Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Preparation of Gelatin Films with Antimicrobial Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Source
2.2. Preparation of Plant Extract
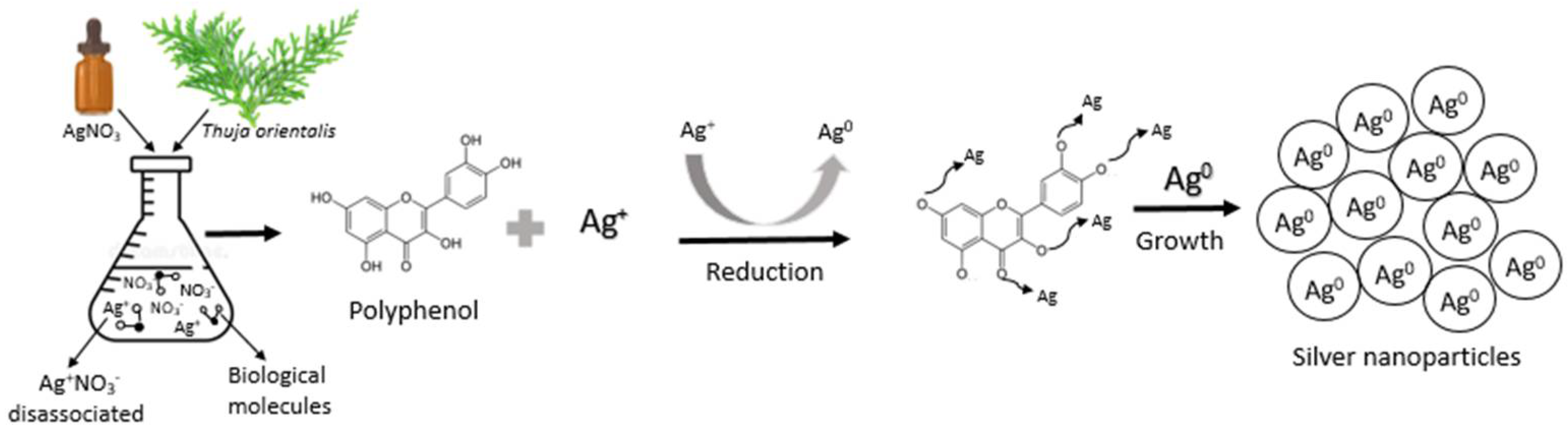
2.3. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
2.4. UV–Vis Spectroscopy
2.5. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
2.6. Zeta Potential Analysis
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.8. Preparation of films
2.9. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.10. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.11. Antibacterial Activity
2.12. Color
2.13. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. UV–Vis Spectral Analysis
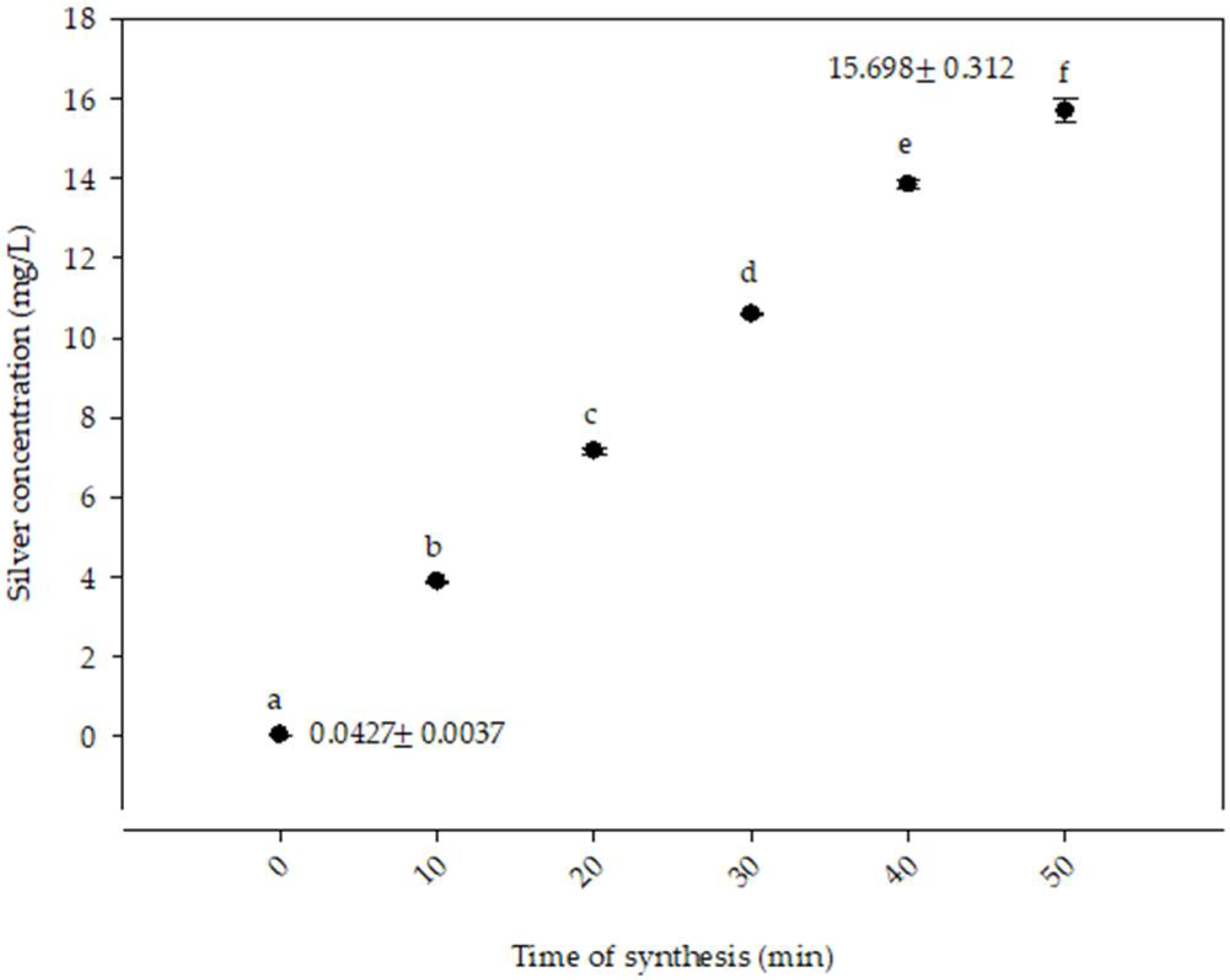
3.2. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
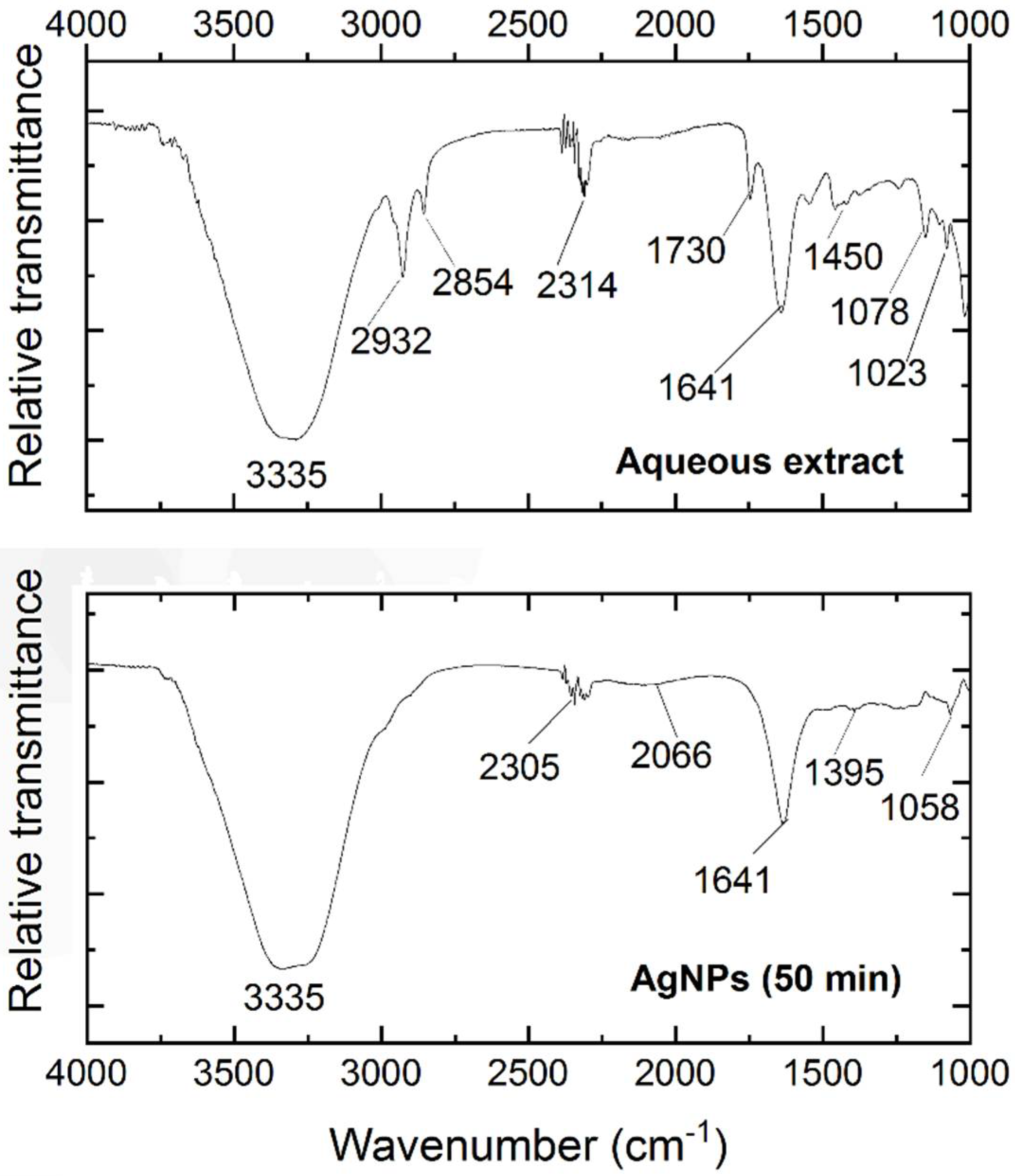
3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.4. Zeta potential Determinations
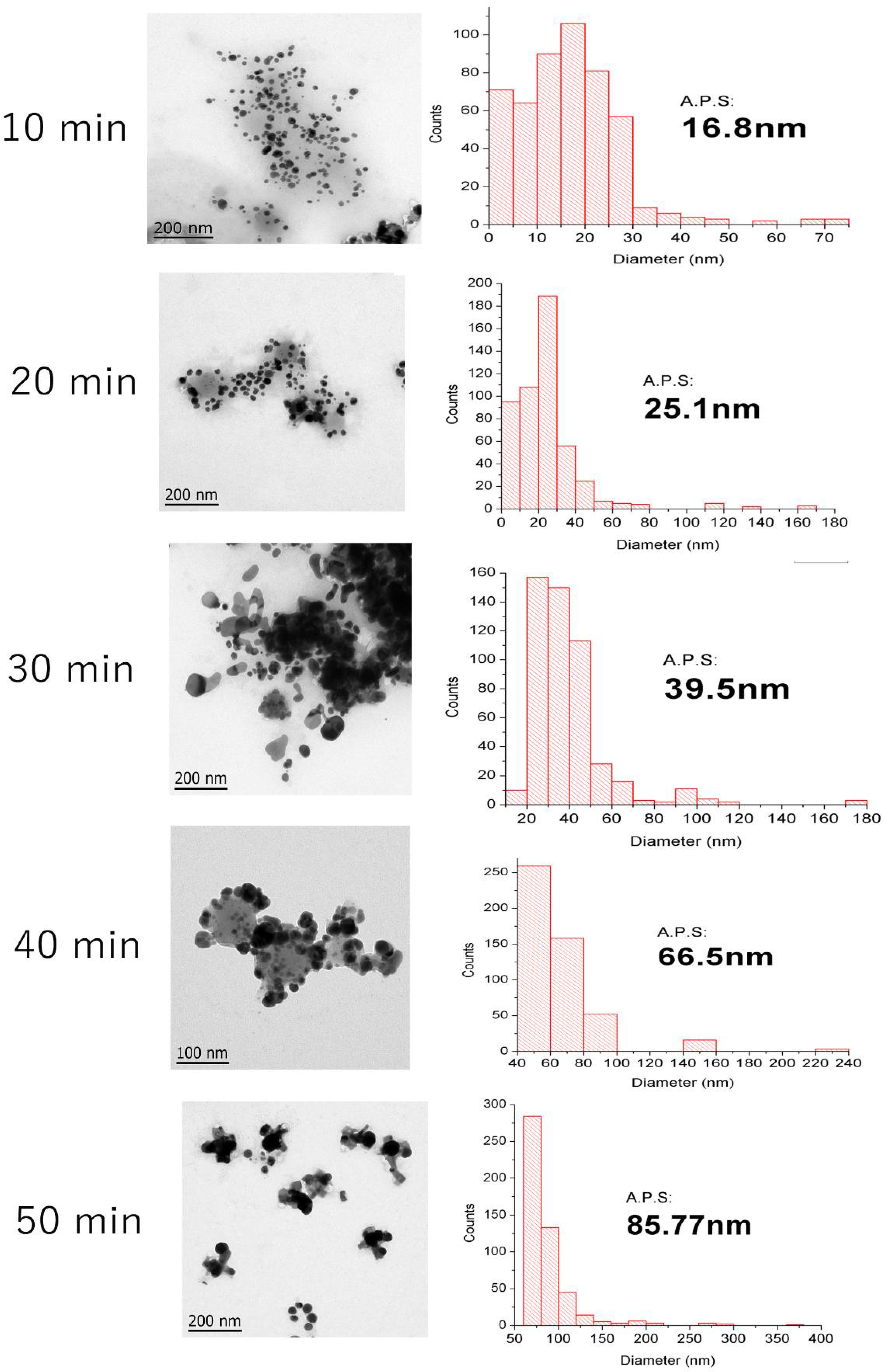
3.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.6. Performance of Silver Nanoparticles on Gelatin Films
Differential Scanning Calorimetry in Films
3.7. FTIR in Films
3.8. Antimicrobial Activity of Films
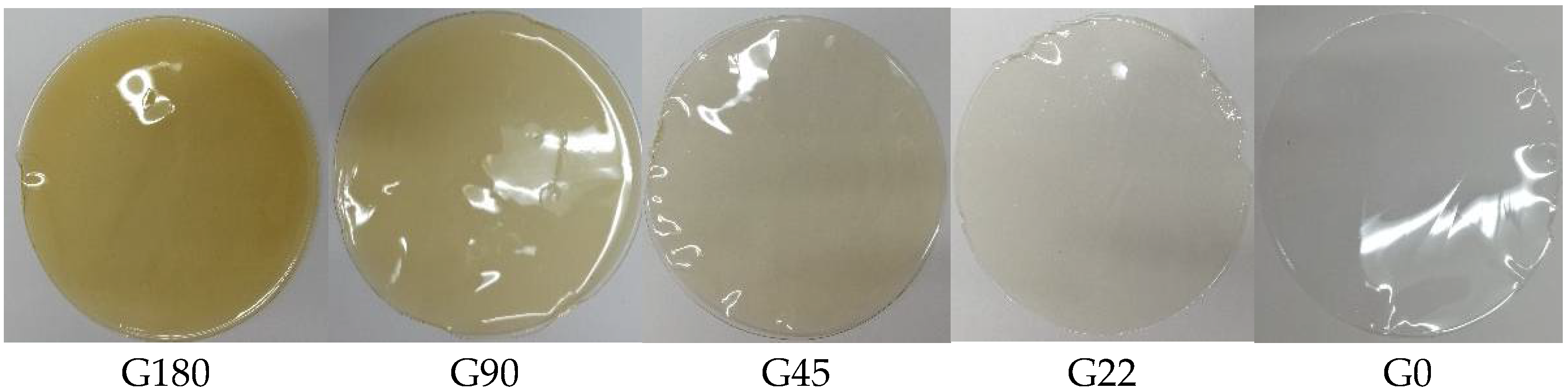
3.9. Color of The Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AgNPs | Silver Nanoparticles |
| SPR | Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
References
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajjadi, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Issaabadi, Z. Chapter 5-Green Nanotechnology. In Interface Science and Technology; Nasrollahzadeh, M., Sajadi, S.M., Sajjadi, M., Issaabadi, Z., Atarod, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 28, pp. 145–198. [Google Scholar]
- Daruich De Souza, C.; Ribeiro Nogueira, B.; Rostelato, M.E.C.M. Review of the methodologies used in the synthesis gold nanoparticles by chemical reduction. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 798, 714–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, A.; Jain, N.K. Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadoun, S.; Arif, R.; Jangid, N.K.; Meena, R.K. Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rónavári, A.; Kovács, D.; Igaz, N.; Vágvölgyi, C.; Boros, I.M.; Kónya, Z.; Pfeiffer, I.; Kiricsi, M. Biological activity of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles depends on the applied natural extracts: A comprehensive study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michna, A.; Adamczyk, Z.; Oćwieja, M.; Bielańska, E. Kinetics of silver nanoparticle deposition onto poly(ethylene imine) modified mica determined by AFM and SEM measurements. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 377, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michna, A.; Morga, M.; Adamczyk, Z.; Kubiak, K. Monolayers of silver nanoparticles obtained by green synthesis on macrocation modified substrates. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 227, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasuja, N.D.; Sharma, S.K.; Saxena, R.; Choudhary, J.; Sharma, R.; Joshi, S.C. Antibacterial, antioxidant and phytochemical investigation of Thuja orientalis leaves. J. Med. Plants Res. 2013, 7, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.-n.; Park, D.K.; Park, H.-J. Hair growth-promoting activity of hot water extract of Thuja orientalis. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, D.; Kang, Y.; Jang, S.; Yang, S.-J.; Kim, H. Ethanol extract of Thuja orientalis L. seeds ameliorated skin lesions in a dinitrofluorobenzene-induced mouse model of contact dermatitis. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2020, 16, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Kumar, P.; Singh, D.; Singh, V. Biological Properties of Thuja Orientalis Linn. Adv. Life Sci. 2012, 2, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ærøe Hyllested, J.; Espina Palanco, M.; Hagen, N.; Mogensen, K.B.; Kneipp, K. Green preparation and spectroscopic characterization of plasmonic silver nanoparticles using fruits as reducing agents. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umadevi, M.; Bindhu, M.R.; Sathe, V. A Novel Synthesis of Malic Acid Capped Silver Nanoparticles using Solanum lycopersicums Fruit Extract. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathna, T.C.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Raichur, A.M.; Mukherjee, A. Biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Citrus limon (lemon) aqueous extract and theoretical prediction of particle size. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 82, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Lozada, G.; Pérez-Marroquín, X.A.; Callejas-Quijada, G.; Campos-Montiel, R.G.; Morales-Peñaloza, A.; León-López, A.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. The Effect of High-Intensity Ultrasound and Natural Oils on the Extraction and Antioxidant Activity of Lycopene from Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) Waste. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khane, Y.; Benouis, K.; Albukhaty, S.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Abomughaid, M.M.; Al Ali, A.; Aouf, D.; Fenniche, F.; Khane, S.; Chaibi, W.; et al. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Citrus limon Zest Extract: Characterization and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, D. Honey mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 75, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Baig, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.; Liaqat, S.; Fatima, S.; Jabeen, S.; Shamim, N.; Othman, N.H. Honey as a Potential Natural Antioxidant Medicine: An Insight into Its Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 8367846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.; Hendi, A.; Mustafa Ortashi, K.; Elradi, D.; Eisa Omer, N.; Allehaib, L.; Al-Otiby, S.; Merghani, N.; Awad, A. Silver Nanoparticles Biogenic Synthesized using Orange Peel extract and their use as an anti-bacterial agent. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Nalini, S.P.K.; Prakash, N.U.; Madhankumar, D. One step green synthesis of silver nano/microparticles using extracts of Trachyspermum ammi and Papaver somniferum. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 94, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.; Sadaf, I.; Rafique, M.S.; Tahir, M.B. A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1272–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, R.; Sivakumar, S.; Kaur, H. Antimicrobial edible films in food packaging: Current scenario and recent nanotechnological advancements- a review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, H.M.; Salah Eldin, R.E.; Abu Serea, E.S.; Gomaa, N.M.; AboElmagd, G.M.; Salem, S.A.; Elsayed, Z.A.; Edrees, A.; Shams-Eldin, E.; Shalan, A.E. Advances in nanotechnology and antibacterial properties of biodegradable food packaging materials. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 20467–20484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, N.S.; Howell, N.K.; Sarbon, N.M. A Review on Potential Use of Gelatin-based Film as Active and Smart Biodegradable Films for Food Packaging Application. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharanathan, R.N. Biodegradable films and composite coatings: Past, present and future. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 14, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Giménez, B.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Montero, M.P. Functional and bioactive properties of collagen and gelatin from alternative sources: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, J.F.; Ruseckaite, R.A. Biodegradation behavior of three-layer sheets based on gelatin and poly (lactic acid) buried under indoor soil conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 116, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Chu, Y.; Tao, N.; Deng, S.; Wang, L.; Li, L. Application of Gelatin in Food Packaging: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) on a request from the Commission related to a 7th list of substances for food contact materials (Question N° EFSA-Q-2003-076, EFSA-Q-2004-144, EFSA-Q-2004-166, EFSA-Q-2004-082, EFSA-Q-2003-204, EFSA-Q-2003-205, EF-SA-Q-2003-206). EFSA J. 2005, 201, 1–28. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/201a (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Luo, Q.; Hossen, M.A.; Zeng, Y.; Dai, J.; Li, S.; Qin, W.; Liu, Y. Gelatin-based composite films and their application in food packaging: A review. J. Food Eng. 2022, 313, 110762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaraj, V.M.; Rambabu, K.; Banat, F.; Mittal, V. Effect of date fruit waste extract as an antioxidant additive on the properties of active gelatin films. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaraj, V.M.; Rambabu, K.; Banat, F.; Mittal, V. Natural antioxidants-based edible active food packaging: An overview of current advancements. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaraj, V.M.; Devaraju, S.; Rambabu, K.; Banat, F.; Mittal, V. Silver-sepiolite (Ag-Sep) hybrid reinforced active gelatin/date waste extract (DSWE) blend composite films for food packaging application. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nur Amila Najwa, I.S.; Mat Yusoff, M.; Nur Hanani, Z.A. Potential of Silver-Kaolin in Gelatin Composite Films as Active Food Packaging Materials. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 26, 100564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Hernández, L.; Arenas Islas, D.; Ramírez Ortega, P.A.; Flores Guerrero, M.U.; Neri Enriquez, D. Green Synthesis, Characterization and Stabilization of Nanoparticles Silver with Thuja orient. J. Nanomater. Mol. Nanotechnol. 2016, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, J.A.A.; Salah Eddine, L.; Abderrhmane, B.; Alonso-González, M.; Guerrero, A.; Romero, A. Green synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles by pheonix dactylifera leaf extract and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 17, 100280–100287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, E.; Ramezani, M. Extraction and Determination of Heavy Metals Using Silver Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles and Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. J. Appl. Chem. Res. 2019, 13, 36–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira, S.S.; de Araujo-Nobre, A.R.; Mafud, A.C.; Guimarães, M.A.; Alves, M.M.M.; Plácido, A.; Carvalho, F.A.A.; Arcanjo, D.D.R.; Mascarenhas, Y.; Costa, F.G.; et al. Silver nanoparticle stabilized by hydrolyzed collagen and natural polymers: Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial-antifungal evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Xu, L.; Wang, R.; Chen, R.; Sun, Y. The size-controllable preparation of chitosan/silver nanoparticle composite microsphere and its antimicrobial performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 220, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Goyal, D.; Kumar, R. Surfactant mediated interaction of vancomycin with silver nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 449, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Kumar, S.; Bafana, A.; Dahoumane, S.A.; Jeffryes, C. Individual and Combined Effects of Extracellular Polymeric Substances and Whole Cell Components of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii on Silver Nanoparticle Synthesis and Stability. Molecules 2019, 24, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroza-Toscano, M.; Lopez-Cuenca, S.; Rabelero, M.; Moreno-Medrano, E.; Mendizabal-Ruiz, A.; Salazar-Peña, R. Silver Nanoparticles Obtained by Semicontinuous Chemical Reduction Using Carboxymethyl Cellulose as a Stabilizing Agent and Its Antibacterial Capacity. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Ali, N.; Jamil, S.U.U.; Waseem, H.; Khan, K.; Pan, G. Insight into eco-friendly fabrication of silver nanoparticles by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its potential impacts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3266–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, V.V.; Love, A.J.; Sinitsyna, O.V.; Makarova, S.S.; Yaminsky, I.V.; Taliansky, M.E.; Kalinina, N.O. “Green” nanotechnologies: Synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Nat. 2014, 6, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, S.; Singh, R.K.; Panigrahi, B.; Suar, M.; Mandal, D. Photo-bioreduction of Ag(+) ions towards the generation of multifunctional silver nanoparticles: Mechanistic perspective and therapeutic potential. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 164, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oseguera-Galindo, D. Una revisión de la síntesis de nanopartículas de plata por reducción biológica. Contactos Rev. De Educ. En Cienc. E Ing. 2019, 114, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco Coello, F. Synthesis and size estimation of silver nanoparticles, by reduction with aqueous extracts of calyces leaves and seeds of hibiscus sabdariffa linn: Promotion of green synthesis. Rev. Boliv. De Química 2021, 38, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszka, J.; Zambrzycka-Szelewa, E.; Kulpa, J.S.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B. Discrimination between ionic silver and silver nanoparticles in consumer products using graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 2133–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Sharma, A.; Kurian, M.; Bhavesh, R.; Nam, J.-S.; Lee, S.-S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle using Myristica fragrans (nutmeg) seed extract and its biological activity. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2014, 9, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Kirmanidou, Y.; Sidira, M.; Bakopoulou, A.; Tsouknidas, A.; Prymak, O.; Papi, R.; Choli-Papadopoulou, T.; Epple, M.; Michailidis, N.; Koidis, P.; et al. Assessment of cytotoxicity and antibacterial effects of silver nanoparticle-doped titanium alloy surfaces. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, e220–e233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Sánchez, J.L.; Jiménez-Pérez, J.L.; Carbajal-Valdez, R.; Lopez-Gamboa, G.; Pérez-González, M.; Correa-Pacheco, Z.N. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Jalapeño Chili extract and thermal lens study of acrylic resin nanocomposites. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 678, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Millán, A.; Del Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Ramos-Enríquez, J.R.; Carrillo-Torres, R.C.; Zavala-Rivera, P.; Esquivel, R.; Álvarez-Ramos, E.; Moreno-Corral, R.; Guzmán-Zamudio, R.; Lucero-Acuña, A. Biosynthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using Parkinsonia florida leaf extract and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.; Das, V.K.; Deka, D. Ginger extract as a nature based robust additive and its influence on the oxidation stability of biodiesel synthesized from non-edible oil. Fuel 2017, 187, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehab-Ali, H.; Khalil -Mostafa, M.H.; Ismail-Eman, H.; Mohamed Heba, E. Grenn synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Psidumguajava leaf extract. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 46, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dada, A.O.; Adekola, F.A.; Dada, F.E.; Adelani-Akande, A.T.; Bello, M.O.; Okonkwo, C.R.; Inyinbor, A.A.; Oluyori, A.P.; Olayanju, A.; Ajanaku, K.O.; et al. Silver nanoparticle synthesis by Acalypha wilkesiana extract: Phytochemical screening, characterization, influence of operational parameters, and preliminary antibacterial testing. Heliyon 2019, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malini, S.; Vignesh Kumar, S.; Hariharan, R.; Pon Bharathi, A.; Renuka Devi, P.; Hemananthan, E. Antibacterial, photocatalytic and biosorption activity of chitosan nanocapsules embedded with Prosopis juliflora leaf extract synthesized silver nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.; Naushad, M.; Prakash Dwivedi, R.; Alothman, Z.A.; Mola, G.T. Novel development of nanoparticles to bimetallic nanoparticles and their composites: A review. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2019, 31, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.; Das, V.K.; Deka, D. A green approach for enhancing oxidation stability including long storage periods of biodiesel via Thuja oreantalis L. as an antioxidant additive. Fuel 2019, 253, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardi, C.N.; Gomes, A.; Rocha, F.; De tommaso, J.; Patience, G. Experimental methods in chemical engineering: Zeta potential. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadavenkatesan, T.; Vinayagam, R.; Selvaraj, R. Green synthesis and structural characterization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using the pod extract of Clitoria ternatea and its application towards dye degradation. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajitha, B.; Ashok Kumar Reddy, Y.; Shameer, S.; Rajesh, K.M.; Suneetha, Y.; Sreedhara Reddy, P. Lantana camara leaf extract mediated silver nanoparticles: Antibacterial, green catalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 149, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oćwieja, M.; Morga, M. Electrokinetic properties of cysteine-stabilized silver nanoparticles dispersed in suspensions and deposited on solid surfaces in the form of monolayers. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 297, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, R.; Chandran, K.; Harper, S.L.; Yun, S.-I.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Plant extract synthesized silver nanoparticles: An ongoing source of novel biocompatible materials. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 70, 356–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.; Khan, M.A.M.; Siddiqui, M.K.J.; Alsalhi, M.S.; Alrokayan, S.A. Green synthesis, characterization and evaluation of biocompatibility of silver nanoparticles. Phys. E-Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostructures 2011, 43, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gengan, R.M.; Anand, K.; Phulukdaree, A.; Chuturgoon, A. A549 lung cell line activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Albizia adianthifolia leaf. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 105, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Urbina, J.; Cruz-Alonso, A.; Santander-González, M.; Méndez-Albores, A.; Vázquez-Durán, A. Nanoscale Zinc Oxide Particles for Improving the Physiological and Sanitary Quality of a Mexican Landrace of Red Maize. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salayová, A.; Bedlovičová, Z.; Daneu, N.; Baláž, M.; Lukáčová Bujňáková, Z.; Balážová, Ľ.; Tkáčiková, Ľ. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles with Antibacterial Activity Using Various Medicinal Plant Extracts: Morphology and Antibacterial Efficacy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélteky, P.; Rónavári, A.; Igaz, N.; Szerencsés, B.; Tóth, I.Y.; Pfeiffer, I.; Kiricsi, M.; Kónya, Z. Silver nanoparticles: Aggregation behavior in biorelevant conditions and its impact on biological activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 667–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S. State diagram of foods: Its potential use in food processing and product stability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theerawitayaart, W.; Prodpran, T.; Benjakul, S.; Sookchoo, P. Properties of films from fish gelatin prepared by molecular modification and direct addition of oxidized linoleic acid. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 88, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughriba, S.; Souissi, N.; Jridi, M.; Li, S.; Nasri, M. Thermal, mechanical and microstructural characterization and antioxidant potential of Rhinobatos cemiculus gelatin films supplemented by titanium dioxide doped silver nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, P.; Rhim, J.-W. Physical, mechanical and antimicrobial properties of gelatin based active nanocomposite films containing AgNPs and nanoclay. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moula Ali, A.M. Effect of squalene rich fraction from shark liver on mechanical, barrier and thermal properties of fish (Probarbus Jullieni) skin gelatin film. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.M.; Kishimura, H.; Benjakul, S. Extraction efficiency and characteristics of acid and pepsin soluble collagens from the skin of golden carp (Probarbus Jullieni) as affected by ultrasonication. Process Biochem. 2018, 66, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-López, A.; Fuentes-Jiménez, L.; Hernández-Fuentes, A.; Campos-Montiel, R.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Hydrolysed Collagen from Sheepskins as a Source of Functional Peptides with Antioxidant Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamróz, E.; Kopel, P.; Juszczak, L.; Kawecka, A.; Bytesnikova, Z.; Milosavljević, V.; Kucharek, M.; Makarewicz, M.; Adam, V. Development and characterisation of furcellaran-gelatin films containing SeNPs and AgNPs that have antimicrobial activity. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Wang, L.-F.; Rhim, J.-W. Effect of melanin nanoparticles on the mechanical, water vapor barrier, and antioxidant properties of gelatin-based films for food packaging application. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamróz, E.; Kopel, P.; Juszczak, L.; Kawecka, A.; Bytesnikova, Z.; Milosavljevic, V.; Makarewicz, M. Development of furcellaran-gelatin films with Se-AgNPs as an active packaging system for extension of mini kiwi shelf life. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, S.; Salem, R.B.S.-B.; Hamdi, M.; Jellouli, K.; Ayadi, W.; Nasri, M.; Boufi, S. Nanocomposite films based on chitosan–poly(vinyl alcohol) and silver nanoparticles with high antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 111, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Castañón, G.A.; Niño-Martínez, N.; Martínez-Gutierrez, F.; Martínez-Mendoza, J.R.; Ruiz, F. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles with different sizes. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2008, 10, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailasa, S.K.; Park, T.-J.; Rohit, J.V.; Koduru, J.R. Chapter 14-Antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles. In Nanoparticles in Pharmacotherapy; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 461–484. [Google Scholar]
- Arfat, Y.A.; Ahmed, J.; Hiremath, N.; Auras, R.; Joseph, A. Thermo-mechanical, rheological, structural and antimicrobial properties of bionanocomposite films based on fish skin gelatin and silver-copper nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathare, P.B.; Opara, U.L.; Al-Said, F.A.-J. Colour Measurement and Analysis in Fresh and Processed Foods: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



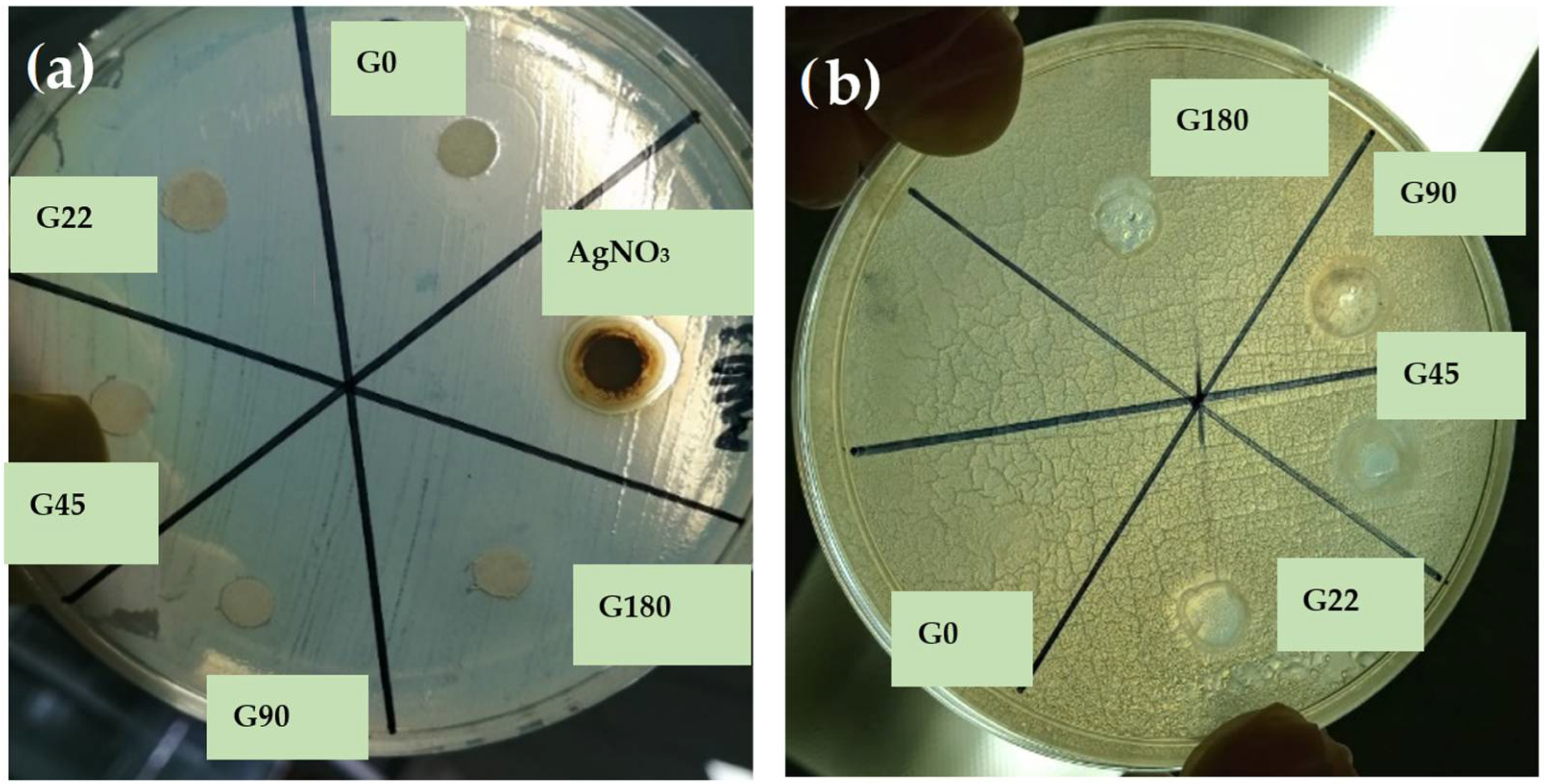
| Key | Distilled Water (mL) | Colloidal Solution (AgNPs)(mL) | Gelatin (g) | Glycerol (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G180 | 0 | 180 | 4 | 2 |
| G90 | 90 | 90 | 4 | 2 |
| G45 | 135 | 45 | 4 | 2 |
| G22 | 157.5 | 22.5 | 4 | 2 |
| G0 | 180 | 0 | 4 | 2 |
| Treatments | Tg (°C) | Tm (°C) | ∆H (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| G0 | 73.71 ± 0.531 a | 102.93 ± 0.132 ab | 1.731 ± 0.754 ab |
| G22 | 73.66 ± 0.316 a | 102.40 ± 0.648 b | 2.227± 0.548 a |
| G45 | 72.41 ± 0.786 a | 103.09 ± 0.188 ab | 1.821 ± 0.014 ab |
| G90 | 66.97 ± 0.347 b | 103.17 ± 0.030 ab | 1.340 ± 0.028 b |
| G180 | 66.42 ± 0.565 b | 103.31 ± 0.179 a | 2.084 ± 0.110 b |
| Treatments | L* | a* | b* |
|---|---|---|---|
| G0 | 91.87 ± 0.182 a | −0.206 ± 0.011 e | 1.883 ± 0.005 e |
| G22 | 90.683 ± 0.073 b | −0.613 ± 0.005 d | 4.27 ± 0 d |
| G45 | 90.49 ± 0 c | −0.666 ± 0.011 c | 5.066 ± 0.005 c |
| G90 | 88.276 ± 0.153 d | 0.14 ± 0 b | 9.68 ± 0.01 b |
| G180 | 85.38 ± 0.199 e | 1.223 ± 0.015 a | 17.1 ± 0.051 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Marroquín, X.A.; Aguirre-Cruz, G.; Campos-Lozada, G.; Callejas-Quijada, G.; León-López, A.; Campos-Montiel, R.G.; García-Hernández, L.; Méndez-Albores, A.; Vázquez-Durán, A.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Preparation of Gelatin Films with Antimicrobial Activity. Polymers 2022, 14, 3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173453
Pérez-Marroquín XA, Aguirre-Cruz G, Campos-Lozada G, Callejas-Quijada G, León-López A, Campos-Montiel RG, García-Hernández L, Méndez-Albores A, Vázquez-Durán A, Aguirre-Álvarez G. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Preparation of Gelatin Films with Antimicrobial Activity. Polymers. 2022; 14(17):3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173453
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Marroquín, Xóchitl A., Gabriel Aguirre-Cruz, Gieraldin Campos-Lozada, Graciela Callejas-Quijada, Arely León-López, Rafael G. Campos-Montiel, Laura García-Hernández, Abraham Méndez-Albores, Alma Vázquez-Durán, and Gabriel Aguirre-Álvarez. 2022. "Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Preparation of Gelatin Films with Antimicrobial Activity" Polymers 14, no. 17: 3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173453
APA StylePérez-Marroquín, X. A., Aguirre-Cruz, G., Campos-Lozada, G., Callejas-Quijada, G., León-López, A., Campos-Montiel, R. G., García-Hernández, L., Méndez-Albores, A., Vázquez-Durán, A., & Aguirre-Álvarez, G. (2022). Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Preparation of Gelatin Films with Antimicrobial Activity. Polymers, 14(17), 3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173453








