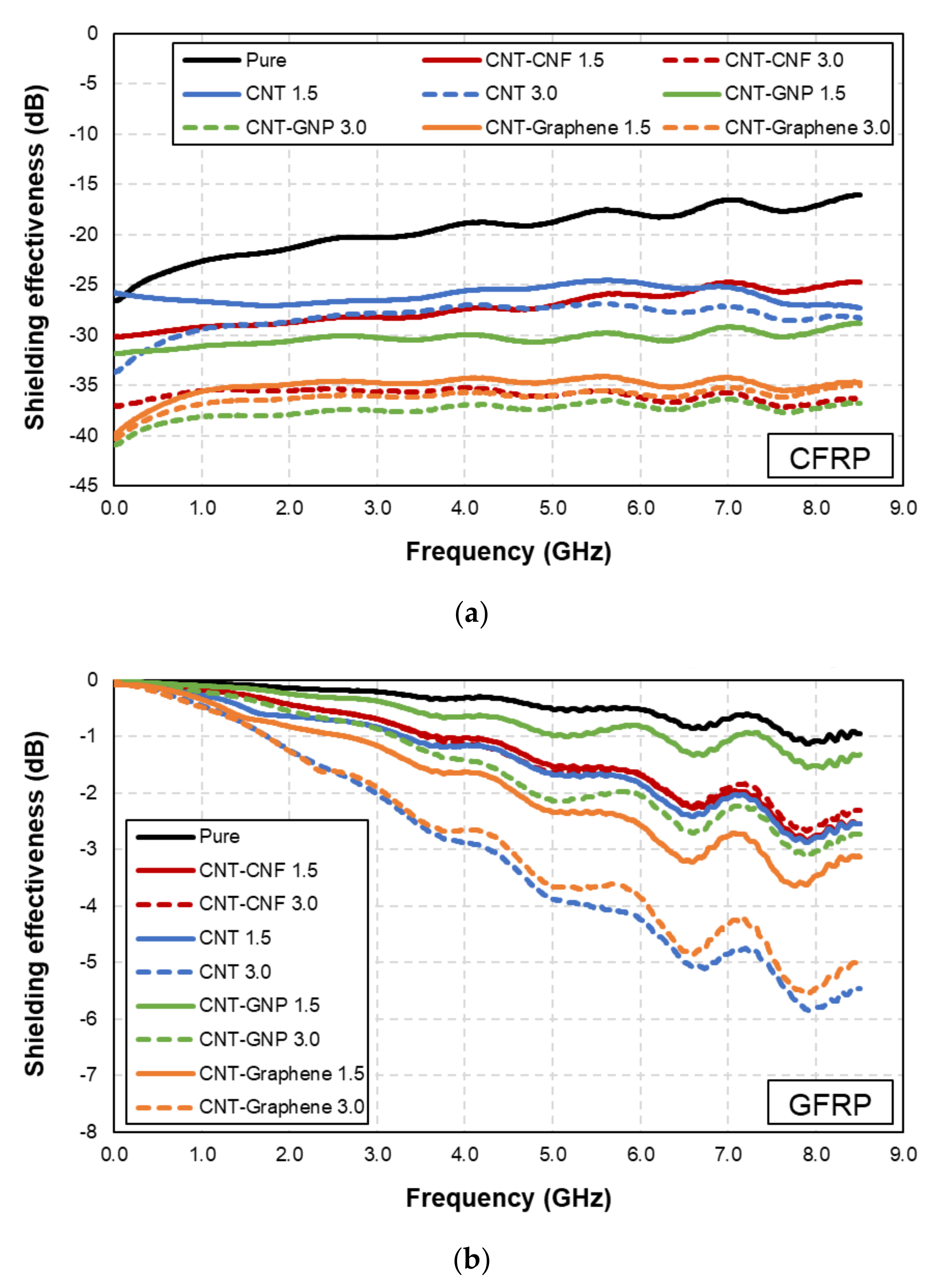
3.1. EMI Shielding Effectiveness as a Function of Frequency
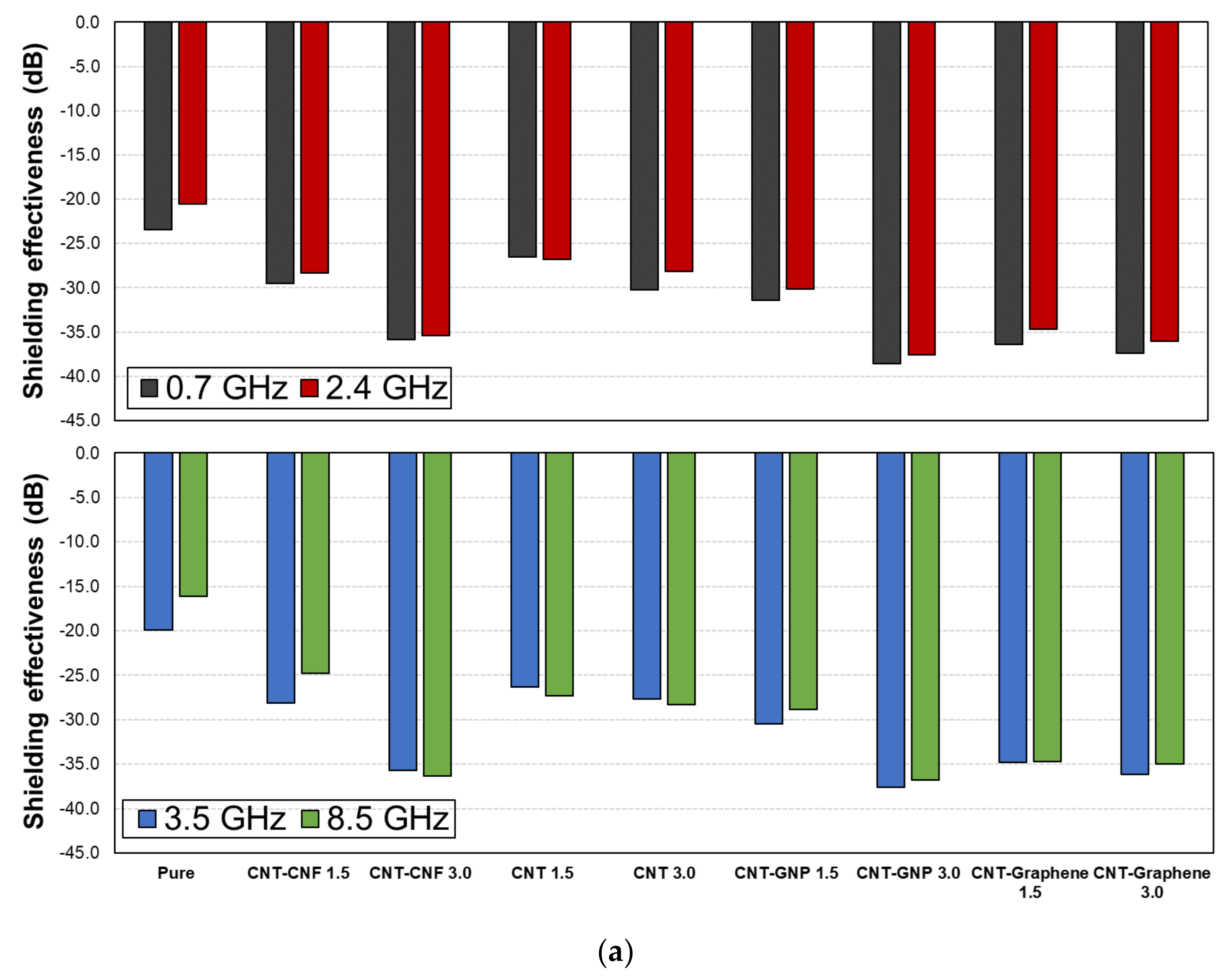
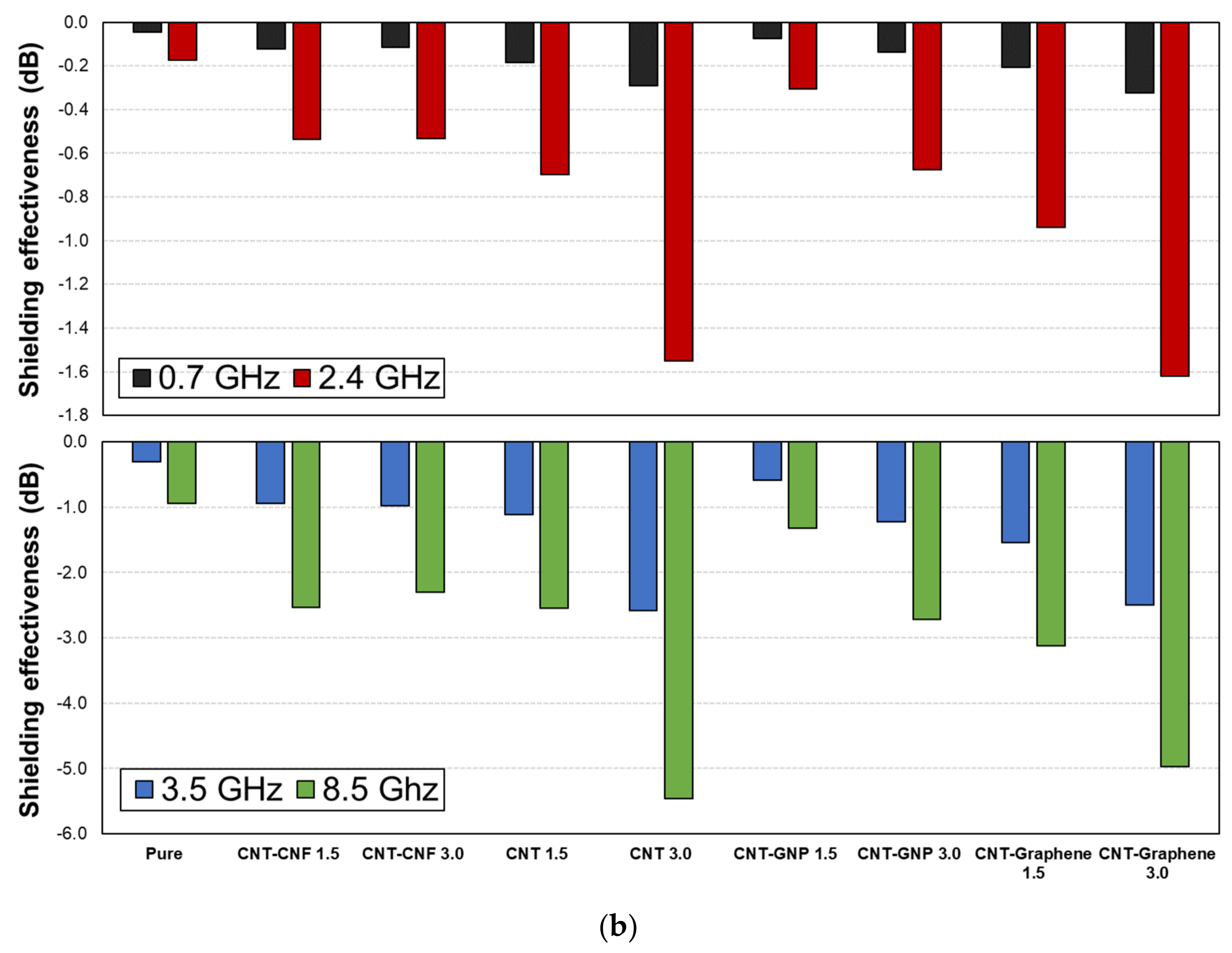
3.2. Effects of Microfiber Type
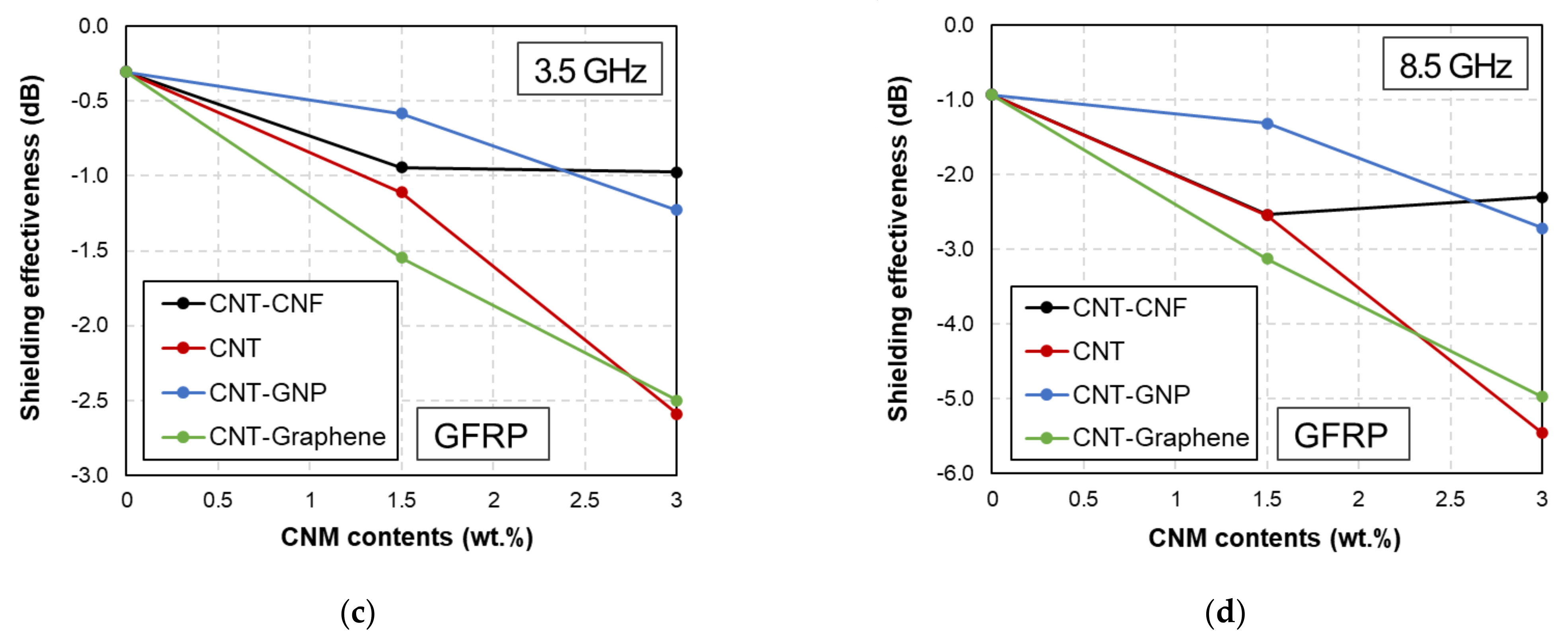
3.3. Effects of CNM Contents
3.4. Effects of CNM Type
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The CFRP-based composites achieved much higher EMI shielding performance than the GFRP-based composites. This can be deduced from the high electrical conductivity of micro-typed carbon fiber which composed CFRP.
- (2)
- The plate-type CNMs (i.e., GNP and graphene) showed improved synergistic effects compared to the fiber-typed CNMs (CNF).
- (3)
- The 3% CNT-GNP CFRP composites, containing plate-typed CNM, exhibited the best EMI shielding effectiveness (38.6 dB at 0.7 GHz).
- (4)
- Based on the aforementioned research, the optimal EMI shielding composites based on the optimized combination of CNMs and CFRP/GFRP are expected to be used in trial tests.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, G.; Kim, S.; Park, G.K.; Lee, N. Influence of carbon fiber on the electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of high-performance fiber-reinforced cementitious composites. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 35, 101982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, H.; Hu, X.; Ju, D. A Novel Processing for CNT-Reinforced Mg-Matrix Laminated Composites to Enhance the Electromagnetic Shielding Property. Coatings 2021, 11, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Yu, R.; Hong, X. Review of carbon-based electromagnetic shielding materials: Film, composite, foam, textile. Text. Res. J. 2021, 91, 1167–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Sambyal, P.; Koo, C.M. 2D MXenes for Electromagnetic Shielding: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Kou, K.; Yin, S.; Feng, A.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Cao, H.; Wu, G. Magnetic Fe nanoparticle to decorate N dotted C as an exceptionally absorption-dominate electromagnetic shielding material. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 189, 107895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Choi, B.H.; Yoon, H.N.; Yang, B.; Lee, H.K. Improved electromagnetic wave shielding capability of carbonyl iron powder-embedded lightweight CFRP composites. Compos. Struct. 2022, 286, 115326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V. Review of electromagnetic interference shielding materials fabricated by iron ingredients. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 1640–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.R.; Yu, M.; Yang, P.A.; Qi, S.; Fu, J. Synthesis of absorbing coating based on magnetorheological gel with controllable electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 044001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Park, J.-E.; Kim, Y.-K. Evaluation of (CNT@CIP)-Embedded Magneto-Resistive Sensor Based on Carbon Nanotube and Carbonyl Iron Powder Polymer Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Feng, L.; Hou, X.; Suo, G.; Ye, X.; Zhang, L. Powerful and lightweight electromagnetic-shielding carbon nanotube/graphene foam/silicon carbide composites. Mater. Lett. 2019, 256, 126634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, L.; Chen, Q.; Peng, Q.; Yang, M.; Zhao, W.; Lin, Z.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; He, X. Highly Conductive Multifunctional rGO/CNT Hybrid Sponge for Electromagnetic Wave Shielding and Strain Sensor. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Yoon, H.N.; Seo, J.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, G.M.; Kim, Y.-K.; Yang, B. Improved electromagnetic interference shielding performances of carbon nanotube and carbonyl iron powder (CNT@CIP)-embedded polymeric composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Lei, Y.; Park, C.B. An Effective Design Strategy for the Sandwich Structure of PVDF/GNP-Ni-CNT Composites with Remarkable Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 36568–36577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Sun, W.J.; Yan, D.X.; Dai, K.; Li, Z.M. Ultralight carbon nanotube/graphene/polyimide foam with heterogeneous interfaces for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding and electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon N. Y. 2021, 176, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ud Din, I.; Naresh, K.; Umer, R.; Khan, K.A.; Drzal, L.T.; Haq, M.; Cantwell, W.J. Processing and out-of-plane properties of composites with embedded graphene paper for EMI shielding applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 134, 105901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Effect of postcuring immersed in water under hydraulic pressure on fatigue performance of large-diameter pultruded carbon/glass hybrid rod. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2019, 42, 1148–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, K.; Lengyel, A. Strengthening Timber Structural Members with CFRP and GFRP: A State-of-the-Art Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Wang, J.C.; Biswas, S.; Kim, H.; Nam, I.W. Mechanical, electrical, and piezoresistive sensing characteristics of epoxy-based composites incorporating hybridized networks of carbon nanotubes, graphene, carbon nanofibers, or graphite nanoplatelets. Sensors 2020, 20, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, H.R.; Jang, D.; Abbas, N.; Haider, M.S.; Bukhari, S.N.A.; Mirza, C.R.; Elboughdiri, N.; Ahmad, F. Electrical Stability and Piezoresistive Sensing Performance of High Strain-Range Ultra-Stretchable CNT-Embedded Sensors. Polymers 2022, 14, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.; Yoon, Y.J.; Park, I. Ultra-stretchable and skin-mountable strain sensors using carbon nanotubes-Ecoflex nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 375501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, I.W.; Lee, H.K.; Jang, J.H. Electromagnetic interference shielding/absorbing characteristics of CNT-embedded epoxy composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saleh, M.H.; Sundararaj, U. Electromagnetic interference shielding mechanisms of CNT/polymer composites. Carbon N. Y. 2009, 47, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkoula, N.M.; Alcock, B.; Cabrera, N.O.; Peijs, T. Flame-Retardancy Properties of Intumescent Ammonium Poly(Phosphate) and Mineral Filler Magnesium Hydroxide in Combination with Graphene. Polym. Compos. 2008, 16, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.B.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, W.G.; Yu, Z.Z. Magnetic and electrically conductive epoxy/graphene/carbonyl iron nanocomposites for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 118, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Chen, Y. Electromagnetic interference shielding of graphene/epoxy composites. Carbon N. Y. 2009, 47, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saleh, M.H. Electrical, EMI shielding and tensile properties of PP/PE blends filled with GNP:CNT hybrid nanofiller. Synth. Met. 2016, 217, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Wu, H.; Fang, J.; Yang, Y.; Miao, M.; Cao, S.; Shi, L.; Feng, X. Yarn-ball-shaped CNF/MWCNT microspheres intercalating Ti3C2Tx MXene for electromagnetic interference shielding films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| CNT | CNF | Graphene | GNP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter or Thickness | 8 nm (outer diameter) 2–5 nm (inner diameter) | 0.15–0.2 μm | 0.55–1.2 nm (thickness) | - |
| Layers | 1–5 | <30 | ||
| Purity | >98% | 99.9% | 99% | >90% |
| Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | >350 | 300 | >500 | |
| Length or width (μm) | 10–30 | 10–30 | 0.5–3 | 2–16 |
| Electrical conductivity (S/cm) | >100 | - | 184.8 | 6.67 |
| Type of Fabric | Carbon Fiber Plain Fabric | Glass Fiber Plain Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Grade (g) | 200, 1st level | 200, 1st level |
| Thickness (mm) | <0.11 | <0.12 |
| Elongation at break (%) | 3 | 3 |
| Samples | CNMs (g) | Epoxy (g) | Curing Agent (g) | Fiber Vol. % * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure CFRP | 0 | 150 | 50 | 29.3 |
| Pure GFRP | 0 | 50.8 | ||
| CNT 1.5% in CFRP | 3.05 | 32.4 | ||
| CNT 1.5% in GFRP | 3.05 | 22.8 | ||
| CNT 3.0% in CFRP | 6.09 | 23.1 | ||
| CNT 3.0% in GFRP | 6.09 | 28.1 | ||
| CNT-Graphene 1.5% in CFRP | 1.525 | 26.7 | ||
| CNT-Graphene 1.5% in GFRP | 1.525 | 47.1 | ||
| CNT-Graphene 3.0% in CFRP | 3.045 | 23.1 | ||
| CNT-Graphene 3.0% in GFRP | 3.045 | 41.3 | ||
| CNT-CNF 1.5% in CFRP | 1.525 | 30.0 | ||
| CNT-CNF 1.5% in GFRP | 1.525 | 33.0 | ||
| CNT-CNF 3.0% in CFRP | 3.045 | 24.0 | ||
| CNT-CNF 3.0% in GFRP | 3.045 | 41.3 | ||
| CNT-GNP 1.5% in CFRP | 1.525 | 29.3 | ||
| CNT-GNP 1.5% in GFRP | 1.525 | 52.8 | ||
| CNT-GNP 3.0% in CFRP | 3.045 | 30.0 | ||
| CNT-GNP 3.0% in GFRP | 3.045 | 45.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, D.; Kim, B.-J.; Nam, I.-W. A Comprehensive Study on EMI Shielding Performance of Carbon Nanomaterials-Embedded CFRP or GFRP Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 5224. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235224
Jang D, Kim B-J, Nam I-W. A Comprehensive Study on EMI Shielding Performance of Carbon Nanomaterials-Embedded CFRP or GFRP Composites. Polymers. 2022; 14(23):5224. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235224
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Daeik, Bum-Jun Kim, and Il-Woo Nam. 2022. "A Comprehensive Study on EMI Shielding Performance of Carbon Nanomaterials-Embedded CFRP or GFRP Composites" Polymers 14, no. 23: 5224. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235224
APA StyleJang, D., Kim, B.-J., & Nam, I.-W. (2022). A Comprehensive Study on EMI Shielding Performance of Carbon Nanomaterials-Embedded CFRP or GFRP Composites. Polymers, 14(23), 5224. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235224







