Direct Growth of Flower-Shaped ZnO Nanostructures on FTO Substrate for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Flower-Shaped ZnO Nanostructures Directly Grown on FTO Substrate
2.2. Characterizations of Flower-Shaped ZnO Nanostructures Directly Grown on FTO Substrate
2.3. Fabrication of ZnO Nanoparticles-Based Flower-Shaped ZnO Nanostructures Directly Grown on FTO Substrate
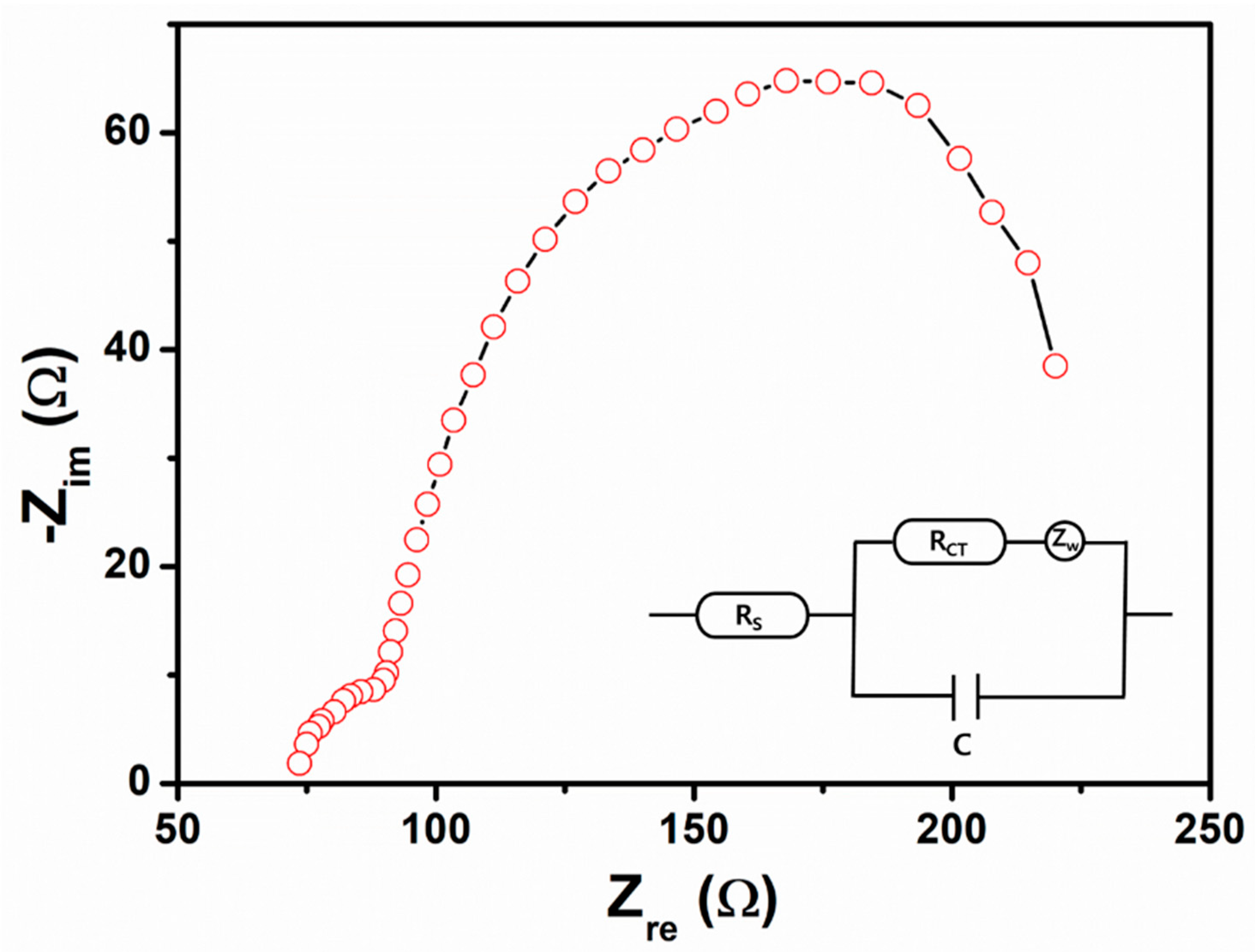
3. Results and Discussion
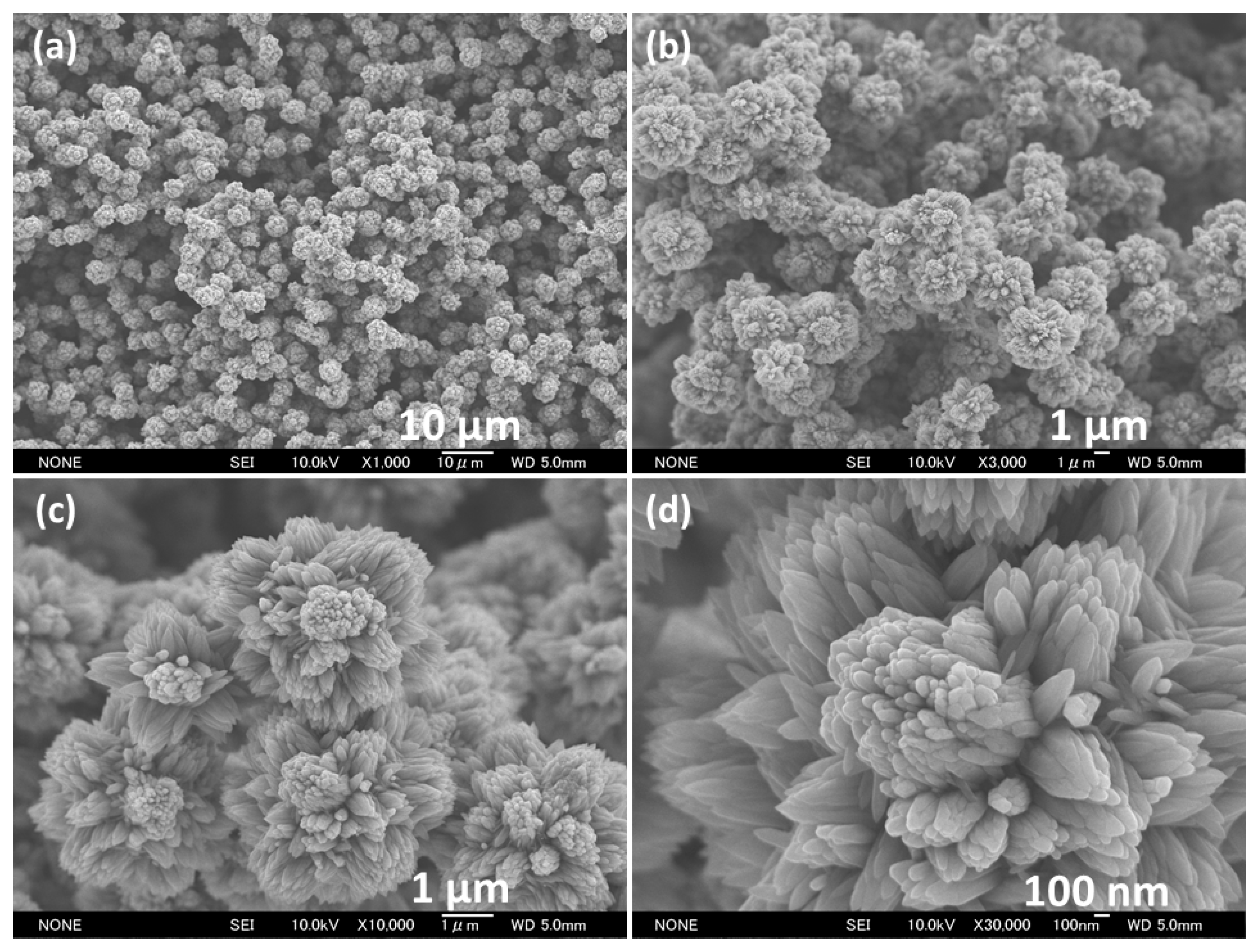
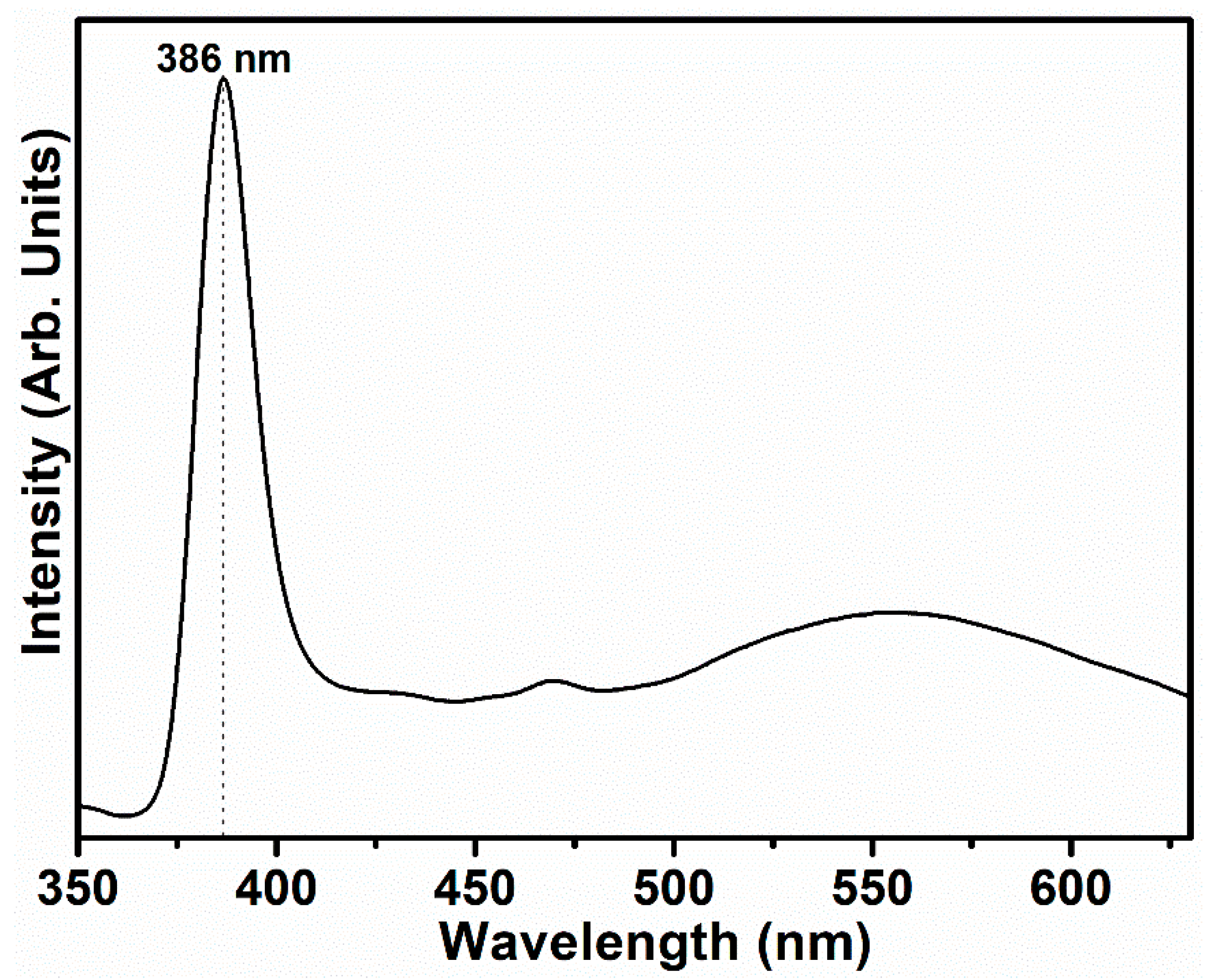
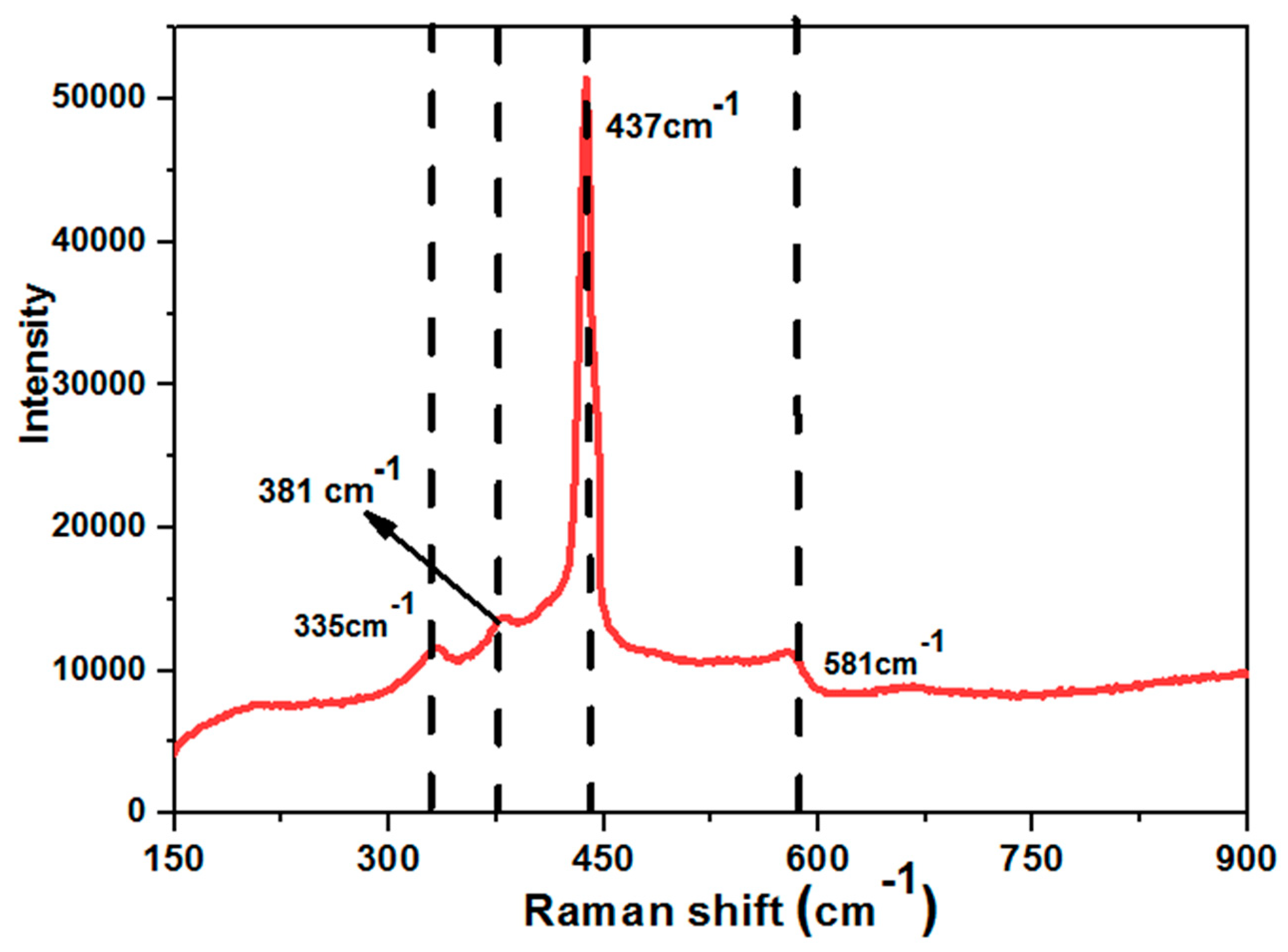
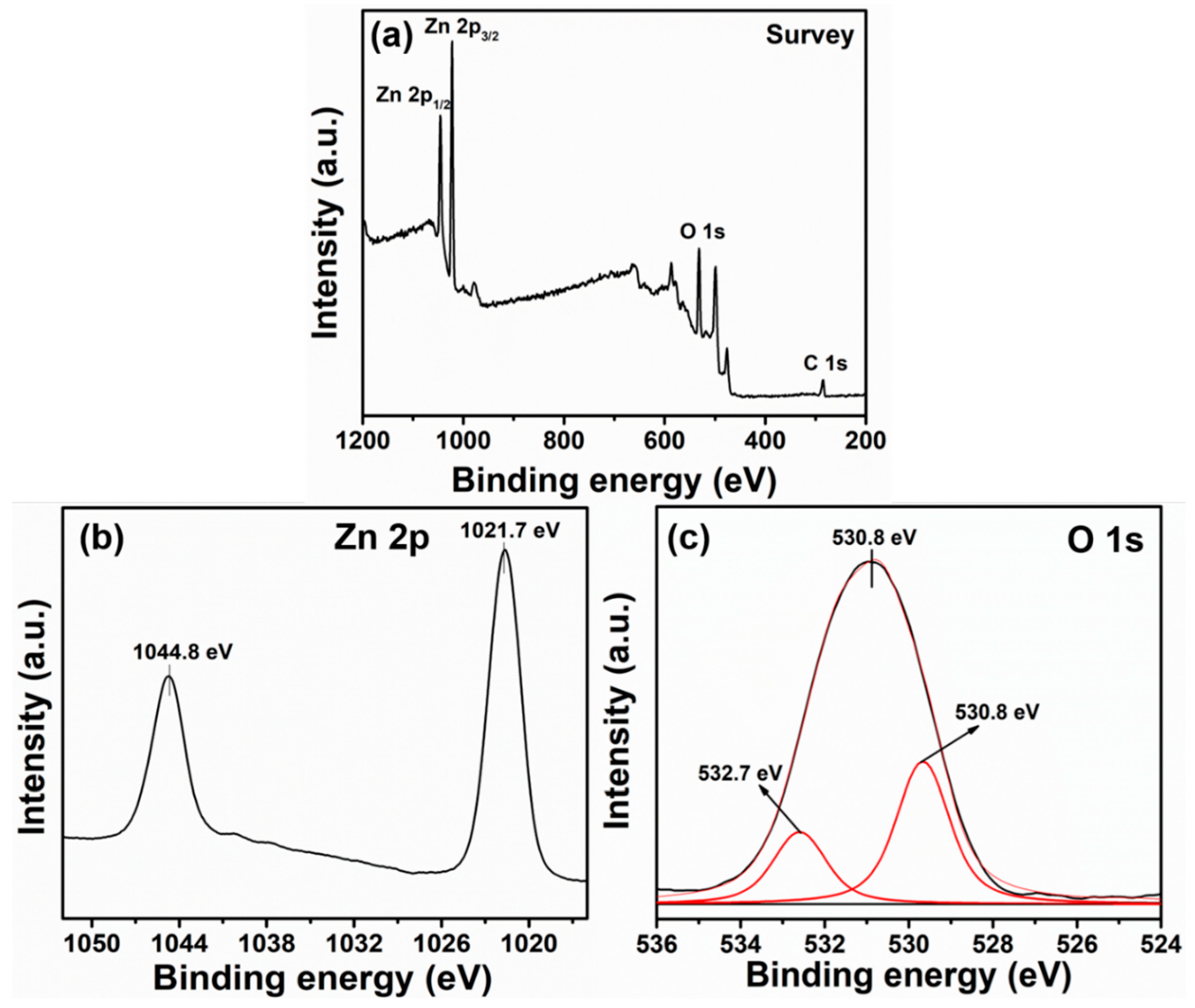
3.1. Characterization and Properties of Flower-Shaped ZnO Nanostructures Directly Grown on FTO Substrate
3.2. Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Application of Flower-Shaped ZnO Nanostructures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, F.; Sun, L. Solution-derived ZnO nanostructures for photoanodes of dye-sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, W.; Yang, Q.; Yang, P.; Sun, W. Cost-Efficient Chemical Bath Synthesized Alloy Catalysts PtM0.05 (M = Fe, Co, Ni) Acting as Counter Electrodes for CdS Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cell. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2018, 10, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.H.; Lee, M.H.; Song, D.H.; Aung, N.M.S.; Lee, J.J.; Song, C.E.; Hong, K.H.; Im, S.H. Highly Stable All-Inorganic Pb-Free Perovskite Solar Cells. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2018, 13, 1764–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Guo, F.; Wang, D.; Jiao, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Feng, P.; Zhao, L. Modification of TiO2 Nanowire Arrays with Sn Doping as Photoanode for Highly Efficient Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Crystals 2019, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.; Patil, A.; Yoon, S.J.; Choi, J.W. Electrochemical Characterization of Si/Al Multilayer Thin Film Anode Materials for High Energy Lithium Secondary Batteries. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2018, 10, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleiter, H. Nanostructured materials: Basic concepts and microstructure. Acta Mater. 2018, 48, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Singh, P.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Al-Heniti, S. Direct Growth of ZnO Nanosheets on FTO Substrate for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells Applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 2010, 10, 6666–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.H.; Lee, W.J.; Wi, J.H.; Yu, H.J.; Han, W.S.; Chung, Y.D. Engineering of Sodium Supply into Cu(In,Ga)Se2 Thin-Film Solar Cells. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2018, 13, 1753–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, V.M.H.; Hwang, S.H.; Lin, J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, J. Effects of Photosintering on Properties of Cadmium Sulfide Thin Films for Highly Efficient Cu(In, Ga)(Se, S)2 Solar Cells. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2018, 10, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yella, A.; Lee, H.W.; Tsao, H.N.; Yi, C.; Chandiran, A.K.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Diau, E.W.G.; Yeh, C.Y.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Gratzel, M. Porphyrin-sensitized solar cells with cobalt (II/III)-based redox electrolyte exceed 12 percent efficiency. Science 2011, 334, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Ameen, S.; Jung, I.S.; Choi, J. Facile Synthesis of Hexagonal ZnO Nanorods for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Application. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2018, 13, 1912–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.C.; Sabastian, N.; Chang, W.C.; Tsia, C.Y.; Lin, C.M. Electrochemical Deposition of ZnO Porous Nanoplate Network for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hajry, A.; Umar, A.; Hahn, Y.B.; Kim, D.H. Growth, properties and dye-sensitized solar cells applications of ZnO nanorods grown by low-temperature solution process. Superlattices Microstruct. 2009, 45, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.S.; Kim, J.; Suryawanshi, M.P.; Lokhande, A.C.; Shin, H.H.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, J.H. Effect of Radio Frequency Power on the Properties of Al-Doped ZnO (AZO) Thin Films and Their Application to Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 Thin-Film Solar Cells. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2018, 13, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittala, R.; Ho, K.C. Zinc oxide based dye-sensitized solar cells: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 920–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, A.; Lamberti, A.; Gazia, R.; Bianco, S.; Manfredi, D.; Shahzad, N.; Cappelluti, F.; Mac, S.; Tresso, E. High efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells exploiting spongelike ZnO nanostructures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 16203–16208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Fung, K.K.; Wang, N. ZnO hierarchical structures for efficient quasi-solid dye-sensitized solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 10631–10634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, D.; Bella, F.; Cauda, V.; Lamberti, A.; Sacco, A.; Tresso, E.; Bianco, S. A chemometric approach for the sensitization procedure of ZnO flowerlike microstructures for dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 11288–11295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, G.A. The isoelectric points of solid oxides, solid hydroxides, and aqueous hydroxo complex systems. Chem. Rev. 1965, 65, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrakala, V.; Steffy, J.A.J.; Bachan, N.; Jeyarani, W.J.; Tenkyong, T.; Shyla, J.M. A Comparative Investigation of Dye-Sensitized Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Nanorods Grown on Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Substrates by Direct and Seed-Mediated Hydrothermal Methods. Acta Metallurgica Sinica Engl. Lett. 2016, 29, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.K.; Alves, H.; Hofmann, D.M.; Kriegseis, W.; Forster, D.; Bertram, F.; Christen, J.; Hoffmann, A.; Straburg, M.; Dworzak, M.; et al. Bound exciton and donor-acceptor pair recombinations in ZnO. Phys. Status Solidi Basic Res. 2004, 241, 231–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yi, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, T.; Chao, Z.; Fan, J. Facile Fabrication of ZnO Nanomaterials and Their Photocatalytic Activity Study. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2018, 10, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, R.A.; Ahmed, N.M.; Mohammad, S.M.; Abdullah, M.J.; Bououdina, M. ZnO Nanorods/Polyaniline Heterojunction onto SiO2 for Photosensor. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2018, 13, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.K.; Hashim, M.R.; Allam, N.K. ZnO nano-tetrapod photoanodes for enhanced solar-driven water splitting. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2012, 549, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, G.; Leem, J.Y. Cadmium Chloride-Assisted ZnO Nanorod Regrowth for Enhanced Photoluminescence and Ultraviolet Sensing Properties. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2018, 10, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.K.; Muto, H.; Ito, T.; Kawamura, G.; Lockman, Z.; Matsuda, A. Facile Fabrication of Plasmonic Enhanced Noble-Metal-Decorated ZnO Nanowire Arrays for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.H.; Yang, C.C.; Yu, H.C.; Peng, Y.M.; Su, Y.K. Electron Emission Enhanced Properties of Gold Nanoparticle-Decorated ZnO Nanosheets Grown at Room Temperature. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2018, 10, 1675–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Doǧan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.J.; Morkoc, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 1–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.B.; Lee, J.E.; Akhtar, M.S.; Ameen, S.; Fijahi, L.; Seo, H.K.; Shin, H.S. Electrical Sensor Based on Hollow ZnO Spheres for Hydrazine Detection. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2018, 13, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, S.; Akhtar, M.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Yang, O.-B.; Shin, H.-S. Influence of seed layer treatment on low temperature grown ZnO nanotubes: Performances in dye sensitized solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Alhammadi, S.; Bouras, K.; Schmerber, G.; Ferblantier, G.; Dinia, A.; Slaoui, A.; Jeon, C.W.; Park, C.; Kim, W.K. Nd-Doped SnO2 and ZnO for Application in Cu(InGa)Se2 Solar Cells. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2017, 9, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Cheralathan, K.K.; Chun, J.M.; Yang, O.B. Composite electrolyte of heteropolyacid (HPA) and polyethylene oxide (PEO) for solid-state dye-sensitized solar cell. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galoppini, E.; Rochford, J.; Chen, H.; Saraf, G.; Lu, Y.; Hagfeldt, A.; Boschloo, G. Fast Electron Transport in Metal Organic Vapor Deposition Grown Dye-sensitized ZnO Nanorod Solar Cells. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.M.; Chen, C.K.; Liu, R.-S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wilkinson, D.P. Nano-architecture and material designs for water splitting photoelectrodes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5654–5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Umar, A.; Mehta, S.K.; Singh, S.; Kansal, S.K.; Fouad, H.; Alothman, O.Y. Rapid solar-light driven photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue using MoS2-ZnO heterostructure nanorods photocatalyst. Materials 2018, 11, 2254. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Umar, A.; Rana, D.S.; Sharma, P.; Chauhan, M.S.; Chauhan, S. Fe-doped ZnO nanoellipsoids for enhanced photocatalytic and highly sensitive and selective picric acid sensor. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 102, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, T.; Anandhan, N. Effect of polyvinyl alcohol on electrochemically deposited ZnO thin films for DSSC applications. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1832, 080014. [Google Scholar]
- Özdal, T.; Taktakoglu, R.; Özdamar, H.; Esen, M.; Takçi, D.K.; Kavak, H. Crystallinity improvement of ZnO nanorods by optimization of low-cost electrodeposition technique. Thin Solid Films 2015, 592 Pt A, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Hahn, Y.B. Ultraviolet-Emitting ZnO Nanostructures on Steel Alloy Substrate: Growth and Properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 2741–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Kim, S.H.; Karunagaran, B.; Suh, E.-K.; Hahn, Y.B. Growth and optical properties of aligned hexagonal ZnO nanoprisms on silicon substrate by non-catalytic thermal evaporation. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 4088–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Kim, S.H.; Suh, E.-K.; Hahn, Y.B. Ultraviolet-emitting javelin-like ZnO nanorods by thermal evaporation: Growth mechanism, structural and optical properties. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 440, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Ribeiro, C.; Al-Hajry, A.; Masuda, Y.; Hahn, Y.B. Growth of highly c-axis oriented ZnO nanorods on ZnO/Glass substrate: Growth mechanism, Structural and Optical properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 14715–14720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madlol, R.A.A. Structural and optical properties of ZnO nanotube synthesis via novel method. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Kong, J.; Jia, H.; Wang, Z. Synthesis of ZnO nanosheets via electrodeposition method and their optical properties, growth mechanism. Opt. Mater. 2015, 46, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, S.; Akhtar, M.S.; Shin, H.-S. Speedy photocatalytic degradation of bromophenol dye over ZnO nanoflowers. Mater. Lett. 2017, 209, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, T.; Anandhan, N.; Thangamuthu, R.; Surya, S. Facile growth of ZnO nanowire arrays and nanoneedle arrays with flower structure on ZnO-TiO2 seed layer for DSSC applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwari, J.; Shyamal, S.; Khan, T.; Ghadi, H.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chakrabarti, S.; Pal, S.K. Inversion of activity in DSSC for TiO2 and ZnO photo-anodes depending on the choice of sensitizer and carrier dynamics. J. Luminescence 2019, 207, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, L.; Kushwaha, S. Structural and optical properties of tripod-like ZnO thin film and its application in dye- sensitized solar cell. J. Solid State Electron. 2013, 17, 2001–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, J.; Li, H.; Su, J.; Zhang, Z. Facile synthesis and photoelectrochemical performance of the bush-like ZnO nanosheets film. Solid State Sci. 2012, 14, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, A.K.; Cindrella, L. Ameliorating the photovoltaic conversion efficiency of ZnO nanorod based dye-sensitized solar cells by strontium doping. Superlatt. Microstruc. 2019, 128, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Wu, F.; Mao, C.; Fang, L.; Guo, S.; Zhou, M. Enhanced photovoltaic performance of ZnO nanorod-based dye-sensitized solar cells by using Ga doped ZnO seed layer. J. Alloys Comp. 2015, 633, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, T.S.; Muthukumarasamy, N.; Kang, M. Applications of highly ordered paddle wheel like structured ZnO nanorods in dye sensitized solar cells. Mater. Lett. 2013, 102–103, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Duan, Y. Magnetic-field effect on dye-sensitized ZnO nanorods-based solar cells. J. Power Sour. 2012, 216, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Valls, I.; Lira-Cantu, M. Effect of testing conditions on the photovoltaic performance of ZnO-based dye sensitized solar cells. Phys. Procedia 2010, 8, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Shan, L.; Tian, X.; Zheng, X.; Sun, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z. Hydrothermal synthesis of oriented ZnO nanorod-nanosheets hierarchical architecture on zinc foil as flexible photoanodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 11663–11670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Ya, J.; Lei, E. Controlled synthesis of ZnO and TiO2 nanotubes by chemical method and their application in dye-sensitized solar cells. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, X.; Zuo, F.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Hui, D. Controllable synthesis of ZnO nanograss with different morphologies and enhanced performance in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Solid State Chem. 2013, 197, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A. Growth of comb-like ZnO nanostructures for Dye-sensitized solar cells applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, X.; Lin, H. One-step large-scale synthesis of porous ZnO nanofibers and their application in dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 2975–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Kawauchi, H.; Kashima, T.; Arakawa, H. Significant influence of TiO2 photoelectrode morphology on the energy conversion efficiency of N719 dye-sensitized solar cell. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golsheikh, A.M.; Kamali, K.Z.; Huang, N.M.; Zak, A.K. Effect of calcination temperature on performance of ZnO nanoparticles for dye-sensitized solar cells. Powder Technol. 2018, 329, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Morphologies of ZnO Nanostructures | Substrate | Dye | Photovoltaic Performances | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JSC(mA /cm2) | VOC(V) | FF | η (%) | ||||
| Nanoparticles | FTO | N719 | 5.4 | 0.58 | 0.35 | 1.1 | 47 |
| Tripods | FTO | N719 | 2.80 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.88 | 48 |
| Bush-like morphology | FTO | N719 | 3.46 | 0.69 | 0.35 | 0.82 | 49 |
| Nanorods | FTO | N3 | 1.37 | 0.845 | 0.69 | 0.80 | 50 |
| Aligned nanorods | FTO | N719 | 2.08 | 0.736 | 0.43 | 0.66 | 51 |
| Paddle wheel like structured ZnO nanorod | FTO | - | 2.82 | 0.70 | 0.65 | 1.3 | 52 |
| ZnO nanorods | FTO | N719 | 1.69–2.13 | - | - | 0.36–0.47 | 53 |
| ZnO nanorods | FTO | N719 | 1.52 | 0.361 | 0.37 | 0.21 | 54 |
| Nanorods + nanosheets | Zn foil | N719 | 3.041 | 0.524 | 0.42 | 0.67 | 55 |
| Nanotubes | ITO | N3 | 4.70 | 0.386 | - | 1.20 | 56 |
| Nanograsses | FTO | N719 | 1.93 | 0.630 | 0.39 | 0.47 | 57 |
| Nanocombs | FTO | N719 | 3.14 | 0.671 | 0.34 | 0.68 | 58 |
| Nanofibers | FTO | N719 | 2.87 | 0.690 | 0.44 | 0.88 | 59 |
| ZnO nanoflowers directly grown on FTO | FTO | N719 | 4.22 | 0.615 | 0.54 | 1.40 | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umar, A.; Akhtar, M.S.; Almas, T.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Al-Assiri, M.S.; Masuda, Y.; Rahman, Q.I.; Baskoutas, S. Direct Growth of Flower-Shaped ZnO Nanostructures on FTO Substrate for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Crystals 2019, 9, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9080405
Umar A, Akhtar MS, Almas T, Ibrahim AA, Al-Assiri MS, Masuda Y, Rahman QI, Baskoutas S. Direct Growth of Flower-Shaped ZnO Nanostructures on FTO Substrate for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Crystals. 2019; 9(8):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9080405
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmar, Ahmad, Mohammad Shaheer Akhtar, Tubia Almas, Ahmed Abdulbaqi Ibrahim, Mohammed Sultan Al-Assiri, Yoshitake Masuda, Qazi Inamur Rahman, and Sotirios Baskoutas. 2019. "Direct Growth of Flower-Shaped ZnO Nanostructures on FTO Substrate for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells" Crystals 9, no. 8: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9080405
APA StyleUmar, A., Akhtar, M. S., Almas, T., Ibrahim, A. A., Al-Assiri, M. S., Masuda, Y., Rahman, Q. I., & Baskoutas, S. (2019). Direct Growth of Flower-Shaped ZnO Nanostructures on FTO Substrate for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Crystals, 9(8), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9080405








