Influence of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles and Surface Plasma Treatment on Bioactivity of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
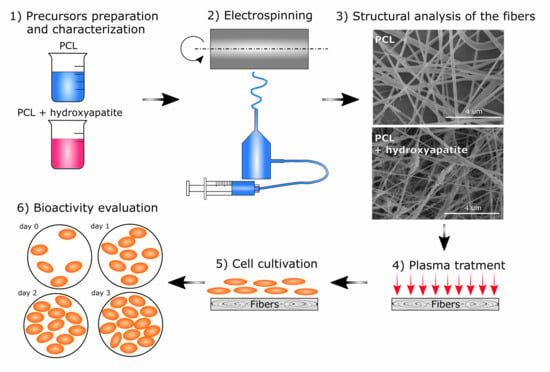
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Precursor Preparation and Analysis
2.2. Electrospinning
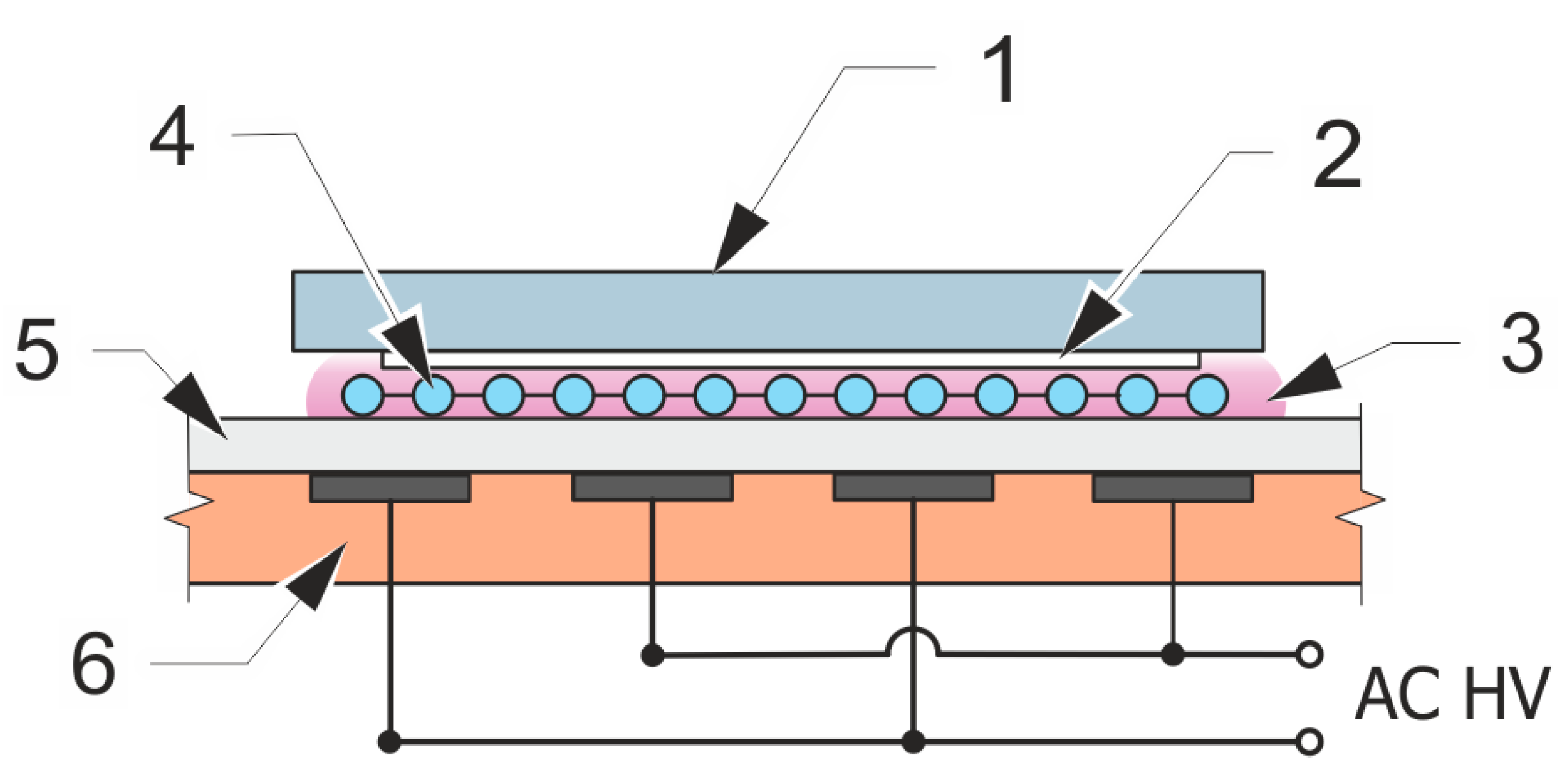
2.3. Surface Plasma Treatment
2.4. Biological Properties
3. Results and Discussion
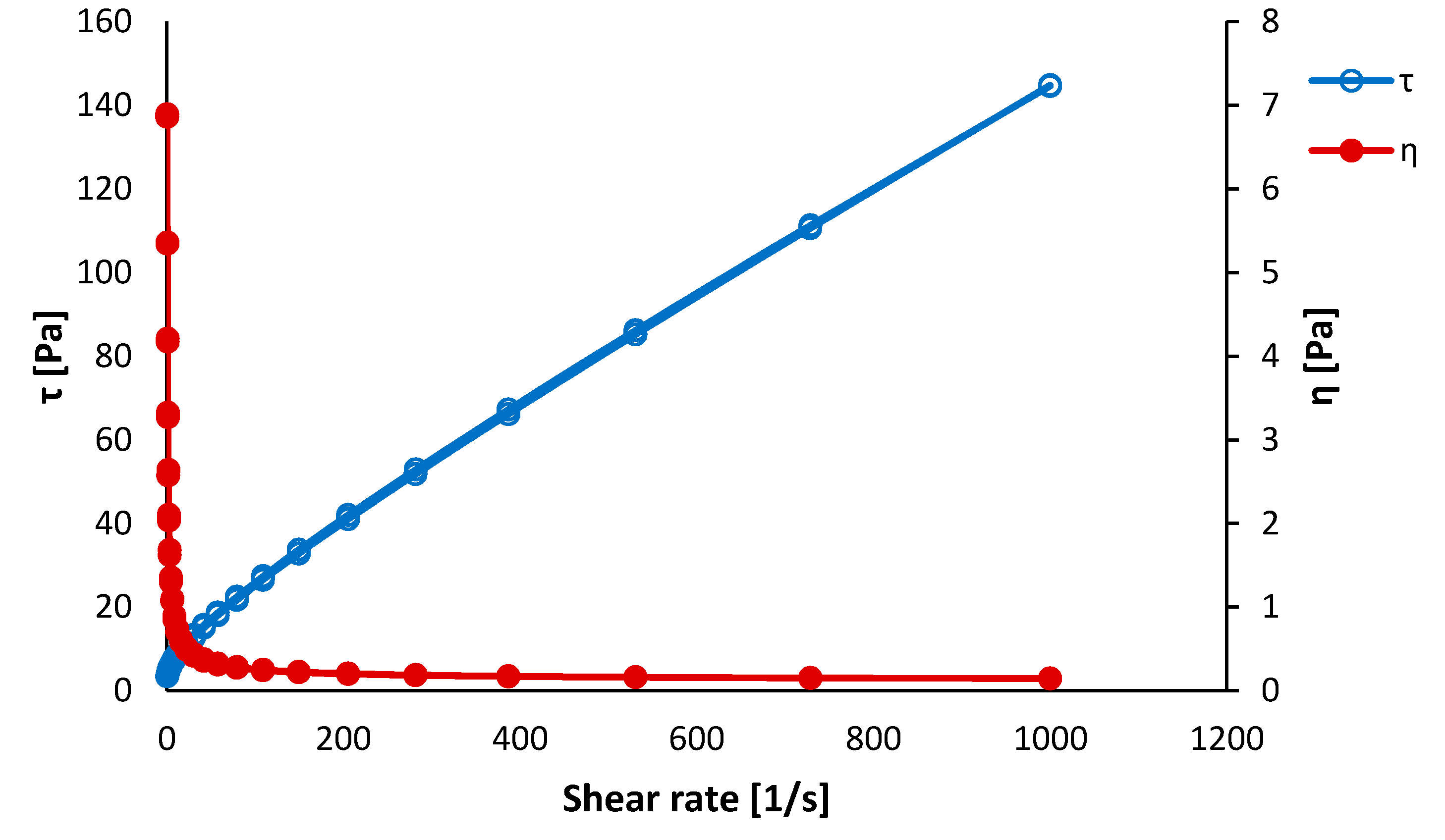
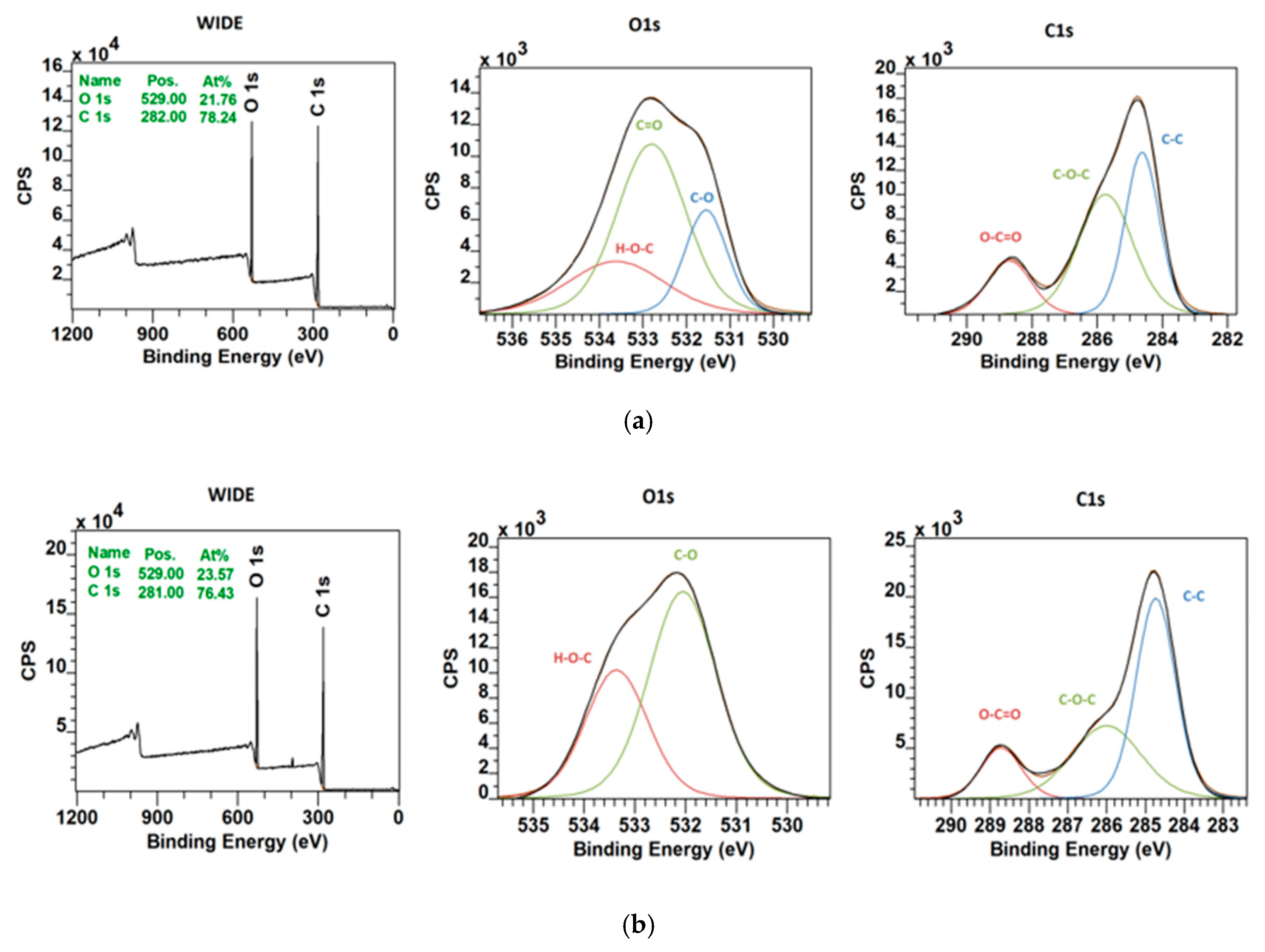
3.1. Precursors Characterization
3.2. Electrospun Fibers Analysis
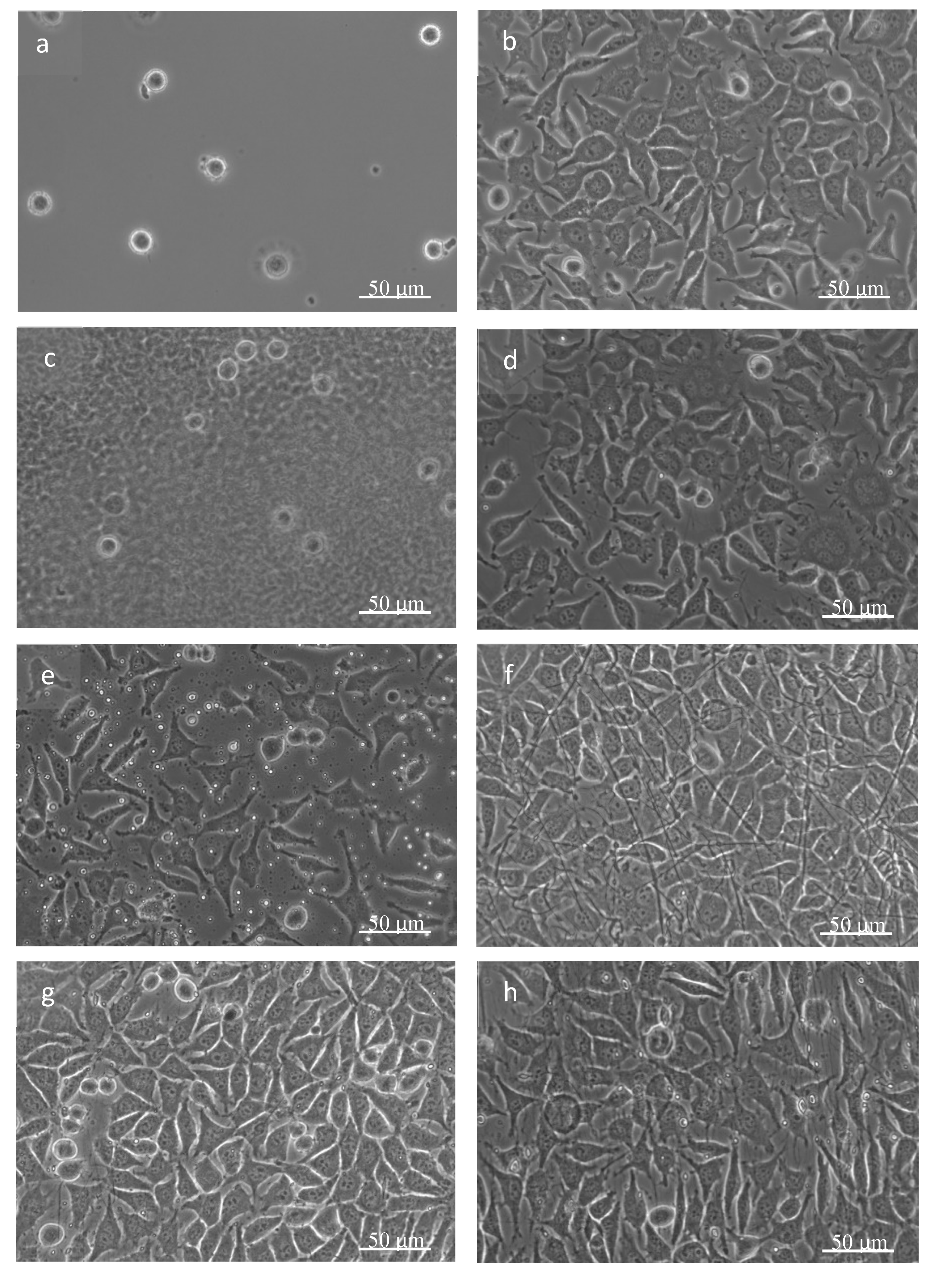
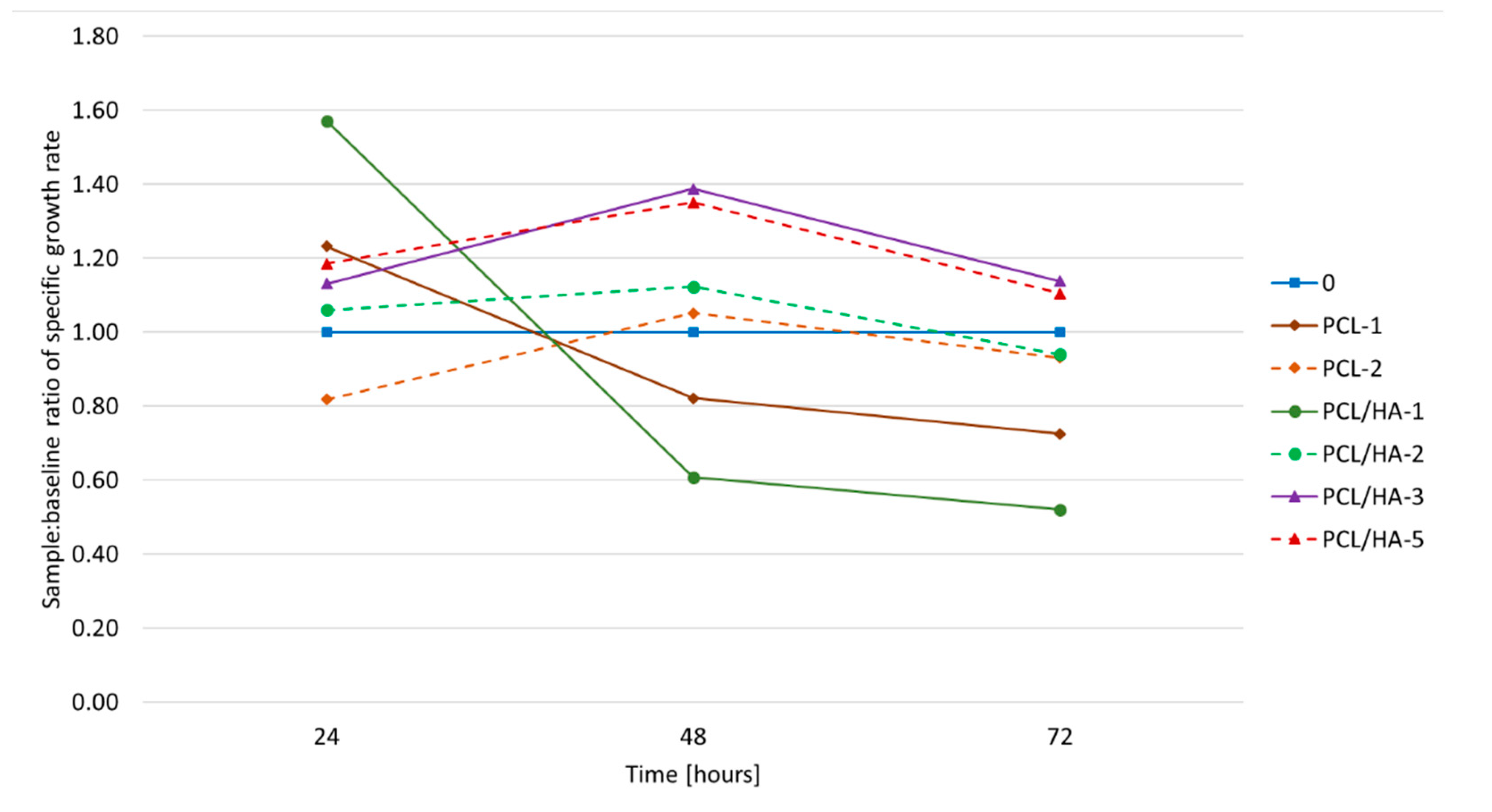
3.3. Biological Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Oosterwyck, H.; Duyck, J.; Sloten, J.V.; Van Der Perre, G.; De Coomans, M.; Lieven, S.; Puers, R.; Naert, L. The influence of bone mechanical properties and implant fixation upon bone loading around oral implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1998, 9, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, E.; Stegaroiu, R.; Nomura, S.; Miyakawa, O. Influence of marginal bone resorption on stress around an implant—A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2005, 32, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, C.R.M.; Goriainov, V.; Gibbs, D.; Kanczler, J.M.; Tare, R.; Oreffo, R.O.C. Bone Tissue Engineering. Curr. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 1, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, S.; Oliveira, J.; Reis, R.L. Natural-Based Nanocomposites for Bone Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: A Review. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1143–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lannutti, J.J.; Reneker, D.; Ma, T.; Tomasko, D.; Farson, D. Electrospinning for tissue engineering scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, D.P.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, C.S. A Review on Properties of Natural and Synthetic Based Electrospun Fibrous Materials for Bone Tissue Engineering. Membranes 2018, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, A.A.; Vig, K.; Baganizi, D.R.; Sahu, R.; Dixit, S.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R.; Pillai, S. Future Prospects for Scaffolding Methods and Biomaterials in Skin Tissue Engineering: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.-E.; Lim, T.-C.; Ma, Z. An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibers, 1st ed.; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Toh Tuck Link, Singapore, 2005; pp. 90–154. [Google Scholar]
- De Vrieze, S.; Van Camp, T.; Nelvig, A.; Hagström, B.; Westbroek, P.; De Clerck, K. The effect of temperature and humidity on electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.S.; Jardini, A.; Filho, R.M. Poly (Lactic Acid) Production for Tissue Engineering Applications. Procedia Eng. 2012, 42, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.A.; Wnek, G.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of Collagen Nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Mirzadeh, H.; Zandi, M. Gelatin–GAG electrospun nanofibrous scaffold for skin tissue engineering: Fabrication and modeling of process parameters. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 48, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.S.; Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G. Surface-functionalized electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Li, B. Biomimetic electrospun nanofibrous structures for tissue engineering. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.-Z.; Zhang, G.-R.; Wang, L.-L.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Ouyang, H.-W.; Zou, X.-H. Novel biodegradable three-dimensional macroporous scaffold using aligned electrospun nanofibrous yarns for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, X.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F. Recent Advances in Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 5726–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.M.; Adewunmi, A.; Schek, R.M.; Flanagan, C.L.; Krebsbach, P.H.; Feinberg, S.E.; Hollister, S.; Das, S. Bone tissue engineering using polycaprolactone scaffolds fabricated via selective laser sintering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4817–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, H.; Shin, Y.; Terai, H.; Vacanti, J.P. A biodegradable nanofiber scaffold by electrospinning and its potential for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2077–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, N.-T.; Williamson, M.; Khammo, N.; Adams, E.; Coombes, A.G. Composite cell support membranes based on collagen and polycaprolactone for tissue engineering of skin. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4263–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitole, A.A.; Raut, P.W.; Sharma, N.; Giram, P.; Khandwekar, A.P.; Garnaik, B. Electrospun polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite/ZnO nanofibers as potential biomaterials for bone tissue regeneration. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keivani, F.; Shokrollahi, P.; Zandi, M.; Irani, S.; Shokrolahi, F.; Khorasani, S. Engineered electrospun poly(caprolactone)/polycaprolactone-g-hydroxyapatite nano-fibrous scaffold promotes human fibroblasts adhesion and proliferation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajzer, I. Fabrication of bioactive polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite scaffolds with final bilayer nano-/micro-fibrous structures for tissue engineering application. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 5799–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, T.M.; Mello, D.C.R.; Elias, C.M.V.; Abdala, J.M.A.; Silva, E.; De Vasconcellos, L.M.R.; Tim, C.R.; Marciano, F.R.; Lobo, A.O. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of rotary-jet-spun poly(ɛ-caprolactone) with high loading of nano-hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosal, K.; Manakhov, A.; Zajíčková, L.; Thomas, S. Structural and Surface Compatibility Study of Modified Electrospun Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) Composites for Skin Tissue Engineering. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 18, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, L.D.; Brack, N.; Postma, A.; Pigram, P.J.; Meagher, L.; Lina, D.S.; Narelle, B.; Almar, P.; J, P.P.; Laurence, M. Surface modification of electrospun fibres for biomedical applications: A focus on radical polymerization methods. Biomaterials 2016, 106, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can-Herrera, L.; Avila-Ortega, A.; De La Rosa-García, S.C.; Oliva, A.; Cauich-Rodriguez, J.; Cervantes-Uc, J. Surface modification of electrospun polycaprolactone microfibers by air plasma treatment: Effect of plasma power and treatment time. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 84, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadian, M.; Grande, S.; Onyshchenko, I.; Morent, R.; Declercq, H.; De Geyter, N. A comparative study on pre- and post-production plasma treatments of PCL films and nanofibers for improved cell-material interactions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 481, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronov, D.; Rosen, R.; Ron, E.; Rosenman, G. Tunable hydroxyapatite wettability: Effect on adhesion of biological molecules. Process. Biochem. 2006, 41, 2367–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D.; Bhushan, B. Durable Lotus-effect surfaces with hierarchical structure using micro- and nanosized hydrophobic silica particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 368, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobeira, R.; Philips, C.; Liefooghe, L.; Verdonck, M.; Asadian, M.; Cools, P.; Declercq, H.; De Vos, W.H.; De Geyter, N.; Morent, R. Synergetic effect of electrospun PCL fiber size, orientation and plasma-modified surface chemistry on stem cell behavior. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 485, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, T.; De Geyter, N.; Morent, R.; Desmet, T.; Dubruel, P.; Leys, C. Plasma treatment of polycaprolactone at medium pressure. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, S543–S547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trunec, M.; Stastny, P.; Kelar, J.; Pazderka, M. Effect of plasma treatment of polymeric tape carriers on wetting behaviour of aqueous ceramic tape casting slurry. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 9381–9385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castkova, K.; Hadraba, H.; Matousek, A.; Roupcová, P.; Chlup, Z.; Novotna, L.; Cihlar, J. Synthesis of Ca,Y-zirconia/hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 2903–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouchly, V.; Rahel, J.; Spusta, T.; Ilčíková, M.; Pavliňák, D.; Morávek, T.; Maca, K. Improved microstructure of alumina ceramics prepared from DBD plasma activated powders. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Turng, L.-S.; Li, Q. Crystalline Morphology of Electrospun Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) Nanofibers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 4939–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, L. Shear thinning and shear thickening of concentrated ceramic suspensions. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 133, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malijevský, A. Does surface roughness amplify wetting? J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 141, 184703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gaens, W.; Bogaerts, A. Kinetic modelling for an atmospheric pressure argon plasma jet in humid air. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 275201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; McHugh, K.J.; Chew, S.Y.; Anderson, J.M. The topographical effect of electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds on thein vivoandin vitroforeign body reaction. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2009, 9999, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Yetter, A.B. Correlation of visual in vitro cytotoxicity ratings of biomaterials with quantitative in vitro cell viability measurements. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Accelerating Voltage (kV) | Feeding Rate (µL/min) | Emitter–Collector Distance (mm) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 28 | 100 | 23 |
| Sample | Material | Morphology | Plasma Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (baseline) | Clear glass | - | No |
| PCL-1 | Polycaprolactone | Continuous layer | No |
| PCL-2 | Polycaprolactone | Randomly organized fibers | No |
| PCL/HA-1 | Polycaprolactone + hydroxyapatite particles | Continuous layer | No |
| PCL/HA-2 | Polycaprolactone + hydroxyapatite particles | Randomly organized fibers | No |
| PCL/HA-3 | Polycaprolactone + hydroxyapatite particles | Randomly organized fibers | Yes |
| PCL/HA-4 | Polycaprolactone + hydroxyapatite particles | Parallel organized fibers | No |
| PCL/HA-5 | Polycaprolactone + hydroxyapatite particles | Parallel organized fibers | Yes |
| Sample | Diameter [nm] |
|---|---|
| PCL-2 | 172 ± 60 |
| PCL/HA-2 | 171 ± 107 |
| PCL/HA-3 | 151 ± 75 |
| PCL/HA-4 | 114 ± 60 |
| PCL/HA-5 | 127 ± 41 |
| Sample | Contact Angle [°] |
|---|---|
| PCL-1 | 75.5 ± 3.5 |
| PCL-2 | 127.2 ± 4.1 |
| PCL/HA-1 | 44.9 ± 1.7 |
| PCL/HA-2 | 128.3 ± 3.6 |
| PCL/HA-3 | complete wetting |
| PCL/HA-4 | 125.3 ± 5.1 |
| PCL/HA-5 | complete wetting |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stastna, E.; Castkova, K.; Rahel, J. Influence of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles and Surface Plasma Treatment on Bioactivity of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091877
Stastna E, Castkova K, Rahel J. Influence of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles and Surface Plasma Treatment on Bioactivity of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091877
Chicago/Turabian StyleStastna, Eva, Klara Castkova, and Jozef Rahel. 2020. "Influence of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles and Surface Plasma Treatment on Bioactivity of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers" Polymers 12, no. 9: 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091877
APA StyleStastna, E., Castkova, K., & Rahel, J. (2020). Influence of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles and Surface Plasma Treatment on Bioactivity of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers. Polymers, 12(9), 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091877