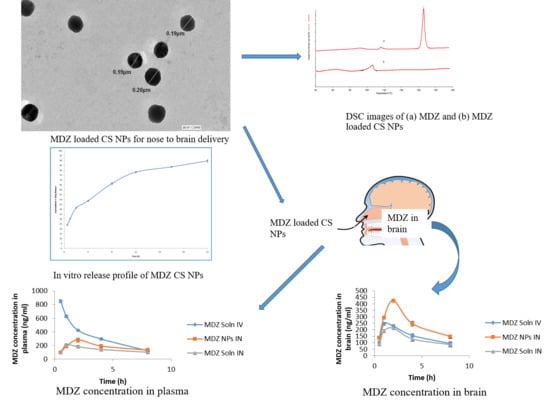
Tailoring Midazolam-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticulate Formulation for Enhanced Brain Delivery via Intranasal Route
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Chitosan Nanoparticles
2.2.2. Physiochemical Characterization of Chitosan Nanoparticles
2.2.3. Entrapment Efficiency (EE) and Loading Capacity (LC) of MDZ-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles
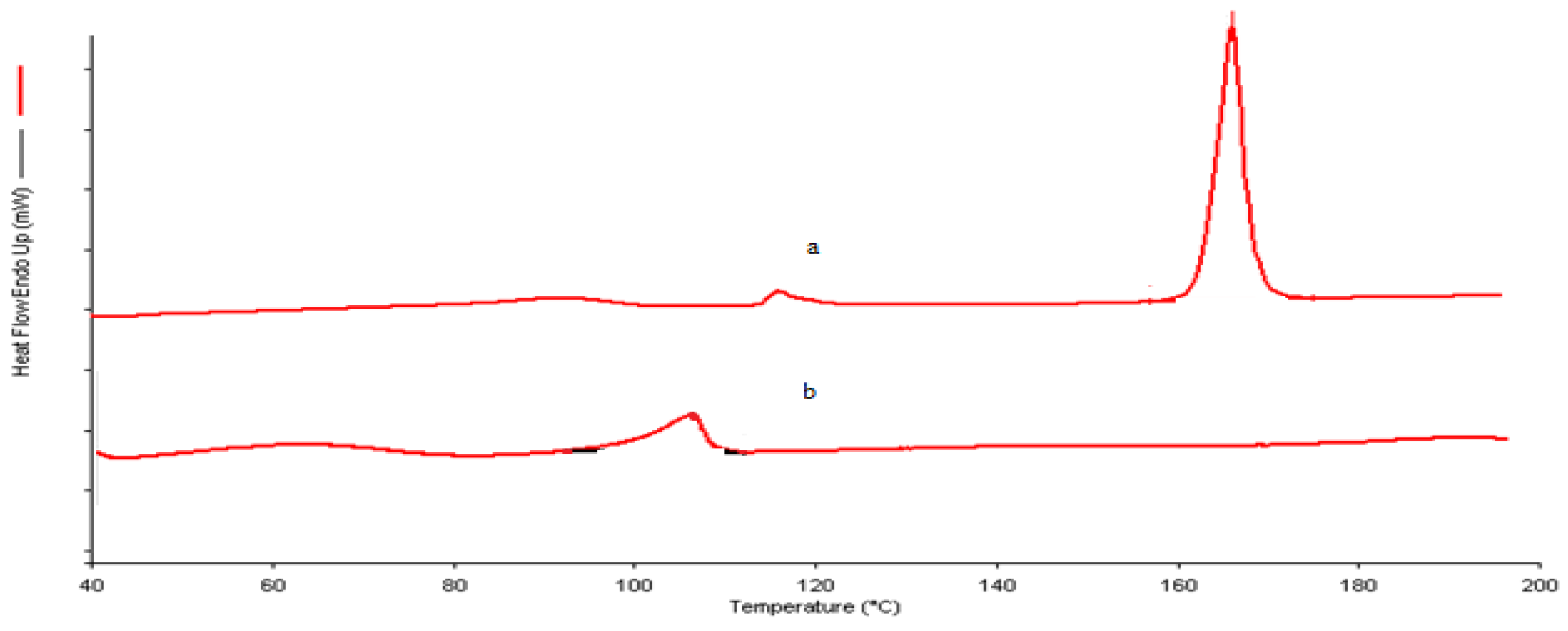
2.2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
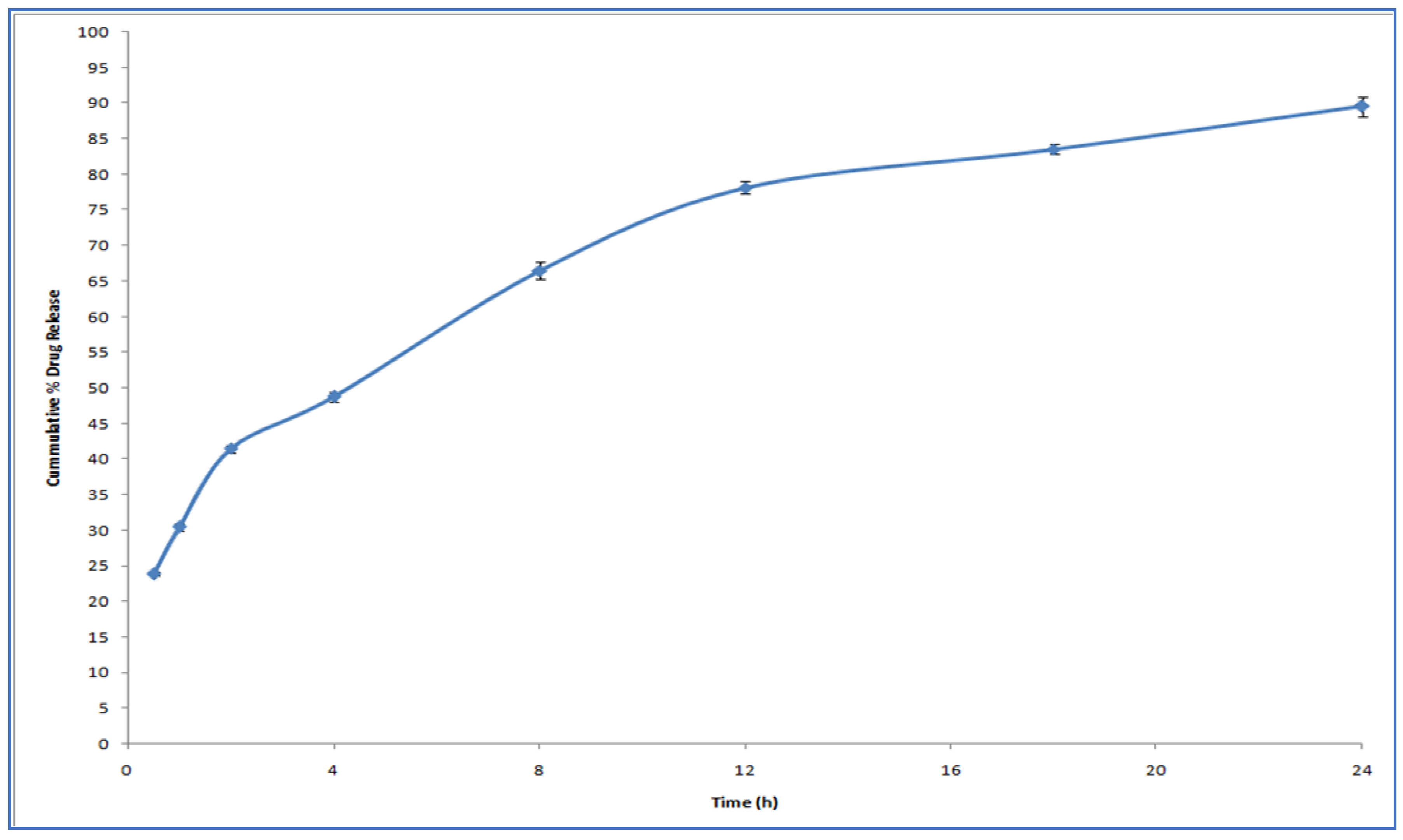
2.3. In Vitro Release Study
2.4. In Vitro Permeation Studies
2.5. In Vivo Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Formulation and Characterization of Chitosan Nanoparticles (CSNPs)
3.2. DSC
3.3. In Vitro Drug Release Study
3.4. In Vitro Permeation Studies
3.5. Study of Pharmacokinetic Parameters and Determination of Drug-Targeting Efficiency (DTE%) and Nose-to-Brain Direct Transport Percentage (DTP%)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brigo, F.; Nardone, R.; Tezzon, F.; Trinka, E. A common reference-based indirect comparison meta-analysis of buccal versus intranasal midazolam for early status epilepticus. CNS Drugs 2015, 29, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieri, L.; Schaffner, R.; Scherschlicht, R.; Polc, P.; Sepinwall, J.; Davidson, A.; Möhler, H.; Cumin, R.; Da Prada, M.; Burkard, W.D.; et al. Pharmacology of midazolam. Arzneimittelforschung 1981, 31, 2180–2201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lévi, S.; le Roux, N.; Eugène, E.; Poncer, J.C. Benzodiazepine ligands rapidly influence GABAA receptor diffusion and clustering at hippocampal inhibitory synapses. Europharmacology 2015, 88, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towne, A.R.; DeLorenzo, R.J. Use of intramuscular midazolam for status epilepticus. Emerg. Med. 1999, 17, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Kumar Sharma, R.; Bhatnagar, A.K.; Nishad, D.; Singh, T.; Gabrani, R.; Sanjeev, S.K.; Javed, A.; Dang, S. Nose to brain delivery of midazolam loaded PLGA nanoparticles: In vitro and in vivo investigations. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudmundsdottir, H.; Sigurjonsdottir, J.F.; Masson, M.; Fjalldal, O.; Stefansson, E.; Loftsson, T. Intranasal administration of midazolam in a cyclodextrin based formulation: Bioavailability and clinical evaluation in humans. Pharmazie 2001, 56, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knoester, P.D.; Jonker, D.M.; Van der Hoeven, R.T.M.; Vermeij, T.A.C.; Edelbroek, P.M.; Brekelmans, G.J.; De Haan, G.J. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam administered as a concentrated intranasal spray. A study in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 53, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Wang, X.U.; Nie, S.; Shin, D.M. Therapeutic nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, A.; Stolnik, S.; Illum, L. Nanoparticles for direct nose-to-brain delivery of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illum, L. Nasal drug delivery—Possibilities, problems and solutions. Control Release 2003, 87, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauland, A.H.; Guggi, D.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Thiolated chitosan microparticles: A vehicle for nasal peptide drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 307, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casettari, L.; Illum, L. Chitosan in nasal delivery systems for therapeutic drugs. Control Release 2014, 190, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassu, G.; Soddu, E.; Cossu, M.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P.; Dalpiaz, A. Particulate formulations based on chitosan for nose-to-brain delivery of drugs. A review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.E.; Gallo, J.M. Targeting anticancer drugs to the brain. I: Enhanced brain delivery of oxantrazole following administration in magnetic cationic microspheres. J. Drug Target. 1993, 1, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Xu, X.; Feng, J.; Liu, M.; Hu, K. Chitosan and chitosan coating nanoparticles for the treatment of brain disease. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 560, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, N.K.; Fazil, M.; Hassan, M.Q.; Haider, M.R.; Gaba, B.; Narang, J.K.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J. Brain delivery of buspirone hydrochloride chitosan nanoparticles for the treatment of general anxiety disorder. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeyung, A.S.; Md, S.; Bhattamisra, S.K.; Madheswaran, T.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Radhakrishnan, A.K. Fabrication, optimization, and evaluation of rotigotine-loaded chitosan nanoparticles for nose-to-brain delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattamisra, S.K.; Shak, A.T.; Xi, L.W.; Safian, N.H.; Choudhury, H.; Lim, W.M.; Shahzad, N.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Alhakamy, M.K.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; et al. Nose to brain delivery of rotigotine loaded chitosan nanoparticles in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells and animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 579, 119148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Wang, A.; Hua, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mu, H.; Wu, Z.; Sun, K. Intranasal delivery of Huperzine A to the brain using lactoferrin-conjugated N-trimethylated chitosan surface-modified PLGA nanoparticles for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, V.; Gaud, R.; Bajaj, A.; Wairkar, S. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of intranasally administered selegiline nanoparticles with improved brain delivery in Parkinson’s disease. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, L.P.; Panah, F.M.; Azadi, A.; Ashrafi, H. A mechanistic investigation on methotrexate-loaded chitosan-based hydrogel nanoparticles intended for CNS drug delivery: Trojan horse effect or not? Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Wairkar, S.; Sridhar, V.; Gaud, R. Pramipexole dihydrochloride loaded chitosan nanoparticles for nose to brain delivery: Development, characterization and in vivo anti-Parkinson activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Zeng, Z.W.; Xiao, R.Z.; Xie, T.; Zhou, G.L.; Zhan, X.R.; Wang, S.L. Recent advances of chitosan nanoparticles as drug carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 765. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Syeda, J.; Wasan, K.M.; Wasan, E.K. An overview of chitosan nanoparticles and its application in non-parenteral drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, K.; Wahid, R.; Richardson, C.; Bargatze, R.F.; El-Kamary, S.S.; Sztein, M.B.; Pasetti, M.F. Intranasal vaccination with an adjuvanted Norwalk virus-like particle vaccine elicits antigen-specific B memory responses in human adult volunteers. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 144, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, M.R.; Izquierdo, I.; Raseira, M.d.C.B.; Zuanazzi, J.Â.; Barros, D.; Henriques, A.T. Effect of lyophilised Vaccinium berries on memory, anxiety and locomotion in adult rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2005, 52, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesus, S.; Schmutz, M.; Som, C.; Borchard, G.; Wick, P.; Borges, O. Hazard Assessment of Polymeric Nanobiomaterials for Drug Delivery: What Can We Learn From Literature So Far. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 261. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00261 (accessed on 27 October 2020). [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Som, C.; Schmutz, M.; Borges, O.; Borchard, G. How the Lack of Chitosan Characterization Precludes Implementation of the Safe-by-Design Concept. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, P.; Remunan-Lopez, C.; Vila-Jato, J.L.; Alonso, M.J. Novel hydrophilic chitosan-polyethylene oxide nanoparticles as protein carriers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 63, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Yan, W.; Xu, Z.; Ni, H. Formation mechanism of monodisperse, low molecular weight chitosan nanoparticles by ionic gelation technique. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotta, S.; Khan, A.W.; Ansari, S.H.; Sharma, R.K.; Ali, J. Anti HIV nanoemulsion formulation: Optimization and in vitro-in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 462, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chime, S.A.; Onunkwo, G.C.; Onyishi, I.I. Kinetics and mechanisms of drug release from swellable and non swellable matrices: A review. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Rassu, G.; Porcu, E.P.; Fancello, S.; Obinu, A.; Senes, N.; Galleri, G.; Migheli, R.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P. Intranasal Delivery of Genistein-Loaded Nanoparticles as a Potential Preventive System against Neurodegenerative Disorders. Pharmaceutics 2018, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Misra, A.; Mishra, A.K.; Mishra, P.; Pathak, K. Mucoadhesive nanoemulsion-based intranasal drug delivery system of olanzapine for brain targeting. J. Drug Target. 2008, 16, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazil, M.; Md, S.; Haque, S.; Kumar, M.; Baboota, S.; kaur Sahni, J.; Ali, J. Development and evaluation of rivastigmine loaded chitosan nanoparticles for brain targeting. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, S.; Bikiaris, D.; Avgoustakis, K.; Karavas, E.; Georgarakis, M. Chitosan nanoparticles loaded with dorzolamide and pramipexole. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 73, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hu, K.; Jiang, X. From nose to brain: Understanding transport capacity and transport rate of drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2008, 5, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.A.; Mallikarjuna, N.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Recent advances on chitosan-based micro-and nanoparticles in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2004, 100, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Zhou, C.; Luo, B. Preparation and characterization of chitosan nanoparticles containing lysozyme. Pharm. Biol. 2006, 44, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Davis, S.S.; Illum, L. Chitosan microspheres prepared by spray drying. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 187, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vllasaliu, D.; Exposito-Harris, R.; Heras, A.; Casettari, L.; Garnett, M.; Illum, L.; Stolnik, S. Tight junction modulation by chitosan nanoparticles: Comparison with chitosan solution. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 400, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, W.; Lu, W.; Su, L.; Shi, Z. Preparation of nimodipine-loaded microemulsion for intranasal delivery and evaluation on the targeting efficiency to the brain. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 275, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illum, L.; Jabbal-Gill, I.; Hinchcliffe, M.; Fisher, A.N.; Davis, S.S. Chitosan as a novel nasal delivery system for vaccines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 51, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Formulation Code | CS (mg/mL) | Na-TPP (mg/mL) | Particle Size (nm) ± SD | PDI ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F32 | 1 | 1 | 147.2 ± 2.21 | 0.268 ± 0.009 |
| F41 | 1.5 | 1 | 188.4 ± 1.09 | 0.391 ± 0.028 |
| F42 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 289.80 ± 3.87 | 0.288 ± 0.016 |
| F51 | 1.75 | 1 | 205.0 ± 5.76 | 0.419 ± 0.007 |
| F52 | 1.75 | 1.5 | 238.5 ± 2.86 | 0.550 ± 0.012 |
| F61 | 2 | 1 | 440.6 ± 4.93 | 0.419 ± 0.017 |
| F62 | 2 | 1.5 | 280.60 ± 2.1 | 0.389 ± 0.006 |
| F71 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 325.6 ± 1.82 | 0.347 ± 0.013 |
| Formulation Code | Drug: Polymer Ratio | Conc. of CS (mg/mL) | Conc. of Na-TPP (mg/mL) | Mean Particle Size (nm) ± (SD) | Mean PDI ± (S.D) | EE (%) | DL (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F32 D1 | 1:1 | 1 | 1 | 241.20 ± 12.25 | 0.389 ± 0.056 | 88.68 ± 1.22 | 36.45 ± 2.14 |
| F32 D2 | 2:1 | 1 | 1 | 320.10 ± 20.80 | 0.423 ± 0.028 | 77.67 ± 2.58 | 26.10 ± 1.84 |
| F32 D3 | 3:1 | 1 | 1 | 380.96 ± 13.81 | 0.483 ± 0.014 | 68.46 ± 0.43 | 16.18 ± 2.01 |
| Formulation | Organ/ Tissue | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | AUC 0–480 min (ng. min/mL) | AUC 0-Inf min (ng. min/mL) | T1/2 (min) | Kelim (min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDZ Sol IV | Brain | 245.44 ± 12.83 | 1 | 1208.94 | 2559.19 | 592.8 | 0.070 |
| Blood | 846.32 ± 22.01 | 0.5 | 2440.03 | 2950.26 | 172.2 | 0.241 | |
| MDZ Sol IN | Brain | 211.67 ± 12.82 | 2 | 1036.78 | 2342.31 | 640.8 | 0.064 |
| Blood | 209.83 ± 11.78 | 1 | 1094.46 | 3152.20 | 823.2 | 0.050 | |
| MDZ CSNPs IN | Brain | 423.41 ± 10.23 | 2 | 1920.87 | 4673.52 | 782.4 | 0.053 |
| Blood | 282.34 ± 31.45 | 2 | 1433.18 | 14792.37 | 4150.2 | 0.010 |
| Formulation | Organ/Tissue | 0.5 h (ng/mL) | 1 h (ng/mL) | 2 h (ng/mL) | 4 h (ng/mL) | 8 h (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDZ Solution (IV) | Brain | 98.29 ± 16.44 | 245.44 ± 12.83 | 227.89 ± 11.76 | 156.33 ± 12.68 | 94.73 ± 13.81 |
| Blood | 846.32 ± 22.01 | 626.65 ± 18.36 | 420.99 ± 11.31 | 293.44 ± 16.35 | 123.33 ± 14.22 | |
| MDZ Solution (IN) | Brain | 87.99 ± 9.82 | 188.64 ± 11.69 | 211.67 ± 12.82 | 128.82 ± 18.94 | 84.67 ± 16.72 |
| Blood | 106.82 ± 9.86 | 209.83 ± 11.78 | 182.32 ± 21.11 | 143.03 ± 19.44 | 103.91 ± 10.63 | |
| MDZ CS NPs (IN) | Brain | 136.38 ± 10.71 | 293.27 ± 11.84 | 423.41 ± 10.23 | 246.36 ± 19.61 | 146.31 ± 14.85 |
| Blood | 97.39 ± 11.65 | 187.33 ± 21.73 | 282.34 ± 31.45 | 192.36 ± 21.46 | 133.88 ± 19.26 |
| Formulation | Organ/Tissue | 0.5 h | 1 h | 2 h | 4 h | 8 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDZ Soln IV | Brain/Blood | 0.12 | 0.39 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.77 |
| MDZ Soln IN | Brain/Blood | 0.82 | 0.90 | 1.16 | 0.90 | 0.81 |
| MDZ NPs IN | Brain/Blood | 1.40 | 1.57 | 1.50 | 1.28 | 1.09 |
| Formulation | DTE% | DTP% |
|---|---|---|
| MDZ solution (IN) | 191.373 | 49.13 |
| MDZ-loaded CS NPs (IN) | 270.707 | 63.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shrestha, N.; Khan, S.; Neupane, Y.R.; Dang, S.; Md, S.; Fahmy, U.A.; Kotta, S.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J. Tailoring Midazolam-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticulate Formulation for Enhanced Brain Delivery via Intranasal Route. Polymers 2020, 12, 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112589
Shrestha N, Khan S, Neupane YR, Dang S, Md S, Fahmy UA, Kotta S, Alhakamy NA, Baboota S, Ali J. Tailoring Midazolam-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticulate Formulation for Enhanced Brain Delivery via Intranasal Route. Polymers. 2020; 12(11):2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112589
Chicago/Turabian StyleShrestha, Nikesh, Saba Khan, Yub Raj Neupane, Shweta Dang, Shadab Md, Usama A. Fahmy, Sabna Kotta, Nabil A. Alhakamy, Sanjula Baboota, and Javed Ali. 2020. "Tailoring Midazolam-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticulate Formulation for Enhanced Brain Delivery via Intranasal Route" Polymers 12, no. 11: 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112589
APA StyleShrestha, N., Khan, S., Neupane, Y. R., Dang, S., Md, S., Fahmy, U. A., Kotta, S., Alhakamy, N. A., Baboota, S., & Ali, J. (2020). Tailoring Midazolam-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticulate Formulation for Enhanced Brain Delivery via Intranasal Route. Polymers, 12(11), 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112589