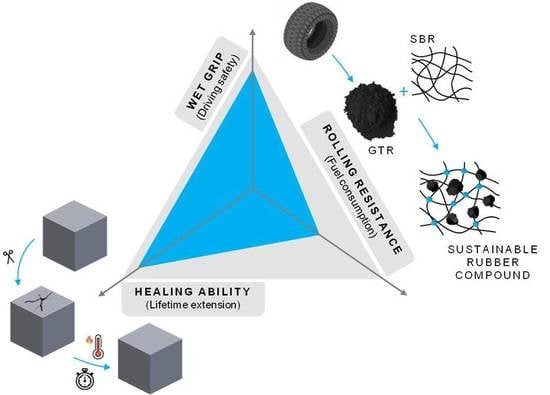
Giving a Second Opportunity to Tire Waste: An Alternative Path for the Development of Sustainable Self-Healing Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Compounds Overcoming the Magic Triangle of Tires
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Compounding
2.2. Material Characterization
2.2.1. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.2.2. Cyclic Deformation Testing
2.2.3. Healing Protocol
2.2.4. Dynamic Properties
3. Results
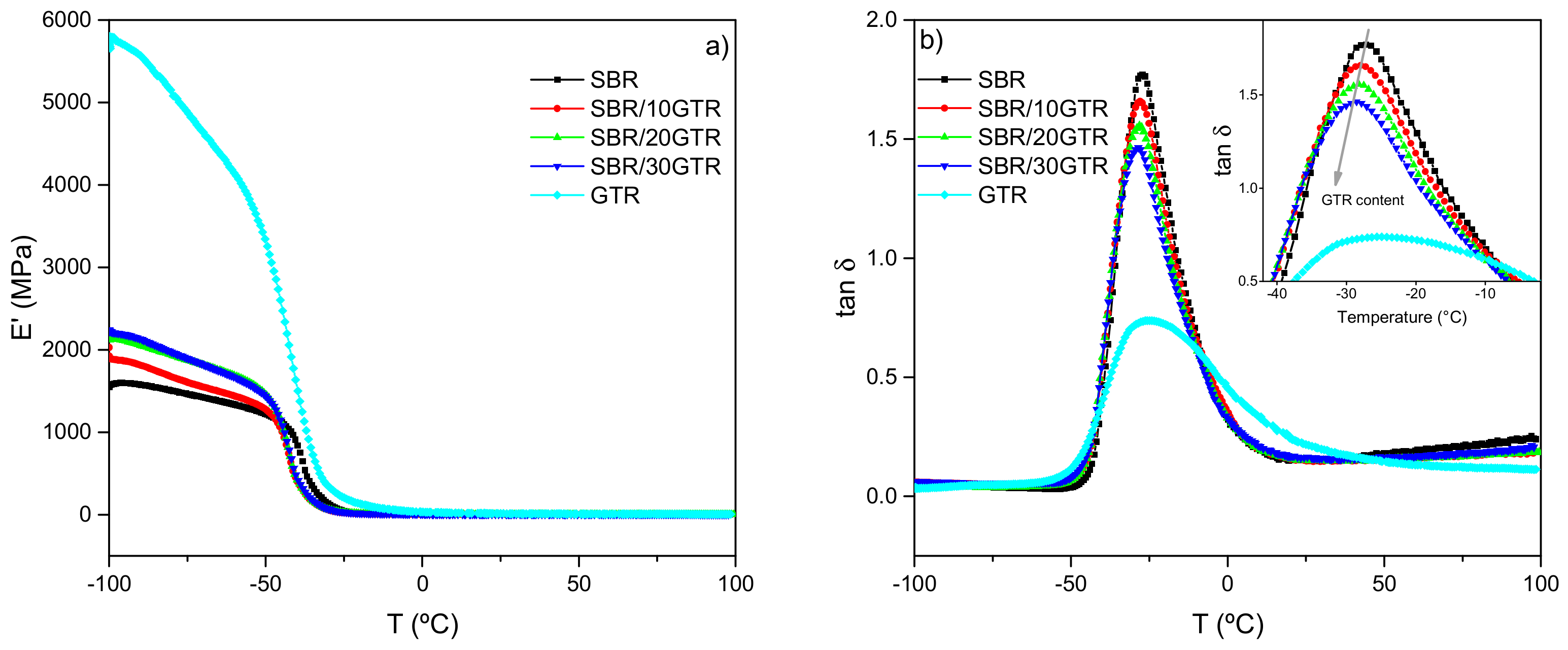
3.1. Effect of GTR Content on the Dynamic Properties of Pristine SBR Compounds
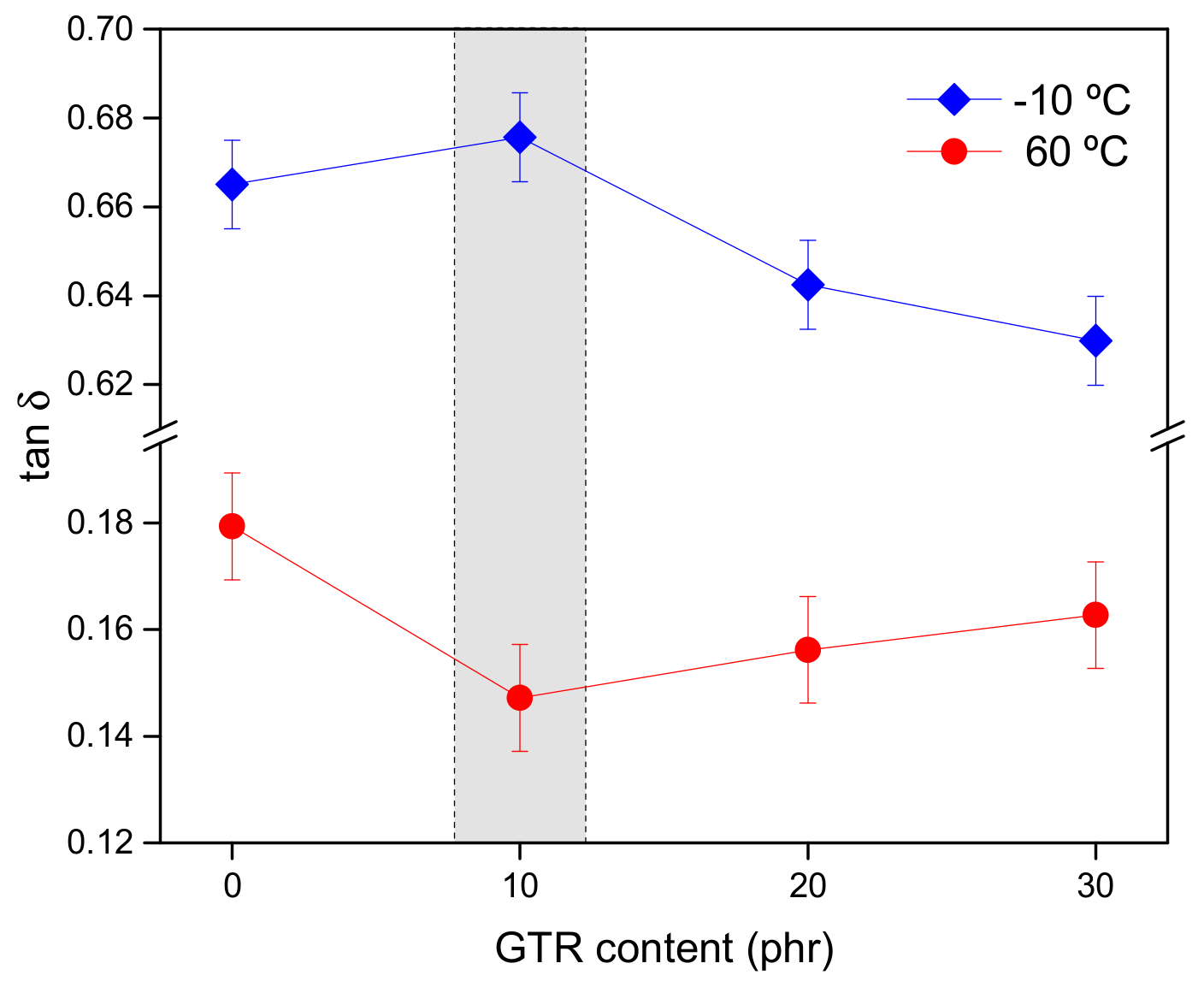
3.1.1. Dynamic-Mechanical Analysis
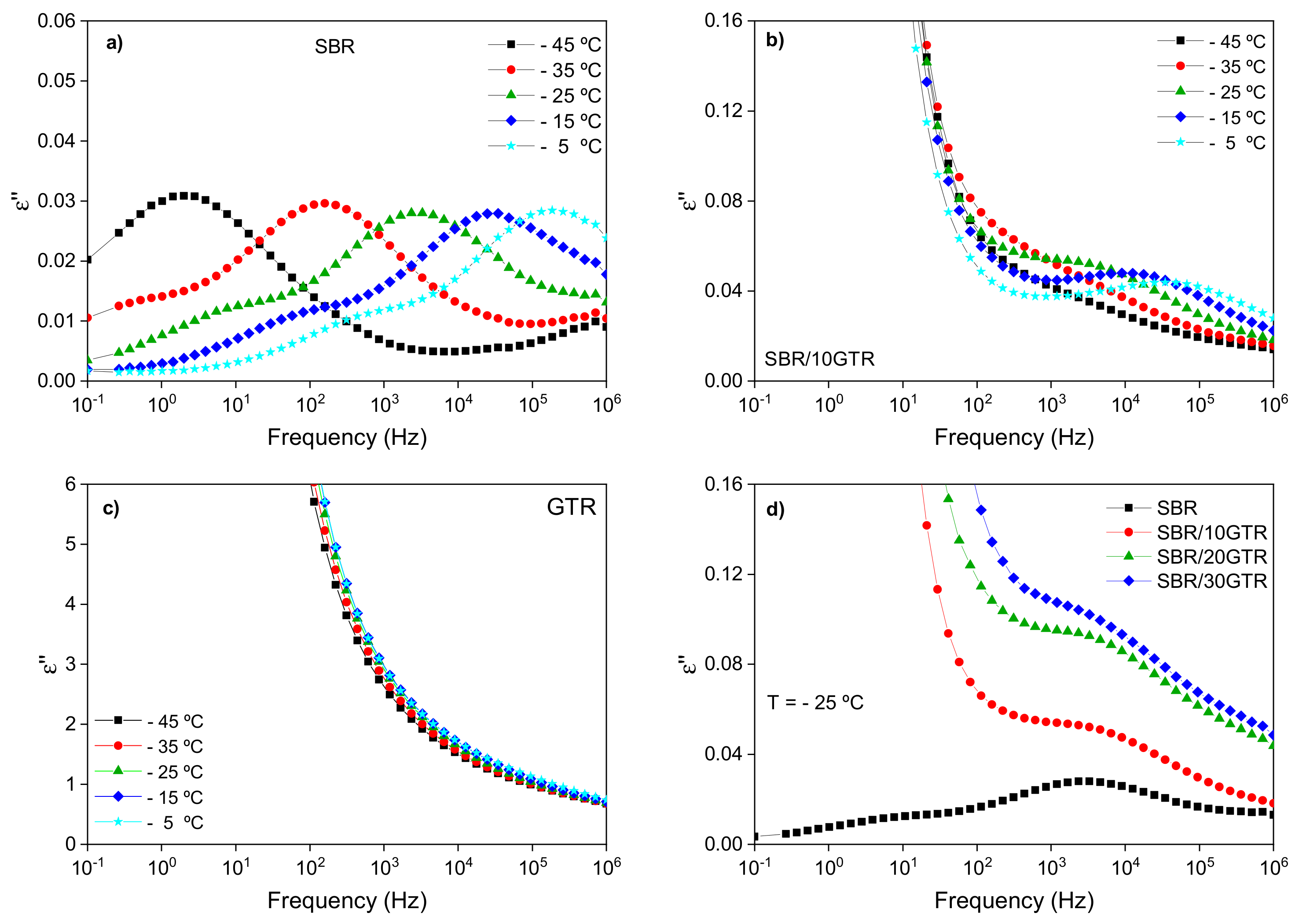
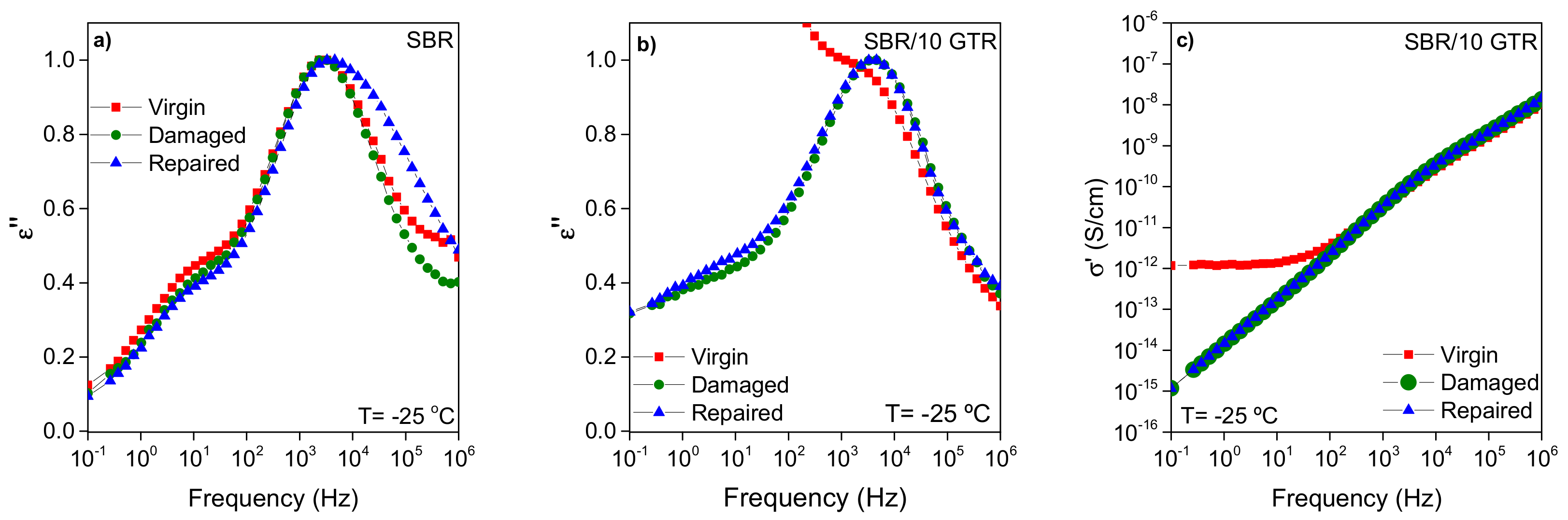
3.1.2. Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy (BDS) Analysis
3.2. Healing Performance of SBR/GTR Compounds
3.2.1. Correlating Dynamics and Structure with Healing
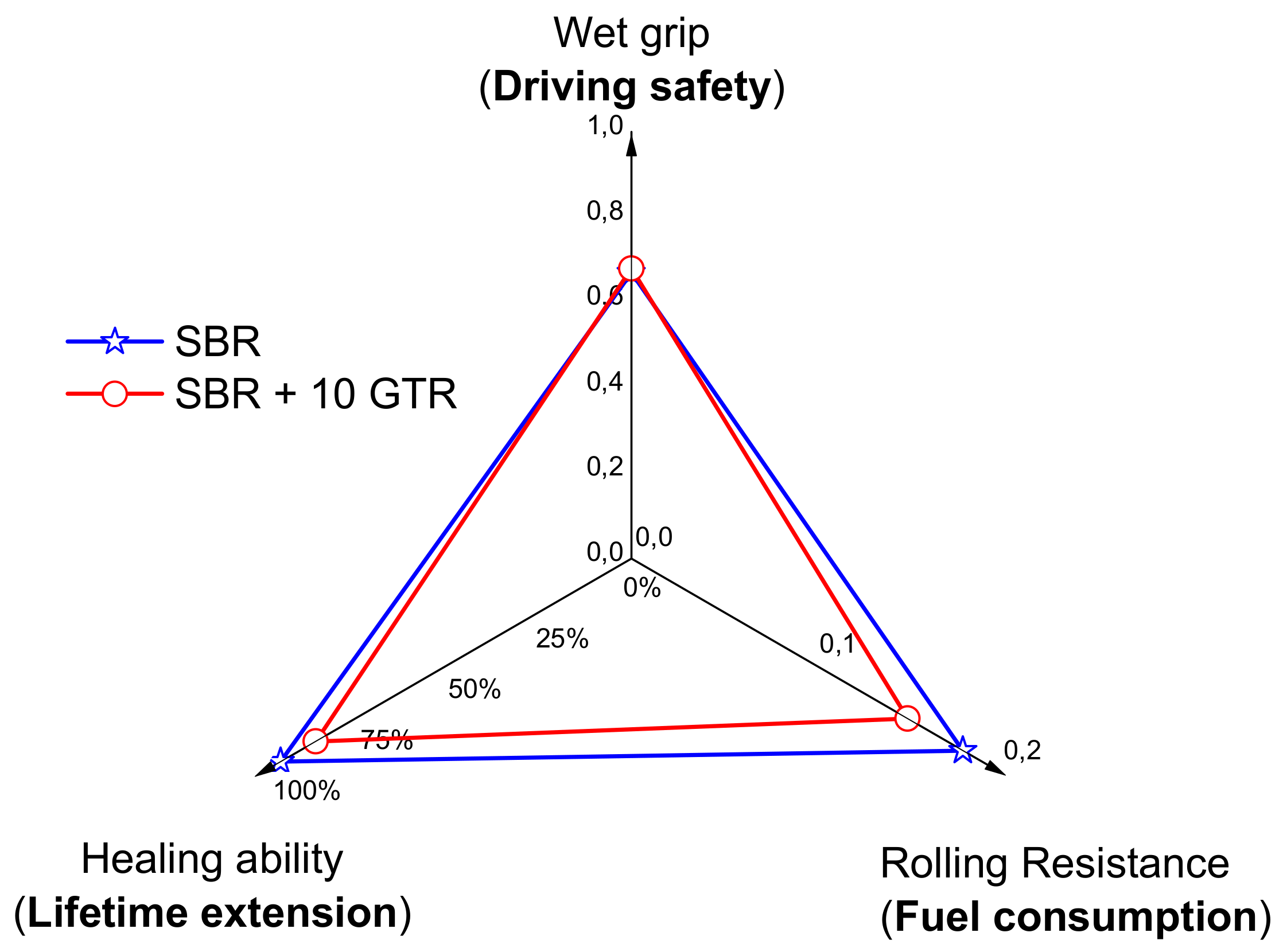
3.2.2. Healing as Part of the Magic Triangle of Tires
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asaro, L.; Gratton, M.; Seghar, S.; Hocine, N.A. Recycling of rubber wastes by devulcanization. Resour. Conserv. Rec. 2018, 133, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Hu, G.-H.; Hoppe, S. Devulcanization of waste tire rubber by microwaves. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2017, 138, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoudia, K.; Azem, S.; Hocine, N.A.; Gratton, M.; Pettarin, V.; Seghar, S. Recycling of waste tire rubber: Microwave devulcanization and incorporation in a thermoset resin. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sripornsawat, B.; Saiwari, S.; Nakason, C. Thermoplastic vulcanizates based on waste truck tire rubber and copolyester blends reinforced with carbon black. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramarad, S.; Khalid, M.; Ratnam, C.T.; Chuah, A.L.; Rashmi, W. Waste tire rubber in polymer blends: A review on the evolution, properties and future. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 72, 100–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockstal, L.; Berchem, T.; Schmetz, Q.; Richel, A. Devulcanisation and reclaiming of tires and rubber by physical and chemical processes: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, A.A.; Ismail, M.N.; Hefny, Y.A.; Abdel-Bary, E.M.; Mull, M.A. Mechano-chemical reclamation of waste rubber powder and its effect on the performance of NR and SBR vulcanizates. J. Elastom. Plast. 2004, 36, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Long, G.; Ma, C.; Fu, Q.; Zeng, X.; Ma, K.; Xie, Y.; Luo, B. Properties of self-compacting concrete (SCC) with recycled tire rubber aggregate: A comprehensive study. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.-J.; Zhou, T.; Luan, H.; Williams, R.C.; Wang, P.; Leng, Z. Composite modification mechanism of blended bio-asphalt combining styrene-butadiene-styrene with crumb rubber: A sustainable and environmental-friendly solution for wastes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 214, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lamminmäki, J.; Hanhi, K. Effect of ground rubber powder and devulcanizates on the properties of natural rubber compounds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoryeva, O.; Fainleib, A.; Starostenko, O.; Danilenko, I.; Kozak, N.; Dudarenko, G. Ground Tire Rubber (GTR) Reclamation: Virgin Rubber/Reclaimed GTR (RE)Vulcanizates. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2004, 77, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.H.; Huete, M.; Lameda, P.; Araujo, J.; Verdejo, R.; López-Manchado, M.A. Design of a new generation of sustainable SBR compounds with good trade-off between mechanical properties and self-healing ability. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 106, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbernon, L.; Norvez, S. From landfilling to vitrimer chemistry in rubber life cycle. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 82, 347–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cao, L.; Lin, B.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y. Design of Self-Healing Supramolecular Rubbers by Introducing Ionic Cross-Links into Natural Rubber via a Controlled Vulcanization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17728–17737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.P.; Rong, M.Z.; Zhang, M.Q. Self-healing, Reshaping, and Recycling of Vulcanized Chloroprene Rubber: A Case Study of Multitask Cyclic Utilization of Cross-linked Polymer. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2715–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.; Grande, A.M.; Dierkes, W.; Bijleveld, J.; van der Zwaag, S.; García, S.J. Turning Vulcanized Natural Rubber into a Self-Healing Polymer: Effect of the Disulfide/Polysulfide Ratio. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5776–5784. [Google Scholar]
- Santana, M.H.; den Brabander, M.; García, S.; van der Zwaag, S. Routes to Make Natural Rubber Heal: A Review. Polym. Rev. 2018, 58, 586–609. [Google Scholar]
- Tanasi, P.; Santana, M.H.; Carretero-González, J.; Verdejo, R.; López-Manchado, M.A. Thermo-reversible crosslinked natural rubber: A Diels-Alder route for reuse and self-healing properties in elastomers. Polymer 2019, 175, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.; Grande, A.M.; van der Zwaag, S.; Garcia, S.J. Monitoring Network and Interfacial Healing Processes by Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy: A Case Study on Natural Rubber. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10647–10656. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, V.; Unseld, K.; Fuchs, H.-B.; Blümich, B. Molecular dynamics of elastomers investigated by DMTA and the NMR-MOUSE®. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2002, 280, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, L.T.; Anastasiadis, S.H.; Giannelis, E.P. Dielectric study of Poly(styrene-co-butadiene) Composites with Carbon Black, Silica, and Nanoclay. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 6162–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, S.; Enke, M.; Hernández, M.; Bose, R.K.; Grande, A.M.; van der Zwaag, S.; Schubert, U.S.; García, S.J.; Hager, M.D. Characterization of Self-Healing Polymers: From Macroscopic Healing Tests to the Molecular Mechanism Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sattar, M.A.; Gangadharan, S.; Patnaik, A. Design of Dual Hybrid Network Natural Rubber–SiO2 Elastomers with Tailored Mechanical and Self-Healing Properties. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 10939–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Sancaktar, E. Use of fly ash as eco-friendly filler in synthetic rubber for tire applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, M. Recycling and Re-Use of Waste Rubber; Smithers Rapra: Shawbury, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Debapriya, D.; Debasish, D.; Singharoy, G. Reclaiming of ground rubber tire by a novel reclaiming agent. I. Virgin natural rubber/reclaimed GRT vulcanizates. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2007, 47, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Zedler, Ł.; Przybysz, M.; Klein, M.; Saeb, M.R.; Formela, K. Processing, physico-mechanical and thermal properties of reclaimed GTR and NBR/reclaimed GTR blends as function of various additives. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2017, 143, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debapriya, D.; Debasish, D. Processing and Material Characteristics of a reclaimed Ground Rubber Tire Reinforced Styrene Butadiene Rubber. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2011, 2, 486–496. [Google Scholar]
- Zefeng, W.; Yong, K.; Zhao, W.; Yi, C. Recycling waste tire rubber by water jet pulverization: Powder characteristics and reinforcing performance in natural rubber composites. J. Polym. Eng. 2017, 38, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-J. Effect of Polymer-Filler and Filler-Filler Interactions on Dynamic Properties of Filled Vulcanizates. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1998, 71, 520–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohjiya, S. Chemistry, Manufacture and Applications of Natural Rubber; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Gong, G.; Zheng, J.; Liang, T.; Yin, C.; Zhang, Q. Influence of Particle Type and Silane Coupling Agent on Properties of Particle-Reinforced Styrene-Butadiene Rubber. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-G.; Kim, H.S.; Cho, S.T.; Jung, I.T.; Cho, C.T. Characterization of Solution Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) Through the Evaluation of Static and Dynamic Mechanical Properties and Fatigue in Silica-Filled Compound. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 5251–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, T.R.; Bhandari, V.; Chandra, A.K.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Chattopadhyay, S. Role of calcium stearate as a dispersion promoter for new generation carbon black-organoclay based rubber nanocomposites for tyre application. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.C.; Adhikari, J.; Kim, J.K.; Saha, P. Preparation of novel bio-elastomers with enhanced interaction with silica filler for low rolling resistance and improved wet grip. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Tao, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Dong, M.; Zhang, L. Effect of the structural characteristics of solution styrene–butadiene rubber on the properties of rubber composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaptong, P.; Sae-oui, P.; Sirisinha, C. Influences of styrene butadiene rubber and silica types on performance of passenger car radial tire tread. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2017, 90, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujal-Rosas, R.; Orrit-Prat, J.; Ramis-Juan, X.; Marin-Genesca, M.; Rahhali, A. Dielectric properties of various polymers (PVC, EVA, HDPE and PP) reinforced with used tires (GTR). Afinidad 2011, 68, 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Klüppel, M.; Schuster, R.H.; Schaper, J. Carbon black distribution in rubber blends: A dynamic-mechanical analysis. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1999, 72, 91–108. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, N.; Ito, M.; Yatsuyanagi, F. Effects of rubber/filler interactions on deformation behavior of silica filled SBR systems. Polymer 2005, 46, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marckmann, G.; Verron, E.; Gornet, L.; Chagnon, G.; Charrier, P.; Fort, P. A theory of network alteration for the Mullins effect. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2002, 50, 2011–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diani, J.; Fayolle, B.; Gilormini, P. A review on the Mullins effect. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.; Diani, J.; Gilormini, P. Physical interpretation of the Mullins softening in a carbon-black filled SBR. Polymer 2014, 55, 4942–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Dillard, D.A.; West, R.L.; Lower, L.D.; Gordon, G.V. Mullins effect recovery of a nanoparticle-filled polymer. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wool, R.P.; Oconnor, K.M. A Theory of Crack Healing in Polymers. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 5953–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, F.; Montarnal, D.; Cantournet, S.; Tournilhac, F.; Corte, L.; Leibler, L. Activation and deactivation of self-healing in supramolecular rubbers. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, M.A.; Esteves, C.; van der Zwaag, S.; Garcia, S.J. Healable dual organic-inorganic crosslinked sol-gel based polymers: Crosslinking density and tetrasulfide content effect. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2014, 52, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar]
- Canadell, J.; Goossens, H.; Klumperman, B. Self-Healing Materials Based on Disulfide Links. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 2536–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönhals, A.; Schlosser, E. Dielectric relaxation in polymeric solids Part 1. A new model for the interpretation of the shape of the dielectric relaxation function. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1989, 267, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Susa, A.; Bijleveld, J.; Santana, M.H.; Garcia, S.J. Understanding the Effect of the Dianhydride Structure on the Properties of Semiaromatic Polyimides Containing a Biobased Fatty Diamine. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Meng, Y.; Li, Y. Electric heating behavior of flexible graphene/natural rubber conductor with self-healing conductive network. Mater. Lett. 2017, 192, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, G.; Childers, C.W.; Rollmann, K.W. Stress softening in carbon black-reinforced vulcanizates. Strain rate and temperature effects. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1966, 10, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredients(phr) | Compound | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBR | SBR/10GTR | SBR/20GTR | SBR/30GTR | |
| SBR | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| ZnO | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| SA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| CBS | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 |
| S | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 |
| TESPT | 0 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Cryo-grounded GTR | 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araujo-Morera, J.; Hernández Santana, M.; Verdejo, R.; López-Manchado, M.A. Giving a Second Opportunity to Tire Waste: An Alternative Path for the Development of Sustainable Self-Healing Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Compounds Overcoming the Magic Triangle of Tires. Polymers 2019, 11, 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122122
Araujo-Morera J, Hernández Santana M, Verdejo R, López-Manchado MA. Giving a Second Opportunity to Tire Waste: An Alternative Path for the Development of Sustainable Self-Healing Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Compounds Overcoming the Magic Triangle of Tires. Polymers. 2019; 11(12):2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122122
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraujo-Morera, Javier, Marianella Hernández Santana, Raquel Verdejo, and Miguel Angel López-Manchado. 2019. "Giving a Second Opportunity to Tire Waste: An Alternative Path for the Development of Sustainable Self-Healing Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Compounds Overcoming the Magic Triangle of Tires" Polymers 11, no. 12: 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122122
APA StyleAraujo-Morera, J., Hernández Santana, M., Verdejo, R., & López-Manchado, M. A. (2019). Giving a Second Opportunity to Tire Waste: An Alternative Path for the Development of Sustainable Self-Healing Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Compounds Overcoming the Magic Triangle of Tires. Polymers, 11(12), 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122122