Formulation of Modified-Release Bilayer Tablets of Atorvastatin and Ezetimibe: An In-Vitro and In-Vivo Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Experimental Animals
2.2. Methods
Preparation of Bilayer Tablets
2.3. Evaluation of ATC/EZB Bilayer Tablets
2.3.1. Thickness
2.3.2. Hardness
2.3.3. Weight Variation Test
2.3.4. Friability
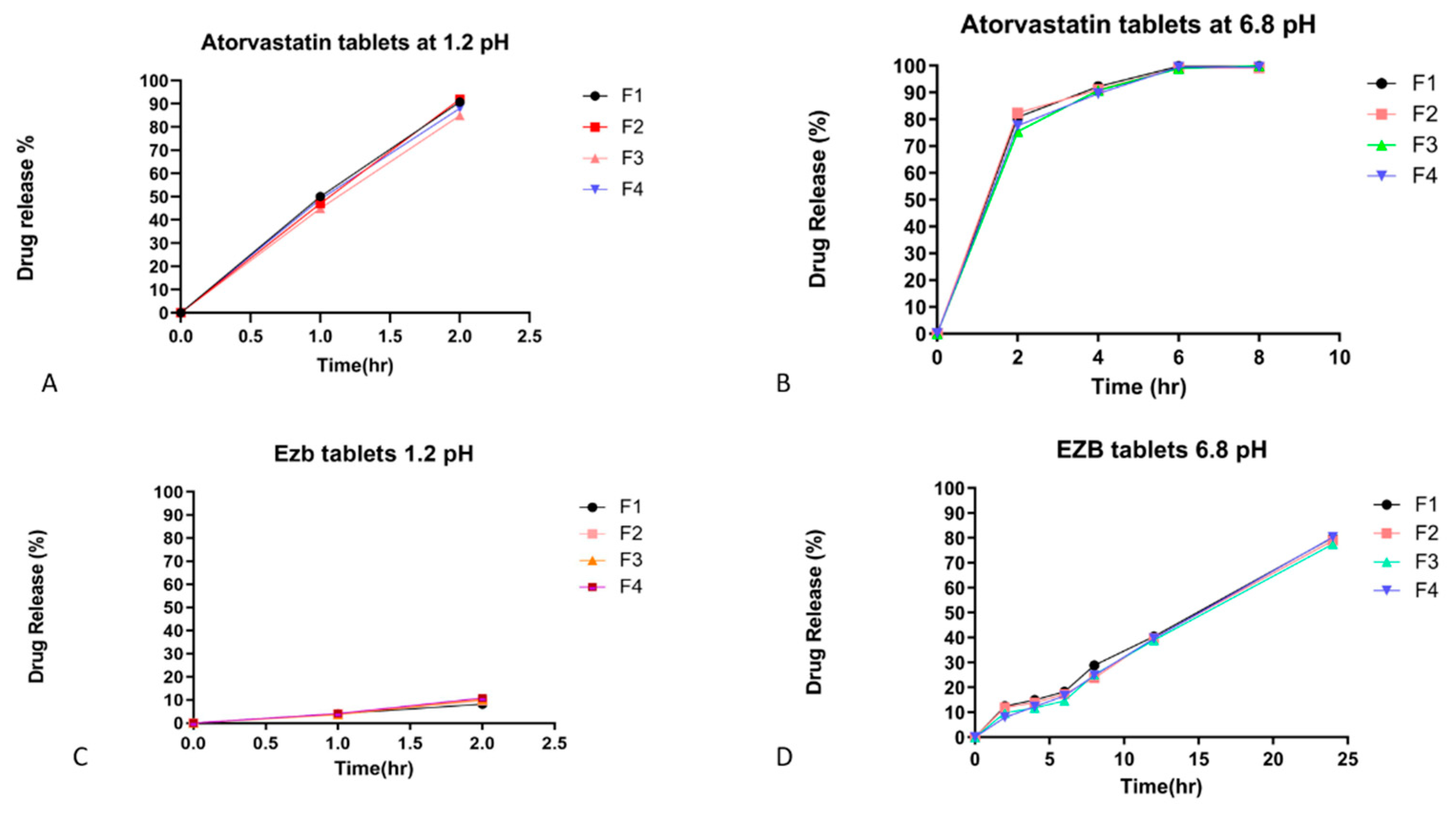
2.3.5. In Vitro Drug Release
2.3.6. Drug–Excipient Compatibility
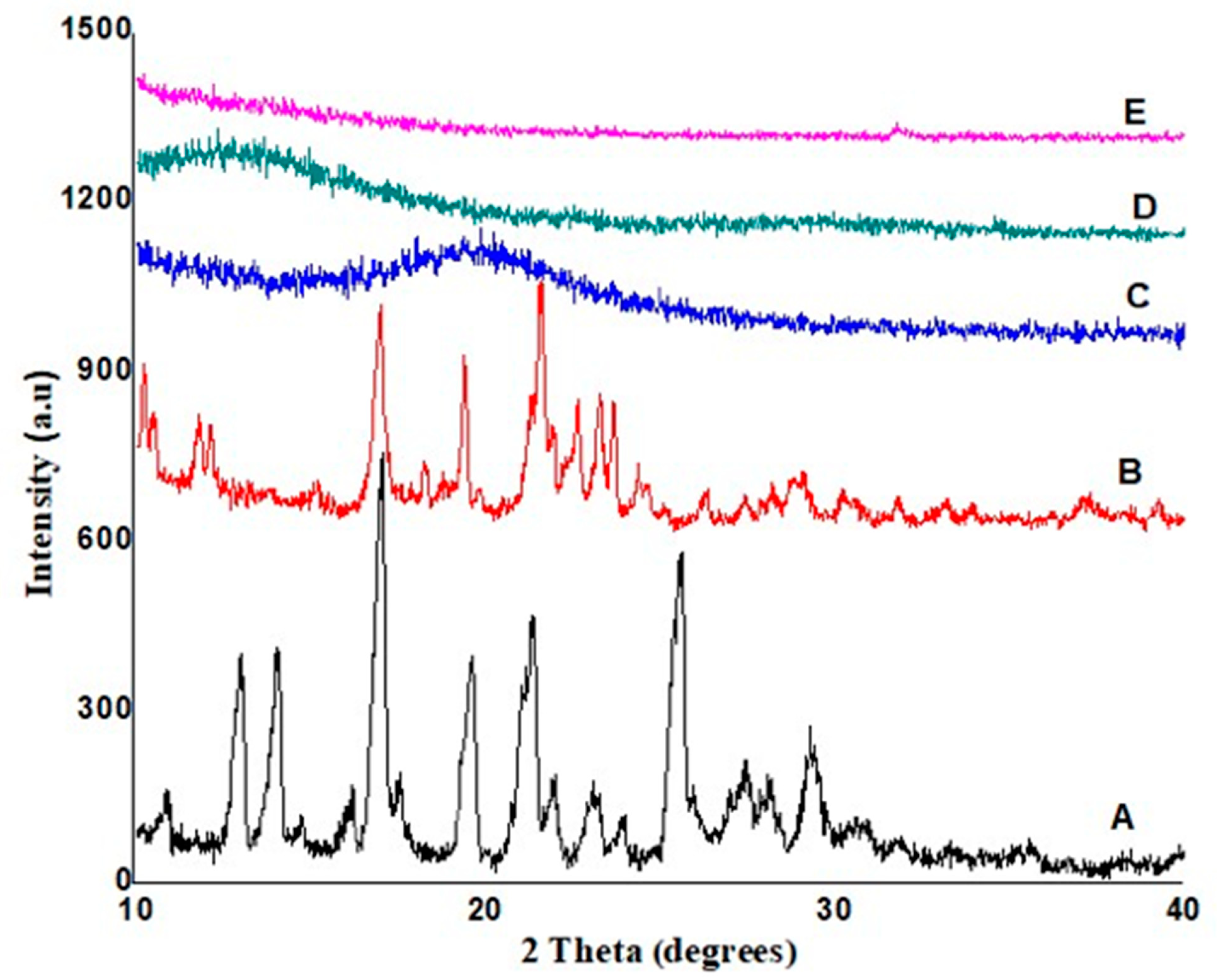
2.3.7. X-ray Diffractometry
2.3.8. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA) of Bilayer Tablets
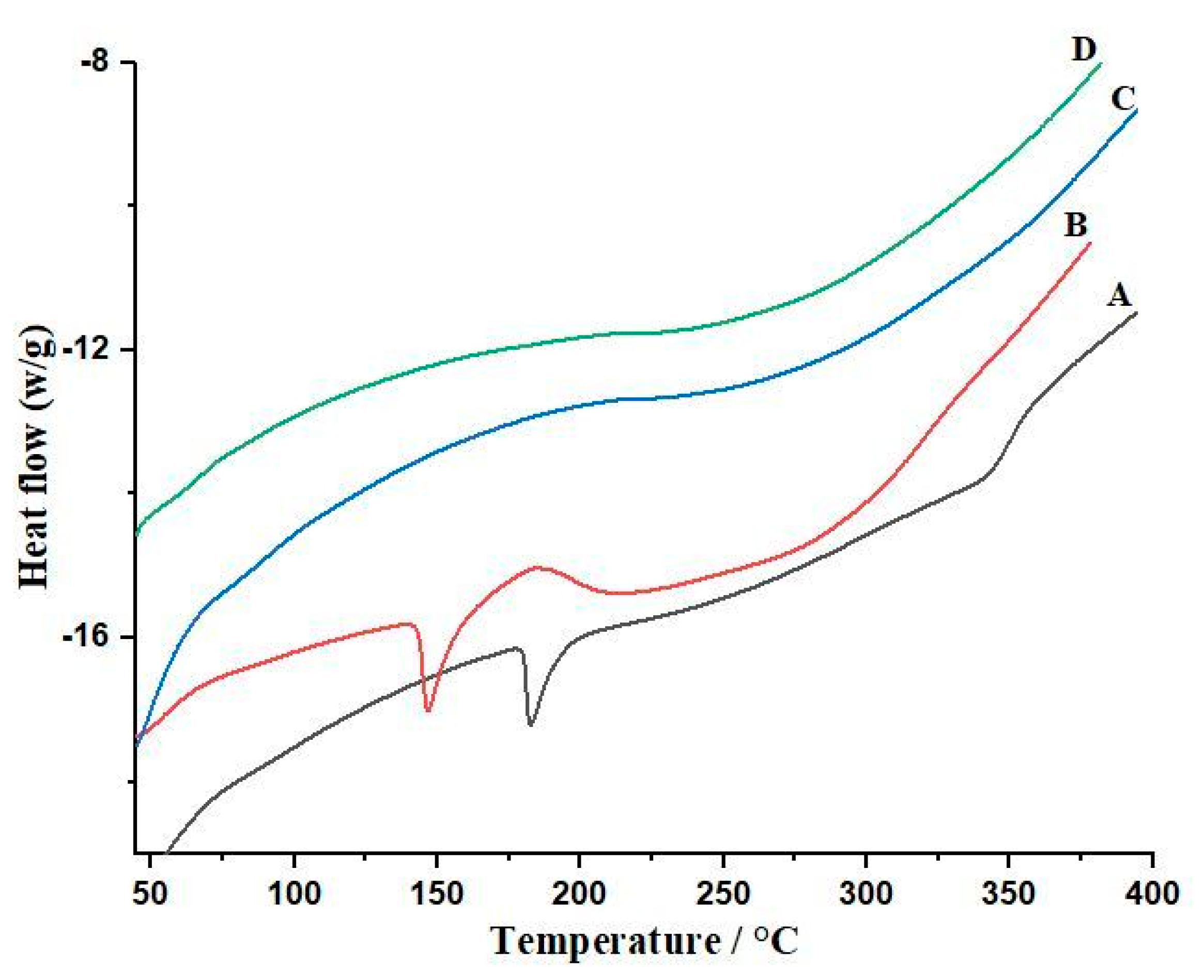
2.3.9. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.4. Animal Selection
2.4.1. Dose and Dose Frequency
2.4.2. Collection of Blood Samples
2.4.3. Determination of Plasma Lipids
2.4.4. Histopathological Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of ATC/EZB Bilayer Tablets
3.2. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
3.3. Chemical Compatibilities
3.4. X-ray Powder Diffraction Analysis of Bilayer Tablets
3.5. Thermal Gravimetrical Analysis of EZB/ATC Tablets
3.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) of Bilayer Tablets
3.7. Pharmacodynamic Studies
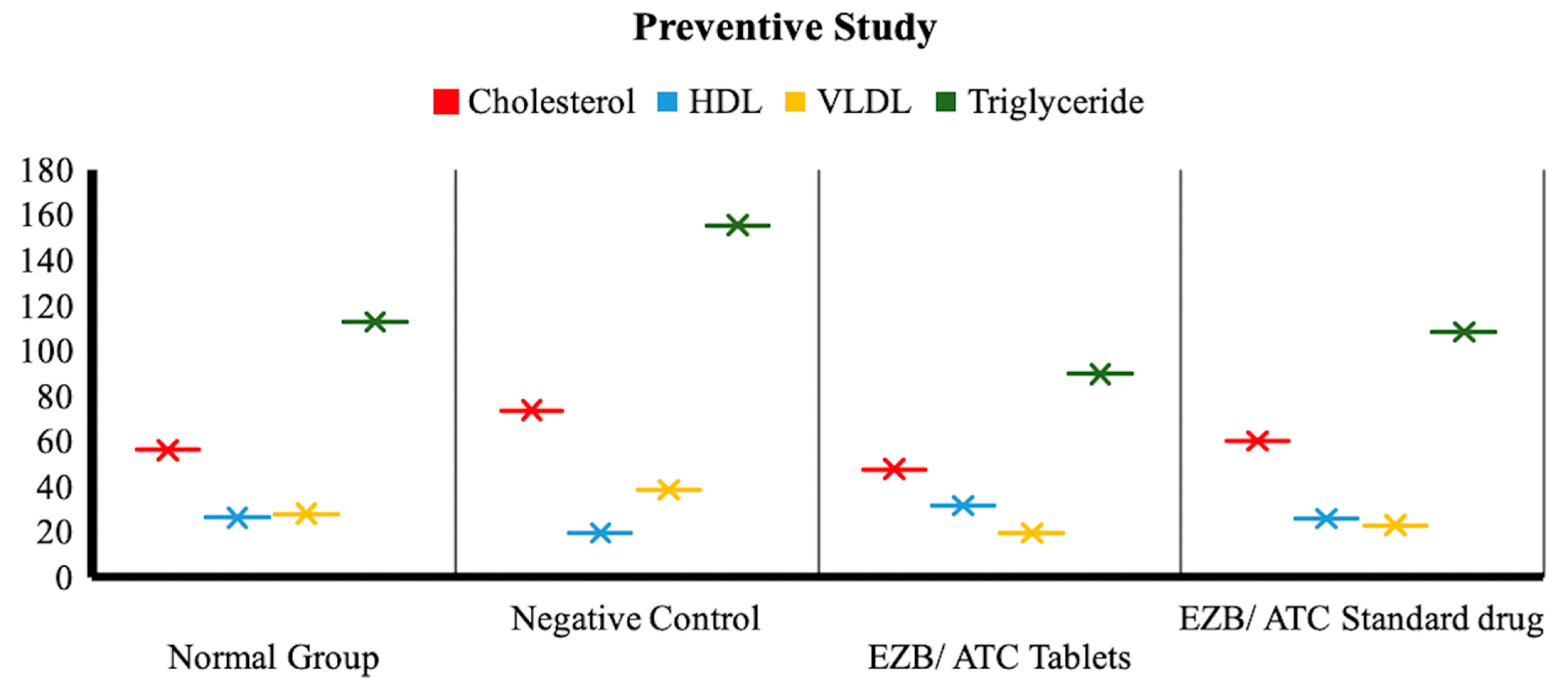
3.7.1. Effectiveness of Drug Treatment in Preventive Studies
Lipid Profile in Normal vs. Negative Control Group
Lipid Profile in Negative Control Group vs. Treated Groups
Effect on Rats’ Vital Organs
3.7.2. Drug Treatment and Its Effects in Curative Model
Plasma Lipoprotein Analysis in Curative Phase
Lipid Profile in Normal vs. Negative Control Group
Lipid Profile in Normal vs. Negative Control Group in Curative Phase
Effect on Rats’ Vital Organs in Curative Phase
3.8. Histopathological Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaya, F.T.; Sing, K.; Milam, R.; Husain, F.; del Aguila, M.A.; Patel, M.Y. Lipid-lowering efficacy of ezetimibe in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2020, 20, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.D.; MacDougall, D.E.; Newton, R.S.; Margulies, J.R.; Hanselman, J.C.; Orloff, D.G.; McKenney, J.M.; Ballantyne, C.M. Treatment with ETC-1002 alone and in combination with ezetimibe lowers LDL cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic patients with or without statin intolerance. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2016, 10, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laufs, U.; Karmann, B.; Pittrow, D. Atorvastatin treatment and LDL cholesterol target attainment in patients at very high cardiovascular risk. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2016, 105, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, P.; Jayakar, B.; Chandira, R.; Venkateshwarlu, B.; Pasupathi, A. Formulation, Evaluation and Development of Immediate Release Film Coated Tablets of Atorvastatin and Sustained Release Film Coated Tablets of Ezetimibe in Capsules Form Usp. Int. J. Med. Pharm. 2013, 1, 33–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bays, H. Ezetimibe. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2002, 11, 1587–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, M.C.; Ramani, C. Oral Tablet Formulation Consisting of Fixed Combination of Rosuvastatin and Ezetimibe for Treatment of Hyperlipidemia and Cardiovascular Diseases. U.S. Patent 10,376,470, 13 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, M.C. Oral Tablet Formulation Consisting of Fixed Combination of Rosuvastatin and Ezetimibe for Treatment of Hyperlipidemia and Cardiovascular Diseases. U.S. Patent 9,763,885, 19 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, C.-Y.; Storey, D.; Byrne, G. Interfacial strength of bilayer pharmaceutical tablets. Powder Technol. 2018, 337, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-Y.; Li, J.-X.; Sun, C.C. Tensile and shear methods for measuring strength of bilayer tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 523, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momin, S.; Khan, S.; Ghadage, D.M.; Yadav, A.V.; Wagh, A. Formulation and evaluation of bilayer tablets of propranolol hydrochloride. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2017, 7, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, R.; Paiement, N. Film Dosage form with Extended Release Mucoadhesive Particles. U.S. Patent 353,628, 11 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Chmiel, K.; Jurkiewicz, K.; Correia, N.T.; Sawicki, W.; Paluch, M. Physical Stability and Viscoelastic Properties of Co-Amorphous Ezetimibe/Simvastatin System. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukr, M.H.; Ismail, S.; Ahmed, S.M. Development and optimization of ezetimibe nanoparticles with improved antihyperlipidemic activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivalli, K.M.R.; Mishra, B. Improved aqueous solubility and antihypercholesterolemic activity of ezetimibe on formulating with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and hydrophilic auxiliary substances. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, M.; Mehta, I. Surface stabilized atorvastatin nanocrystals with improved bioavailability, safety and antihyperlipidemic potential. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biplav, S.; Sindhura, G.; Shivalinge, G.K. To evaluate the anti-atherosclerotic potential of quercetin in alloxan-induced diabetic rats fed with high-fat diet. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2018, 11, 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Rebouh, S.; Lefnaoui, S.; Bouhedda, M.; Yahoum, M.M.; Hanini, S. Neuro-fuzzy modeling of ibuprofen-sustained release from tablets based on different cellulose derivatives. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.M.A.; Aboelez, M.O.; Mohamed, M.S.; Mahmoud, R.A.; El-Shenawy, A.A.; Mahmoud, E.A.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A.; Santali, E.Y.; Alshehri, S.; Elsadek, M.E.M.; et al. Tailoring of Rosuvastatin Calcium and Atenolol Bilayer Tablets for the Management of Hyperlipidemia Associated with Hypertension: A Preclinical Study. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, M.; Hanif, M.; Qaiser, A.A. Effect of polymer and plasticizer on thin polymeric buccal films of meloxicam designed by using central composite rotatable design. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2016, 73, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tavousi, A.; Ahmadi, E.; Mohammadi-Behzad, L.; Riahifar, V.; Maghemi, F. Sensitive electrochemical sensor using polypyrrole-coated Fe3O4 core-shell nanoparticles/multiwall carbon nanotubes modified graphite electrode for atorvastatin analysis. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Mazumder, B. Formulation and evaluation of fixed-dose combination of bilayer gastroretentive matrix tablet containing atorvastatin as fast-release and atenolol as sustained-release. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 396106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, T.N. Design and Evaluation of Ezetimibe rapidmelts by direct compression and sublimation methods. Asian J. Pharm. 2016, 10, S518–S526. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Man, Z.; Yu-Zhen, Y.; Yan-Jie, H.; Xiao-Hui, Z.; Kai, S.; Ling, F.; Na, D.L. Dissolution rate enhancement of new co-crystals of ezetimibe with maleic acid and isonicotinamide. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 32, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar]



| Citric Acid (mg) | Cross Povidone (mg) | Sodium Bicarbonate (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| 24.50 | 48.65 | 83.50 |
| 28.50 | 44.65 | 83.50 |
| 32.50 | 40.65 | 83.50 |
| 36.50 | 36.65 | 83.50 |
| Constant quantity (10 mg) of EZB was used in all the formulations | ||
| Polymer (mg) | Binder (mg) | Glidant (mg) | Diluent (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 16 | 2 | 132 |
| 20 | 15 | 2 | 153 |
| 68 | 12.5 | 2 | 107.50 |
| 60 | 15 | 2 | 113 |
| Constant quantity (10 mg) of EZB was used in all the formulations | |||
| Post-Compression Studies | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter (mm) | 7.02 ± 0.104 | 7.01 ± 0.109 | 7.01 ± 0.052 | 7.01 ± 0.063 |
| Thickness (mm) | 7.01 ± 0.08 | 7.01 ± 0.09 | 7.01 ± 0.076 | 7.01 ± 0.077 |
| Weight Variation (%) | Within Limit (±7.5%) | Within Limit (±7.5%) | Within Limit (±7.5%) | Within Limit (±7.5%) |
| Hardness (N) | 10.9–11.2 ± 0.012 | 9.8–10.1 ± 0.10 | 10.4–10.9 ± 0.23 | 10.8–11.2 ± 0.132 |
| Friability (%) | 0.26 ± 0.007 | 0.21 ± 0.005 | 0.36 ± 0.07 | 0.37 ± 0.12 |
| Drug Content (%) | 102.04 ± 2.06 | 101.09 ± 1.77 | 99.88 ± 0.988 | 104.15 ± 2.84 |
| Parameters | Normal Group | Negative Control | EZB/ATC Tablets | EZB/ATC Standard Drug |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triglyceride | 113 ± 14.00 | 155.66 ± 31.19 | 90.00 ± 25.12 | 108.66 ± 16.07 |
| VLDL | 28.33 ± 6.35 | 39.00 ± 3.606 | 20.00 ± 5.19 | 23.33 ± 9.29 |
| HDL | 26.66 ± 8.50 | 20.00 ± 5.508 | 32.00 ± 3.606 | 26.33 ± 6.80 |
| Cholesterol | 56.33 ± 11.59 | 74.00 ± 11.54 | 48.00 ± 2.64 | 60.33 ± 4.04 |
| Group | Units | Liver | Spleen | Heart | Kidneys | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | R | |||||
| Normal Group | Weight (g) | 0.760 ± 0.010 | 8.7466 ± 1.017 | 0.953 ± 0.104 | 1.0233 ± 0.32 | 1.0233 ± 0.32 |
| Width (cm) | 3.066 ± 0.115 | 5.2666 ± 0.321 | 1.246 ± 0.12 | 1.233 ± 0.153 | 1.233 ± 0.153 | |
| L (cm) | 0.966 ± 0.058 | 3.800 ± 0.200 | 1.233 ± 0.058 | 1.933 ± 0.058 | 1.933 ± 0.058 | |
| Vol (mL) | 0.556 ± 0.075 | 5.720 ± 0.491 | 0.733 ± 0.035 | 0.570 ± 0.026 | 0.570 ± 0.026 | |
| Negative Control | Weight (g) | 0.846 ± 0.025 | 8.8333 ± 1.041 | 1.200 ± 0.10 | 1.3666 ± 0.153 | 1.3666 ± 0.153 |
| Width (cm) | 3.866 ± 0.153 | 5.7666 ± 0.153 | 1.500 ± 0.10 | 1.313 ± 0.032 | 1.313 ± 0.032 | |
| L (cm) | 1.200 ± 0.100 | 3.8333 ± 0.115 | 1.690 ± 0.101 | 2.200 ± 0.100 | 2.200 ± 0.100 | |
| Vol (mL) | 0.820 ± 0.130 | 6.666 ± 0.473 | 0.956 ± 0.055 | 0.840 ± 0.036 | 0.840 ± 0.036 | |
| EZB/ATC Tablets | Weight (g) | 0.343 ± 0.049 | 4.6633 ± 0.386 | 0.530 ± 0.030 | 0.420 ± 0.020 | 0.420 ± 0.020 |
| Width (cm) | 2.333 ± 0.153 | 4.200 ± 0.265 | 0.483 ± 0.029 | 0.906 ± 0.012 | 0.906 ± 0.012 | |
| L (cm) | 0.653 ± 0.047 | 2.9333 ± 0.058 | 0.656 ± 0.051 | 1.366 ± 0.058 | 1.366 ± 0.058 | |
| Vol (mL) | 0.290 ± 0.010 | 3.4533 ± 0.423 | 0.376 ± 0.040 | 0.386 ± 0.045 | 0.386 ± 0.045 | |
| EZB/ATC Standard Drug | Weight (g) | 0.386 ± 0.023 | 4.4533 ± 0.528 | 0.536 ± 0.057 | 0.430 ± 0.020 | 0.430 ± 0.020 |
| Width (cm) | 2.366 ± 0.252 | 4.100 ± 0.173 | 0.486 ± 0.081 | 0.866 ± 0.058 | 0.866 ± 0.058 | |
| L (cm) | 0.766 ± 0.058 | 2.9333 ± 0.058 | 0.780 ± 0.020 | 1.400 ± 0.100 | 1.400 ± 0.100 | |
| Vol (mL) | 0.296 ± 0.015 | 3.3966 ± 0.100 | 0.363 ± 0.055 | 0.450 ± 0.030 | 0.450 ± 0.030 | |
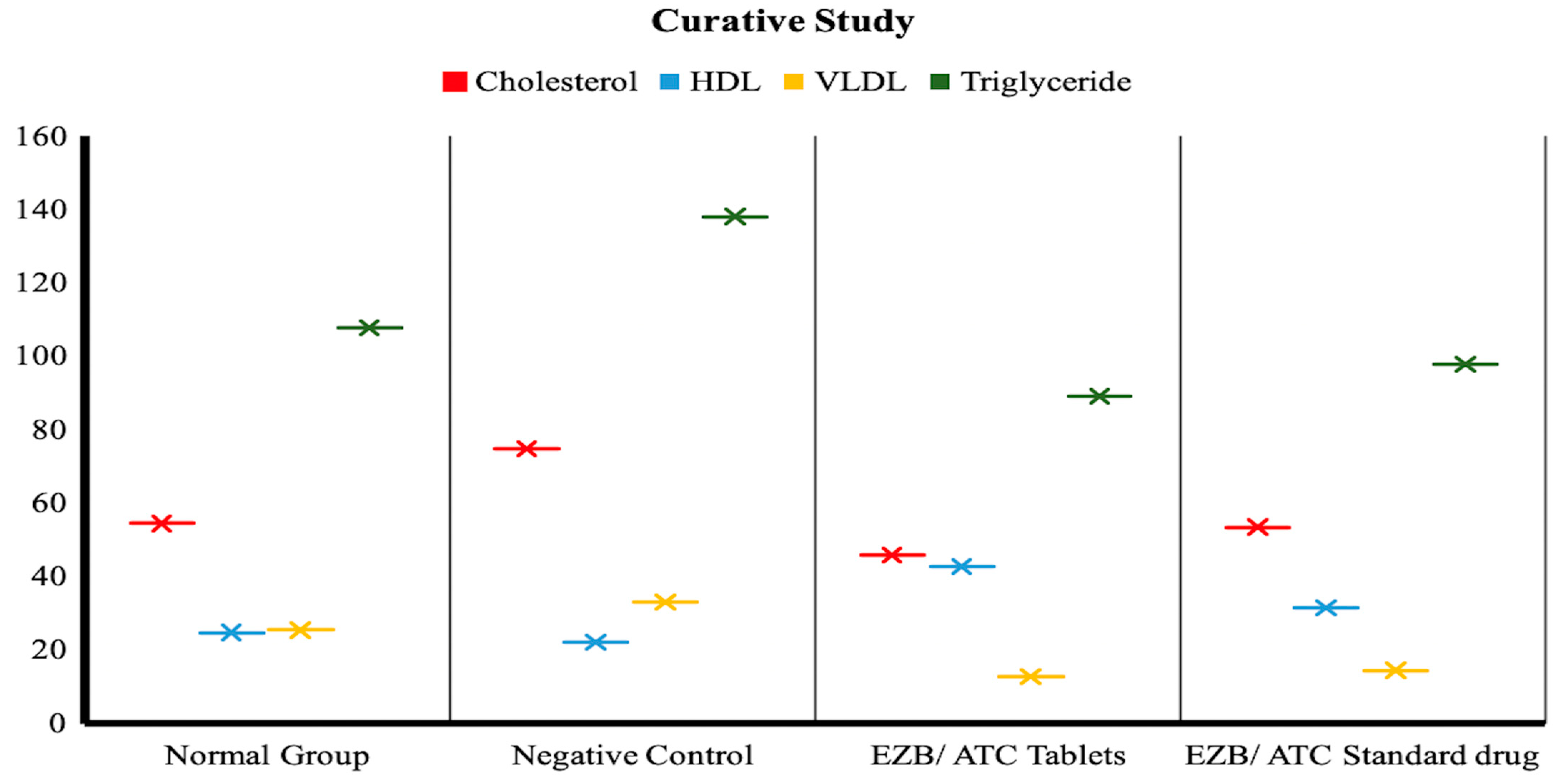
| Parameters | Normal Group | Negative Control | EZB/ATC Tablets | EZB/ATC Standard Drug |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triglyceride | 107.66 ± 5.77 | 138 ± 30.199 | 89.00 ± 1.00 | 97.66 ± 6.55 |
| VLDL | 25.333 ± 1.155 | 33.00 ± 6.028 | 12.633 ± 0.577 | 14.33 ± 1.00 |
| HDL | 24.66 ± 8.083 | 22.00 ± 3.215 | 42.667 ± 3.055 | 31.333 ± 3.60 |
| Cholesterol | 54.33 ± 8.66 | 74.667 ± 5.77 | 45.66 ± 3.214 | 53.333 ± 4.61 |
| Group | Units | Liver | Spleen | Heart | Kidneys | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | R | |||||
| Normal Group | Weight (g) | 8.7466 ± 1.017 | 0.673 ± 0.150 | 0.953 ± 0.104 | 1.140 ± 0.095 | 1.140 ± 0.095 |
| Width (cm) | 5.2666 ± 0.321 | 3.566 ± 0.115 | 1.300 ± 0.100 | 1.233 ± 0.153 | 1.233 ± 0.153 | |
| L (cm) | 3.800 ± 0.200 | 0.983 ± 0.029 | 1.300 ± 0.173 | 1.933 ± 0.058 | 1.933 ± 0.058 | |
| Vol (mL) | 7.000 ± 0.529 | 0.670 ± 0.040 | 0.733 ± 0.035 | 0.570 ± 0.026 | 0.570 ± 0.026 | |
| Negative Control | Weight (g) | 7.266 ± 0.462 | 0.503 ± 0.023 | 0.800 ± 0.087 | 1.027 ± 0.025 | 1.027 ± 0.025 |
| Width (cm) | 3.667 ± 0.289 | 2.533 ± 0.025 | 1.033 ± 0.058 | 1.167 ± 0.153 | 1.167 ± 0.153 | |
| L (cm) | 3.200 ± 0.100 | 0.900 ± 0.100 | 1.033 ± 0.101 | 1.050 ± 0.050 | 1.050 ± 0.050 | |
| Vol (mL) | 6.390 ± 0.248 | 0.513 ± 0.130 | 0.746 ± 0.05 | 0.613 ± 0.050 | 0.613 ± 0.050 | |
| EZB/ATC Tablets | Weight (g) | 4.103 ± 0.18 | 0.296 ± 0.068 | 0.440 ± 0.01 | 0.423 ± 0.025 | 0.423 ± 0.025 |
| Width (cm) | 2.400 ± 0.100 | 1.840 ± 0.053 | 0.463 ± 0.029 | 0.600 ± 0.100 | 0.600 ± 0.100 | |
| L (cm) | 1.873 ± 0.110 | 0.516 ± 0.067 | 0.286 ± 0.051 | 0.740 ± 0.036 | 0.740 ± 0.036 | |
| Vol (mL) | 2.700 ± 0.100 | 0.290 ± 0.010 | 0.370 ± 0.030 | 0.390 ± 0.010 | 0.390 ± 0.010 | |
| EZB/ATC Standard Drug | Weight (g) | 4.786 ± 0.280 | 0.433 ± 0.023 | 0.393 ± 0.006 | 0.650 ± 0.050 | 0.650 ± 0.050 |
| Width (cm) | 2.783 ± 0.104 | 1.950 ± 0.050 | 0.553 ± 0.057 | 0.900 ± 0.050 | 0.900 ± 0.050 | |
| L (cm) | 2.166 ± 0.05 | 0.653 ± 0.129 | 0.396 ± 0.020 | 0.923 ± 0.025 | 0.923 ± 0.025 | |
| Vol (mL) | 3.696 ± 0.270 | 0.316 ± 0.015 | 0.400 ± 0.017 | 0.573 ± 0.032 | 0.573 ± 0.032 | |
| Slide No. | Photo Name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| N | N 40X N 100X N 400X | Uniform intact layer of endothelial lining, uniform thickness of tunica media and adventia. No sign of necrosis or atherosclerosis. |
| -Ve | -Ve 40X -Ve 100X -Ve 400X | Endothelial cell layer is normal. Uniform thickness of tunica media and tunca adventia. Localized disarrangement of the elastic tissue is observed. Overall, no sign of necrosis or atherosclerosis. The endothelial cells have basophilic pink cytoplasm. |
| Ve2 | Ve2 40X Ve2 100X Ve2 400X | Intact endothelial lining with uniform tunical media and adventia. Occasionally, endothelial cells contained brownish pigment. |
| A4 | A4 40X A4 100X A4 400X | Intact endothelial lining with uniform tunical media and adventia. Occasionally, endothelial cells contained brownish pigment. Brown prigmented crystals were seen in the clotted blood smear in the aotic lumen. However, no sign of atherosclerosis. |
| A7 | A7 40X A7 100X A7 400X | Intact endothelial lining with uniform tunical media and adventia. No sign of etherosclerosis. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mubeen, I.; Zaman, M.; Farooq, M.; Mehmood, A.; Azeez, F.K.; Rehman, W.; Akhtar, S.; Chaudhry, M.A.; Butt, M.H.; Shamim, Q.-u.-a.; et al. Formulation of Modified-Release Bilayer Tablets of Atorvastatin and Ezetimibe: An In-Vitro and In-Vivo Analysis. Polymers 2022, 14, 3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14183770
Mubeen I, Zaman M, Farooq M, Mehmood A, Azeez FK, Rehman W, Akhtar S, Chaudhry MA, Butt MH, Shamim Q-u-a, et al. Formulation of Modified-Release Bilayer Tablets of Atorvastatin and Ezetimibe: An In-Vitro and In-Vivo Analysis. Polymers. 2022; 14(18):3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14183770
Chicago/Turabian StyleMubeen, Iqra, Muhammad Zaman, Muhammad Farooq, Asim Mehmood, Fahad Khan Azeez, Wajiha Rehman, Sohail Akhtar, Mueen Ahmad Chaudhry, Muhammad Hammad Butt, Qurat-ul-ain Shamim, and et al. 2022. "Formulation of Modified-Release Bilayer Tablets of Atorvastatin and Ezetimibe: An In-Vitro and In-Vivo Analysis" Polymers 14, no. 18: 3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14183770
APA StyleMubeen, I., Zaman, M., Farooq, M., Mehmood, A., Azeez, F. K., Rehman, W., Akhtar, S., Chaudhry, M. A., Butt, M. H., Shamim, Q.-u.-a., Adnan, S., Khan, M. R., & Atta-ur-Rehman. (2022). Formulation of Modified-Release Bilayer Tablets of Atorvastatin and Ezetimibe: An In-Vitro and In-Vivo Analysis. Polymers, 14(18), 3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14183770







