A Self-Healing Ionic Liquid-Based Ionically Cross-Linked Gel Polymer Electrolyte for Electrochromic Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
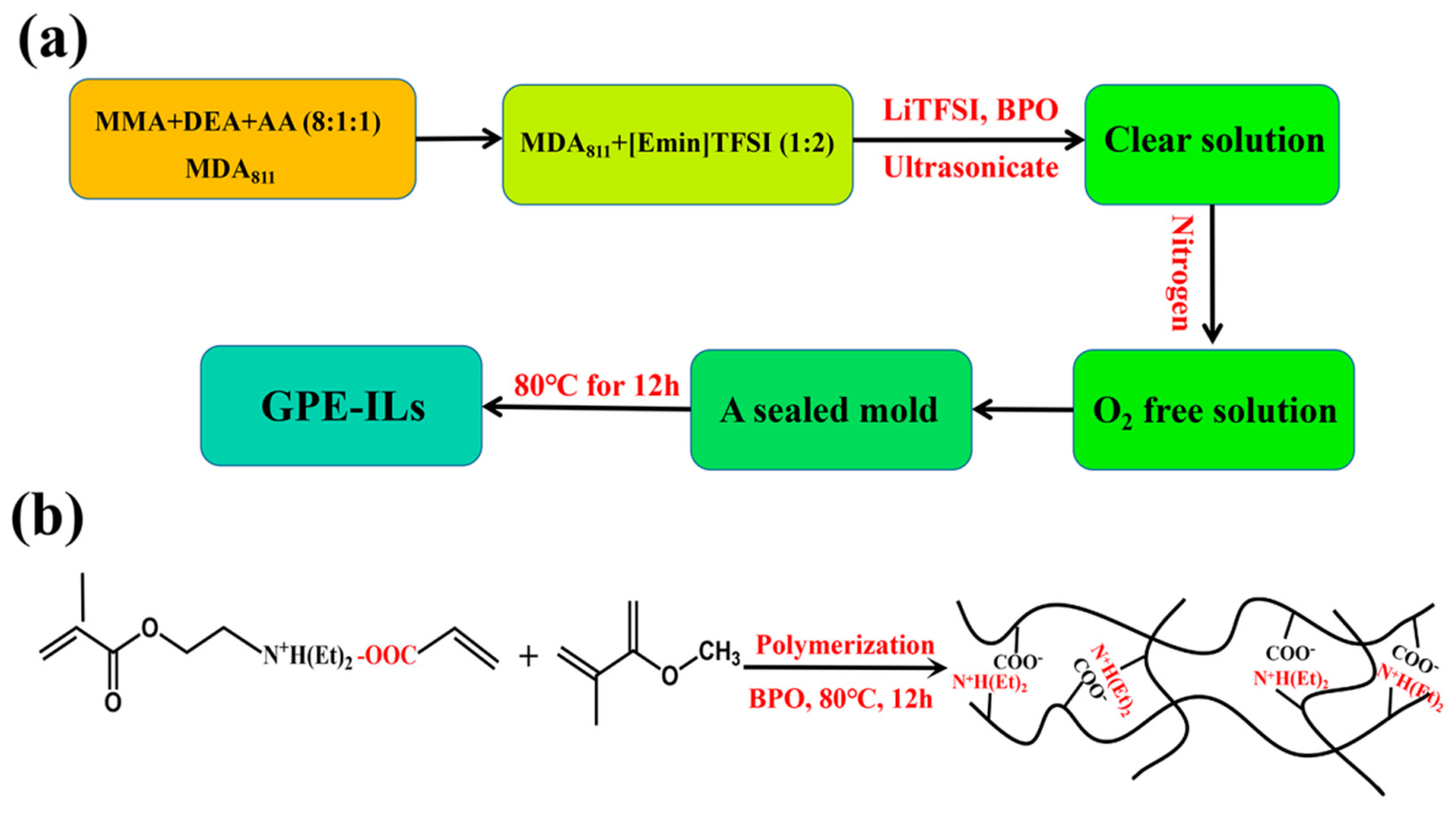
2.2. Preparation of the GPE-ILs
2.3. Fabrication of the Electrochromic Layers
2.4. Assembly of EC Device
2.5. Characterization
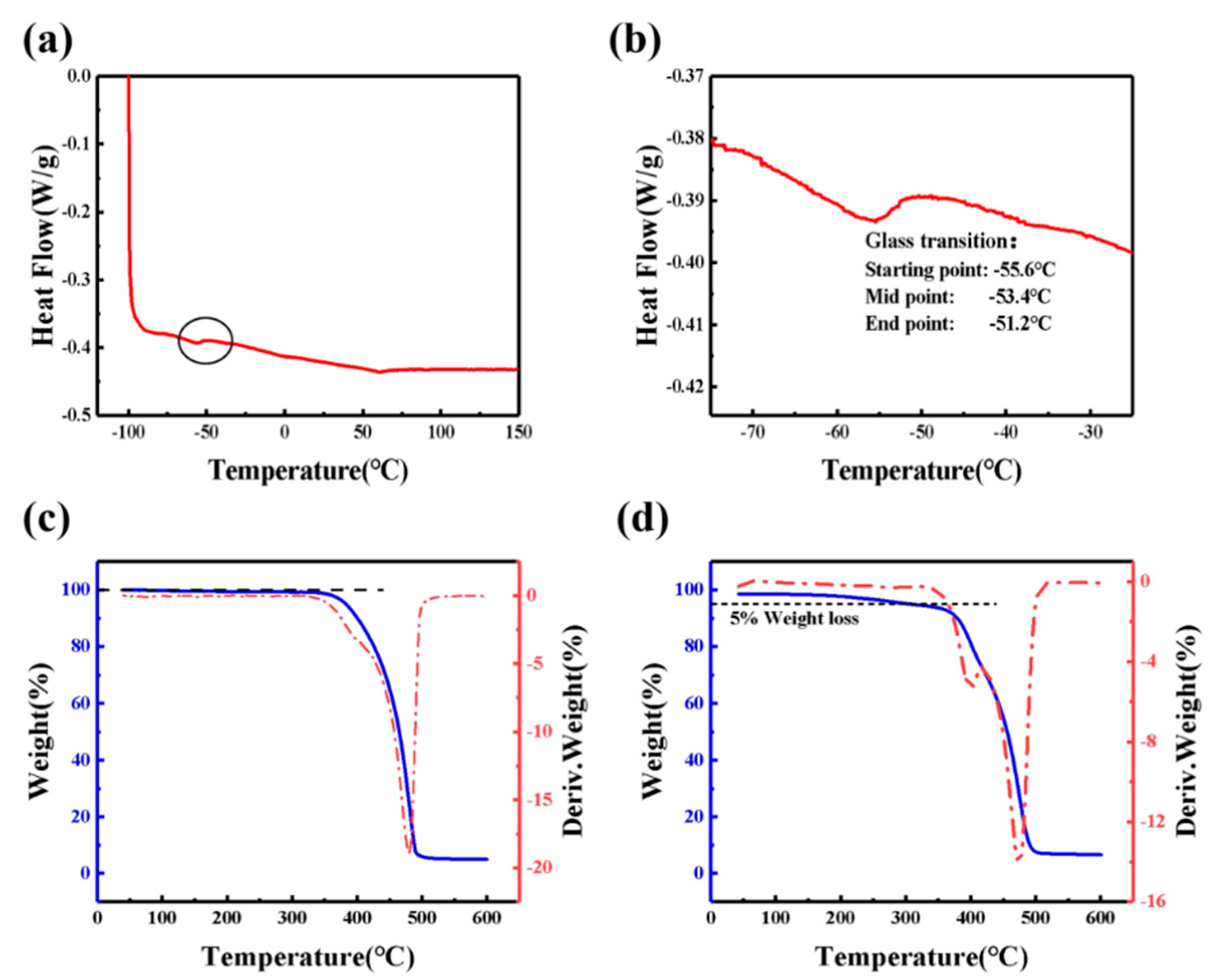
2.5.1. The Thermal Properties of GPE-ILs
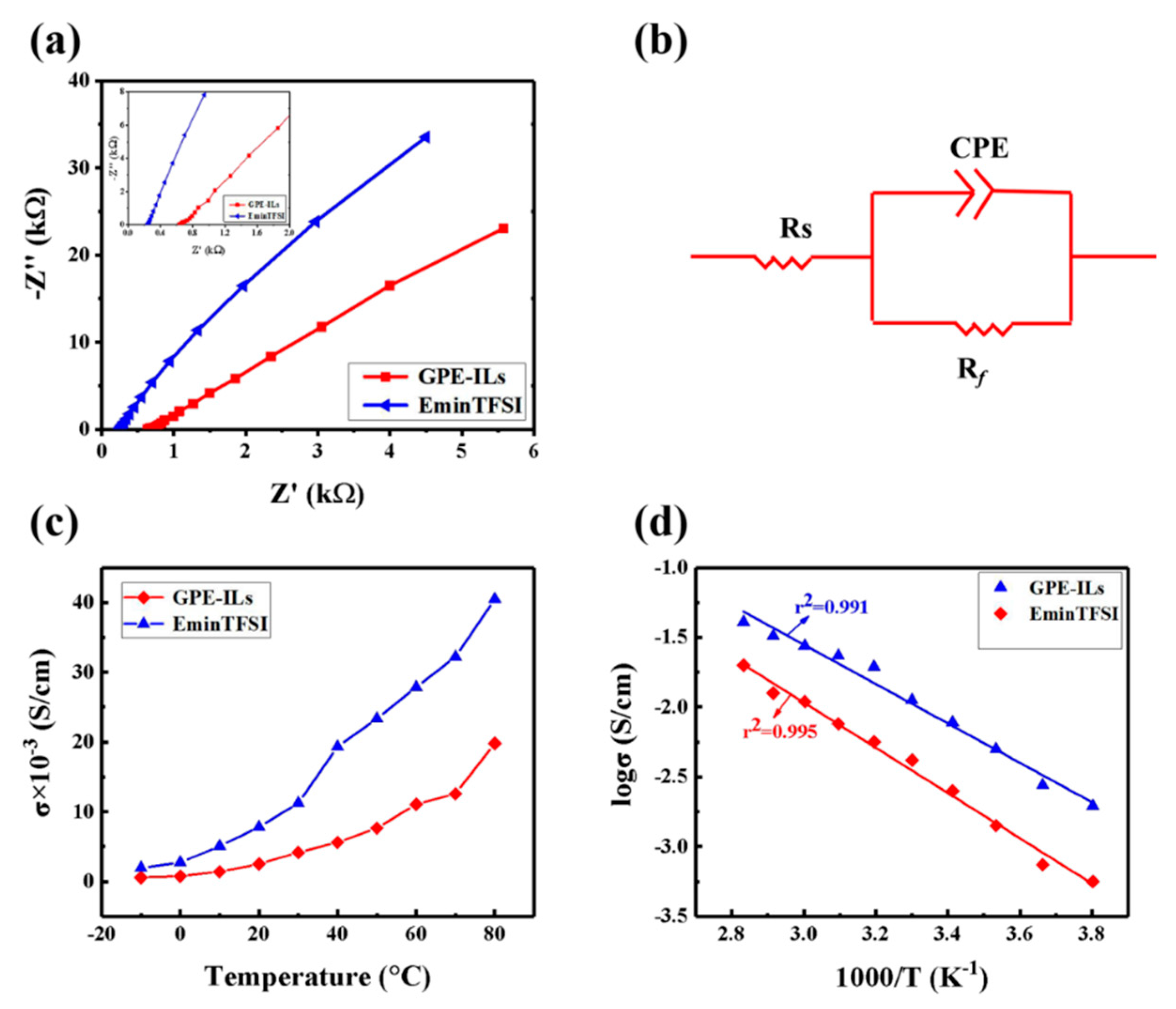
2.5.2. The Electrochemical Performance of GPE-ILs
2.5.3. The Optical Transmittances of the ECDs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Thermal Properties of GPE-ILs
3.2. The Ionic Conductivity of GPE-ILs
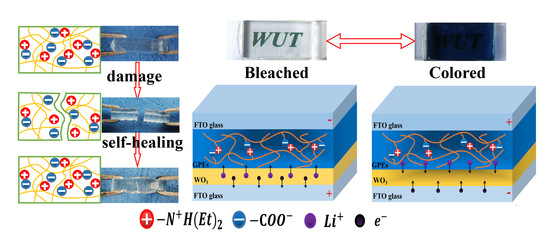
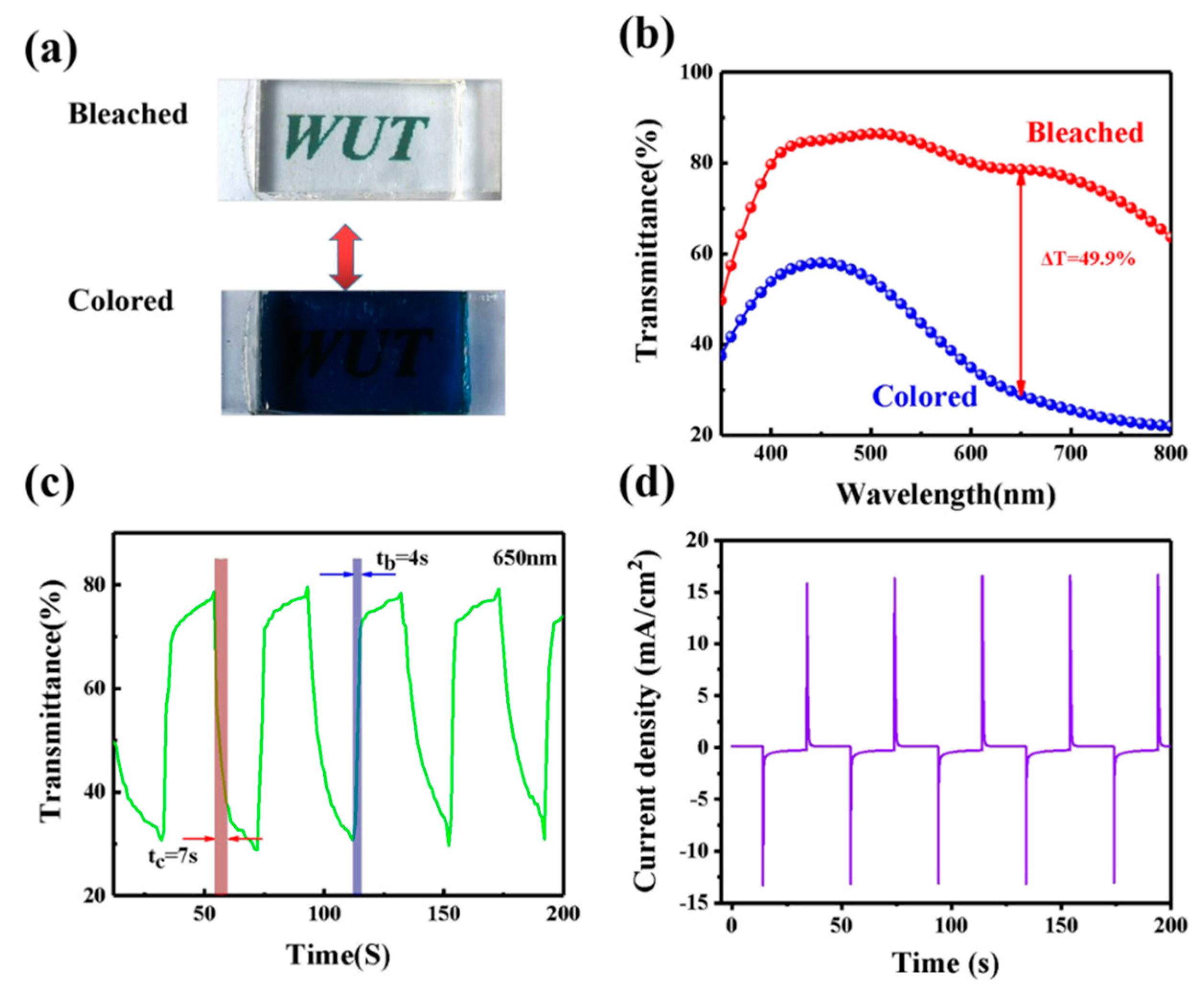
3.3. The Analysis of the ECD
3.4. The Coloration Efficiency and Cycling Durability of ECD
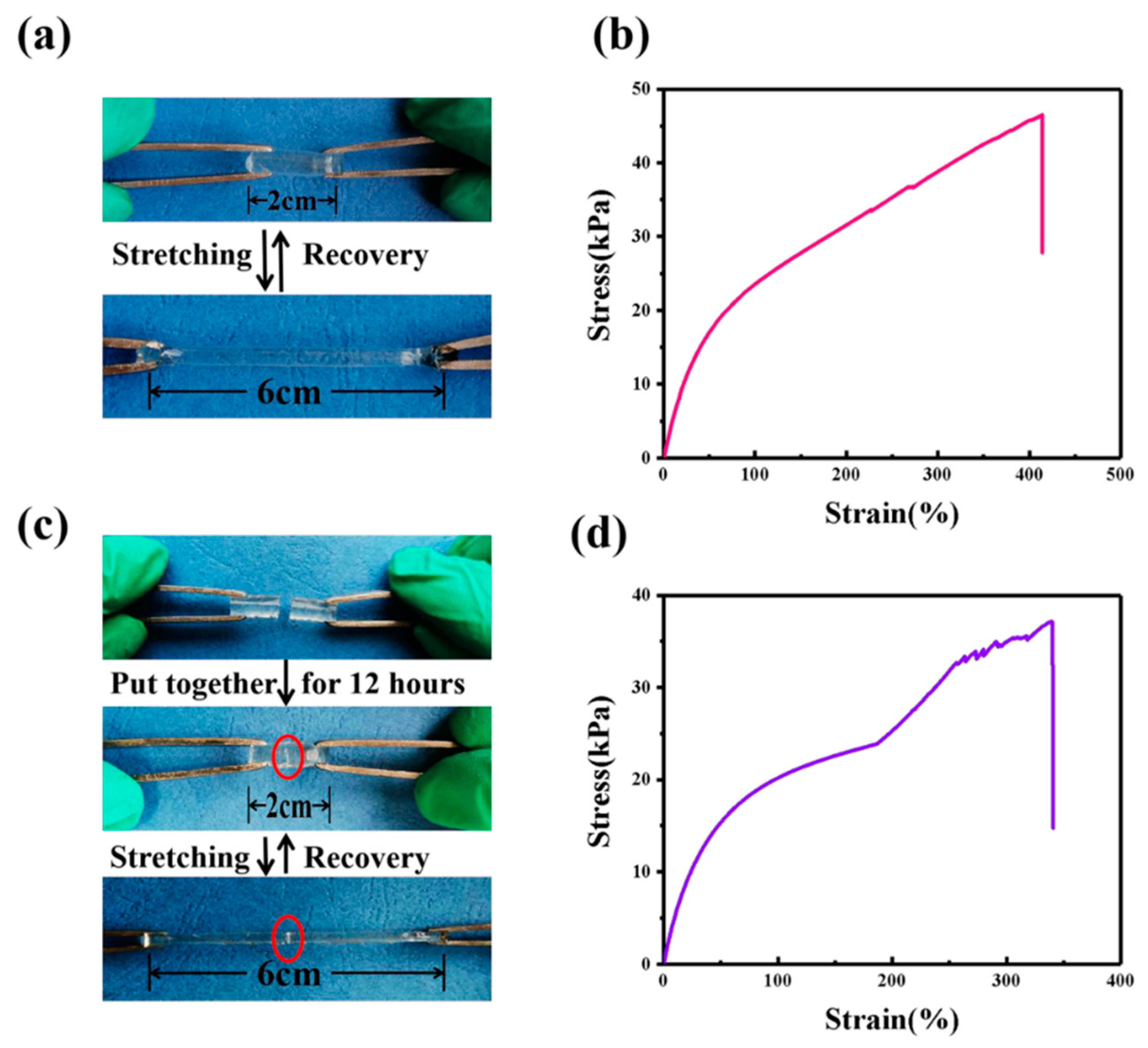
3.5. The Self-Healing Ability of GPE-ILs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.T.; Shao, S.; Yan, l.j.; Meng, H.; He, y.w.; Yao, C.; Xu, P.P.; Zhang, X.T.; Hu, W.P.; Huang, W. Highly robust and flexible WO3·2H2O/PEDOT films for improved electrochromic performance in near-infrared region. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 2269–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.W.; Wang, S.X.; Soo, D.X.Y.; Xu, J.W. Viologen-Based Electrochromic Materials: From Small Molecules, Polymers and Composites to Their Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.W.; Li, K.R.; Liu, X.L.; Xu, K.X.; Su, Y.; Hou, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.H.; Li, Y.G.; Wang, H.Z. Continuously Processed, Long Electrochromic Fibers with Multi-Environmental Stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 28451–28462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Li, R.; Li, C.; Hou, C.Y.; Li, Y.G.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, H.Z. Regulation of carbon content in MOF-derived hierarchical-porous NiO@C films for high-performance electrochromism. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Barrett, M.; Duane, B.; Gu, J.; Zenhausern, F. Materials and processing of polymer-based electrochromic devices. Mater. Sci. Eng. B-Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2018, 288, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.J.; Bhatt, G.G.; Ray, J.R.; Suryavanshi, P.; Panchal, C.J. All-inorganic solid-state electrochromic devices: A review. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2010, 21, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.K.; Ding, G.Q.; Ma, J.; Lee, P.S.; Lu, X.H. Hybrid Materials and Polymer Electrolytes for Electrochromic Device Applications. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4071–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, Y.; Cirpan, A.; Toppare, L. Construction of electrochromic devices using thiophene based conducting polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Perera, K.; He, J.Z.; Gumyusenge, A.; Mei, J.G. Solution-processable electrochromic materials and devices: Roadblocks and strategies towards large-scale applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 12761–12789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eh, A.L.S.; Tan, A.W.M.; Cheng, X.; Magdassi, S.; Lee, P.S. Recent Advances in Flexible Electrochromic Devices: Prerequisites, Challenges, and Prospects. Energy Technol. 2018, 6, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, R.J. Electrochromic Materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 2011, 41, 241–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, R.; Elshorbagy, M.H.; Kamal, H.; Hashem, H.M.; Abdelhady, K. Preparation and characterization of protonic solid electrolyte applied to a smart window device with high optical modulation. Optik 2017, 135, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.Y.; Zhang, Y.D.; Que, M.M.; Xiao, Y.B.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Yuan, K.; Chen, Y.W. A facile in situ approach to ion gel based polymer electrolytes for flexible lithium batteries. Rsc Adv. 2017, 7, 54391–54398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ileperuma, O.A. Gel polymer electrolytes for dye sensitised solar cells: A review. Mater. Technol. 2013, 28, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.S.; Fan, S.C.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.C.; Li, Y.; Fang, J.G.; Meng, C.Z. Al-ion polymer solid electrolyte. Acta Chim. Sin. 2019, 77, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlicka, A.; Dragunski, D.C.; Guimaraes, K.V.; Avellaneda, C.O. Electrochromic devices with solid electrolytes based on natural polymers. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2004, 216, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, E.; Aydin, M.F.; Oksuz, A.U. A practical approach for generation of WO3-based flexible electrochromic devices. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2020, 24, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.Y.; Li, X.L.; Bae, J.; Kim, S.H.; Moon, H.C. Non-volatile, Li-doped ion gel electrolytes for flexible WO3-based electrochromic devices. Mater. Des. 2019, 162, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, F.M.; Meunier, L.; Cochrane, C.; Koncar, V. Evaluation of Solid or Liquid Phase Conducting Polymers Within a Flexible Textile Electrochromic Device. J. Disp. Technol. 2013, 9, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Dong, G.B.; Liu, J.; Ye, S.B.; Diao, X.G. Polyvinyl butyral-based gel polymer electrolyte films for solid-state laminated electrochromic devices. Ionics 2017, 23, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.F.; Li, H.Z.; Yue, Y.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, H.Z.; Li, Y.G.; Chen, P. 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate-doped high ionic conductivity gel electrolytes with reduced anodic reaction potentials for electrochromic devices. Mater. Des. 2017, 118, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.R.; Jiang, H.Y.; Chang, Z.G.; Wu, W.; Wu, G.H.; Wu, R.M.; Li, J.Q. Recent achievements in self-healing materials based on ionic liquids: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 13543–13558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Morrissey, T.G.; Acome, E.; Allec, S.I.; Wong, B.M.; Keplinger, C.; Wang, C. A Transparent, Self-Healing, Highly Stretchable Ionic Conductor. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Martin, P.; Vasilyev, G.; Nandi, R.; Amdursky, N.; Zussman, E. Processable, Ion-Conducting Hydrogel for Flexible Electronic Devices with Self-Healing Capability. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 11130–11141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.Y.; Duan, Y.R.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, H.Z.; Li, Y.G. Bio-applicable and electroactive near-infrared laser-triggered self-healing hydrogels based on graphene networks. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 14991–14996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.L.; Panhuis, M.I.H. Self-Healing Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9060–9093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Ou, Z.W.; Tang, H.T.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.J. Study of the formation of a solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) in ionically crosslinked polyampholytic gel electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 4414–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Zhu, C.Z.; Guo, L.; Yan, M.Y.; Wu, L.L.; Zhu, B.; Qi, C.J.; Liu, S.Y.; Zhang, H.; Peng, Y. A novel ionically crosslinked gel polymer electrolyte as an ion transport layer for high-performance electrochromic devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 3744–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.N.; Lin, T.R.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Peng, J.; Li, J.Q.; Zhai, M.L. One-step radiation synthesis of novel star-shaped polymeric ionic liquid-POSS gel electrolytes with high ionic conductivity and mechanical properties for supercapacitor. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 16347–16359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.C.; Lodge, T.P.; Frisbie, C.D. DC-Driven, Sub-2 V Solid-State Electrochemiluminescent Devices by Incorporating Redox Coreactants into Emissive Ion Gels. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 5358–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castner, E.W.; Wishart, J.F. Spotlight on ionic liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 120901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yu, H.J. Ionic liquids for electrochemical energy storage devices applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, M.C.; Pereira, R.F.P.; Alves, R.; Nunes, S.C.; Fernandes, M.; Goncalves, H.M.R.; Pereira, S.; Silva, M.M.; Fortunato, E.; Rego, R.; et al. Electrochromic Device Composed of a Di-Urethanesil Electrolyte Incorporating Lithium Triflate and 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; Leones, R.; Costa, A.M.S.; Silva, M.M.; Pereira, S.; Mano, J.F.; Fortunato, E.; Rego, R.; de Zea Bermudez, V. Electrochromic devices incorporating biohybrid electrolytes doped with a lithium salt, an ionic liquid or a mixture of both. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 161, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.J.; Song, J.; Feng, R.X.; Shan, Z.Q. Ionic liquid gel electrolytes for quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 69, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.P.; Yamada, K.; Park, J.S.; Sekhon, S.S. Correlation between Ion Diffusional Motion and Ionic Conductivity for Different Electrolytes Based on Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 113, 5381–53390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egashira, M.; Yoshimoto, N.; Morita, M. The Addition of Ethylene Carbonate to Ionic Liquid Gel Electrolyte for Lithium Batteries. Electrochemistry 2009, 77, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, J.H.; Lan, Z.; Lin, J.M.; Huang, M.L.; Huang, Y.F.; Fan, L.Q.; Luo, G.G. Electrolytes in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2136–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.P.; Lin, F.; Richards, R.M.; Engtrakul, C.; Tencet, R.C.; Wolden, C.A. The influence of sol-gel processing on the electrochromic properties of mesoporous WO3 films produced by ultrasonic spray deposition. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol Cells 2014, 121, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.S.; Zhou, J.P.; Shen, F.L. A hybrid gel polymer electrolyte with imide groups modified by the coupling agent and its application in electrochromic devices. J. Sol.-Gel. Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akashi, H.; Shibuya, M.; Orui, K.; Shibamoto, G.; Sekai, K. (Practical performances of Li-ion polymer batteries with LiNi0.8Co0.2O2, MCMB, and PAN-based gel electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AFlora, X.H.; Ulaganathan, M.; Rajendran, S. Role of Different Plasticizers in Li-Ion Conducting Poly(Acrylonitrile)-Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Hybrid Polymer Electrolyte. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2013, 62, 737–742. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, H.Y.; Lian, F.; Wen, Y.; Pan, X.R.; Sun, J.L. Thermal Stability of Novel Polyvinyl Formal Based Gel Polymer Electrolyte. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. Chin. 2014, 35, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.; Nguyen, C.; Kim, B.; Han, M.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J. Synthesis and characteristics of acrylol borate as new acrylic gelator for lithium secondary battery. Macromol. Res. 2008, 16, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.H.; Li, Q.; Xia, Y.Q.; Liang, Y.M. Synthesis, Characterization, Thermal Analyses, and Spectroscopic Properties of Novel Naphthyl-Functionalized Imidazolium Ionic Liquids. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 92, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ECDs Construction | Ionic Conductivity (S/cm) | Switching Time (s) tc/tb | Coloration Efficiency (cm2 C−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTO/WO3/protonic gelatin-based solid electrolyte/NiO/FTO | 1.28 × 10−5 (25 °C) | 30/30 | 38.1 | 12 |
| ITO/WO3/PVB-based GPEFs/Ni1−xO/ITO | 4.0 × 10−5 (25 °C) | 16.5/9.5 | 175.3 | 20 |
| FTO/WO3/PMMA-[Emim]BF4/LiClO4/FTO | 2.9 × 10−3 (25 °C) | 62.6/41.2 | 55.3 | 21 |
| FTO/WO3/PADA gel electrolyte/NiO/FTO | 1.33 × 10−2 (25 °C) | 7.5/8.5 | 78.7 | 28 |
| ITO/WO3/d-PCL(530)/siloxane2[Emim]BF4/LiCF3SO3/ITO | 4.0 × 10−4 (36 °C) | 30/50 | 152 | 34 |
| ITO/PANI:DBSA/PVdFHFP-ICPTES-ZrO2 /PEDOT:PSS/ITO | 2.5 × 10−4 (25 °C) | 10.06/9.50 | / | 46 |
| FTO/WO3/GPE-ILs/FTO | 3.29 × 10−3 (25 °C) | 7/4 | 96.2 | This paper |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.; Liu, S.; Guo, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Cao, M.; Wu, L.; Xiang, T.; Peng, Y. A Self-Healing Ionic Liquid-Based Ionically Cross-Linked Gel Polymer Electrolyte for Electrochromic Devices. Polymers 2021, 13, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050742
Chen W, Liu S, Guo L, Zhang G, Zhang H, Cao M, Wu L, Xiang T, Peng Y. A Self-Healing Ionic Liquid-Based Ionically Cross-Linked Gel Polymer Electrolyte for Electrochromic Devices. Polymers. 2021; 13(5):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050742
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wanyu, Siyuan Liu, Le Guo, Guixia Zhang, Heng Zhang, Meng Cao, Lili Wu, Tianxing Xiang, and Yong Peng. 2021. "A Self-Healing Ionic Liquid-Based Ionically Cross-Linked Gel Polymer Electrolyte for Electrochromic Devices" Polymers 13, no. 5: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050742
APA StyleChen, W., Liu, S., Guo, L., Zhang, G., Zhang, H., Cao, M., Wu, L., Xiang, T., & Peng, Y. (2021). A Self-Healing Ionic Liquid-Based Ionically Cross-Linked Gel Polymer Electrolyte for Electrochromic Devices. Polymers, 13(5), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050742