Influence of Ultra-Heat Treatment on Properties of Milk Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Milk Proteins and Their Fractions
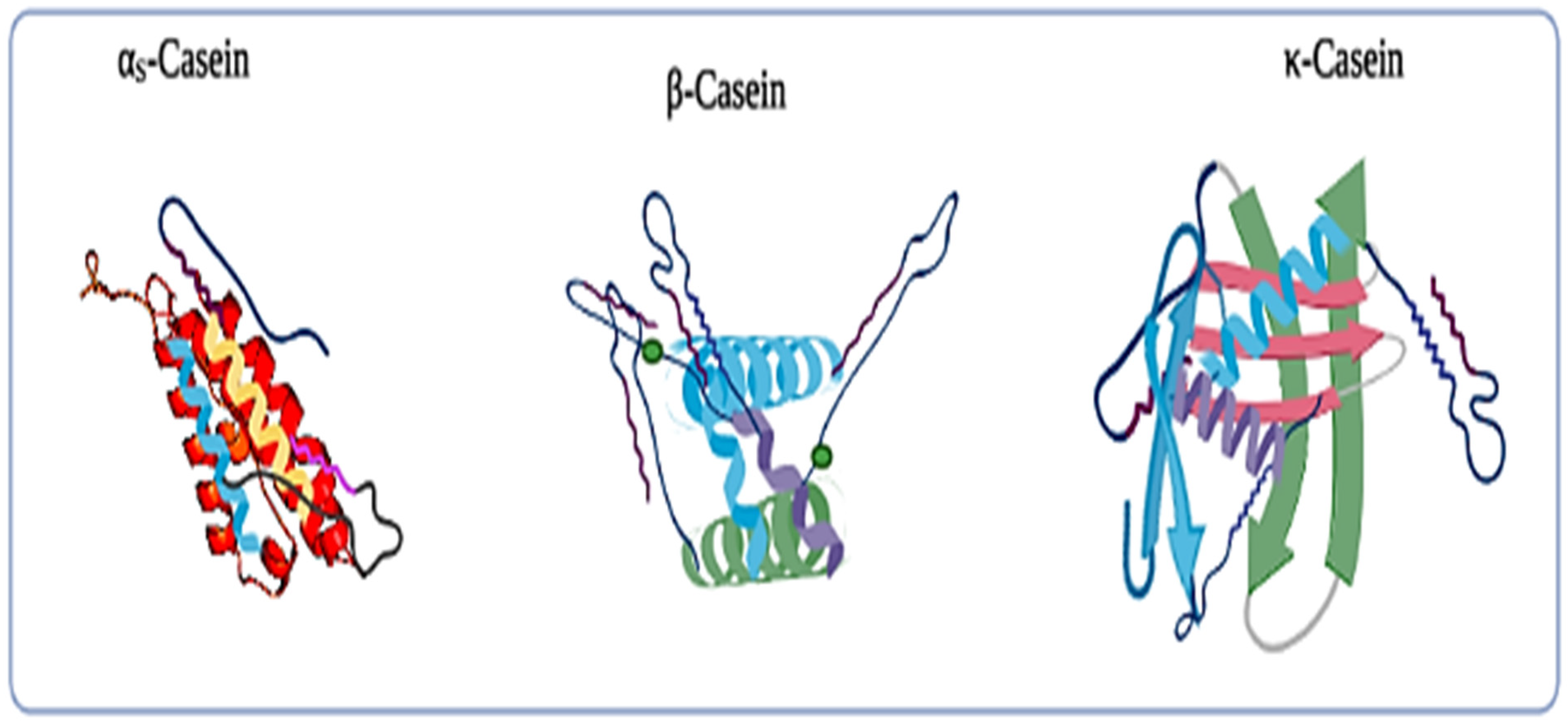
2.1. Casein and Their Fractions
2.1.1. αs1-Casein
2.1.2. αs2-Casein
2.1.3. β-Casein
2.1.4. κ-Casein
2.2. Whey Proteins and Their Fractions
2.2.1. β-Lactoglobulin
2.2.2. α-Lactalbumin
2.2.3. Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA)
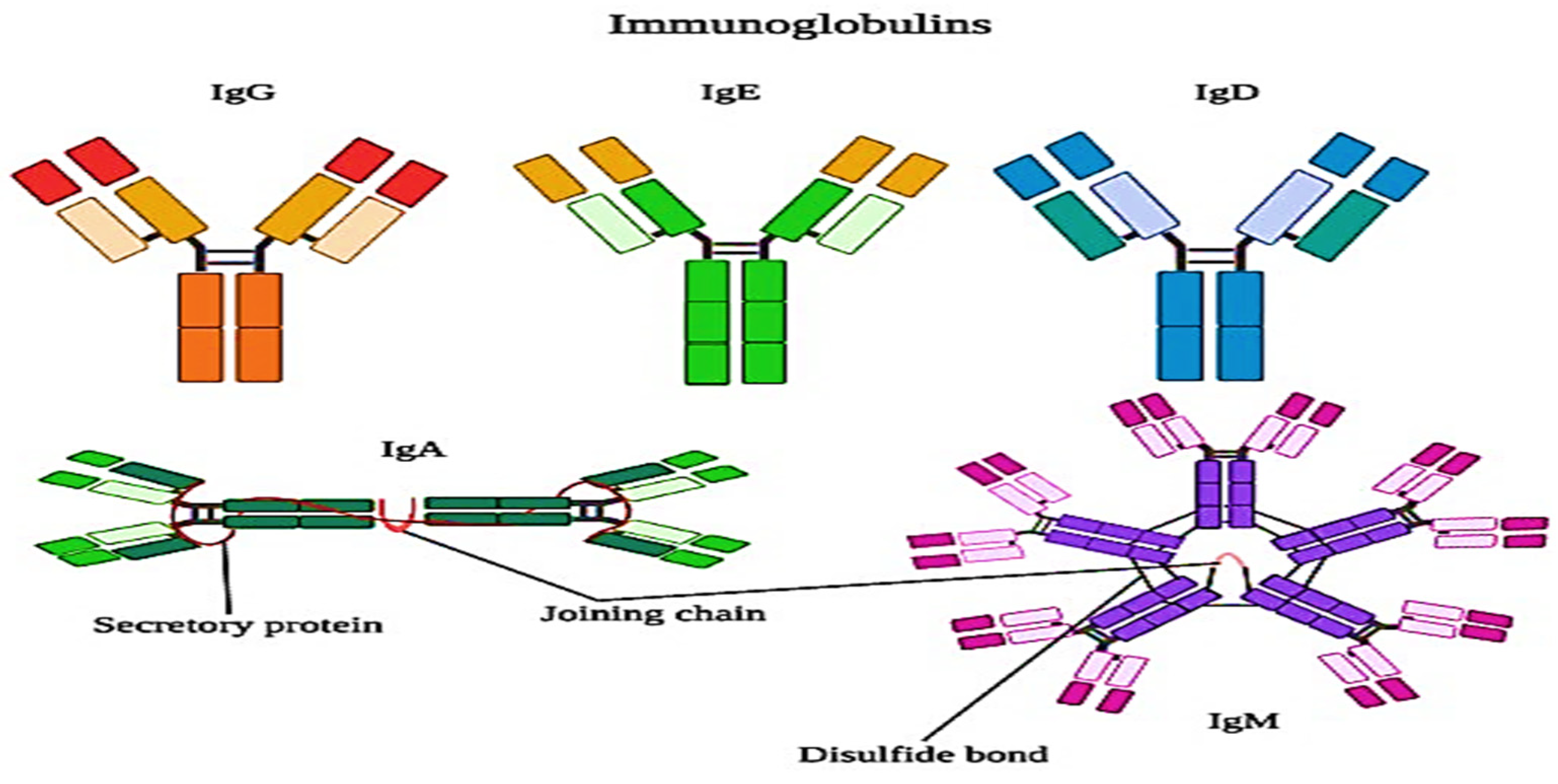
2.2.4. Immunoglobulins (IG)
2.2.5. Minor Proteins
3. Types of UHT Processing Systems for Milk
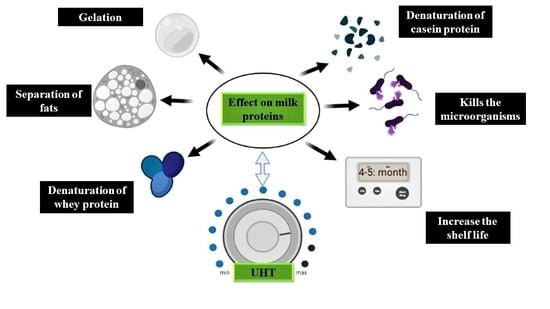
4. Effects of UHT Processing on Milk Proteins
4.1. Effect of UHT Process on Casein Proteins
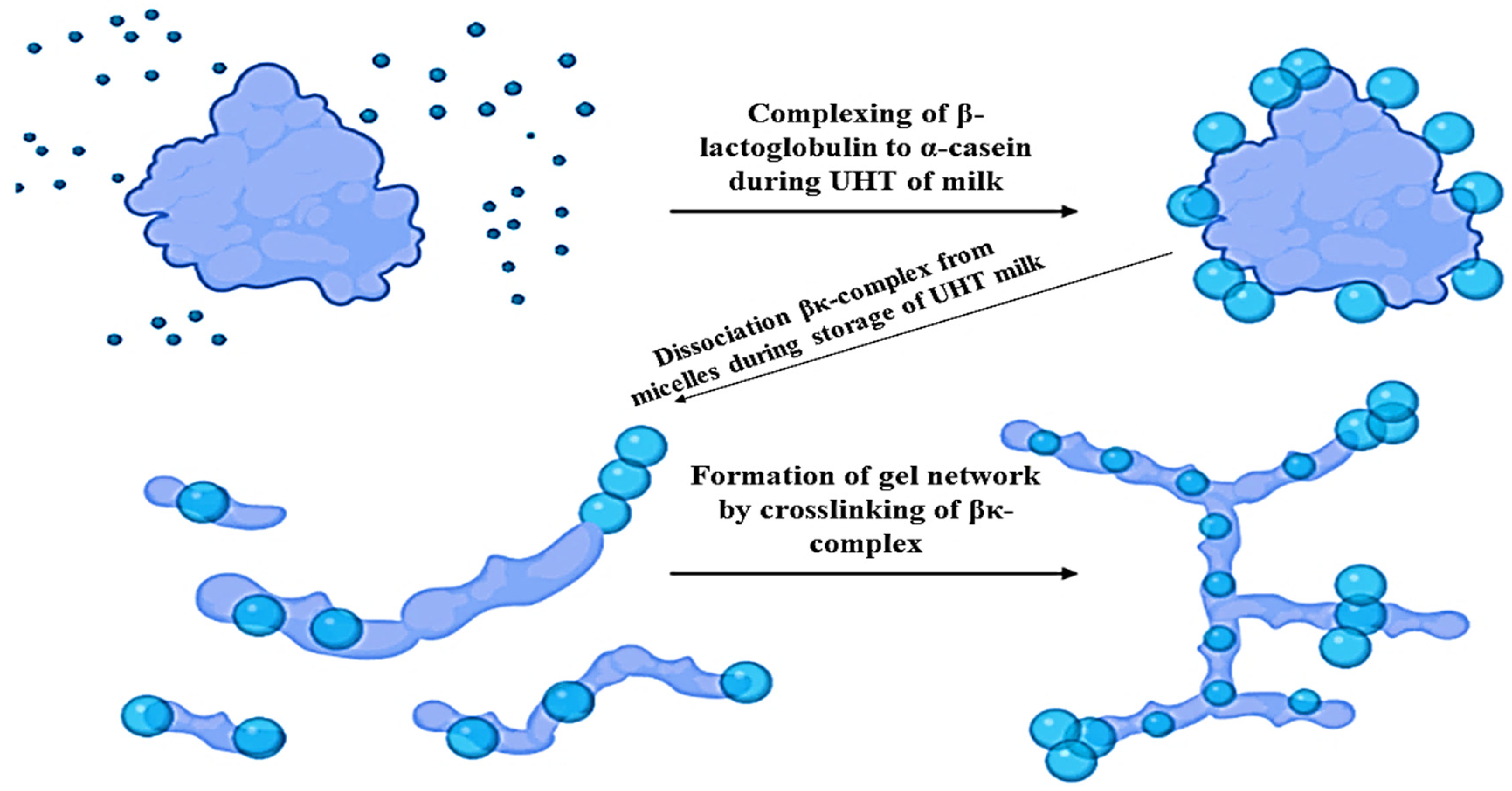
Dissociation of Casein Proteins from the Casein Micelles
4.2. Effect of UHT Process on Whey Proteins
The Process of Whey Protein Denaturation
5. Changes in the Protein during Processing and Storage
5.1. Proteolysis
5.2. Age Gelation
Process of Age Gelation
5.3. Temperature-Time Conditions of Heat Treatment and Storage
5.4. Sedimentation
5.5. Lactosylation
5.6. Deamidation
6. Challenges for UHT-Treated Milk Consumption
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Figueiredo, B.; Dias, C.C.; Brandão, S.; Canário, C.; Nunes-Costa, R. Breastfeeding and postpartum depression: Review of the state of the art. J. Pediatr. 2013, 89, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; O’Mahony, J.A. Milk proteins. In Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 145–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moughan, P.J. Milk Proteins—A Cornucopia for Developing Functional Foods. In Milk Proteins; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anema, S.G. Storage stability and age gelation of reconstituted ultra-high temperature skim milk. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 75, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Tomé, D. Milk proteins: Digestion and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. In Milk Proteins; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.; Grandison, A.; Lin, M.; Tsioulpas, A. Ionic calcium and pH as predictors of stability of milk to UHT processing. Milchwissenschaft 2011, 66, 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Rauh, V.M.; Johansen, L.B.; Bakman, M.; Ipsen, R.; Paulsson, M.; Larsen, L.B.; Hammershøj, M. Protein lactosylation in UHT milk during storage measured by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and quantification of furosine. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2015, 68, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimbo, F.; Bonanno, A.; Liu, X.; Viscecchia, R. Hedonic analysis of the price of UHT-treated milk in Italy. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decimo, M.; Morandi, S.; Silvetti, T.; Brasca, M. Characterization of gram-negative psychrotrophic bacteria isolated from Italian bulk tank milk. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, M2081–M2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavan, R.S.; Chavan, S.R.; Khedkar, C.D.; Jana, A.H. UHT milk processing and effect of plasmin activity on shelf life: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaucher, I.; Mollé, D.; Gagnaire, V.; Gaucheron, F. Effects of storage temperature on physico-chemical characteristics of semi-skimmed UHT milk. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orcajo, J.; de Marañon, I.M.; Lavilla, M. Antigenic response of bovine β-lactoglobulin influenced by ultra-high pressure treatment in combination with high temperature. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2015, 5, P49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzano, R.; Manzo, C.; Adalgisa Nicolai, M.; Addeo, F. Occurrence of major whey proteins in the pH 4.6 insoluble protein fraction from UHT-treated milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8044–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Agarwal, A.; Pathera, A.K.; Kaushik, R.; Kumar, N.; Dhull, S.B.; Arora, S.; Chawla, P. Succinylation of milk proteins: Influence on micronutrient binding and functional indices. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, M.A.; Langton, M.; Innings, F.; Malmgren, B.; Höjer, A.; Wikström, M.; Lundh, Å. Changes in stability and shelf-life of ultra-high temperature treated milk during long term storage at different temperatures. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walstra, P. Casein sub-micelles: Do they exist? Int. Dairy J. 1999, 9, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazlett, R.; Schmidmeier, C.; O’Mahony, J.A. Milk Proteins. In Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Elsevier Science & Technology: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2018; p. 138. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, A.A.; Rubenstein, E. Proline: The distribution, frequency, positioning, and common functional roles of proline and polyproline sequences in the human proteome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadungath, C. Casein micelle structure: A concise review. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2005, 27, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, P.F.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; O’Mahony, J.A. Heat-induced changes in milk. In Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 345–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, T. Chemistry of the caseins. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, T.; Fox, P.F.; Kelly, A.L. High pressure treatment of bovine milk: Effects on casein micelles and whey proteins. J. Dairy Res. 2004, 71, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, M. Whey proteins. In Handbook of Food Proteins; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 30–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’mahony, J.A.; Fox, P.F. Milk proteins: Introduction and historical aspects. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 43–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, L. β-Lactoglobulin. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 211–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brew, K. α-Lactalbumin. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.P.; Wolmarans, M.R.; Park, G.R. The role of albumin in critical illness. Br. J. Anaesth. 2000, 85, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, W.L.; Theil, P.K. Immunoglobulins 9 Secretions. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry, Volume 1A: Proteins: Basic Aspects; Springer US: New York City, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, P.C.; Sheehy, P.A. Minor proteins, including growth factors. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeth, H.C.; Lewis, M.J. High Temperature Processing of Milk and Milk Products; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, G.L. Heat Treatment of Milk: Ultra-High Tempterature Treatment (UHT: Aspect Packaging. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences; John, W.F., Patrick, E.F., Paul, L.H., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeth, H.C. The effect of UHT processing and storage on milk proteins. In Milk Proteins; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 385–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Latham, J.M. Heat stability of milk: Aggregation and dissociation of protein at ultra-high temperatures. Int. Dairy J. 1993, 3, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anema, S.G.; Li, Y. Further studies on the heat-induced, pH-dependent dissociation of casein from the micelles in reconstituted skim milk. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 33, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Creamer, L.K. Influence of concentration of milk solids on the dissociation of micellar κ-casein on heating reconstituted milk at 120 °C. J. Dairy Res. 1991, 58, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumpler, J.; Wohlschläger, H.; Kulozik, U. Dissociation and coagulation of caseins and whey proteins in concentrated skim milk heated by direct steam injection. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2017, 96, 807–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanti, H.B.; Bansal, N.; Deeth, H.C. Stability of whey proteins during thermal processing: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 1235–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, D.J.; Singh, H.; Taylor, M.W. Association of β-lactoglobulin and β-lactalbumin with the casein micelles in skim milk heated in an ultra-high temperature plant. Int. Dairy J. 1998, 8, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanti, H.B.; Brodkorb, A.; Hogan, S.A.; Murphy, E.G. Thermal denaturation, aggregation, and methods of prevention. In Whey Proteins; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 185–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havea, P.; Singh, H.; Creamer, L.K. Characterization of heat-induced aggregates of beta-lactoglobulin, alpha-lactalbumin and bovine serum albumin in a whey protein concentrate environment. J. Dairy Res. 2001, 68, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anema, S.G. On heating milk, the dissociation of [kappa]-casein from the casein micelles can precede interactions with the denatured whey proteins. J. Dairy Res. 2008, 75, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anema, S.G.; Li, Y. Effect of pH on the association of denatured whey proteins with casein micelles in heated reconstituted skim milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anema, S.G. Effect of milk solids concentration on the pH, soluble calcium and soluble phosphate levels of milk during heating. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2009, 89, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borad, S.G.; Kumar, A.; Singh, A.K. Effect of processing on nutritive values of milk protein. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3690–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.X.; Ren, D.; Xiao, Y.; Tomasula, P.M. Effect of homogenization and pasteurization on the structure and stability of whey protein in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2884–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikos, V. Effect of heat treatment on milk protein functionality at emulsion interfaces. A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaucher, I.; Molle, D.; Gagnaire, V.; Leonil, J.; Rousseau, F.; Gaucheron, F. Destabilization of commercial UHT milks: Proteolysis and changes in milk particles. Milchwissenschaft 2009, 64, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, N.; Deeth, H.C. Diagnosing the cause of proteolysis in UHT milk. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 36, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeth, H.; Lewis, M. Protein stability in sterilised milk and milk products. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 247–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, N.; Deeth, H.C. Age gelation of UHT milk—A review. Food Bioprod. Process. 2001, 79, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.E.; Ewings, K.N. Quantification of bacterial proteolysis causing gelation in UHT-treated milk. N. Z. J. Dairy Sci. Technol. 1985, 20, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Button, P.D.; Roginski, H.; Deeth, H.C.; Craven, H.M. Improved shelf-life estimation of UHT milk by prediction of proteolysis. J. Food Qual. 2011, 34, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmgren, B.; Ardö, Y.; Langton, M.; Altskär, A.; Bremer, M.G.; Dejmek, P.; Paulsson, M. Changes in proteins, physical stability and structure in directly heated UHT milk during storage at different temperatures. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 71, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckel, M.; Lidolt, M.; Achberger, V.; Glück, C.; Krewinkel, M.; Stressler, T.; Hinrichs, J. Growth of Pseudomonas weihenstephanensis, Pseudomonas proteolytica and Pseudomonas sp. in raw milk: Impact of residual heat-stable enzyme activity on stability of UHT milk during shelf-life. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 59, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumpa, T.; Tsioulpas, A.; Grandison, A.S.; Lewis, M.J. Effects of phosphates and citrates on sediment formation in UHT goats’ milk. J. Dairy Res. 2008, 75, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, M.K.; Chandrapala, J.; Donkor, O.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Stojanovska, L.; Vasiljevic, T. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis of physicochemical changes in UHT milk during accelerated storage. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 66, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, V.; Schalk, J.; Anema, S.G. Sedimentation in UHT milk. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 78, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, B.M.; Deeth, H.C. Blocked lysine in dairy products: Formation, occurrence, analysis, and nutritional implications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenelon, M.A.; Hickey, R.M.; Buggy, A.; McCarthy, N.; Murphy, E.G. Whey proteins in infant formula. In Whey Proteins; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 439–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.W.; Gupta, R.; Deeth, H.C.; Alewood, P.F. Proteomic analysis of temperature-dependent changes in stored UHT milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, J.W.; Gupta, R.; Deeth, H.C.; Alewood, P.F. UHT milk contains multiple forms of αS1-casein that undergo degradative changes during storage. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.; Nielsen, S.D.; Villumsen, N.S.; Kristiansen, G.H.; Nielsen, L.R.; Nielsen, S.B.; Larsen, L. BUsing proteomics to characterise storage-induced aggregates in acidic whey protein isolate drinks. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 60, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, N.; Yokoyama, K.; Wakabayashi, H.; Nio, N. Effect of deamidation by protein-glutaminase on physicochemical and functional properties of skim milk. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, S.; Masotti, F.; Pellegrino, L. Effects of overprocessing on heat damage of UHT milk. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, T. Homogenization of Milk|Other Types of Homogenizer (High-Speed Mixing, Ultrasonics, Microfluidizers, Membrane Emulsification). In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 12, pp. 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumay, E.; Chevalier-Lucia, D.; Picart-Palmade, L.; Benzaria, A.; Gràcia-Julià, A.; Blayo, C. Technological aspects and potential applications of (ultra) high-pressure homogenisation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlender, M.; Minke, K.; Spiegel, B.; Schuchmann, H.P. High-pressure double stage homogenization processes: Influences of plant setup on oil droplet size. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 131, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Incecco, P.; Rosi, V.; Cabassi, G.; Hogenboom, J.A.; Pellegrino, L. Microfiltration and ultra-high-pressure homogenization for extending the shelf-storage stability of UHT milk. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Milk Proteins (Caseins) | Molecular Mass | Amino Acids | Proline Residues | Cysteine Residues | PO4 Groups | Concentration (g/L) | Glycoproteins | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| αs1-casein | 23,164 | 199 | 17 | 0 | 8 | 10 | No | [2,17] |
| αs2-casein | 25,388 | 207 | 10 | 2 | 10–13 | 2.6 | No | [2,17] |
| β-casein | 23,983 | 209 | 35 | 0 | 5 | 9.3 | No | [2,17] |
| κ-casein | 19,038 | 169 | 20 | 2 | 1 | 10.3 | Yes | [2,17] |
| Milk Proteins (Whey Proteins) | % of Whey Protein | Isoelectric Point (pI) | Concentration (g/L) | Molecular Weight (kDa) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-lactoglobulin | 55–65 | 5.35–5.49 | 3.3 | 18.4 | [2,24] |
| α-lactalbumin | 15–25 | 4.2–4.5 | 1.2 | 14.2 | [2,24] |
| Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | 5–6 | 5.1 | 0.3 | 66.3 | [2,24] |
| Immunoglobulins | 10–15 | 5.5–8.3 | 0.5 | 80–900 | [2,24] |
| Proteose peptones | 10–20 | 5.1–6.0 | 0.2 | 4.1–80 | [2,24] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krishna, T.C.; Najda, A.; Bains, A.; Tosif, M.M.; Papliński, R.; Kapłan, M.; Chawla, P. Influence of Ultra-Heat Treatment on Properties of Milk Proteins. Polymers 2021, 13, 3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183164
Krishna TC, Najda A, Bains A, Tosif MM, Papliński R, Kapłan M, Chawla P. Influence of Ultra-Heat Treatment on Properties of Milk Proteins. Polymers. 2021; 13(18):3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183164
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrishna, Thummalacharla Chaitanya, Agnieszka Najda, Aarti Bains, Mansuri M. Tosif, Rafał Papliński, Magdalena Kapłan, and Prince Chawla. 2021. "Influence of Ultra-Heat Treatment on Properties of Milk Proteins" Polymers 13, no. 18: 3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183164
APA StyleKrishna, T. C., Najda, A., Bains, A., Tosif, M. M., Papliński, R., Kapłan, M., & Chawla, P. (2021). Influence of Ultra-Heat Treatment on Properties of Milk Proteins. Polymers, 13(18), 3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183164