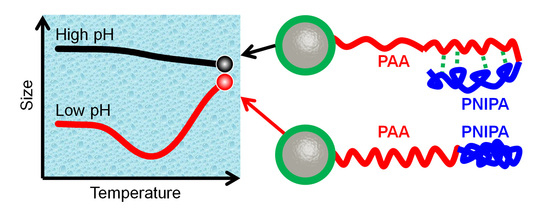
Conformation Study of Dual Stimuli-Responsive Core-Shell Diblock Polymer Brushes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
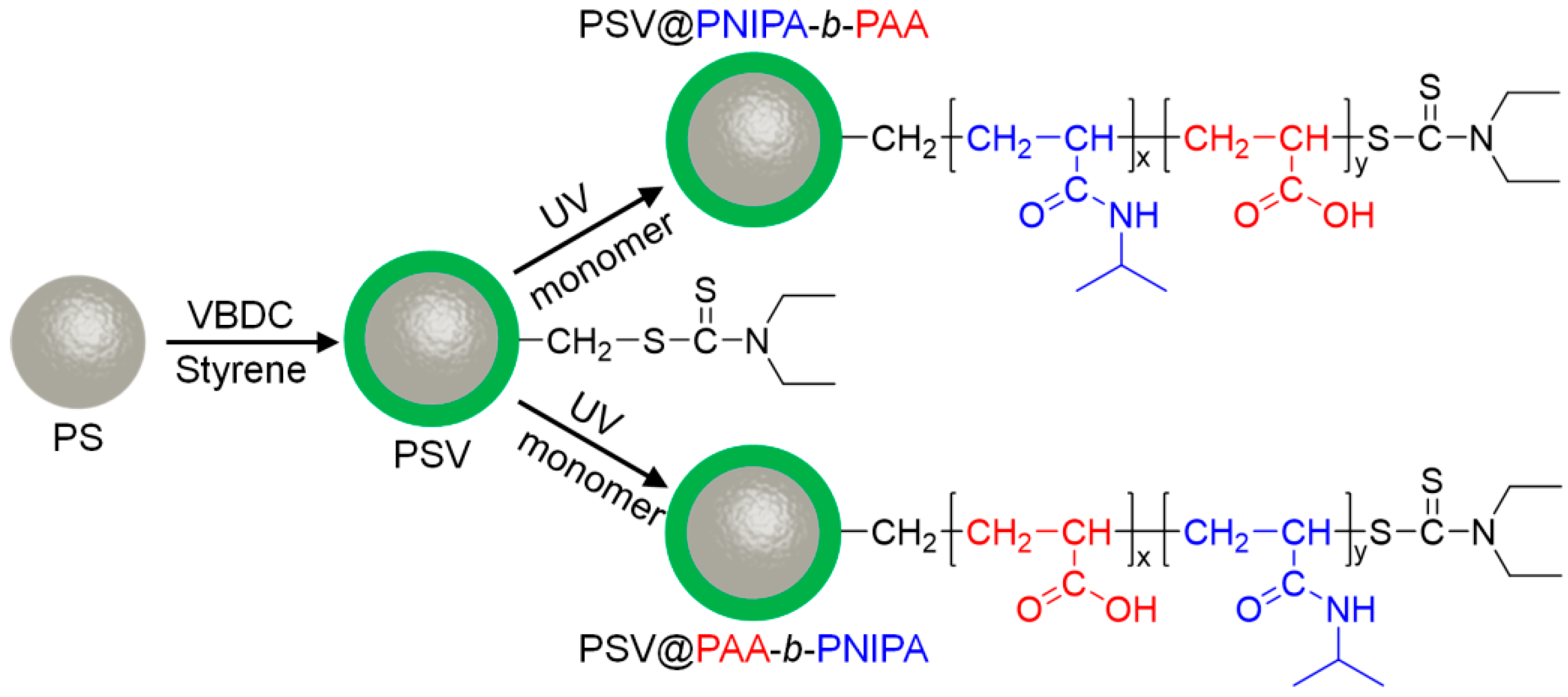
2.2. Synthesis of Active PSV (PS Cores with Photoiniferter VBDC)
2.3. Synthesis of Diblock Polymer Brushes (PSV@PNIPA-b-PAA, and PSV@PAA-b-PNIPA)
2.4. Characterization
2.4.1. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.4.2. Turbidimetric Titration (Turbidimetry)
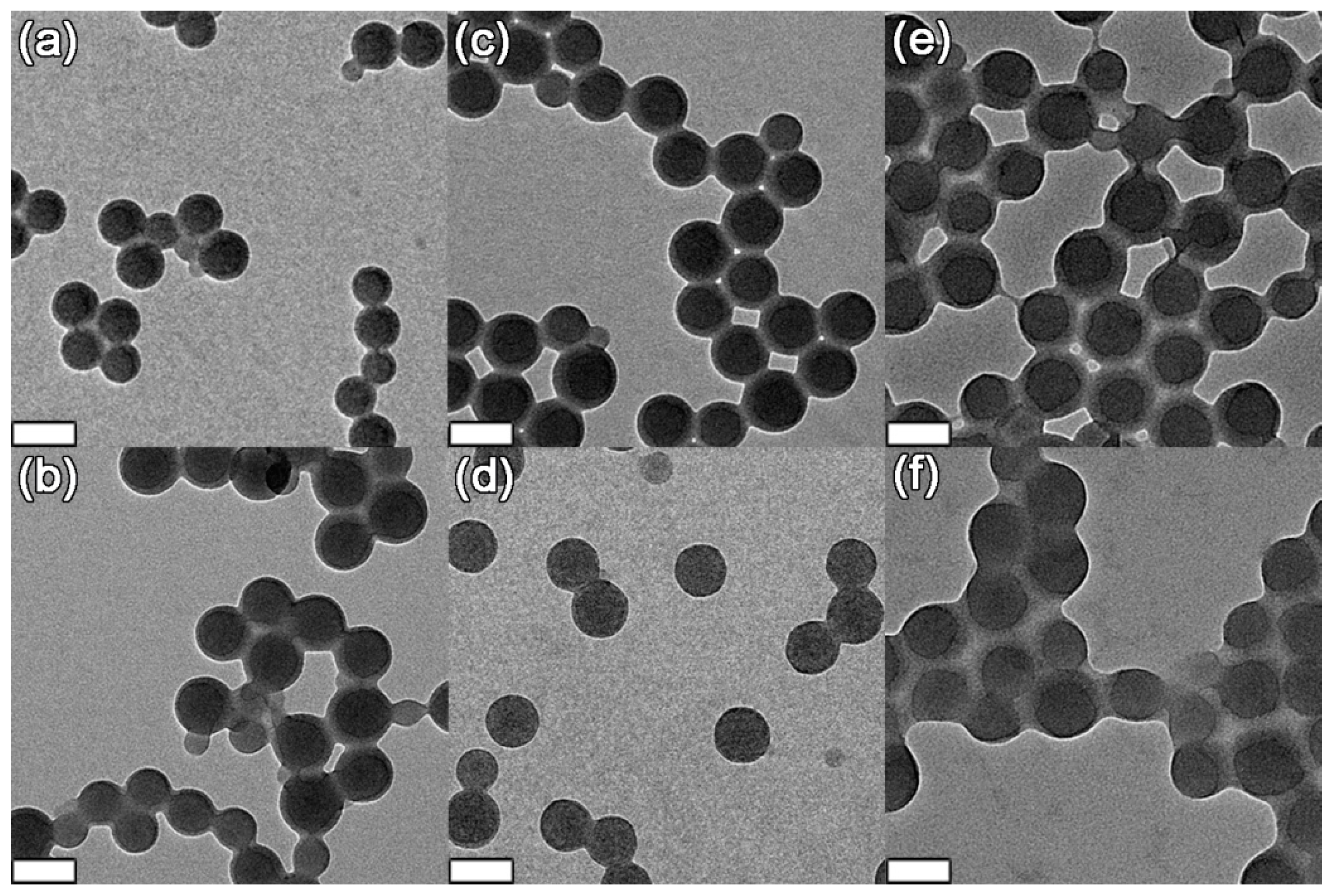
2.4.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Size of Core-shell Diblock Polymer Brushes
3.2. Stimuli-Responsive Properties
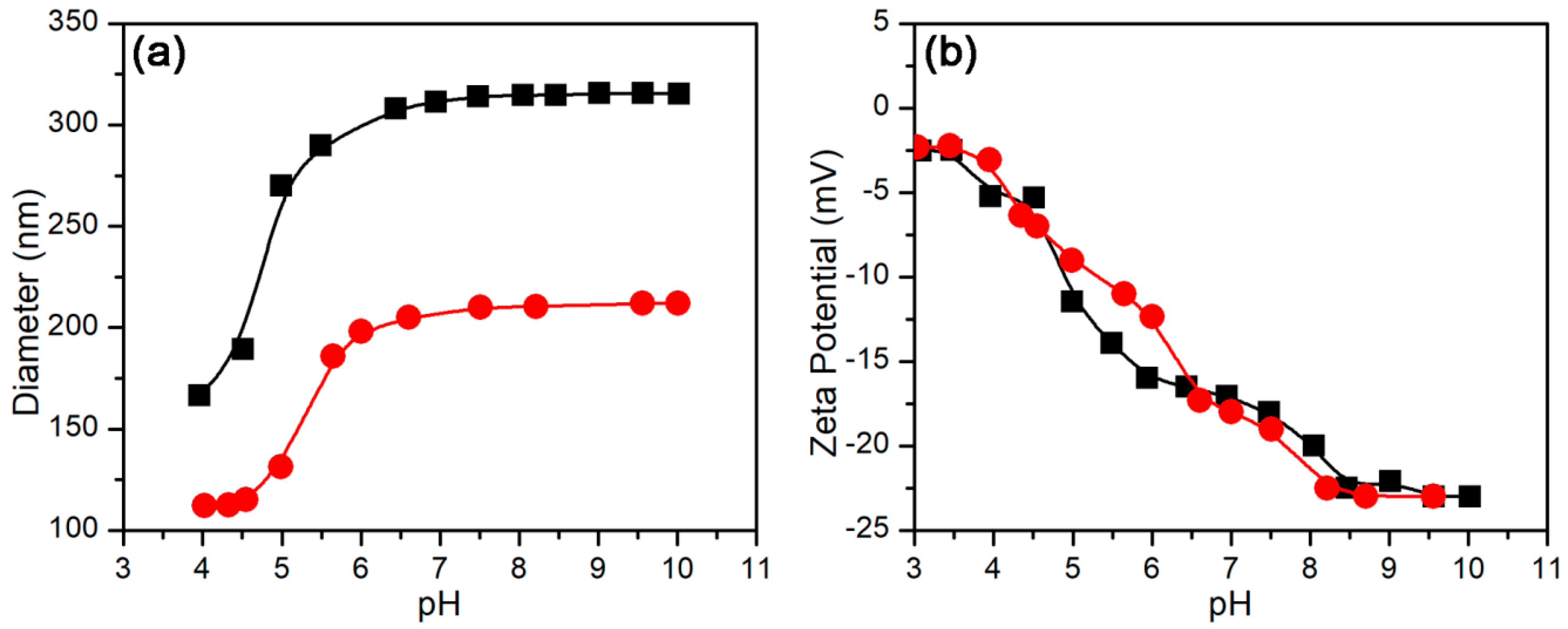
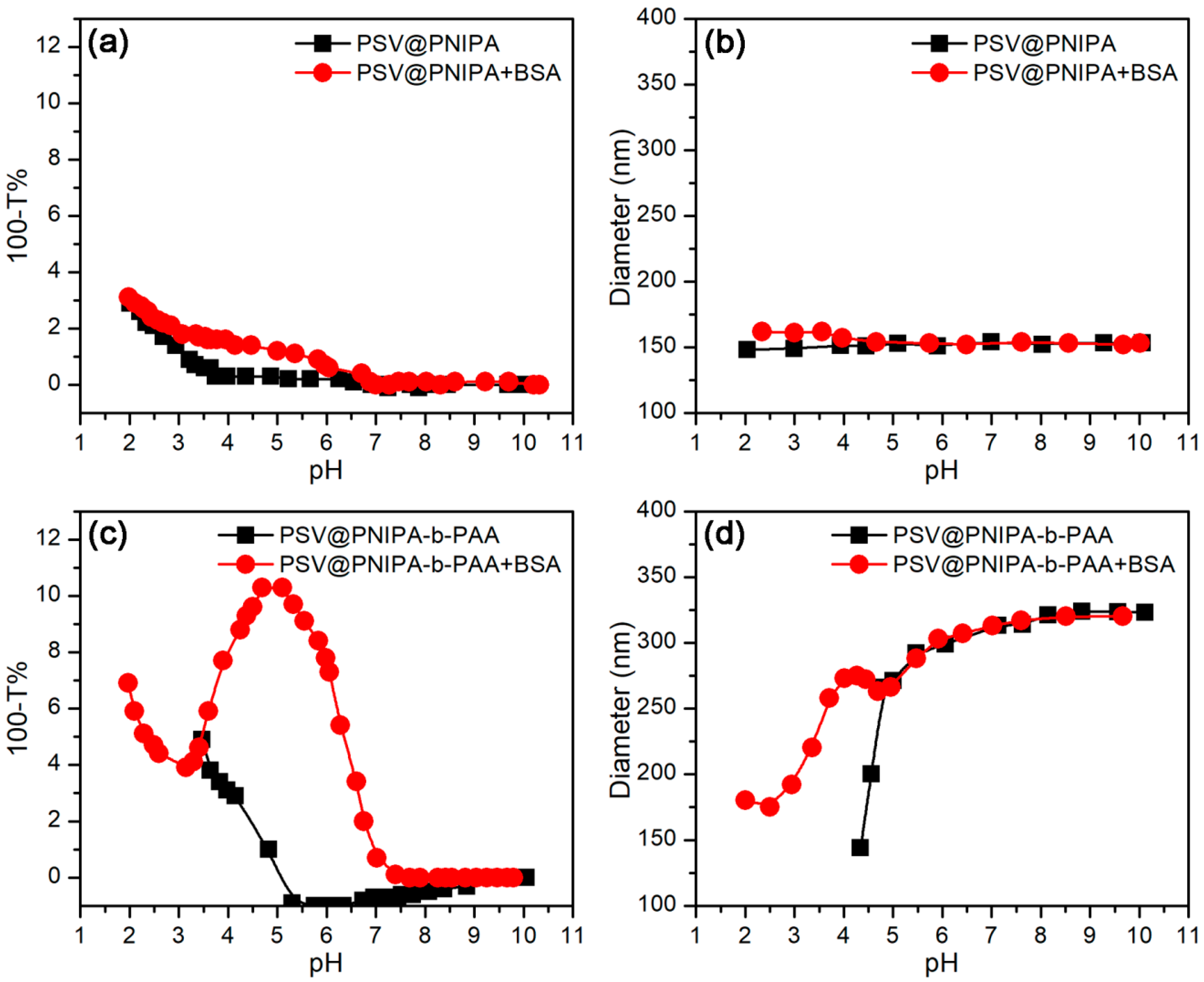
3.2.1. pH-Stimulus Response
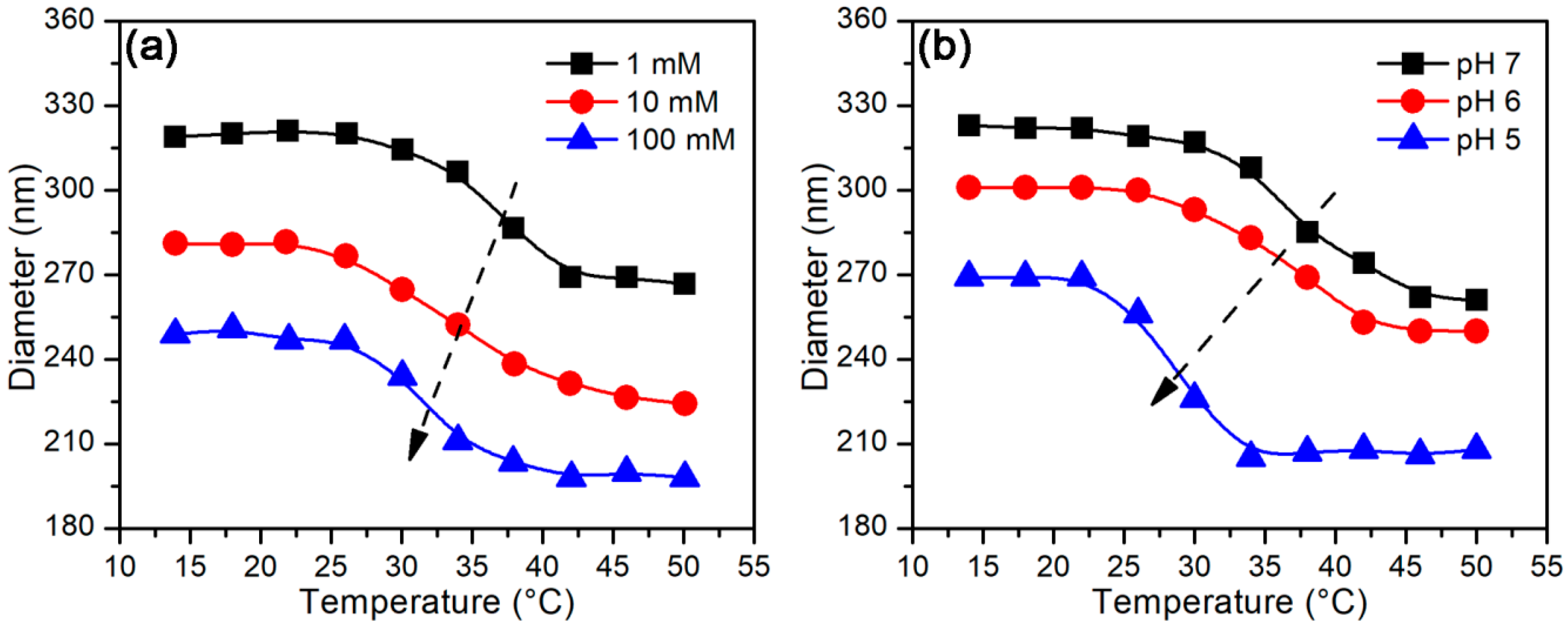
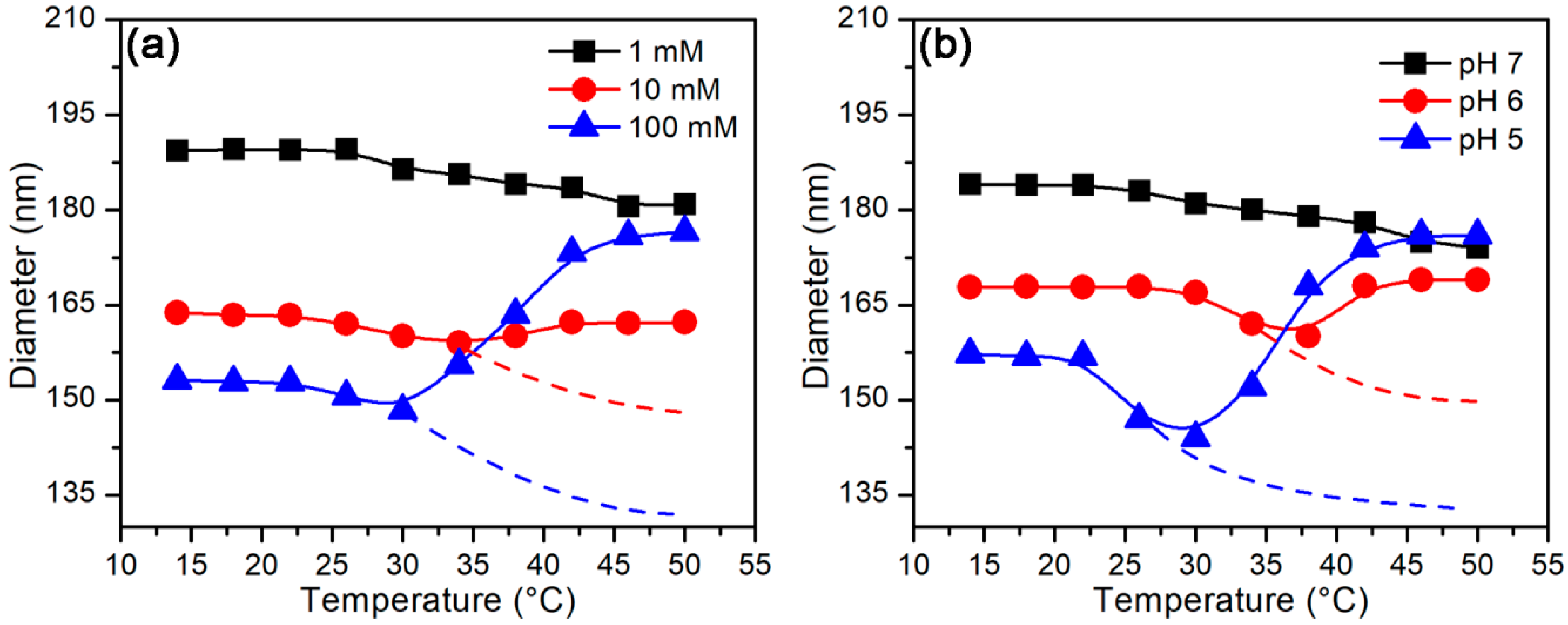
3.2.2. Temperature-Stimulus Response
3.3. Protein Adsorption Behaviors
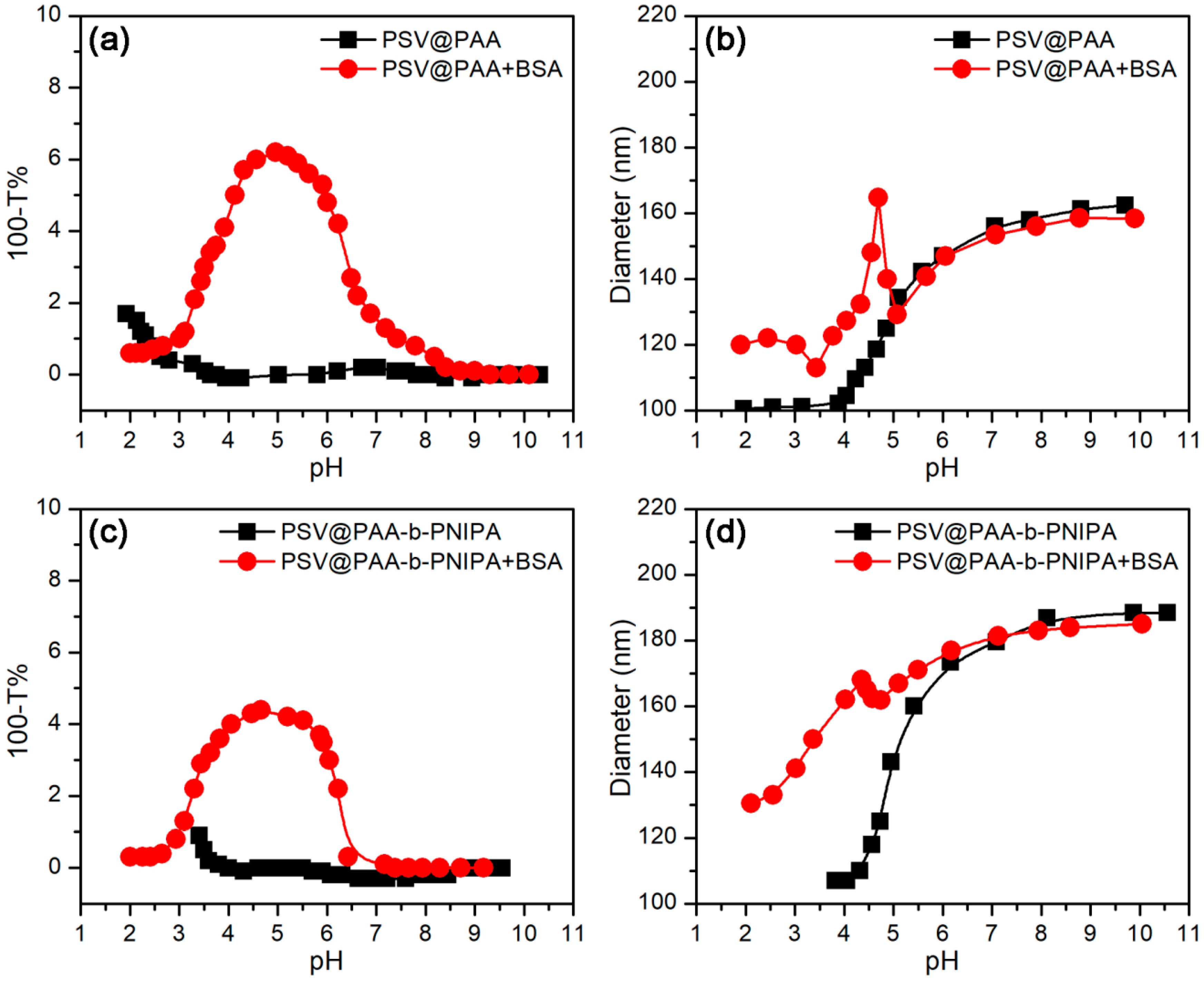
3.3.1. Effect of pH
3.3.2. Effect of Temperature
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Y.; Wittemann, A.; Ballauff, M.; Drechsler, M. Preparation of polystyrene-poly(N-isopropy-lacrylamide) (PS-PNIPA) core-shell particles by photoemulsion polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Weiss, A.; Ballauff, M. Synthesis of spherical polyelectrolyte brushes by photoemulsion polymerization. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 6043–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Lyon, L.A. Photoinduced phase transitions in poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 2623–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Wang, T.; Liu, P. Double-walled hollow polymeric microspheres with independent pH and temperature dual-responsive and magnetic-targeting function from onion-shaped core-shell structures. Colloid Surf. B 2013, 102, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillich, T.; Acikgöz, C.; Isa, L.; Schlüter, A.D.; Spencer, N.D.; Textor, M. PEG-stabilized core-shell nanoparticles: Impact of linear versus dendritic polymer shell architecture on colloidal properties and the reversibility of temperature-induced aggregation. ACS Nano 2012, 7, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupitskyy, R.; Motornov, M.; Minko, S. Single nanoparticle plasmonic devices by the “grafting to” method. Langmuir 2008, 24, 8976–8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.; Sun, X.; Lacaze, E.; Winkler, P.M.; Hohenau, A.; Krenn, J.R.; Bourdillon, C.; Lamouri, A.; Grand, J.; Lévi, G.; et al. Engineering thermoswitchable lithographic hybrid gold nanorods as plasmonic devices for sensing and active plasmonics applications. ACS Photonics 2015, 2, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, K.; Huang, Y.; Huang, B.; Huang, C.; Chen, J. Real-time packing behavior of core-shell silica@poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microspheres as photonic crystals for visualizing in thermal sensing. Polymers 2016, 8, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Ma, P.A.; Cheng, Z.; Kang, X.; Zhang, X.; Hou, Z.; Li, C.; Yang, D.; Zhai, X.; Lin, J. Up-conversion cell imaging and pH-Induced thermally controlled drug release from NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+@hydrogel core-shell hybrid microspheres. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3327–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, K.; Li, L.; Guo, X. Binding between proteins and cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brushes: Effect of pH, ionic strength, and stoichiometry. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Chen, K.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Guo, X. Antifouling performance of nano-sized spherical poly(N-hydroxyethyl acrylamide) brush. Colloid Surf. B 2017, 155, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, J.E.; Brault, N.D.; Li, Y.; Xue, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, S. Photoiniferter-mediated polymerization of zwitterionic carboxybetaine monomers for low-fouling and functionalizable surface coatings. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 9213–9220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Proch, S.; Schrinner, M.; Drechsler, M.; Kempe, R.; Ballauff, M. Thermosensitive core-shell microgel as a “nanoreactor” for catalytic active metal nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3955–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Hong, L.; Ngai, T. Tunable pickering emulsions with environmentally responsive hairy silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 32250–32258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Nakai, K.; Ohno, S.; Butt, H.; Koynov, K.; Yusa, S. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy monitors the hydrophobic collapse of pH-Responsive hairy nanoparticles at the individual particle level. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 7237–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of salt responsive spherical polymer brushes. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Kumano, N.; Seki, T.; Katagirib, K.; Takeoka, Y. An amorphous array of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) brush-coated silica particles for thermally tunable angle-independent photonic band gap materialsw. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 2171–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Selin, V.; Wang, Y.; Sukhishvili, S.A. Multiresponsive block copolymer-modified “hairy” gold nanoparticles for remote control of interfaces. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2013, 30, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marten, G.U.; Gelbrich, T.; Ritter, H.; Schmidt, A.M. A magnetoresponsive drug delivery system via β-cyclodextrin functionalized magnetic polymer brushes. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ye, S.; Wu, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, L. Functional polyaniline-assisted decoration of polystyrene microspheres with noble metal nanoparticles and their enhanced catalytic properties. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 10398–10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Mei, Y.; Schrinner, M.; Ballauff, M.; Möller, M.W.; Breu, J. In situ formation of Ag nanoparticles in spherical polyacrylic acid brushes by UV irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 7676–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, L.; Henzler, K.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Lotze, G.; et al. Protein immobilization onto cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brushes studied by small angle X-ray scattering. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Kong, J.; Yang, C.; Fu, G. Facile synthesis of hairy core-shell structured magnetic polymer submicrospheres and their adsorption of bovine serum albumin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 445, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, K.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Guo, X. Protein immobilization and separation using anionic/cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brushes based on charge anisotropy. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 11276–11278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballauff, M.; Lu, Y. “Smart” nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization and applications. Polymer 2007, 48, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferjaoui, Z.; Schneider, R.; Meftah, A.; Gaffet, E.; Alem, H. Functional responsive superparamagnetic core/shell nanoparticles and their drug release properties. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 26243–26249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, B.; Wang, T.; Wu, Z.; Shi, H.; Xue, D.; Liu, P. Fabrication of functional block copolymer grafted superparamagnetic nanoparticles for targeted and controlled drug delivery. Colloid Surf. A 2011, 375, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkert, S.; Bittrich, E.; Kuntzsch, M.; Müller, M.; Eichhorn, K.; Bellmann, C.; Uhlmann, P.; Stamm, M. Protein resistance of PNIPAAm brushes: Application to switchable protein adsorption. Langmuir 2010, 26, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; Fu, G.; He, B. Double-responsive polymer brushes on the surface of colloid particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 301, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Xu, J.; Han, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y. pH-modulated double LCST behaviors with diverse aggregation processes of random-copolymer grafted silica nanoparticles in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 86584–86592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhang, R.; Fang, D.; Guo, X.; Zhu, X. Fabrication and characterization of bifunctional spherical polyelectrolyte brushes. Des. Monomers Polym. 2016, 19, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.P.; Moura, L.; Fokkink, R.; Farinha, J.P.S. Preparation and characterization of low dispersity anionic multiresponsive core-shell polymer nanoparticles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 5802–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zhong, M.; Johnson, J.A. Light-controlled radical polymerization: Mechanisms, methods, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10167–10211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; She, Y.; Peng, Z.; Wei, J.; He, X. Enzyme-mediated in situ formation of pH-sensitive nanogels for proteins delivery. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 8032–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, L.G.; Ho, V.T.T.; Quynh, B.T.P.; Lim, K.T.; Anh, T.C. Synthesis of well-defined amphiphilic diblock copolymer brushes on halloysite nanotubes via surface-initiated reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 5834–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, K.; Li, J.; Fei, J.; Ji, Q.; Hill, J.P. Nanoarchitectonics for dynamic functional materials from atomic-/molecular-level manipulation to macroscopic action. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1251–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raftopoulos, K.N.; Pielichowski, K. Segmental dynamics in hybrid polymer/POSS nanomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 52, 136–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Glebe, U.; Böker, A. Synthesis of hybrid silica nanoparticles densely grafted with thermo and pH dual-responsive brushes via surface-initiated ATRP. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 9586–9596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, S.; Kawaguchi, H. Effect of graft chain length and structure design on temperature-sensitive hairy particles. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4338–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, S.; Kawaguchi, H. Temperature-sensitive hairy particles prepared by living radical graft polymerization. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2449–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.M.I.; Mayes, A.G. Preparation of polymeric core-shell and multilayer nanoparticles: Surface-initiated polymerization using in situ synthesized photoiniferters. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchyk, N.; Maximilien, J.; Beyazit, S.; Haupt, K.; Sum Bui, B.T. One-pot synthesis of iniferter-bound polystyrene core nanoparticles for the controlled grafting of multilayer shells. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2872–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayuji, O.; Keiji, Y.; Kazuichi, T. Synthesis, reactivity, and role of 4-vinylbenzyl N,N-diethyldithiocarbamate as a monomer-iniferter in radical polymerization. Macromolecules 1986, 19, 287–290. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Huh, K.M.; Shi, S.; Kuroda, S. Synthesis, characterization, and temperature-dependent colloidal stability of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-grafted polystyrene/poly(styrene-co-4-vinylbenzyl N,N-diethyldithiocarbamate) hairy particles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Chen, K.; Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Guo, X. Effect of block sequence on responsive behavior of core-shell diblock polymer brushes. Mater. Lett. 2018, 223, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Wang, C.; Yan, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Zha, L. pH/temperature dual stimuli-responsive microcapsules with interpenetrating polymer network structure. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henzler, K.; Haupt, B.; Lauterbach, K.; Wittemann, A.; Borisov, O.; Ballauff, M. Adsorption of beta-lactoglobulin on spherical polyelectrolyte brushes: Direct proof of counterion release by isothermal titration calorimetry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 3159–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
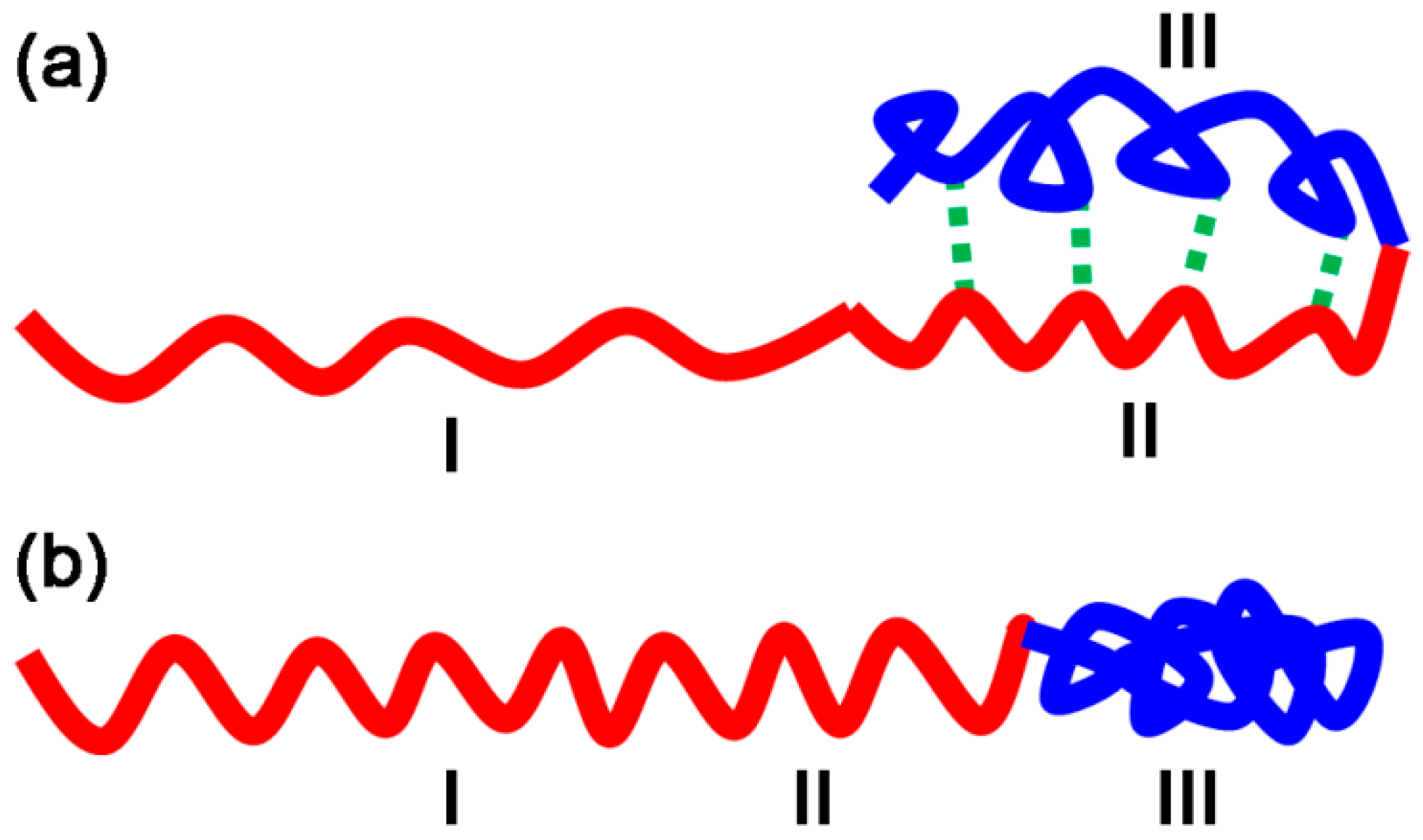


| Entry | PS/nm | PSV/nm | First block/nm | L1 1/nm | Diblock/nm | L2 2/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSV@PNIPA-b-PAA | 70 | 100 | 160 | 30 | 330 | 85 |
| PSV@PAA-b-PNIPA | 70 | 100 | 180 | 40 | 210 | 15 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, K.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Qin, X.; Guo, X. Conformation Study of Dual Stimuli-Responsive Core-Shell Diblock Polymer Brushes. Polymers 2018, 10, 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101084
Chen K, Cao L, Zhang Y, Li K, Qin X, Guo X. Conformation Study of Dual Stimuli-Responsive Core-Shell Diblock Polymer Brushes. Polymers. 2018; 10(10):1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101084
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Kaimin, Lan Cao, Ying Zhang, Kai Li, Xue Qin, and Xuhong Guo. 2018. "Conformation Study of Dual Stimuli-Responsive Core-Shell Diblock Polymer Brushes" Polymers 10, no. 10: 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101084
APA StyleChen, K., Cao, L., Zhang, Y., Li, K., Qin, X., & Guo, X. (2018). Conformation Study of Dual Stimuli-Responsive Core-Shell Diblock Polymer Brushes. Polymers, 10(10), 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101084