Evaluation of the Rheological Properties of Virgin and Aged Asphalt Blends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Materials
2.2. Asphalt Viscosity Evaluation Test
2.3. Asphalt Viscoelasticity Evaluation Test
3. Results and Discussion
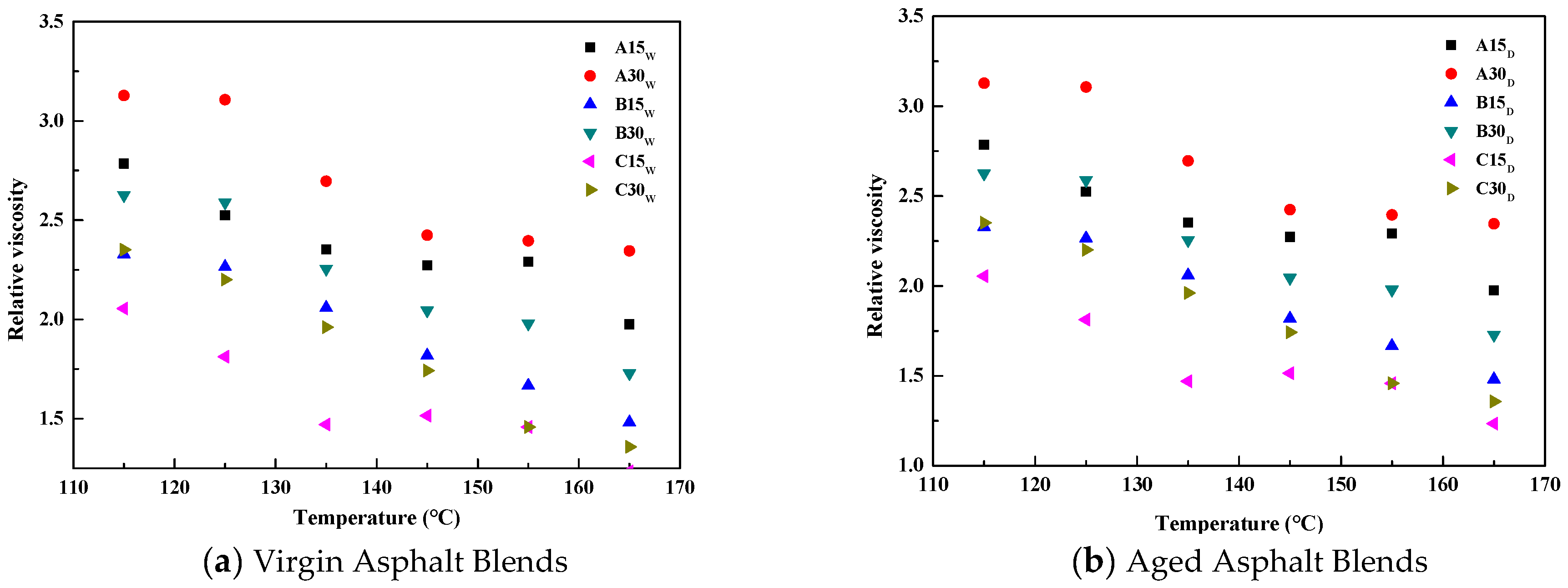
3.1. Asphalt Viscosity Evaluation Test Results and Analysis
3.2. Asphalt Rutting Factor Test Results and Analysis
3.3. Asphalt Rutting Factor Evaluation Test Results and Analysis
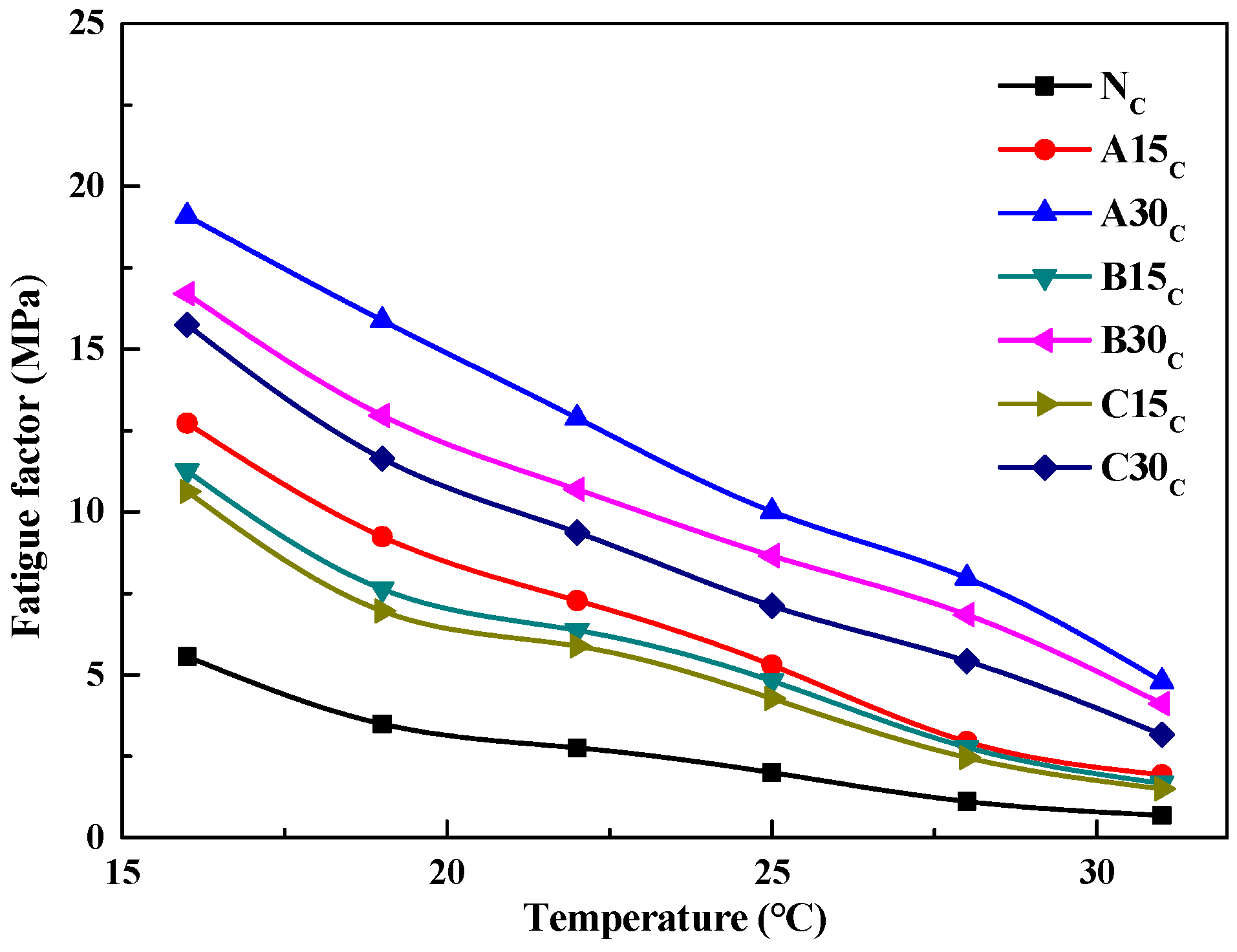
3.4. Asphalt Fatigue Factor Evaluation Test Results and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ržek, L.; Turk, M.R.; Tušar, M. Increasing the rate of reclaimed asphalt in asphalt mixture by using alternative rejuvenator produced by tire pyrolysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 177177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, M.I.; Dotelli, G.; Brandini, N.; Zampori, L. Comparative life cycle assessment of asphalt pavements using reclaimed asphalt, warm mix technology and cold in-place recycling. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 104, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Jiang, W.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Xiao, J.; Xu, Z. Application of atomic force microscopy in bitumen materials at the nanoscale: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 128059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Tan, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Improvement of evaluation indicator of interfacial interaction between asphalt binder and mineral fillers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Hu, K.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Kapyelata, C. Analysis of the Storage Stability Property of Carbon Nanotube/Recycled Polyethylene-Modified Asphalt Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Polymers 2021, 13, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Yu, C.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Chen, G.; Ma, R. Multi–scale enhancement mechanisms of graphene oxide on styrene–butadiene–styrene modified asphalt: An exploration from molecular dynamics simulations. Mater. Des. 2021, 208, 109901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, R.; Isacsson, U. Material-Related Aspects of Asphalt Recycling—State-of-the-Art. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2006, 18, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.H.; Hu, K.; Chen, G.X.; Chang, R.; Wang, Y. Molecular dynamics simulation and microscopic observation of compatibility and interphase of composited polymer modified asphalt with carbon nanotubes. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2021, 22, 528–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, F.; Caihua, Y.; Kui, H.; Yujing, C.; Yu, L.; Taoli, Z. A study of the microscopic interaction mechanism of styrene–butadiene-styrene modified asphalt based on density functional theory. Mol. Simul. 2021, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, A.; Hamzah, M.O.; Shahadan, Z. Selection of reclaimed asphalt pavement sources and contents for asphalt mix production based on asphalt binder rheological properties, fuel requirements and greenhouse gas emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 23, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dony, A.; Colin, J.; Bruneau, D.; Drouadaine, I.; Navaro, J. Reclaimed asphalt concretes with high recycling rates: Changes in reclaimed binder properties according to rejuvenating agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 41, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Leng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lin, S. Characterization of the effect of foaming water content on the performance of foamed crumb rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Z.; Yan, Q.; Ji, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, A. The aging behavior of reclaimed asphalt mixture with vegetable oil rejuvenators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Ruan, K.; Tao, W.; Sun, C.; Luo, L. Reducing the variability of multi-source reclaimed asphalt pavement materials: A practice in China. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 122389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, W.; Napiah, M.; Habib, N.Z.; Sutanto, M.H.; Alaloul, W.S.; Khan, M.I.; Musarat, M.A.; Memon, A.M. Modeling and design optimization of reclaimed asphalt pavement containing crude palm oil using response surface methodology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 291, 123288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirodkar, P.; Mehta, Y.; Nolan, A.; Sonpal, K.; Norton, A.; Tomlinson, C.; Dubois, E.; Sullivan, P.; Sauber, R. A study to determine the degree of partial blending of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) binder for high RAP hot mix asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacEachern, M.; Sanchez, X.; Oh, W.T. Mechanical Properties of Aggregates for Roadbase Partially Replaced with Reclaimed Asphalt Shingles. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 19, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrajfi, E.; Ashteyat, A.M.; Murad, Y.Z. Shear behaviour of RC beams made with natural, recycled aggregate concrete and reclaimed asphalt aggregates under normal and elevated temperature. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 40, 102681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Category | Penetration (25 °C/0.1 mm) | Softening Point (°C) | Ductility (15 °C/cm) | Viscosity (135 °C/Pa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test method | T0604 | T0606 | T0605 | T0625 |
| A | 27 | 73 | 3.2 | 2.99 |
| B | 31 | 71 | 4.6 | 2.67 |
| C | 35 | 67 | 6.5 | 2.23 |
| Indicators | Test Results | Specification | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C/0.1 mm) | 87 | 80~100 | |
| Softening point (°C) | 46.5 | ≥44 | |
| Ductility (15 °C/cm) | >100 | ≥100 | |
| Viscosity (135 °C/Pa·s) | 0.36 | - | |
| Residue after TFOT | Mass loss/% | −0.48 | ≤±0.8 |
| penetration ratio (25 °C/%) | 63.5 | ≥57 | |
| Ductility (10 °C/cm) | 12.9 | ≥8 | |
| Asphalt Types | Test Temperature (°C) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 115 | 125 | 135 | 145 | 155 | 165 | |
| NW, ND | 0.93, 1.46 | 0.66, 1.03 | 0.38, 0.68 | 0.29, 0.44 | 0.23, 0.32 | 0.19, 0.27 |
| A15W, A30W | 1.33, 1.87 | 0.94, 1.29 | 0.52, 0.72 | 0.39, 0.53 | 0.31, 0.42 | 0.25, 0.33 |
| B15W, B30W | 1.29, 1.72 | 0.89, 1.19 | 0.56, 0.68 | 0.38, 0.52 | 0.30, 0.39 | 0.24, 0.31 |
| C15W, C30W | 1.23, 1.61 | 0.85, 1.12 | 0.48, 0.65 | 0.36, 0.45 | 0.28, 0.34 | 0.23, 0.28 |
| A15D, A30D | 2.07, 2.83 | 1.42, 1.99 | 0.92, 1.23 | 0.59, 0.76 | 0.43, 0.55 | 0.35, 0.46 |
| B15D, B30D | 1.97, 2.61 | 1.38, 1.83 | 0.89, 1.14 | 0.56, 0.71 | 0.40, 0.51 | 0.33, 0.41 |
| C15D, C30D | 1.91, 2.49 | 1.31, 1.71 | 0.83, 1.08 | 0.54, 0.67 | 0.39, 0.46 | 0.32, 0.38 |
| Category | Sources of Aged Asphalt | Admixture of Aged Asphalt | Test Temperature | Aging Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical probability p-value (Δη) | 3.9 × 10−5 | 0.004 | 3.3 × 10−7 | 0.039 |
| Statistical probability p-value (η) | 0.851 | 0.100 | 2.9 × 10−4 | 0.013 |
| Category | Sources of Aged Asphalt | Admixture of Aged Asphalt | Test Temperature | Aging Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical probability p-value (ΔG*/sinδ) | 0.001 | 0.029 | 5.10 × 10−7 | 0.031 |
| Statistical probability p-value (G*/sinδ) | 0.533 | 0.056 | 1.35 × 10−5 | 0.068 |
| Category | Sources of Aged Asphalt | Admixture of Aged Asphalt | Test Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical probability p-value (ΔG*sinδ) | 0.009 | 0.016 | 0.009 |
| Statistical probability p-value (G*sinδ) | 0.524 | 0.003 | 2.87 × 10−3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Duan, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Qin, Y.; Chang, R. Evaluation of the Rheological Properties of Virgin and Aged Asphalt Blends. Polymers 2022, 14, 3623. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173623
Liu T, Duan W, Zhang J, Li Q, Xu J, Wang J, Qin Y, Chang R. Evaluation of the Rheological Properties of Virgin and Aged Asphalt Blends. Polymers. 2022; 14(17):3623. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173623
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tao, Weidang Duan, Jialin Zhang, Qiuping Li, Jian Xu, Jie Wang, Yongchun Qin, and Rong Chang. 2022. "Evaluation of the Rheological Properties of Virgin and Aged Asphalt Blends" Polymers 14, no. 17: 3623. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173623
APA StyleLiu, T., Duan, W., Zhang, J., Li, Q., Xu, J., Wang, J., Qin, Y., & Chang, R. (2022). Evaluation of the Rheological Properties of Virgin and Aged Asphalt Blends. Polymers, 14(17), 3623. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173623









