Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystalline ZnO Doped with Al3+ and Ni2+ by a Sol–Gel Method Coupled with Ultrasound Irradiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Powders
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
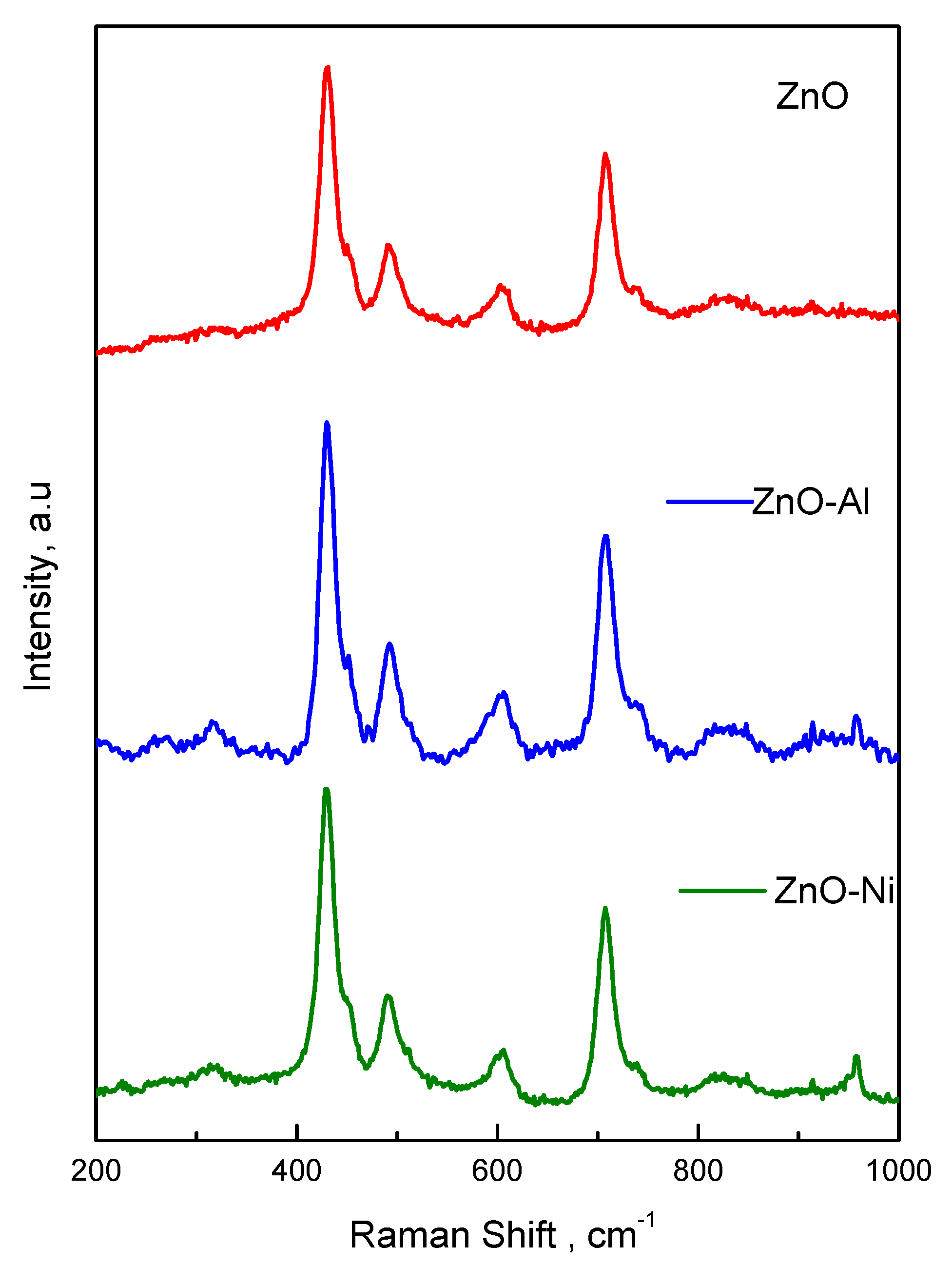
3.1. Structure from XRD Patterns and Raman Spectra
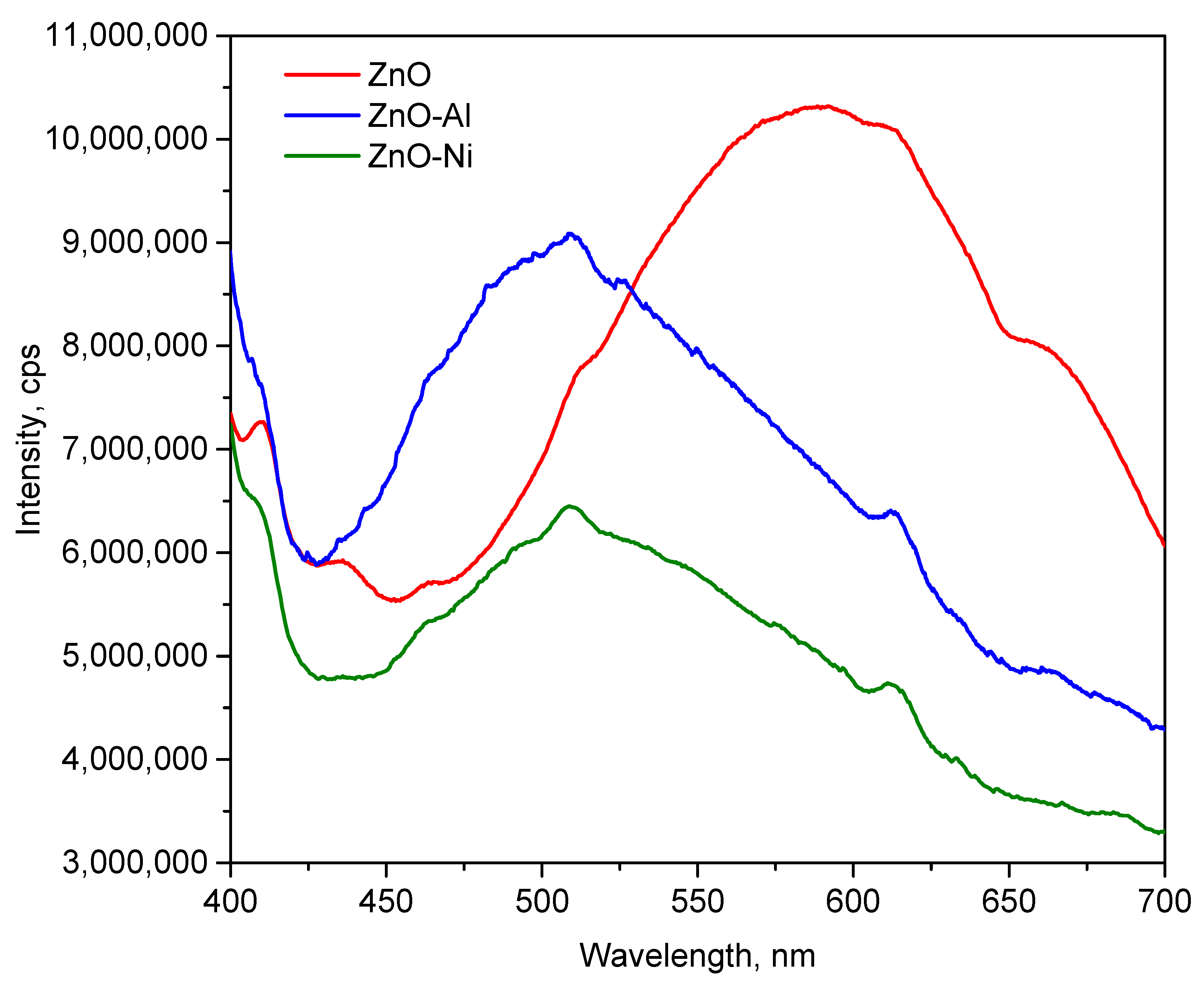
3.2. Optical Properties
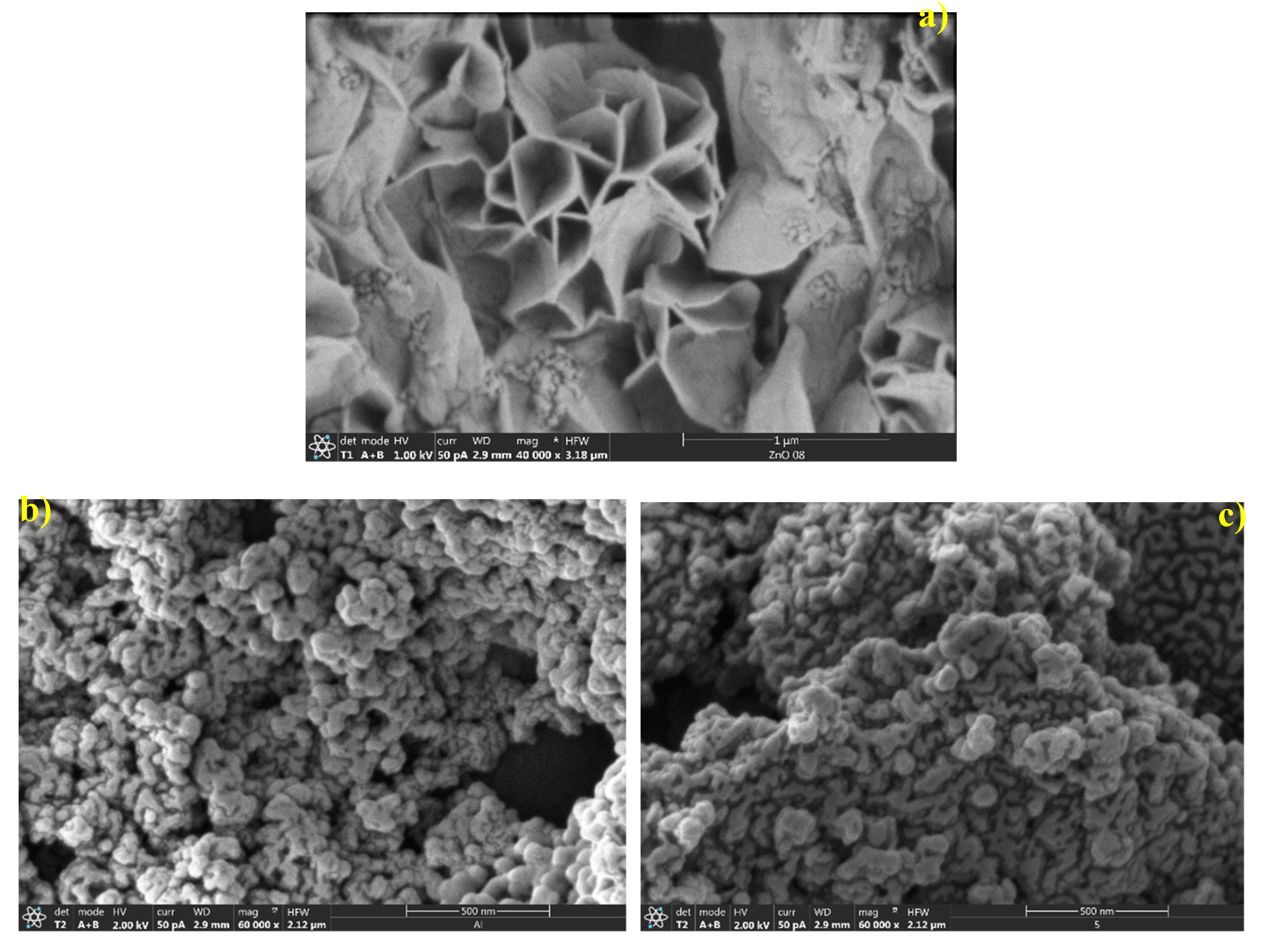
3.3. Surface Morphological Studies
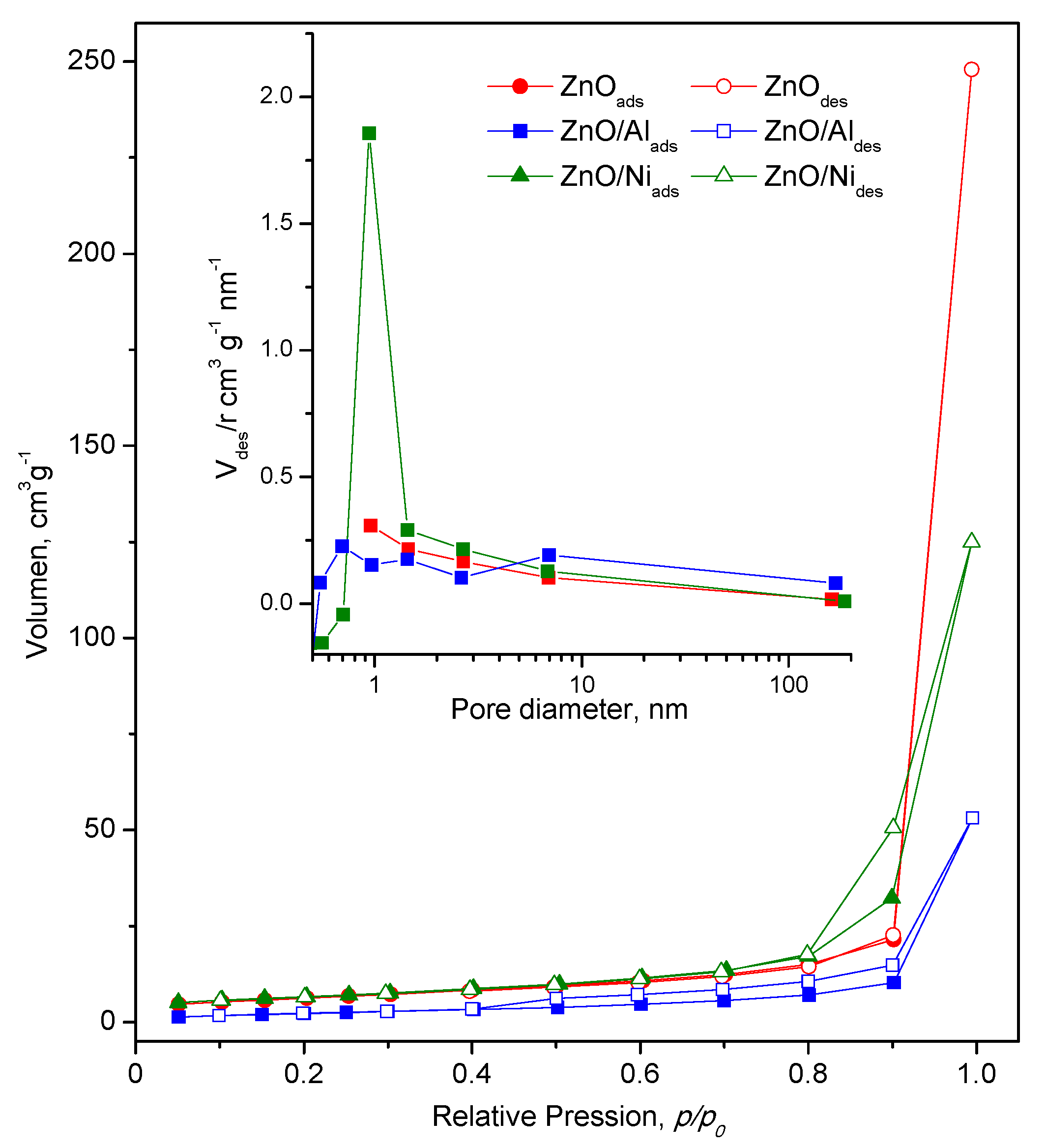
3.4. Textural Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samadi, M.; Zirak, M.; Naseri, A.; Khorashadizade, E.; Moshfegh, A.Z. Recent progress on doped ZnO nanostructures for visible-light photocatalysis. Thin Solid Films 2015, 605, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morko, H.; Özgur, U. Zinc Oxide: Fundamentals, Materials and Device Technology; Wiley-VCH Verlag GMBH&Co: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; ISBN 9783527408139. [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc oxide—from synthesis to application: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahtar, A.; Benramache, S.; Benhaoua, B.; Chabane, F. Preparation of transparent conducting ZnO:Al films on glass substrates by ultrasonic spray technique. J. Semicond. 2013, 34, 073002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, M.H.; Khusaimi, Z.; Zahidi, M.M.; Mahmood, M.R. ZnO nanorod arrays synthesised using ultrasonic-assisted sol-gel and immersion methods for ultraviolet photoconductive sensor applications. Nanorods 2012, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, N.T.; Noh, J.; Park, S. Role of ZnO thin film in the vertically aligned growth of ZnO nanorods by chemical bath deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 379, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lojkowski, W.; Gedanken, A.; Grzanka, E.; Opalinska, A.; Strachowski, T.; Pielaszek, R.; Tomaszewska-Grzeda, A.; Yatsunenko, S.; Godlewski, M.; Matysiak, H.; et al. Solvothermal synthesis of nanocrystalline zinc oxide doped with Mn2+, Ni2+, Co2+ and Cr3+ ions. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, K.P.; Pawar, R.C.; Sinha, B.B.; Kim, H.S.; Oh, S.S.; Chung, K.C. Optical and magnetic properties of Ni doped ZnO planetary ball milled nanopowder synthesized by co-precipitation. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 16799–16804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, M.Y.; Hussain, I.; Bano, N.; Lu, J.; Hultman, L.; Nur, O.; Willander, M. Growth, structural and optical characterization of ZnO nanotubes on disposable-flexible paper substrates by low-temperature chemical method. J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2012, 251863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddheswaran, R.; Netrvalová, M.; Savková, J.; Novák, P.; Očenášek, J.; Šutta, P.; Kováč, J.; Jayavel, R. Reactive magnetron sputtering of Ni doped ZnO thin film: Investigation of optical, structural, mechanical and magnetic properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 636, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Than Htay, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Momose, N.; Ito, K. Position-selective growth of ZnO nanowires by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 4499–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Feng, C.; Li, X. Ultraviolet-assisted synthesis of hourglass-like ZnO microstructure through an ultrasonic and microwave combined technology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alammar, T.; Mudring, A.-V. Sonochemical Synthesis of 0D, 1D, and 2D Zinc Oxide Nanostructures in Ionic Liquids and Their Photocatalytic Activity. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeh, S.; Mhamdi, A.; Khirouni, K.; Amlouk, M.; Guermazi, S. Optics & Laser Technology Experiments on ZnO: Ni thin fi lms with under 1 % nickel content. Opt. Laser Technol. 2014, 69, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayari, A.; El Mir, L.; Jürgen von Bardeleben, H. Structural, EPR and optical properties of Zn0.75TM0.25O (TM = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) aerogel nanoparticles. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 67, 10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalakshmi, R.; Angappane, S. Synthesis, characterization and photoresponse study of undoped and transition metal (Co, Ni, Mn) doped ZnO thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2013, 178, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Doǧan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.J.; Morkoç, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 1–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, G.K.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Selective detection of ammonia using spray pyrolysis deposited pure and nickel doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 311, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, B.; Sarkar, D.; Giri, P.K. Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Ni Doped ZnO nanoparticles: correlation of magnetic moment with defect density. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.H.; Suslick, K.S. Applications of Ultrasound to the Synthesis of Nanostructured Materials. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1039–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, G.; Pal, U.; Serrano, J.G. Correlations among size, defects, and photoluminescence in ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 024317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabekkodu, S.N.; Faber, J.; Fawcett, T. New Powder Diffraction File (PDF-4) in relational database format: Advantages and data-mining capabilities. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. 2002, 58, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-saadi, T.M.; Bakr, N.A.; Hameed, N.A. Study of nanocrystalline structure and micro properties of ZnO powders by using Rietveld method. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Res. 2014, 2, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Guruvammal, D.; Selvaraj, S.; Meenakshi Sundar, S. Effect of Ni-doping on the structural, optical and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles by solvothermal method. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, M.; Muthukumaran, S. Effect of Ni doping on electrical, photoluminescence and magnetic behavior of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 2015, 162, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneva, N.V.; Dimitrov, D.T.; Dushkin, C.D. Effect of nickel doping on the photocatalytic activity of ZnO thin films under UV and visible light. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 8113–8120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.K.; Sreenivas, K.; Gupta, V.; Katiyar, R.S. Structural studies and Raman spectroscopy of forbidden zone boundary phonons in Ni-doped ZnO ceramics. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 40, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, V.; Singh, A.; Pugh, D.C.; Parkin, I.P. Ethanol sensing characteristics of Zn0.99M0.01O (M = Al/Ni) nanopowders. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 2016, 213, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuruangrat, A.; Thongtem, S.; Thongtem, T. Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis and photocatalytic performance of ZnO nanoplates and microflowers. Mater. Des. 2016, 107, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayari, A.; El Mir, L. Structural and optical characterization of Ni and Al co-doped ZnO nanopowders synthesized via the sol-gel process. KONA Powder Part. J. 2015, 32, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yang, Y.; Yang, G. Great blue-shift of luminescence of ZnO nanoparticle array constructed from ZnO quantum dots. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearton, S.J.; Norton, D.P.; Ivill, M.P.; Hebard, A.F.; Zavada, J.M.; Chen, W.M.; Buyanova, I.A. ZnO Doped With Transition Metal Ions. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2007, 54, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuśnieruk, S.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Chodara, A.; Chudoba, T.; Gierlotka, S.; Lojkowski, W. Influence of hydrothermal synthesis parameters on the properties of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1586–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sample | Composition (by XRF) | Structural Parameters | Textural Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a [Å] | c [Å] | V [Å3] | Rwp [%] | % Zn | % O | % Ni,Al | Crystallite Size t (nm) | Band Gap Eg (eV) | SBET (m2 g−1) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | |
| ZnO | 3.252 (2) | 5.209 (4) | 47.72 | 8.45 | 78.8 | 21.2 | 0.00 | 21.0 | 3.60 | 22.0 | 68.0 |
| ZnO/Al | 3.252 (3) | 5.211 (2) | 47.35 | 8.27 | 77.9 | 21.1 | 0.99 | 22.0 | 3.44 | 23.0 | 33.0 |
| ZnO/Ni | 3.252 (1) | 5.211 (5) | 46.10 | 8.34 | 78.0 | 21.2 | 0.80 | 24.5 | 3.39 | 9.0 | 36.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robles-Águila, M.J.; Luna-López, J.A.; Hernández de la Luz, Á.D.; Martínez-Juárez, J.; Rabanal, M.E. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystalline ZnO Doped with Al3+ and Ni2+ by a Sol–Gel Method Coupled with Ultrasound Irradiation. Crystals 2018, 8, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110406
Robles-Águila MJ, Luna-López JA, Hernández de la Luz ÁD, Martínez-Juárez J, Rabanal ME. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystalline ZnO Doped with Al3+ and Ni2+ by a Sol–Gel Method Coupled with Ultrasound Irradiation. Crystals. 2018; 8(11):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110406
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobles-Águila, M. J., J. A. Luna-López, Álvaro D. Hernández de la Luz, J. Martínez-Juárez, and M. E. Rabanal. 2018. "Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystalline ZnO Doped with Al3+ and Ni2+ by a Sol–Gel Method Coupled with Ultrasound Irradiation" Crystals 8, no. 11: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110406
APA StyleRobles-Águila, M. J., Luna-López, J. A., Hernández de la Luz, Á. D., Martínez-Juárez, J., & Rabanal, M. E. (2018). Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystalline ZnO Doped with Al3+ and Ni2+ by a Sol–Gel Method Coupled with Ultrasound Irradiation. Crystals, 8(11), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110406








