Humidity-Induced Phase Transitions of Surfactants Embedded in Latex Coatings Can Drastically Alter Their Water Barrier and Mechanical Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Latex Coatings
2.2. Pendulum Hardness
2.3. Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM-D)
Data Analysis
2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
3. Results
3.1. Pendulum Hardness
3.2. Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM-D)
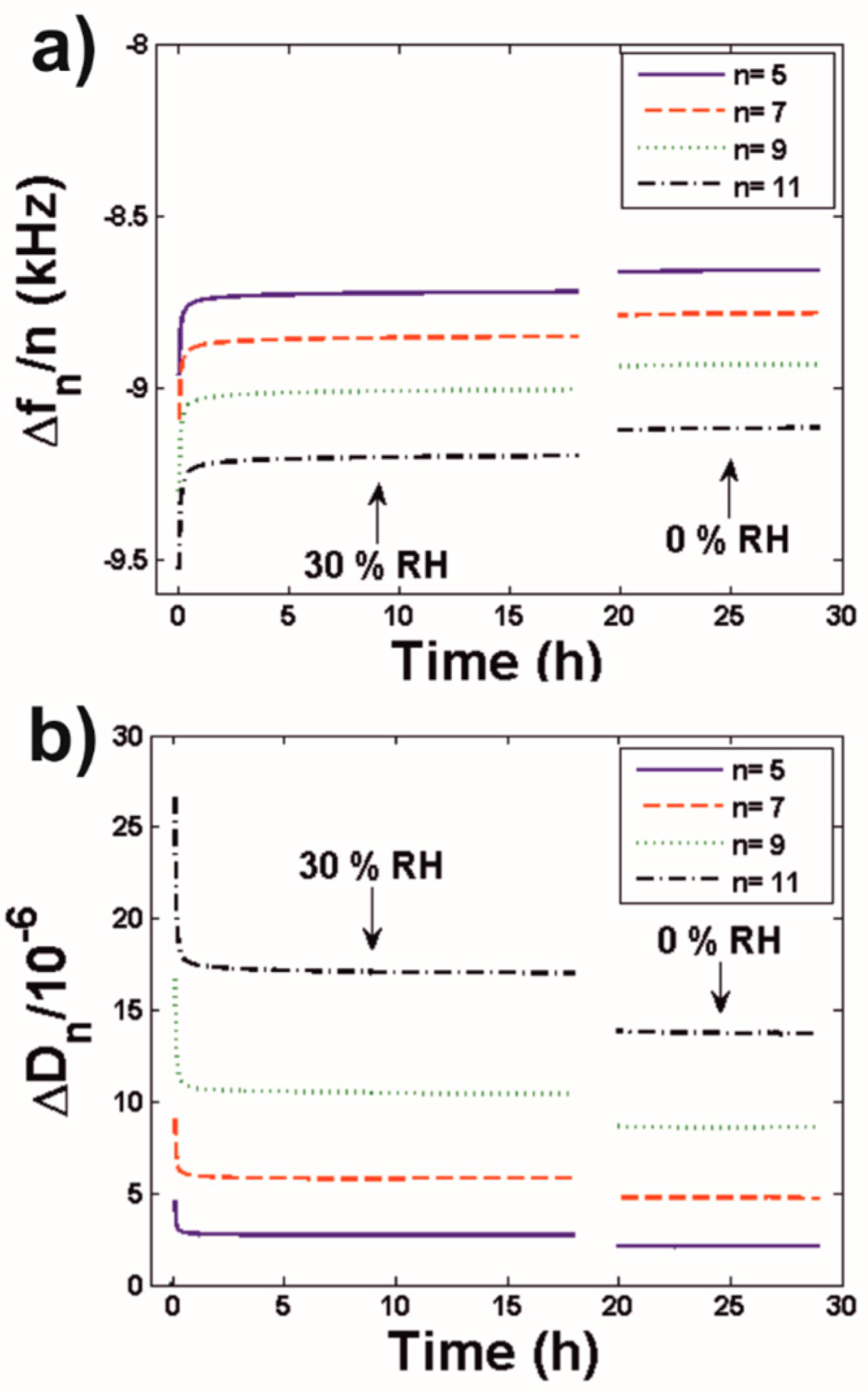
3.2.1. Latex Film Formation
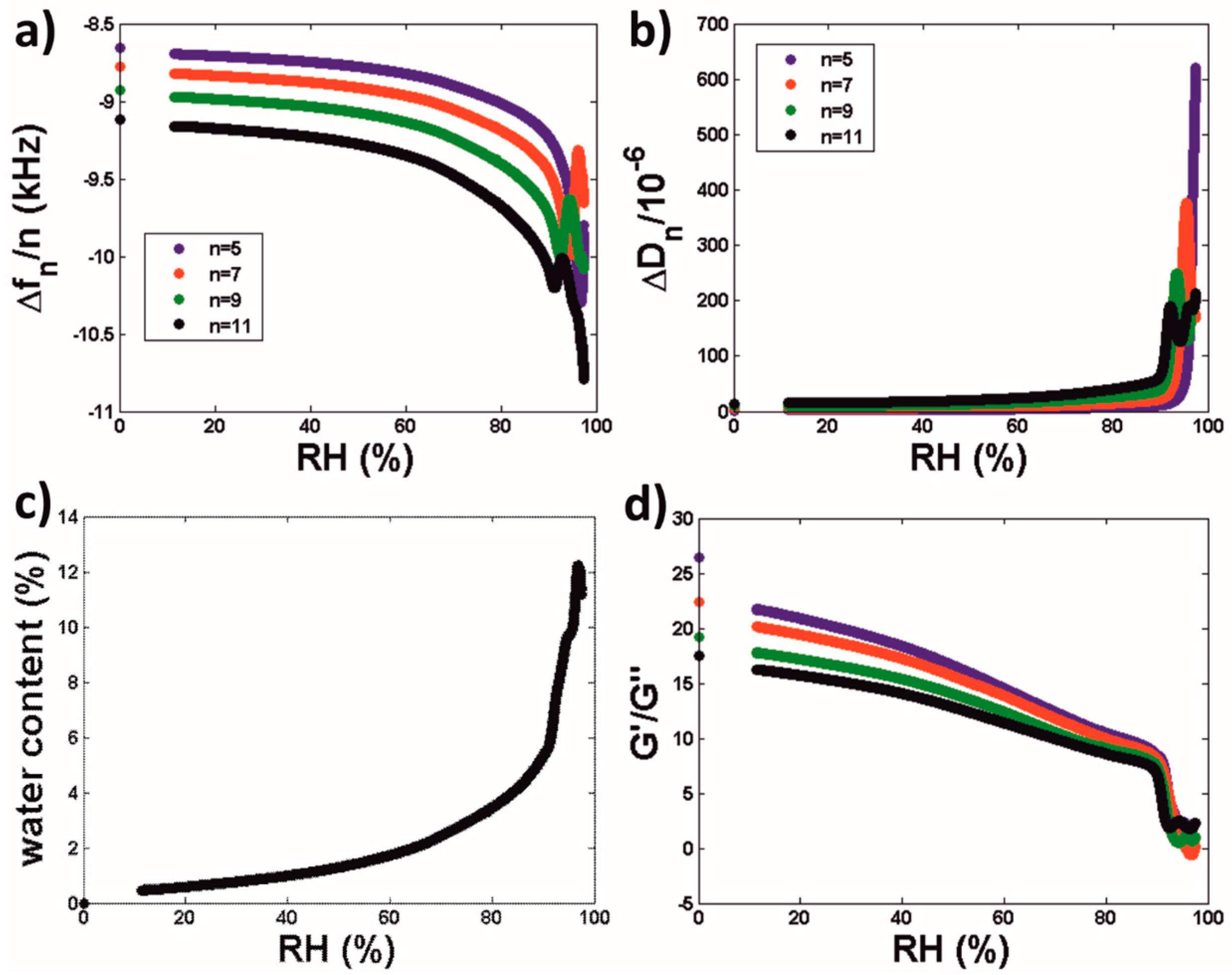
3.2.2. Water Sorption Isotherms of Latex Coatings
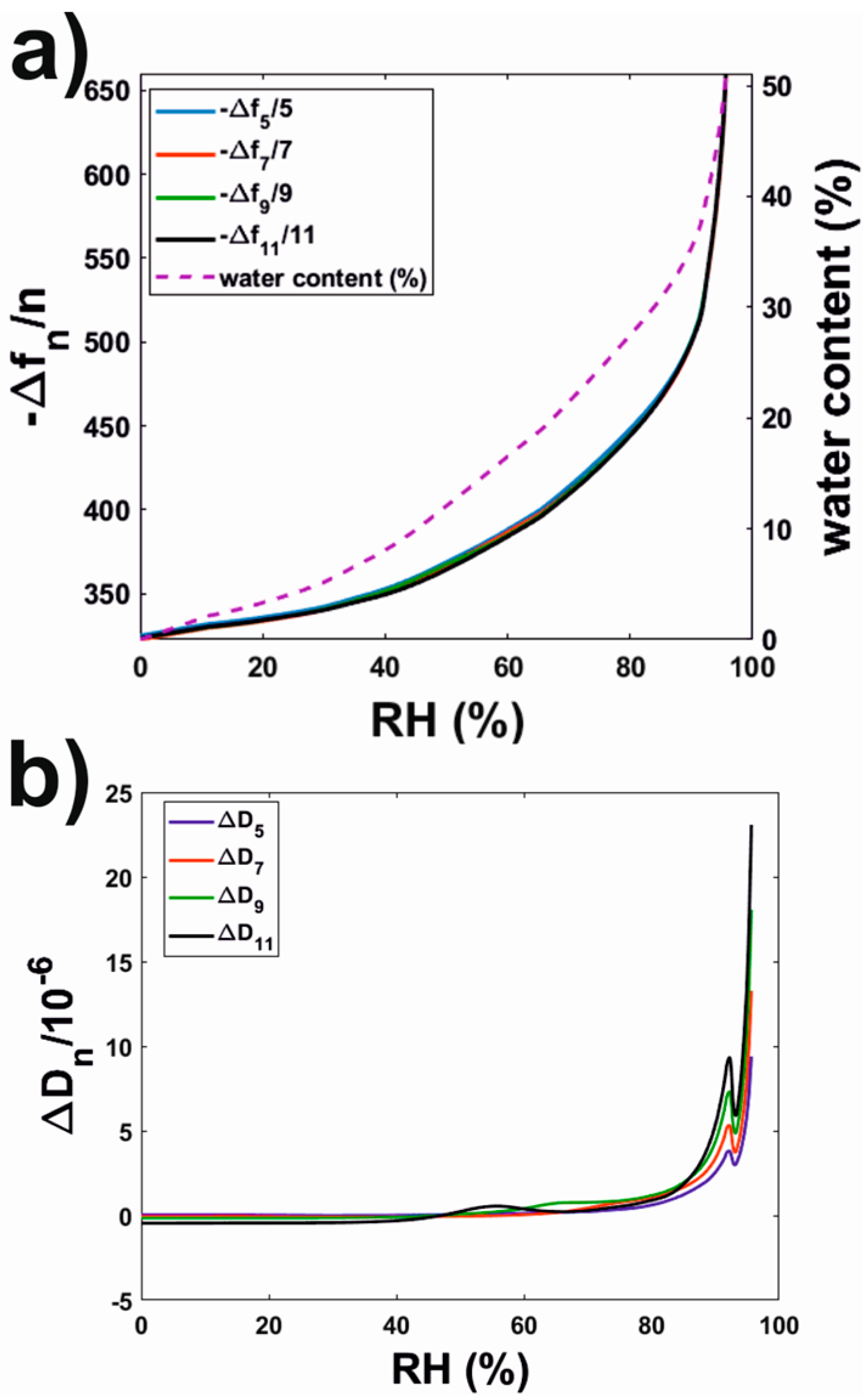
3.2.3. Water Sorption Isotherms of Rhodacal® DSB Films
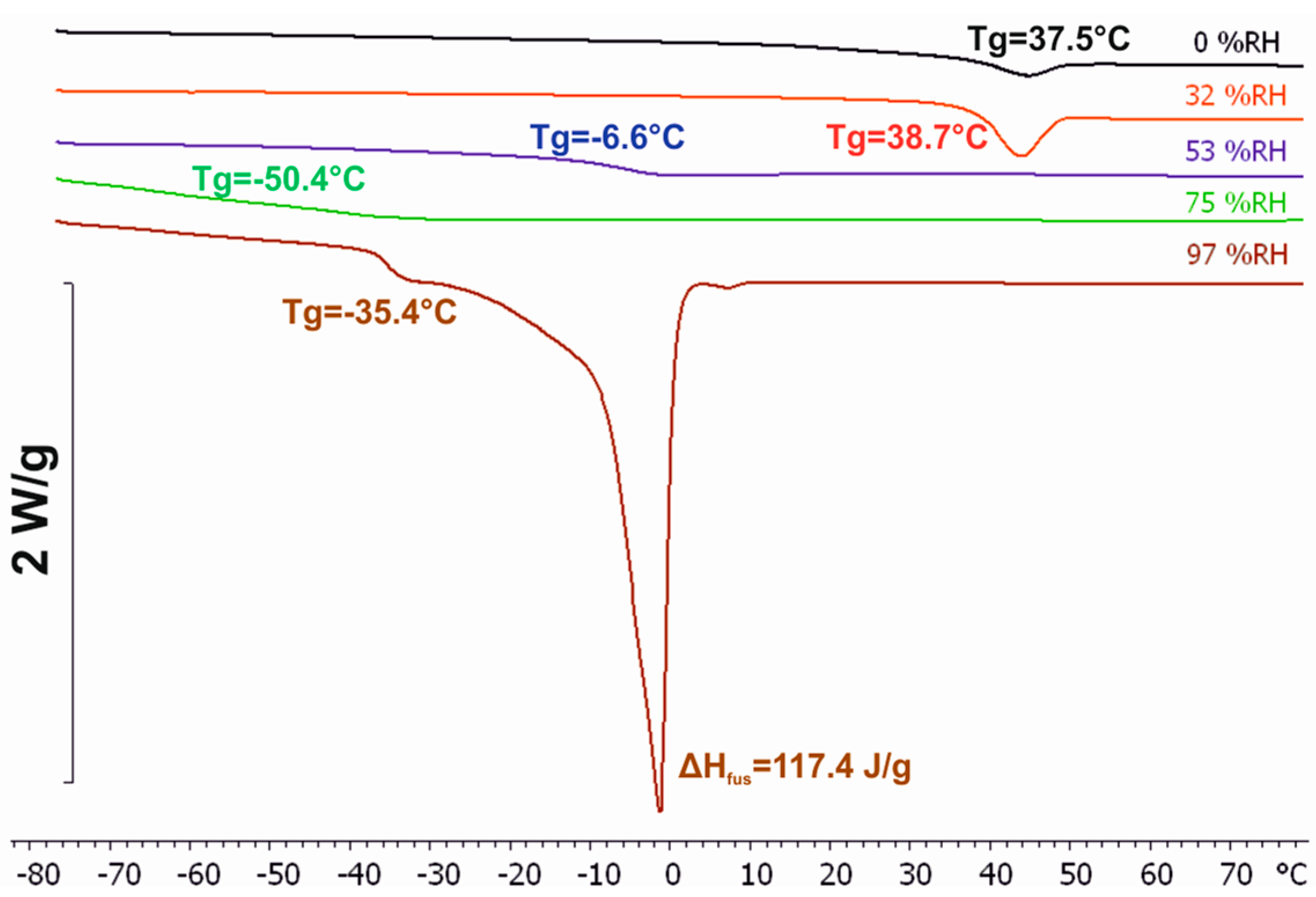
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
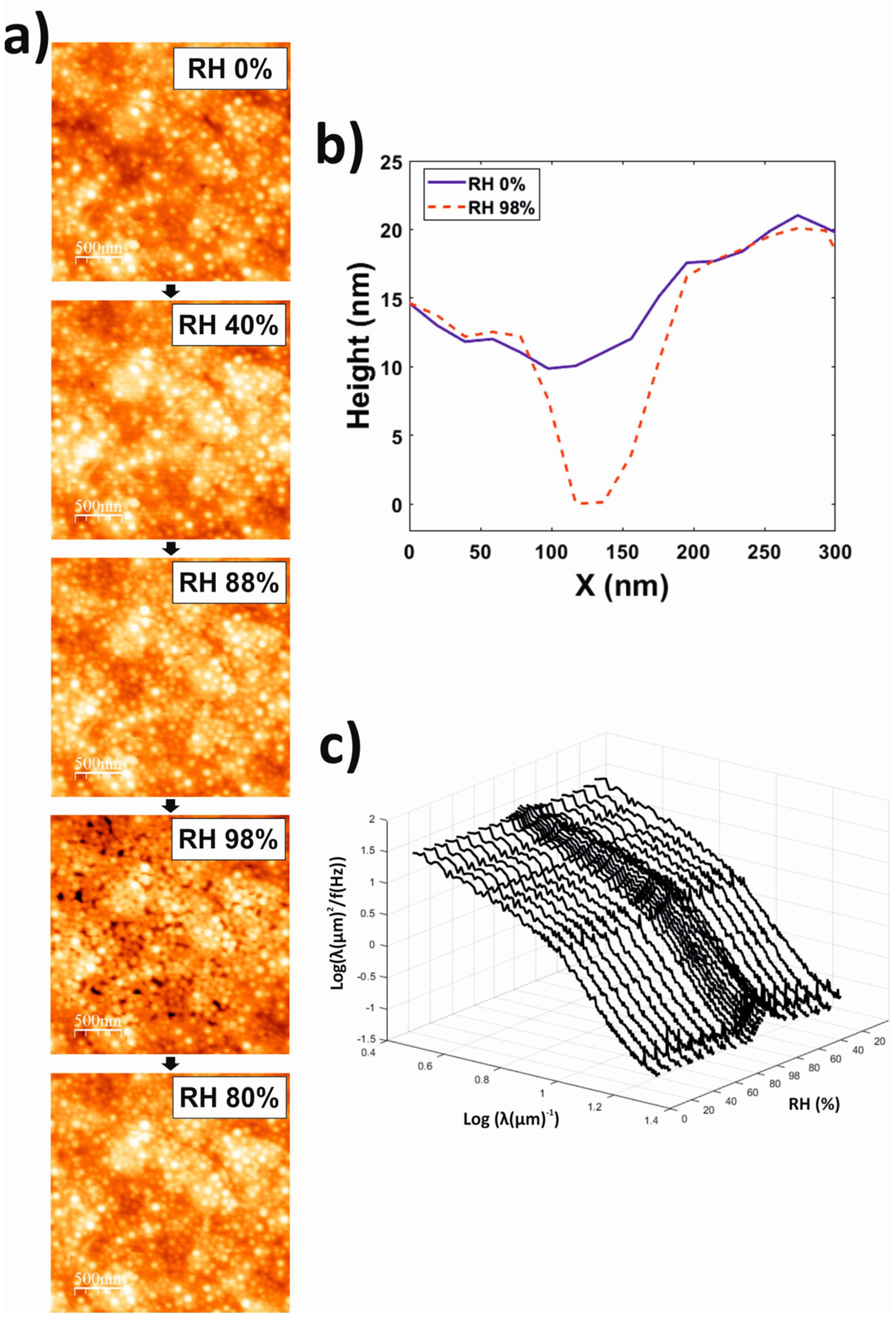
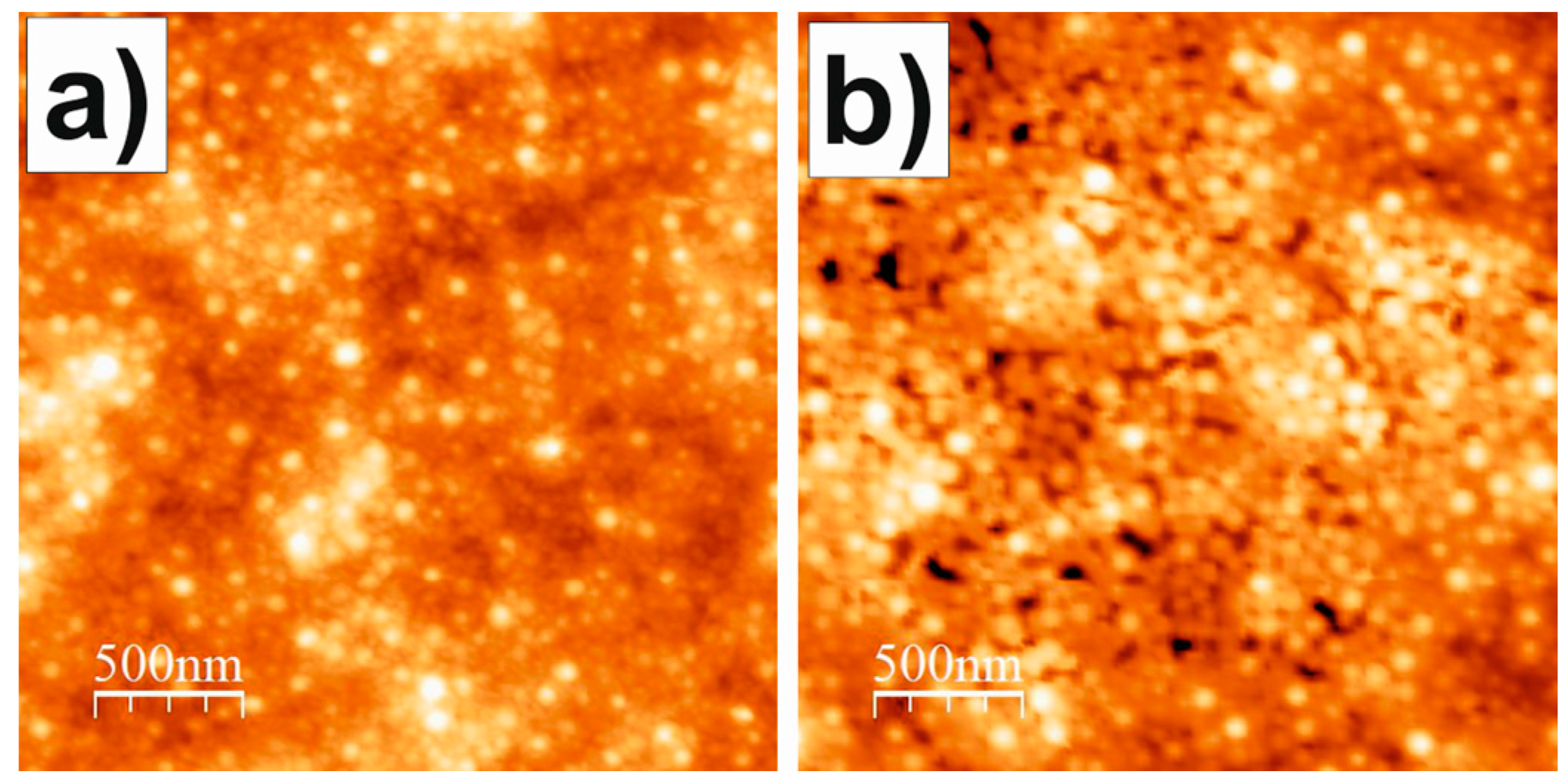
3.4. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keddie, J.L.; Routh, A.F. Fundamentals of Latex Film Formation: Processes and Properties; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hellgren, A.-C.; Weissenborn, P.; Holmberg, K. Surfactants in water-borne paints. Prog. Org. Coat. 1999, 35, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.; Klein, G.; Maaloum, M.; Ernstsson, M.; Larsson, A.; Marie, P.; Holl, Y. Surfactant distribution in waterborne acrylic films: 2. Surface investigation. Colloids Surf. A 2011, 374, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.; Thalmann, F.; Marques, C.; Marie, P.; Holl, Y. Surfactant Distribution in Waterborne Acrylic Films. 1. Bulk Investigation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 9135–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromer, A.; Thalmann, F.; Hébraud, P.; Holl, Y. Simulation of Vertical Surfactant Distributions in Drying Latex Films. Langmuir 2017, 33, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.H.; Dong, J.; Severtson, S.J.; Houtman, C.J.; Gwin, L.E. Modifications of Surfactant Distributions and Surface Morphologies in Latex Films Due to Moisture Exposure. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 10189–10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, L.N.; Fellows, C.M.; Gilbert, R.G. Effect of surfactants used for binder synthesis on the properties of latex paints. Prog. Org. Coat. 2005, 53, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asua, J.M.; Schoonbrood, H.A.S. Reactive surfactants in heterophase polymerisation. Acta Polym. 1998, 49, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, E.; Hayes, J.; Learner, T.; Golden, M. Conservation concerns for acrylic emulsion paints. Rev. Conserv. 2003, 4, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gajewicz, A.M.; Rodin, V.; Soer, W.-J.; Scheerder, J.; Satgurunathan, G.; Mcdonald, P.J.; Keddie, J.L. Explanations for water whitening in secondary dispersion and emulsion polymer films. J. Polym. Sci. B 2016, 54, 1658–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kats, A.; Juhue, D.; Winnik, M.A.; Shivers, R.R.; Dinsdale, C.J. Freeze-fracture studies of latex films formed in the absence and presence of surfactant. Langmuir 1992, 8, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-L.; Holl, Y.; Pith, T.; Lambla, M. Surface analysis and adhesion properties of coalesced latex films. Br. Polym. J. 1989, 21, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, L.N.; Fellows, C.M.; Gilbert, R.G. Effect of surfactant systems on the water sensitivity of latex films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward, P.A.; Hearn, J.; Wilkinson, M.C. Studies on permeation through polymer latex films, I. Films containing no or only low levels of additives. Polym. Int. 1995, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckersley, S.T.; Rudin, A. The effect of plasticization and pH on film formation of acrylic latexes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1993, 48, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Tsavalas, J.; Sundberg, D. Measuring the Glass Transition of Latex-Based Polymers in the Hydroplasticized State via Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Langmuir 2010, 26, 9408–9415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsavalas, J.G.; Sundberg, D.C. Hydroplasticization of Polymers: Model Predictions and Application to Emulsion Polymers. Langmuir 2010, 26, 6960–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodahl, M.; Hook, F.; Fredriksson, C.; Keller, C.A.; Krozer, A.; Brzezinski, P.; Voinova, M.; Kasemo, B. Simultaneous frequency and dissipation factor QCM measurements of biomolecular adsorption and cell adhesion. Faraday Discuss. 1997, 107, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodahl, M.; Höök, F.; Krozer, A.; Brzezinski, P.; Kasemo, B. Quartz crystal microbalance setup for frequency and Q-factor measurements in gaseous and liquid environments. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1995, 66, 3924–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, S.; Kocherbitov, V. Humidity scanning quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring setup for determination of sorption-desorption isotherms and rheological changes. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2015, 86, 055105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, G.; Kocherbitov, V. Determination of Sorption Isotherm and Rheological Properties of Lysozyme Using a High-Resolution Humidity Scanning QCM-D Technique. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 10017–10026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, R.A. The water activities of lithium chloride solutions up to high concentrations at 25°. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1945, 41, 756–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauerbrey, G. Verwendung von schwingquarzen zur wägung dünner schichten und zur mikrowägung. Z. Phys. A 1959, 155, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsmann, D. Viscoelastic Analysis of Organic Thin Films on Quartz Resonators. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1999, 200, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znamenskaya, Y.; Sotres, J.; Gavryushov, S.; Engblom, J.; Arnebrant, T.; Kocherbitov, V. Water Sorption and Glass Transition of Pig Gastric Mucin Studied by QCM-D. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 2554–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenspan, L. Humidity Fixed Points of Binary Saturated Aqueous Solutions. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. Sect. A 1977, 81, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcas, I.; Fernández, R.; Gómez-Rodríguez, J.M.; Colchero, J.; Gómez-Herrero, J.; Baro, A.M. WSXM: A software for scanning probe microscopy and a tool for nanotechnology. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 78, 013705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, D.J.; Thielmann, F.; Booth, J. Determining the critical relative humidity for moisture-induced phase transitions. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 287, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González Martínez, J.F.; Nieto-Carvajal, I.; Abad, J.; Colchero, J. Nanoscale measurement of the power spectral density of surface roughness: How to solve a difficult experimental challenge. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.J. Wood Handbook: Wood as an Engineering Material; General Technical Report FPL-GTR-190; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory: Madison, WI, USA, 2010.
- Immergut, E.H.; Mark, H.F. Principles of Plasticization. In Plasticization and Plasticizer Processes; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Denolf, G.C.; Haack, L.; Holubka, J.; Straccia, A.; Blohowiak, K.; Broadbent, C.; Shull, K.R. High Frequency Rheometry of Viscoelastic Coatings with the Quartz Crystal Microbalance. Langmuir 2011, 27, 9873–9879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denolf, G.C.; Sturdy, L.F.; Shull, K.R. High-Frequency Rheological Characterization of Homogeneous Polymer Films with the Quartz Crystal Microbalance. Langmuir 2014, 30, 9731–9740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellgren, A.C.; Wallin, M.; Weissenborn, P.K.; Mcdonald, P.J.; Glover, P.M.; Keddie, J.L. New techniques for determining the extent of crosslinking in coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2001, 43, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, S.; Kocherbitov, V. Hydration-Induced Phase Transitions in Surfactant and Lipid Films. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5223–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Equilibration RH | # Oscillations (König Hardness) Equilibration Period 7 days | # Oscillations (König Hardness) Equilibration Period 14 days |
|---|---|---|
| 50% | 60.5 ± 0.7 | 63.5 ± 0.7 |
| 100% | 43.0 ± 4.2 | 35.0 ± 7.1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzalez-Martinez, J.F.; Znamenskaya Falk, Y.; Björklund, S.; Erkselius, S.; Rehnberg, N.; Sotres, J. Humidity-Induced Phase Transitions of Surfactants Embedded in Latex Coatings Can Drastically Alter Their Water Barrier and Mechanical Properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030284
Gonzalez-Martinez JF, Znamenskaya Falk Y, Björklund S, Erkselius S, Rehnberg N, Sotres J. Humidity-Induced Phase Transitions of Surfactants Embedded in Latex Coatings Can Drastically Alter Their Water Barrier and Mechanical Properties. Polymers. 2018; 10(3):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030284
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzalez-Martinez, Juan F., Yana Znamenskaya Falk, Sebastian Björklund, Stefan Erkselius, Nicola Rehnberg, and Javier Sotres. 2018. "Humidity-Induced Phase Transitions of Surfactants Embedded in Latex Coatings Can Drastically Alter Their Water Barrier and Mechanical Properties" Polymers 10, no. 3: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030284
APA StyleGonzalez-Martinez, J. F., Znamenskaya Falk, Y., Björklund, S., Erkselius, S., Rehnberg, N., & Sotres, J. (2018). Humidity-Induced Phase Transitions of Surfactants Embedded in Latex Coatings Can Drastically Alter Their Water Barrier and Mechanical Properties. Polymers, 10(3), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030284






