Supramolecular Switching by Substituent Tuning: A Crystal Engineering Study of 2-Amino- and 2,3-Diamino-5-Halogenopyridines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
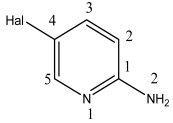
3.1. Analysis of the Molecular Structure
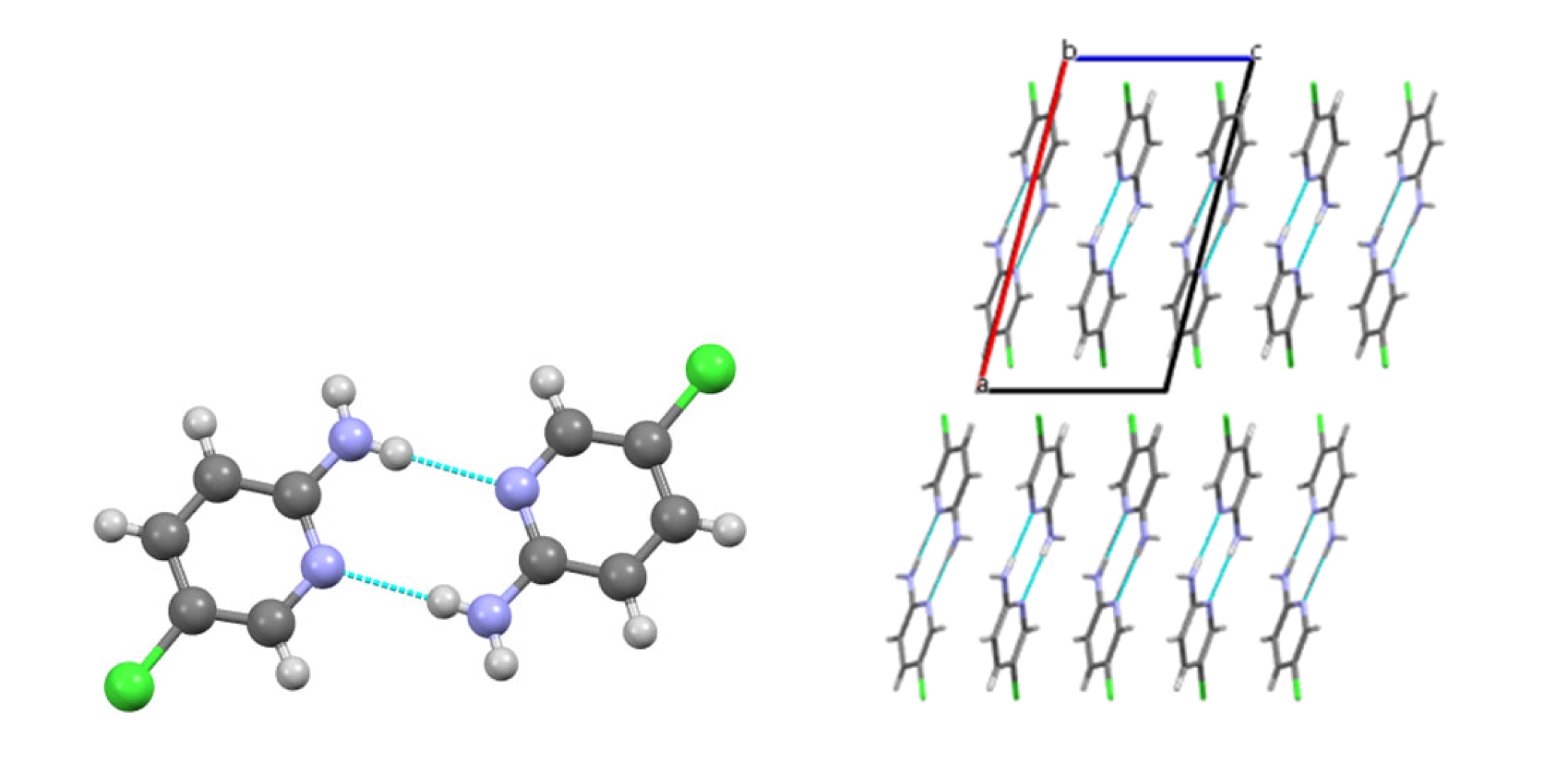
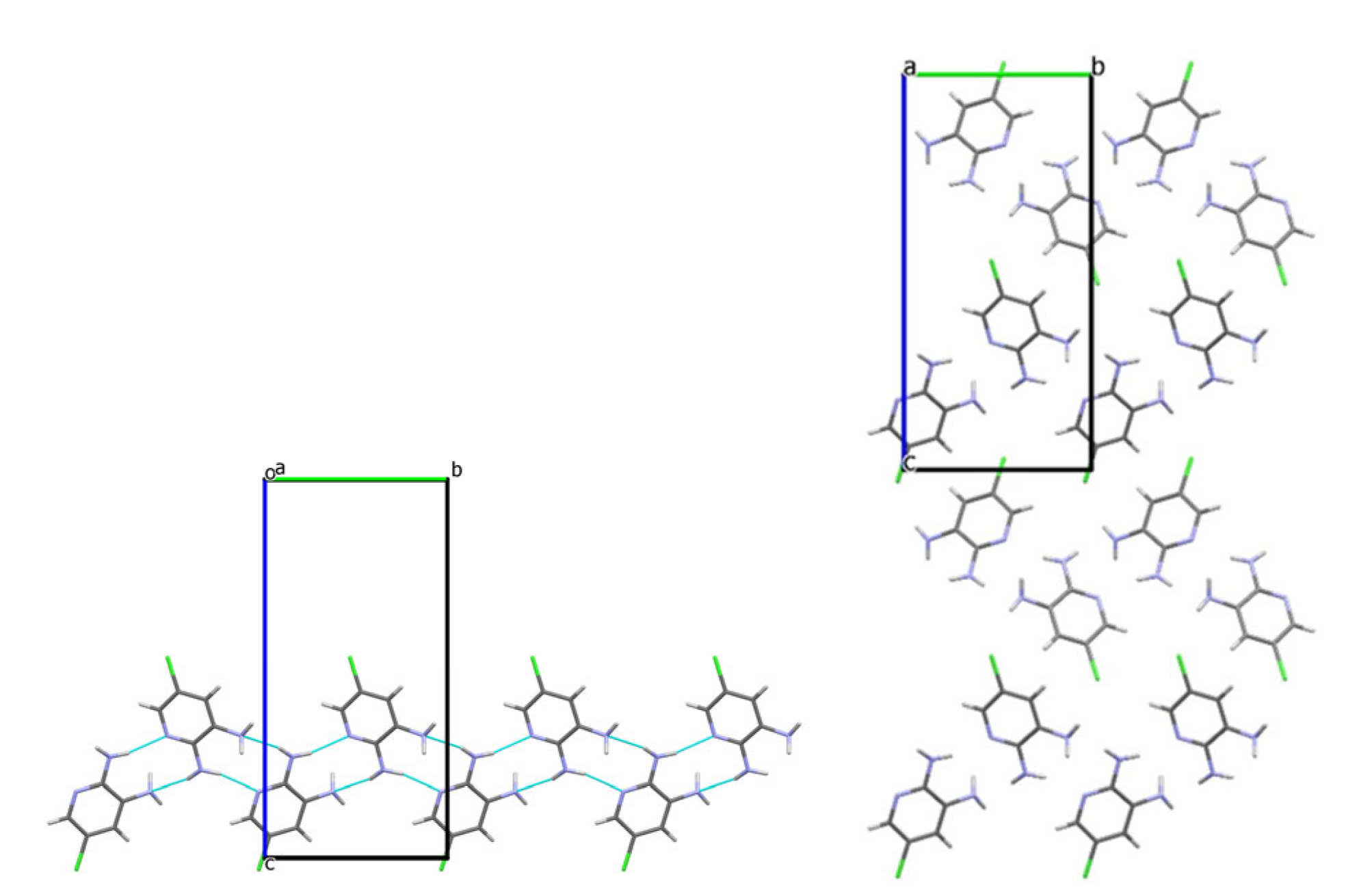
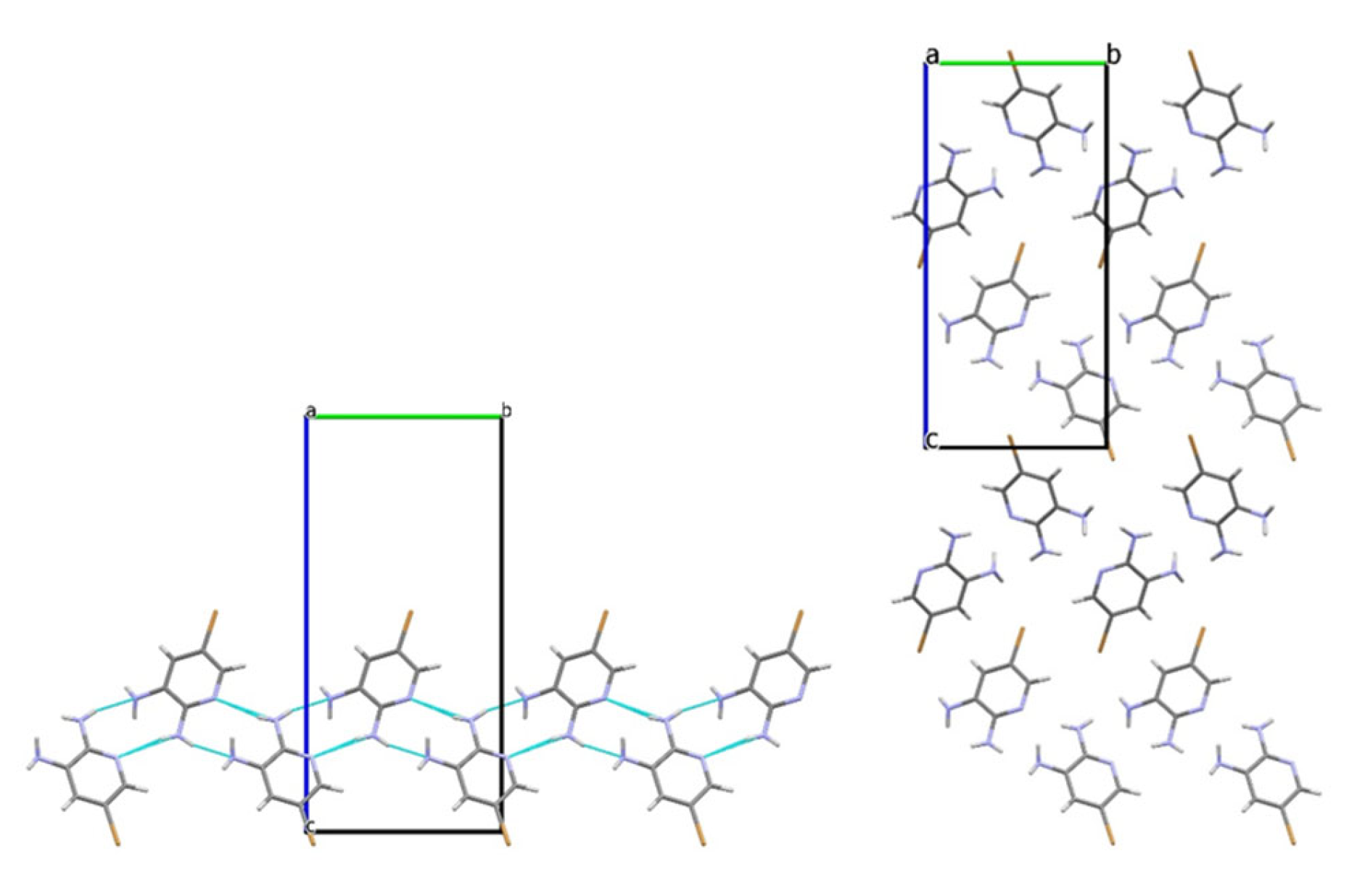
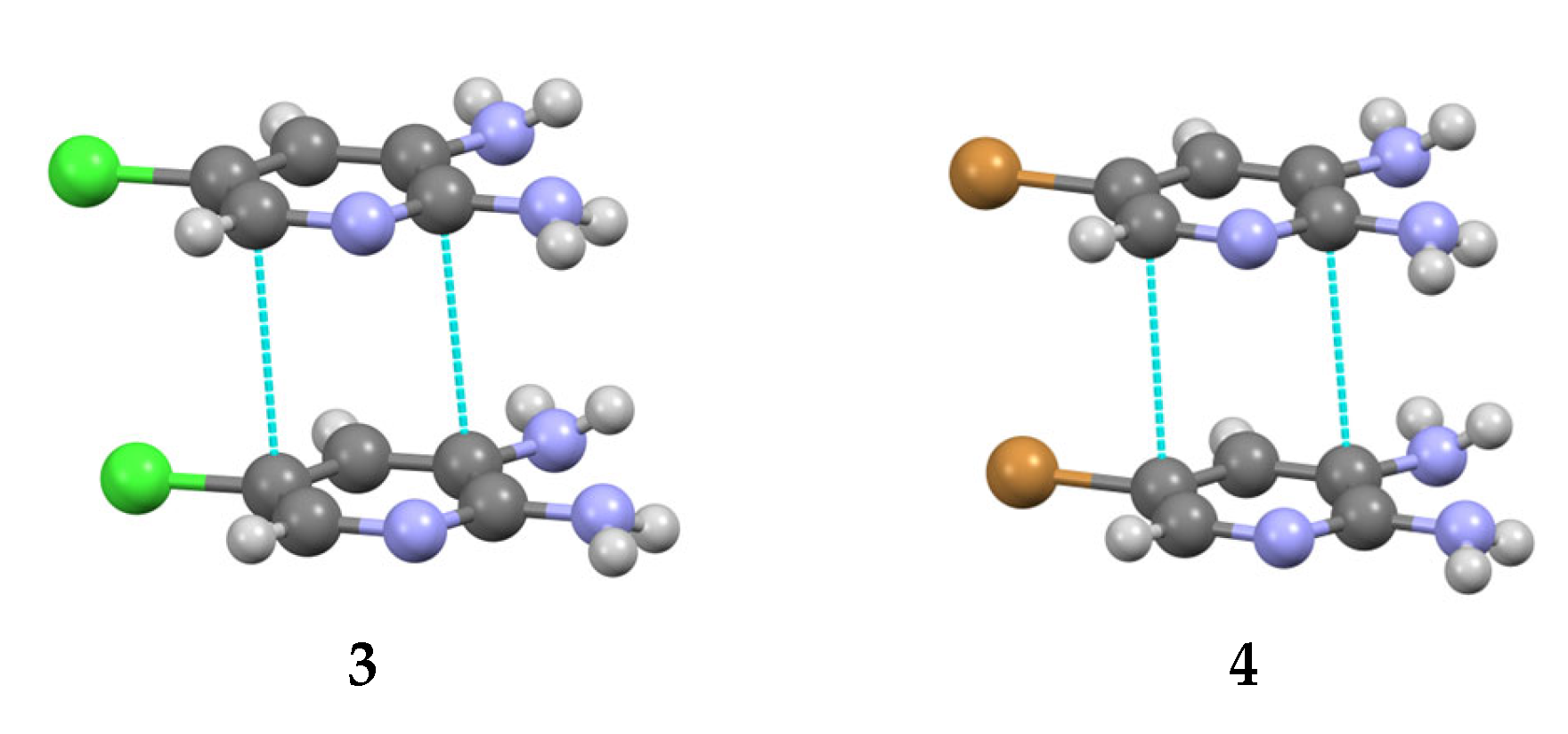
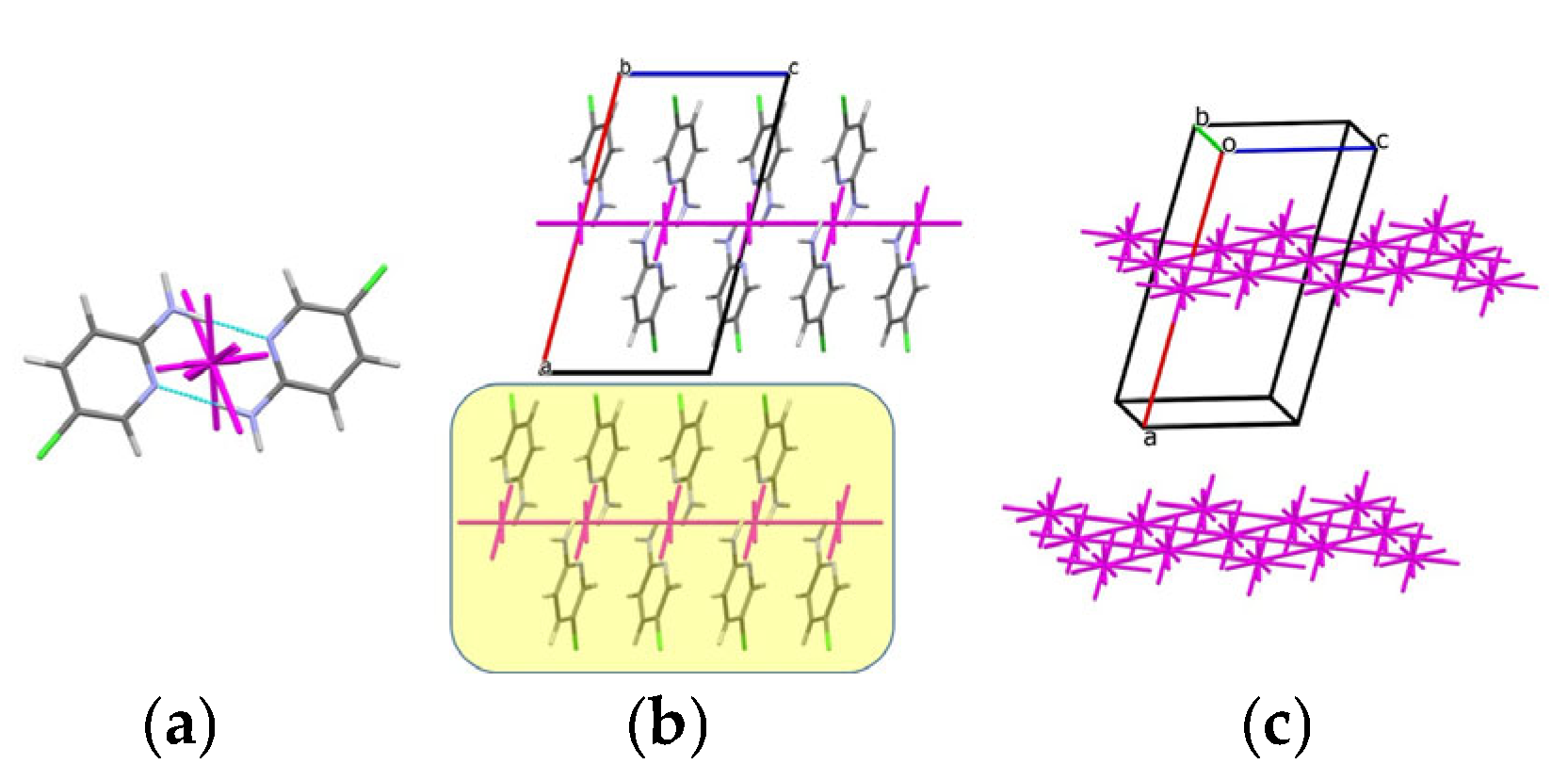
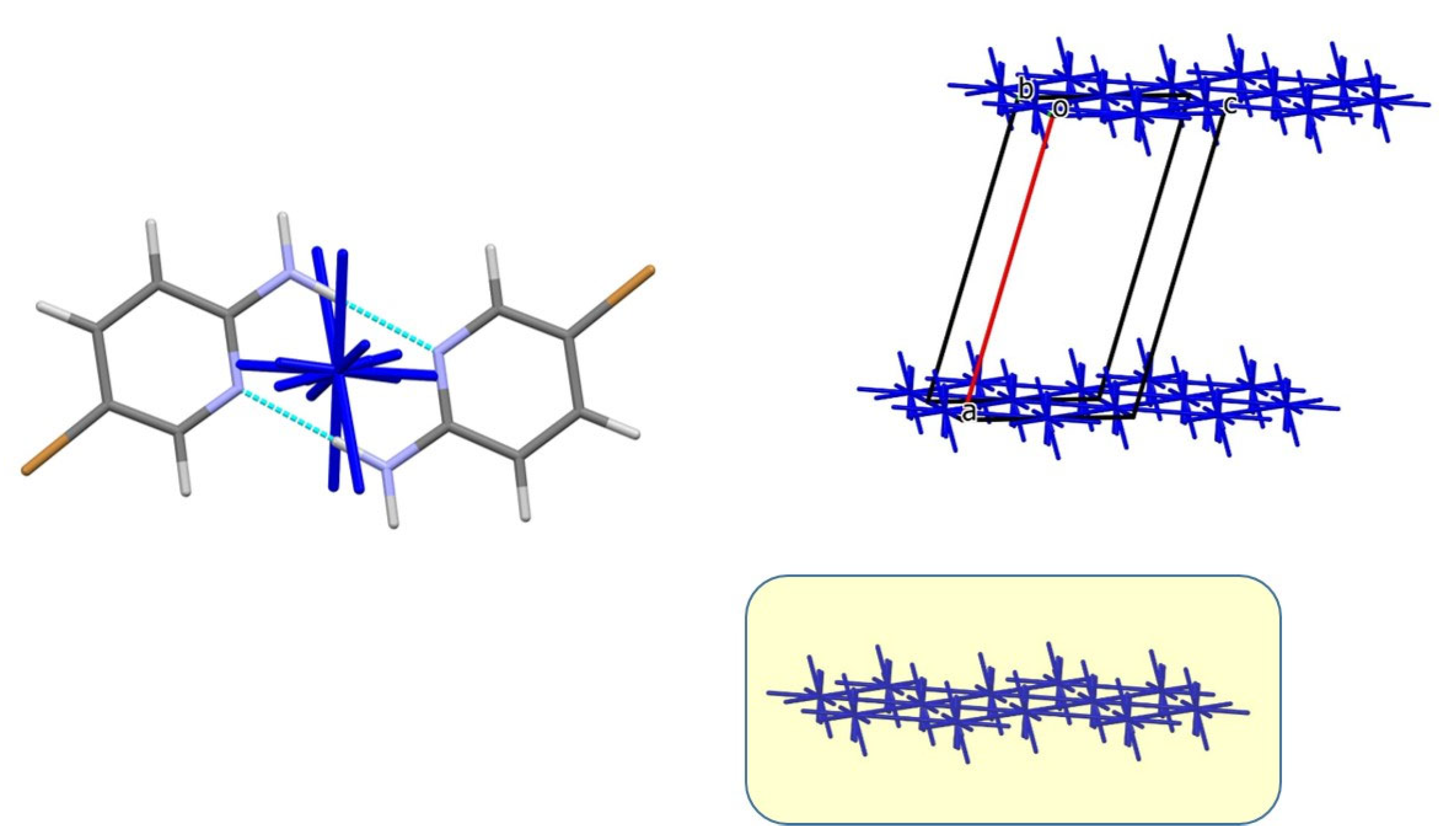
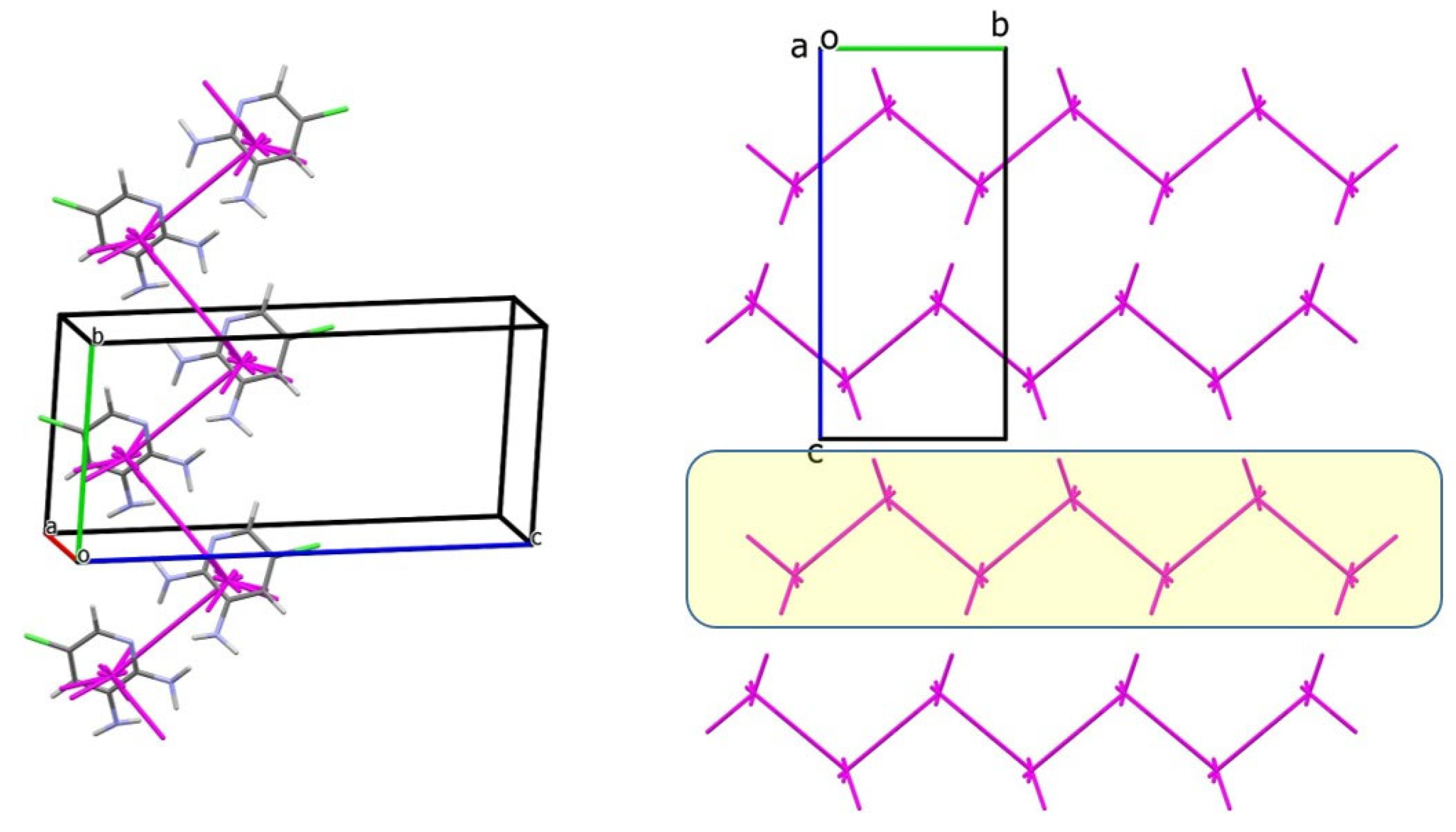
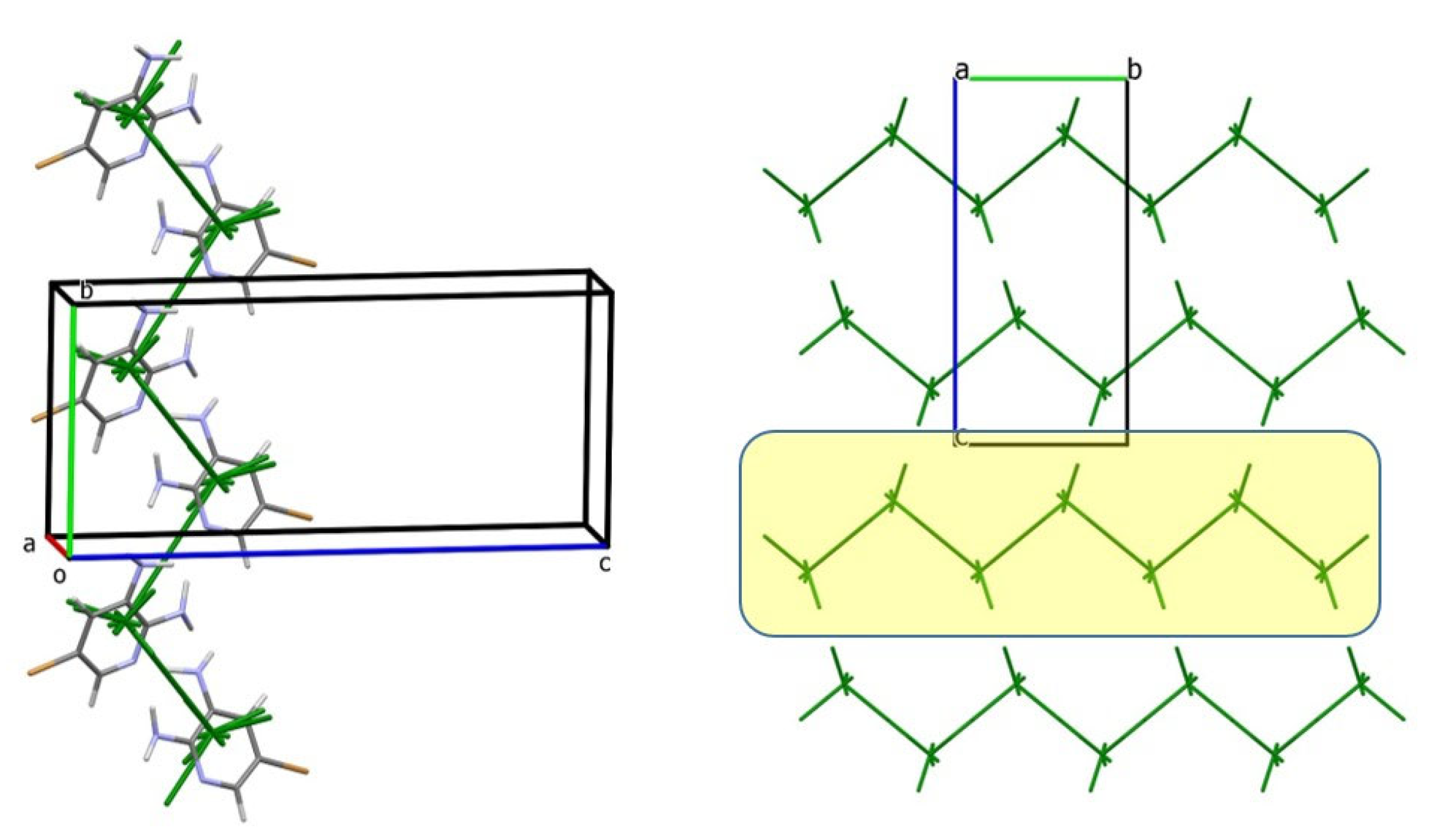
3.2. Analysis of the Crystal Structures of Compounds 1–4: Focus on Geometrical Parameters of Intermolecular Interactions
- (a)
- In mono-amino halogen pyridines 1 and 2, the amino group primarily participates in hydrogen bonding as a H donor;
- (b)
- Due to the presence of two amino groups, compounds 3 and 4 are simultaneously involved in hydrogen bonding interactions, acting as bifunctional proton donors and acceptors;
- (c)
- Stacking interactions are not observed in mono-amino-halogenopyridines;
- (d)
- Although geometric analysis is informative, it does not always allow for unambiguous interpretation of crystal packing motifs or the role of weak or non-specific interactions.
3.3. Energetic Perspective on the Crystal Structures of Compounds 1–4
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konovalova, I.S.; Shishkina, S.V.; Bani-Khaled, G.; Muzyka, K.; Boyko, A.N. Intermolecular interactions in crystals of benzene and its mono- and dinitro- derivatives: Study from the energetic viewpoint. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 2908–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiraju, G.R. Crystal Design: Structure and Function Perspectives in Supramolecular Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Desiraju, G.R. Supramolecular synthons in crystal engineering—A new organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 2311–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiraju, G.R. Chemistry beyond the molecule. Nature 2001, 412, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishkina, S.V.; Konovalova, I.S.; Shishkin, O.V.; Boyko, A.N. Acceptor properties of amino groups in aminobenzene crystals: Study from the energetic viewpoint. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 6274–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkina, S.V.; Konovalova, I.S.; Shishkin, O.V.; Boyko, A.N. Influence of substituents on the acceptor properties of the amino groups in the diaminobenzene analogues. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 7162–7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalova, I.S.; Muzyka, E.N.; Urzhuntseva, V.V.; Shishkina, S.V. Role of intermolecular interactions in formation of mono- and diaminopyridine crystals: Study from the energetic viewpoint. Struct. Chem. 2021, 32, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, R.; Gerber, T.; Hosten, E.; Schalekamp, H. Pyridine-2,3-diamine. Acta Crystallogr. 2011, E67, o2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalova, I.S.; Reiss, G.J. Halogen bonds versus hydrogen bonds in the crystal packing formation of halogen substituted anilines. Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater. 2025, 240, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalova, I.S.; Nöthling, N.; Reiss, G.J. Energetic perspective on the crystal structure organization principles of meta-halogen anilines. J. Mol. Struct. 2025; in print. [Google Scholar]
- Goubitz, K.; Sonneveld, E.J.; Schenk, H. Crystal structure determination of a series of small organic compounds from powder data. Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater. 2001, 216, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulovari, A.; Tanski, J.M. Crystallographic and spectroscopic characterization of 5-chloropyridine-2,3-diamine. Acta. Crystallogr. 2017, E73, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, G.J.; Leske, P.B. 2-Amino-pyridin-1-ium triiodide. Acta. Crystallogr. E 2013, 69, o1060–o1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, M.; Loganathan, K.; Sithick, A.K. Synthesis, characterization and biological importance of aminocyanopyridines. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2012, 4, 479–483. [Google Scholar]
- Huckle, W.R.; Drag, M.D.; Acker, W.R.; Powers, M.; McFall, R.C.; Holder, D.J.; Fujita, T.; Stabilito, I.I.; Kim, D.; Ondeyka, D.L.; et al. Effects of Subtype-Selective and Balanced Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists in a Porcine Coronary Artery Model of Vascular Restenosis. Circulation 1996, 93, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Rho, M.-C.; Gajulapati, K.; Jung, H.-Y.; Boovanahalli, S.K.; Lee, J.-H.; Song, G.-Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-K.; Lee, K.; et al. Synthesis of a novel series of imidazo[1,2-α]pyridines as acyl-CoA: Cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitors. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2009, 30, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Temple, C.J.; Rener, G.A.; Waud, W.R.; Noker, P.E. Antimitotic agents: Structure–activity studies with some pyridine derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 3686–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishkin, O.V.; Dyakonenko, V.V.; Maleev, A.V. Supramolecular architecture of crystals of fused hydrocarbons based on topology of intermolecular interactions. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 1795–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkin, O.V.; Zubatyuk, R.I.; Shishkina, S.V.; Dyakonenko, V.V.; Medviediev, V.V. Role of supramolecular synthons in the formation of the supramolecular architecture of molecular crystals revisited from an energetic viewpoint. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 6773–6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkina, S.V. Analysis of intermolecular interactions in organic crystals using quantum-chemical methods. Struct. Chem. 2019, 30, 1565–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, C.F.; Bruno, I.J.; Chisholm, J.A.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Rodriquez-Monge, L.; Taylor, R.; van de Streek, J.; Wood, P.A. Mercury CSD 2.0—New features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppens, P. The use of a polarized hydrogen atom in X-ray structure refinement. Acta Crystallogr. Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem. 1972, B28, 1638–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S. Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Goerigk, L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.; Horn, H.; Ahlrichs, R. Fully optimized contracted Gaussian basis sets for atoms Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2571–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boys, S.F.; Bernardi, F. The calculation of small molecular interactions by the differences of separate total energies. Some procedures with reduced errors. Mol. Phys. 1970, 19, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerigk, L.; Grimme, S. A thorough benchmark of density functional methods for general main group thermochemistry, kinetics, and noncovalent interactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 6670–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neese, F. The ORCA program system. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2012, 2, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, C.R.; Bruno, I.J.; Lightfoot, M.P.; Ward, S.C. The Cambridge Structural Database. Acta Cryst. B 2016, 72, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalova, I.S.; Reiss, G.J. Crystal and molecular structure of 5-bromopyridine-2,3-diamine. Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 891–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourayoubi, M.; Ghadimi, S.; Valmoozi, A.A.E. A redetermination of 2-amino-5-chloro-pyridine at 100 K. Acta Cryst. 2007, E63, o4631. [Google Scholar]
- Corozzi, A.; Mennucci, B.; Cammi, R.; Tomasi, J. Structure versus solvent effects on nonlinear optical properties of push–pull systems: A quantum-mechanical study based on a polarizable continuum model. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 14774–14784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishkin, O.V.; Konovalova, I.S.; Zubatyuk, R.I.; Palamarchuk, G.V.; Shishkina, S.V.; Biitseva, A.V.; Rudenko, I.V.; Tkachuk, V.A.; Kornilov, M.Y.; Hordiyenko, O.V.; et al. Remarkably strong polarization of amidine fragment in the crystals of 1-imino-1H-isoindol-3-amine. Struct. Chem. 2013, 24, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orpen, A.G.; Brammer, L.; Allen, F.H.; Kennard, O.; Watson, D.G.; Taylor, R. Typical interatomic distances in organic compounds and organometallic compounds and coordination complexes of the d- and f-block metals. In Structure Correlation; Bürgi, H.-B., Dunitz, J.D., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1994; Volume 2, pp. 741–926. [Google Scholar]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S.; Clark, T. Halogen bonding: An electrostatically driven highly directional noncovalent interaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 7748–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.S.; Lane, P.; Politzer, P. A predicted new type of directional noncovalent interaction. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2007, 107, 2286–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkin, O.V.; Konovalova, I.S.; Gorb, L.; Leszczynski, J. Novel type of mixed O–H···N/O–H···π hydrogen bonds: Monohydrate of pyridine. Struct Chem. 2009, 20, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthe, E. Elements of Inorganic Structural Chemistry, 2nd ed.; K. Sutter Parthe Publisher: Petit-Lancy, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
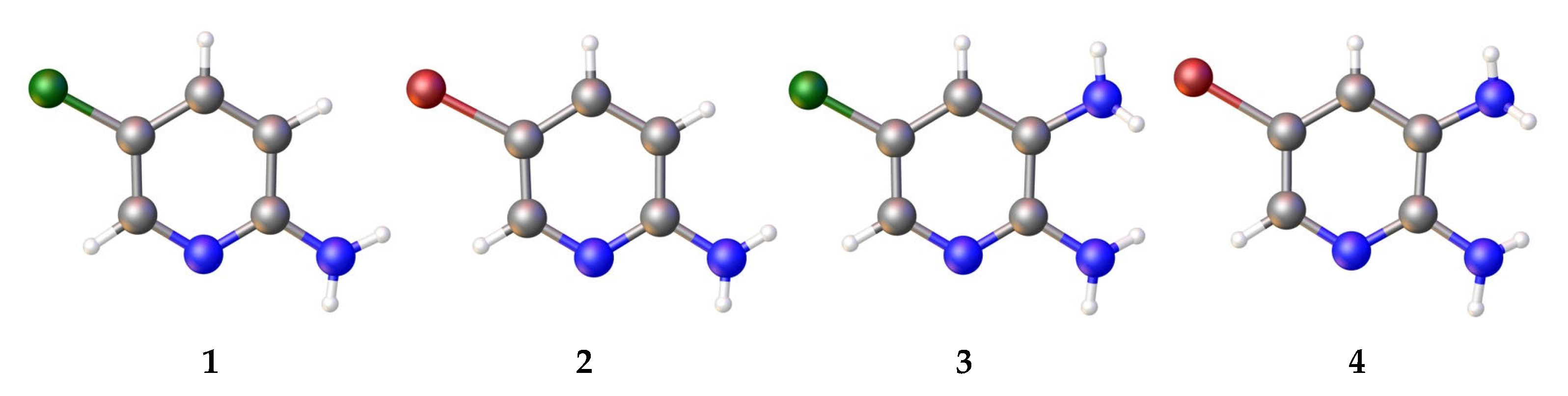

| № | Refcode | Space Group | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AMCLPY12 | P21/c | [33] |
| 2 | CAJXAN | P21/c | [11] |
| 3 | XEFMIH | P212121 | [12] |
| 4 | CUFBAK | P212121 | [32] |
Compound 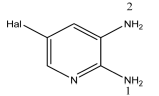 | C–N1, Å | C–N2, Å | ∑N(1), Deg. | ∑N(2), Deg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.360(7) | 359 | ||
| 2 | 1.355(6) | 360 | ||
| 3 | 1.385(4) | 1.407(4) | 348 | 342 |
| 4 | 1.380(5) | 1.408(4) | 346 | 333 |
 | Interaction | Symmetry Operations | H…A, Å | D–H…A, Deg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N2–H···N1pyr | 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z | 2.20 | 179 |
| N2–H···N1mix | x, 0.5 − y, 0.5 + z | 2.83 | 137 | |
| C2–H···C5π | x, 0.5 − y, 0.5 + z | 2.75 | 157 | |
| C2–H···N1π | x, 0.5 − y, 0.5 + z | 2.77 | 131 | |
| C3–H···Cl | 2 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z | 2.98 | 167 | |
| Cl···π | x, 1.5 − y, −0.5 + z | 3.47 | ||
| 2 | N2–H···N1pyr | 2 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z | 2.25 | 176 |
| C2–H···N1π | x, 1.5 − y, −0.5 + z | 2.88 | 136 | |
| C2–H···C1π | x, 1.5 − y, −0.5 + z | 2.93 | 159 | |
| Br···Br | 1 − x, 0.5 + y, 1.5 − z | 3.77 |
 | Interaction | Symmetry Operations | H…A, Å | D–H…A, Deg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | N2–H···N1pyr | 2 − x, −0.5 + y, 1.5 − z | 2.19 | 167 |
| N2–H···N3LP | 2 − x, −0.5 + y, 1.5-z | 2.38 | 166 | |
| N3–H···N1mix | −x, −0.5 + y, 1.5 − z | 2.48 | 151 | |
| C3–H···C3π | 0.5 + x, 1.5 − y, 1 − z | 2.89 | 153 | |
| C5–H···Cl | 1.5 − x, −y, 0.5 + z | 2.87 | 169 | |
| N3–H···Cl | 0.5 + x, 1.5 − y, 1 − z | 2.93 | 164 | |
| C3–H···Cl | 0.5 + x, 1.5 − y, 1 − z | 3.01 | 148 | |
| C2···C1, stacking | −1 + x, y, z | 3.39 | ||
| 4 | N2–H···N1pyr | −1 − x, 0.5 + y, 1.5 − z | 2.31 | 167 |
| N2–H···N3LP | −1 − x, 0.5 + y, 1.5 − z | 2.37 | 167 | |
| N3–H···N1mix | −1.5 + x, 1.5 − y, 2 − z | 2.46 | 153 | |
| N3–H···C1π | −1.5 + x, 1.5 − y, 2 − z | 2.81 | 130 | |
| C5–H···Br | −0.5 − x, 2 − y, 0.5 + z | 2.91 | 164 | |
| N3–H···Br | −0.5 − x, 1 − y, 0.5 + z | 3.09 | 166 | |
| C2···C1, stacking | −1 + x, y, z | 3.44 |
| Dimer | Symmetry Operation | Eint, kcal/mol | ER, % | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building unit is a molecule | ||||
| 1-m1 | 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z | −12.02 | 24.3 | N–H…Npyr 2.07 Å, 161° |
| 1-m2 | x, 1/2 − y, 1/2 + z | −6.44 | 13.0 | N–H…Nmix 2.75 Å, 135°; C–H…π 2.68 Å, 156°; 2.72 Å, 130° |
| 1-m3 | x, 1/2 − y, −1/2 + z | −6.44 | 13.0 | N–H…Nmix 2.75 Å, 135°; C–H…π 2.68 Å, 156°; 2.72 Å, 130° |
| 1-m4 | x, 1 + y, z | −3.66 | 7.4 | non-specific |
| 1-m5 | x, −1 + y, z | −3.66 | 7.4 | non-specific |
| 1-m6 | x, 3/2 − y, 1/2 + z | −3.58 | 7.3 | C–H…π 2.83 Å, 157° |
| 1-m7 | x, 3/2 − y, −1/2 + z | −3.58 | 7.3 | C–H…π 2.83 Å, 157° |
| 1-m8 | 2 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z | −2.77 | 5.6 | C–H…Cl 2.85 Å, 167° |
| Building unit is a dimer | ||||
| 1-d1 | 1 − x, 1/2 + y, 3/2 − z | −11.18 | 15.1 | N–H…Nmix 2.75 Å, 135°; C–H…π 2.68 Å, 156°; 2.72 Å, 130°; 2.83 Å, 157° |
| 1-d2 | 1 − x, −1/2 + y, 3/2 − z | −11.18 | 15.1 | N–H…Nmix 2.75 Å, 135°; C–H…π 2.68 Å, 156°; 2.72 Å, 130°; 2.83 Å, 157° |
| 1-d3 | 1 − x, −1/2 + y, 1/2 − z | −11.18 | 15.1 | N–H…Nmix 2.75 Å, 135°; C–H…π 2.68 Å, 156°; 2.72 Å, 130°; 2.83 Å, 157° |
| 1-d4 | 1 − x, 1/2 + y, 1/2 − z | −11.18 | 15.1 | N–H…Nmix 2.75 Å, 135°; C–H…π 2.68 Å, 156°; 2.72 Å, 130°; 2.83 Å, 157° |
| 1-d5 | x, −1 + y, z | −8.60 | 11.6 | non-specific |
| 1-d6 | x, 1 + y, z | −8.60 | 11.6 | non-specific |
| Dimer | Symmetry Operation | Eint, kcal/mol | ER, % | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building unit is a molecule | ||||
| 2-m1 | 2 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z | −12.55 | 24.7 | N–H…Npyr 2.03 Å, 175° |
| 2-m2 | x, 3/2 − y, −1/2 + z | −5.97 | 11.8 | C–H…π 2.79 Å, 158°; C–H…Nπ 2.77 Å, 134° |
| 2-m3 | x, 3/2 − y, 1/2 + z | −5.97 | 11.8 | C–H…π 2.79 Å, 158°; C–H…Nπ 2.77 Å, 134° |
| 2-m4 | x, −1 + y, z | −3.88 | 7.7 | non-specific |
| 2-m5 | x, 1 + y, z | −3.88 | 7.7 | non-specific |
| 2-m6 | x, 1/2 − y, −1/2 + z | −3.86 | 7.6 | C–H…π 2.88 Å, 136° |
| 2-m7 | x, 1/2 − y, 1/2 + z | −3.86 | 7.6 | C–H…π 2.88 Å, 136° |
| 2-m8 | 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z | −2.97 | 5.9 | C–H…Br 3.10 Å, 173° |
| Building unit is a dimer | ||||
| 2-d1 | 2 − x, 1/2 + y, 5/2 − z | −10.94 | 14.4 | C–H…π 2.79 Å, 158°; 2.88 Å, 136°; C–H…Nπ 2.77 Å, 134°; |
| 2-d2 | 2 − x, −1/2 + y, 3/2 − z | −10.94 | 14.4 | C–H…π 2.79 Å, 158°; 2.88 Å, 136°; C–H…Nπ 2.77 Å, 134°; |
| 2-d3 | 2 − x, −1/2 + y, 5/2 − z | −10.94 | 14.4 | C–H…π 2.79 Å, 158°; 2.88 Å, 136°; C–H…Nπ 2.77 Å, 134°; |
| 2-d4 | 2 − x, 1/2 + y, 3/2 − z | −10.94 | 14.4 | C–H…π 2.79 Å, 158°; 2.88 Å, 136°; C–H…Nπ 2.77 Å, 134°; |
| 2-d5 | x, 1 + y, z | −8.82 | 11.6 | non-specific |
| 2-d6 | x, −1 + y, z | −8.82 | 11.6 | non-specific |
| Dimer | Symmetry Operation | Eint, kcal/mol | ER, % | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-m1 | 2 − x, −1/2 + y, 3/2 − z | −8.85 | 16.5 | N–H…Npyr 2.08 Å, 166°; N–H…NLP 2.26 Å, 166° |
| 3-m2 | 2 − x, 1/2 + y, 3/2 − z | −8.85 | 16.5 | N–H…Npyr 2.08 Å, 166°; N–H…NLP 2.26 Å, 166° |
| 3-m3 | 1 + x, y, z | −6.19 | 11.6 | stacking, 3.45 Å |
| 3-m4 | −1 + x, y, z | −6.19 | 11.6 | stacking, 3.45 Å |
| 3-m5 | 1/2 + x, 3/2 − y, 1 − z | −5.69 | 10.6 | N–H…Cl 2.79 Å, 163°; Cl…N 3.44 Å |
| 3-m6 | −1/2 + x, 3/2 − y, 1 − z | −5.69 | 10.6 | N–H…Cl 2.79 Å, 163°; Cl…N 3.44 Å |
| 3-m7 | 1 − x, −1/2 + y, 3/2 − z | −4.18 | 7.8 | N–H…Npyr 2.35 Å, 149° |
| 3-m8 | 1 − x, 1/2 + y, 3/2 − z | −4.18 | 7.8 | N–H…Npyr 2.35 Å, 149° |
| Dimer | Symmetry Operation | Eint, kcal/mol | ER, % | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-m1 | −x, 1/2 + y, 3/2 − z | −8.94 | 16.1 | N–H…Npyr 2.08 Å, 166°; N–H…NLP 2.29 Å, 167° |
| 4-m2 | −x, −1/2 + y, 3/2 − z | −8.94 | 16.1 | N–H…Npyr 2.08 Å, 166°; N–H…NLP 2.29 Å, 167° |
| 4-m3 | −1 + x, y, z | −6.79 | 12.2 | stacking, 3.49 Å |
| 4-m4 | 1 + x, y, z | −6.79 | 12.2 | stacking, 3.49 Å |
| 4-m5 | 1/2 + x, 1/2 − y, 1 − z | −5.70 | 10.3 | N–H…Br 2.89 Å, 165°; Br…N 3.47 Å |
| 4-m6 | −1/2 + x, 1/2 − y, 1 − z | −5.70 | 10.3 | N–H…Br 2.89 Å, 165°; Br…N 3.47 Å |
| 4-m7 | 1 − x, 1/2 + y, 3/2 − z | −4.38 | 7.9 | N–H…Npyr 2.34 Å, 152° |
| 4-m8 | 1 − x, −1/2 + y, 3/2 − z | −4.38 | 7.9 | N–H…Npyr 2.34 Å, 152° |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konovalova, I.S.; Reiss, G.J. Supramolecular Switching by Substituent Tuning: A Crystal Engineering Study of 2-Amino- and 2,3-Diamino-5-Halogenopyridines. Crystals 2025, 15, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15080700
Konovalova IS, Reiss GJ. Supramolecular Switching by Substituent Tuning: A Crystal Engineering Study of 2-Amino- and 2,3-Diamino-5-Halogenopyridines. Crystals. 2025; 15(8):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15080700
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonovalova, Irina S., and Guido J. Reiss. 2025. "Supramolecular Switching by Substituent Tuning: A Crystal Engineering Study of 2-Amino- and 2,3-Diamino-5-Halogenopyridines" Crystals 15, no. 8: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15080700
APA StyleKonovalova, I. S., & Reiss, G. J. (2025). Supramolecular Switching by Substituent Tuning: A Crystal Engineering Study of 2-Amino- and 2,3-Diamino-5-Halogenopyridines. Crystals, 15(8), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15080700





