New Insights into the Morphology of Silica and Carbon Black Based on Their Different Dispersion Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Types of Silica
2.2. Analytical Properties of the Silica
2.2.1. Oil Adsorption Method
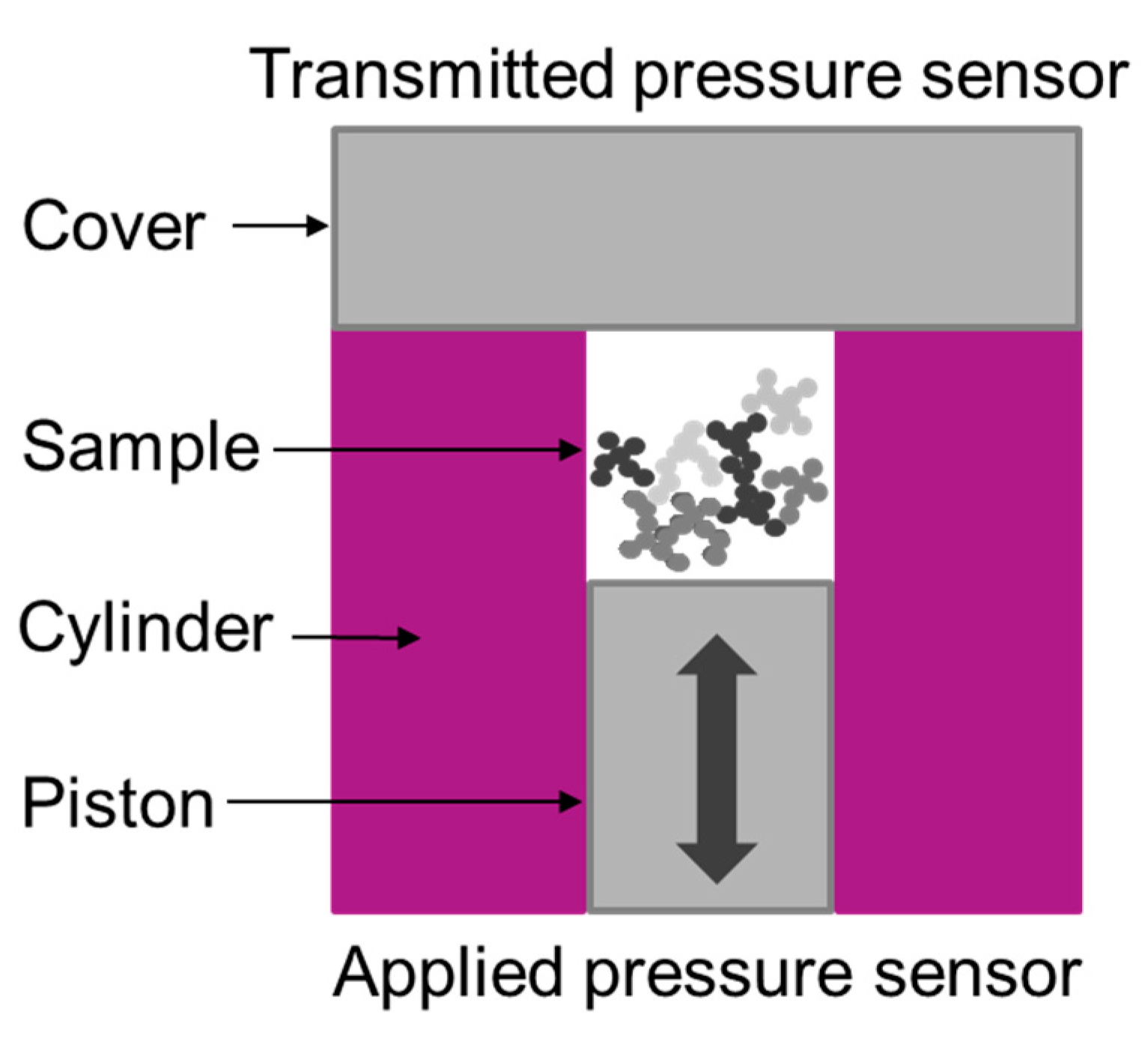
2.2.2. Compressed Void Volume Measurement
2.2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.2.4. X-ray Diffraction Measurements
2.2.5. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Study
2.3. Further Used Materials
- Precipitated silica 158GR190 (2.0 g/cm3 [32]) with a three-dimensional structure;
- Carbon black N330 (1.8 g/cm3 [35]) with a three-dimensional structure;
- Clay Kaolin Advafill-S (2.6 g/cm3 [35]) with a two-dimensional layered structure;
- Glass beads Omicron NP3 P0 (2.46 g/cm3 [35]) nonstructured (2–10 µm in diameter).
2.4. Compound Formulation and Mixing
2.5. In-Rubber Properties
2.5.1. Macrodispersion Measurement via Topography
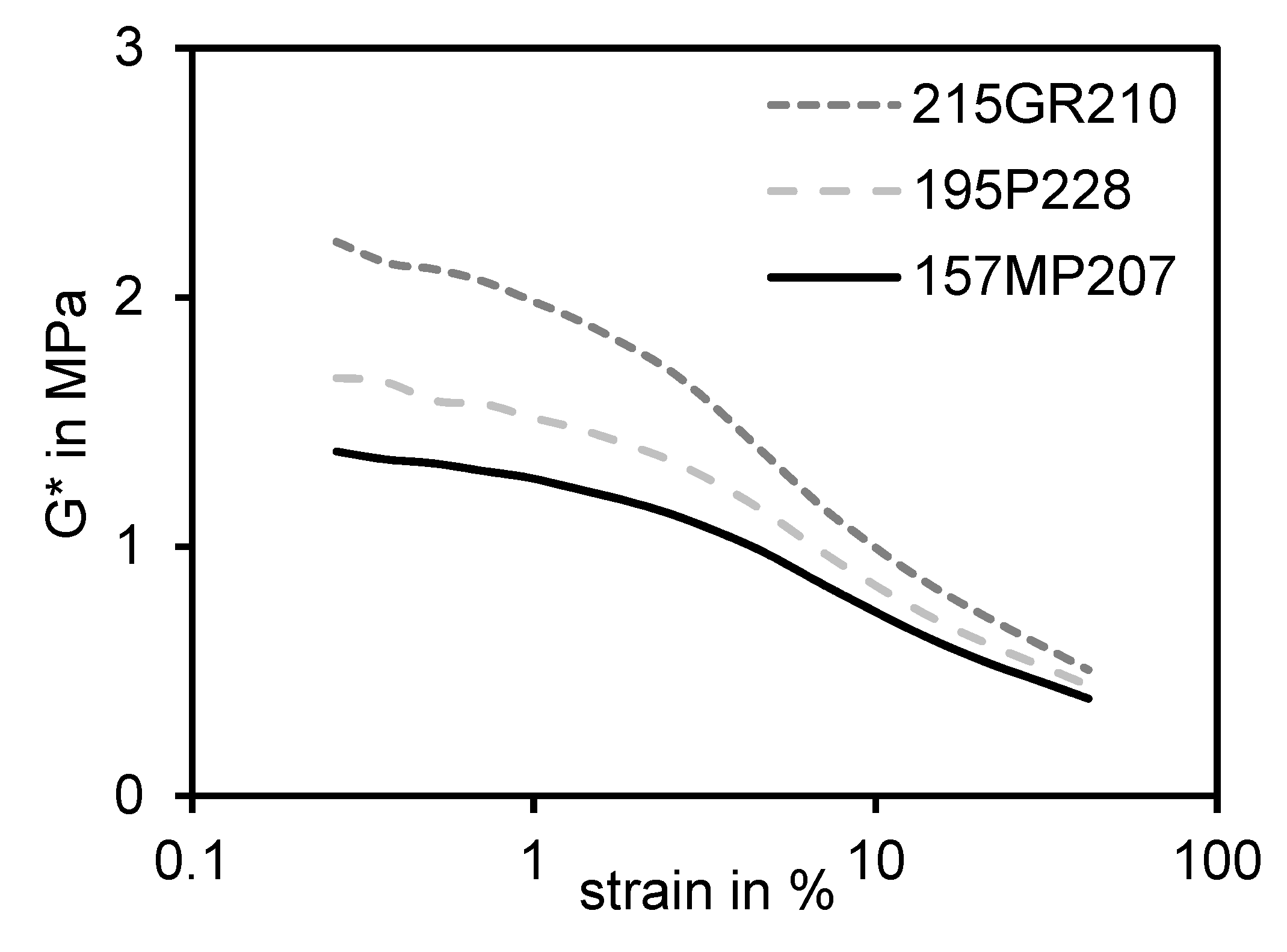
2.5.2. PAYNE-Effect Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
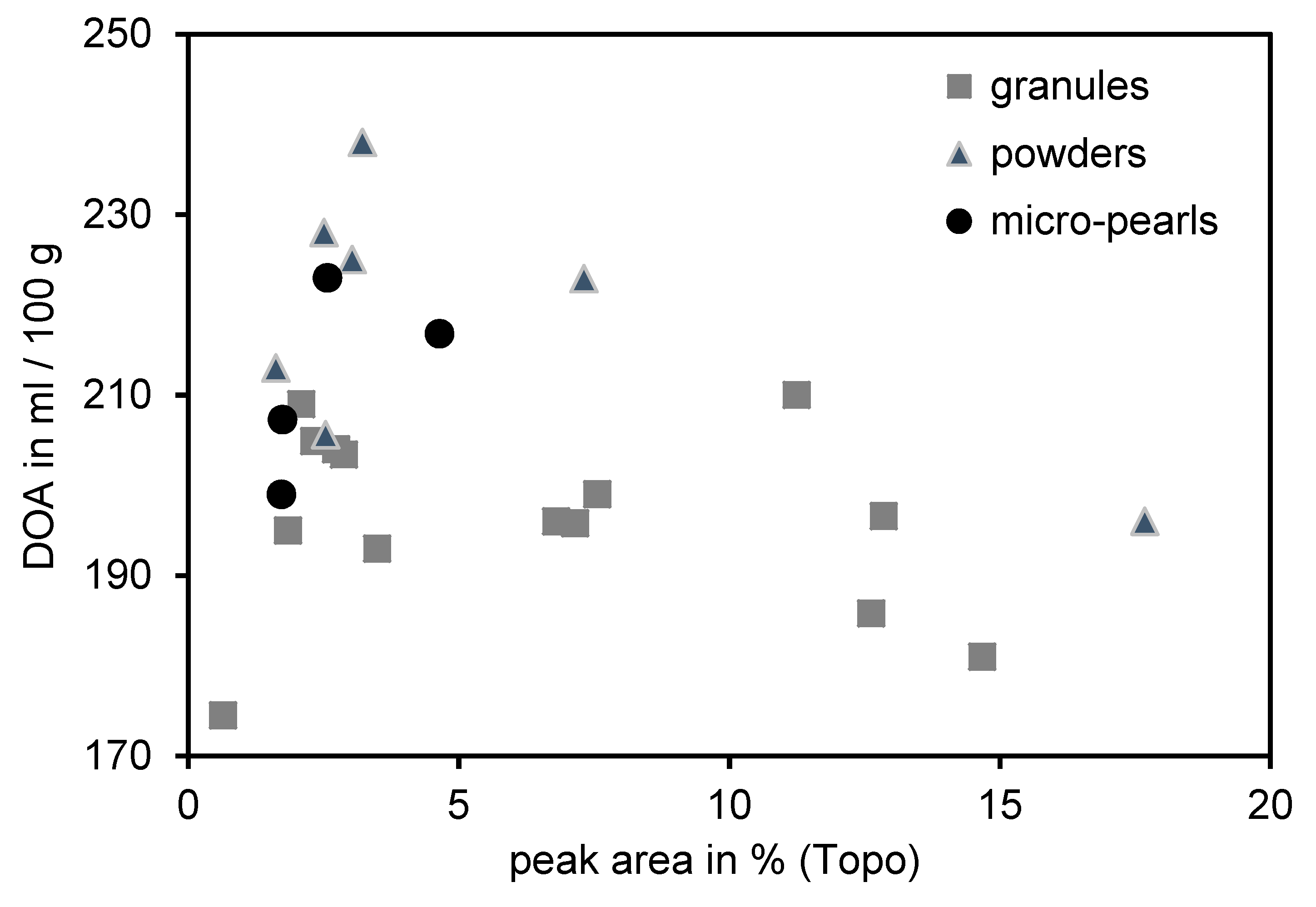
3.1. Correlation between DOA Measurements and Topography
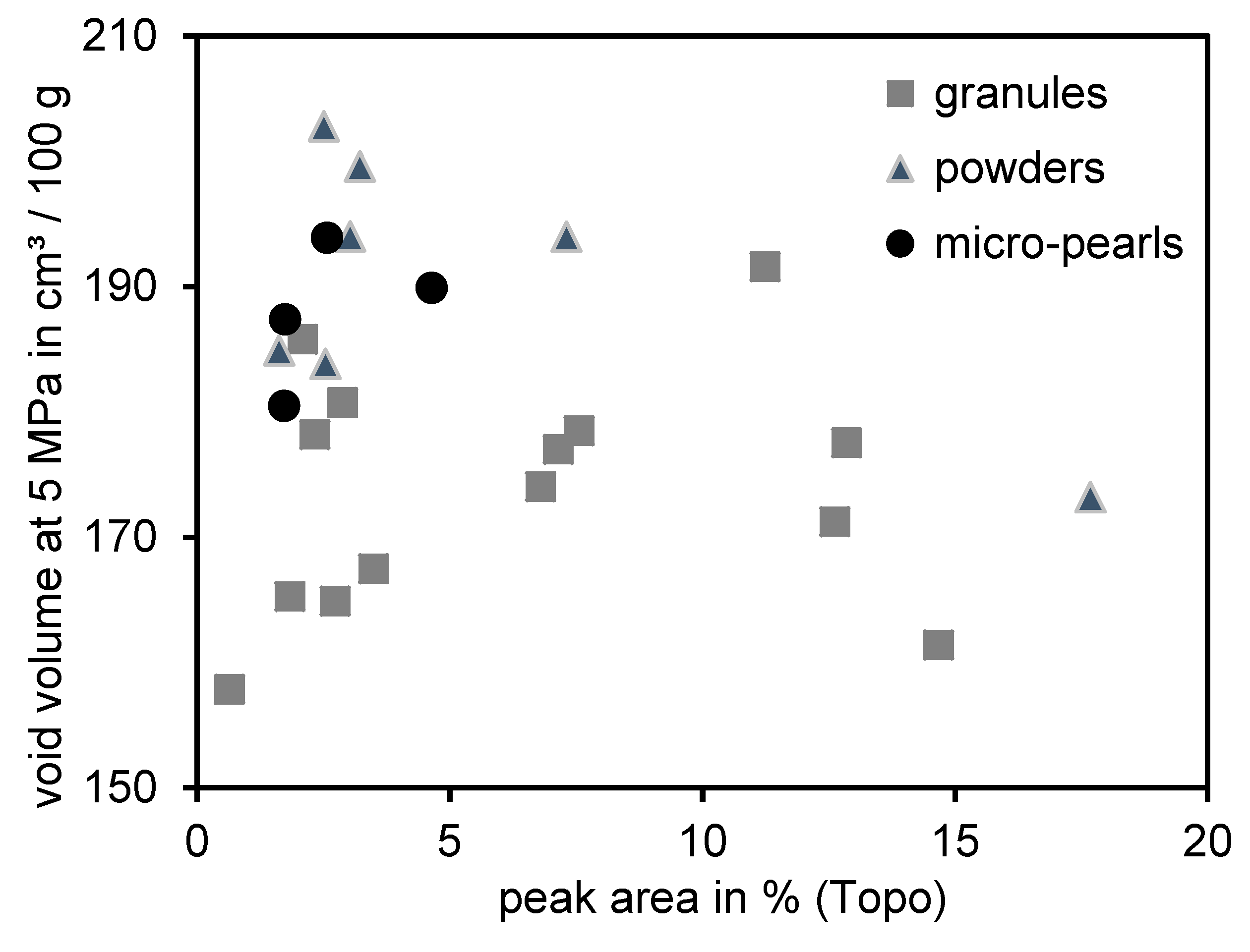
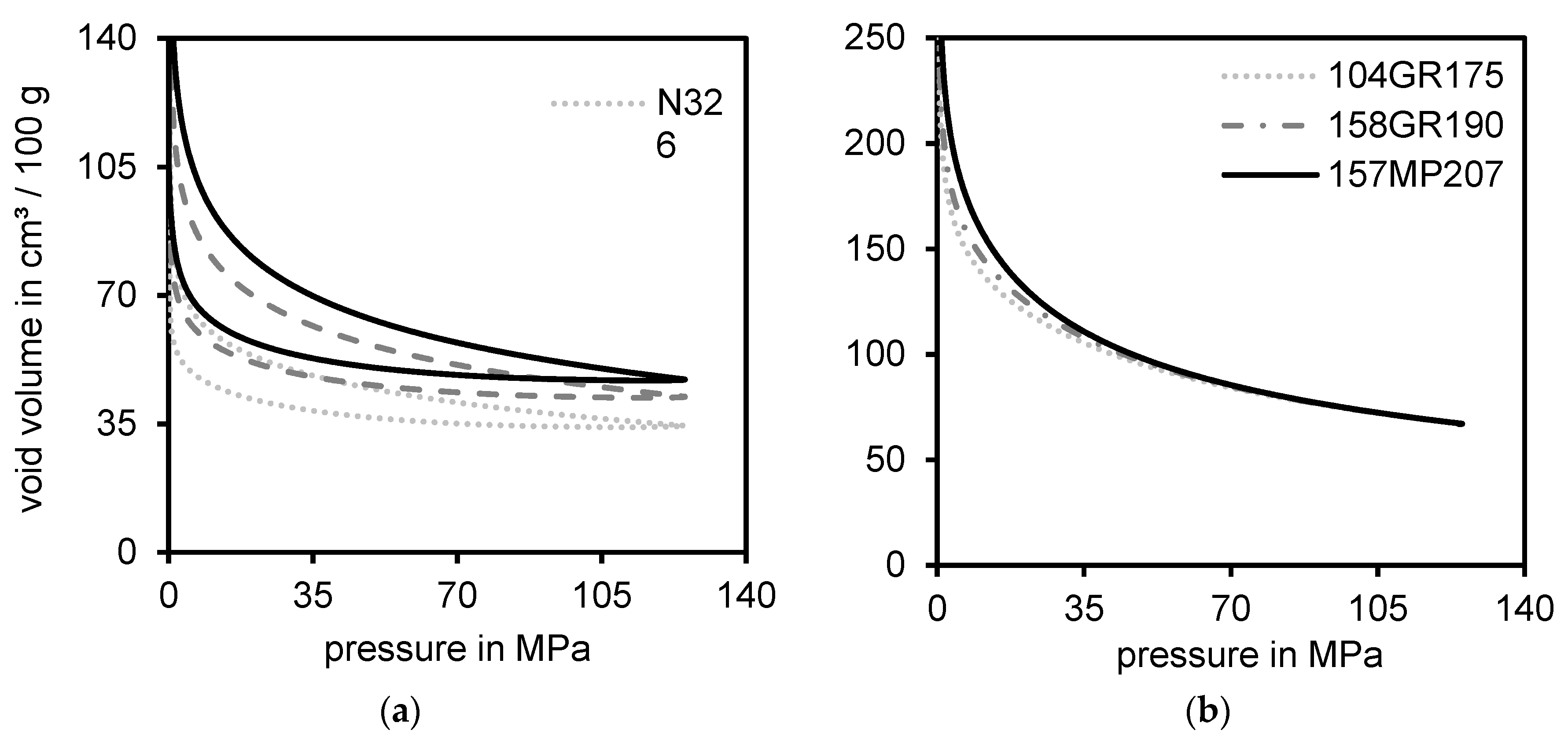
3.2. Correlation between Void Volume Measurements and Topography
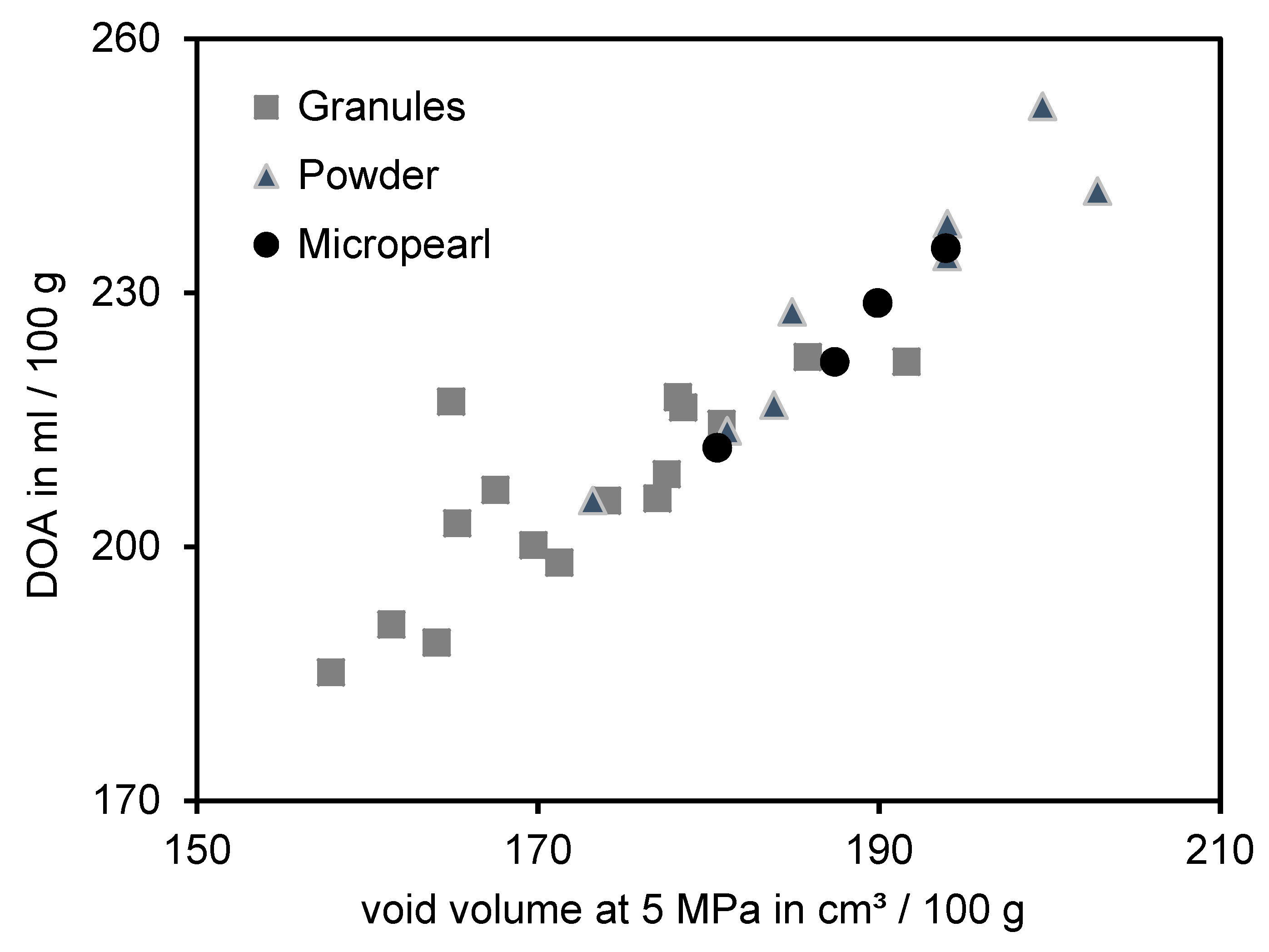
3.3. Comparison of the DOA and Void Volume Measurement
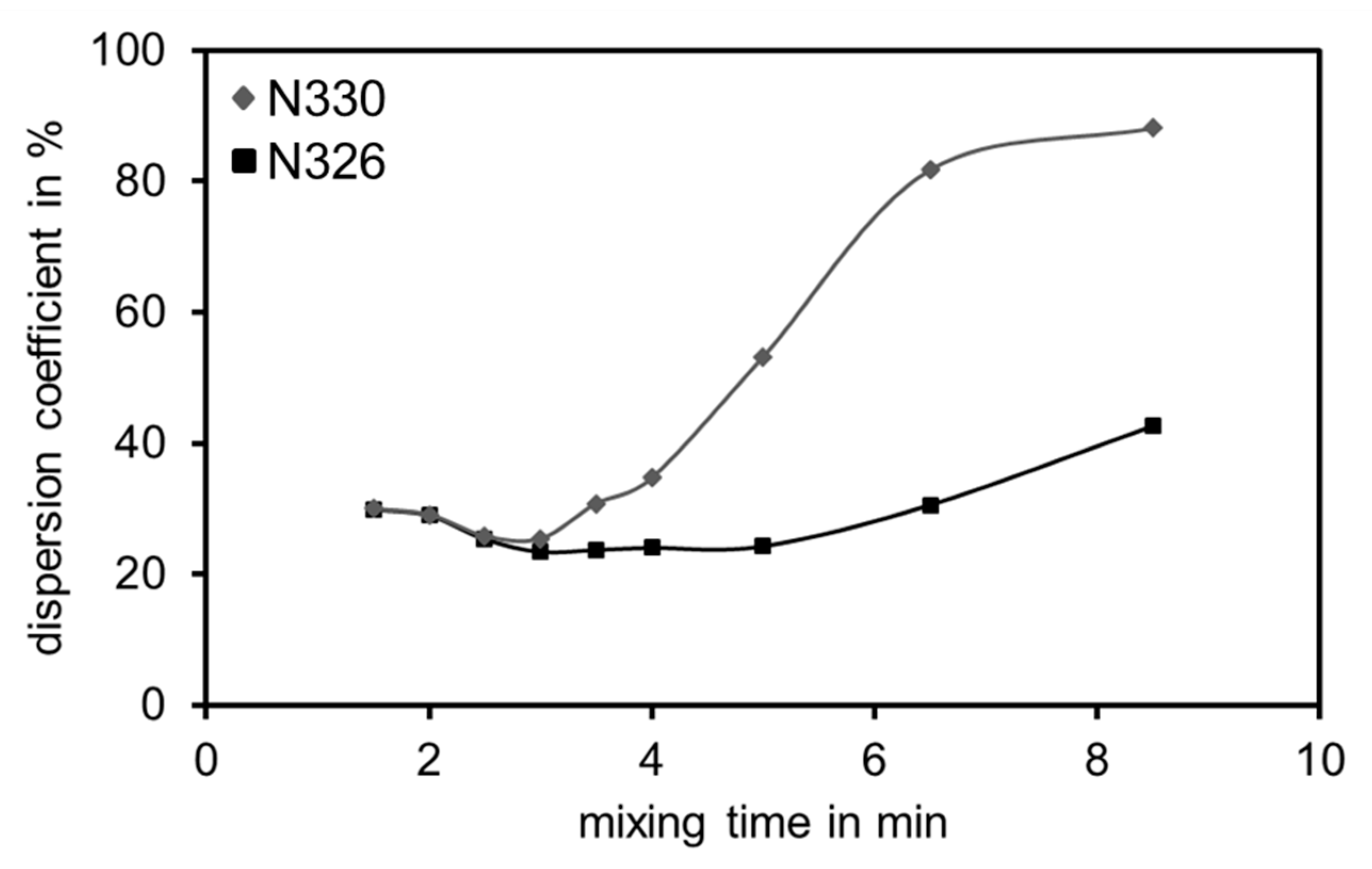
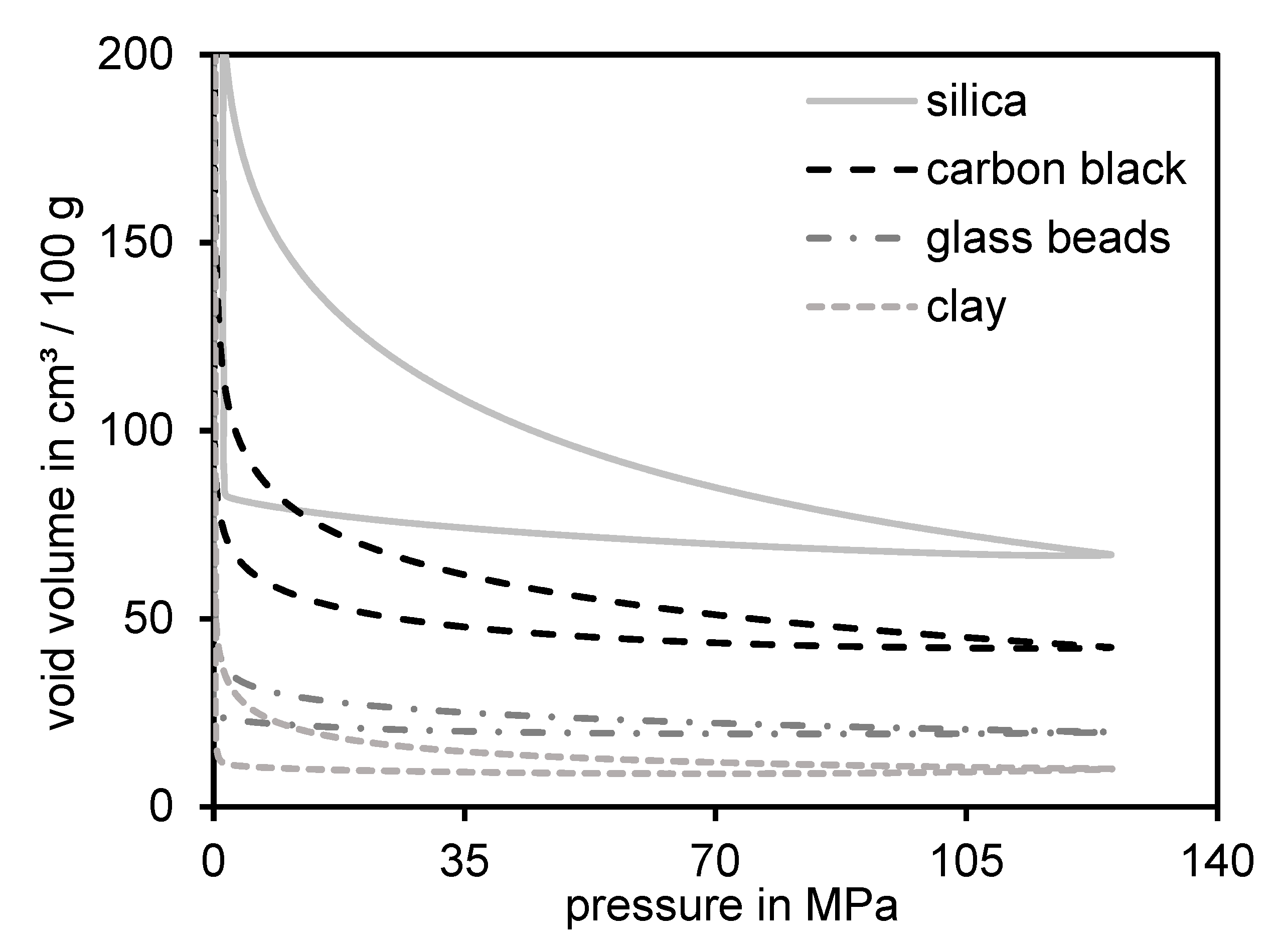
3.4. Differences between the Morphology of Carbon Black and Silica
3.5. Residual Structure of Different Materials
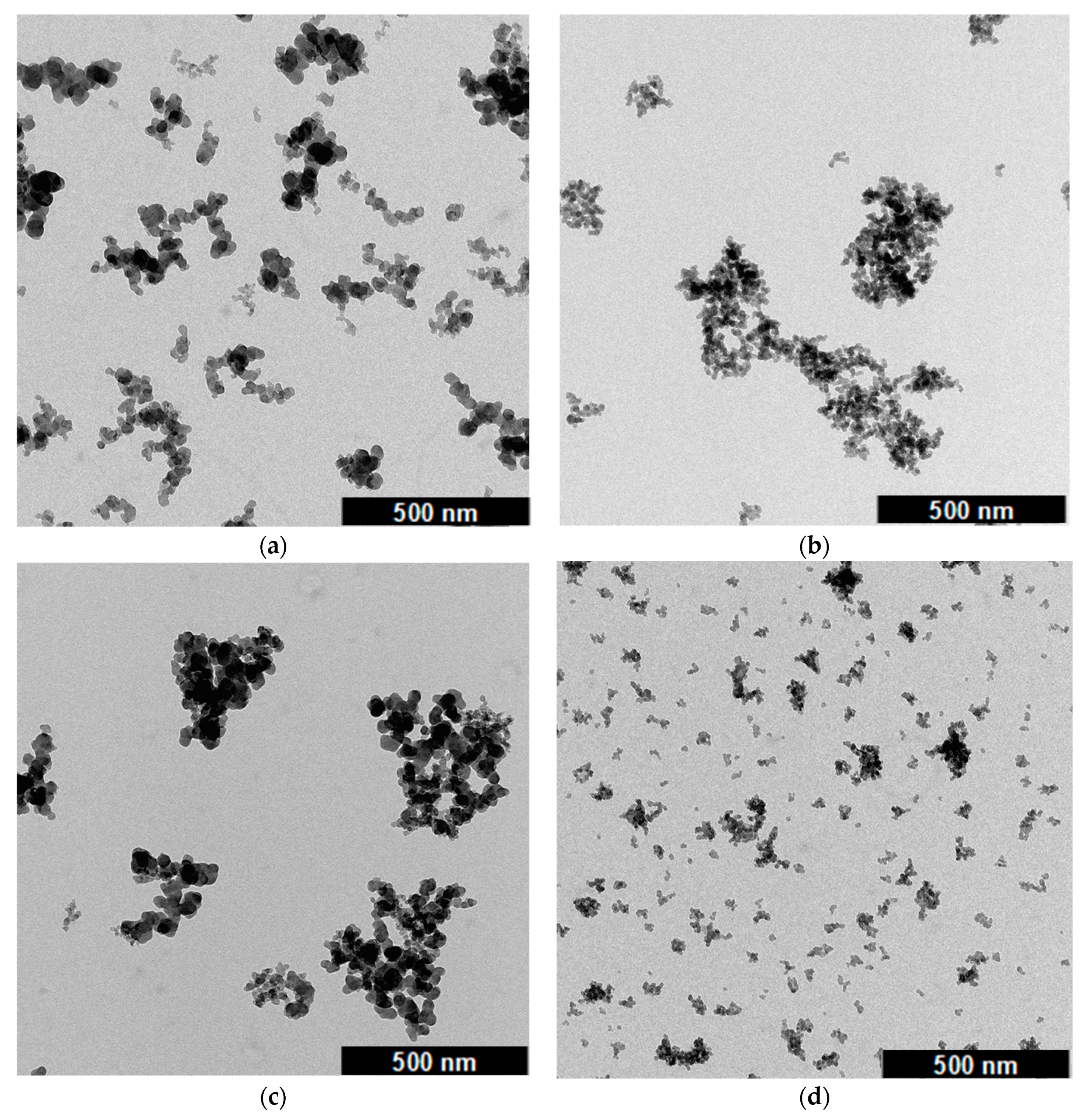
3.6. Structural Differences by Means of Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
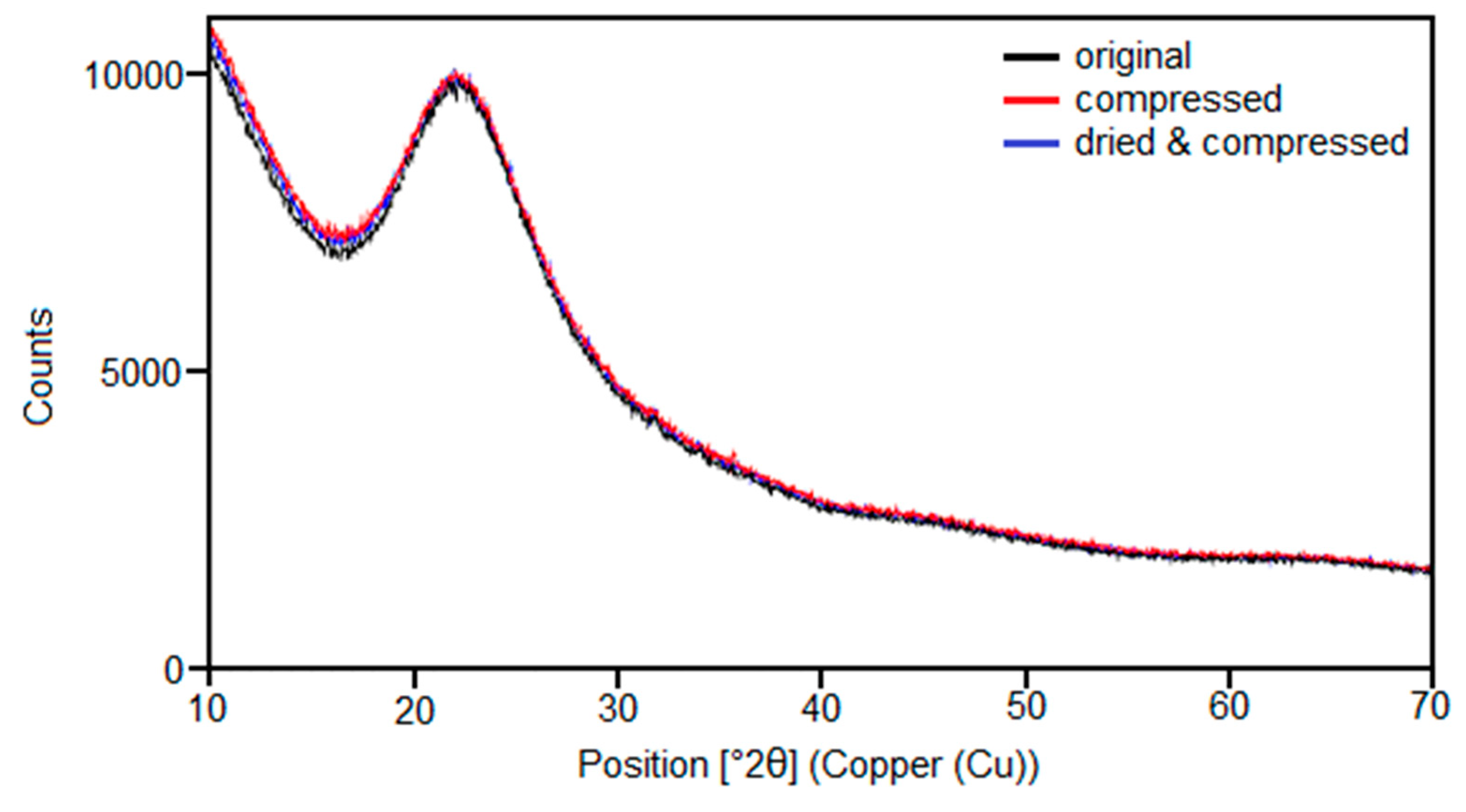
3.7. Structural Changes Examined by X-ray Diffraction Measurements
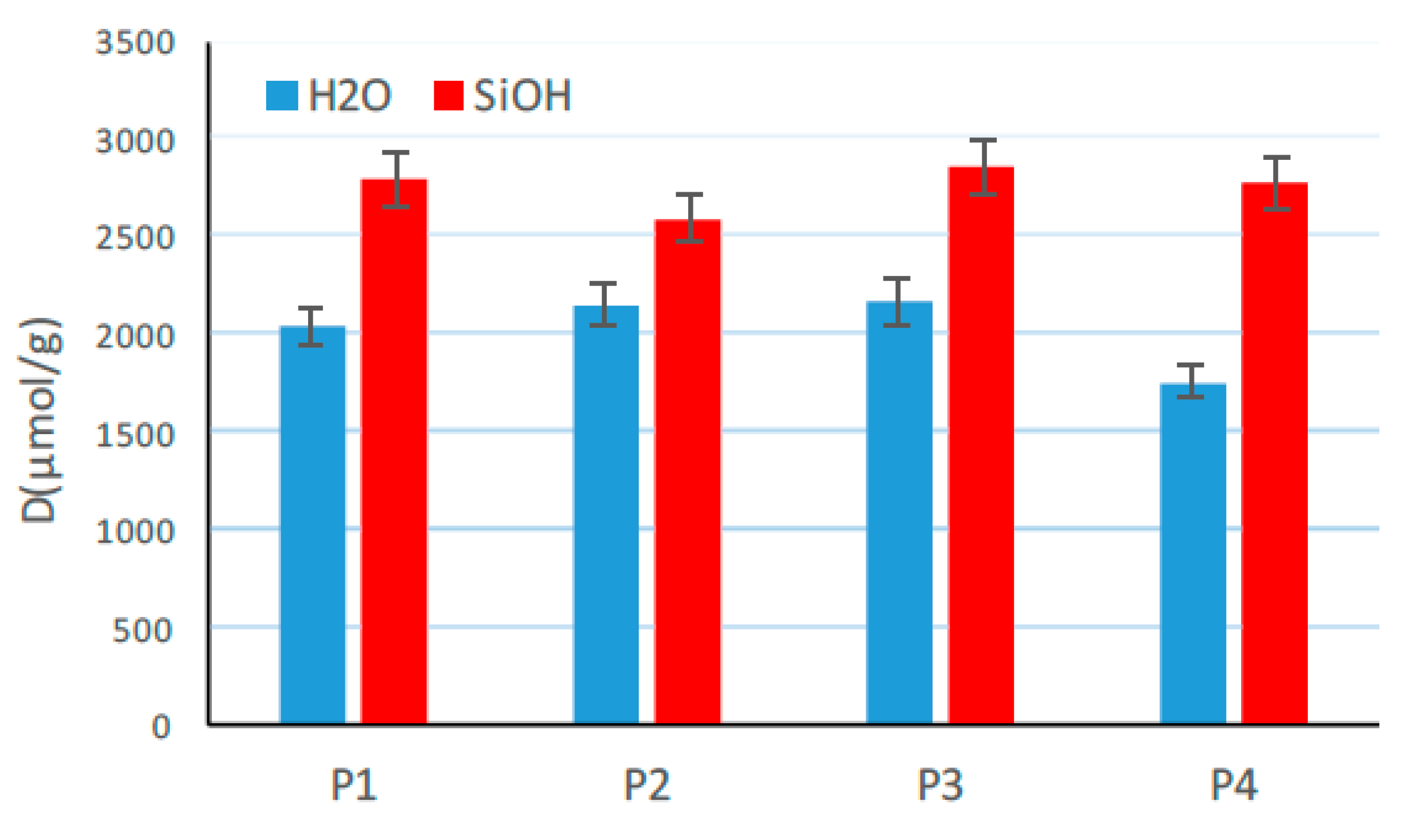
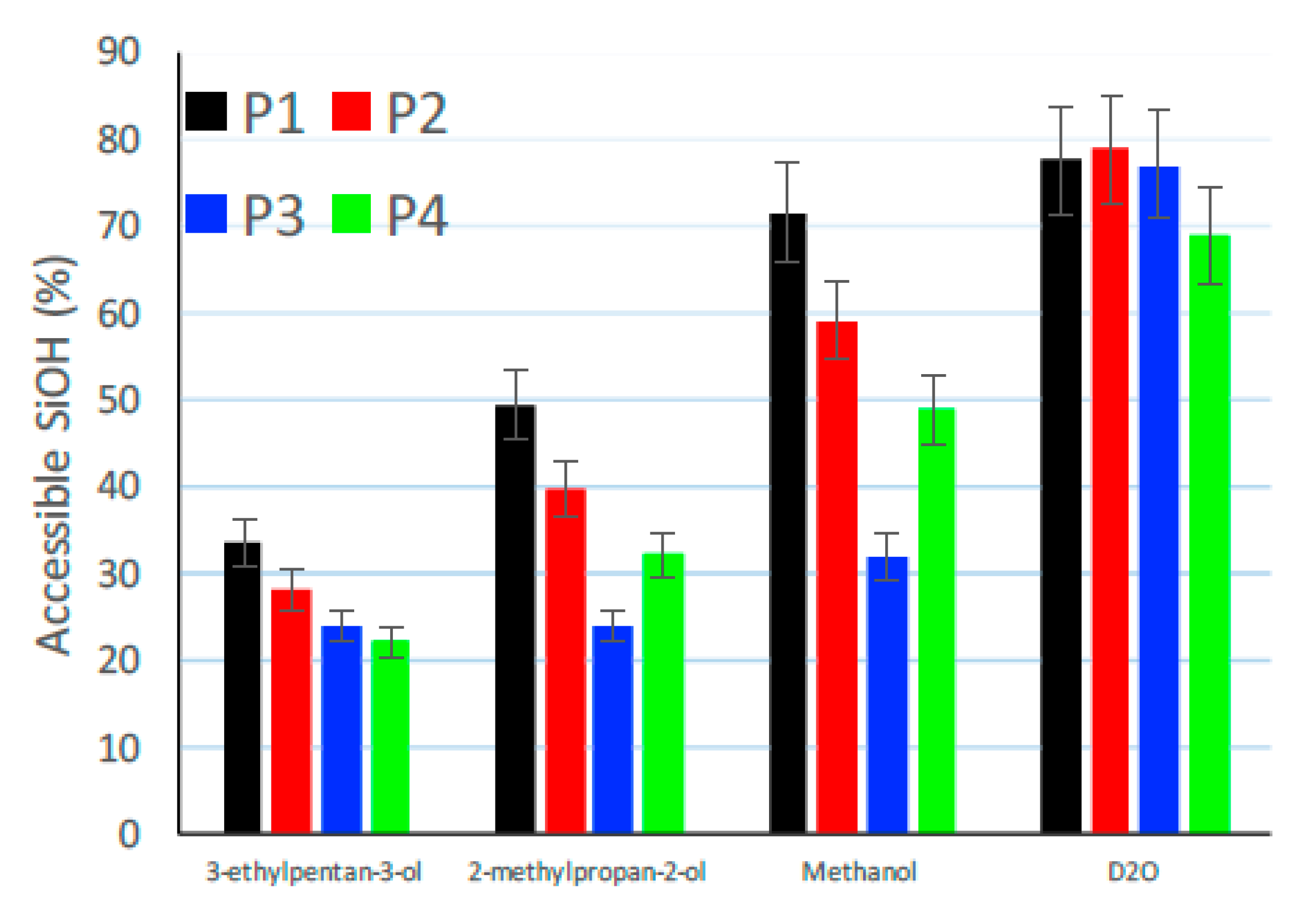
3.8. Changes in Surface Chemistry Examined by FTIR Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rauline, R. Compagnie Generale des Establissements Michelin et Cie, Rubber compound and tires based on such a compound. EP 0501227 B1, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Blume, A.; Uhrlandt, S. Development of HD Silicas for Tires. In Proceedings of the Processes, Properties, Performance, ACS-Meetings, Dallas, TX, USA, 4–6 April 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Medalia, A.I. Microscopic estimation of carbon black dispersion. Rubber Age 1965, 97, 82–93. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D3053:2015. Standard Terminology Relating to Carbon Black; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Wehmeier, A. Determination of the Macro-Dispersion of Advanced Fillers in Rubber Compounds. In Proceedings of the Evonik Industries Customer Seminar, Wesseling, Germany, 1–4 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, B. Rubber Compounding—Chemistry and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grunert, F.; Wehmeier, A.; Blume, A. Prediction of In-Rubber Dispersibility of Silica by Analytical Methods. Presented at the 12th Fall-Rubber-Colloquium, Hannover, Germany, 22–24 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Luginsland, H.-D. A Review on the Chemistry and the Reinforcement of the Silica-Silane Filler System for Rubber Applications; Shaker Verlag: Cologne, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Grunert, F. Analytical Method Development to Predict the in-Rubber Dispersibility of Silica; University of Twente: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Zhong, J.; Guan, W.; Tian, R.; Lu, C.; Ding, C. Three-dimensional direct visualization of silica dispersion in polymer-based composites. Analyst 2018, 143, 2090–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siot, A.; Longuet, C.; Léger, R.; Otazaghine, B.; Ienny, P.; Caro-Bretelle, A.S.; Azéma, N. Correlation between process and silica dispersion/distribution into composite: Impact on mechanical properties and Weibull statistical analysis. Polym. Test. 2018, 70, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savetlana, S.; Sukmana, I.; Saputra, F.A. The effect of carbon black loading and structure on tensile property of natural rubber composite. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Medan, Indonesia, 7–10 November 2016; Volume 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, T. Structure Factors of Dispersible Units of Carbon Black Filler in Rubbers. Langmuir 2015, 21, 11409–11413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spahr, M.E.; Rothon, R. Fillers for Polymer Applications; Carbon Black as a Polymer Filler; Part of the Polymers and Polymeric Composites: A Reference Series Book Series (POPOC); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 261–291. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D6556:2016. Standard Test Method for Carbon Black—Total and External Surface Area by Nitrogen Adsorption; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- ASTM D2414:2016. Tandard Test Method for Carbon Black—Oil Absorption Number (OAN); ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- ASTM D3493:2016. Standard Test Method for Carbon Black—Oil Absorption Number of Compressed Sample (COAN); ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- Wehmeier, A. Entwicklung Eines Verfahrens zur Charakterisierung der Füllstoffdispersion in Gummimischungen Mittels Einer Oberflächentopographie; Fachhochschule Münster: Münster, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Limper, A. Mixing of Rubber Compounds; Carl Hanser Verlag: Munich, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Blume, A. Analytical Properties of Silica a Key for Understanding Silica Reinforcement. Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 2000, 53, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Blume, A.; Uhrlandt, S. Development of HD Silicas for tires—Processes, Properties, Performance. Rubber World 2002, 226, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Malashevich, A.; Ismail-Beigi, S.; Altman, E.I. Directing the Structure of Two-Dimensional Silica and Silicates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 26770–26781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Dong, X.; Li, N.; Ren, J. Novel Two-Dimensional Silicon Dioxide with in-Plane Negative Poisson’s Ratio. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 19246:2016. Rubber Compounding Ingredients—Silica—Oil Absorption of Precipitated Silica; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- ASTM D7854:2016. Standard Test Method for Carbon Black-Void Volume at Mean Pressure; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- ISO 9277:2010. Determination of the Specific Surface Area of Solids by Gas Adsorption-BET Method; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- ISO 5794:2010. Rubber Compounding Ingredients-Silica, Precipitated, Hydrated—Part 1: Non-Rubber Tests; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Voet, A.; Morawski, J.C.; Donnet, J.B. Reinforcement of Elastomers by Silica. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1977, 50, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 787-2:1981. General Methods of Test for Pigments and Extenders—Part 2: Determination of Matter Volatile at 105 Degrees C; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 787-9:1981. General Methods of Test for Pigments and Extenders—Part 9: Determination of pH Value of an Aqueous Suspension; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1981.
- Hirtt, P.; Leiner, Y. HITEC Luxembourg S.A. U.S. Patent 8464592B2, 18 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Iler, R.K. The Chemistry of Silica; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Blume, A.; Grunert, F.; Wehmeier, A.; Dierkes, W.K. Void Volume Measurement—An Alternative Approach to Determine the Initial Structure of Silica. Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 2018, 71, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- el Roz, M. Infrared Characterisation of Silica Samples (I); Laboratoire Catalyse et Spectrochimie—ENSICAEN: Caen, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Internal Information. Evonik Resource Efficiency GmbH.
- ASTM D2663-14. Standard Test Method for Carbon Black—Dispersion in Rubber, Test Method C—Microroughness Measurement with Profilometer; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Payne, A.R. Effect of dispersion on dynamic properties of filler-loaded rubbers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1966, 39, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermeier, W.; Fröhlich, J. Moderne Füllstoffsysteme in der Gummiindustrie. Presented at the Lehrstuhlseminar AG Prof. Göritz, Regensburg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Luginsland, H.D.; Frohlich, J.; Wehmeier, A. Influence of Different Silanes on the Reinforcement of Silica-Filled Rubber Compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2002, 75, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, P.; Maier, M.; Reisinger, M.; Hannebauer, B.; Weinand, R. Physical boundaries within aggregates—Differences between amorphous, para-crystalline, and crystalline Structures. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2015, 50, 846–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3849:2007. Standard Test Method for Carbon Black-Morphological Characterization of Carbon Black Using Electron Microscopy; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Blume, A.; El-Roz, M.; Thibault-Starzyk, F. Infrared Study of the Silica/Silane Reaction; KGK Kautschuk Gummi Kunststoffe: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 10, pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- El-Roz, M.; Thibault-Starzyk, F.; Blume, A. Infrared Study of the Silica/Silane Reaction, 2nd ed.; KGK Kautschuk Gummi Kunststoffe: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 5, pp. 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Blume, A.; Gallas, J.-P.; Janik, M.; Thibault-Starzyk, F.; Vimont, A. Operando Infrared Study of the Reaction of Triethoxypropylsilane with Silica; KGK Kautschuk Gummi Kunststoffe: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 7–8, pp. 359–362. [Google Scholar]
- Göritz, D.; Schneider, G. Reinforcement with precipitated silica. Presented at the 6th Fall Rubber Colloquium, Hannover, Germany, 10–13 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
| Silica | CTAB [27] in m2/g | DOA [24] in mL/100g | BET [26] in m2/g | Moisture Content in % [29] | pH-Value [30] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 122GR195 | 122 | 195 | 120 | 3.8 | 7.1 |
| 104GR175 | 104 | 175 | 107 | 5.8 | 6.7 |
| 190GR197 | 190 | 197 | 208 | 5.7 | 6.7 |
| 157GR186 | 157 | 186 | 152 | 6.2 | 6.7 |
| 110GR205 | 110 | 205 | 120 | 5.9 | 6.8 |
| 171GR196 | 171 | 196 | 199 | 4.8 | 6.6 |
| 175GR203 | 175 | 203 | 198 | 5.2 | 6.8 |
| 173GR196 | 173 | 196 | 190 | 4.6 | 6.9 |
| 158GR209 | 158 | 209 | 153 | 6.0 | 7.0 |
| 215GR210 | 215 | 210 | 215 | 4.7 | 6.6 |
| 197GR199 | 197 | 199 | 213 | 8.1 | 6.6 |
| 161GR193 | 161 | 193 | 163 | 6.6 | 6.6 |
| 159GR204 | 159 | 204 | 163 | 6.1 | 6.5 |
| 165GR181 | 165 | 181 | 185 | 5.2 | 6.1 |
| 127P206 | 127 | 206 | 124 | 5.1 | 6.8 |
| 173P223 | 173 | 223 | 203 | 4.9 | 6.6 |
| 176P238 | 176 | 238 | 193 | 5.6 | 6.8 |
| 195P228 | 195 | 228 | 225 | 5.8 | 6.5 |
| 162P225 | 162 | 225 | 165 | 5.5 | 6.6 |
| 155P213 | 155 | 213 | 162 | 6.5 | 6.6 |
| 165P196 | 165 | 196 | 181 | 4.6 | 5.8 |
| 157MP207 | 157 | 207 | 150 | 6.6 | 6.6 |
| 173MP217 | 173 | 217 | 188 | 5.2 | 7.0 |
| 176MP223 | 176 | 223 | 189 | 5.2 | 6.3 |
| 114MP199 | 114 | 199 | 109 | 6.0 | 7.1 |
| 1st Stage | ||
| Material | Type | phr |
| Buna VSL 4526-2 | oil-extended (26.25 phr) S-SBR | 96.25 |
| Buna CB 24 | Nd-BR; cis1,4 > 96% | 30.00 |
| Silica | variable | 80.00 |
| Si 266 | silane | adjusted to CTAB |
| N330 | carbon black | 5.00 |
| ZnO RS RAL 844 C | zinc oxide | 2.00 |
| Edenor ST1 GS | stearic acid | 2.00 |
| Vivatec 500 | TDAE * oil | 8.75 |
| Vulkanox HS/LG | TMQ ** protector | 1.50 |
| Vulkanox 4020/LG | 6PPD *** anti-aging | 2.00 |
| Protektor G 3108 | Wax | 2.00 |
| 2nd stage | ||
| batch 1st stage | ||
| Rhenogran DPG-80 | 80% DPG **** accelerator | 2.50 |
| 3rd stage | ||
| batch 2nd stage | ||
| Richon TBZTD OP | TBzTD ***** accelerator | 0.20 |
| Vulkacit CZ/EG-C | CBS ****** accelerator | 1.60 |
| Sulfur 80/90 | soluble sulfur | 2.00 |
| Stage and Time | Action |
|---|---|
| 1st stage min:sec | fill factor 0.73; 70 rpm; chamber temperature: 70 °C measured temperature: 130–150 °C |
| 00:00–00:15 | polymer |
| 00:15–00:45 | 1/3 silica; 1/3 silane |
| 00:45–01:15 | 1/3 silica; 1/3 silane |
| 01:15–02:15 | (a) oil adsorbed on CB in a PE pouch |
| (b) 1/3 silica; silane | |
| (c) protector | |
| 02:15–04:15 | ZnO, stearic acid; Vulkanox HS; Vulkanox 4020; |
| 04:15 | dump and control temperature |
| 45 s on open mill (4 mm nip), sheet out | |
| weigh compound for the 2nd step; storage for 24 h/RT | |
| 2nd stage min:sec | fill factor 0.70; 70 rpm; chamber temperature: 90 °C measured temp.: 130–150 °C |
| 00:00–01:00 | plasticize 1st stage |
| 01:00–03:00 | DPG; mix; |
| 03:00 | dump and control temperature |
| 45 section on open mill (4 mm nip), sheet out | |
| weigh compound for the 3rd step; storage for 4–24 h/RT | |
| 3rd stage min:sec | fill factor 0.68; 55 rpm, chamber temperature: 50 °C measured temperature: > 110 °C |
| 00:00–02:00 | batch stage 2; accelerators; sulfur |
| 02:00 | dump batch; process on open mill 20 sec. with 3–4 mm nip |
| cut 3× left, 3× right with 3 mm nip | |
| roll up and pass through a 3 mm nip ×3 | |
| sheet off; store for a minimum of 12 h before vulcanization |
| Carbon Black Grade | STSA [15] in m2/g | OAN [16] in cm3/100 g | COAN [17] in cm3/100 g | Residual VV [25] in cm3/100 g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N326 | 77 | 72 | 69 | 70 ± 0.2 |
| N330 | 76 | 102 | 88 | 93 ± 0.3 |
| N339 | 88 | 120 | 99 | 107 ± 0.3 |
| Parameter | Silica 158GR190 | Silica 158GR190 at 125 MPa | CB N330 | CB N330 at 125 MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Evaluated Primary Particles | 2013 | 2017 | 2002 | 2002 |
| Arithmetical Average in nm | 12.6 | 11.0 | 24.6 | 25.8 |
| Numbers of Structures | 1095 | 1062 | 1034 | 1044 |
| Area in nm2 | 4282 | 2030 | 17625 | 20819 |
| ECD in nm | 55 | 42 | 118 | 133 |
| Void Area in % | 40 | 45 | 37 | 38 |
| Branching Factor | 8.5 | 5.6 | 12.0 | 12.8 |
| Probe Molecules | Molar Mass in g/mol | Molecular Size in nm2 |
|---|---|---|
| 3-ethylpentan-3-ol | 116.2 | 0.41 |
| 2-methylpropan-2-ol | 74.1 | 0.32 |
| Methanol | 32.0 | 0.18 |
| D2O | 20.0 | 0.11 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grunert, F.; Wehmeier, A.; Blume, A. New Insights into the Morphology of Silica and Carbon Black Based on Their Different Dispersion Behavior. Polymers 2020, 12, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030567
Grunert F, Wehmeier A, Blume A. New Insights into the Morphology of Silica and Carbon Black Based on Their Different Dispersion Behavior. Polymers. 2020; 12(3):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030567
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrunert, Fabian, André Wehmeier, and Anke Blume. 2020. "New Insights into the Morphology of Silica and Carbon Black Based on Their Different Dispersion Behavior" Polymers 12, no. 3: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030567
APA StyleGrunert, F., Wehmeier, A., & Blume, A. (2020). New Insights into the Morphology of Silica and Carbon Black Based on Their Different Dispersion Behavior. Polymers, 12(3), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030567





