Effect of Stabilizer States (Solid Vs Liquid) on Properties of Stabilized Natural Rubbers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of NR Samples
2.3. Characterizations
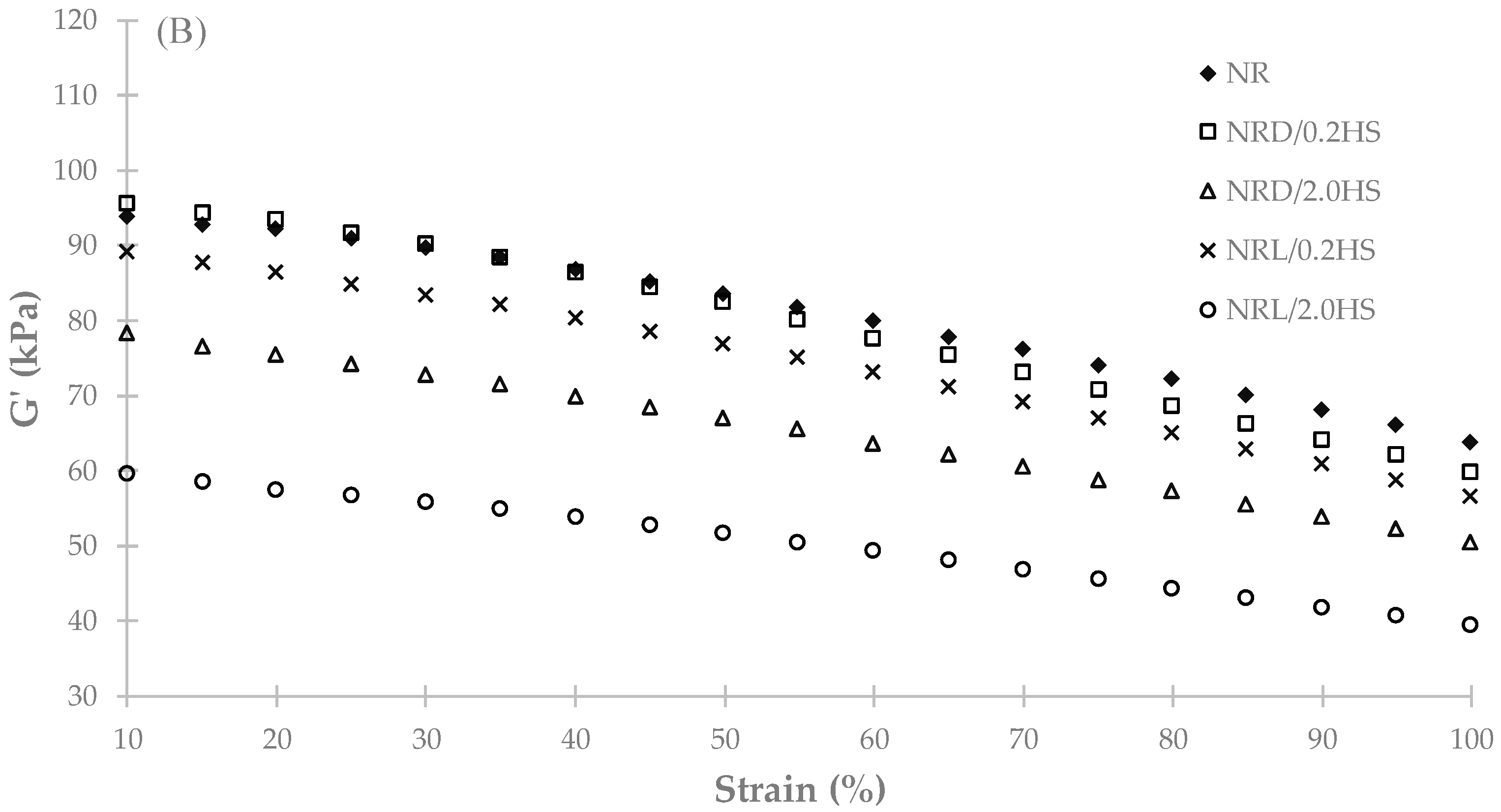
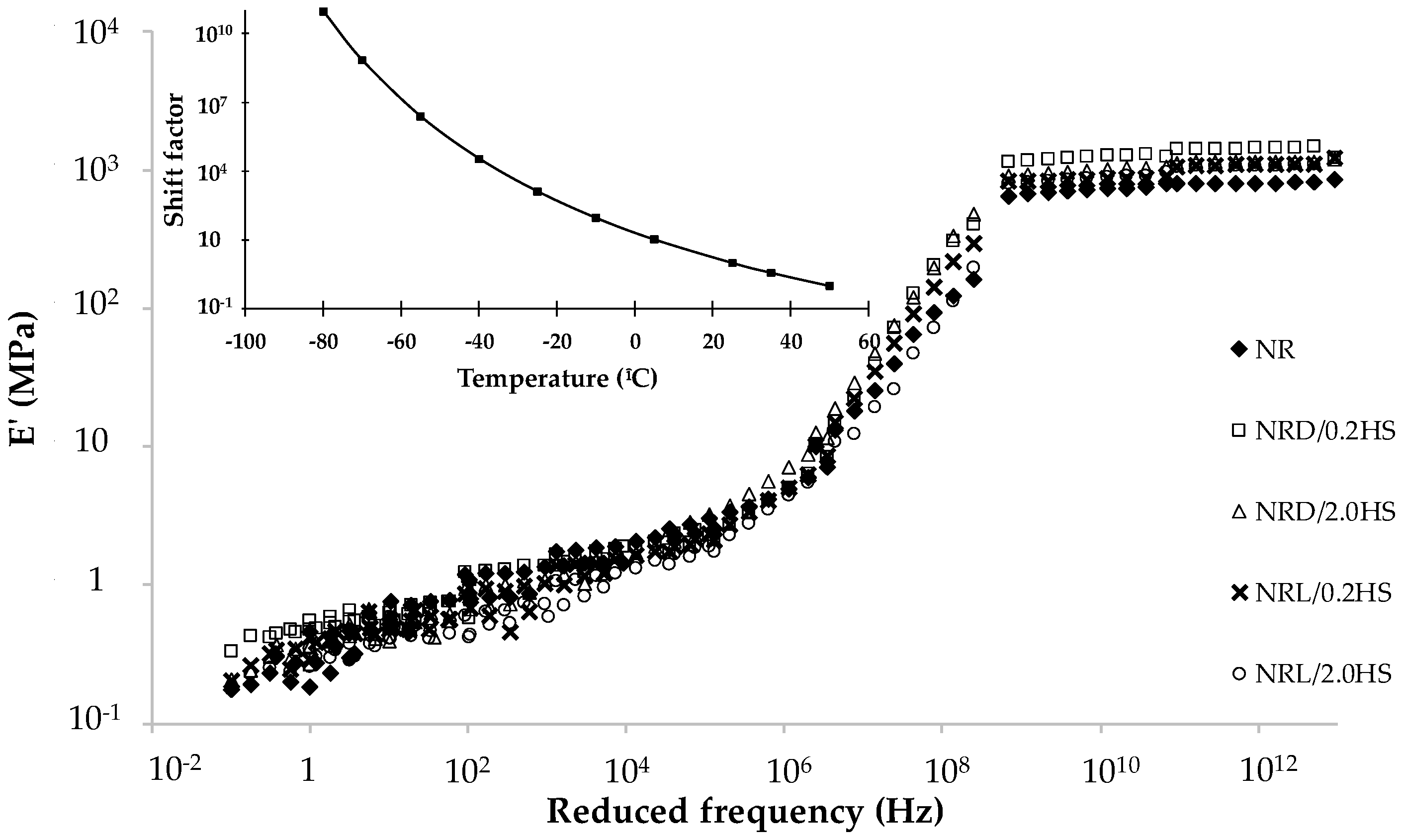
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smitthipong, W.; Nardin, M.; Schultz, J.; Nipithakul, T.; Suchiva, K. Study of tack properties of uncrosslinked natural rubber. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2004, 18, 1449–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitthipong, W.; Nardin, M.; Schultz, J.; Suchiva, K. Adhesion and self-adhesion of rubbers, crosslinked by electron beam irradiation. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2007, 27, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitthipong, W.; Nardin, M.; Schultz, J.; Suchiva, K. Adhesion and self-adhesion of immiscible rubber blends. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2009, 29, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksup, R.; Sun, Y.; Sukatta, U.; Smitthipong, W. Foam rubber from centrifuged and creamed latex. J. Polym. Eng. 2019, 39, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhaus, R.A. Rubber formation in plants—A mini-review. Isr. J. Bot. 1985, 34, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Tarachiwin, L.; Tanaka, Y.; Sakdapipanich, J. Structure and origin of long-chain branching and gel in natural rubber. Kautschuk Gummi Kunststoffe 2005, 58, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Tarachiwin, L.; Sakdapipanich, J.; Ute, K.; Kitayama, T.; Tanaka, Y. Structural Characterization of α-Terminal Group of Natural Rubber. 2. Decomposition of Branch-Points by Phospholipase and Chemical Treatments. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimpaiboon, A.; Sriring, M.; Sakdapipanich, J. Molecular structure and storage hardening of natural rubber: Insight into the reactions between hydroxylamine and phospholipids linked to natural rubber molecule. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollakup, R.; Suwanruji, P.; Tantatherdtam, R.; Smitthipong, W. New approach on structure-property relationships of stabilized natural rubbers. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Ding, A.; Jin, L.; Zhang, H.; Liao, S. Quantitative Analysis of Abnormal Groups on Molecular Chain of Natural Rubber. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2019, 61, 856–864. [Google Scholar]
- Nimpaiboon, A.; Amnuaypornsri, S.; Sakdapipanich, J. Obstruction of storage hardening in nr by using polar chemicals. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2016, 89, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.D. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Montha, S.; Suwandittakul, P.; Poonsrisawat, A.; Oungeun, P.; Kongkaew, C. Maillard Reaction in Natural Rubber Latex: Characterization and Physical Properties of Solid Natural Rubber. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rungsanthie, K.; Suwanruji, P.; Tantatherdtam, R.; Chollakup, R. Effect of non-rubber components on viscosity stabilization of natural rubber. Int. Conf. Polym. Process. Soc. 2012, 11, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Smitthipong, W.; Tantatherdtam, R.; Rungsanthien, K.; Suwanruji, P.; Klanarong, S.; Radabutra, S.; Thanawan, S.; Vallat, M.F.; Nardin, M.; Mougin, K.; et al. Effect of Non-Rubber Components on Properties of Sulphur Crosslinked Natural Rubbers. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 844, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amnuaypornsri, S.; Sakdapipanich, J.; Toki, S.; Hsiao, B.; Ichikawa, N.; Tanaka, Y. Strain-Induced Crystallization of Natural Rubber: Effect of Proteins and Phospholipids. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2008, 81, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
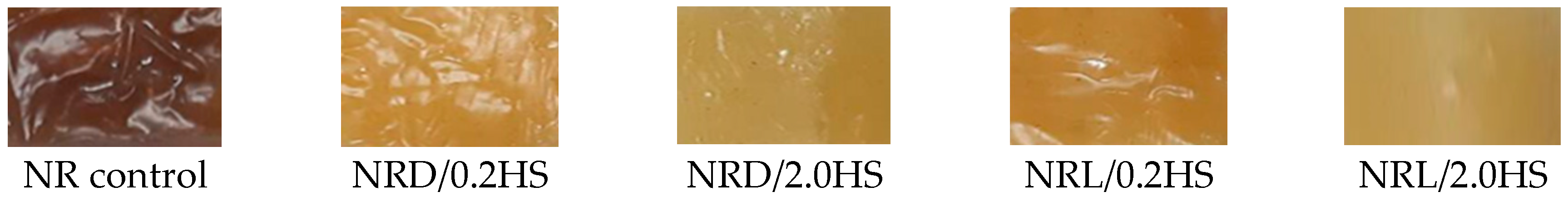

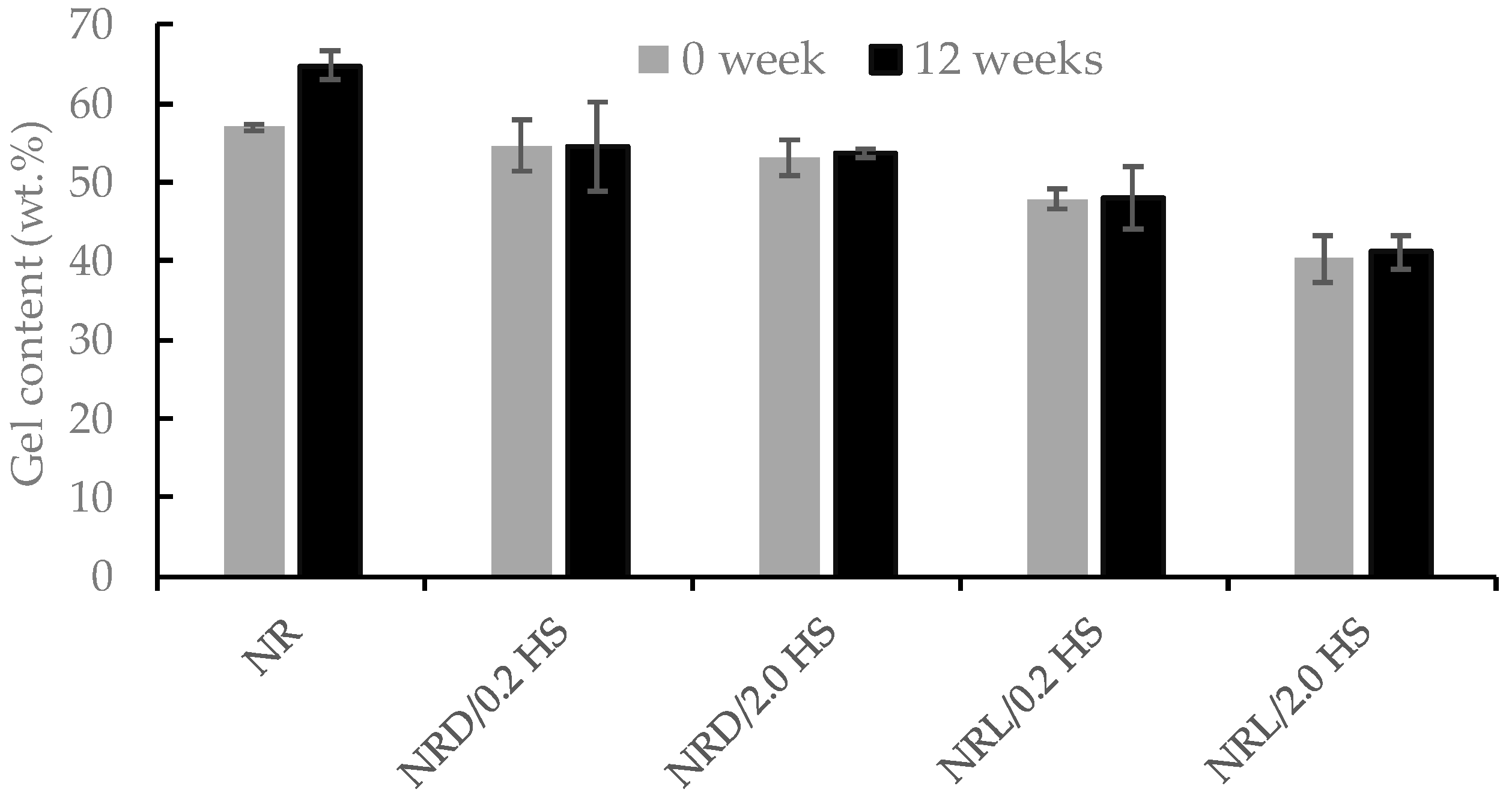
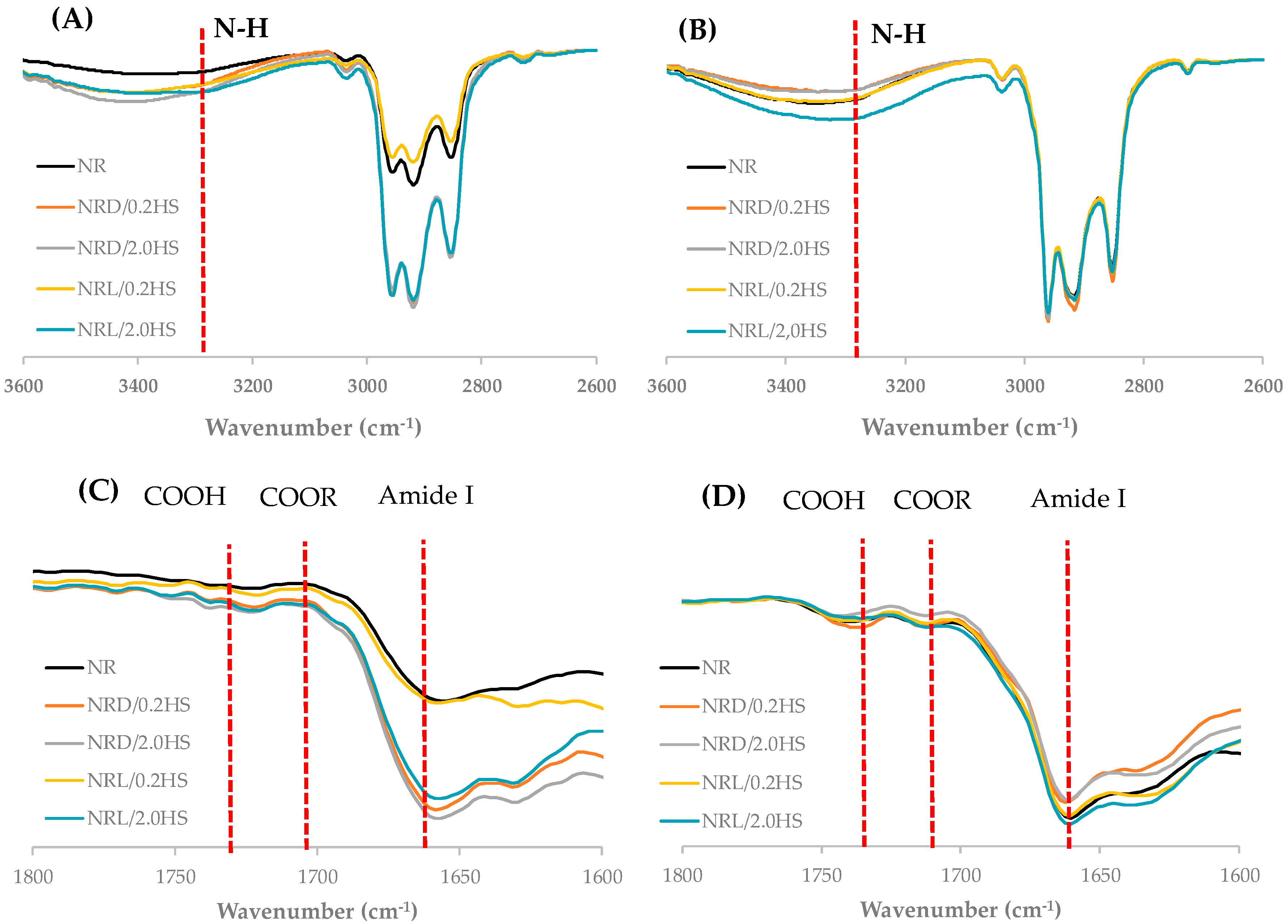
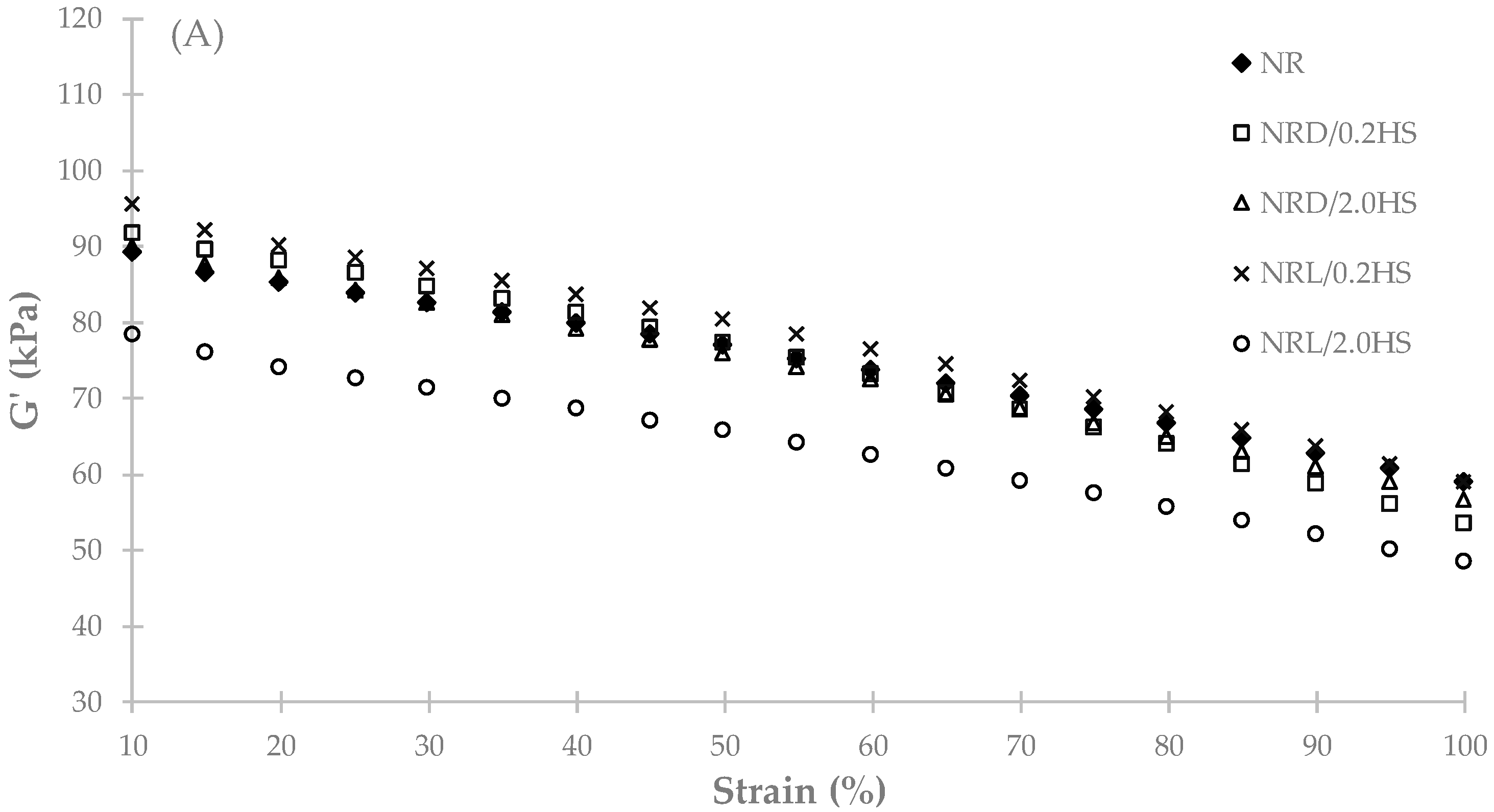

| Name | Samples |
|---|---|
| Control NR | Unstabilized NR |
| NRD/0.2 HS | Dry NR with dry hydroxylamine sulfate 0.2 phr |
| NRD/2.0 HS | Dry NR with dry hydroxylamine sulfate 2.0 phr |
| NRL/0.2 HS | Natural latex with liquid hydroxylamine sulfate 0.2 phr |
| NRL/2.0 HS | Natural latex with liquid hydroxylamine sulfate 2.0 phr |
| Sample Name | Po (± 5 a.u.) | PRI (± 5 a.u.) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Weeks | 12 Weeks | 0 Weeks | 12 Weeks | |
| NR | 20.0 | 28.0 | 85.0 | 67.9 |
| NRD/0.2 HS | 28.5 | 32.0 | 61.4 | 59.4 |
| NRD/2.0 HS | 22.0 | 21.5 | 54.6 | 51.2 |
| NRL/0.2 HS | 22.5 | 24.5 | 62.2 | 59.2 |
| NRL/2.0 HS | 18.5 | 18.0 | 56.8 | 54.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Promhuad, K.; Smitthipong, W. Effect of Stabilizer States (Solid Vs Liquid) on Properties of Stabilized Natural Rubbers. Polymers 2020, 12, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040741
Promhuad K, Smitthipong W. Effect of Stabilizer States (Solid Vs Liquid) on Properties of Stabilized Natural Rubbers. Polymers. 2020; 12(4):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040741
Chicago/Turabian StylePromhuad, Khwanchat, and Wirasak Smitthipong. 2020. "Effect of Stabilizer States (Solid Vs Liquid) on Properties of Stabilized Natural Rubbers" Polymers 12, no. 4: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040741
APA StylePromhuad, K., & Smitthipong, W. (2020). Effect of Stabilizer States (Solid Vs Liquid) on Properties of Stabilized Natural Rubbers. Polymers, 12(4), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040741




