Double-Crosslinked Polyurethane Acrylate for Highly Conductive and Stable Polymer Electrolyte
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Gel PUA Membranes
2.3. Characterization of PUA Prepolymers and Membranes
2.4. Electrochemical Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
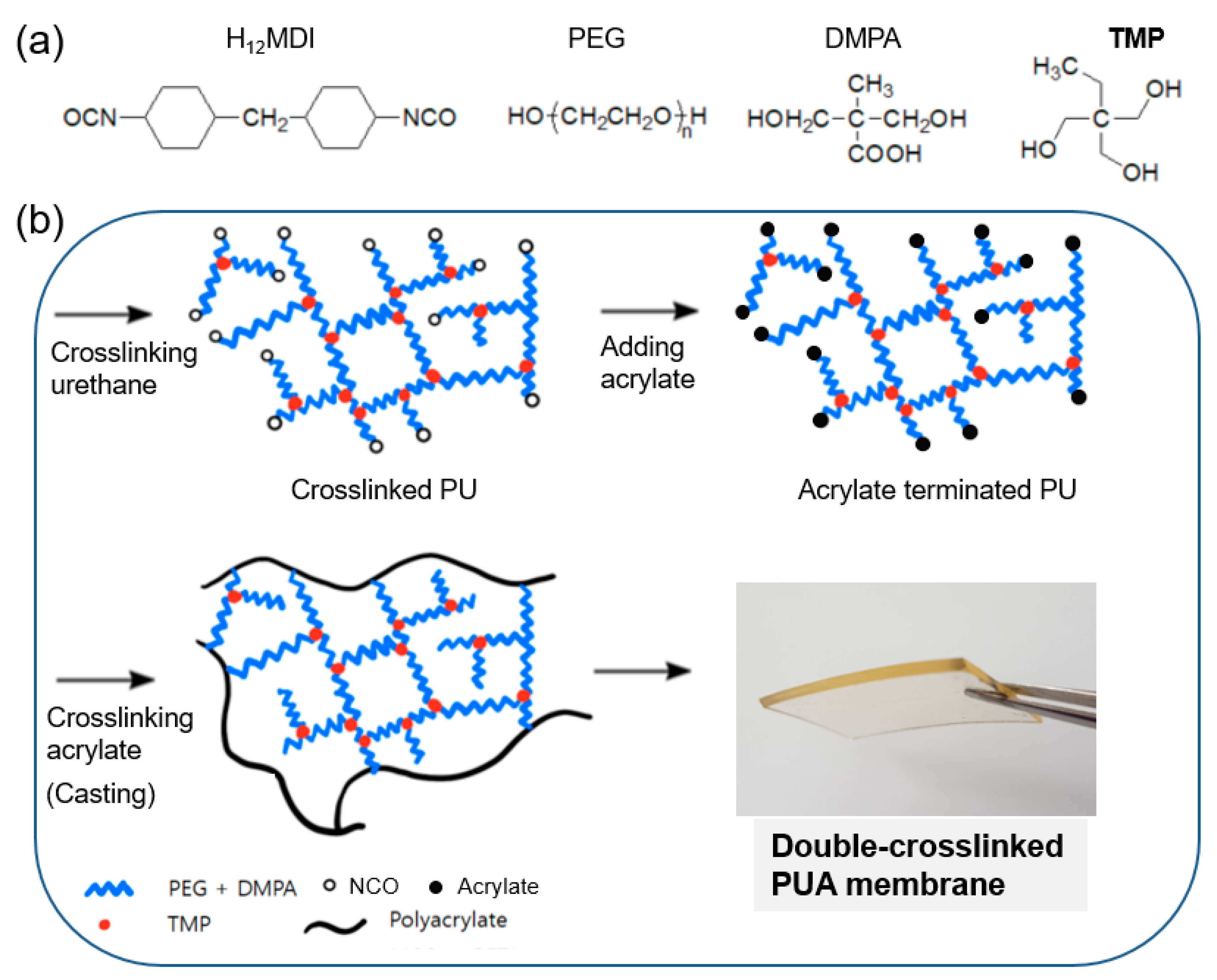
3.1. Preparation of Polymer Membranes
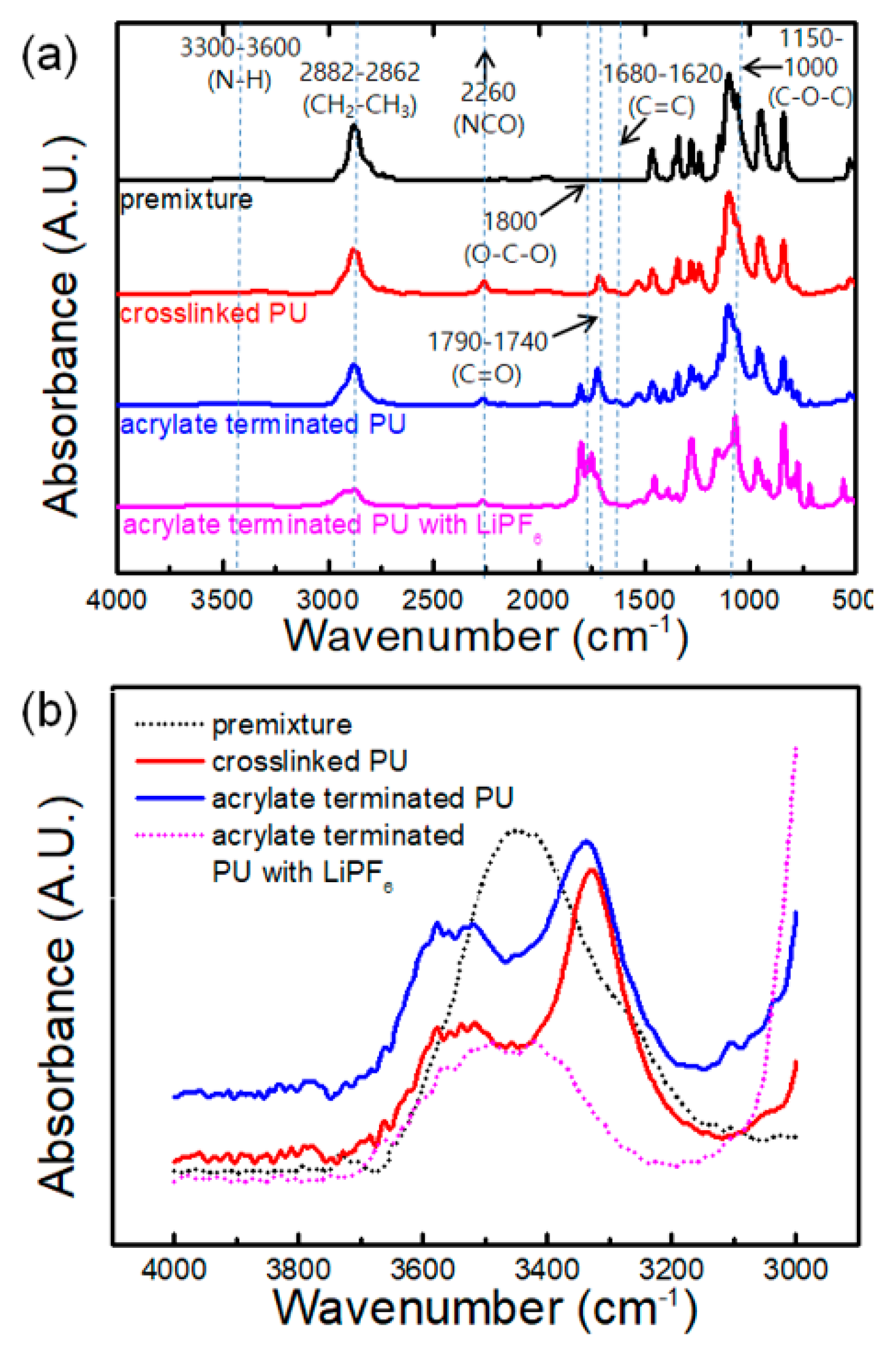
3.2. Functional Groups of Prepolymers and Their Interactions with Lithium Salt
3.3. Optical and Mechanical Properties
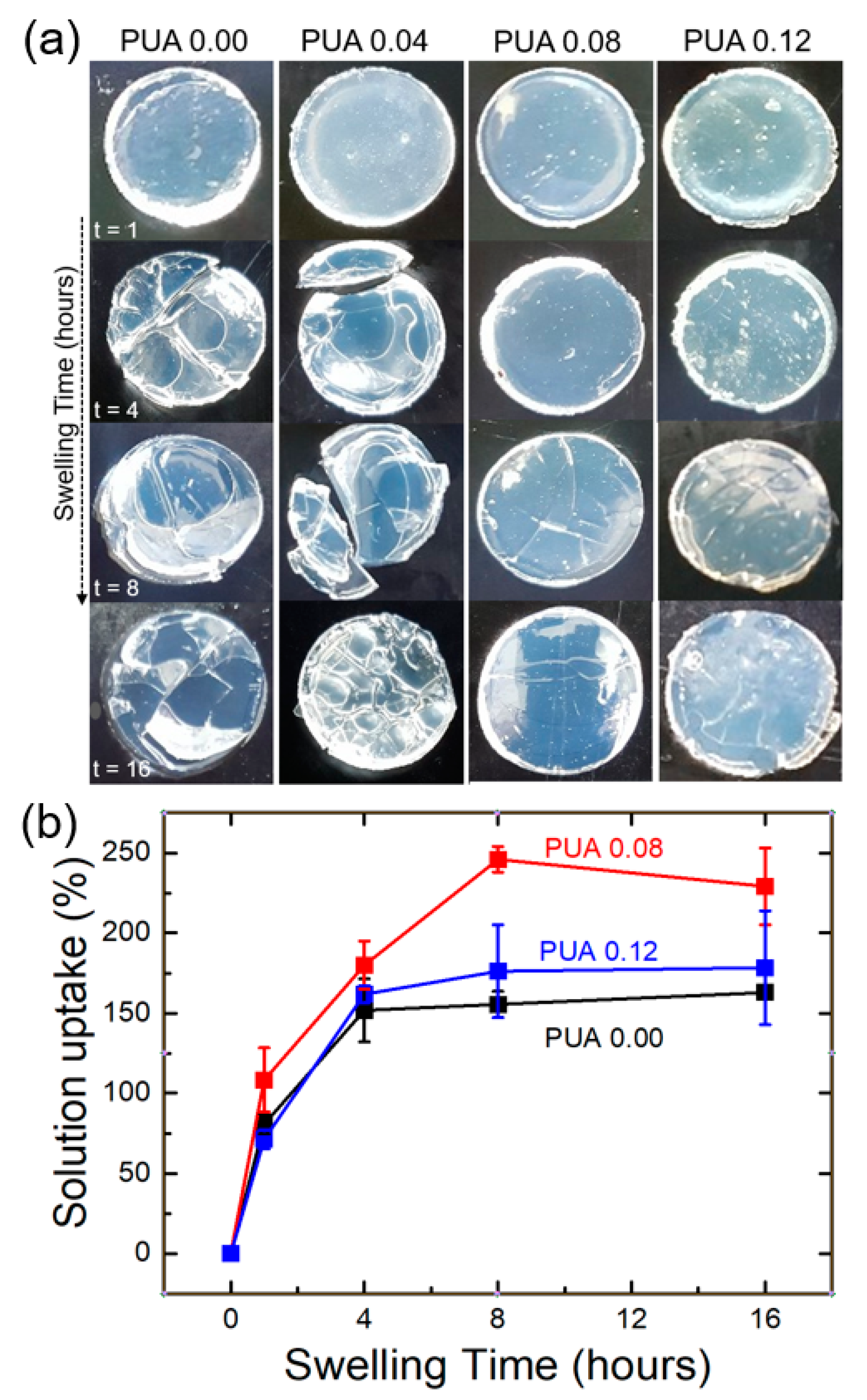
3.4. Swelling Characteristics of the PUA Membranes: Stability of the PUA Gel Membranes
3.5. Ionic Conductivity of the PUA Electrolytes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, N.; Cao, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Deng, H. In situ ceramic fillers of electrospun thermoplastic polyurethane/poly(vinylidene fluoride) based gel polymer electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 9751–9756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, M.; Kumar, A.; Deka, H.; Karak, N. Ionic transport studies in hyperbranched polyurethane/clay nanocomposite gel polymer electrolytes. Ionics 2011, 18, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.-C.; Wang, Y.-J.; Cheng, T.-T.; Yang, C.-H. The effect of DMPA units on ionic conductivity of PEG–DMPA–IPDI waterborne polyurethane as single-ion electrolytes. Polymer 1999, 40, 3979–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Luo, Y.; Huang, X.; Tang, X. Synthesis and characterization of novel crosslinked polyurethane-acrylate electrolyte. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Park, K.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kim, K.; Jeong, Y.U.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.-D. Poly(urethane acrylate)-based gel polymer films for mechanically stable, transparent, and highly conductive polymer electrolyte applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, C.A.; Silva, G.G.; Machado, J.C.; Pimenta, M.A.; Silva, R.A. Study of Correlations between Microstructure and Conductivity in a Thermoplastic Polyurethane Electrolyte. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 7102–7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, P.; Vasudevan, T.; Gopalan, A.; Lee, K.-P. Preparation and properties of new cross-linked polyurethane acrylate electrolytes for lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 2006, 160, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jeung, S.; Min, K. The effects of anion structure of lithium salts on the properties of in-situ polymerized thermoplastic polyurethane electrolytes. Polymer 2010, 51, 2864–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, M.; Long, L.; Siyal, S.H.; Yang, X.; Sui, G. Recent advances in gel polymer electrolyte for high-performance lithium batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2019, 37, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Wang, S.; Xiao, M.; Meng, Y. Polymer electrolytes for lithium polymer batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 10038–10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; He, D.; Xie, X. Poly(ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19218–19253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Tang, C.; Mei, J.; Li, Y.; Hui, D. Flexible solid electrolyte based on UV cured polyurethane acrylate/succinonitrile-lithium salt composite compatibilized by tetrahydrofuran. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 120, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskakova, Y.V.; Yarmolenko, O.V.; Efimov, O.N. Polymer gel electrolytes for lithium batteries. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2012, 81, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Qiu, J.; Sakai, E.; Ito, K. Rapid Recovery Double Cross-Linking Hydrogel with Stable Mechanical Properties and High Resilience Triggered by Visible Light. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 13593–13601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Ma, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F. Molecularly Engineered Dual-Crosslinked Hydrogel with Ultrahigh Mechanical Strength, Toughness, and Good Self-Recovery. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2054–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.; Sun, Y.; Mackanic, D.G.; Lee, M.; Foudeh, A.M.; Song, M.-S.; Cui, Y.; Bao, Z. A Dual-Crosslinking Design for Resilient Lithium-Ion Conductors. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, D.W.; Kang, M.G.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.Y. Stress/strain and curvature analysis of laser-scribed polyethylene terephthalate films with multiple grooves using finite element method. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digar, M.; Hung, S.; Wang, H.; Wen, T.-C.; Gopalan, A. Study of ionic conductivity and microstructure of a cross-linked polyurethane acrylate electrolyte. Polymer 2002, 43, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.-C.; Du, Y.-L.; Digar, M. Compositional effect on the morphology and ionic conductivity of thermoplastic polyurethane based electrolytes. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yu, P.; Dong, S. The Influence of Crosslink Density on the Failure Behavior in Amorphous Polymers by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Materials 2016, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.H.; Ahmad, M.B.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Zainuddin, N. Effect of crosslinking concentration on properties of 3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl methacrylate/N-vinyl pyrrolidone gels. Chem. Central J. 2018, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahkam, M.; Doostie, L. The Relation Between Swelling Properties and Cross-Linking of Hydrogels Designed for Colon-Specific Drug Delivery. Drug Deliv. 2005, 12, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, D.; Kumar, A. Ionic conduction in P(VDF-HFP)/PVDF-(PC + DEC)-LiClO4 polymer gel electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 2581–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Designation | PUA Composition (Molar Ratio) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUA TMP/PEG | H12MDI | TMP | PEG | TMP/PEG | DMPA | PETA |
| PUA 0.00 | 1.1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.00 | 0.1 | 1 |
| PUA 0.04 | 1.1 | 0.02 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 1 |
| PUA 0.08 | 1.1 | 0.04 | 0.5 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 1 |
| PUA 0.12 | 1.1 | 0.06 | 0.5 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-N.; Kim, K.-G.; Jeong, Y.U.; Kim, S.Y. Double-Crosslinked Polyurethane Acrylate for Highly Conductive and Stable Polymer Electrolyte. Polymers 2020, 12, 2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112557
Kim H-N, Kim K-G, Jeong YU, Kim SY. Double-Crosslinked Polyurethane Acrylate for Highly Conductive and Stable Polymer Electrolyte. Polymers. 2020; 12(11):2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112557
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Han-Na, Kyung-Geun Kim, Yeon Uk Jeong, and Sung Yeol Kim. 2020. "Double-Crosslinked Polyurethane Acrylate for Highly Conductive and Stable Polymer Electrolyte" Polymers 12, no. 11: 2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112557
APA StyleKim, H.-N., Kim, K.-G., Jeong, Y. U., & Kim, S. Y. (2020). Double-Crosslinked Polyurethane Acrylate for Highly Conductive and Stable Polymer Electrolyte. Polymers, 12(11), 2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112557





