Conformation Variation and Tunable Protein Adsorption through Combination of Poly(acrylic acid) and Antifouling Poly(N-(2-hydroxyethyl) acrylamide) Diblock on a Particle Surface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of PS@VBDC Core Particles (PSV Core)
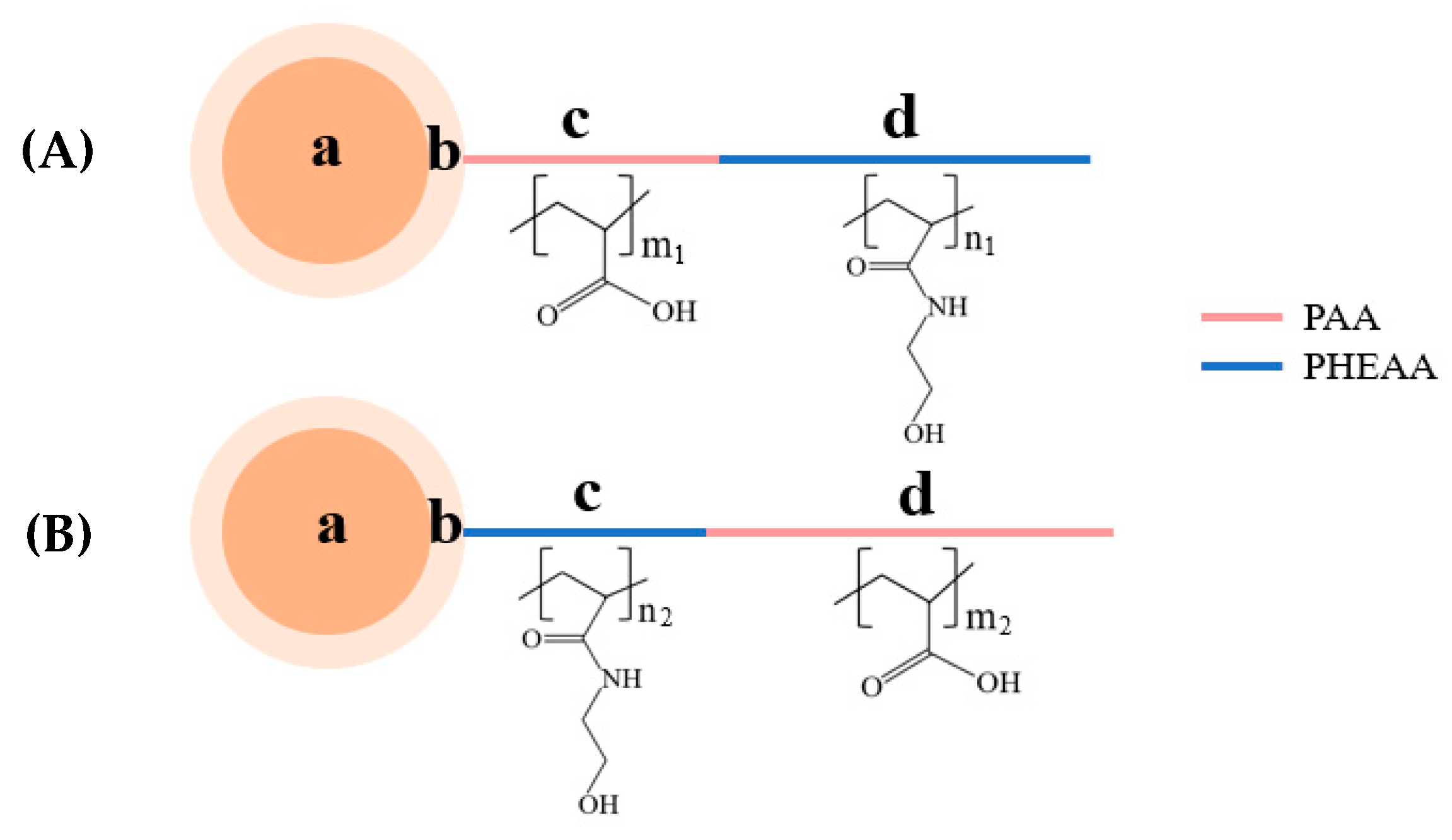
2.3. Synthesis of Diblock Polymer Brushes (PSV@PAA-b-PHEAA, PSV@PHEAA-b-PAA)
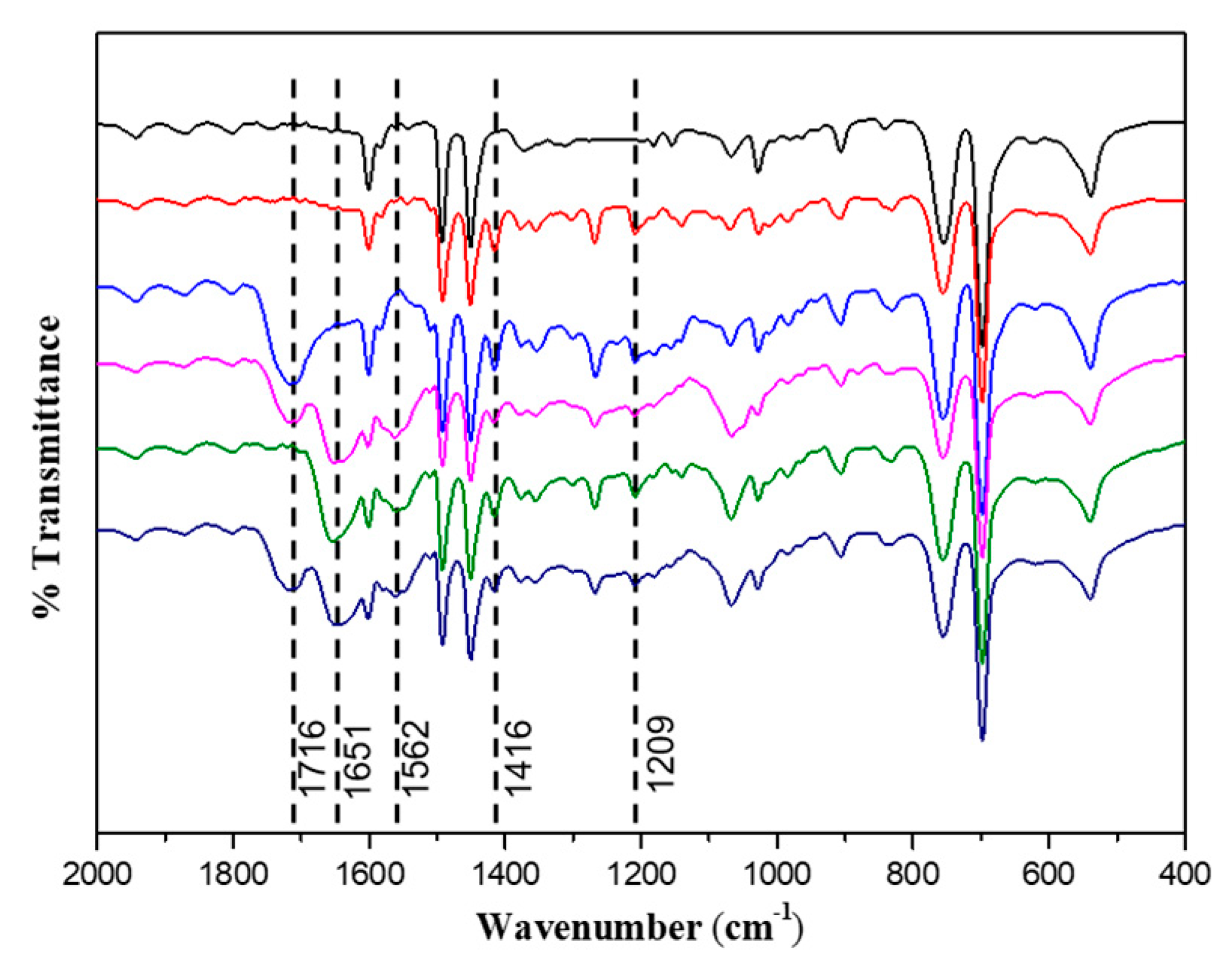
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
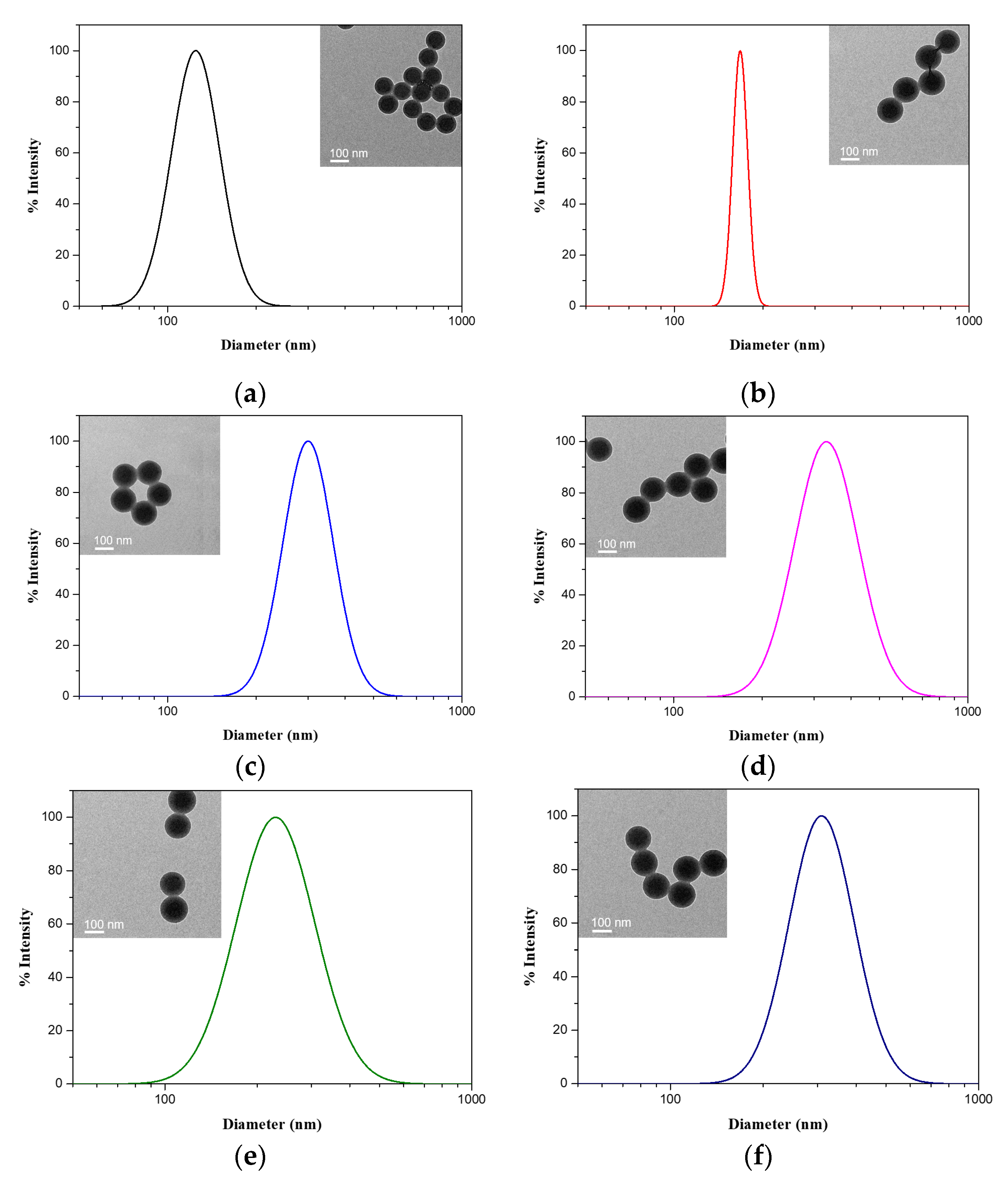
3.1. Synthesis of Diblock Polymer Brushes
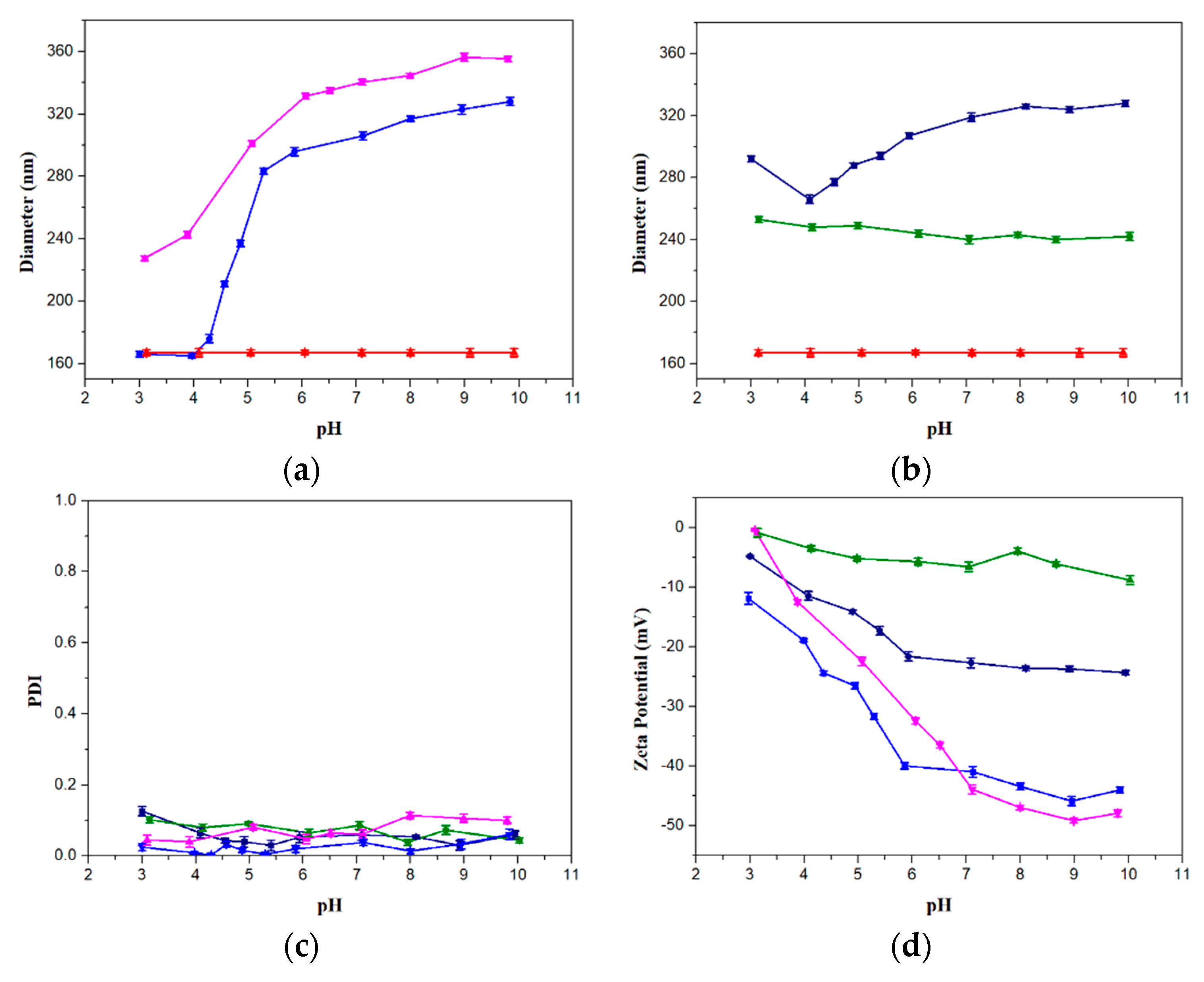
3.2. Conformation Variation of Polymer Brushes
3.3. Interaction Between Polymer Brushes and Protein
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Brigger, I.; Dubernet, C.; Couvreur, P. Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, P.; Dai, Y.; Ma, P.; Li, X.; Cheng, Z.; Hou, Z.; Kang, X.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Multifunctional Up-Converting Nanocomposites with Smart Polymer Brushes Gated Mesopores for Cell Imaging and Thermo/pH Dual-Responsive Drug Controlled Release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4067–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, J.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Griffith, M.; Liu, W. Cationic polymer brush grafted-nanodiamond via atom transfer radical polymerization for enhanced gene delivery and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7755–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.M.; Thaxton, C.S.; Mirkin, C.A. Nanoparticle-based bio-bar codes for the ultrasensitive detection of proteins. Science 2003, 301, 1884–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, T.J.; Schadler, L.S.; Siegel, R.W.; Bizios, R. Mechanisms of enhanced osteoblast adhesion on nanophase alumina involve vitronectin. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, P.; Farrar, D.; Perry, C.C. Surface tailoring for controlled protein adsorption: Effect of topography at the nanometer scale and chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3939–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Engel, Y.; Yan, Y.; Chen, K.; Moyano, D.F.; Dubin, P.; Rotello, V.M. Enhanced Electrostatic Discrimination of Proteins on Nanoparticle-Coated Surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5230–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeslik, C.; Jansen, R.; Ballauff, M.; Wittemann, A.; Royer, C.A.; Gratton, E.; Hazlett, T. Mechanism of protein binding to spherical polyelectrolyte brushes studied in situ using two-photon excitation fluorescence fluctuation spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2004, 69, 021401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.L.; Welsch, N.; Schneider, C.; Ballauff, M. Adsorption of RNase A on cationic polyelectrolyte brushes: A study by isothermal titration calorimetry. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3936–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, Y.; Yue, Z.; Liu, W.; Cao, Z. Ultrastable core–shell structured nanoparticles directly made from zwitterionic polymers. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15030–15033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Ma, L.; Liu, C. Diblock Polymer Brush (PHEAA-b-PFMA): Microphase Separation Behavior and Anti-Protein Adsorption Performance. Langmuir 2018, 34, 11101–11109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilge, I.; Steuber, M.; Tranchida, D.; Sperotto, E.; Schönherr, H. Tailored (Bio) interfaces via surface initiated polymerization: Control of grafting density and new responsive diblock copolymer brushes. Macromol. Symp. 2013, 328, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Qin, X.; Guo, X. Conformation Study of Dual Stimuli-Responsive Core-Shell Diblock Polymer Brushes. Polymers 2018, 10, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, J.; Niu, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F. Surface-induced reversible addition-fragmentation chain-transfer (RAFT) polymerization on magnetic nanoparticles to resist nonspecific adsorption of proteins. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeslik, C.; Jackler, G.; Steitz, R.; von Grünberg, H.H. Protein binding to like-charged polyelectrolyte brushes by counterion evaporation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 13395–13402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Tang, J.; Xu, P.; Johnson, P.A.; Radosz, M.; Van Kirk, E.A.; Murdoch, W.J. Multifunctioning pH-responsive nanoparticles from hierarchical self-assembly of polymer brush for cancer drug delivery. AIChE J. 2008, 54, 2979–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Pattanayek, S.K.; Pandey, L.M. Effect of Functional Groups of Self-Assembled Monolayers on Protein Adsorption and Initial Cell Adhesion. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 3224–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, Y.; Iwata, H. Effects of surface functional groups on protein adsorption and subsequent cell adhesion using self-assembled monolayers. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 4079–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Waibhaw, G.; Pandey, L.M. Conformational and organizational insights into serum proteins during competitive adsorption on self-assembled monolayers. Langmuir 2018, 34, 8178–8194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, M.; Verdes, D.; Seeger, S. Understanding protein adsorption phenomena at solid surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 162, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Huang, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Cheng, W.; He, J.; Tian, H.; Huang, Y. Preparation of pH-responsive mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for intracellular controlled release of an anticancer drug. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Chen, K.; Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Guo, X. Effect of block sequence on responsive behavior of core-shell diblock polymer brushes. Mater. Lett. 2018, 223, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ballauff, M. Spherical polyelectrolyte brushes: Comparison between annealed and quenched brushes. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2001, 64, 051406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, K.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Guo, X. Protein immobilization and separation using anionic/cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brushes based on charge anisotropy. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 11276–11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Patel, K.; Aichinger, L.M.; Liu, Z.; Hu, R.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, G.; Chang, Y. Antifouling and biodegradable poly (N-hydroxyethyl acrylamide)(polyHEAA)-based nanogels. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 19991–20000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Chen, K.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Guo, X. Antifouling performance of nano-sized spherical poly (N-hydroxyethyl acrylamide) brush. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 155, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.J.; Cai, T.; Neoh, K.G.; Kang, E.T.; Teo, S.L.M.; Rittschof, D. Barnacle Cement as Surface Anchor for “Clicking” of Antifouling and Antimicrobial Polymer Brushes on Stainless Steel. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Ni, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Q. Excellent hydrophilic and anti-bacterial fouling PVDF membrane based on ag nanoparticle self-assembled PCBMA polymer brush. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 35, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Pompe, T.; Amin, I.; Luxenhofer, R.; Werner, C.; Jordan, R. Tailored Poly(2-oxazoline) Polymer Brushes to Control Protein Adsorption and Cell Adhesion. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zheng, J. Synthesis and characterization of poly (N-hydroxyethylacrylamide) for long-term antifouling ability. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 4071–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Chang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, J. Probing the structural dependence of carbon space lengths of poly (N-hydroxyalkyl acrylamide)-based brushes on antifouling performance. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 2982–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Gong, X.; Li, L.; Zheng, J. Probing structure–antifouling activity relationships of polyacrylamides and polyacrylates. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4714–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigal, G.B.; Mrksich, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Effect of surface wettability on the adsorption of proteins and detergents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 3464–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, Q.; Patel, K.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, J. Synthesis and characterization of pH-sensitive poly (N-2-hydroxyethyl acrylamide)–acrylic acid (poly (HEAA/AA)) nanogels with antifouling protection for controlled release. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 7848–7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, T. Iniferter concept and living radical polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part. A Polym. Chem. 2000, 38, 2121–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, T.; Yamashita, K.; Tsuda, K. Synthesis, reactivity, and role of 4-vinylbenzyl N, N-diethyldithiocarbamate as a monomer-iniferter in radical polymerization. Macromolecules 1986, 19, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Qin, L.; Jia, M.; He, X.; Li, W. Novel surface-modified molecularly imprinted membrane prepared with iniferter for permselective separation of lysozyme. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 363, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Huh, K.M.; Shi, S.; Kuroda, S. Synthesis, characterization, and temperature-dependent colloidal stability of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)-grafted polystyrene/poly (styrene-co-4-vinylbenzyl N, N-diethyldithiocarbamate) hairy particles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irigoyen, J.; Arekalyan, V.B.; Navoyan, Z.; Iturri, J.; Moya, S.E.; Donath, E. Spherical polyelectrolyte brushes constant zeta potential with varying ionic strength: An electrophoretic study using a hairy layer approach. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 11609–11617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
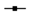 ) and BSA-free system (
) and BSA-free system (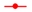 ) and (c) diameters and (d) turbidity of the mixture system of PSV@PHEAA with the BSA (
) and (c) diameters and (d) turbidity of the mixture system of PSV@PHEAA with the BSA ( ) and BSA-free system (
) and BSA-free system (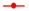 ) from pH 2 to pH 10.
) from pH 2 to pH 10.
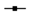 ) and BSA-free system (
) and BSA-free system ( ) and (c) diameters and (d) turbidity of the mixture system of PSV@PHEAA with the BSA (
) and (c) diameters and (d) turbidity of the mixture system of PSV@PHEAA with the BSA ( ) and BSA-free system (
) and BSA-free system ( ) from pH 2 to pH 10.
) from pH 2 to pH 10.
 ) and BSA-free system (
) and BSA-free system ( ) and (c) diameters and (d) turbidity of the mixture system of PSV@PHEAA-b-PAA with the BSA (
) and (c) diameters and (d) turbidity of the mixture system of PSV@PHEAA-b-PAA with the BSA ( ) and BSA-free system (
) and BSA-free system (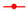 ) from pH 2 to pH 10.
) from pH 2 to pH 10.
 ) and BSA-free system (
) and BSA-free system ( ) and (c) diameters and (d) turbidity of the mixture system of PSV@PHEAA-b-PAA with the BSA (
) and (c) diameters and (d) turbidity of the mixture system of PSV@PHEAA-b-PAA with the BSA ( ) and BSA-free system (
) and BSA-free system ( ) from pH 2 to pH 10.
) from pH 2 to pH 10.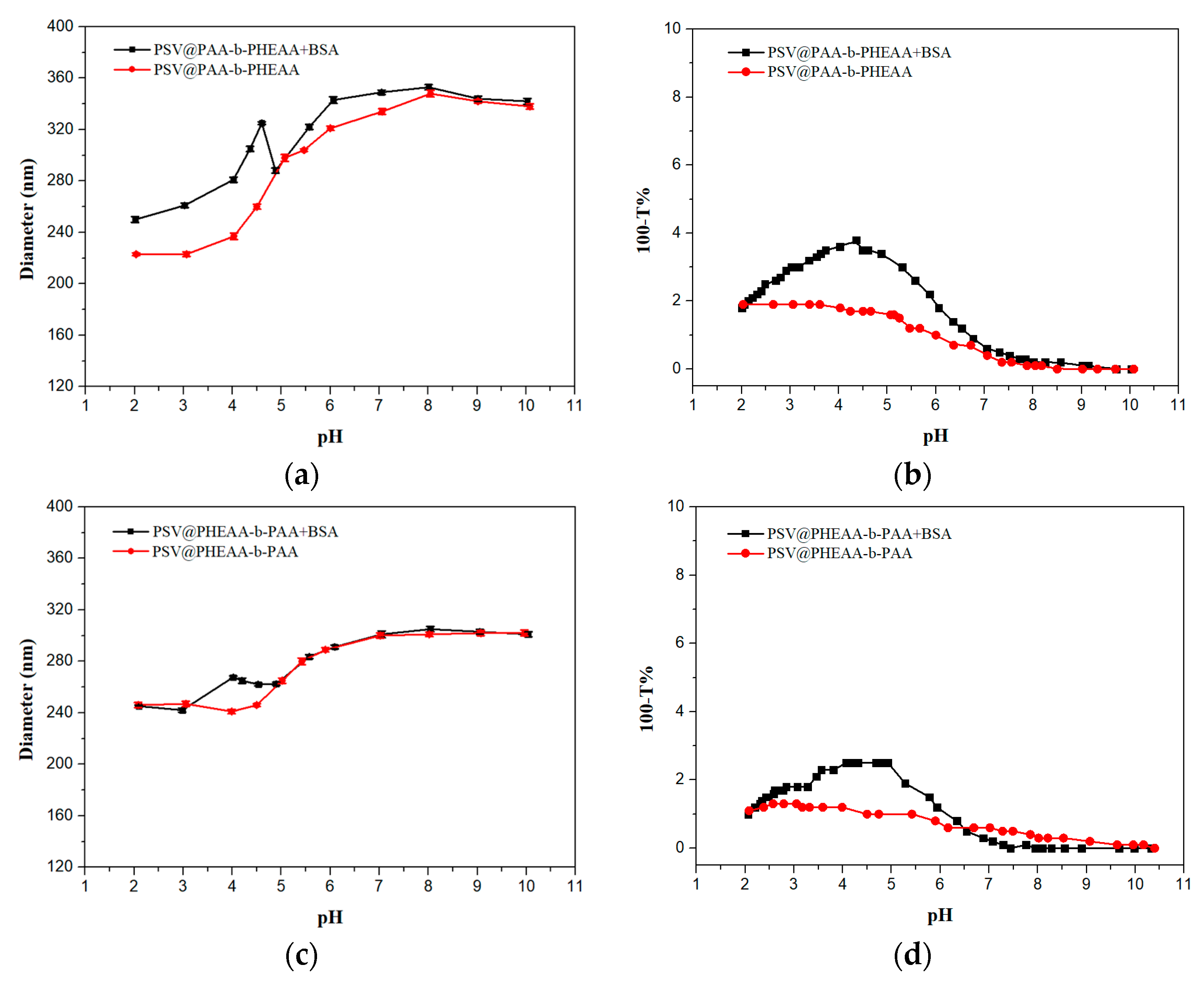
| Samples | C% | N% | S% | S/N a | S/N b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS | 90.88 | ||||
| PSV Core | 87.40 | 0.70 | 3.18 | 4.58 | 4.57 |
| PSV@PAA | 84.59 | 0.60 | 2.66 | 4.47 | 4.57 |
| PSV@PAA-b-PHEAA | 78.48 | 2.08 | 1.94 | 0.93 | – |
| PSV@PHEAA | 80.98 | 2.07 | 2.46 | 1.19 | – |
| PSV@PHEAA-b-PAA | 79.12 | 1.85 | 1.99 | 1.08 | – |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Chen, K.; Hua, C.; Guo, X. Conformation Variation and Tunable Protein Adsorption through Combination of Poly(acrylic acid) and Antifouling Poly(N-(2-hydroxyethyl) acrylamide) Diblock on a Particle Surface. Polymers 2020, 12, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030566
Wang Z, Chen K, Hua C, Guo X. Conformation Variation and Tunable Protein Adsorption through Combination of Poly(acrylic acid) and Antifouling Poly(N-(2-hydroxyethyl) acrylamide) Diblock on a Particle Surface. Polymers. 2020; 12(3):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030566
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zun, Kaimin Chen, Chen Hua, and Xuhong Guo. 2020. "Conformation Variation and Tunable Protein Adsorption through Combination of Poly(acrylic acid) and Antifouling Poly(N-(2-hydroxyethyl) acrylamide) Diblock on a Particle Surface" Polymers 12, no. 3: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030566
APA StyleWang, Z., Chen, K., Hua, C., & Guo, X. (2020). Conformation Variation and Tunable Protein Adsorption through Combination of Poly(acrylic acid) and Antifouling Poly(N-(2-hydroxyethyl) acrylamide) Diblock on a Particle Surface. Polymers, 12(3), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030566






