Water Immersion Aging of Epoxy Resin and Fique Fabric Composites: Dynamic–Mechanical and Morphological Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Fique Fabric–Epoxy Matrix Composites
2.3. Water Absorption
2.4. Accelerated Aging
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
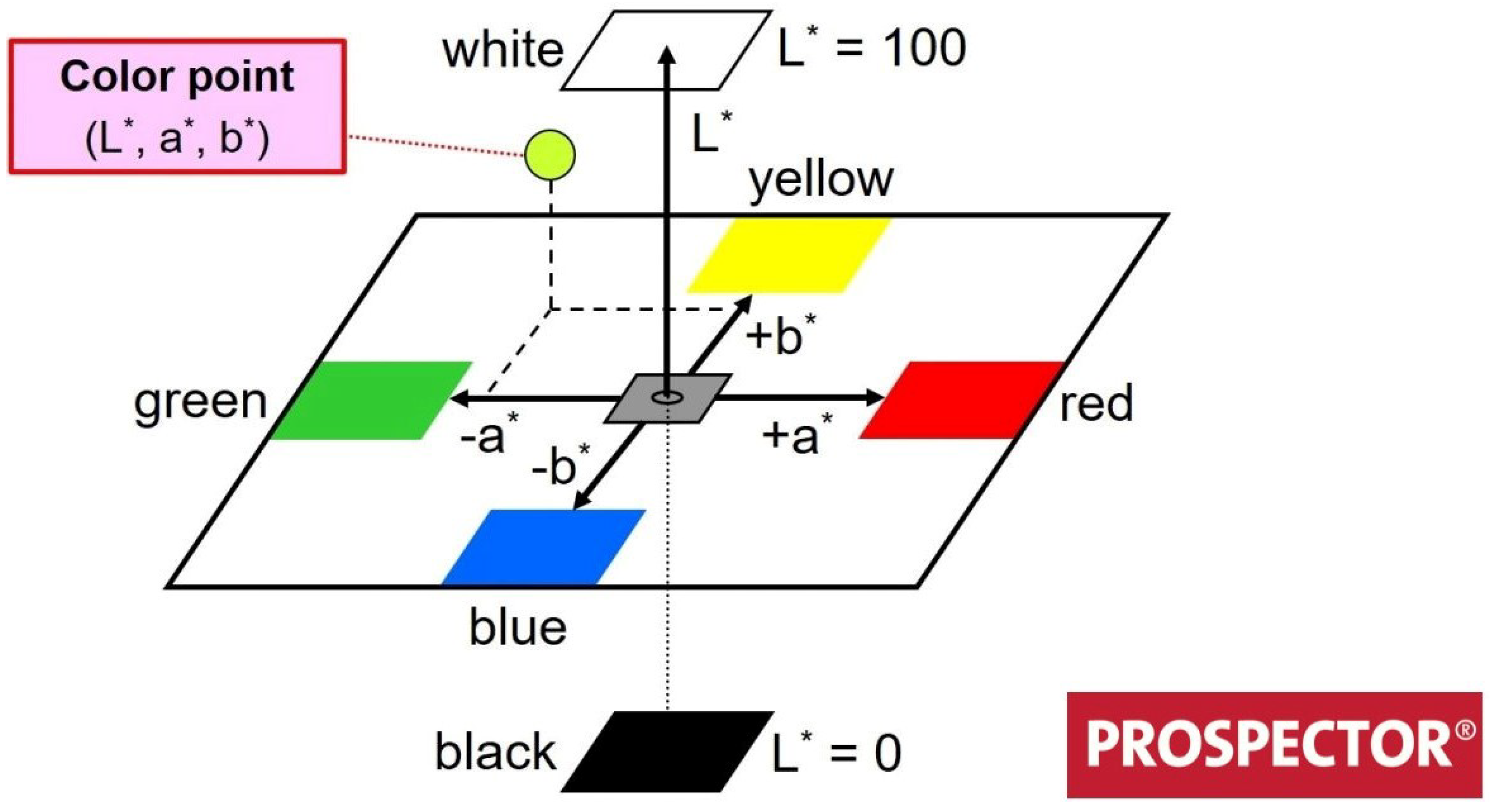
2.6. Colorimetry Analyses: CIELAB Color Space
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.8. Dynamic–Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Absorption
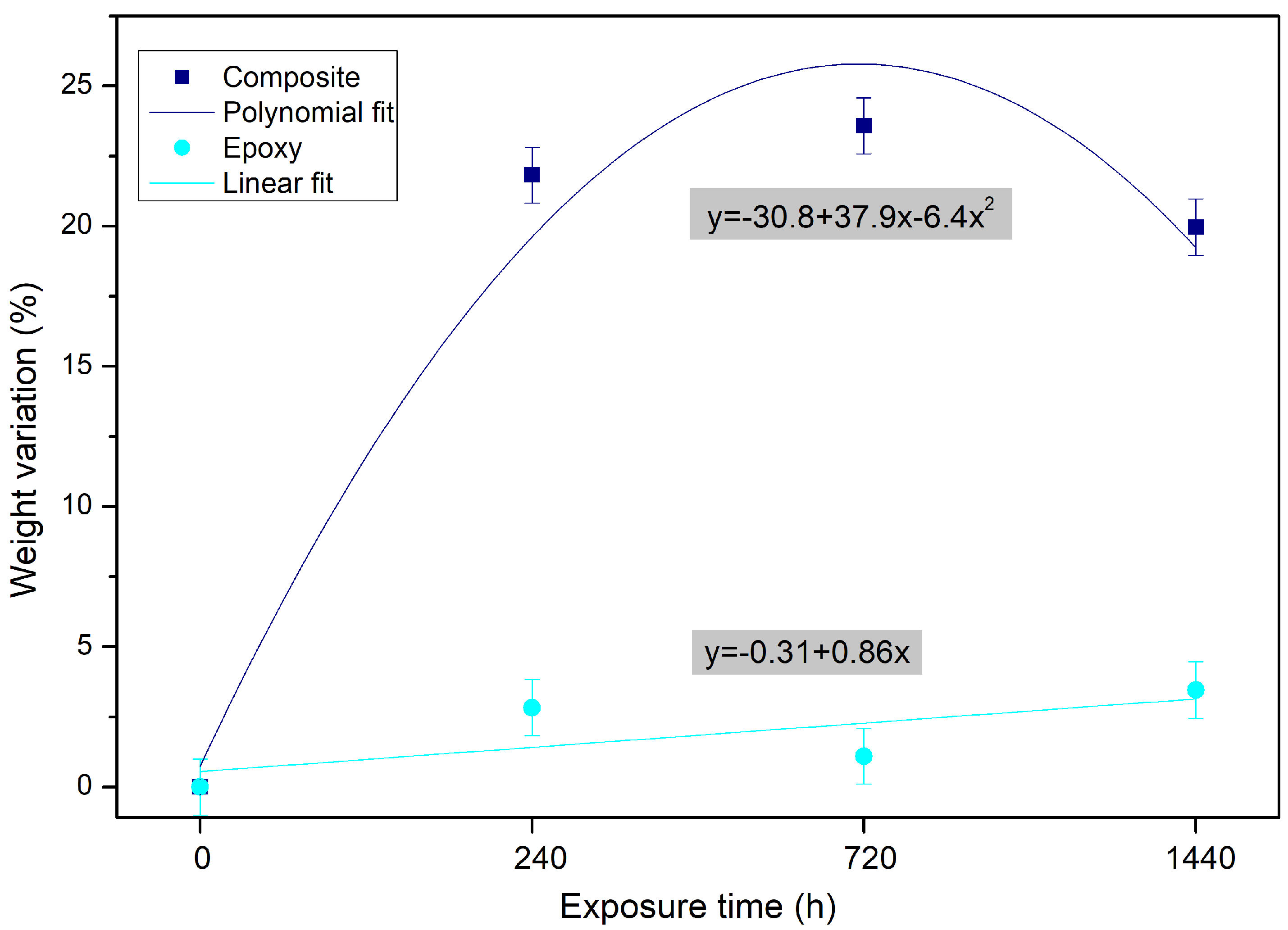
3.2. Weight Variation
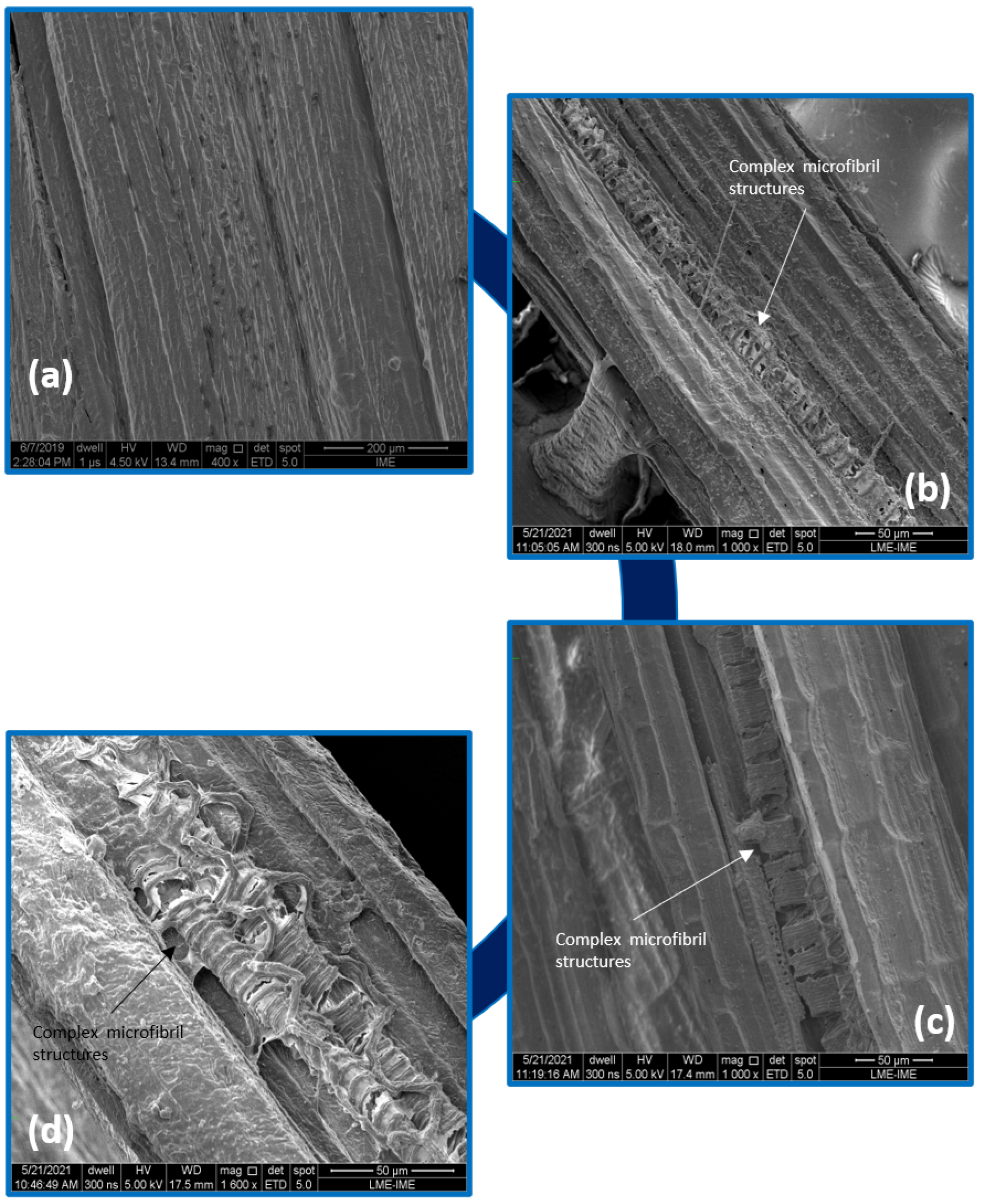
3.3. Effects of Water Immersion Aging on Fique Fabric
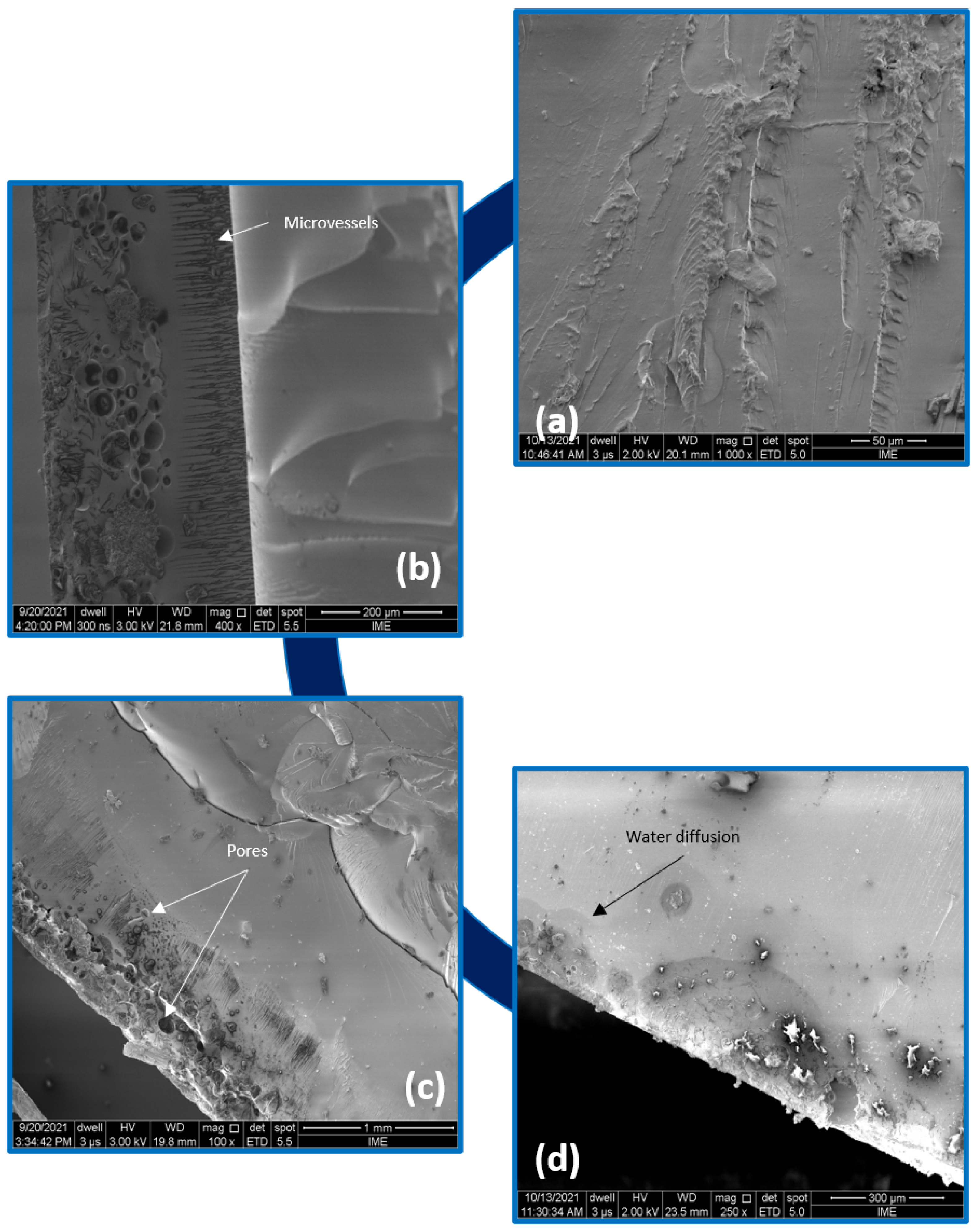
3.4. Effects of Water Immersion Aging on Epoxy
3.5. Effects of Water Immersion Aging on Fique-Fabric-Reinforced Epoxy Composite
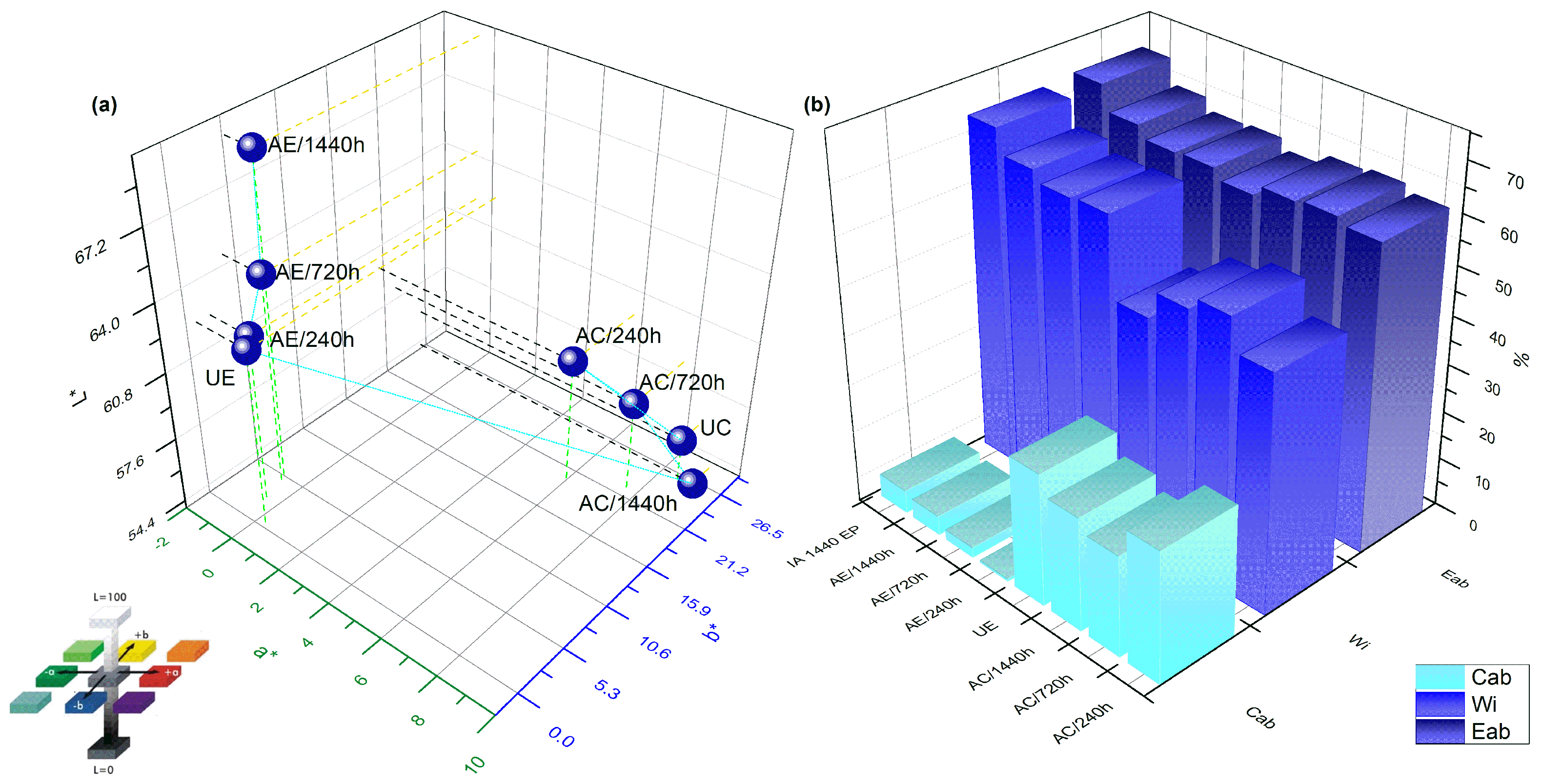
3.6. Colorimetry Analysis: CIELAB
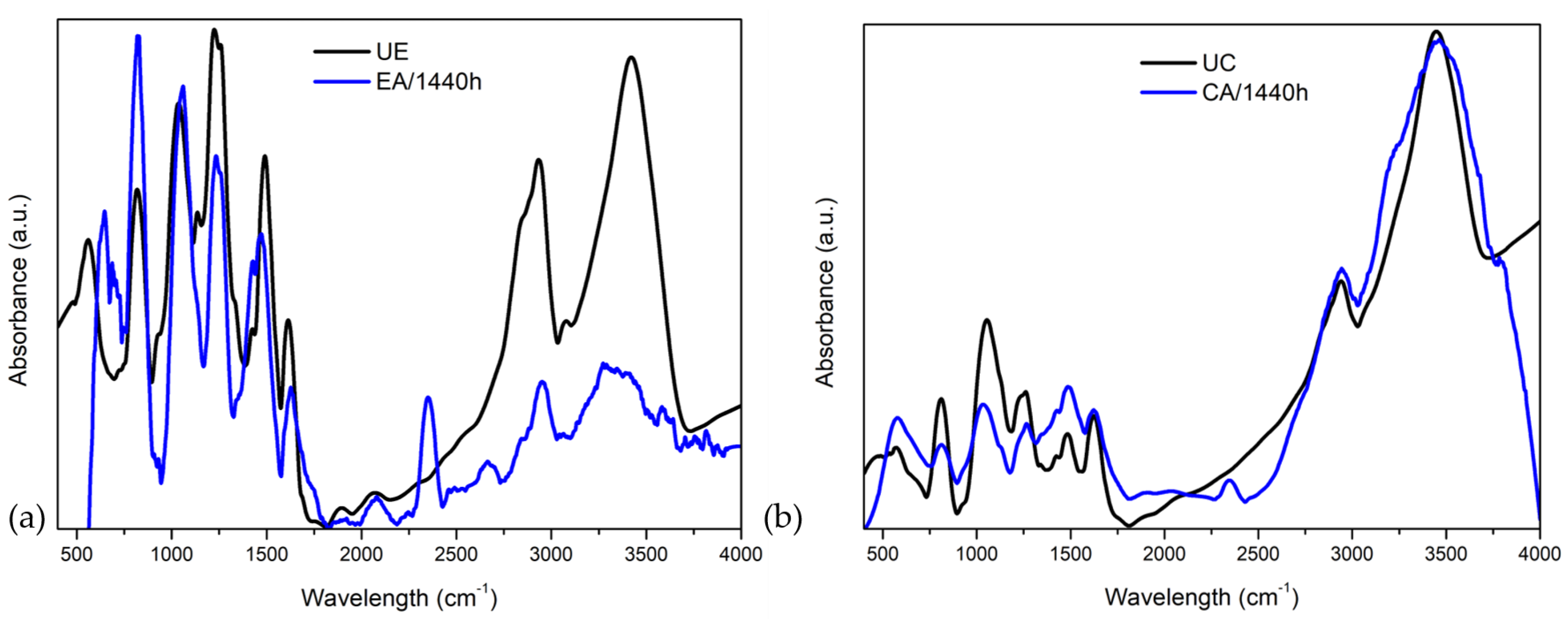
3.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.8. Effects of Water Immersion Aging on DMA
3.8.1. Storage Modulus (E)
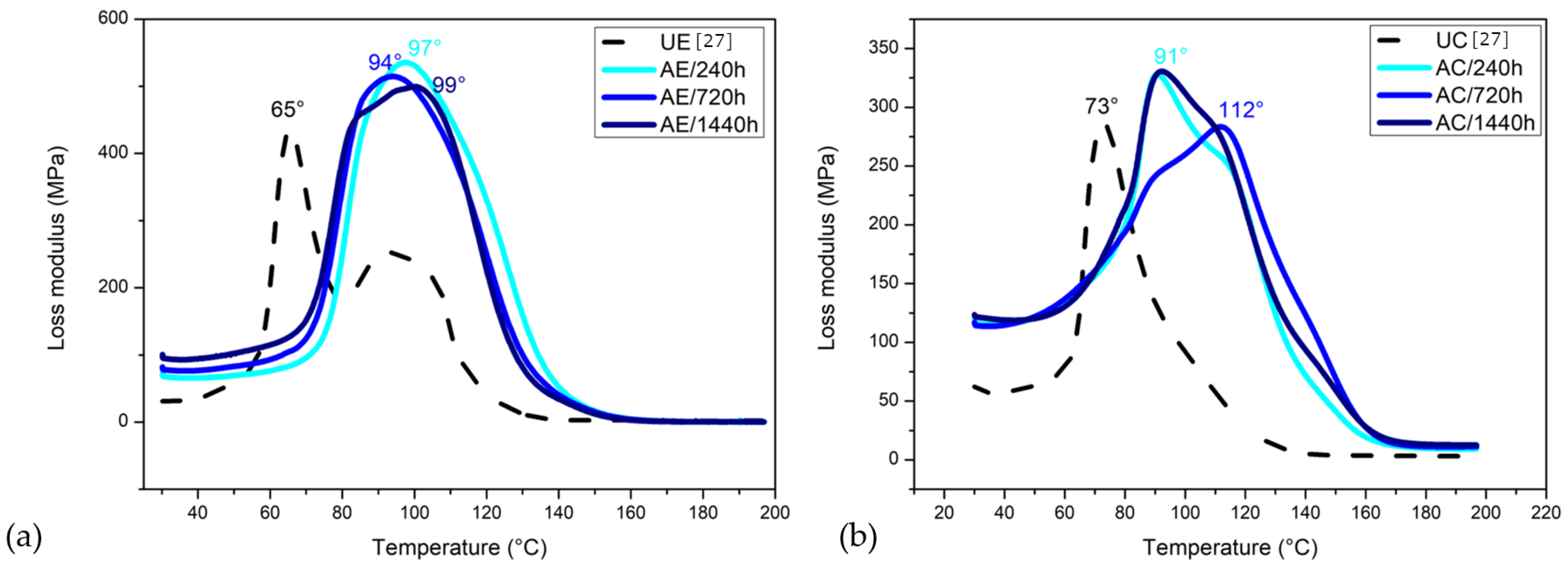
3.8.2. Loss Modulus (E)
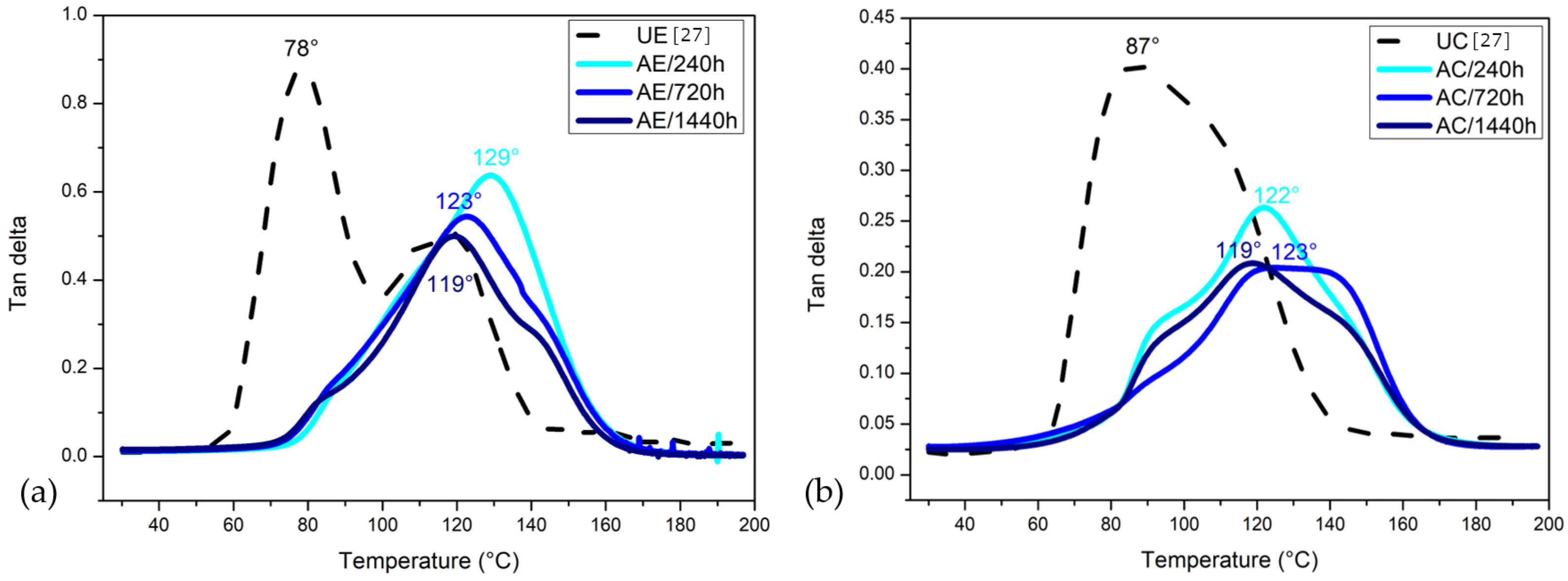
3.8.3. Tangent Delta (tan )
3.9. Qualitative Discussion
3.10. The Cole–Cole Plot
4. Summary and Conclusions
- The analysis of water absorption showed a large increase in water diffusion coefficient when comparing the epoxy resin and the fique fabric composites. The weight variation did not show a clear connection between the amount of water absorbed and the duration of exposure. However, a general trend in the obtained values suggests an increase in the weight with the increase in exposure duration.
- The SEM analyses showed the deteriorated structure and, in particular, that the interface may initiate complex microfibril structures, microvessels, pores and microcracking of the epoxy matrix due to fiber swelling or fique fiber/epoxy matrix debonding. Consequently, this may additionally influence the composite’s behavior and/or structure integrity. The process of water immersion aging, especially for the epoxy resin, was dominated by residual crosslinking interfering with the color change in the sample.
- Based on the specific reductions in the absorbance bands (943 and 810 cm) of the epoxy and composite observed, respectively, it can be inferred that the curing process occurred through exposure by water immersion.
- The dynamic moduli behavior confirms the degradation of the investigated epoxy resin and composite during accelerated aging. The E decreased and the E increased during continued water exposure. The penetration of water molecules inside the composite’s structure caused the plasticization of the epoxy matrix and initiated the degradation process, possibly by breaking the hydrogen bondings. This behavior is related to the degradation process, which decreases the strength of a structure and increases its viscosity and damping under elevated temperatures. After the accelerated aging, all three aging conditions show considerably higher T values for both materials, which is attributed to residual crosslinking.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- da Luz, F.S.; Garcia Filho, F.d.C.; Oliveira, M.S.; Nascimento, L.F.C.; Monteiro, S.N. Composites with Natural Fibers and Conventional Materials Applied in a Hard Armor: A Comparison. Polymers 2020, 12, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinloch, A.J.; Taylor, A.C.; Techapaitoon, M.; Teo, W.S.; Sprenger, S. From matrix nano- and micro-phase tougheners to composite macro-properties. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Wang, Y. A Review on Artificial Aging Behaviors of Fiber Reinforced Polymer-matrix Composites. MATEC Web Conf. 2016, 67, 06041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhoulda, B.; Adda-Bedia, E.; Madani, K. The effect of fiber orientation angle in composite materials on moisture absorption and material degradation after hygrothermal ageing. Compos. Struct. 2006, 74, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, S.S.; Jawaid, M.; Sultan, M.; Alothman, O.Y.; Abdullah, L.C. Accelerated weathering and soil burial effects on colour, biodegradability and thermal properties of bamboo/kenaf/epoxy hybrid composites. Polym. Test. 2019, 79, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, A.M.; Ramasastry, D.; Waddar, S.; Shaikh, T.M.; Tamboli, A.A. Water Absorption and Thickness Swelling Behaviour of Woven Roselle Fibre Epoxy Composites. Int. J. Veh. Struct. Syst. 2022, 14, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shettahalli Mantaiah, V.K. Water Absorption Behavior and Its Effect on Static Mechanical and Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Flax Fabric Reinforced Epoxy Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ul Haq, M.I.; Sharma, S.M.; Raina, A.; Anand, A. Effect of water absorption on mechanical and tribological properties of Indian ramie/epoxy composites. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2022, 236, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, A.; Thawre, M.; Ballal, A. Hygrothermal aging effect on physical and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy cross-ply composite laminate. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chateauminois, A.; Vincent, L.; Chabert, B.; Soulier, J. Study of the interfacial degradation of a glass-epoxy composite during hygrothermal ageing using water diffusion measurements and dynamic mechanical thermal analysis. Polymer 1994, 35, 4766–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badyankal, P.V.; Manjunatha, T.; Vaggar, G.B.; Praveen, K. Compression and water absorption behaviour of banana and sisal hybrid fiber polymer composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 35, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espert, A.; Vilaplana, F.; Karlsson, S. Comparison of water absorption in natural cellulosic fibres from wood and one-year crops in polypropylene composites and its influence on their mechanical properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwe, M.M.; Liao, K. Effects of environmental aging on the mechanical properties of bamboo–glass fiber reinforced polymer matrix hybrid composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2002, 33, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haameem, J.A.M.; Abdul Majid, M.; Afendi, M.; Marzuki, H.; Hilmi, E.A.; Fahmi, I.; Gibson, A. Effects of water absorption on Napier grass fibre/polyester composites. Compos. Struct. 2016, 144, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Salazar, M.A.; Correa-Aguirre, J.P.; García-Navarro, S.; Roca-Blay, L. Injection Molding of Coir Coconut Fiber Reinforced Polyolefin Blends: Mechanical, Viscoelastic, Thermal Behavior and Three-Dimensional Microscopy Study. Polymers 2020, 12, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.; Isac, D.J. Dynamic mechanical analysis and thermal degradation of jute fiber reinforced BSFT (Ba0.6Sr0.4FexTi(1-x) O3-δ), (x = 0.1)-polypropylene composite. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2017, 55, 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, M.; Garcia, F.D.C.; Luz, F.; Demosthenes, L.; Pereira, A.; Colorado, H.; Nascimento, L.; Monteiro, S. Evaluation of Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Fique Fabric/Epoxy Composites. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabet, S.M.; Ohadi, A. Sound transmission loss comparision for compression molded polycarbonate and PMMA. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Congress on Sound and Vibration, ICSV 2015, Florence, Italy, 12–16 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Katunin, A.; Gnatowski, A.; Kajzer, W. Evolution of Static and Dynamic Properties of Gfrp Laminates during Ageing in Deionized and Seawater. Adv. Compos. Lett. 2015, 24, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, U.O.; Nascimento, L.F.C.; Bezerra, W.B.A.; Neves, P.P.; Huaman, N.R.C.; Monteiro, S.N.; Pinheiro, W.A. Dynamic and Ballistic Performance of Graphene Oxide Functionalized Curaua Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Nanocomposites. Polymers 2022, 14, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, G.; Dorigato, A.; Pegoretti, A. Dynamic-mechanical response of carbon fiber laminates with a reactive thermoplastic resin containing phase change microcapsules. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2020, 24, 395–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves Monteiro, S.; Salgado de Assis, F.; Ferreira, C.L.; Tonini Simonassi, N.; Pondé Weber, R.; Souza Oliveira, M.; Colorado, H.A.; Camposo Pereira, A. Fique Fabric: A Promising Reinforcement for Polymer Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, T.; Navacerrada, M.; Díaz, C.; Fernández-Morales, P. Fique fibres as a sustainable material for thermoacoustic conditioning. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 164, 107240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, C.; Bacterióloga, L.; Hernández, H.; Castro, L. Influence of Particle Size and Temperature on Methane Production From Fique’s Bagasse Influencia del tamaño de partícula y la temperatura sobre la producción de metano a partir del bagazo de fique. Iteckne 2012, 9, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Gañán, P.; Mondragon, I. Surface modification of fique fibers. Effect on their physico-mechanical properties. Polym. Compos. 2002, 23, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvasto, S.; Toro, E.; Perdomo, F.; de Gutiérrez, R.M. An appropriate vacuum technology for manufacture of corrugated fique fiber reinforced cementitious sheets. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, L.B.; De Santis, H. Influence of the addition of montmorillonite to the matrix of unidirectional glass fibre/epoxy composites on their mechanical and water absorption properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 39, 1726–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.J.; Thomas, S. Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.S.; Luz, F.S.d.; Lopera, H.A.C.; Nascimento, L.F.C.; Garcia Filho, F.d.C.; Monteiro, S.N. Energy Absorption and Limit Velocity of Epoxy Composites Incorporated with Fique Fabric as Ballistic Armor—A Brief Report. Polymers 2021, 13, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D570-98; Standard Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics. American Society For Testing Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Muñoz, E.; Garcia-Manrique, J. Water Absorption Behaviour and Its Effect on the Mechanical Properties of Flax Fibre Reinforced Bioepoxy Composites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 390275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, J.d.S.C.; Nascimento, L.F.C.; da Luz, F.S.; Monteiro, S.N.; Lemos, M.F.; da Silva, C.G.; Simonassi, N.T. Physical and Mechanical Characterization of Titica Vine (Heteropsis flexuosa) Incorporated Epoxy Matrix Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevulova, N.; Cigasova, J.; Purcz, P.; Schwarzova, I.; Kacik, F.; Geffert, A. Water Absorption Behavior of Hemp Hurds Composites. Materials 2015, 8, 2243–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Hoyos, C.; Vázquez, A. Flexural properties loss of unidirectional epoxy/fique composites immersed in water and alkaline medium for construction application. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 3120–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.M.; Van Vuure, A.W. Effects of water immersion ageing on composites made of non-dry flax fibres. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 31, S206–S208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 7724-1; Paints and Varnishes—Colorimetry. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1984.
- ASTM D4065-20; Standard Practice for Plastics: Dynamic Mechanical Properties: Determination and Report of Procedures. American Society For Testing Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Chaudhary, V.; Bajpai, P.K.; Maheshwari, S. Effect of moisture absorption on the mechanical performance of natural fiber reinforced woven hybrid bio-composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2020, 17, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.S.; da Luz, F.S.; da Costa Garcia Filho, F.; Pereira, A.C.; de Oliveira Aguiar, V.; Lopera, H.A.C.; Monteiro, S.N. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis of Thermally Aged Fique Fabric-Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balla, V.K.; Kate, K.H.; Satyavolu, J.; Singh, P.; Tadimeti, J.G.D. Additive manufacturing of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites: Processing and prospects. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 174, 106956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Echtermeyer, A.T. Mechanism of Yellowing: Carbonyl Formation during Hygrothermal Aging in a Common Amine Epoxy. Polymers 2018, 10, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, H.; Zhang, Z.; Richardson, M. Effect of water absorption on the mechanical properties of hemp fibre reinforced unsaturated polyester composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Miao, M.; Ding, X. Influence of moisture absorption on the interfacial strength of bamboo/vinyl ester composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Meyer, C. Degradation rate of natural fiber in cement composites exposed to various accelerated aging environment conditions. Corros. Sci. 2014, 88, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, J.P.M.; Bernal, C.; Vázquez, A.; Escobar, M.M. Aging in Water and in an Alkaline Medium of Unsaturated Polyester and Epoxy Resins: Experimental Study and Modeling. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthaman, A.; Xian, G.; Thomas, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, X. Durability of an Epoxy Resin and Its Carbon Fiber- Reinforced Polymer Composite upon Immersion in Water, Acidic, and Alkaline Solutions. Polymers 2020, 12, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panchagnula, S.S.; Mitra, N.; Ghindani, D.; Prabhu, S. Epoxy Resin (DGEBA/TETA) Exposed to Water: A Spectroscopic Investigation to Determine Water-Epoxy Interactions. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2021, 42, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezulier, Q.; Clement, A.; Davies, P.; Arhant, M.; Flageul, B.; Jacquemin, F. Water ageing effects on the elastic and viscoelastic behaviour of epoxy-based materials used in marine environment. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Oever, M.J.A.; Snijder, M.H.B. Jute fiber reinforced polypropylene produced by continuous extrusion compounding, part 1: Processing and ageing properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, B.C.; Rathore, D. Durability and integrity studies of environmentally conditioned interfaces in fibrous polymeric composites: Critical concepts and comments. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañavate, J.; Colom, X.; Pages, P.; Carrasco, F. Study of the curing process of an epoxy resin by FTIR spectroscopy. Polym.-Plast. Technol.-Eng. 2000, 39, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.; Cabanelas, J.; Baselga, J. Applications of FTIR on Epoxy Resins—Identification, Monitoring the Curing Process, Phase Separation and Water Uptake. Infrared Spectrosc. Mater. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 2, 261–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, P.; Tatar, J.; Douglas, E.; Hamilton, H. Effects of Hygrothermal Conditioning on Epoxy Adhesives Used in FRP Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H. Dynamic mechanical analysis of the seawater treated glass/polyester composites. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 2774–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Fique | Cellulose (wt%) | Hemicellulose (wt%) | Lignin (wt%) | Wax (mm) | Pectin (wt%) | Ash (wt%) |
| 18.7–70 | 22.1–27.1 | 6.81–16.6 | - | - | - | |
| Microfibril Angle (°) | Apparently Density (g/cm3) | Real Density (g/cm3) | Fiber Diameter (mm) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | |
| 29.4 | 0.65–0.87 | 1.47 | 0.16–0.24 | 132.4–237 | 6–9.8 |
| Specimen | Nomenclature |
|---|---|
| Unaged Epoxy | UE |
| Water Immersion Epoxy Aged for 240 h | AE/240 h |
| Water Immersion Epoxy Aged for 720 h | AE/720 h |
| Water Immersion Epoxy Aged for 1440 h | AE/1440 h |
| Unaged Composite | UC |
| Water Immersion Composite Aged for 240 h | AC/240 h |
| Water Immersion Composite Aged for 720 h | AC/720 h |
| Water Immersion Composite Aged for 1440 h | AC/1440 h |
| DMA Parameter | UE | AE/240 h | AE/720 h | AE/1440 h | UC | AC/240 h | AC/720 h | AC/1440 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E at RT (GPa) | 3.21 | 5.33 | 5.82 | 2.26 | 2.81 | 1.70 | 4.14 | 4.87 |
| End of Glass condition (°C) | 58 | 77 | 78 | 74 | 64 | 83 | 84 | 83 |
| Onset of Rubbery condition (°C) | 79 | 157 | 158 | 159 | 135 | 158 | 160 | 160 |
| E at RT (GPa) | 0.038 | 0.072 | 0.082 | 0.100 | 0.062 | 0.119 | 0.117 | 0.123 |
| Maximum Internal friction (GPa) | 0.434 | 0.535 | 0.514 | 0.500 | 0.286 | 0.329 | 0.283 | 0.330 |
| Begin glass transition T (°C) | 68 | 112 | 112 | 110 | 90 | 110 | 113 | 118 |
| Maximum damping (dimensionless) | 0.87 | 0.64 | 0.54 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.21 |
| Dynamic T | 78 | 129 | 123 | 119 | 87 | 122 | 123 | 119 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, M.S.; da Luz, F.S.; Pereira, A.C.; Costa, U.O.; Bezerra, W.B.A.; da Cunha, J.d.S.C.; Lopera, H.A.C.; Monteiro, S.N. Water Immersion Aging of Epoxy Resin and Fique Fabric Composites: Dynamic–Mechanical and Morphological Analysis. Polymers 2022, 14, 3650. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173650
Oliveira MS, da Luz FS, Pereira AC, Costa UO, Bezerra WBA, da Cunha JdSC, Lopera HAC, Monteiro SN. Water Immersion Aging of Epoxy Resin and Fique Fabric Composites: Dynamic–Mechanical and Morphological Analysis. Polymers. 2022; 14(17):3650. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173650
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Michelle Souza, Fernanda Santos da Luz, Artur Camposo Pereira, Ulisses Oliveira Costa, Wendell Bruno Almeida Bezerra, Juliana dos Santos Carneiro da Cunha, Henry Alonso Colorado Lopera, and Sergio Neves Monteiro. 2022. "Water Immersion Aging of Epoxy Resin and Fique Fabric Composites: Dynamic–Mechanical and Morphological Analysis" Polymers 14, no. 17: 3650. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173650
APA StyleOliveira, M. S., da Luz, F. S., Pereira, A. C., Costa, U. O., Bezerra, W. B. A., da Cunha, J. d. S. C., Lopera, H. A. C., & Monteiro, S. N. (2022). Water Immersion Aging of Epoxy Resin and Fique Fabric Composites: Dynamic–Mechanical and Morphological Analysis. Polymers, 14(17), 3650. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173650











