Microstructures and Magnetic Properties of Rare-Earth-Free Co-Zr-Mo-B Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Melt-Spinning
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
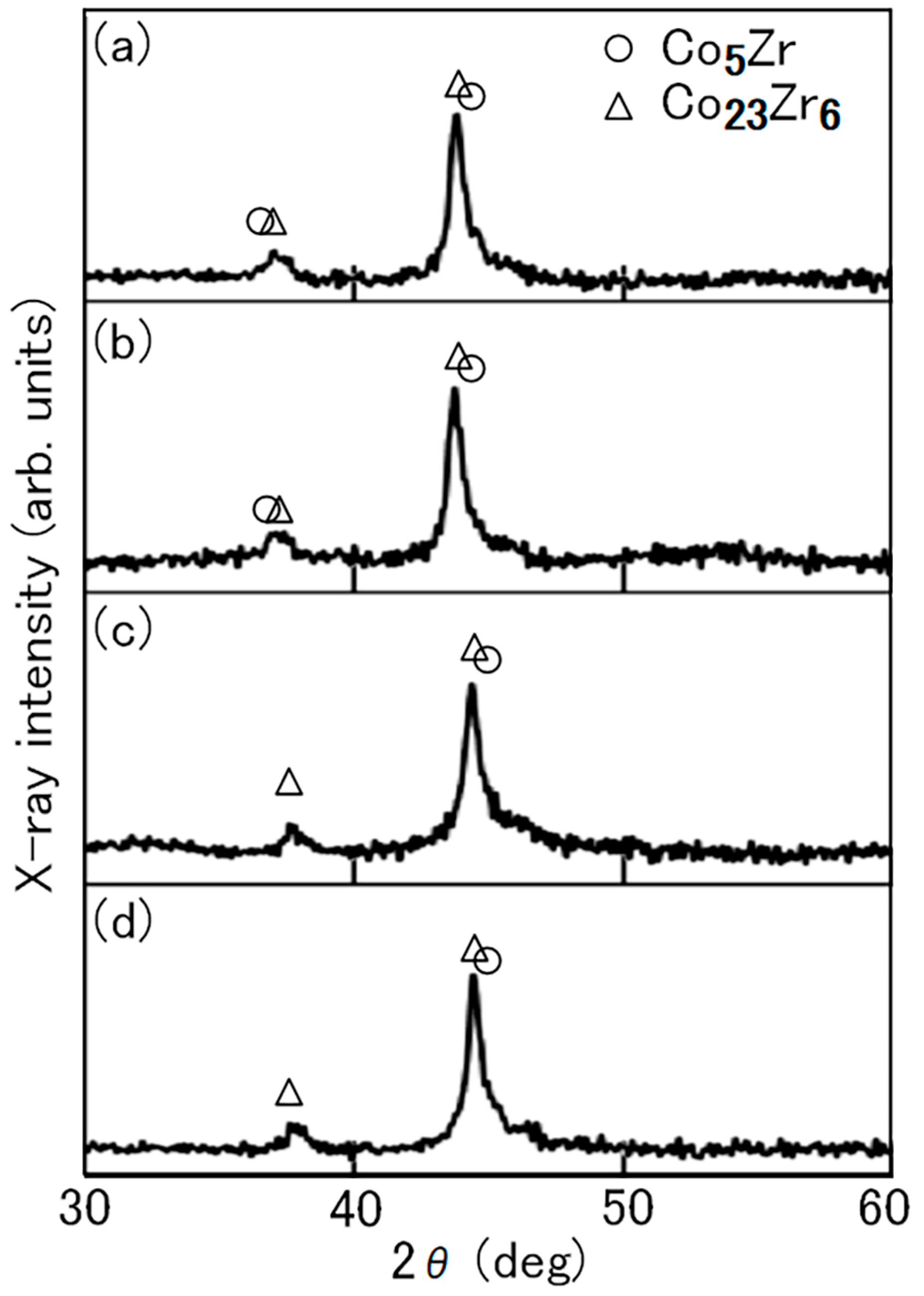
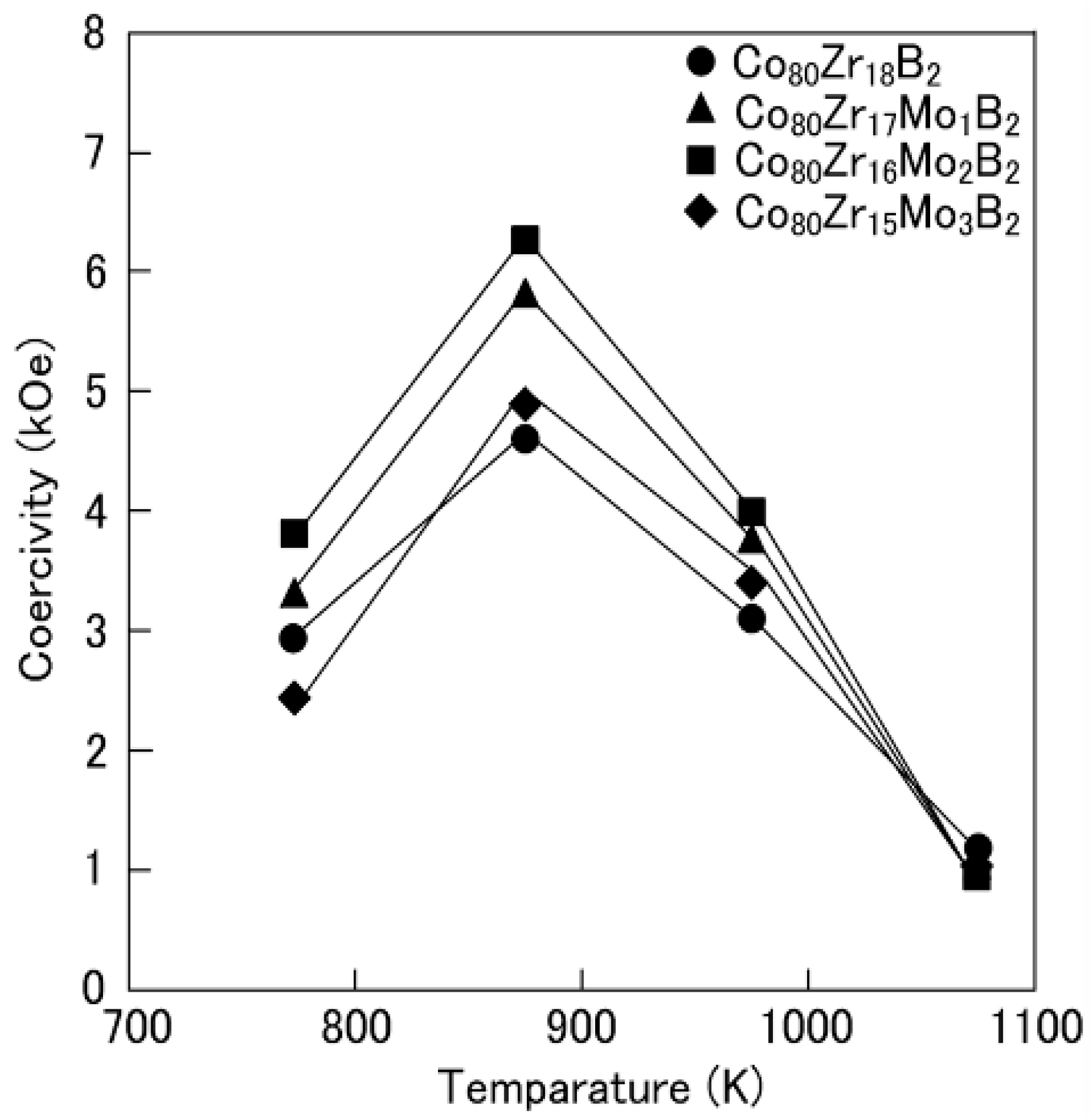
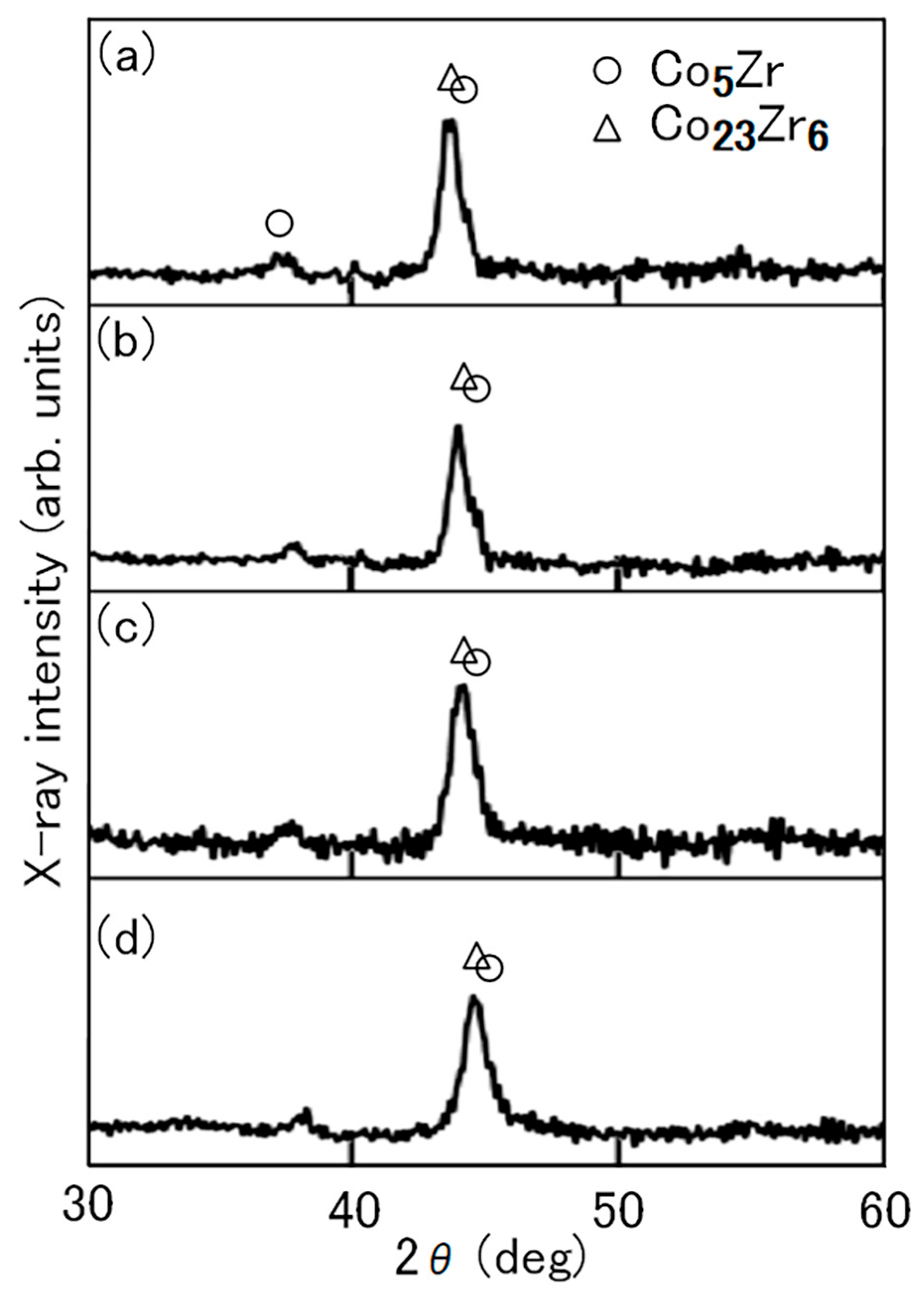
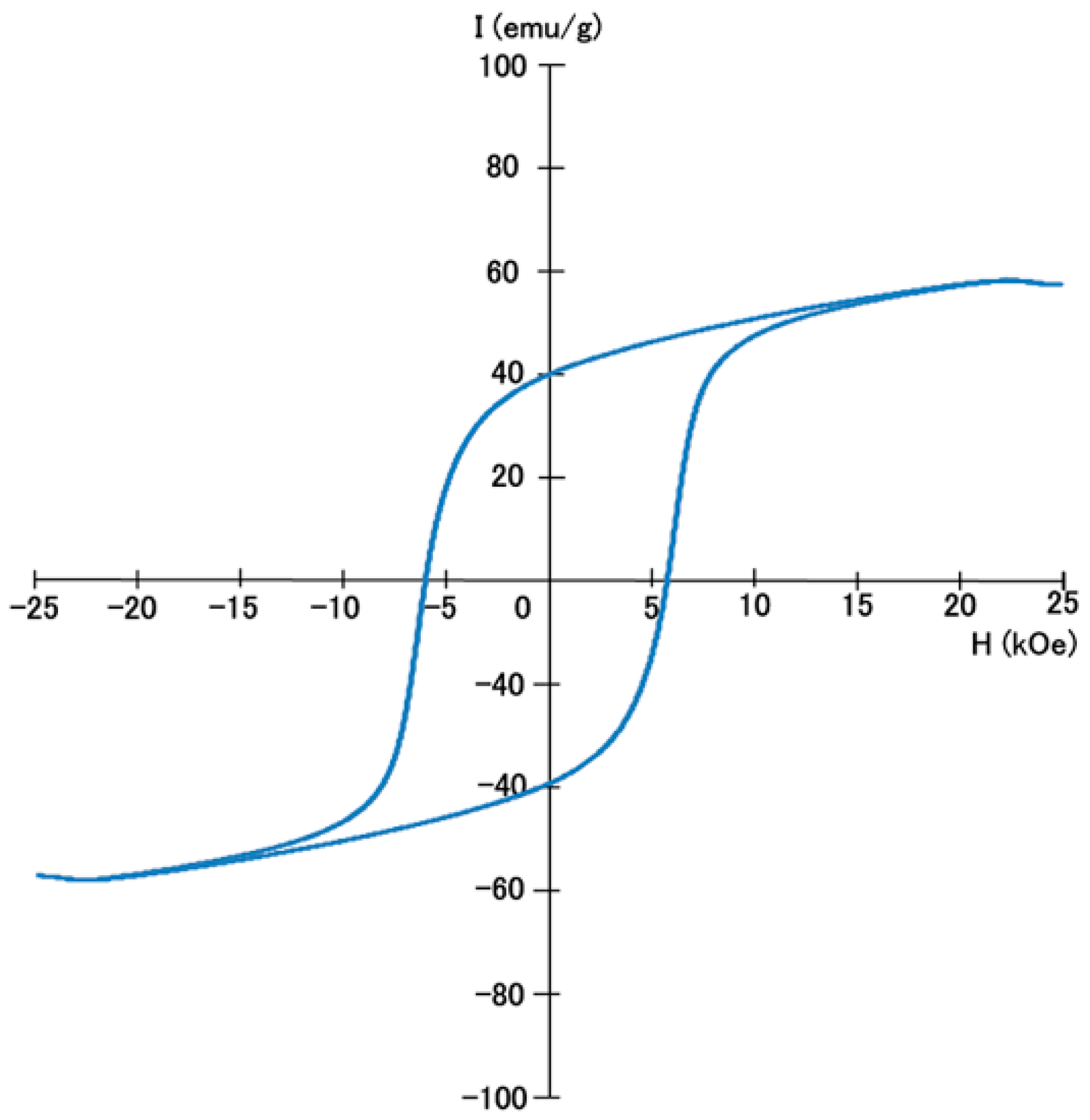
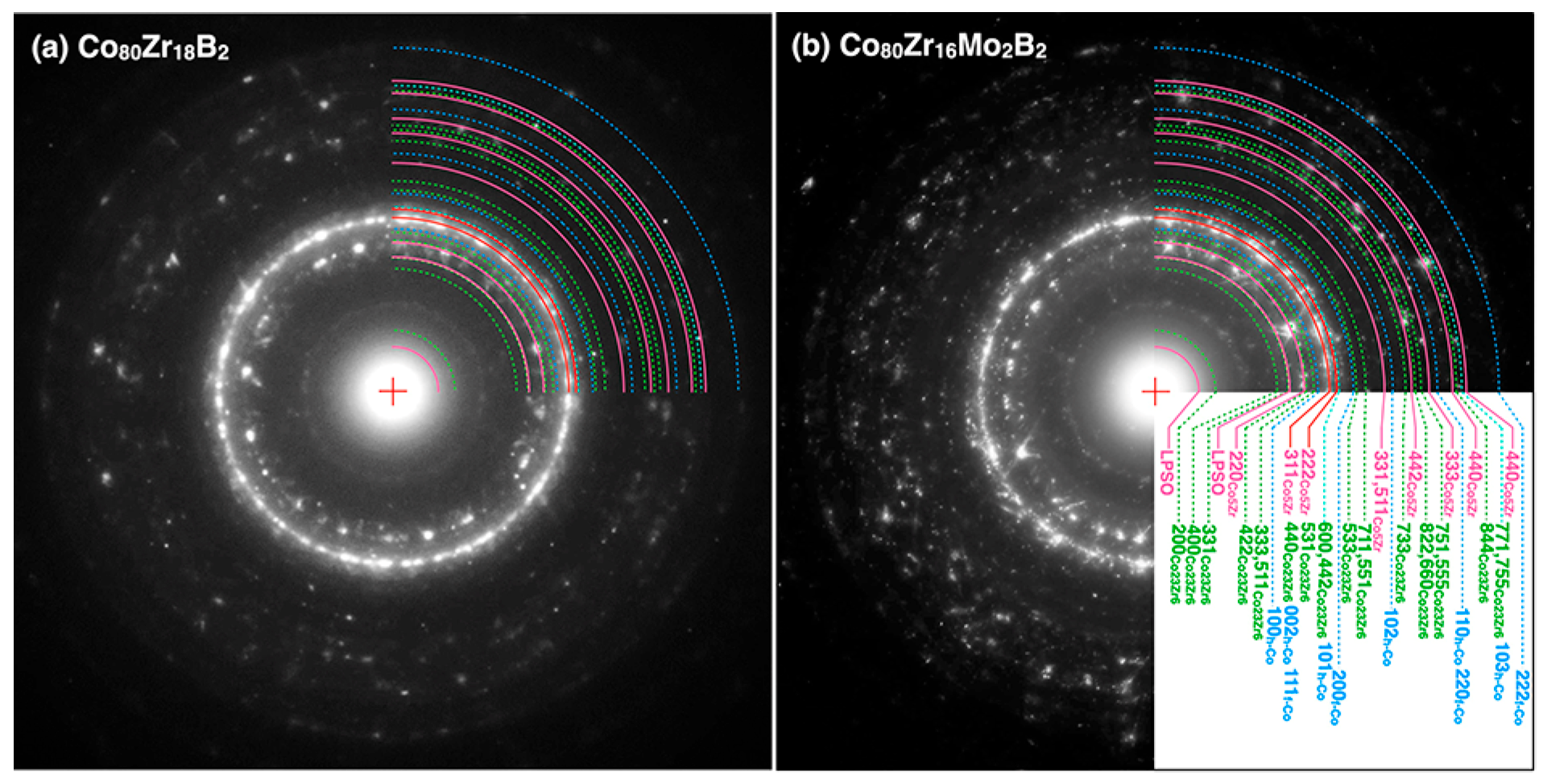
3.1. Structures and Magnetic Properties
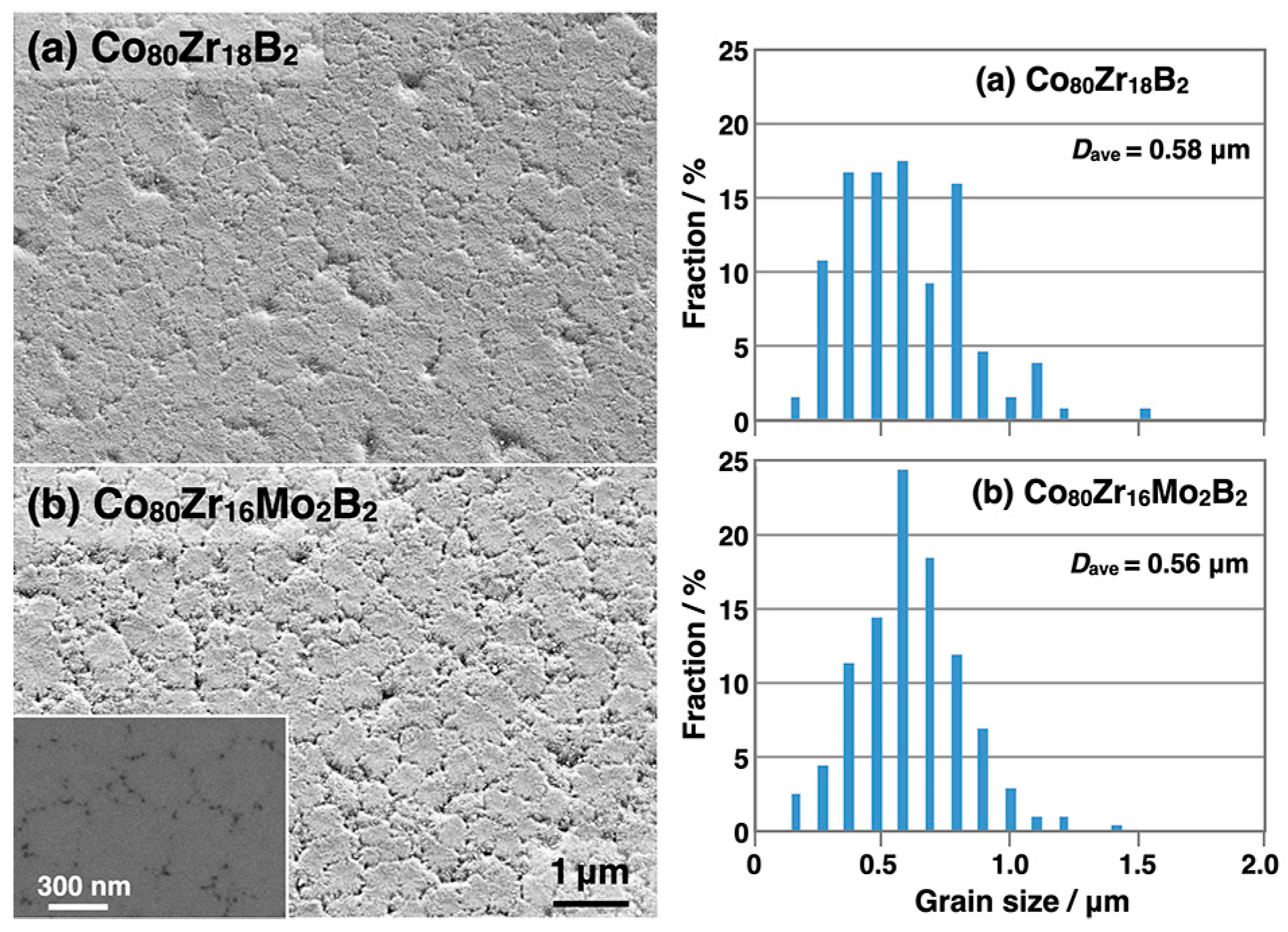
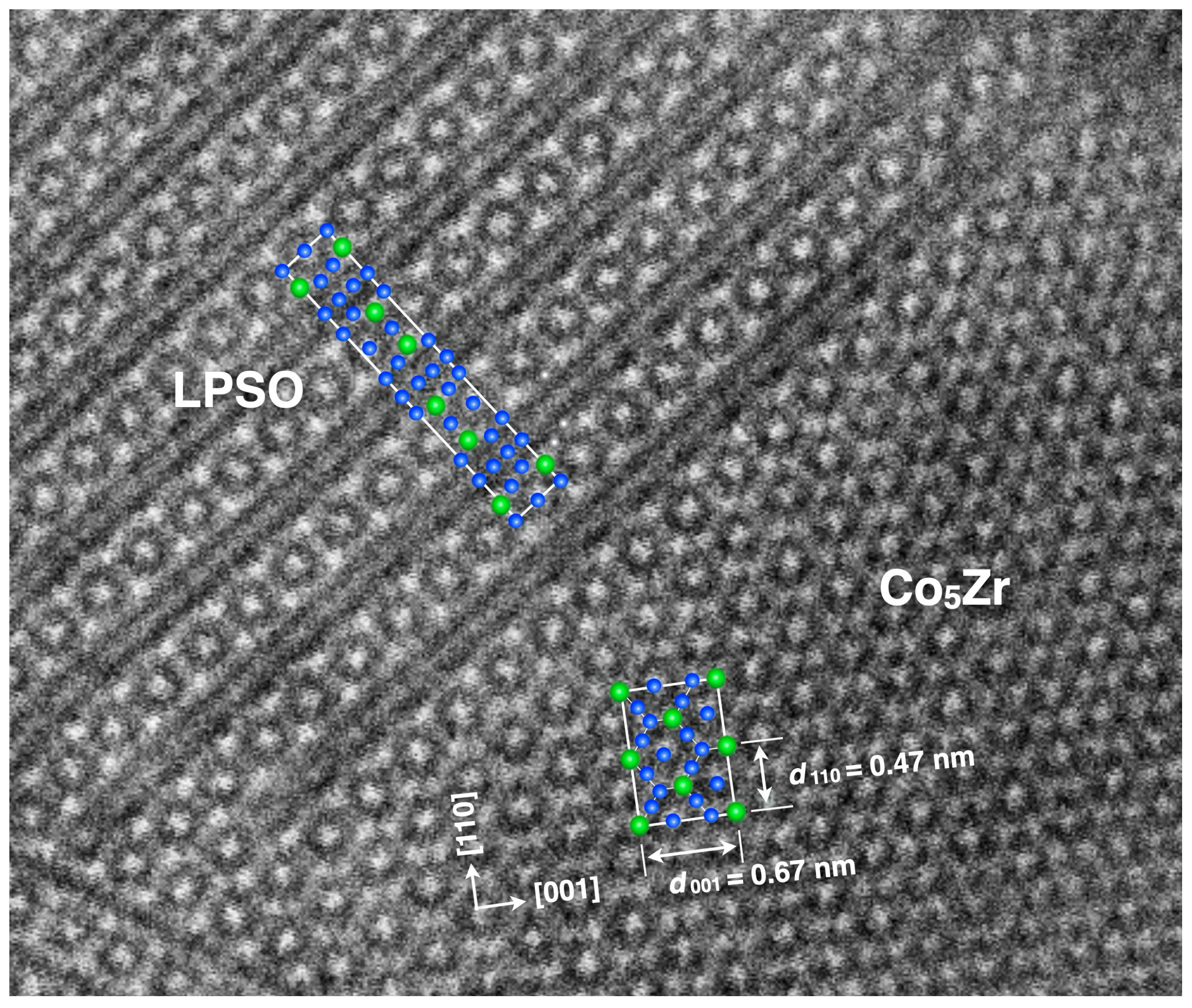
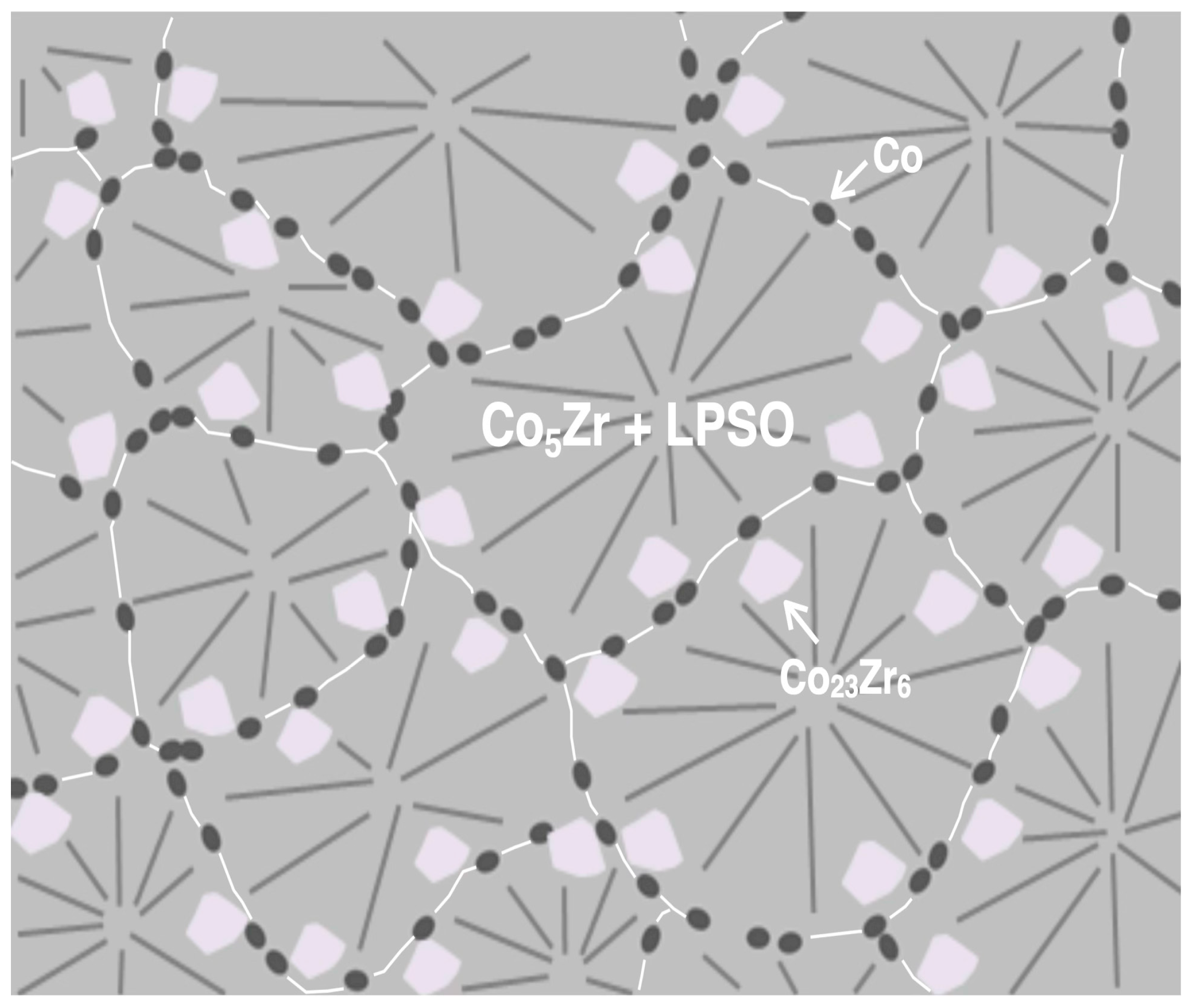
3.2. Microstructures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sagawa, M.; Fujimura, S.; Togawa, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsuura, Y. New material for permanent magnets on a base of Nd and Fe. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 55, 2083–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croat, J.J.; Herbst, J.F.; Lee, R.W.; Pinkerton, F.E. Pr-Fe and Nd-Fe-based materials: A new class of high-performance permanent magnets. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 55, 2078–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Sasaki, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Hono, K. Most frequently asked questions about the coercivity of Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mate. 2021, 22, 386–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Verob, K.; Borah, J.P. Historical overview and recent advances in permanent magnet materials. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Luo, J.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Chai, W.X.; Zhang, X.S.; Hou, Y.H.; Li, W.; Yu, X.; Zhong, C.C.; Mao, H.Y.; et al. Significantly improved magnetic properties and thermal stability for sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets via grain boundary diffusion of DyCo alloy. Intermetallics 2024, 165, 108158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hioki, K. Development of high-performance hot-deformed Neodymium–Iron–Boron magnets without heavy rare-earth elements. Materials 2023, 16, 6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Fujita, M.; Kuji, T.; Fukuoka, K.; Syono, Y. The development of high performance Nd-Fe-Co-Ga-B die upset magnets. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 6390–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri-Amin, H.; Liu, L.; Ohkubo, T.; Yano, M.; Shoji, T.; Kato, A.; Schrefl, T.; Hono, K. Microstructure and temperature-dependent coercivity of hot-deformed Nd–Fe–B magnets diffusion processed with Pr–Cu alloy. Acta Mater. 2015, 99, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulesh, N.; Bolyachkin, A.; Dengina, E.; Tang, X.; Ohkubo, T.; Kajiwara, T.; Miyawaki, H.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Hono, K. Coercivity limits in Nd-Fe-B hot-deformed magnets with ultrafine microstructure. Acta Mater. 2024, 276, 120159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsugi, M.; Mitsumata, C.; Maruyama, H.; Wakita, T.; Taniuchi, T.; Ono, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kawamura, N.; Ishimatsu, N.; Oshima, M.; et al. Novel magnetic domain structure in iron meteorite induced by the presence of L10-FeNi. Appl. Phys. Exp. 2010, 3, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, Y.; Mitsuoka, K.; Komuro, M.; Hoshiya, H.; Kozono, Y.; Hanazono, M. Giant magnetic moment and other magnetic properties of epitaxially grown Fe16N2 single-crystal films. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 70, 5977–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S.; Kura, H.; Watanabe, E.; Hayashi, Y.; Yanagihara, H.; Shimada, Y.; Mizuguchi, M.; Takanashi, K.; Kita, E. Synthesis of single-phase L10-FeNi magnet powder by nitrogen insertion and topotactic extraction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Ogata, Y.; Gallage, R.; Kobayashi, N.; Hayashi, N.; Kusano, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Kohara, K.; Doi, M.; Takano, M.; et al. Challenge to the synthesis of α″-Fe16N2 phase compound nanoparticle with high saturation magnetization for rare earth free new permanent magnetic material. Appl. Phys. Exp. 2013, 6, 073007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghemawat, A.M.; Foldeaki, M.; Dunlap, R.A.; O’Handley, R.C. New microcrystalline hard magnets in a Co-Zr-B alloy system. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1989, 25, 3312–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadelmaier, H.H.; Jang, T.S.; Henig, E.-T. What is responsible for the magnetic hardness in Co-Zr (-B) alloys? Mater. Lett. 1991, 12, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, M.; Wang, R.; Liao, T.; Zhang, C.; Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Balasubramanian, B.; et al. Discovering rare-earth-free magnetic materials through the development of a database. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2020, 4, 114408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Cobalt-rich magnetic phases in Zr-Co alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 236, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, G.V.; Shchegoleva, N.N.; Gabay, A.M. Crystal structure of Zr2Co11 hard magnetic compound. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 432, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Itakura, M. Microstructures of Co-Zr-B alloys produced by melt-spinning technique. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 572, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, P.T.; Duong, N.V.; Lam, N.M.; Hung, L.T.; Hau, K.X.; Ngoc, N.H.; Yen, N.H.; Dan, N.H. Investigation of Structure and Magnetic Properties of Melt-Spun Co-Zr-(B, Al) Ribbons. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2022, 35, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroink, G.; Stadnik, Z.M.; Viau, G.; Dunlop, R.A. The influence of quenching rate on the magnetic properties of microcrystalline alloys Co80Zr20−xBx. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 67, 4963–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Ohmori, K. Hard magnetic phase in rapidly quenched Zr-Co-B alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1990, 26, 1370–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T. Magnetization process in Co-Zr-B permanent magnet materials. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2004, 40, 2919–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Sun, Q.W.; Wang, W.Q.; Su, F. Effects of Mo additive on structure and magnetic properties of Co82Zr18 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 474, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.P.; Zhang, J.B.; Xu, S.F.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, K.; Wang, W.Q.; Du, X.; Su, F. Effects of Nb substitution for Zr on the phases, microstructure and magnetic properties of Co80Zr18−xNbxB2 melt-spun ribbons. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2771–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Pal, S.P.; Rao, N.V.R.; Chatterjee, R. Structural and magnetic properties of [1 1 0] oriented Co5Zr hard magnetic thin films. Mater. Lett. 2020, 260, 126869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T. High performance Co-Zr-B melt-spun ribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 2305–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ke, L.Q.; Nguyen, M.C.; Wang, C.Z.; Ho, K.M. Structures and magnetic properties of Co-Zr-B magnets studied by first-principles calculation. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 243902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.P.; Yang, C.L.; Xu, S.F.; Zhang, J.B.; Liu, D.; Su, F.; Wang, W.Q. Effects of W substitution on the magnetic properties, phase evolution and microstructure of rapidly quenched Co80Zr18B2 alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 324, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Valloppilly, S.; Skomski, R.; Shield, J.E.; Sellmyer, D.J. Magnetism of rapidly quenched rhombohedral Zr2Co11-based nanocomposites. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 135004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraon, A.; Adhikary, T.; Tirugabathina, M.; Kumar, B.; Ghosh, S.; Aich, S. Microstructure and magnetic properties of Co82-(x+y)Zr13V5BxSiy melt-spun ribbons. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 965, 171436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtyaz, M.D.; Rama Rao, N.V.; Aravindha Babu, D.; Ramesh Chandra, B.; Pandian, S. Effect of Cu substitution on structural and hard magnetic properties of rapidly solidified Zr18Co82-xCux melt spun ribbons. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 699, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, N.; Anand, K.; Singh, N. Enhancement of hard magnetic properties in rapidly quenched Zr–Co–Fe–B ribbons through vacuum annealing. Solid State Commun. 2021, 323, 114118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.P.; Jin, Y.L.; Sellmyer, D.J. Effect of Boron Addition on Magnetic-Domain Structure of Rapidly Quenched Zr2Co11-Based Nanomaterials. MRS Adv. 2016, 34, 2379–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraon, A.; Adhikary, T.; Das, G.P.; Ghosh, S.; Garg, A.; Raja, A.; Aich, S. Combined experimental and DFT studies of Co82Zr12V6-xBx melt-spun ribbons to investigate structure and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 547, 168940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Nominal Composition | Weight Percent | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | Zr | Mo | B | |
| Co80Zr18B2 | 73.92 (wt%) | 25.74 (wt%) | 0.339 (wt%) | |
| Co80Zr17Mo1B2 | 73.86 (wt%) | 24.30 (wt%) | 1.50 (wt%) | 0.339 (wt%) |
| Co80Zr16Mo2B2 | 73.81 (wt%) | 22.85 (wt%) | 3.00 (wt%) | 0.338 (wt%) |
| Co80Zr15Mo3B2 | 73.75 (wt%) | 24.41 (wt%) | 4.50 (wt%) | 0.338 (wt%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saito, T.; Itakura, M. Microstructures and Magnetic Properties of Rare-Earth-Free Co-Zr-Mo-B Alloys. Crystals 2025, 15, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15080698
Saito T, Itakura M. Microstructures and Magnetic Properties of Rare-Earth-Free Co-Zr-Mo-B Alloys. Crystals. 2025; 15(8):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15080698
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaito, Tetsuji, and Masaru Itakura. 2025. "Microstructures and Magnetic Properties of Rare-Earth-Free Co-Zr-Mo-B Alloys" Crystals 15, no. 8: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15080698
APA StyleSaito, T., & Itakura, M. (2025). Microstructures and Magnetic Properties of Rare-Earth-Free Co-Zr-Mo-B Alloys. Crystals, 15(8), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15080698






