Rheological Properties of Fish Gelatin Modified with Sodium Alginate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2.2. Rheological Tests
- periodic oscillations with a constant frequency of ω = 6.28 rad/s, and amplitude sweep changes in the range of 0.01–1000%.
- periodic oscillations with a constant amplitude of γ = 1% (corresponding to the domain of linear viscoelasticity), and a frequency sweep in the range of 0.01–100 rad/s.
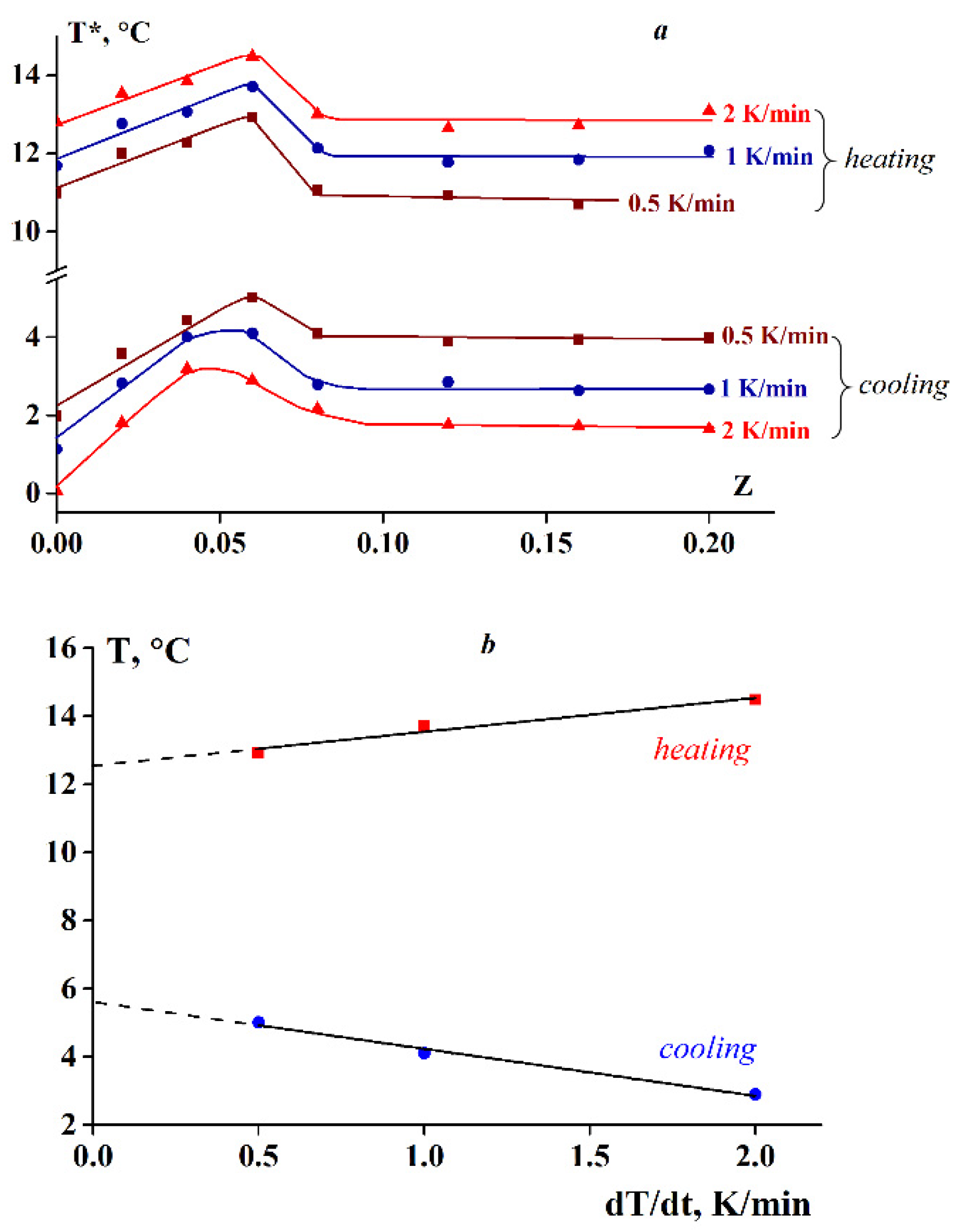
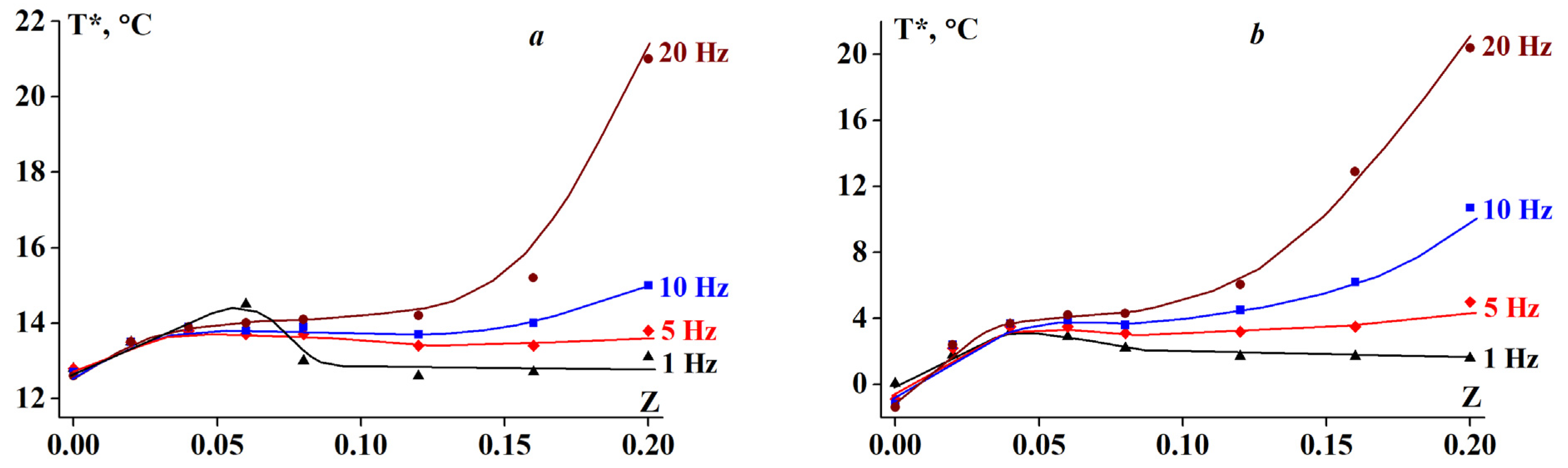
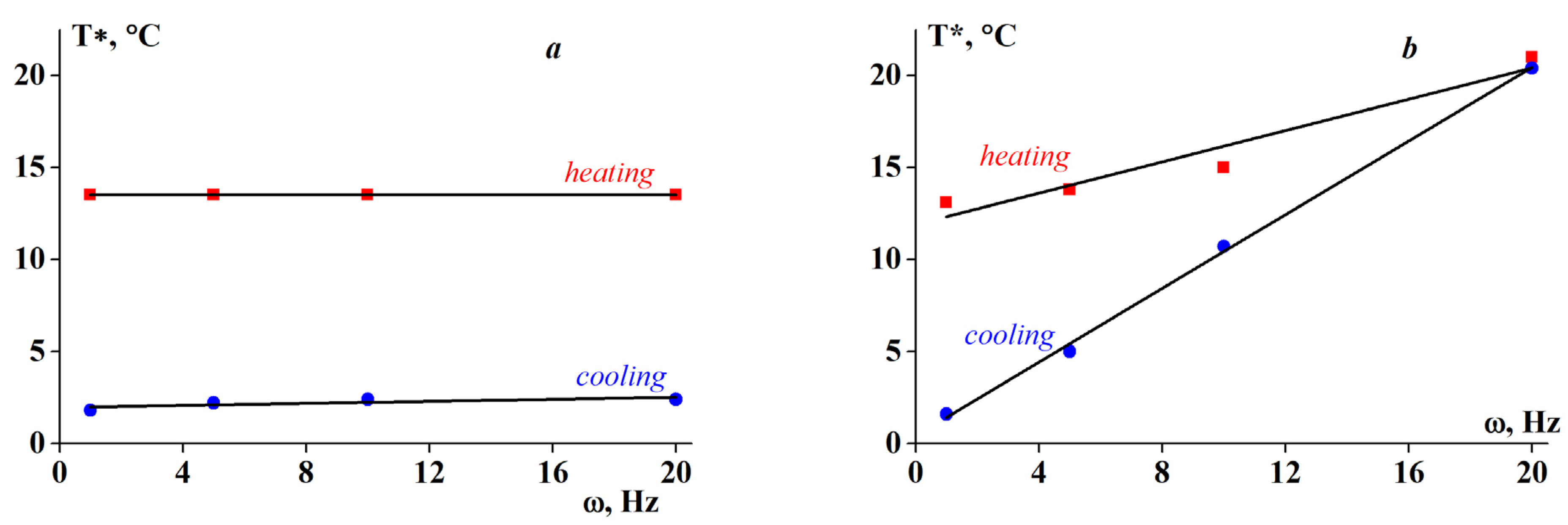
- temperature scanning with ramp rates of 0.5, 1 and 2 K/min at constant frequencies of 6.28 (1 Hz), 31.42 (5 Hz), 62.83 (10 Hz) and 125.66 rad/s (20 Hz) and a constant amplitude of deformation of γ = 1%;
- time dependence of the elastic modulus at temperatures ranging from 4 to 14 °C at a constant frequency of ω = 6.28 rad/s and constant amplitude of deformation of γ = 1% (to monitor the gelation kinetics), the initial temperature was 25 °C; the samples were sealed with silicone oil to prevent water evaporation;
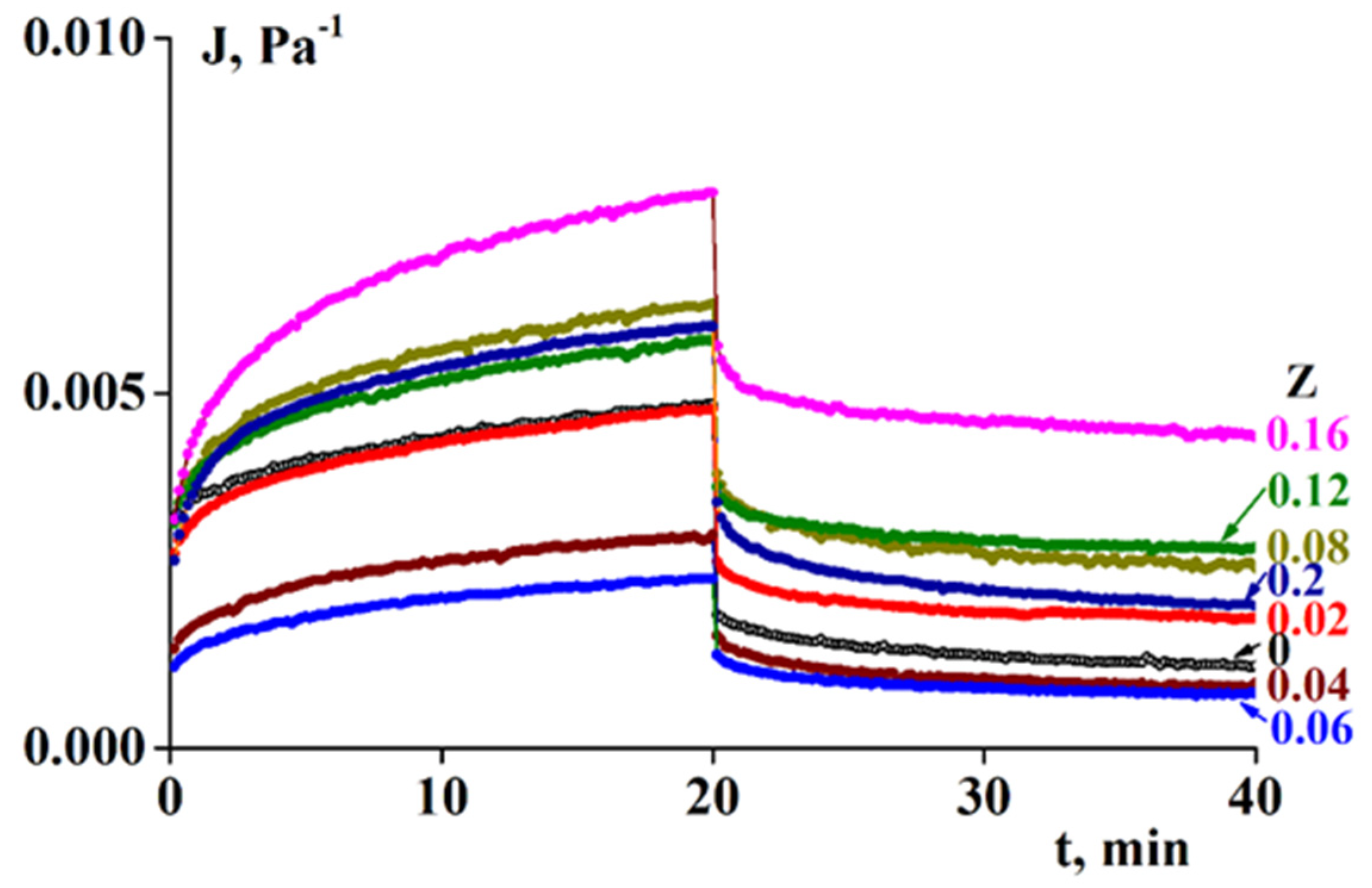
- isothermal creep and elastic recovery at temperatures ranging from 4 to 10 °C and a constant stress in the range of 5–400 Pa for loading for 20 min and recovery for 20 min.
2.2.3. Turbidimetric Measurements and UV-Spectroscopic Analysis
3. Results
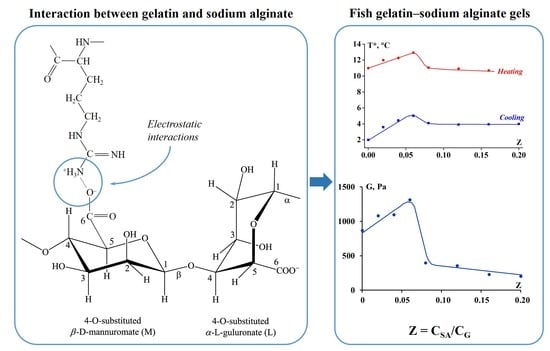
3.1. Temperature Transitions
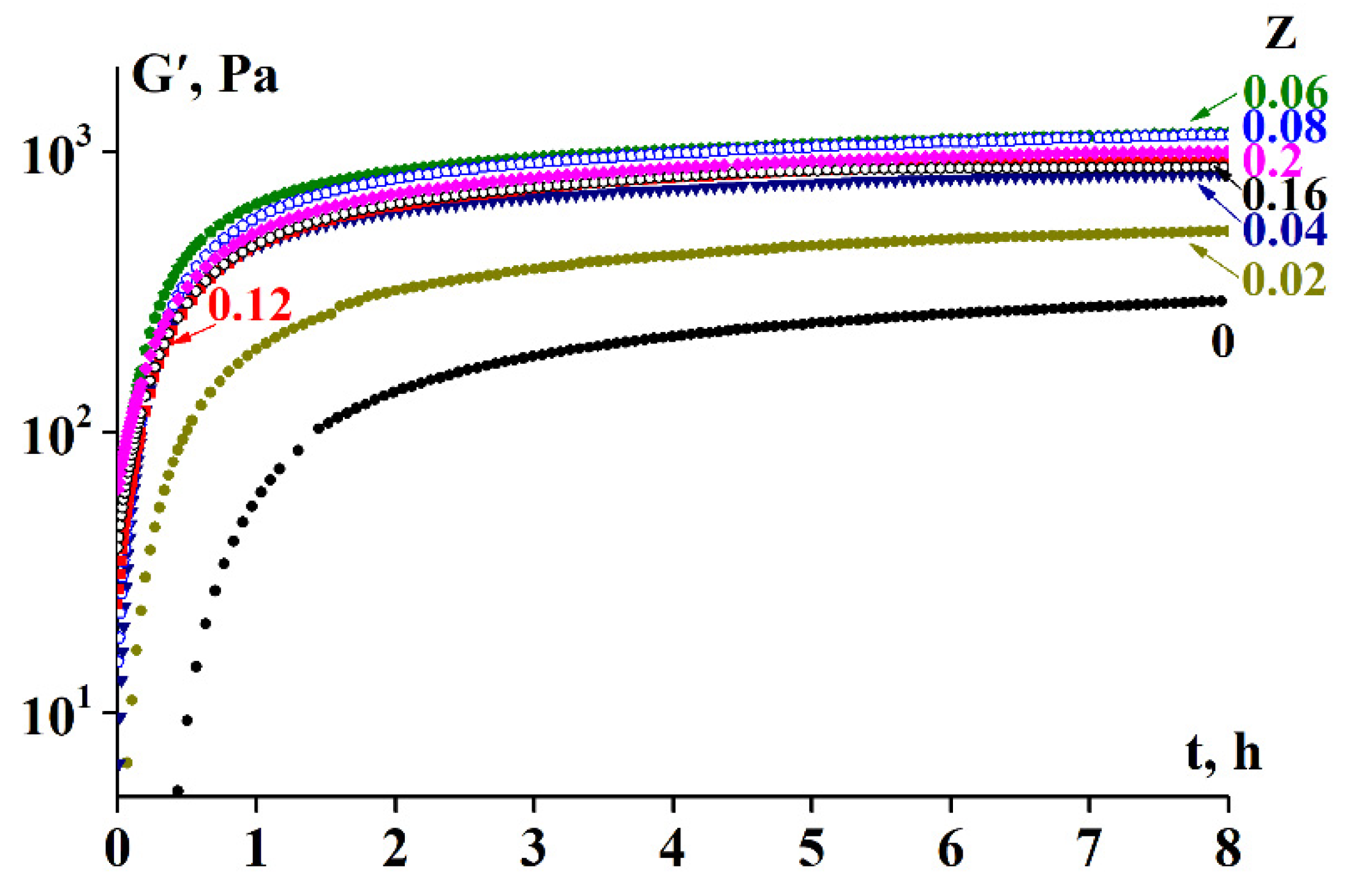
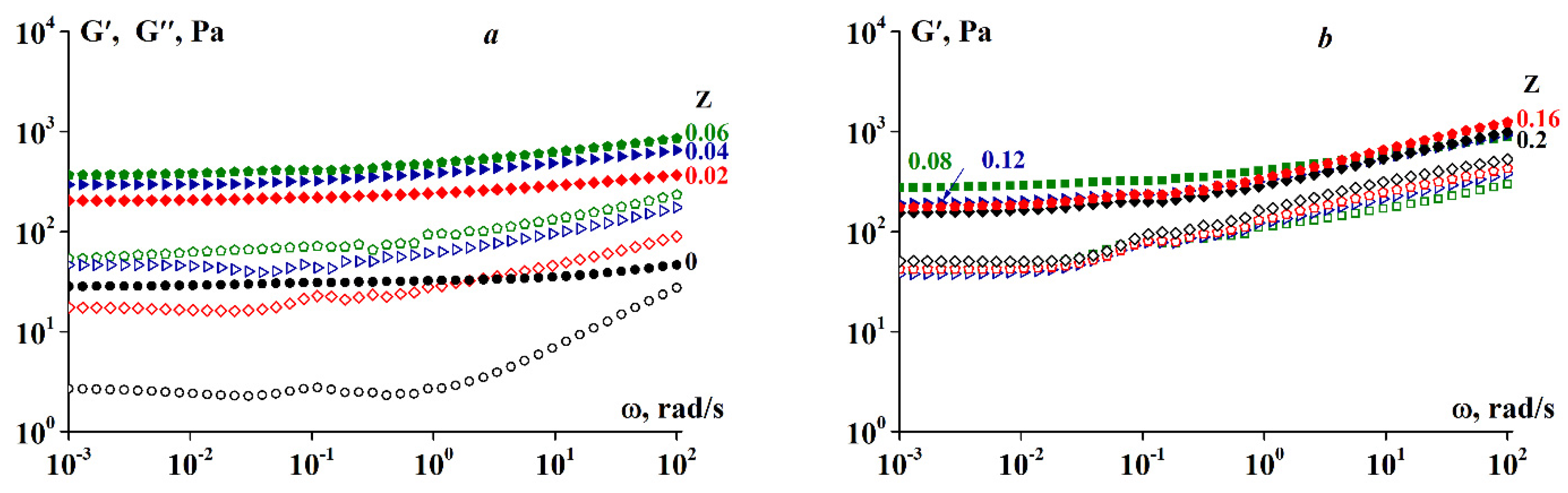
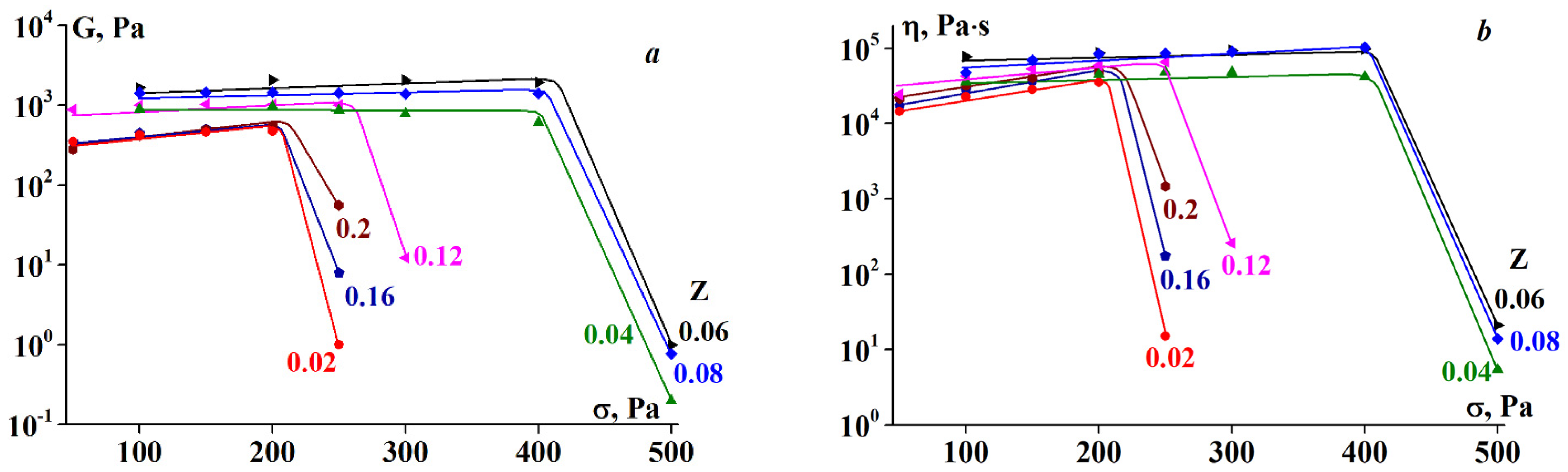
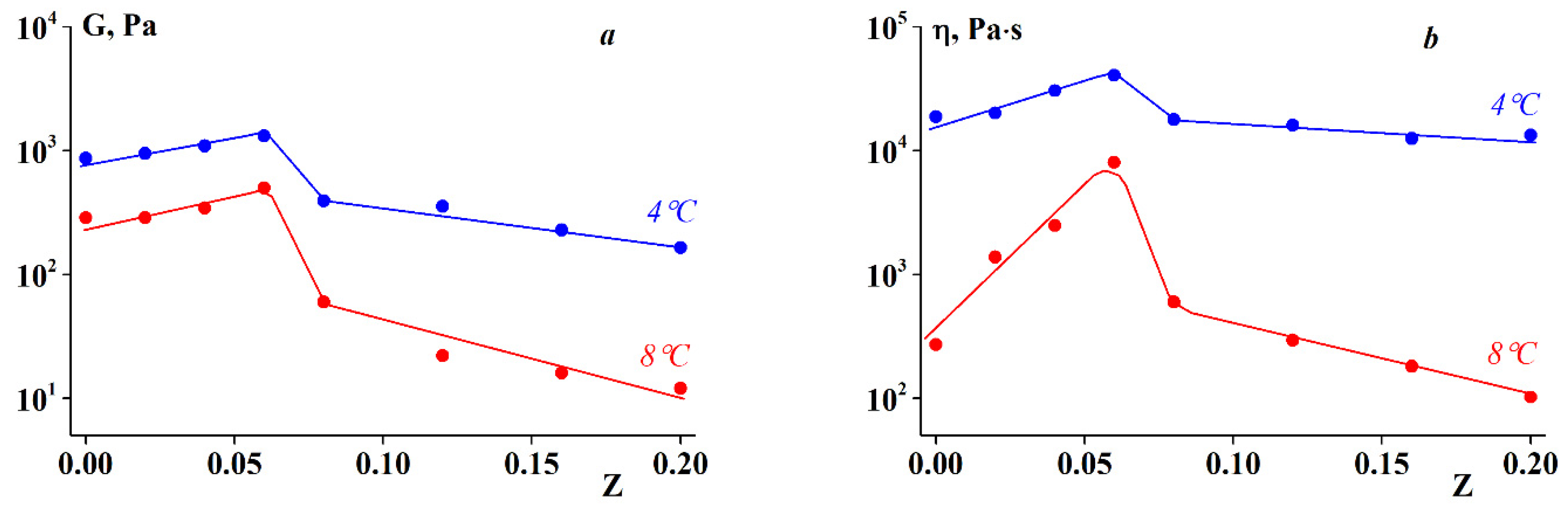
3.2. Rheology of Fish Gelatin Modified with Alginate
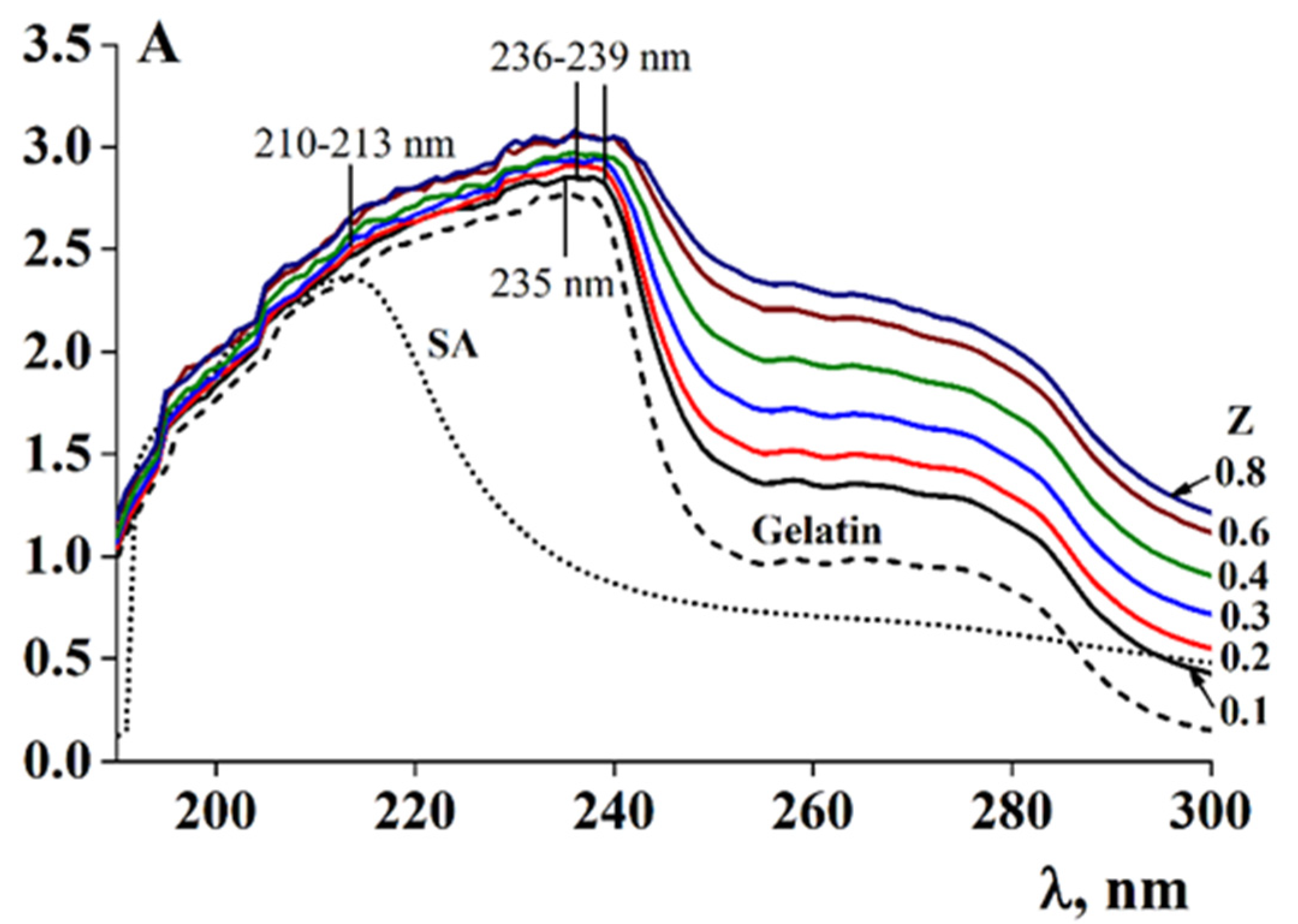
3.3. Composition of Gelatin/Sodium Alginate Systems
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Djagny, K.B.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S. Gelatin: A valuable protein for food and pharmaceutical industries. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2001, 41, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish gelatin: Properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siburian, W.Z.; Rochima, E.; Andriani, Y.; Praseptiangga, D. Fish gelatin (Definition, Manufacture, Analysis of Quality Characteristics, and Application): A Review. Int. J. Fish. 2020, 8, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, K.; de Santiago, G.T.; Alvarez, M.M.; Tamayol, A.; Annabi, N.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rastin, H.; Zhang, B.; Mazinani, A.; Hassan, K.; Bi, J.; Tung, T.T.; Losic, D. 3D bioprinting of cell-laden electroconductive MXene nanocomposite bioinks. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 16069–16080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastin, H.; Ormsby, R.T.; Atkins, G.J.; Losic, D. 3D bioprinting of methylcellulose/gelatin-methacryloyl (MC/GelMA) bioink with high shape integrity. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayannakidis, P.D.; Zotos, A. Fish processing by-products as a potential source of gelatin: A review. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 65–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Gelatin alternatives for the food industry: Recent developments, challenges and prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Giménez, B.; López-Caballero, M.A.; Montero, M.P. Functional and bioactive properties of collagen and gelatin from alternative sources: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, L.C.; Huang, Q.Y.; Ding, W.; Xiao, X.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xiong, L.X. Fish gelatin: The novel potential applications. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 63, 103581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakila, R.J.; Jeevithan, E.; Varatharajakumar, A.; Jeyasekaran, G.; Sukumar, D. Functional characterization of gelatin extracted from bones of red snapper and grouper in comparison with mammalian gelatin. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 48, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I. Gelatin. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids, 2nd ed.; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 142–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Verma, A.K.; Patel, R. Collagen extraction and recent biological activities of collagen peptides derived from sea-food waste: A review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 18, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasswa, J.B.; Tang, J.; Gu, X. Utilization of Fish processing By-Products in the Gelatin Industry. Food Rev. Int. 2007, 23, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Kassaveti, A. Fish industry waste: Treatments, environmental impacts, current and potential uses. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 726–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustainability in Action. Food and Agriculture Organization—State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2020; p. 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, L.; Gallo, N.; Natali, M.L.; Campa, L.; Lunetti, P.; Madaghiele, M.; Blasi, F.S.; Corallo, A.; Capobianco, L.; Sannino, A. Marine collagen and its derivatives: Versatile and sustainable bio-resources for healthcare. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2020, 113, 110963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I.; Smidsrød, O. Physical and rheological properties of fish gelatin compared to mammalian gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, M. Rheological properties of fish gelatins. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 2172–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysturskarð, J.; Haug, I.J.; Elharfaoui, N.; Djabourov, M.; Draget, K.I. Structural and mechanical properties of fish gelatin as a function of extraction conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1702–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Turnay, J.; Fernández-Díaz, M.D.; Ulmo, N.; Lizarbe, M.A.; Montero, P. Structural and physical properties of gelatin extracted from different marine species: A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Saidi, G.S.; Al-Alawi, A.; Rahman, M.S.; Guizani, N. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic study of extracted gelatin from shaari (Lithrinus microdon) skin: Effects of extraction conditions. Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 19, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Derkach, S.R.; Kuchina, Y.A.; Baryshnikov, A.V.; Kolotova, D.S.; Voron’ko, N.G. Tailoring cod gelatin structure and physical properties with acid and alkaline extraction. Polymers 2019, 11, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Mulvaney, S.J.; Regenstein, J.M. Properties of Alaska pollock skin gelatin: A comparison with tilapia and pork skin gelatins. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, C313–C321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwandi, J.; Faridayanti, S.; Mohamed, E.S.M.; Hamzah, M.S.; Torla, H.H.; Che Man, Y.B. Extraction and characterization of gelatin from different marine fish species in Malaysia. Int. Food Res. J. 2009, 16, 381–390. [Google Scholar]
- Kołodziejska, I.; Skierka, E.; Sadowska, M.; Kołodziejski, W.; Niecikowska, C. Effect of extracting time and temperature on yield of gelatin from different fish offal. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tu, Z.C.; Shangguan, X.; Sha, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Bansal, N. Fish gelatin modifications: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranoto, Y.; Lee, C.M.; Park, H.J. Characterization of fish gelatin films added with gellan and κ-carrageenan. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, L.C.; Kong, K.; Yang, H. Structural modification of fish gelatin by the addition of gellan, κ-carrageenan, and salts mimics the critical physicochemical properties of pork gelatin. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1280–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I.; Smidsrød, O. Physical behaviour of fish gelatin-κ-carrageenan mixtures. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 56, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voron’ko, N.G.; Derkach, S.R.; Izmailova, V.N. Rheological properties of gels of gelatin with sodium alginate. Rus. J. Appl. Chem. 2002, 75, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, L.C.; Toh, N.Z.Y.; Wong, C.W.; Yang, H. Combination of sodium alginate with tilapia fish gelatin for improved texture properties and nanostructure modification. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Kuchina, Y.A.; Kolotova, D.S.; Voron’ko, N.G. Polyelectrolyte polysaccharide–gelatin complexes: Rheology and structure. Polymers 2020, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razzak, M.A.; Kim, M.; Chung, D. Elucidation of aqueous interactions between fish gelatin and sodium alginate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 148, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meka, V.S.; Sing, M.K.; Pichika, M.R.; Nali, S.R.; Kolapalli, V.R.; Kesharwani, P.A. Comprehensive review on polyelectrolyte complexes. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkach, S.R.; Ilyin, S.O.; Maklakova, A.A.; Kulichikhin, V.G.; Malkin, A.Y. The rheology of gelatin hydrogels modified by κ-carrageenan. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Virgilio, N.; Wood-Adams, P.M.; Heuzey, M.C. A gelation mechanism for gelatin/polysaccharide aqueous mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Sokolan, N.I. The rheology of hydrogels based on chitosan–gelatin (bio) polyelectrolyte complexes. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panouille, M.; Larreta-Garde, V. Gelation behavior of gelatin and alginate mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudoulas, T.B.; Germann, N. Phase transition kinetics and rheology of gelatin-alginate mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, K.; Chu, X.; Hou, H. Physical properties and antioxidant activity of gelatin-sodium alginate edible films with tea polyphenols. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovchenko, V.V.; Bushneva, O.A.; Ovodova, R.G.; Shashkov, A.S.; Chizhov, A.O.; Ovodov, Y.S. Structural study of bergenan, a pectin from Bergenia crassifolia. Russ. J. Bioorganic Chem. 2007, 33, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usov, A.I.; Bilan, M.I.; Klochkova, N.G. Polysaccharides of algae, 48. Polysaccharide composition of several calcareous red algae: Isolation of alginate from Corallina pilulitara. Bot. Mar. 1995, 38, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, A.Y.; Isayev, A.I. Rheology: Concepts, Methods, and Applications, 3rd ed.; ChemTec Publishing: Scarborough, ON, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rabek, J.F. Experimental Methods in Polymer Chemistry: Physical Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Ross-Murphy, S.B. Structure and rheology of gelatin gels. Imaging Sci. J. 1997, 45, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, H.H. Can the gel point of a cross-linking polymer be detected by the G′–G″ crossover? Polym. Eng. Sci. 1987, 27, 1698–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewoldt, R.H.; Hosoi, A.E.; McKinley, G.H. New measures for characterizing nonlinear viscoelasticity in large amplitude oscillatory shear. J. Rheol. 2008, 52, 1427–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyun, K.; Wilhelm, M.; Klein, C.O.; Cho, K.S.; Nam, J.G.; Ahn, K.H.; Lee, S.J.; Ewoldt, R.H.; McKinley, G.H. A review of nonlinear oscillatory shear tests: Analysis and application of large amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1697–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.X.; Huang, L.Z.; Yang, Y.R.; Liu, X.X.; Tong, Z. Large amplitude oscillatory shear studies on the strain-stiffening behavior of gelatin gels. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 33, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.P. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Kabanov, V.A. Polyelectrolyte complexes in solution and in a bulk. Rus. Chem. Rev. 2005, 74, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumrudov, V.A. Self-assembly and molecular ‘recognition’ phenomena in solutions of (bio)polyelectrolyte complexes. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2008, 77, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, S.L.; Laneuville, S.I. Protein + Polysaccharide Coacervates and Complexes: From Scientific Background to their Application as Functional Ingredients in Food Products. In Modern Biopolymer Science; Kasapis, I.T.S., Norton, J.B., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2009; pp. 327–363. [Google Scholar]
- Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Sokolan, N.I.; Kolotova, D.S.; Kuchina, Y.A. Interactions between gelatin and sodium alginate: UV and FTIR studies. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundblad, R.L.; Macdonald, F.M. Handbook of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dranca, I.; Vyazovkin, S. Thermal stability of gelatin gels: Effect of preparation conditions on the activation energy barrier to melting. Polymer 2009, 50, 4859–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, M.; Chung, D. Effect of cooling–heating rate on sol-gel transformation of fish gelatin–gum arabic complex coacervate phase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michon, C.; Cuvelier, G.; Relkin, P.; Launay, B. Influence of thermal history on the stability of gelatin gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1997, 20, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, M.; Pan, C.H.; Yoon, W.B.; Chung, D. Characterization of fish gelatin–gum arabic complex coacervates as influenced by phase separation temperature. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonkwe, L.G.; Narsimhan, G.; Cha, A.S. Characterization of gelation time and texture of gelatin and gelatin–polysaccharide mixed gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesarinejad, M.A.; Koocheki, A.; Razavi, S.M.A. Dynamic rheological properties of Lepidium perfoliatum seed gum: Effect of concentration, temperature and heating/cooling rate. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, R.I.; Carp, D.J.; Pérez, O.E.; Pilosof, A.M.R. κ-Carrageenan—protein interactions: Effect of proteins on polysaccharide gelling and textural properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 35, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, S.; Klok, H.J.; Van de Velde, F. The mechanism behind microstructure formation in mixed whey protein–polysaccharide cold-set gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.J.; Wu, M.; Adhikari, B. The effect of addition of flaxseed gum on the rheological behavior of mixed flaxseed gum–casein gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstoguzov, V.B. Functional properties of protein–polysaccharide mixtures. In Functional Properties of Food Macromolecules; Mitchell, J.R., Ledward, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 1986; pp. 385–415. [Google Scholar]
- Cutter, C.N. Microbial control by packaging: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2002, 42, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Amino Acid | Amount (g/100 g) | Amino Acid | Amount (g/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycine | 18.6 | Alanine | 9.4 |
| Proline | 12.9 | Taurine | 2.9 |
| Hydroxyproline | 9.6 | Tyrosine | 0.8 |
| Aspartic acid | 5.6 | Valine | 2.1 |
| Glutamic acid | 9.3 | Methionine | 1.6 |
| Serine | 6.7 | Isoleucine | 1.5 |
| Histidine | 1.7 | Leucine | 2.8 |
| Threonine | 2.6 | Lysine | 2.3 |
| Arginine | 7.6 | Phenylalanine | 2.4 |
| Peak Number | Mn, kDa | Mw, kDa | Peak Area, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 839–975 | 990–1150 | 32–34% |
| 2 | 523–540 | 610–630 | 38–40% |
| 3 | 175–193 | 200–220 | 5.5–7.5% |
| 4 | 89–143 | 100–160 | 2–14% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Derkach, S.R.; Kolotova, D.S.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Malkin, A.Y. Rheological Properties of Fish Gelatin Modified with Sodium Alginate. Polymers 2021, 13, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050743
Derkach SR, Kolotova DS, Voron’ko NG, Obluchinskaya ED, Malkin AY. Rheological Properties of Fish Gelatin Modified with Sodium Alginate. Polymers. 2021; 13(5):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050743
Chicago/Turabian StyleDerkach, Svetlana R., Daria S. Kolotova, Nikolay G. Voron’ko, Ekaterina D. Obluchinskaya, and Alexander Ya. Malkin. 2021. "Rheological Properties of Fish Gelatin Modified with Sodium Alginate" Polymers 13, no. 5: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050743
APA StyleDerkach, S. R., Kolotova, D. S., Voron’ko, N. G., Obluchinskaya, E. D., & Malkin, A. Y. (2021). Rheological Properties of Fish Gelatin Modified with Sodium Alginate. Polymers, 13(5), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050743