Polymers Containing Non-Covalently Bound Cyclodextrins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Formation of (n-s) Polymer–CD ICs
3. Characterization of (n-s) Polymer–CD ICs
3.1. FTIR
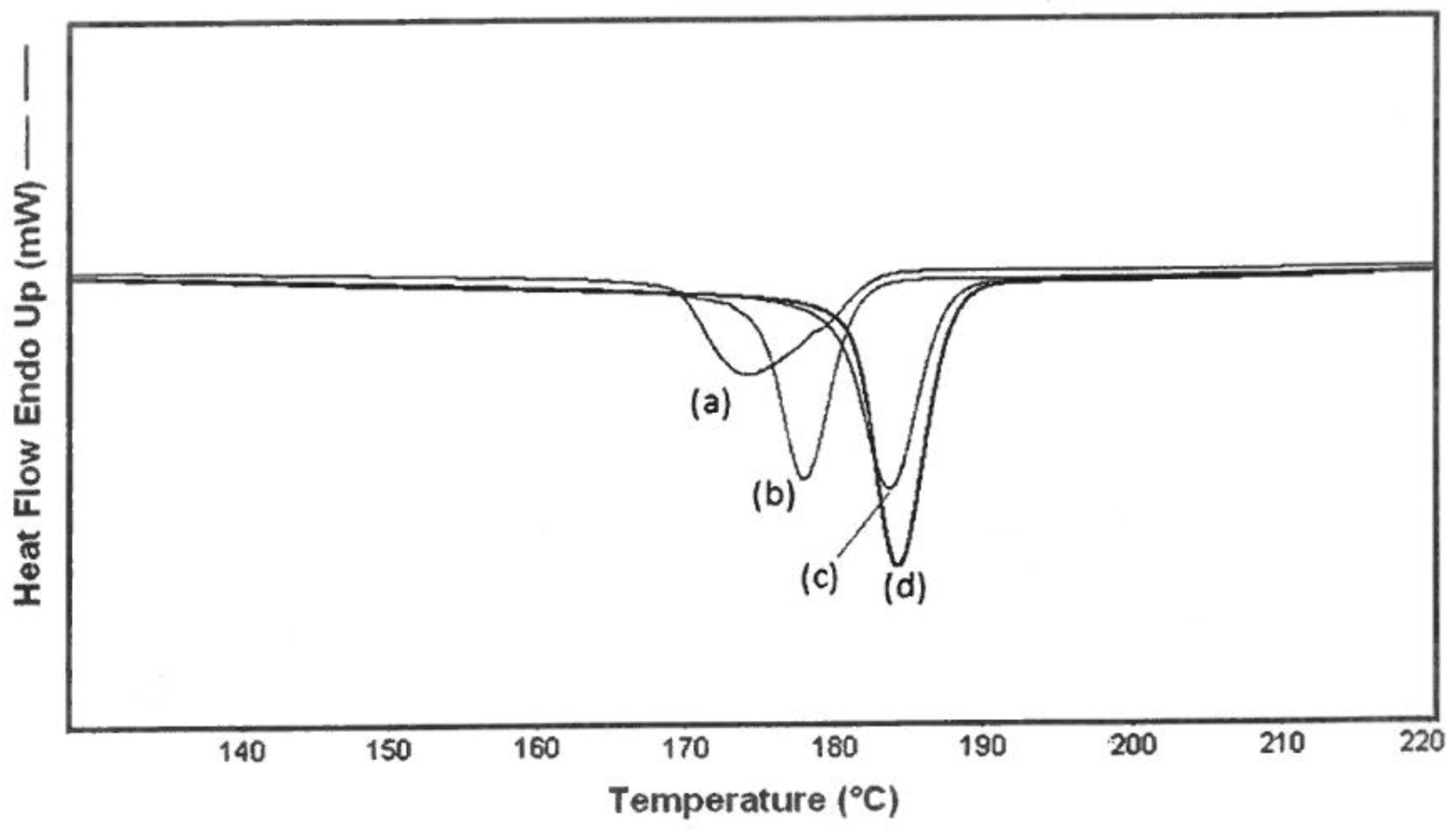
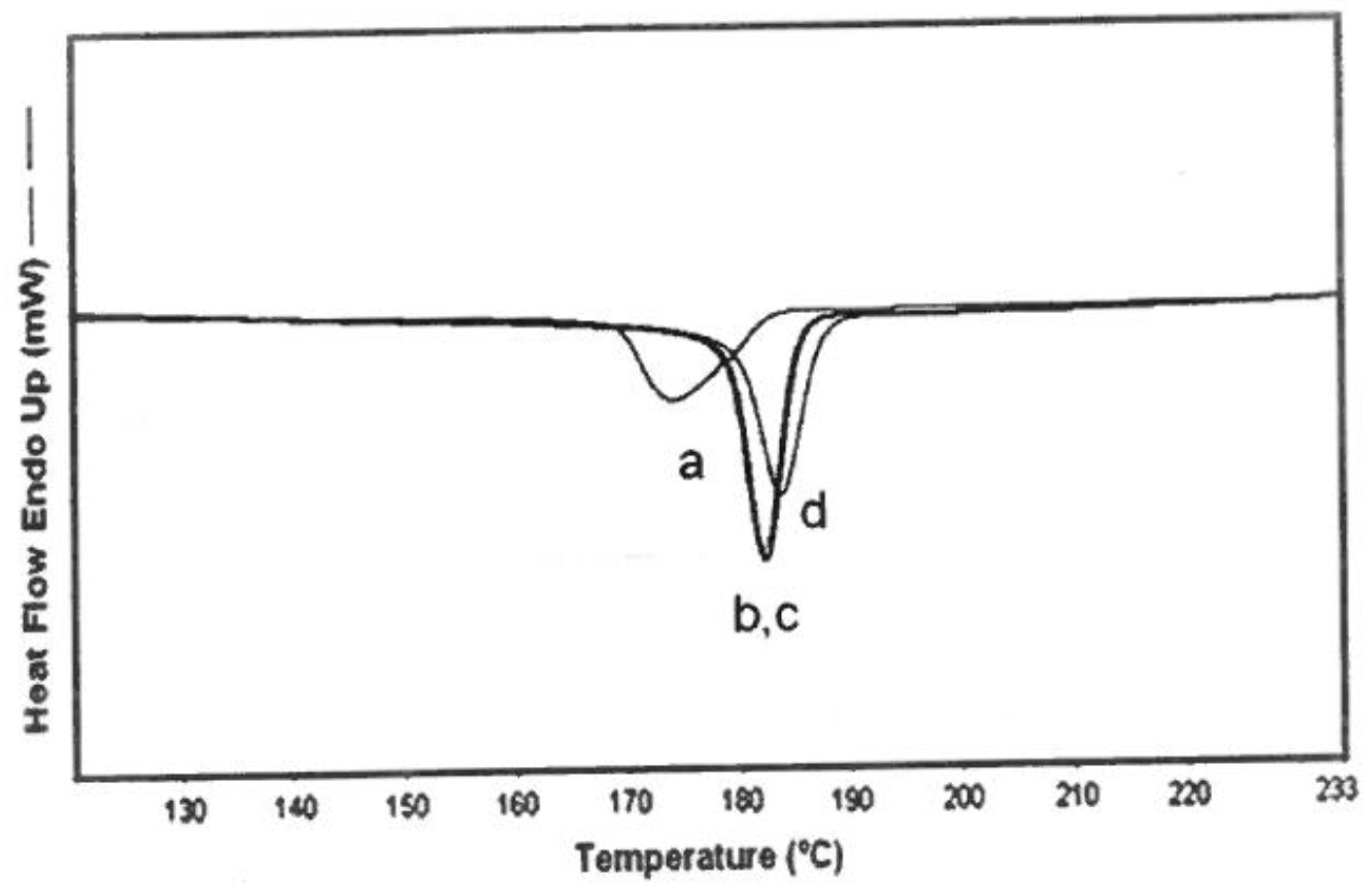
3.2. DSC
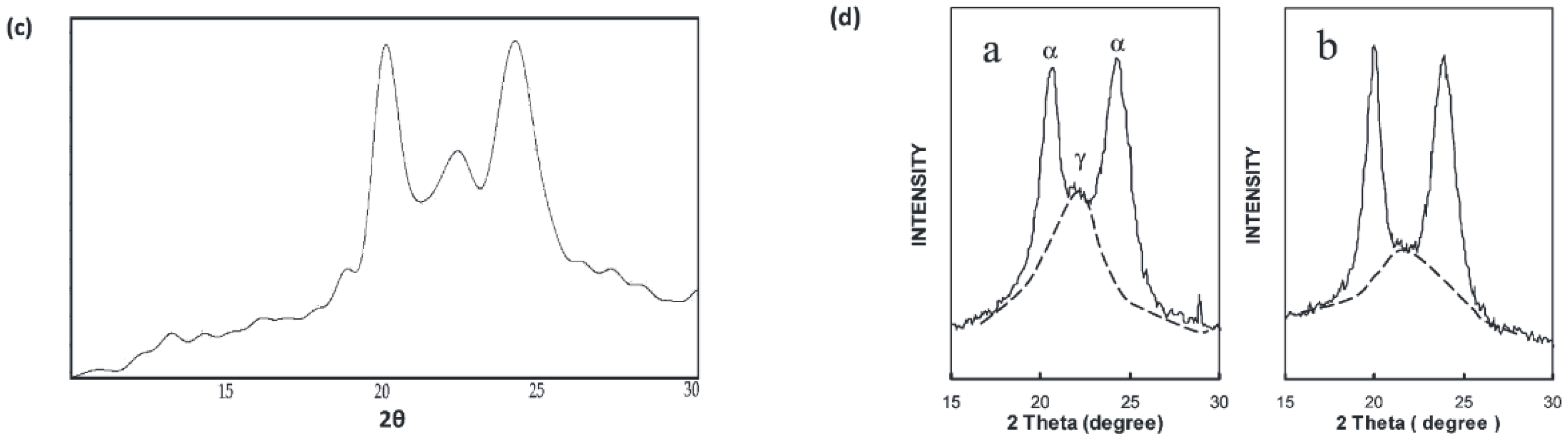
3.3. WAXD
3.4. Microscopy
3.5. Shape-Memory Testing
4. Characterization Results
4.1. FTIR
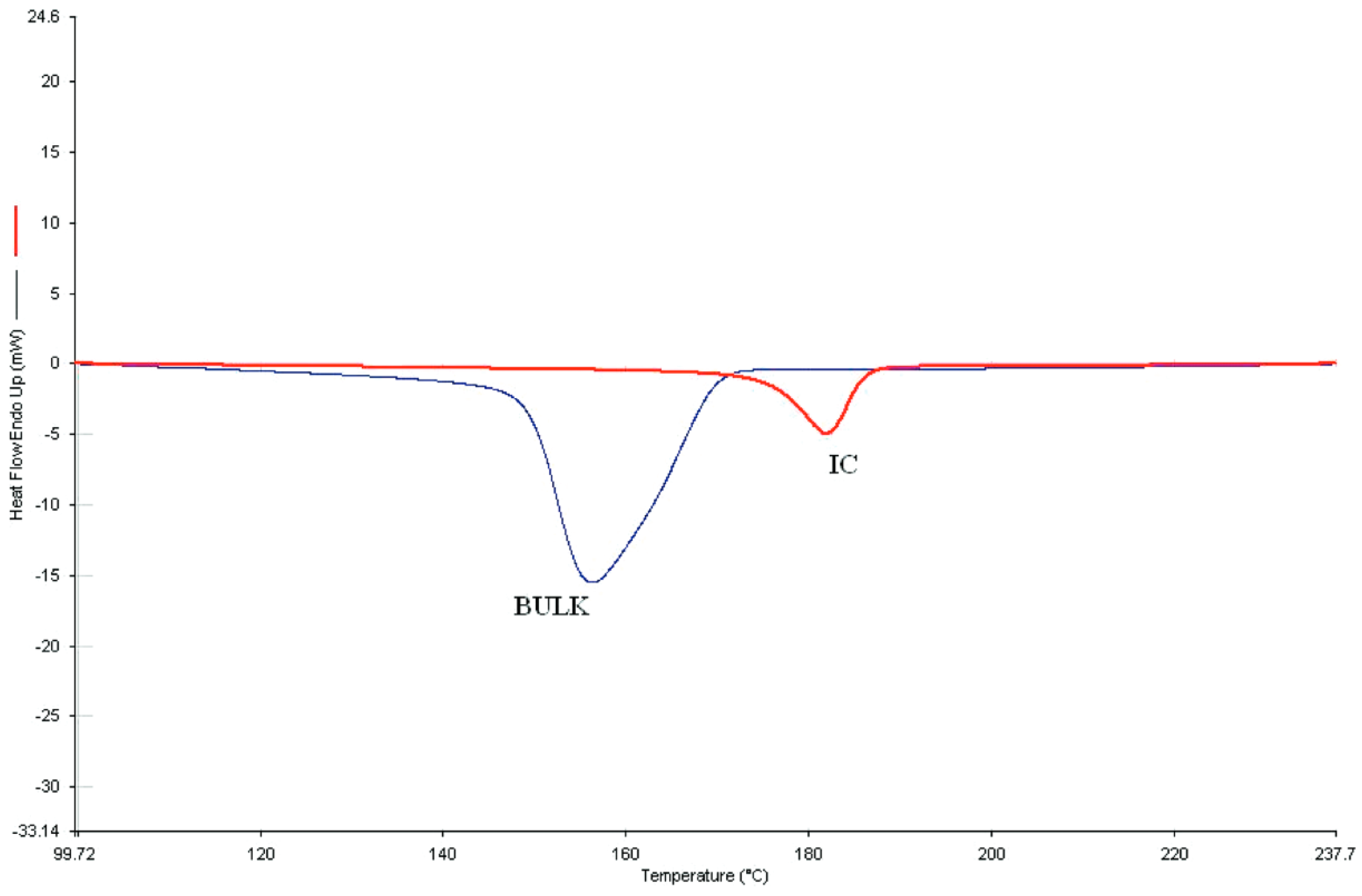
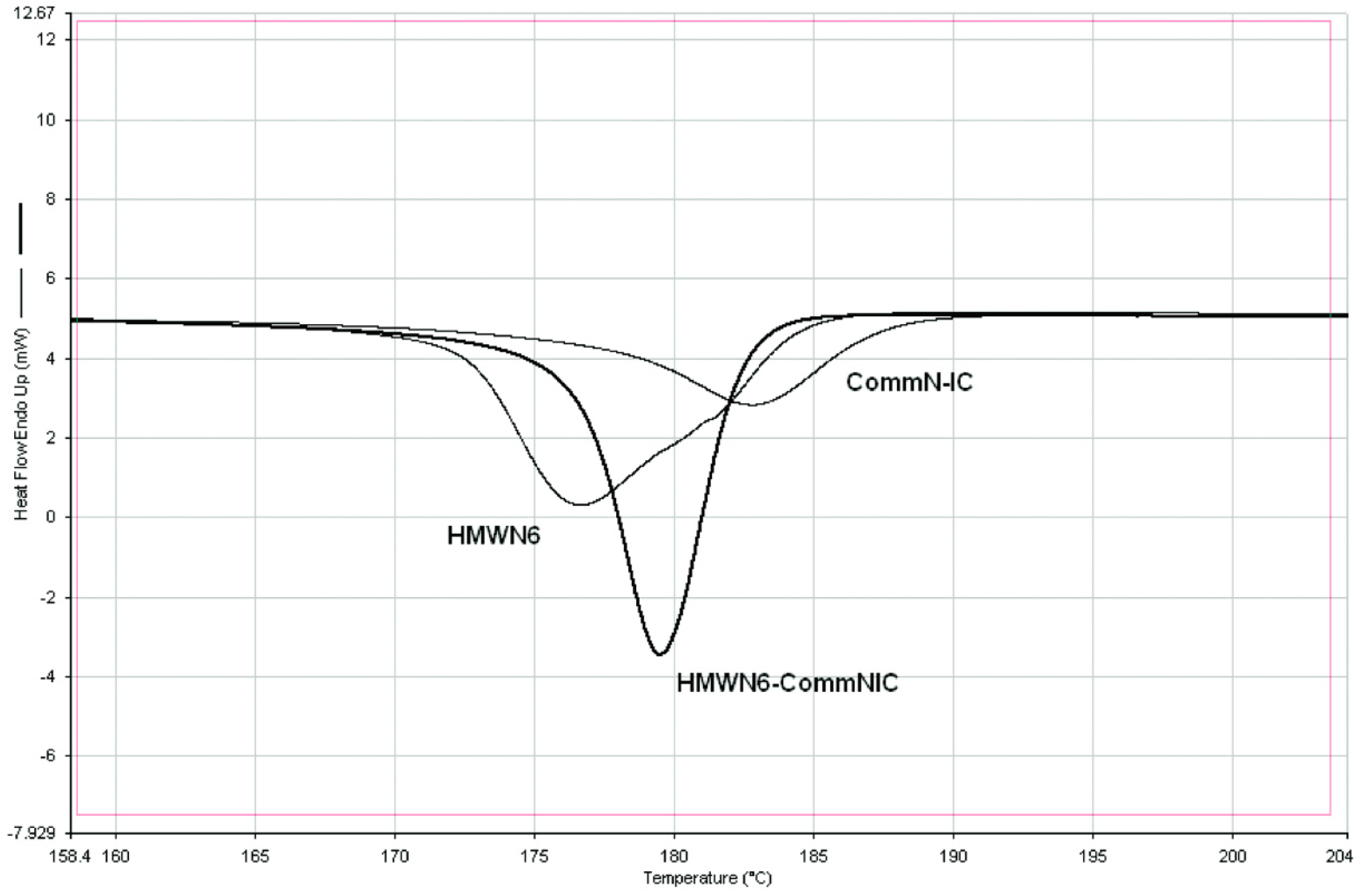
4.2. DSC
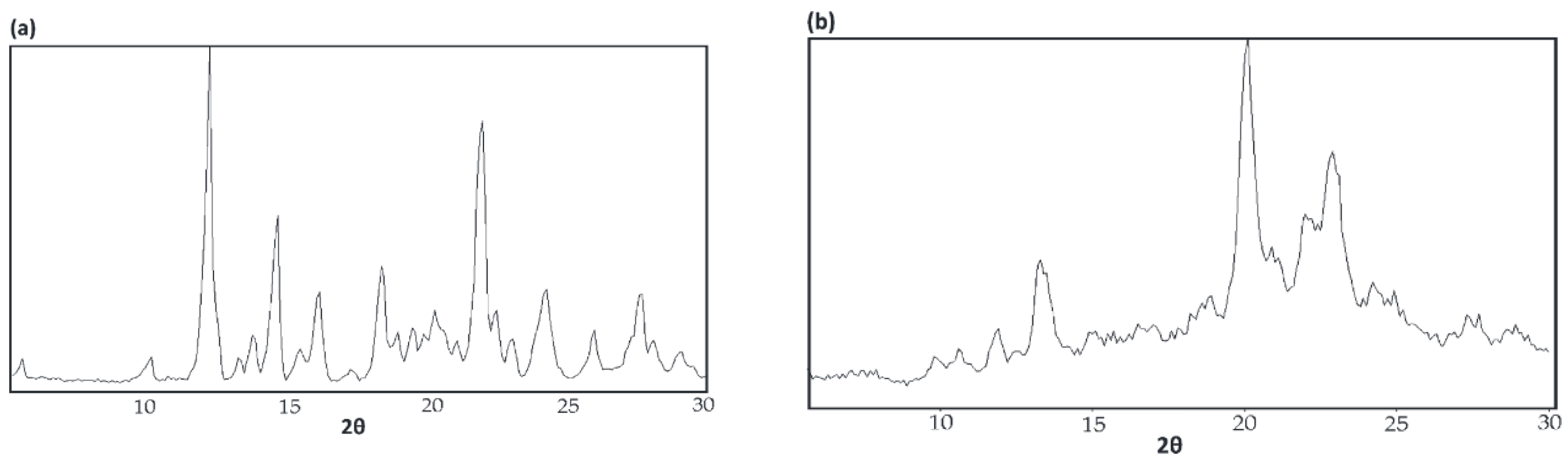
4.3. WAXD
4.4. Microscopy
4.5. Shape-Memory Testing
4.6. Summary of Characterization Results
5. Uses for (n-s) Polymer–CD ICs
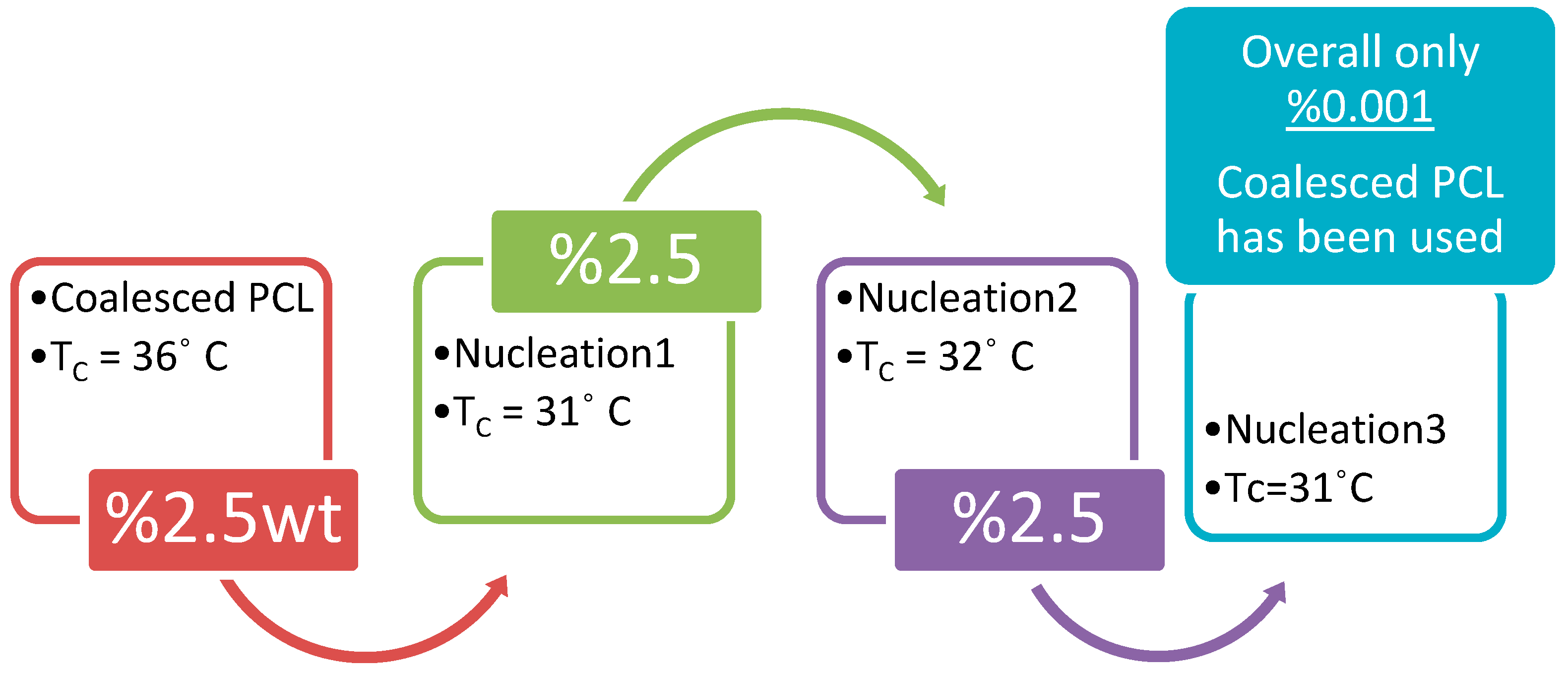
5.1. As Melt-Crystallization Nucleants
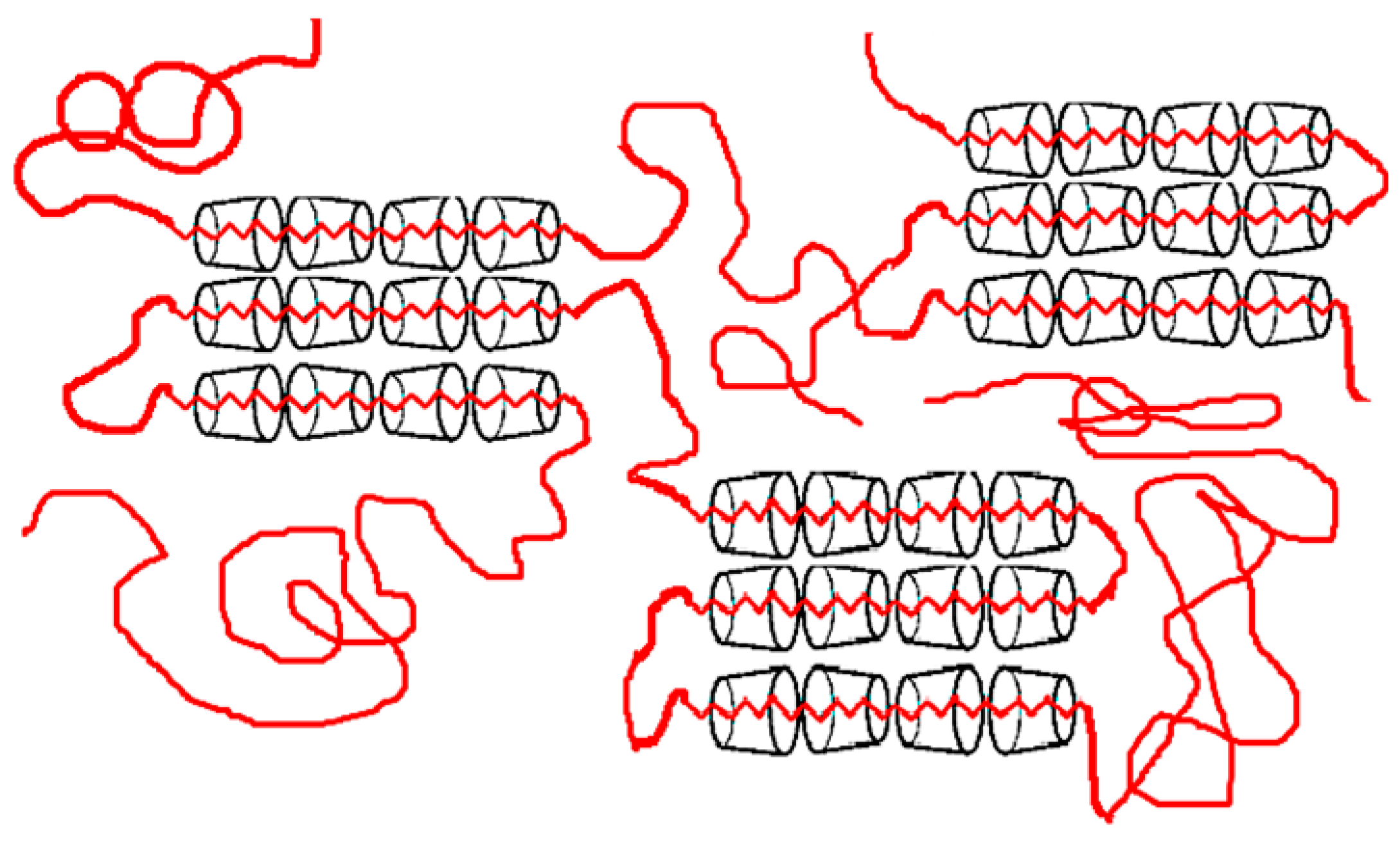
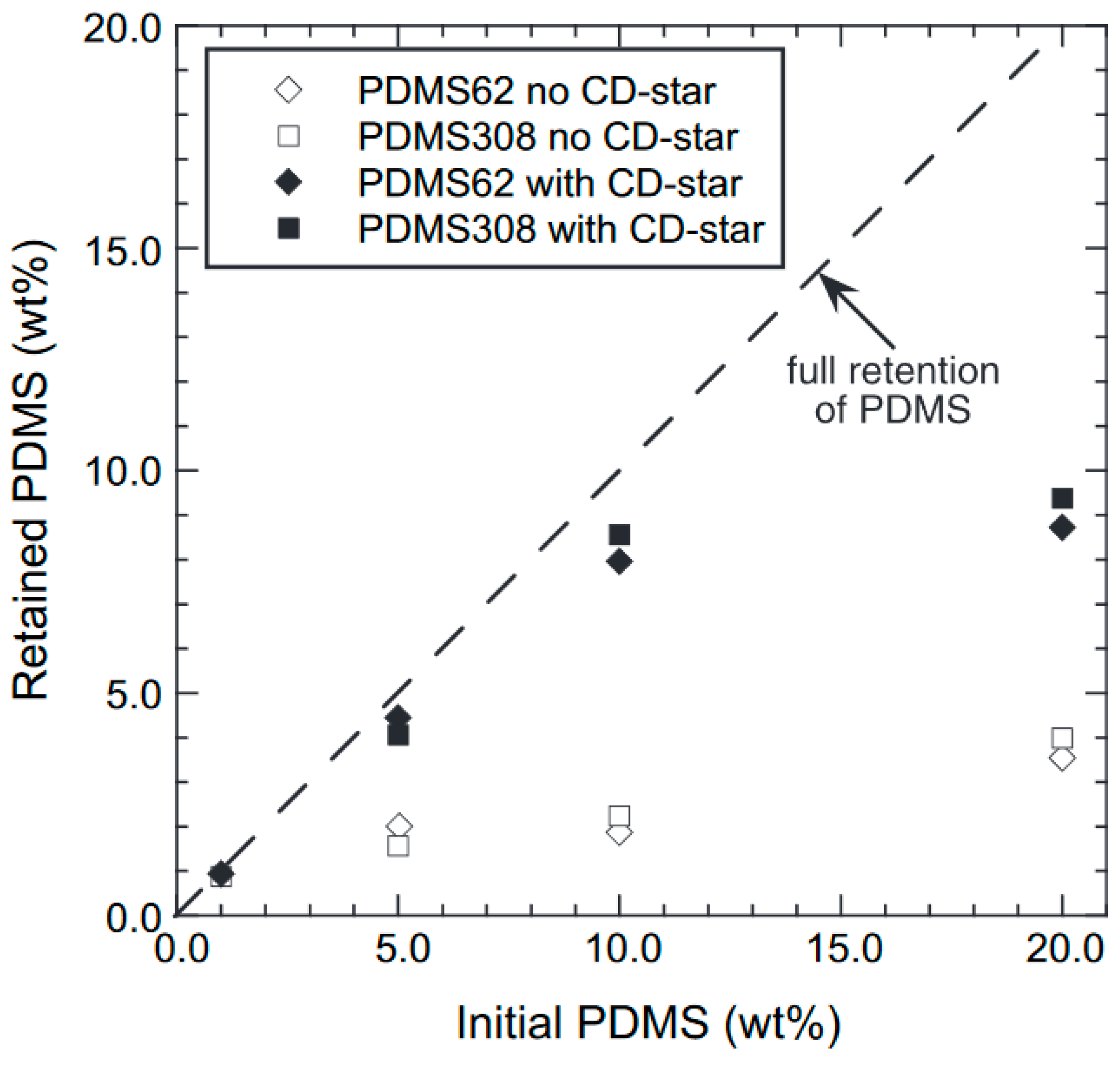
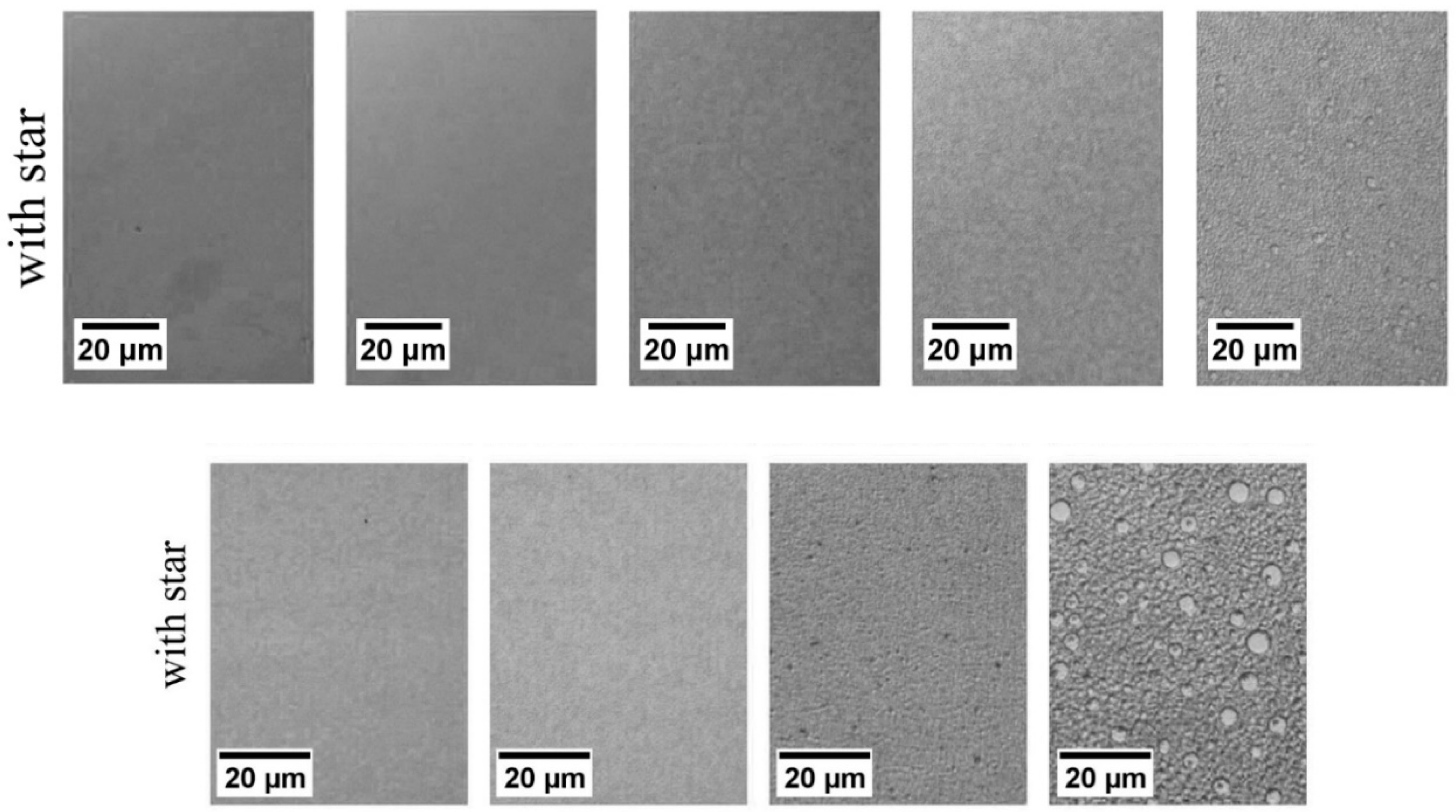
5.2. As Potential Compatiblizers
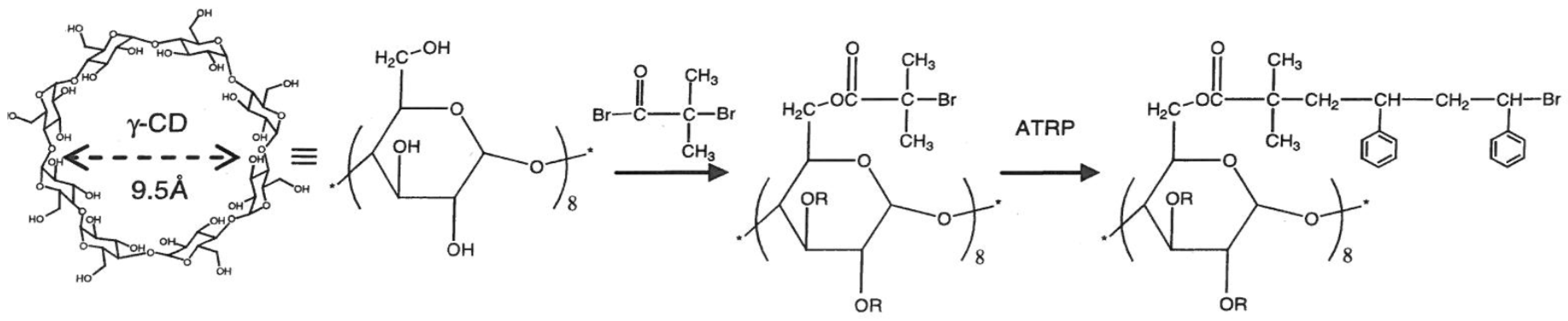
CD-Stars
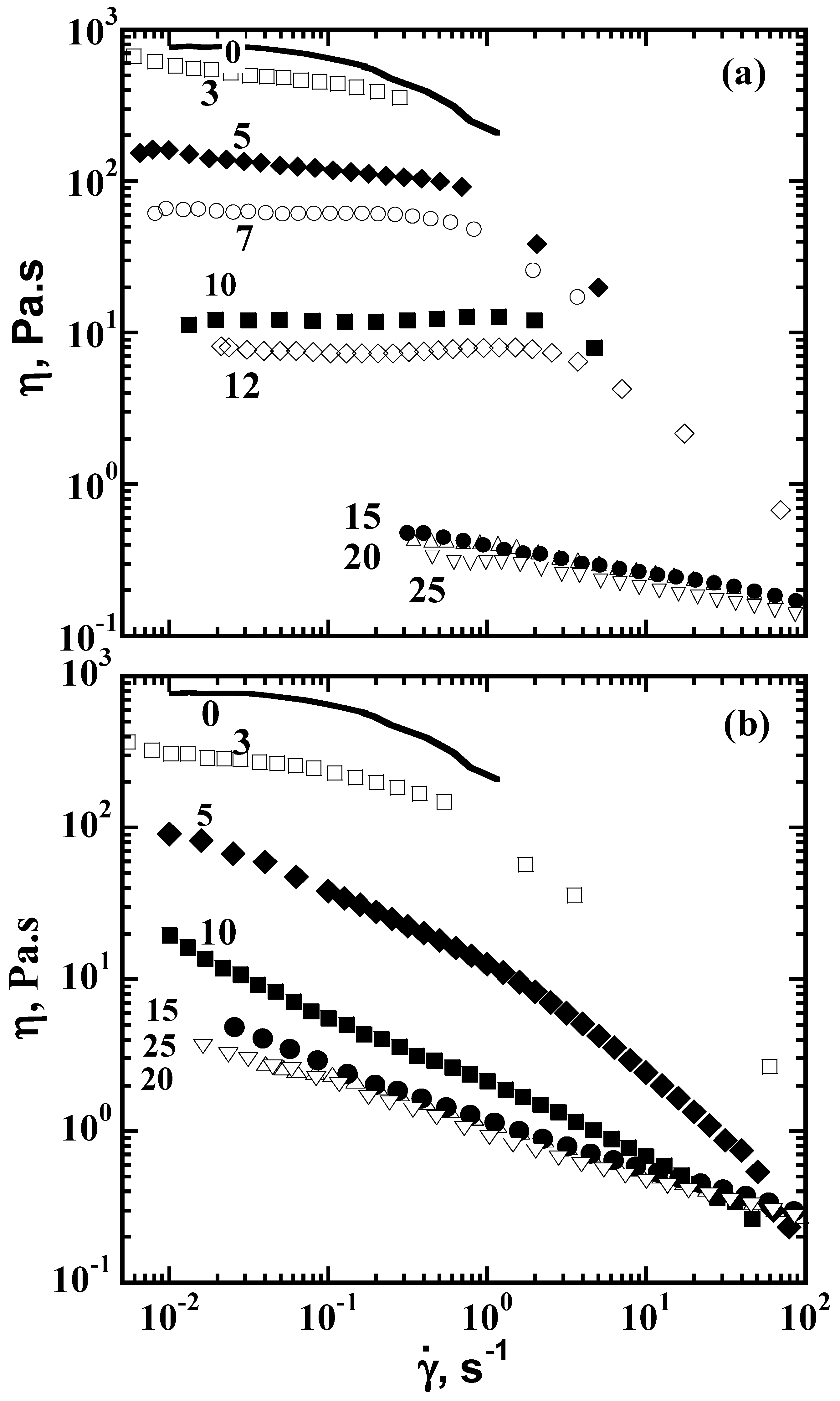
6. Viscosity Control of Polymer Solutions with CDs
7. Summary
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, T.; He, Y.; Zhu, B.; Shin, K.; Inoue, Y. Nucleation mechanism of α-cyclodextrin-enhanced crystallization of some semicrystalline aliphatic polymers. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 7736–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Shin, K.; Zhu, B.; Inoue, Y. Nucleation and crystallization behavior of poly (butylene succinate) induced by its α-cyclodextrin inclusion complex: Effect of stoichiometry. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 2427–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Kai, W.; Pan, P.; Cao, A.; Inoue, Y. Effects of Host−Guest Stoichiometry of α-Cyclodextrin−Aliphatic Polyester Inclusion Complexes and Molecular Weight of Guest Polymer on the Crystallization Behavior of Aliphatic Polyesters. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 7244–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.; Tandler, B.; Haussler, L.; Jehnichen, D.; Brunig, H. Melt Spinning of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Fibers for Tissue Engineering Using α-Cyclodextrin/Polymer Inclusion Complexes as the Nucleation Agent. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Dong, T.; Yazawa, K.; Inoue, Y. Preparation of Highly Transparent and Thermally Stable Films of α-Cyclodextrin/Polymer Inclusion Complexes. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 2095–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Gurarslan, A.; Joyner, X.; Child, R.; Tonelli, A.E. Melt-crystallized nylon-6 nucleated by the constrained chains of its non-stoichiometric cyclodextrin inclusion compounds and the nylon-6 coalesced from them. Polymer 2011, 52, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joijode, A.S.; Antony, G.J.; Tonelli, A.E. Glass-transition temperatures of nanostructured amorphous bulk polymers and their blends. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2013, 51, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Joyner, X.; Kotek, R.; Tonelli, A.E. Constrained/directed crystallization of nylon-6. I. nonstoichiometric inclusion compounds formed with cyclodextrins. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 8983–8991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, B.R.; Krishnaswamy, R.; Tonelli, A.E. Physical properties of poly (ɛ-caprolactone) coalesced from its α-cyclodextrin inclusion compound. Polymer 2011, 52, 4517–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, B.R.; Tonelli, A.E. Constrained polymer chain behavior observed in their non-stoichiometric cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocyclic Chem. 2012, 72, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Davis, W.; Urban, B.; Song, Y.; Porbeni, F.E.; Wang, X.; White, J.L.; Balik, C.M.; Rusa, C.C.; Fox, J.; et al. Manipulation of Nylon-6 crystal structures with its α-Cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8039–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujii, Y.; Ohno, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Goto, A.; Fukada, T. Structure and properties of high-density polymer brushes prepared by surface-initiated living radical polymerization. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2006, 197, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Tonelli, A.E. Non-Stoichiometric Polymer-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Compounds: Constraints Placed on Un-Included Chain Portions Tethered at Both Ends and Their Relation to Polymer Brushes. Polymers 2014, 6, 2166–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busche, B.J.; Tonelli, A.E.; Balik, C.M. Properties of polystyrene/poly(dimethyl siloxane) blends partially compatibilized with star polymers containing a γ-cyclodextrin core and polystyrene arms. Polymer 2010, 51, 6013–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joijode, A.S.; Hawkins, K.; Tonelli, A.E. Improving Poly (ethylene terephthalate) Through Self-nucleation. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurarslan, A.; Caydamli, Y.; Shen, J.; Tse, S.; Yetukuri, M.; Tonelli, A.E. Coalesced Poly(ε-caprolactone) Fibers Are Stronger. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 890–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdala, A.A.; Tonelli, A.E.; Khan, S.A. Modulation of hydrophobic interactions in associative polymers using inclusion compounds and surfactants. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 7833–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdala, A.A.; Wu, W.; Olesen, K.R.; Jenkins, R.D.; Tonelli, A.E.; Khan, S.A. Solution rheology of hydrophobically modified associative polymers: Effects of backbone composition and hydrophobe concentration. J. Rheol. 2004, 48, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tonelli, A.E. Polymers Containing Non-Covalently Bound Cyclodextrins. Polymers 2019, 11, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030425
Tonelli AE. Polymers Containing Non-Covalently Bound Cyclodextrins. Polymers. 2019; 11(3):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030425
Chicago/Turabian StyleTonelli, Alan E. 2019. "Polymers Containing Non-Covalently Bound Cyclodextrins" Polymers 11, no. 3: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030425
APA StyleTonelli, A. E. (2019). Polymers Containing Non-Covalently Bound Cyclodextrins. Polymers, 11(3), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030425



