Hydrothermal Synthesis of (001) Facet Highly Exposed ZnO Plates: A New Insight into the Effect of Citrate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Synthesis
2.2. Characterization
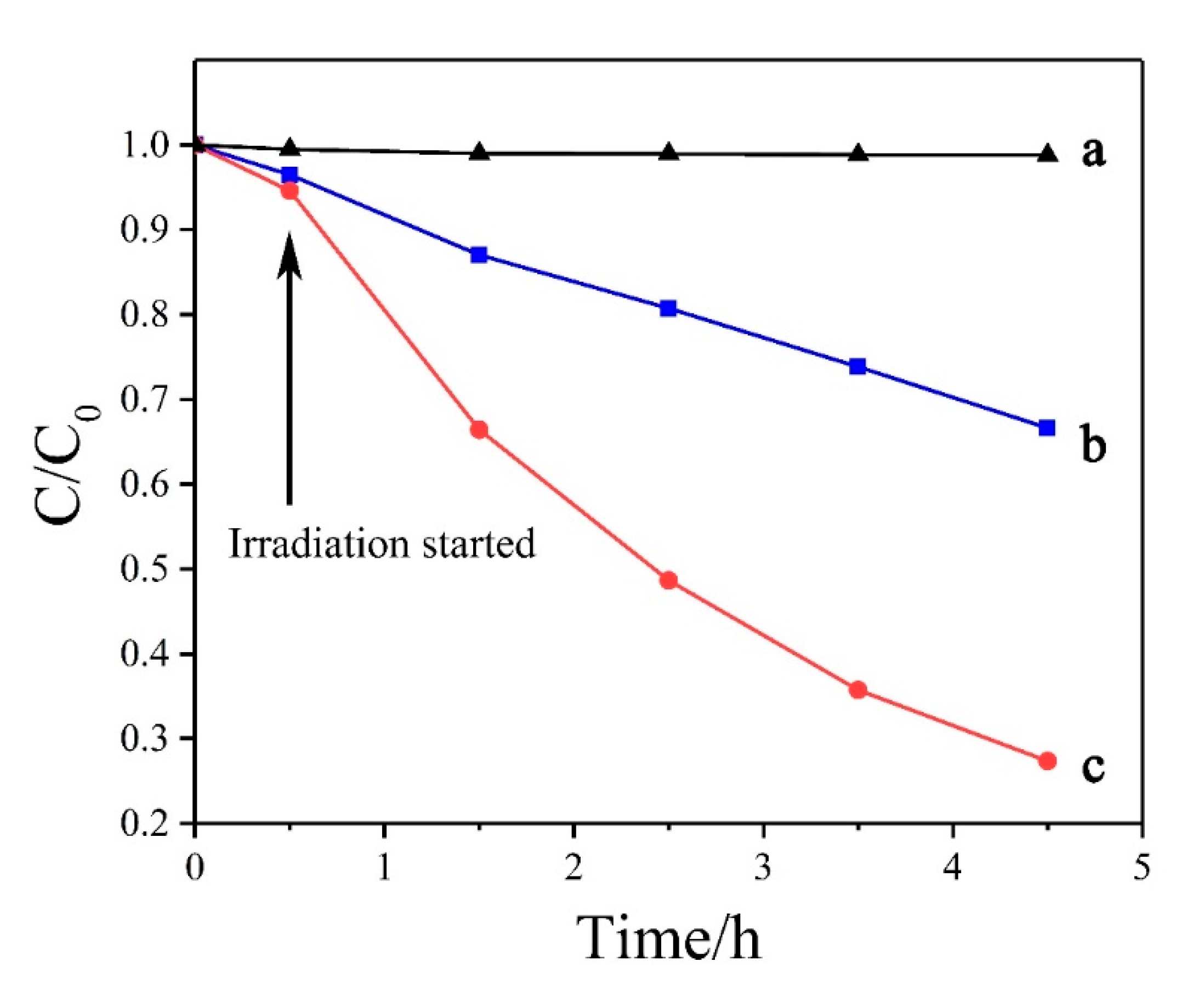
2.3. Photocatalytic Activity
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Tian, N.; Li, J.T.; Broadwell, I.; Sun, S.G. Nanomaterials of high surface energy with exceptional properties in catalysis and energy storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4167–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Z.; Chen, M.D.; Ma, Y.; Yang, J.; Yuan, Y.K.; Liu, J.F.; Liu, B.; Du, Q.; Ren, Y.; Liu, S.Z.; et al. Improving sensing performance of the ZnO foam structure with exposed {001} facets by hydrogenation and sensing mechanism at molecule level. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 479, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.P.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, C.H.; Ni, Y.R.; Kou, J.H.; Xu, Z.Z. Construction of (001) facets exposed ZnO nanosheets on magnetically driven cilia film for highly active photocatalysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 394, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, X.W. ZnO disk-like structures and their application in dye sensitized solar cell. Solid State Commun. 2016, 240, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Nanostructures of zinc oxide. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.X.; Sun, X.W.; Dong, Z.L.; Yu, M.B. Zinc oxide nanodisk. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 3878–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demel, J.; Plestil, J.; Bezdicka, P.; Janda, P.; Klementova, M.; Lang, K. Layered zinc hydroxide salts: Delamination, preferred orientation of hydroxide lamellae, and formation of ZnO nanodiscs. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 360, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, B.; Yang, H.Q. Charge separation between wurtzite ZnO polar {001} surfaces and their enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 163, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ding, Y.; Gao, P.X.X.; Xin, X.Q.; Wang, Z.L. Single-cystal hexagonal disks and rings of ZnO: Low-temperature, large-scale synthesis and growth mechanism. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2004, 43, 5238–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.F.; Guo, Y.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, J.P.; Xu, D.S. Morphological control of ZnO nanostructures by electrodeposition. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 13519–13522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Rycenga, M.; Tao, J.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.A.; Zhu, Y.M.; Xia, Y.N. Controlling the Shapes of Silver Nanocrystals with Different Capping Agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8552–8553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallin, M.P.; Murphy, C.J. Solution-phase synthesis of sub-10 nm Au-Ag alloy nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 1235–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Q.; Chen, Q.; Xie, Z.X.; Han, G.B.; Wang, R.H.; Ren, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Tian, Z.Q. A simple and effective route for the synthesis of crystalline silver nanorods and nanowires. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.R.R.; Voigt, J.A.; Liu, J.; McKenzie, B.; McDermott, M.J.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Konishi, H.; Xu, H.F. Complex and oriented ZnO nanostructures. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.R.R.; Voigt, J.A.; Liu, J.; Mckenzie, B.; Mcdermott, M.J. Biommetic arrays of oriented helical ZnO nanorods and columns. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12954–12955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.L.; Kuo, T.J.; Huang, M.H. Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO microspheres and hexagonal microrods with sheetlike and platelike nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 20115–20121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.S.; Guo, H.Z.; Zhang, X.X.; Lu, A.L.; Zeng, D.Q.; Chen, Y.Z.; Peng, D.L. A facile approach to fabrication of well-dispersed NiO-ZnO composite hollow microspheres (vol 3, pg 24430, 2013). RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 47164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, D.R.; Li, D.S.; Ma, X.Y.; Li, S.Z.; Que, D.L. Controllable growth of ZnO microcrystals by a capping-molecule-assisted hydrothermal process. Cryst. Growth Des. 2005, 5, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.B.; Liu, J.W.; Xie, Q.; Bai, S.; Yu, W.C.; Qian, Y.T. Hydrothermal growth and optical properties of doughnut-shaped ZnO microparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 9463–9467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.R.; Dong, W.J.; Keeter-Brewer, M.; Konar, S.; Njabon, R.N.; Tian, Z.R. Site-specific nucleation and growth kinetics in hierarchical nanosyntheses of branched ZnO crystallites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 10960–10968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andeen, D.; Kim, J.H.; Lange, F.F.; Goh, G.K.L.; Tripathy, S. Lateral epitaxial overgrowth of ZnO in water at 90 degrees C. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meagley, K.L.; Garcia, S.P. Chemical Control of Crystal Growth with Multidentate Carboxylate Ligands: Effect of Ligand Denticity on Zinc Oxide Crystal Shape. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Dutta, K.; Pramanik, A. Morphology control of ZnO with citrate: A time and concentration dependent mechanistic insight. Crystengcomm 2013, 15, 6349–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Song, G.H.; Jia, X.D.; Cheng, F.F.; Zhu, J.J. Fast One-Step Synthesis of Biocompatible ZnO/Au Nanocomposites with Hollow Doughnut-Like and Other Controlled Morphologies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 4517–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, N.J.; Franks, G.V.; Ducker, W.A. Selective Adsorption to Particular Crystal Faces of ZnO. Langmuir 2012, 28, 7189–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milek, T.; Zahn, D. A Surfactants Walk to Work: Modes of Action of Citrate Controlling (10-10) and (000-1) Zinc Oxide Surface Growth from Solution. Z Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2016, 642, 902–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, P.Y.; Xiang, L. Effects of NaOH on formation of ZnO nanorods from epsilon-Zn(OH)2. Mater. Lett. 2015, 141, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujuan, W.Z.L. Infrared Spectra Characteristics of Zinc Hydroxide and Zinc Oxide. Chin. J. Spectrosc. Lab. 2012, 29, 2172–2175. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, J.A. Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry, 15th ed.; McGraw-Hill Companies: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, U.K. Ionic elastomer based on carboxylated nitrile rubber: Infrared spectral analysis. Polym. Int. 2000, 49, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Jang, J.W.; Jung, A.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, K.H. Formation of Amorphous Zinc Citrate Spheres and Their Conversion to Crystalline ZnO Nanostructures. Langmuir 2011, 27, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, L.; Liu, J.F. Study the effect of functional molecule types on the surface properties of ZnO nanorods. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 62505–62510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelman, A.M.; Fortner, J.D.; Pennell, K.D. Effects of ultraviolet light on silver nanoparticle mobility and dissolution. Environ. Sci. Nano 2015, 2, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, K.; Niedermaier, M.; Kasparek, V.; Bernardi, J.; Redhammer, G.; Bockstedte, M.; Berger, T.; Diwald, O. From Anhydrous Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Powders to Aqueous Colloids: Impact of Water Condensation and Organic Salt Adsorption on Free Exciton Emission. Langmuir 2019, 35, 8741–8747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Xiang, L. Influence of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfonate on the Formation of ZnO Nanorods from epsilon-Zn(OH)2. J. Nanomater 2013, 2013, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.J.; Huang, D.; Liu, H.X.; Li, T.D.; Wang, J.G. ZnO Tetrakaidecahedrons with Coexposed {001}, {101}, and {100} Facets: Shape-Selective Synthesis and Enhancing Photocatalytic Performance. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 2758–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclaren, A.; Valdes-Solis, T.; Li, G.Q.; Tsang, S.C. Shape and Size Effects of ZnO Nanocrystals on Photocatalytic Activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 12540–12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Yin, L.W.; Wang, C.X.; Lun, N.; Qi, Y.X. Sol-Gel Growth of Hexagonal Faceted ZnO Prism Quantum Dots with Polar Surfaces for Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1769–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.N.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Dong, W.J.; Tang, W.H.; Chen, B.Y.; Li, C.R.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.R.; Xu, W. Nanostructured porous ZnO film with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Thin. Solid Films 2011, 519, 5673–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Lai, C.W.; Ngai, K.S.; Juan, J.C. Recent developments of zinc oxide based photocatalyst in water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2016, 88, 428–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.H.; Jin, B.B.; Wang, Y.F. Facet enhanced photocatalytic effect with uniform single-crystalline zinc oxide nanodisks. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2009, 472, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.N.; Ning, L.C.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, B.; Yang, H.Q. Superior photocatalytic activity of porous wurtzite ZnO nanosheets with exposed {001} facets and a charge separation model between polar (001) and (00(1)over-bar) surfaces. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
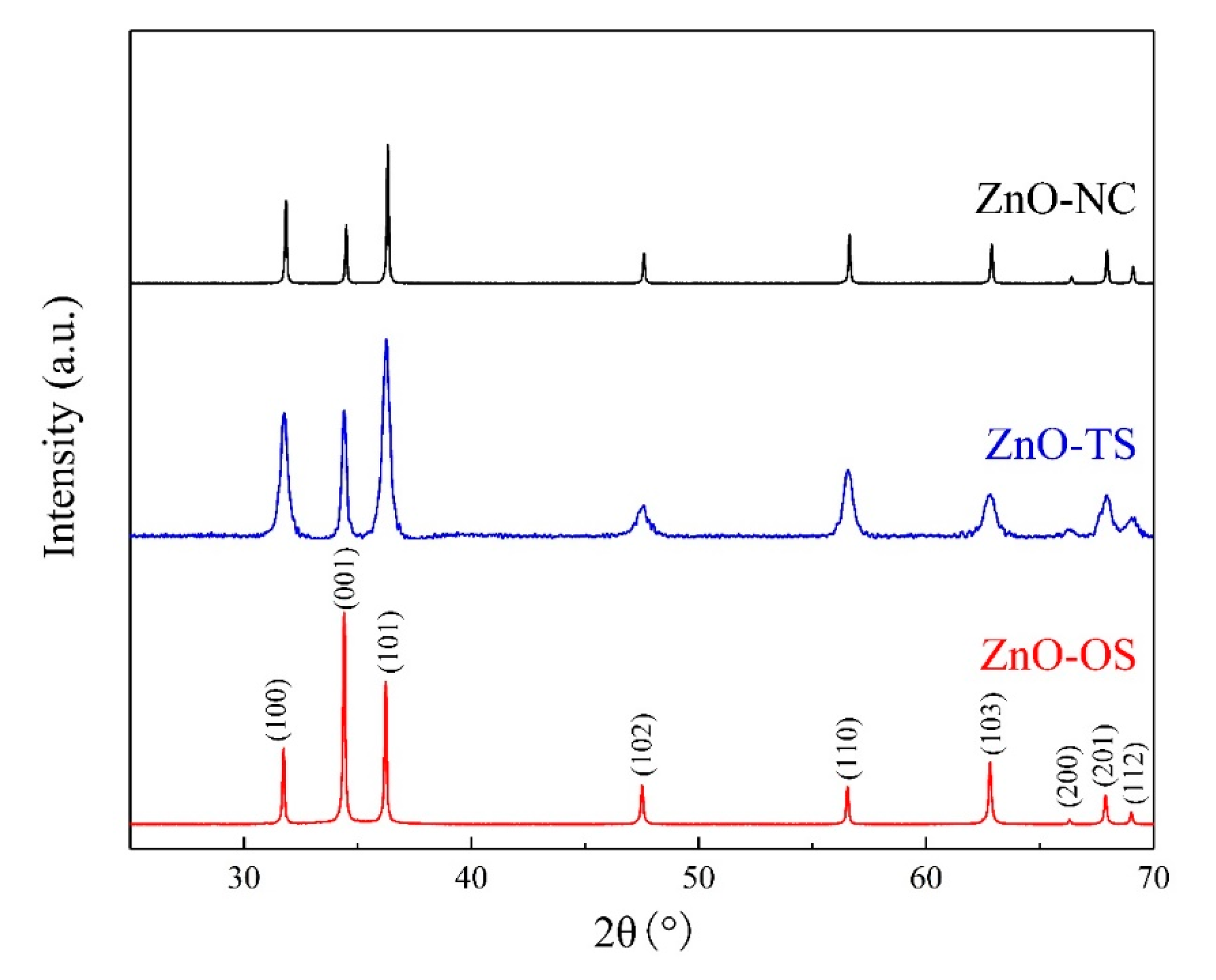

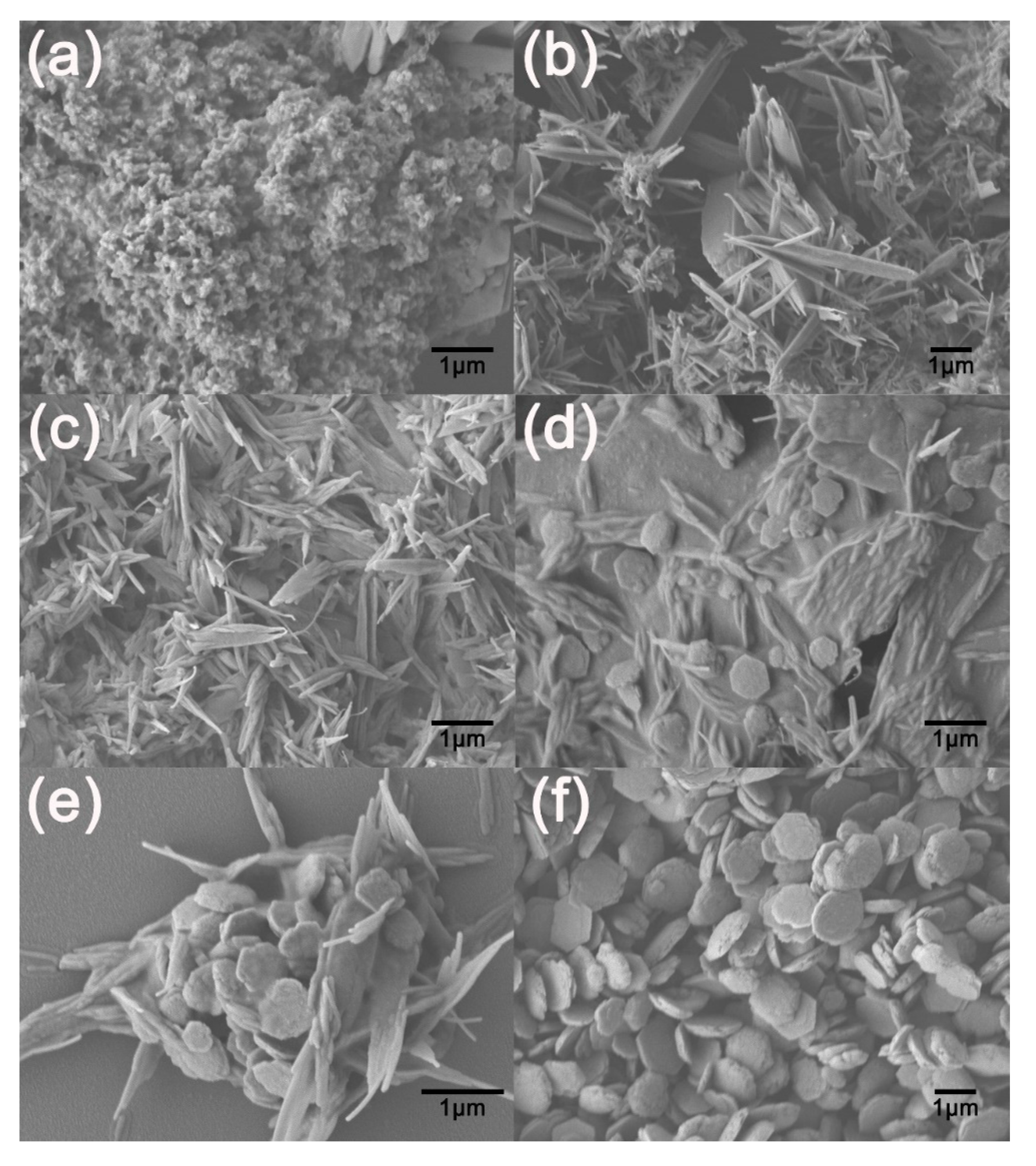
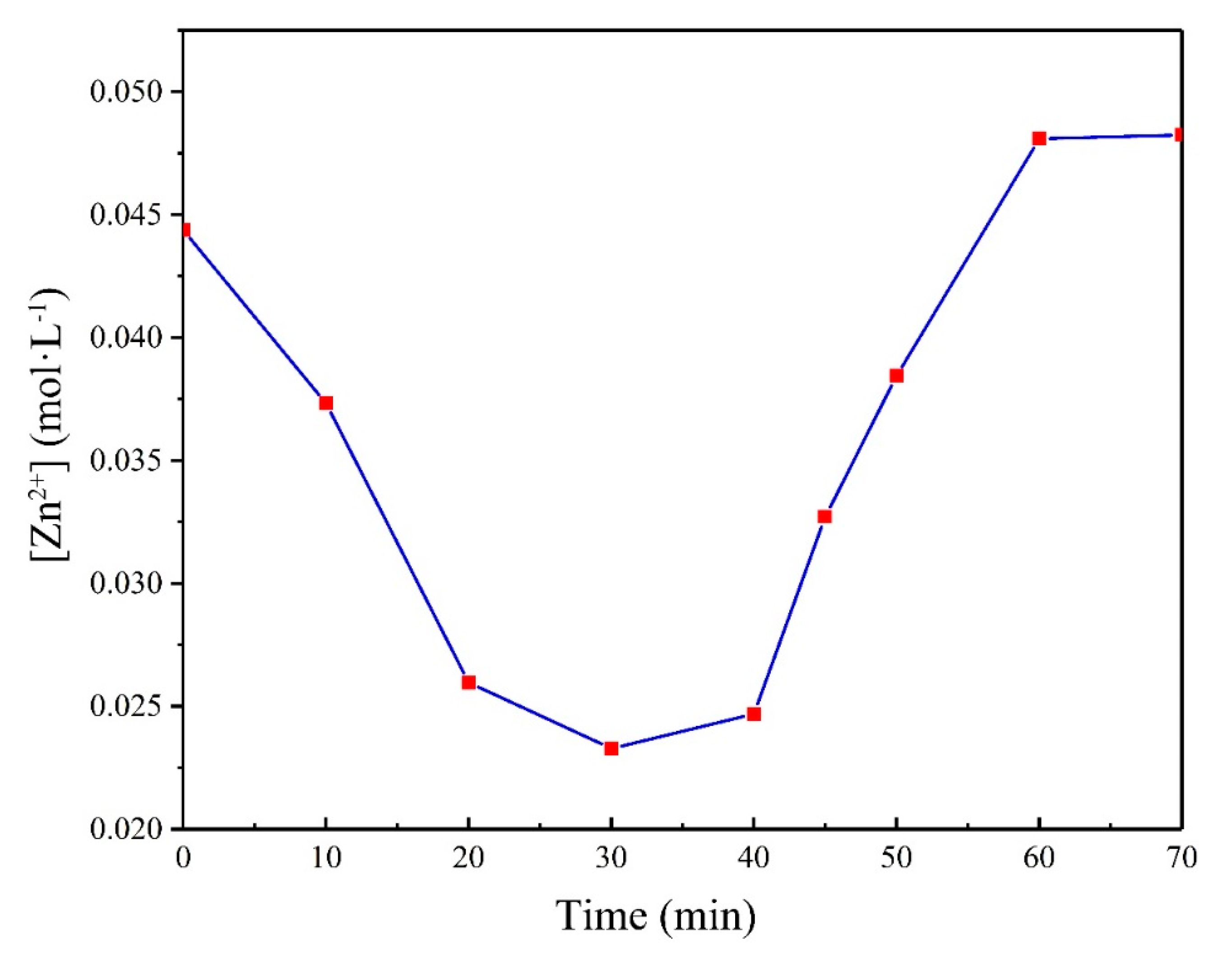
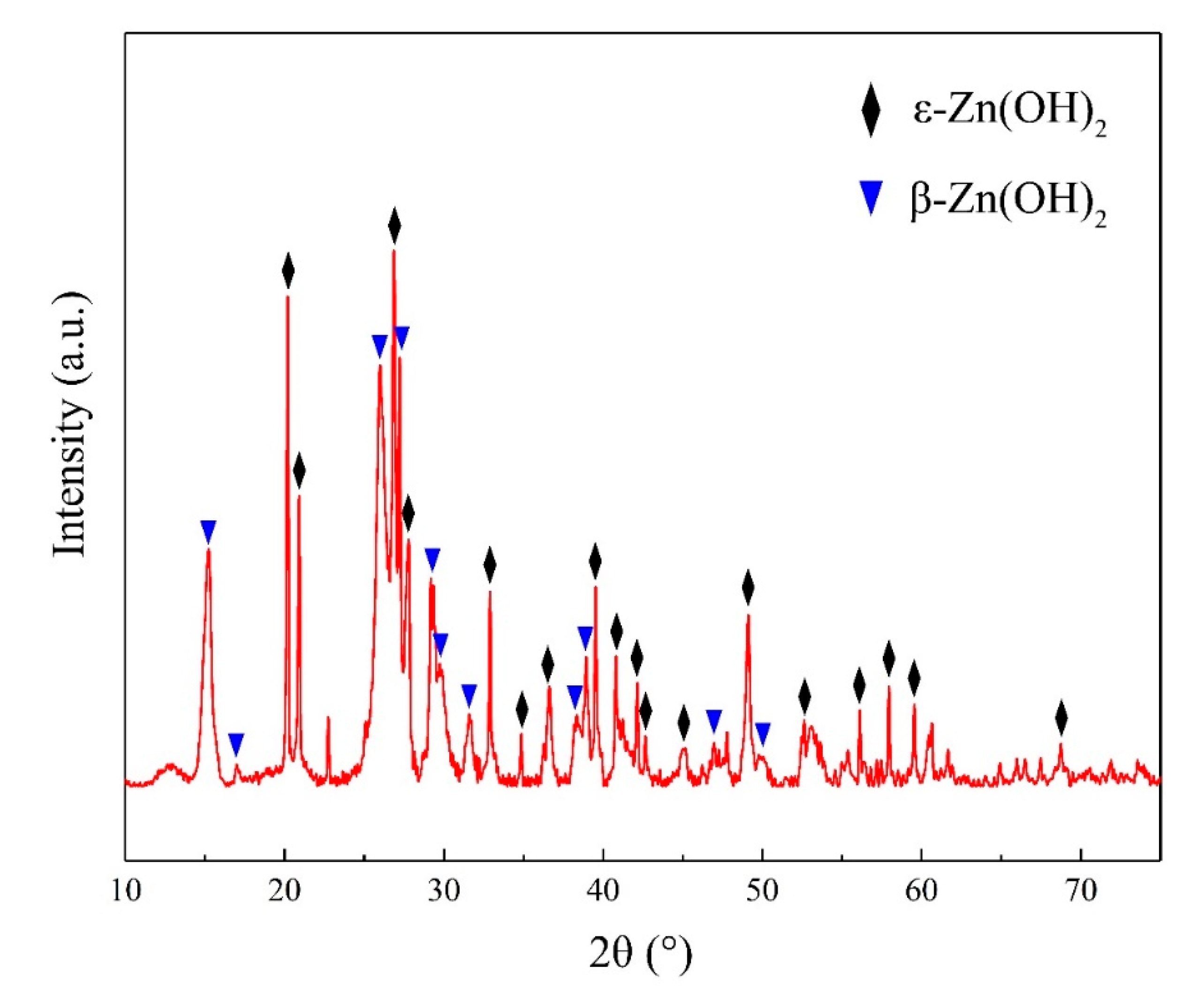
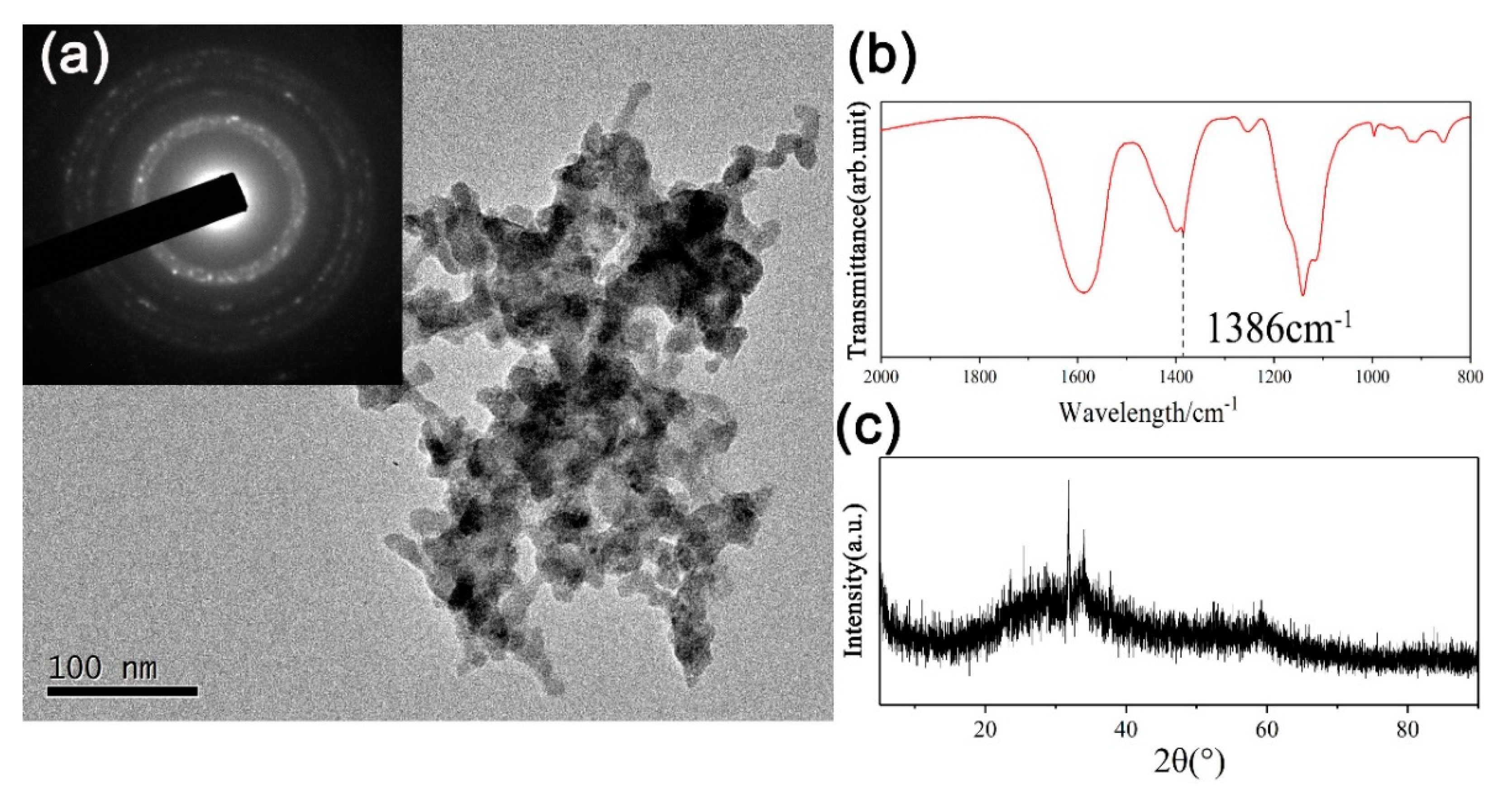
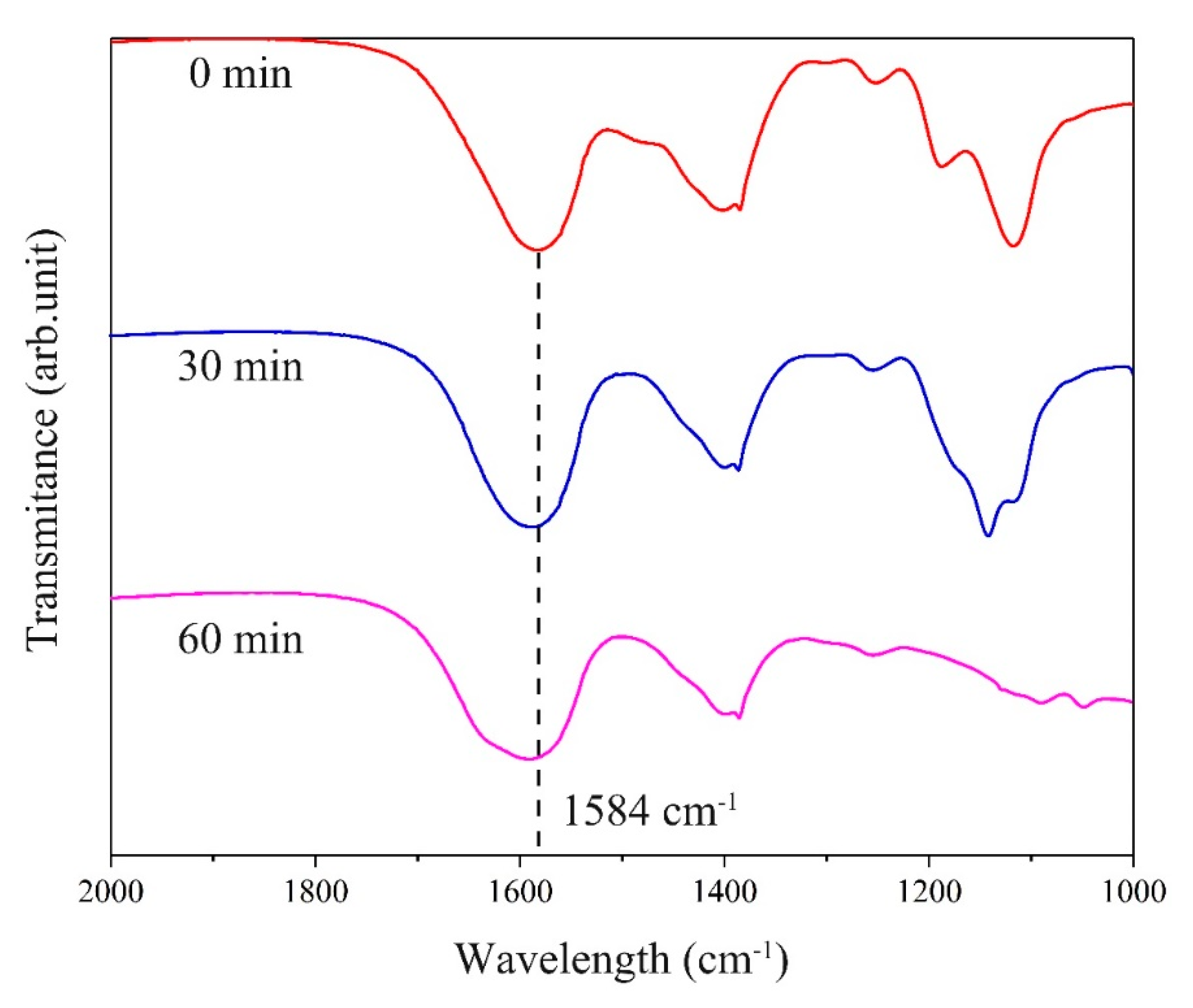
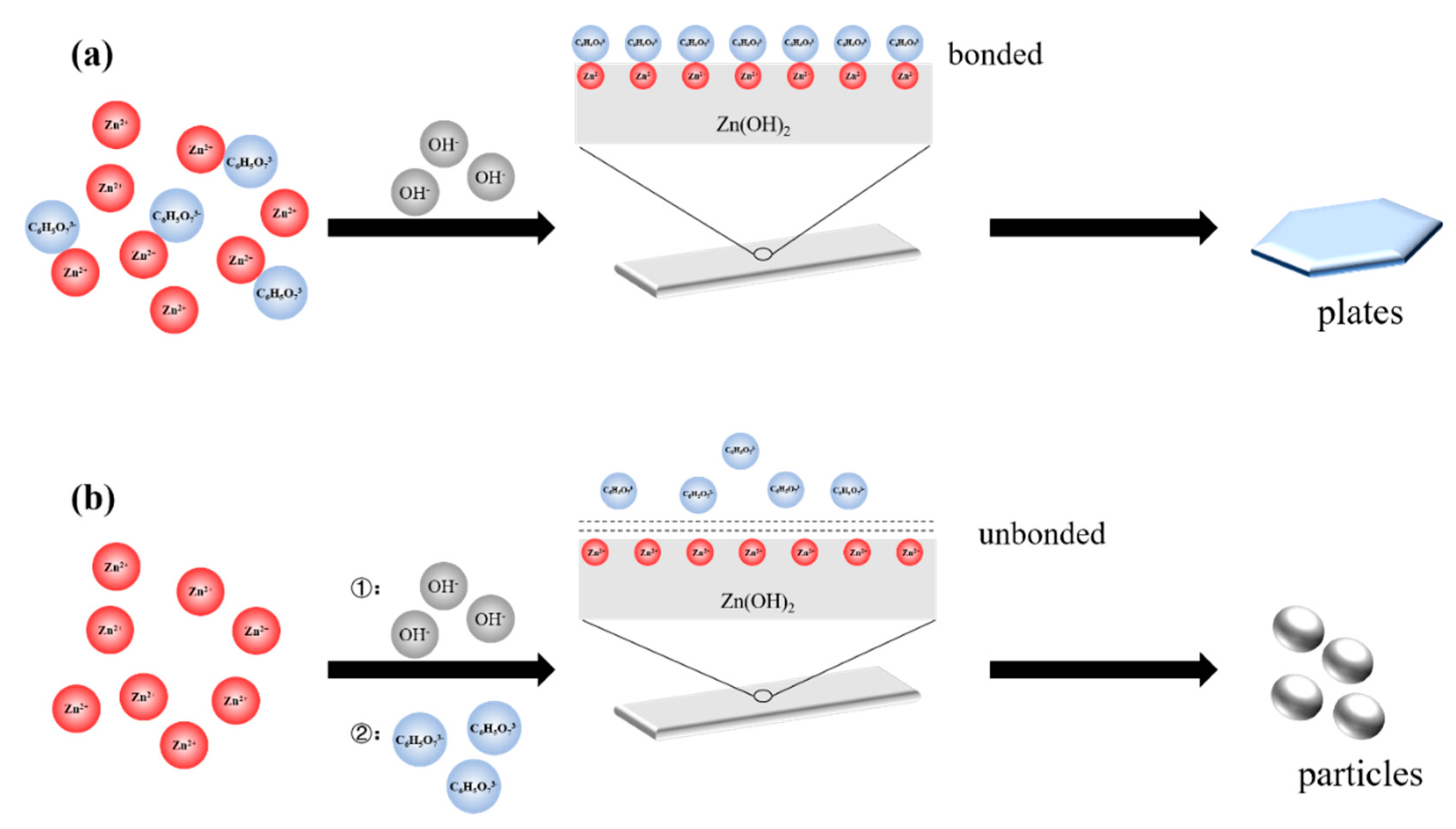
| Zinc Species | Concentration (OS) | Ratio (OS) | Concentration (TS) | Ratio (TS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn2+ | 4.59 × 10−2 | 45.9% | 9.23 × 10−2 | 92.3% |
| Zn2+-C6H6O72− | 3.15 × 10−7 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Zn2+-C6H5O73− | 4.99 × 10−2 | 49.9% | 0 | 0 |
| ZnSO4(aq) | 4.10 × 10−3 | 4.1% | 7.70 × 10−3 | 7.7% |
| Zn(OH)+ | 1.82 × 10−6 | 0 | 3.67 × 10−6 | 0 |
| Zn(OH)2(aq) | 2.30 × 10−8 | 0 | 2.92 × 10−8 | 0 |
| Zn(OH)3− | 2.52 × 10−14 | 0 | 2.54 × 10−14 | 0 |
| Zn(OH)42− | 3.33 × 10−19 | 0 | 1.06 × 10−19 | 0 |
| Sample | Zeta Potential [mV] |
|---|---|
| OS precursor (0 min) | −25.8 |
| ZnO-OS (70 min) | −30.2 |
| TS precursor in water | −9.5 |
| TS precursor in citrate solution | −10.3 |
| ZnO-TS (70 min) | −26.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, S.; Chen, R.; Xiang, L.; Wang, J. Hydrothermal Synthesis of (001) Facet Highly Exposed ZnO Plates: A New Insight into the Effect of Citrate. Crystals 2019, 9, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9110552
Luo S, Chen R, Xiang L, Wang J. Hydrothermal Synthesis of (001) Facet Highly Exposed ZnO Plates: A New Insight into the Effect of Citrate. Crystals. 2019; 9(11):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9110552
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Shirui, Ruosong Chen, Lan Xiang, and Jing Wang. 2019. "Hydrothermal Synthesis of (001) Facet Highly Exposed ZnO Plates: A New Insight into the Effect of Citrate" Crystals 9, no. 11: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9110552
APA StyleLuo, S., Chen, R., Xiang, L., & Wang, J. (2019). Hydrothermal Synthesis of (001) Facet Highly Exposed ZnO Plates: A New Insight into the Effect of Citrate. Crystals, 9(11), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9110552






