Crystal Structure of Bacterial Cystathionine Γ-Lyase in The Cysteine Biosynthesis Pathway of Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
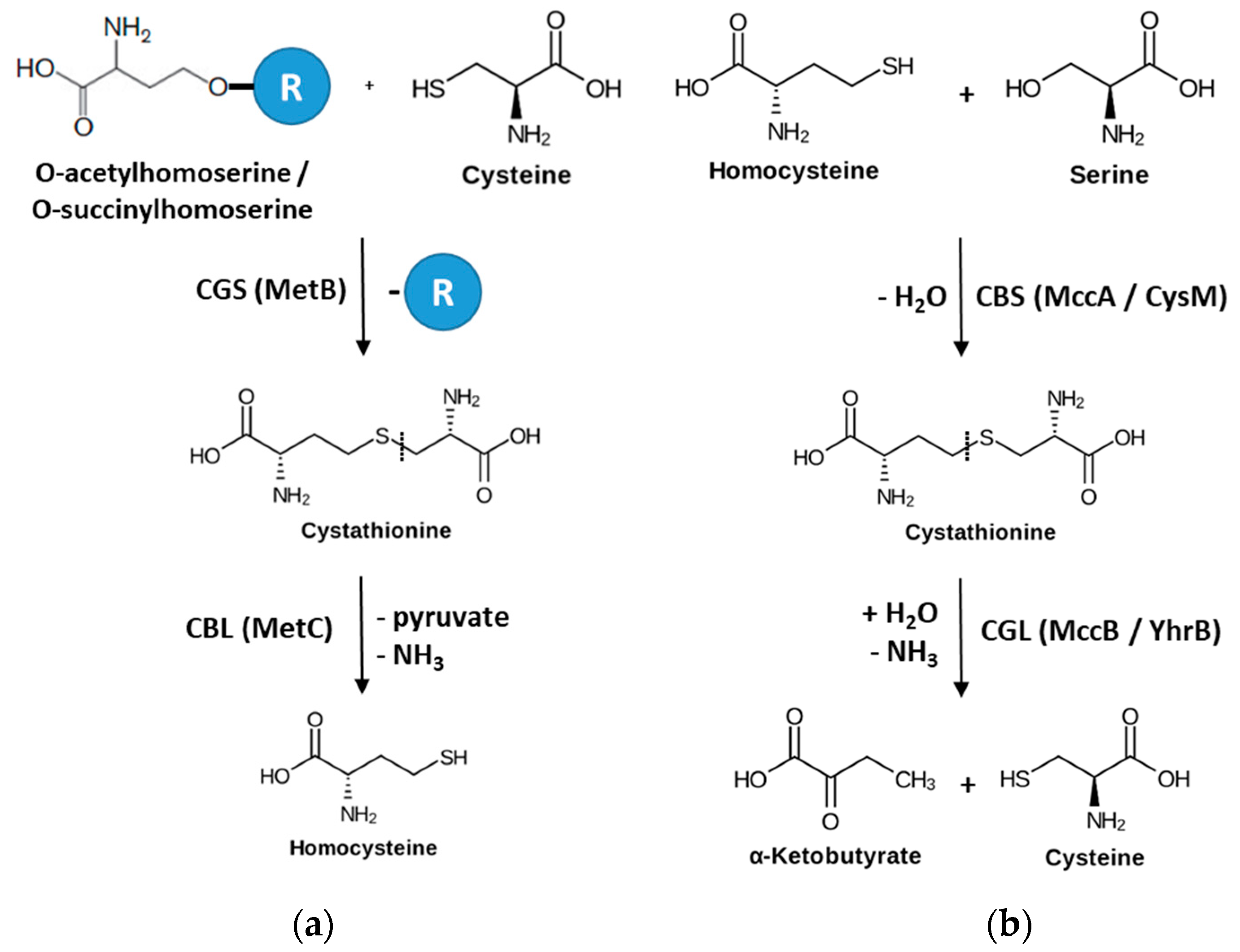
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cloning, Protein Expression, and Purification
2.2. Crystallization
2.3. Structural Determination
2.4. Multi-Angle Light Scattering Analysis
2.5. Data Availibility
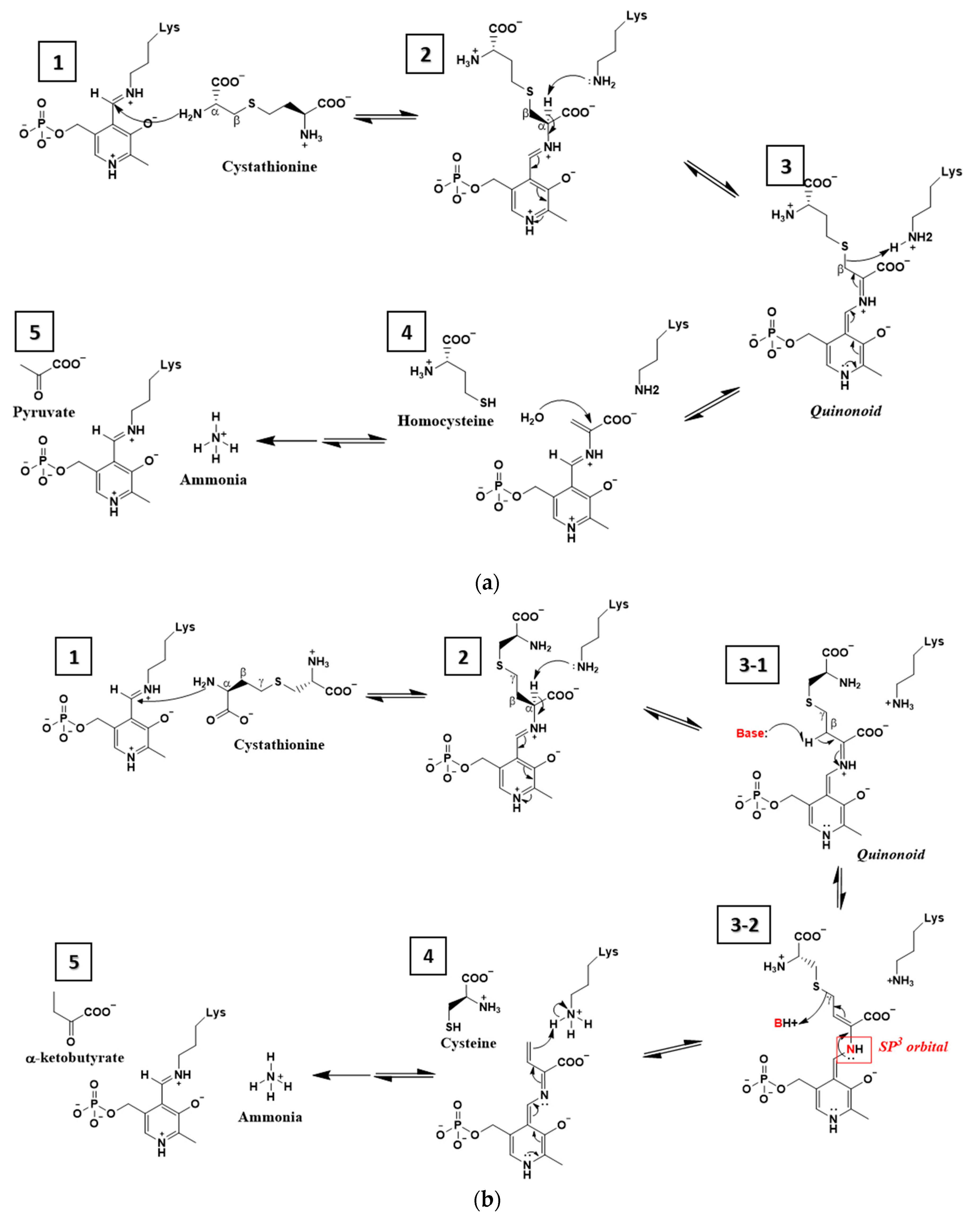
3. Results
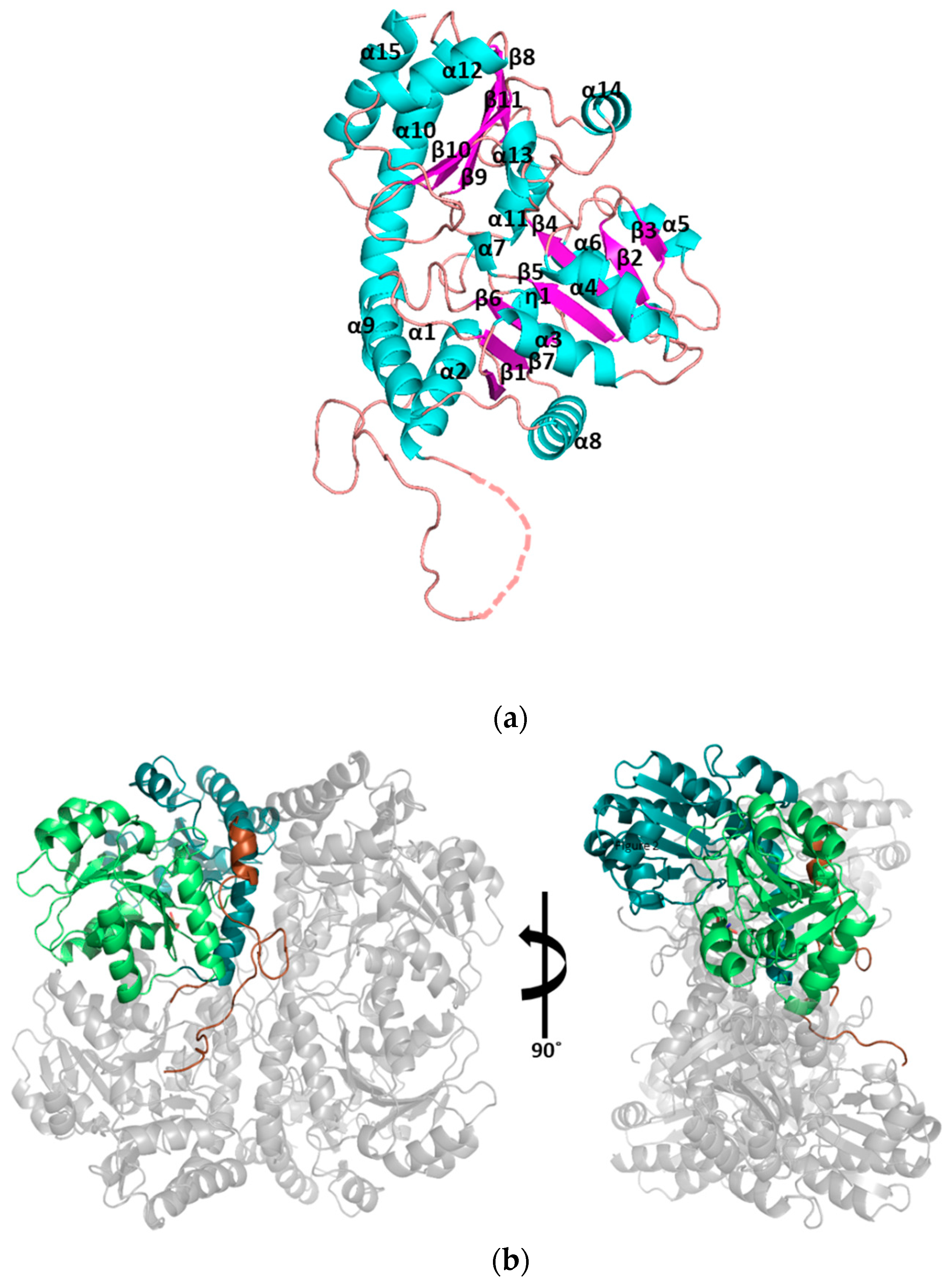
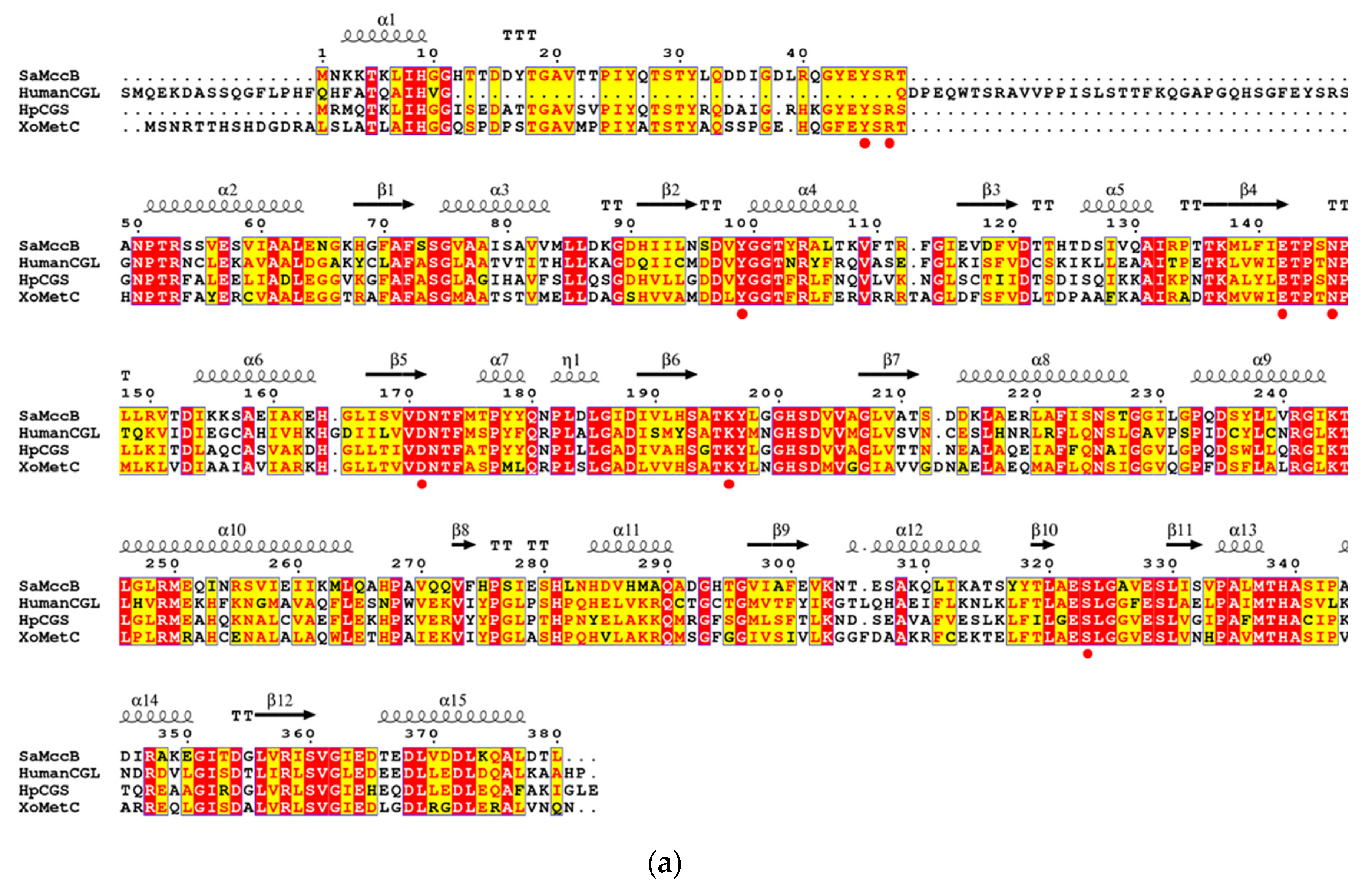
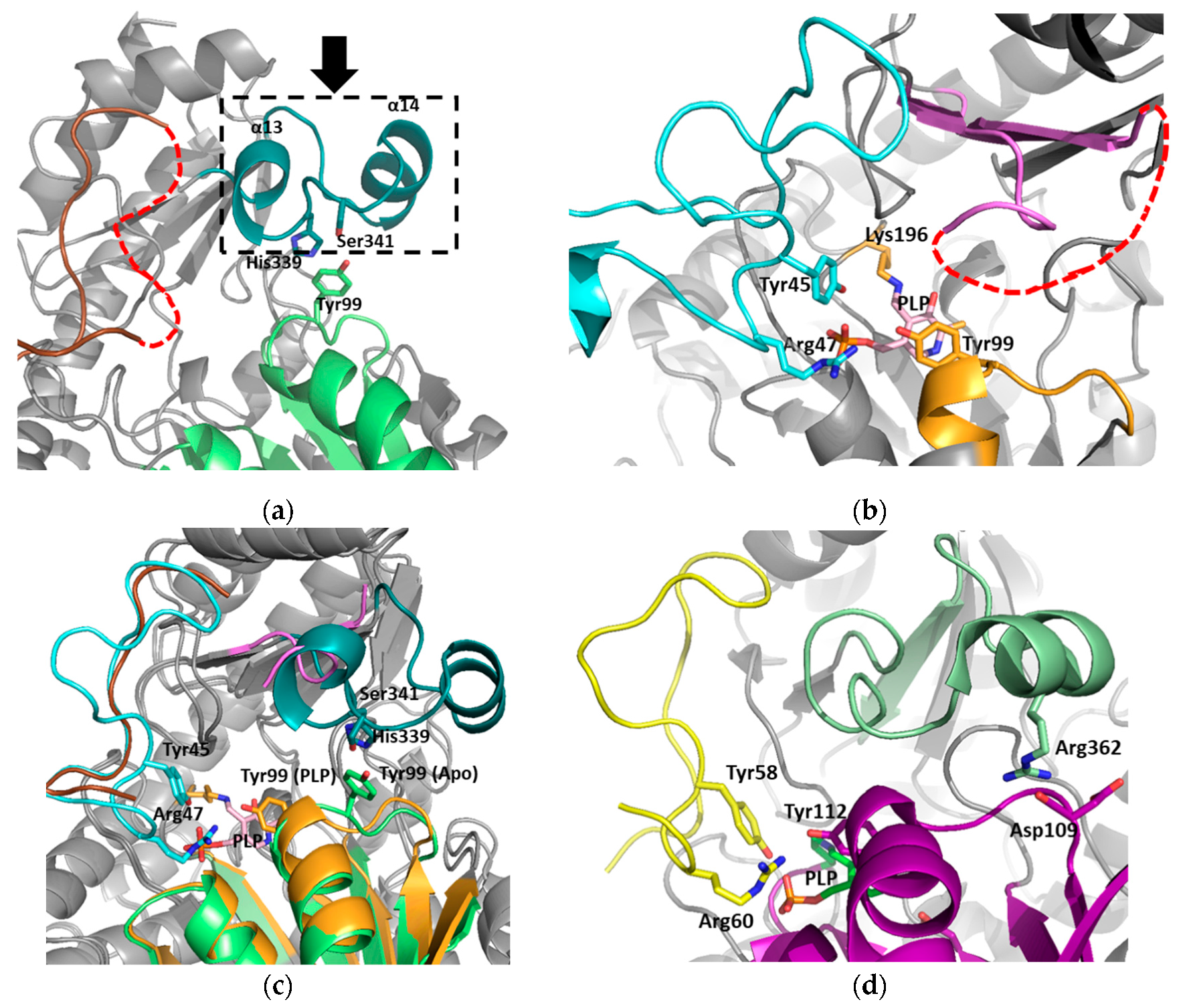
3.1. Structural Determination of SaMccB
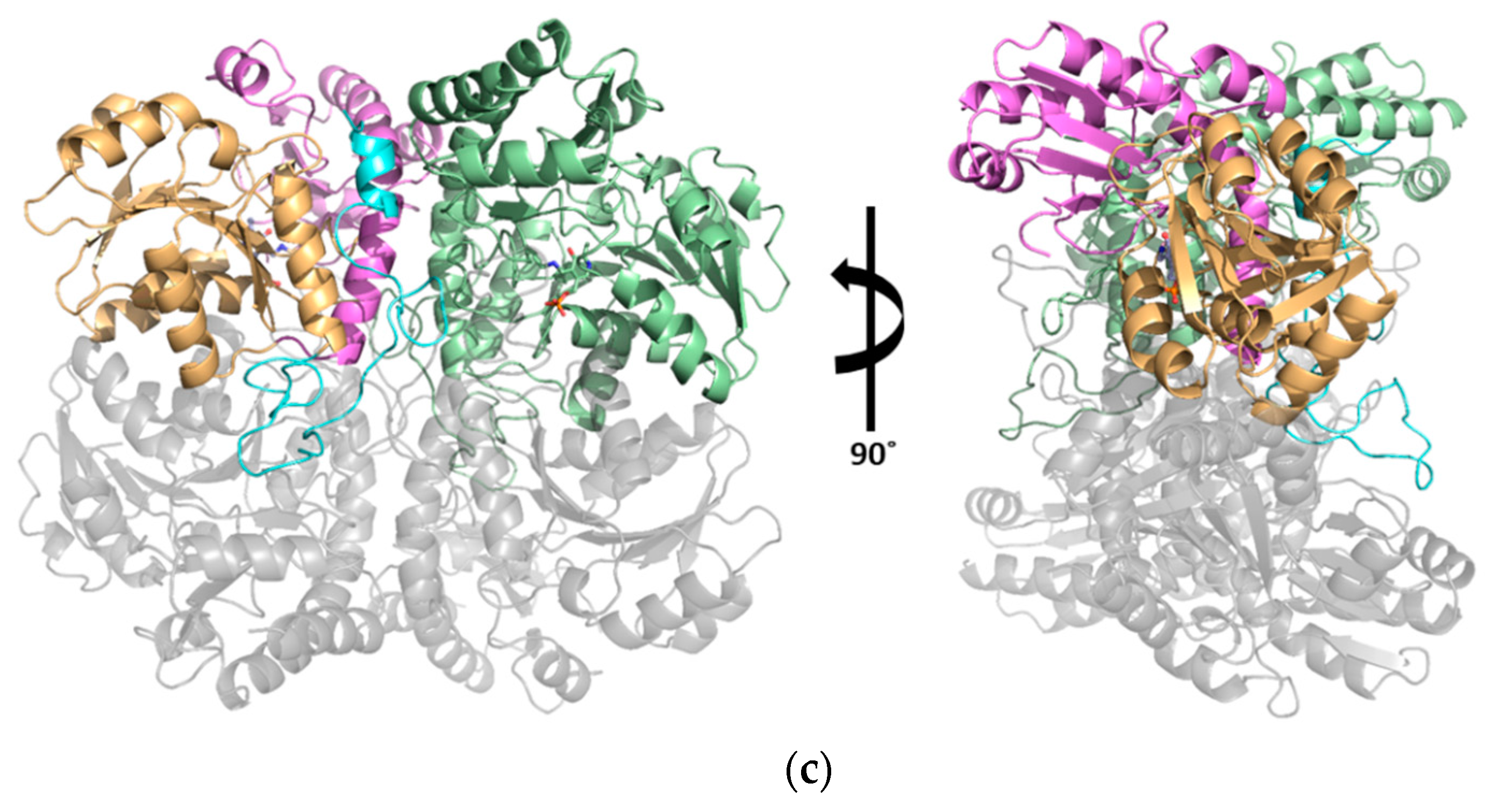
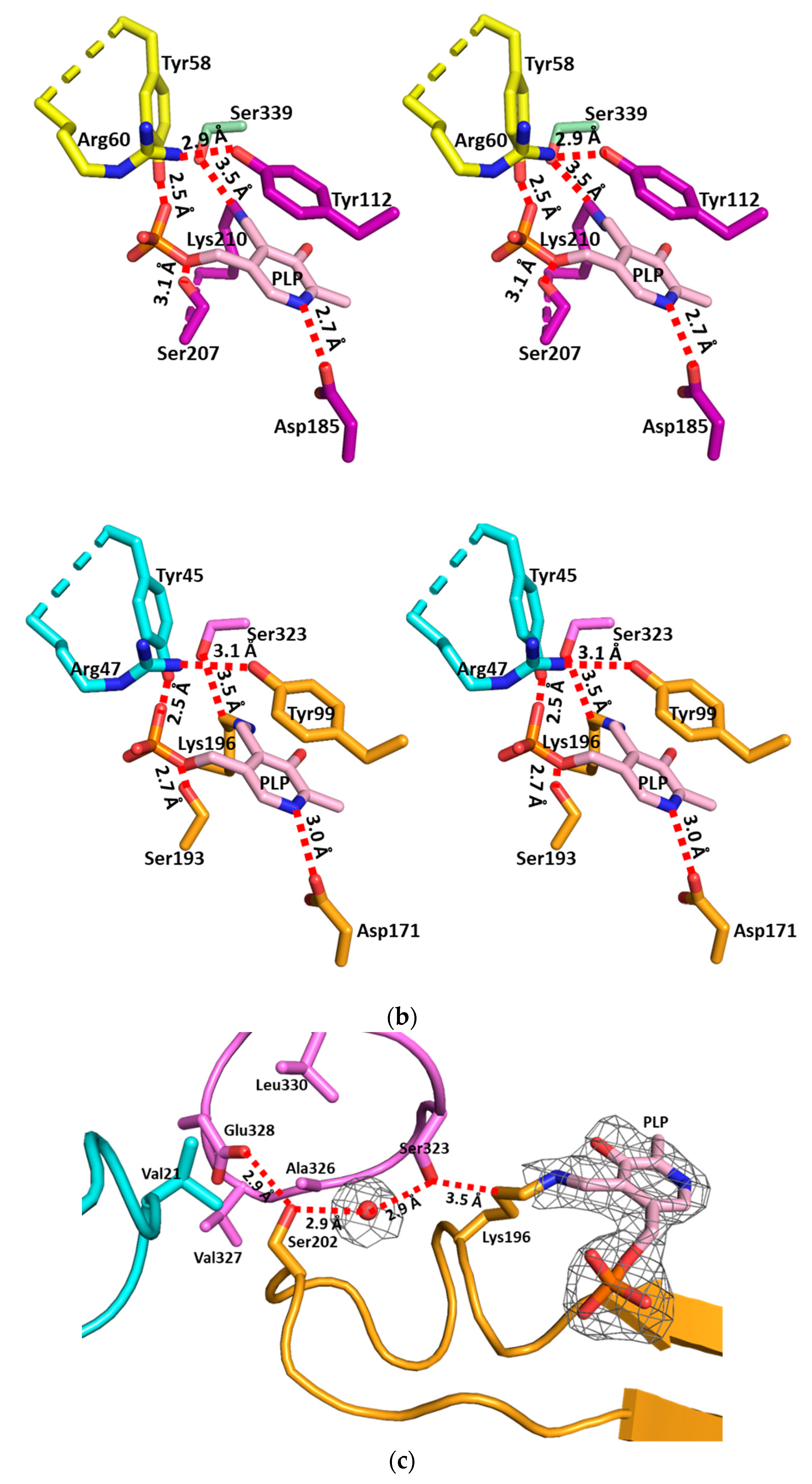
3.2. The Active Site and the Ser–Water–Ser–Glu Network
3.3. Structural Flexibility Depending on PLP Binding
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berlett, B.S.; Stadtman, E.R. Protein oxidation in aging, disease, and oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 20313–20316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirtz, M.; Droux, M. Synthesis of the sulfur amino acids: Cysteine and methionine. Photosynth. Res. 2005, 86, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagong, H.Y.; Kim, K.J. Structural insights into substrate specificity of cystathionine gamma-synthase from Corynebacterium glutamicum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6002–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, H.P.; Cerqueira, N.M.; Kim, J.K.; Hong, M.K.; Fernandes, P.A.; Ramos, M.J.; Kang, L.W. PLP undergoes conformational changes during the course of an enzymatic reaction. Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 2014, 70, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhee, K.-H.; Kruger, W.D. The role of cystathionine β-synthase in homocysteine metabolism. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Collins, R.; Huang, S.; Holmberg-Schiavone, L.; Anand, G.S.; Tan, C.H.; van-den-Berg, S.; Deng, L.W.; Moore, P.K.; Karlberg, T.; et al. Structural basis for the inhibition mechanism of human cystathionine gamma-lyase, an enzyme responsible for the production of H2S. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3076–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clausen, T.; Schlegel, A.; Peist, R.; Schneider, E.; Steegborn, C.; Chang, Y.S.; Haase, A.; Bourenkov, G.P.; Bartunik, H.D.; Boos, W. X-ray structure of MalY from Escherichia coli: A pyridoxal 5’-phosphate-dependent enzyme acting as a modulator in mal gene expression. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, J.P.; Hašek, J.; Kožich, V.; Collard, R.; Venezia, S.; Janošíková, B.; Wang, J.; Stabler, S.P.; Allen, R.H.; Jakobs, C. Cystathionine γ-lyase: Clinical, metabolic, genetic, and structural studies. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2009, 97, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Banerjee, R. PLP-dependent H2S biogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2011, 1814, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecker, M.; Becher, D.; Fuchs, S.; Engelmann, S. A proteomic view of cell physiology and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 300, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, G.A.; Proctor, R.A. At the crossroads of bacterial metabolism and virulence factor synthesis in Staphylococci. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.A.; Luo, Q. A ligation-independent cloning method using nicking DNA endonuclease. Biotechniques 2010, 49, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrita, L.D.; Dai, W.; Bottomley, S.P. A family of E. coli expression vectors for laboratory scale and high throughput soluble protein production. BMC Biotechnol. 2006, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otwinowski, Z.; Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 1997, 276, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkoczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Davis, I.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.W.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; et al. PHENIX: A comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 2010, 66, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, B.E. Bateman domains and adenosine derivatives form a binding contract. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, G.L. Staphylococcus aureus: A well-armed pathogen. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1998, 26, 1179–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, C.; Colice, G. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia in adults. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2014, 8, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohanski, M.A.; Dwyer, D.J.; Hayete, B.; Lawrence, C.A.; Collins, J.J. A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell 2007, 130, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Imlay, J.A. High levels of intracellular cysteine promote oxidative DNA damage by driving the Fenton reaction. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Apo-SaMccB | PLP-bound SaMccB | |
|---|---|---|
| Data collection | ||
| Beam line | PAL5C | PAL5C |
| Wavelength (Å) | 1.00003 | 1.00003 |
| Space group | I4122 | P42212 |
| Cell dimensions | ||
| a, b, c (Å) | 105.567, 105.567, 287.986 | 132.281, 132.281, 97.954 |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 90, 90 |
| Resolution (Å) | 50.0–2.30 (2.34–2.30) | 50.0–2.30 (2.34–2.30) |
| Rmerge | 0.121 (0.415) | 0.070 (0.349) |
| Rpim | 0.030 (0.159) | 0.017 (0.126) |
| I/σI | 16.7 (2.4) | 28.11 (3.92) |
| Completeness (%) | 99.6 (99.6) | 99.5 (98.7) |
| Redundancy | 14.7 (6.2) | 14.1 (7.5) |
| Wilson B-factor (Å2) | 25.9 | 24.3 |
| Refinement | ||
| Resolution (Å) | 46.59–2.30 | 42.21–2.30 |
| No. reflections | 33271 | 38561 |
| Rwork/Rfree | 0.202/0.220 | 0.203/0.249 |
| Number of total atoms | 2867 | 5828 |
| Average B-factor (Å2) | ||
| All atoms | 30.0 | 30.0 |
| Lysine-PLP | ND | 20.89 |
| Solvent atoms | 25.56 | 22.94 |
| R.M.S deviations | ||
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| Bond angles (°) | 0.471 | 0.491 |
| Ramachandran plot | ||
| Favored (%) | 96.7 | 97.0 |
| Allowed (%) | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Outliers (%) | 0.3 | 0.0 |
| PDB code | 6KGZ | 6KHQ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Jeong, S.; Ahn, J.; Ha, N.-C.; Kwon, A.-R. Crystal Structure of Bacterial Cystathionine Γ-Lyase in The Cysteine Biosynthesis Pathway of Staphylococcus aureus. Crystals 2019, 9, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9120656
Lee D, Jeong S, Ahn J, Ha N-C, Kwon A-R. Crystal Structure of Bacterial Cystathionine Γ-Lyase in The Cysteine Biosynthesis Pathway of Staphylococcus aureus. Crystals. 2019; 9(12):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9120656
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dukwon, Soyeon Jeong, Jinsook Ahn, Nam-Chul Ha, and Ae-Ran Kwon. 2019. "Crystal Structure of Bacterial Cystathionine Γ-Lyase in The Cysteine Biosynthesis Pathway of Staphylococcus aureus" Crystals 9, no. 12: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9120656
APA StyleLee, D., Jeong, S., Ahn, J., Ha, N.-C., & Kwon, A.-R. (2019). Crystal Structure of Bacterial Cystathionine Γ-Lyase in The Cysteine Biosynthesis Pathway of Staphylococcus aureus. Crystals, 9(12), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9120656





