Temperature Behavior of Aqueous Solutions of Poly(2-Oxazoline) Homopolymer and Block Copolymers Investigated by NMR Spectroscopy and Dynamic Light Scattering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization
2.3. NMR Measurements
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
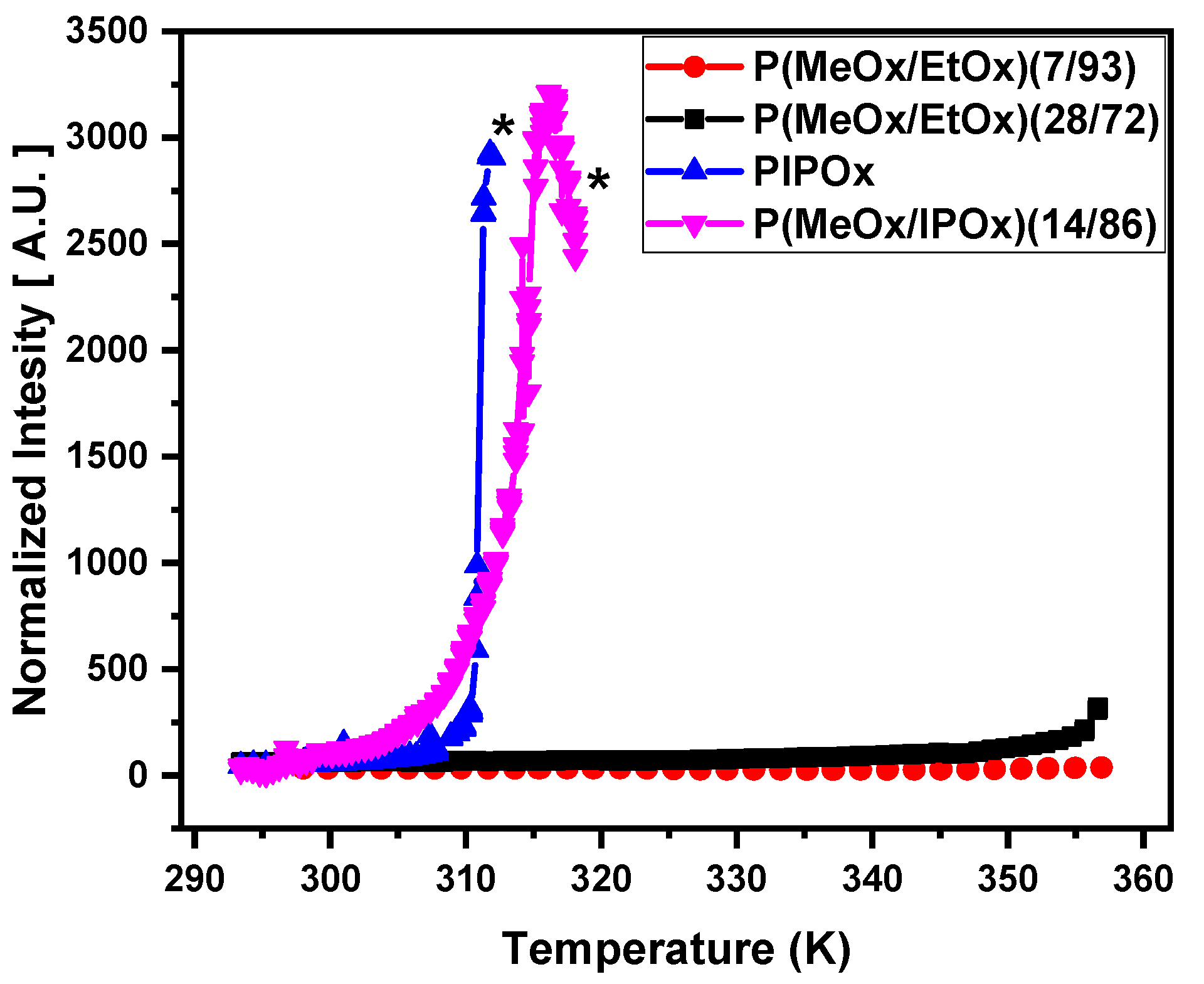
3.1. DLS
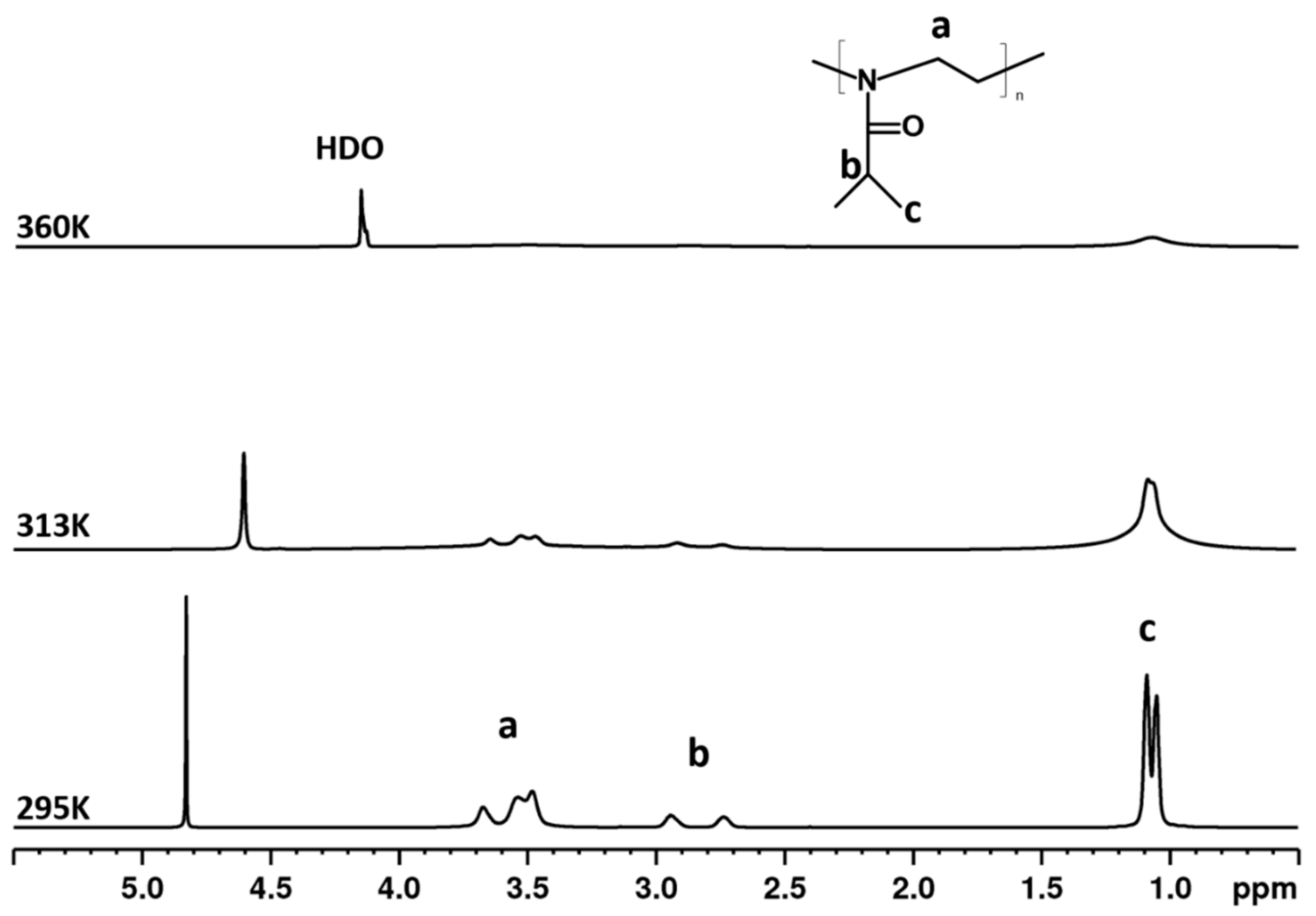
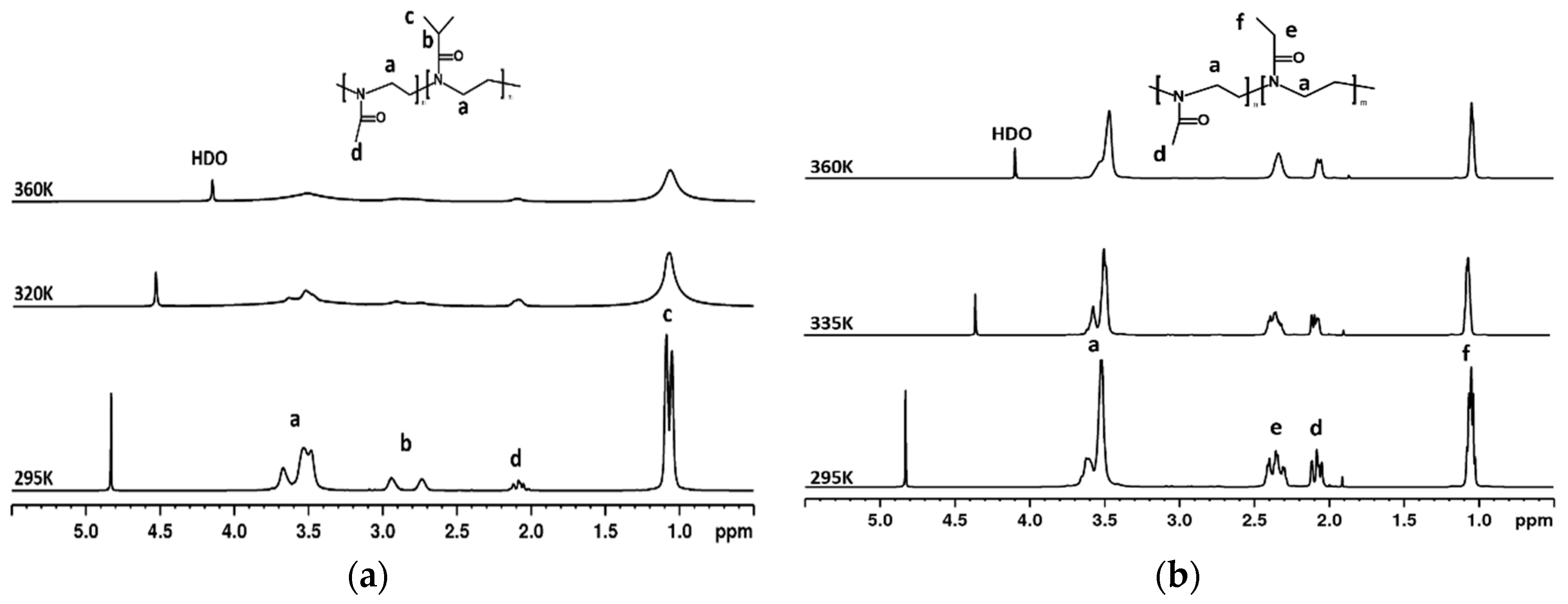
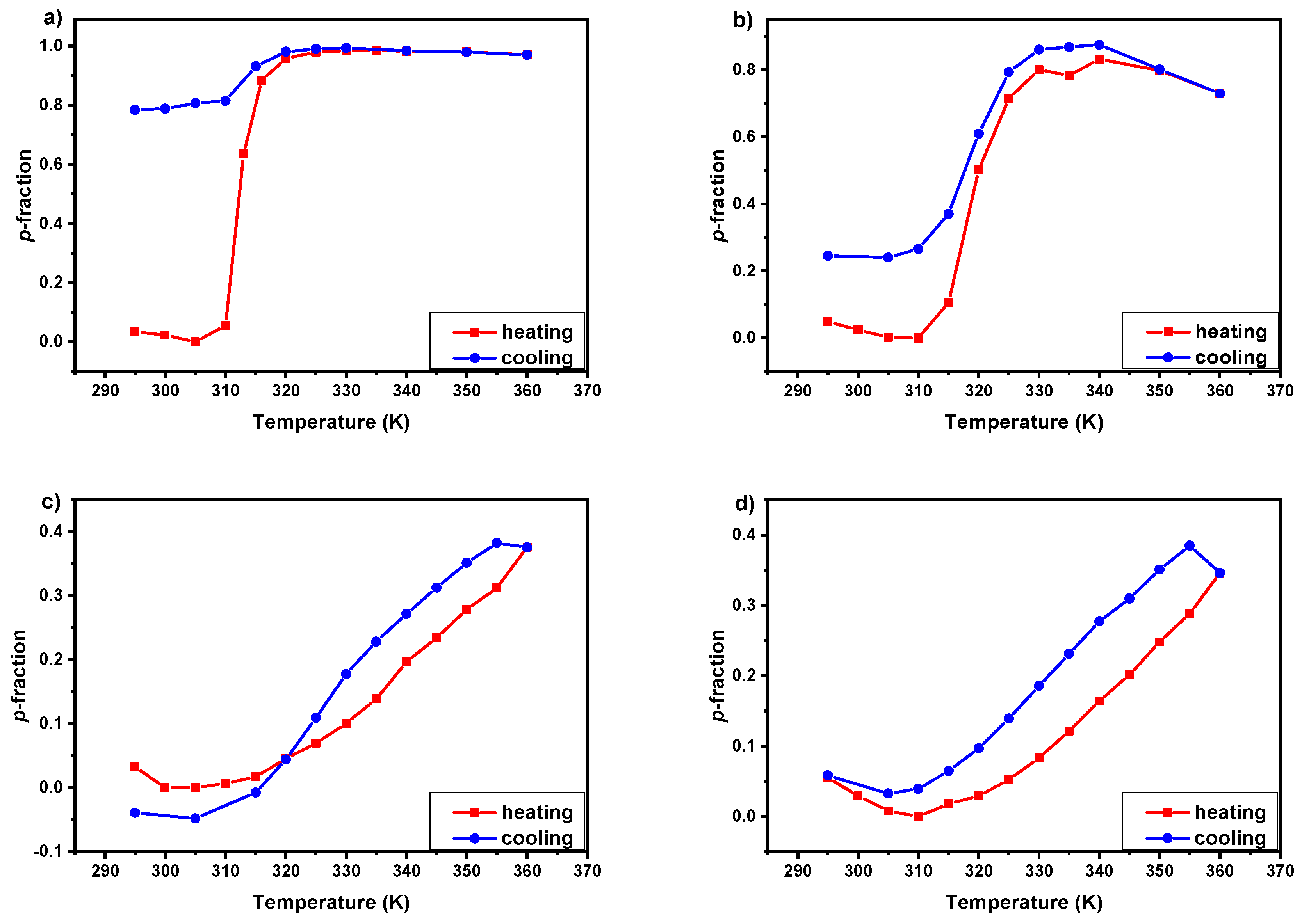
3.2. 1H NMR Spectra and Fraction p of Proton Groups (units) with Significantly Reduced Mobility
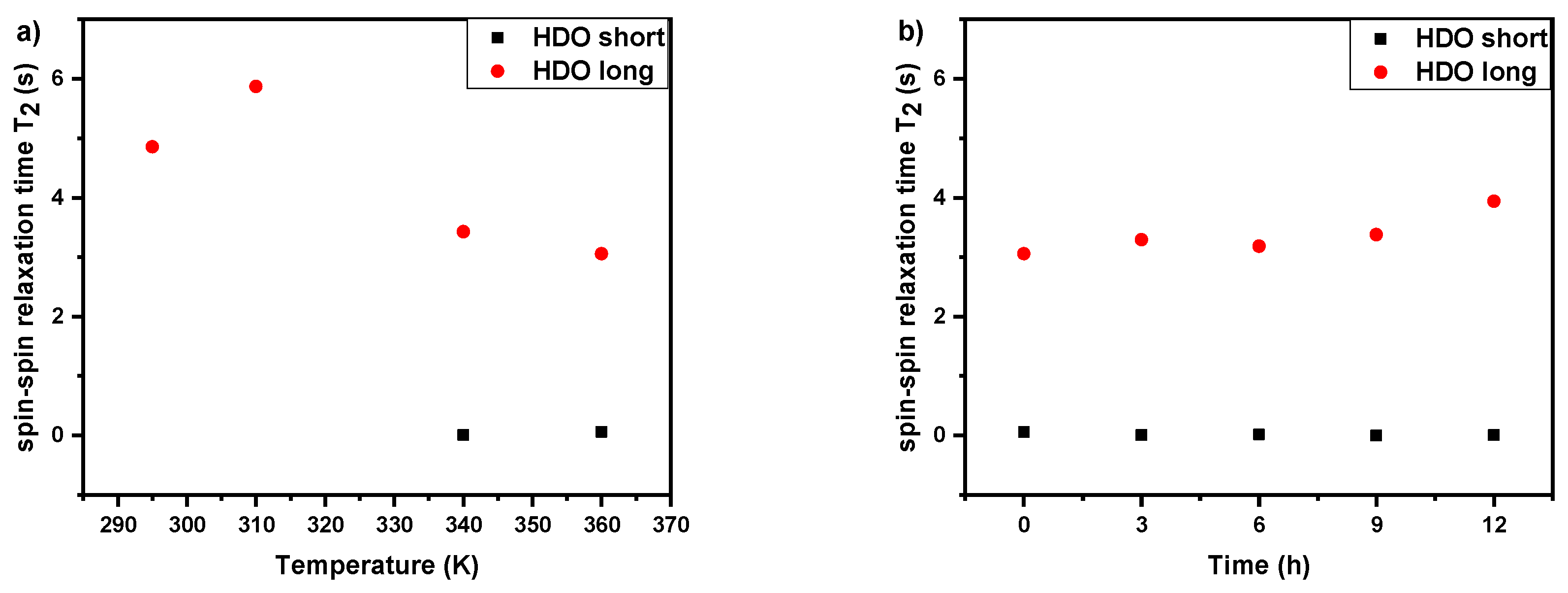
3.3. Spin–Spin Relaxation Times T2 of Water (HDO) Molecules
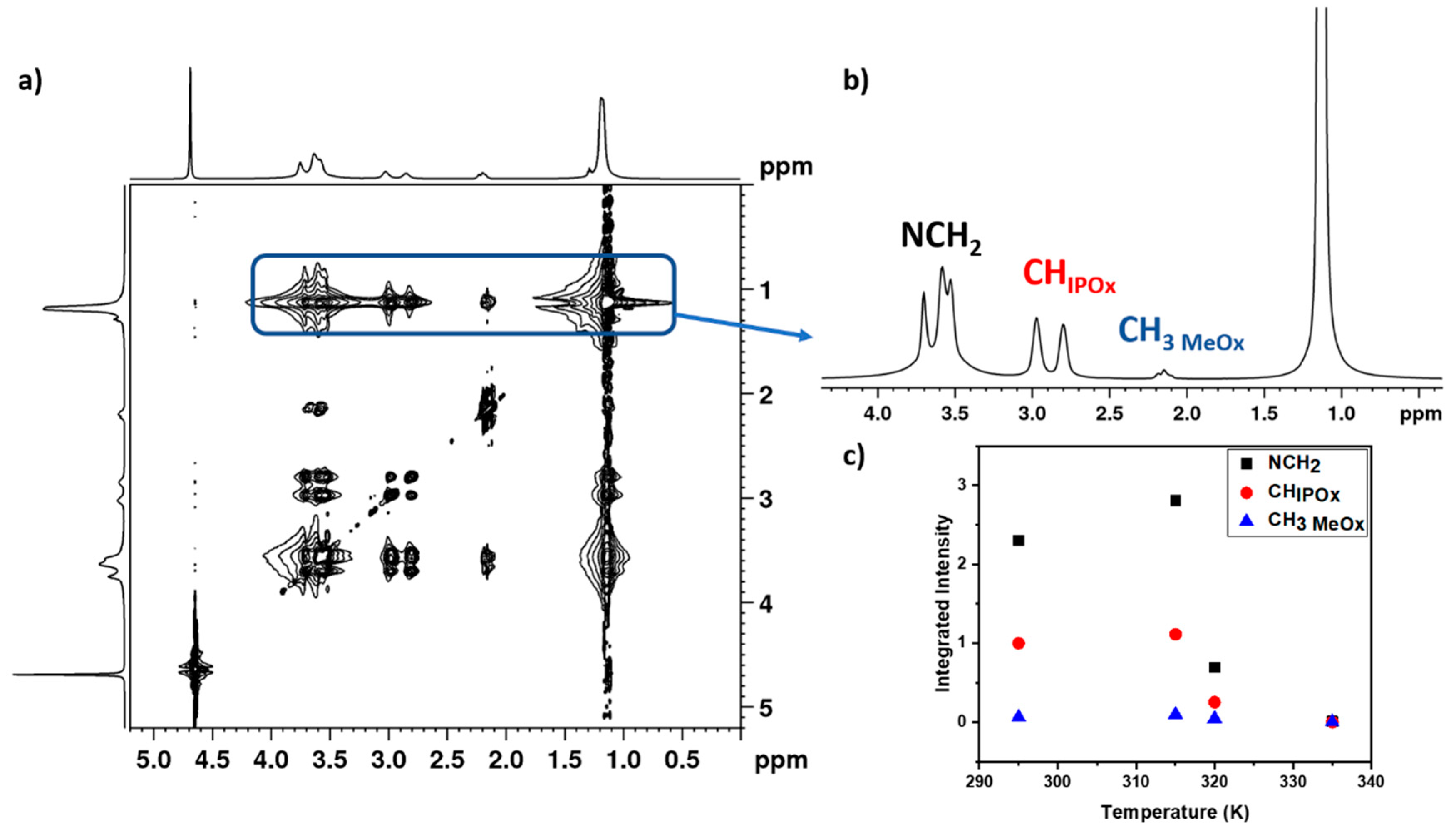
3.4. 2D 1H-1H NOESY NMR Spectra
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zarrintaj, P.; Jouyandeh, M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Hadavand, B.S.; Mozafari, M.; Sheiko, S.S.; Vatankhah-Varnoosfaderani, M.; Gutiérrez, T.J.; Saeb, M.R. Thermo-sensitive polymers in medicine: A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 117, 402–423. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Urban, M.W. Recent advances and challenges in designing stimuli-responsive polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, M.; Štěpánek, P.; Pánek, J.; Papadakis, C.M. Crosstalk between responsivities to various stimuli in multiresponsive polymers: Change in polymer chain and external environment polarity as the key factor. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2019, 297, 1383–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouras, T.; Vamvakaki, M. Field responsive materials: Photo-, electro-, magnetic-and ultrasound-sensitive polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 74–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, G.; Kim, J.; Kim, W.J. Reactive-oxygen-species-responsive drug delivery systems: Promises and challenges. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.G.; De, P. PH responsive polymers with amino acids in the side chains and their potential applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 41084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, C.M.; Harris, M.; Choi, L.; Murali, V.P.; Guerra, F.D.; Jennings, J.A. Stimuli-responsive drug release from smart polymers. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; He, C.; Xiao, C.; Chen, X. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) responsive polymers for biomedical applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 16, 635–646. [Google Scholar]
- Sedlacek, O.; Hoogenboom, R. Drug delivery systems based on poly(2-oxazoline)s and poly(2-oxazine)s. Adv. Ther. 2020, 3, 1900168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sanchez, R.J.P.; Fu, C.; Clayden-Zabik, R.; Peng, H.; Kempe, K.; Whittaker, A.K. Importance of thermally induced aggregation on 19 f magnetic resonance imaging of perfluoropolyether-based comb-shaped poly(2-oxazoline)s. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Herbst, S.; Zhang, C.; Whittaker, A.K. Polymeric 19F MRI agents responsive to reactive oxygen species. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 4585–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlacek, O.; de la Rosa, V.R.; Hoogenboom, R. Poly(2-oxazoline)-protein conjugates. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 120, 109246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aseyev, V.; Tenhu, H.; Winnik, F.M. Non-ionic thermoresponsive polymers in water. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2010, 242, 29–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, I.; Trzebicka, B.; Mu, A.H.E.; Dworak, A. Thermosensitive water-soluble copolymers with doubly responsive reversibly interacting entities. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 1275–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.A.; Georgiou, T.K. Thermoresponsive polymers for biomedical applications. Polymers 2011, 3, 1215–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Uchman, M. Poly(2-oxazoline)-based stimulus-responsive (Co)polymers: An overview of their design, solution properties, surface-chemistries and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 106, 101252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworak, A.; Trzebicka, B.; Kowalczuk, A.; Tsvetanov, C.; Rangelov, S. Polyoxazolines—mechanism of synthesis and solution properties. Polimery 2014, 59, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, A.; Kronek, J.; Bosowska, K.; Trzebicka, B.; Dworak, A. Star poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)s-synthesis and thermosensitivity. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, R.; Thijs, H.M.L.; Jochems, M.J.H.C.; van Lankvelt, B.M.; Fijten, M.W.M.; Schubert, U.S. Tuning the LCST of poly(2-oxazoline)s by varying composition and molecular weight: Alternatives to poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)? Chem. Commun. Camb. 2008, 5758–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, M.; Schmidt, M.; Xia, H.; Storkmann, J.; Plothe, R.; Santos, D.D.; Bednarzick, U.; Krumm, C.; Tiller, J.C. Investigations on the thermoresponsive behavior of copoly(2-oxazoline)s in water. Polym. Guildf. 2019, 175, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, R.; Schlaad, H. Thermoresponsive poly(2-oxazoline)s, polypeptoids, and polypeptides. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 24–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bloksma, M.M.; Weber, C.; Perevyazko, I.Y.; Kuse, A.; Baumgärtel, A.; Vollrath, A.; Hoogenboom, R.; Schubert, U.S. Poly(2-cyclopropyl-2-oxazoline): From rate acceleration by cyclopropyl to thermoresponsive properties. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4057–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, C.; Akiyama, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Winnik, F.M. microcalorimetric study of the temperature-induced phase separation in aqueous solutions of poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazolines). Macromolecules 2004, 37, 2556–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezonenko, T.; Qiu, X.P.; Winnik, F.M.; Sato, T. Dehydration, micellization, and phase separation of thermosensitive polyoxazoline star block copolymers in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schild, H.G. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): Experiment, theory and application. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1992, 17, 163–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y. IR Spectroscopic study on the hydration and the phase transition of poly(vinyl methyl ether) in water. Langmuir 2001, 17, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spěváček, J. Application of NMR spectroscopy to study thermoresponsive polymers. In Temperature-Responsive Polymers: Chemistry, Properties, and Applications; Khutoryanskiy, V.V., Georgiou, T.K., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 225–247. ISBN 978-1-119-15778-6. [Google Scholar]
- Che, L.T.; Hiorth, M.; Hoogenboom, R.; Kjøniksen, A.L. Complex temperature and concentration dependent self-assembly of poly(2-oxazoline) block copolymers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukotová, L.; Bogomolova, A.; Konefal, R.; Špírková, M.; Štěpánek, P.; Hrubý, M. Hybrid κ-carrageenan-based polymers showing “schizophrenic” lower and upper critical solution temperatures and potassium responsiveness. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 210, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konefał, R.; Spěváček, J.; Mužíková, G.; Laga, R. Thermoresponsive behavior of poly(DEGMA)-based copolymers. NMR and dynamic light scattering study of aqueous solutions. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 124, 109488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, W.; Engelhardt, N.; Kampmann, A.L.; Degen, P.; Weberskirch, R. Micellization and mobility of amphiphilic poly(2-oxazoline) based block copolymers characterized by 1H nmr spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 4032–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.K.; Jang, M.K.; Nah, J.W.; Park, M.R.; Cho, C.S. Effect of temperature on the mobility of core-shell-type nanoparticles composed of poly(γ-benzyl-l-glutamate) and poly(n-isopropylacrylamide). Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2006, 207, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, M.; Wohlrab, S.; Kuckling, D.; Möhwald, H.; Schönhoff, M. Coil-to-globule transition of PNIPAM graft copolymers with charged side chains: A 1H and 2H NMR and spin relaxation study. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 7358–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronek, J.; Kroneková, Z.; Lustoň, J.; Paulovičová, E.; Paulovičová, L.; Mendrek, B. In vitro bio-immunological and cytotoxicity studies of poly(2-oxazolines). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Schroeder, S.; Tauhardt, L.; Kempe, K.; Schubert, U.S.; Fischer, D. In vitro hemocompatibility and cytotoxicity study of poly(2-methyl-2- oxazoline) for biomedical applications. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaad, H.; Diehl, C.; Gress, A.; Meyer, M.; Demirel, A.L.; Nur, Y.; Bertin, A. Poly(2-oxazoline)s as Smart Bioinspired Polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, C.; Schlaad, H. Polyoxazoline-based Crystalline Microspheres for Carbohydrate-Protein Recognition. Chem. A Eur. J. 2009, 15, 11469–11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konefał, R.; Spěváček, J.; Jäger, E.; Petrova, S. Thermoresponsive behaviour of terpolymers containing poly(ethylene oxide), poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) and poly(ε-caprolactone) blocks in aqueous solutions: An NMR study. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakeš, J. Regularized Positive Exponential Sum (REPES) Program-A Way of Inverting Laplace Transform Data Obtained by Dynamic Light Scattering. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 1995, 60, 1781–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konefał, R.; Spěváček, J.; Černoch, P. Thermoresponsive poly(2-oxazoline) homopolymers and copolymers in aqueous solutions studied by NMR spectroscopy and dynamic light scattering. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 100, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszko-Torbus, N.; Utrata-Wesołek, A.; Wałach, W.; Dworak, A. Solution behavior of thermoresponsive random and gradient copolymers of 2-n-propyl-2-oxazoline. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 88, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirova, A.I.; Kirile, T.Y.; Ten’kovtsev, A.V.; Filippov, A.P. Effect of terminal hydrophobic groups on the behavior of linear poly-2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline in aqueous solution. Fibre Chem. 2018, 50, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Tong, Z.; Feng, H. NMR investigation of phase separation in poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)/water solutions. Polym. Guildf 1997, 38, 5539–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouřilová, H.; Spěváček, J.; Hanyková, L. 1H NMR study of temperature-induced phase transitions in aqueous solutions of poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide)/poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) mixtures. Polym. Bull. 2013, 70, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spěváček, J.; Konefał, R.; Dybal, J.; Čadová, E.; Kovářová, J. Thermoresponsive behavior of block copolymers of PEO and PNIPAm with different architecture in aqueous solutions: A study by NMR, FTIR, DSC and quantum-chemical calculations. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 94, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legros, C.; de Pauw-Gillet, M.C.; Tam, K.C.; Taton, D.; Lecommandoux, S. Crystallisation-driven self-assembly of poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline)-block-poly(2-methyl-2-oxazoline) above the LCST. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 3354–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spěváček, J. NMR investigations of phase transition in aqueous polymer solutions and gels. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 14, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spěváček, J.; Dybal, J.; Starovoytova, L.; Zhigunov, A.; Sedláková, Z. Temperature-induced phase separation and hydration in poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) aqueous solutions: A study by NMR and IR spectroscopy, SAXS, and quantum-chemical calculations. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 6110–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszko-Torbus, N.; Utrata-Wesołek, A.; Bochenek, M.; Lipowska-Kur, D.; Dworak, A.; Wałach, W. Thermal and crystalline properties of poly(2-oxazoline)s. Polym. Chem. 2019, 11, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumoto, Y.; Tsuchiizu, A.; Qiu, X.; Winnik, F.M. Dissecting the mechanism of the heat-induced phase separation and crystallization of poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) in water through vibrational spectroscopy and molecular orbital calculations. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 3531–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzebicka, B.; Haladjova, E.; Otulakowski, Ł.; Oleszko, N.; Wałach, W.; Libera, M.; Rangelov, S.; Dworak, A. Hybrid nanoparticles obtained from mixed mesoglobules. Polym. Guildf. 2015, 68, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, A.L.; Meyer, M.; Schlaad, H. Formation of polyamide nanofibers by directional crystallization in aqueous solution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8622–8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aseyev, V.O.; Tenhu, H.; Winnik, F.M. Temperature dependence of the colloidal stability of neutral amphiphilic polymers in water. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2006, 196, 1–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Martín, B.; Romero-Cano, M.S.; Cosgrove, T.; Vincent, B.; Fernández-Barbero, A. Solvent relaxation of swelling PNIPAM microgels by NMR. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 270–271, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, H.; Puttick, S.; Reid, J.; Bernardi, S.; Searles, D.J.; Whittaker, A.K. Conformation of hydrophobically modified thermoresponsive poly(OEGMA-co-TFEA) across the LCST revealed by NMR and molecular dynamics studies. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 3310–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, H.; Li, W.; Liu, L.; Puttick, S.; Reid, J.; Bernardi, S.; Searles, D.J.; Zhang, A.; Whittaker, A.K.; et al. Conformation transitions of thermoresponsive dendronized polymers across the lower critical solution temperature. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Mn [g/mol] | Mw [g/mol] | Ð | MeOx/EtOx(IPOx) NMR * | MeOx/EtOx(IPOx) (eq) ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(MeOx/EtOx)(28/72) | 10,200 | 11,800 | 1.16 | 28/72 | 25/75 |
| PIPOx | 13,000 | 13,900 | 1.07 | 0/100 | 0/100 |
| P(MeOx/IPOx)(14/86) | 13,000 | 13,700 | 1.05 | 14/86 | 10/90 |
| P(MeOx/EtOx)(7/93) | 7300 | 8100 | 1.10 | 7/93 | 10/90 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konefał, R.; Černoch, P.; Konefał, M.; Spěváček, J. Temperature Behavior of Aqueous Solutions of Poly(2-Oxazoline) Homopolymer and Block Copolymers Investigated by NMR Spectroscopy and Dynamic Light Scattering. Polymers 2020, 12, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091879
Konefał R, Černoch P, Konefał M, Spěváček J. Temperature Behavior of Aqueous Solutions of Poly(2-Oxazoline) Homopolymer and Block Copolymers Investigated by NMR Spectroscopy and Dynamic Light Scattering. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091879
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonefał, Rafał, Peter Černoch, Magdalena Konefał, and Jiří Spěváček. 2020. "Temperature Behavior of Aqueous Solutions of Poly(2-Oxazoline) Homopolymer and Block Copolymers Investigated by NMR Spectroscopy and Dynamic Light Scattering" Polymers 12, no. 9: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091879
APA StyleKonefał, R., Černoch, P., Konefał, M., & Spěváček, J. (2020). Temperature Behavior of Aqueous Solutions of Poly(2-Oxazoline) Homopolymer and Block Copolymers Investigated by NMR Spectroscopy and Dynamic Light Scattering. Polymers, 12(9), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091879






