Abstract
Transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR) is a disease caused by the deposition of transthyretin-derived fibrils in the body. Despite extensive research conducted over the years, there are currently only four drugs available in clinical use to treat this condition, two of which are repurposed drugs used off-label. However, these treatments present several limitations; therefore, there is an urgent need for new therapeutic options. In this context, dietary supplements containing natural compounds capable of stabilizing the transthyretin (TTR) protein could represent a promising approach to contrast the disease progression, potentially supporting the therapeutic effects of the aforementioned drugs. In light of this, the present review highlights and analyzes the natural compounds that have most recently been reported in the literature as TTR stabilizers. In particular, the studies elucidating the potential of these compounds in the treatment of ATTR, along with the available crystallographic data explaining their binding mode to TTR, are reported. Overall, although the use of natural compounds as supplements shows promise in managing ATTR, further research is still needed to explore its feasibility and confirm its effectiveness. Hopefully, this work will help shed light on these issues and serve as a useful starting point for the development of new strategies to treat this disease.
1. Introduction
In recent years, growing evidence has suggested that natural compounds present in fruit and vegetables can reduce the risk of developing several diseases, ranging from cancer to neurodegenerative disorders [1,2,3,4,5]. In this context, some studies have also investigated their role in transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR) [6,7,8,9], a disease originating from the dissociation and consequent misfolding of the transthyretin (TTR) protein, which results in the deposition of TTR-derived fibrils in various tissues of the body [10,11,12].
TTR is mainly synthesized by the liver and released in plasma [13], where it acts as a transporter of thyroxine (T4). However, the main carriers of T4 are thyroxine-binding protein and albumin; therefore, only 10−20% of T4 is transported by TTR [14]. TTR can also transport retinol by forming a complex with retinol binding protein (RBP) [15]. Other sites of TTR production are the choroid plexus in the brain [16], the retinal pigment epithelium of the mammalian eye [17], pancreatic cells in the pancreas [18], and trophoblasts in placenta [19].
Experimental evidence suggests that, in the brain, TTR plays a protective role against Alzheimer’s disease (AD) through its interaction with amyloid-β (Aβ) [20,21,22]. In vivo studies in AD patients showed a close connection between TTR and AD physiopathology. Results showed that TTR levels decrease both in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) as AD progresses [23].
TTR is characterized by four identical monomers (A, A’, B, B’) organized as a homotetramer (55 kDa) around a 2-fold axis. From a structural point of view, each monomer, composed by 127 amino acids (14 kDa), is formed by eight β-strands labelled from “A” to “H” and one α-helix (located between strands E and F) called the “EF-helix” (Figure 1A). The eight strands are arranged in two twisted β-sheets where strands A and G are parallel while all the others are anti-parallel. The symmetric operations drive the formation of the TTR tetramer, whereby two monomers assemble into a dimer, and two dimers subsequently combine to form the tetramer (Figure 1B). In the middle of the 2-fold symmetry axes, at the dimer–dimer interface, there is a channel called the thyroxin binding pocket (T4-BP) that spans the entire protein [24,25]. The name T4-BPs is derived from the binding of the endogenous ligand T4 to these hydrophobic sites [25]. The two T4-BPs are characterized by three pairs of symmetric cavities, known as halogen binding pockets (HBP1/1′, 2/2′, 3/3′), which accommodate the iodine atoms of T4. HBP1 is located in the outer pocket near Lys15, Thr106, and Ala108. HBP2 is placed in the middle pocket, surrounded by Lys15, Ala108, and Leu11. HBP3 resides in the inner pocket, close to Ala108, Leu110, Ser117, and Thr119 (Figure 1C) [25].
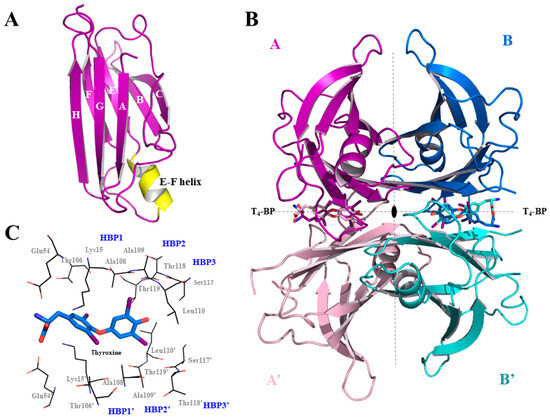
Figure 1.
Structure of TTR. (A) Focus on one monomer characterized by eight β-strands (labelled A-H) and one α-helix (EF-helix). (B) Tetrameric structure of TTR in complex with T4 (pdb id 2ROX). (C) Representation of one of the two symmetric T4-BPs. All structural images were generated using the Pymol program 3.1 [26].
As previously mentioned, recently TTR has gained attention for its pathological role in ATTR [27]. ATTR is a rare, progressive, and fatal disease associated with the presence of either wild-type TTR (wt-TTR) or mutant TTR (mTTR), which gradually lose their three-dimensional structure, leading to the formation of insoluble, toxic protein aggregates. These amorphous, β-sheet-rich aggregates accumulate in organs and tissues, particularly in the heart (leading to a condition known as cardiac amyloidosis) [28,29] and in the peripheral nervous system (causing polyneuropathy) [30,31]. In this regard, the most common point mutations in mTTR are V122I and V30M, which are associated with polyneuropathy and cardiomyopathy, respectively [32,33]. Although it is known that several factors contribute to the acceleration of protein misfolding, including acidic pH, metals dyshomeostasis, and oxidative stress [34], the exact mechanism triggering the onset of amyloidosis remains poorly understood [35,36,37].
Over the years, several therapeutic approaches have been studied for the treatment of ATTR, ranging from liver transplantation to small RNA-interfering drugs, antisense oligonucleotides, and drugs capable of stabilizing the TTR tetramer [38,39,40]. The latter approach is related to the ability of some small molecules to bind the T4-BPs stabilizing the TTR tetramer structure and contrasting the dissociation of TTR in its corresponding monomers, which is the first step of the amyloidogenic pathway [41]. Currently, four drugs are used in clinical practice to manage this disease, namely, tafamidis [42,43,44], acoramidis [45], diflunisal, and tolcapone [38]—the latter two are repurposed drugs used off-label [46,47]. On the other hand, tafamidis and acoramidis (also called AG10) have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of ATTR [45,48]. Crystallographic studies report that these two drugs bind to the T4-BPs similarly to the endogenous ligand T4, both in wt-TTR and related mutants. The carboxylic group is oriented toward Glu54 and Lys15 at the entrance of the pocket, while the aromatic portions are positioned within HBP2 and HBP3, as well as in the endogenous ligand thyroxine (Figure 1C) [49,50].
A comprehensive discussion of these drugs and therapeutic approaches can be found in our recent reviews [38,51]. In this context, the aim of the present work is to provide a concise overview of the natural compounds that have most recently been reported in the literature as stabilizers of the TTR (from 2020 to 2025). For natural TTR stabilizers published prior to this timeframe, we refer readers to previous reviews [51,52]. Noteworthy, in the present paper, we have used paragraph titles analogous to those of previous reviews [51,52] to help readers easily link the compounds discussed here with those presented earlier. The importance of this topic is evident, as natural molecules might prove useful to enhance the therapeutic action of the approved ATTR therapies [51,52,53]. In fact, several studies have highlighted their positive effect in amyloidosis diseases [6,7,8,9]. In this regard, one approach to slow the progression of ATTR might consist of the constant consumption of dietary supplements containing natural compounds capable of inhibiting amyloid fibril formation [54,55]. From this perspective, the following paragraphs summarize the latest natural molecules reported as TTR stabilizing agents. Additionally, we refer readers to the following publications for further insight into the legal frameworks regulating dietary supplements [56,57].
Hopefully, this review will inspire the development of new clinical strategies for treating ATTR.
2. Isoflavone-Derivatives and Flavonoid Metabolites
Natural products encompass a wide array of chemical scaffolds with therapeutic potential against ATTR. Within this diverse chemical space, flavonoids have emerged as particularly promising candidates. As a matter of fact, over the years, they have been extensively investigated as potential TTR inhibitors. Notably, this research also extended to isoflavones, a sub-class of flavonoids [58,59]. In this context, a recent paper examined the activity of a series of isoflavones on ATTR, revealing that millexatin F (1) (Figure 2)—which occurs naturally in Millettia extensa [60,61]—was the most promising compound among those examined. Nevertheless, derrone (2) (Figure 2)—which occurs naturally in Ulex jussiaei (Leguminosae) [62]—also demonstrated notable activity [63]. Interestingly, although both of these compounds are indeed natural products, the authors synthesized them in this study. In an acid-mediated aggregation experiment performed on V30M-TTR, compound 2 exhibited the highest inhibitory activity against amyloid aggregation, followed by compound 1 [63]. Interestingly, in an ex vivo competitive binding assay on human plasma, compound 1 also possessed a higher degree of selectivity toward TTR compared with compound 2, although it was still to a lesser extent than tafamidis. As highlighted by the authors, the selectivity toward TTR is an important feature for a potential drug candidate because there are many other proteins in plasma besides TTR [59]. Given this encouraging results, the authors suggested 1 as a lead compound for structural optimization for the development of new therapeutics for the treatment of ATTR [63].
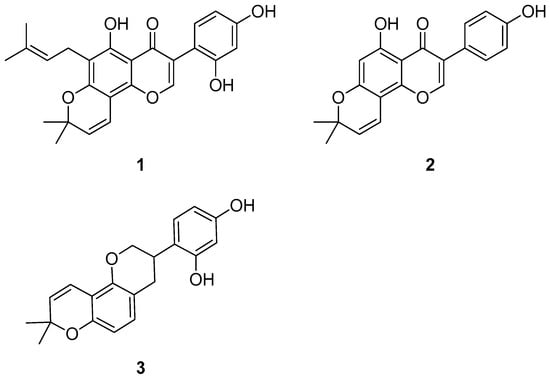
Figure 2.
Molecular structures of millexatin F (1), derrone (2), and glabridin (3).
Another member of this class of molecules that has been subject of research is glabridin (3) (Figure 2), a natural isoflavone that occurs naturally in G. glabra L. (Favaceae) [55]. In this context, building on the fact that it had already been proven to be capable of stabilizing the TTR tetramer in previous in vitro experiments [64], Matsushita et al. performed additional studies on it and also investigated the activity of glavonoid, a natural supplement whose main constituent is glabridin [55,65,66,67]. However, it should be noted that the authors also hypothesized a possible contribution of the other polyphenols present in glavonoid to its stabilizing activity of the TTR tetramer observed in their study. In the study by Matsushita et al., glabridin, glavonoid, and Kaneka Glavonoid (the latter being a soft gel capsule used in human studies) were purchased from appropriate suppliers [55].
According to the authors, the results point to a possible employment of glavonoid in ATTR as a dietary supplement. Indeed, not only does it not cause significant side effects, but in vitro tests on human plasma from healthy patients also showed that, contrary to compound 3, glavonoid is capable of enhancing the tetramer levels while reducing those of the monomer, thus suggesting that it is capable of stabilizing the TTR tetramer. In addition, glavonoid decreased the monomer/tetramer ratio of TTR in healthy patients both at 300 mg/day and 600 mg/day oral dosage (although the effect appeared earlier in the 600 mg/day regimen). Notably, the plasma concentration of compound 3 after a 12-week oral administration of glavonoid at 300 mg/day to healthy patients (n = 7) was found to be approximately 2.5 ng/mL. In light of this, it is possible to hypothesize the use of glavonoid as a dietary supplement for the prevention of ATTR [55].
In parallel, others studies explored flavonoids metabolites, particularly glycosylated derivatives of quercetin (quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucuronopyranoside (4), quercetin 3-O-β-D-galactopyranoside (5), and quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (6), Figure 3) as potential TTR inhibitors [68,69], building on previous evidence that quercetin itself can bind to the T4-BPs, thereby reducing TTR misfolding and aggregation [70]. The 3-O-glycosylated derivatives, as well as quercetin, are naturally present in several commonly consumed foods, including apple, orange, onion, black tea, molokheya, broccoli, kale, and blueberry [68]. In an acid turbidimetric assay on wt-TTR, compounds 4–6 (isolated from Cornus mas, Cornus sanguinea, and Ruprechtia polystacya [71,72]) showed a moderate capability of inhibiting the amyloid fibril formation (the percentage of fibril formation was 45% in the presence of compounds 4 and 6 and 40% in the presence of compound 5), thus suggesting that they have a low affinity for the T4 binding sites, which was confirmed using the ANS displacement binding assay [73,74]. These results were further validated using thioflavin T binding assays [75] on wt-TTR, in which the percentage of fibril formation in the presence of compounds 4–6 was assessed to be between 23% and 38% (with respect to TTR alone, in which the percentage of fibril formation was 100%). Moreover, all compounds were also shown to have a strong antioxidant activity, which, according to the authors, could help preserve the TTR protein in its tetrameric state by avoiding the oxidation of Cys10 (an amino- acid with an important role in the native structure of TTR [76,77]). The in vitro tests were performed in triplicate (n = 3) [69].
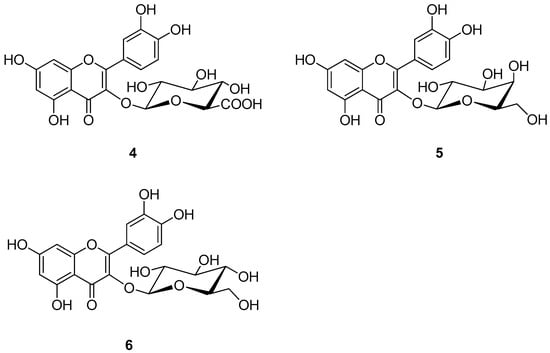
Figure 3.
Molecular structures of quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucuronopyranoside (4), quercetin 3-O-β-D-galactopyranoside (5), and quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (6).
Structural insights into the binding mode of these quercetin derivatives with TTR were obtained from the crystal structure of the TTR–compound 5 (3-O-β-D-galactopyranoside) complex. Crystallographic analysis revealed that compound 5 binds to only one of the T4-BPs, positioning its dihydroxyphenyl group in the outer cavity, while the dihydroxyphenyl ring fits into the inner pocket near Ser117 and Thr119. This binding mode is opposite to that observed for quercetin, likely due to the steric hindrance caused by the galactopyranoside moiety of compound 5 (Figure 4).
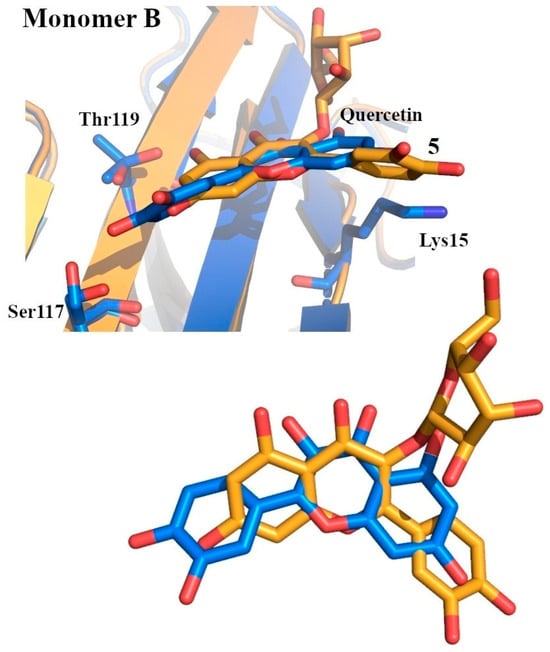
Figure 4.
Superposition between quercetin (colored in marine) and quercetin 3-O-β-D-galactopyranoside (5) (colored in bright orange) within the T4-BPs. Bottom: close-up view of the ligand superposition [69].
All in all, these results suggest that patients suffering from ATTR might possibly benefit to some extent from dietary intake of these compounds. However, further research is still needed in this field to determine their real usefulness.
3. Natural Derivatives of Resveratrol
Previous studies have shown that resveratrol (7) (Figure 5)—which naturally occurs in peanuts, raspberries, grape skins, blueberries, and mulberries—is an interesting compound in the field of ATTR [54,78,79,80]. However, its use is limited by some drawbacks, such as its rapid elimination following oral administration [54,78,79]. In light of this, natural derivatives of resveratrol have been investigated with the aim of finding compounds with improved properties. In this context, Yokoyama et al. evaluated two natural derivatives of resveratrol (pinostilbene (8) and pterostilbene (9), (Figure 5)) for their ability to inhibit amyloid fibril formation, using an acid-induced aggregation assay on V30M-TTR [54,81]. In particular, compound 8 is a metabolite of compound 9, which in turn is derived from compound 7. Noteworthy, compound 9 naturally occurs in berries and peanuts and is also available as a dietary supplement [54,81,82]. However, it should be noted that in the study by Yokoyama et al. compounds (7, 8, and 9) were purchased from appropriate companies. The results of Yokoyama and colleagues showed that the inhibitory potencies of compounds 8 and 9 are similar to that of tafamidis, as evidenced by their inhibition constants (3.4 µM, 3.5 µM, and 3.1 µM for 8, 9, and tafamidis, respectively). Subsequently, the apparent dissociation constant of these compounds (1.2 µM and 1.9 µM for 8 and 9, respectively) was measured using an intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence quenching assay, which revealed that these derivatives inhibit the amyloid fibril formation by binding to the TTR. In addition, isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) experiments were performed to assess the binding affinity of these compounds to V30M-TTR (the values of the dissociation constant are 1.5 ± 0.38 µM, 2.4 ± 0.27 µM, and 4.6 ± 0.29 µM for 7, 8, and 9, respectively) [54].
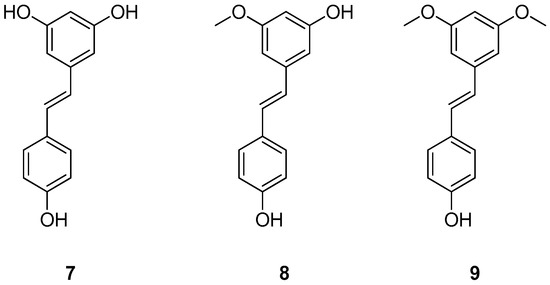
Figure 5.
Chemical structures of resveratrol (7), pinostilbene (8) and pterostilbene (9).
The binding modes of compound 7 and of its derivatives 8 and 9 were further investigated using X-ray crystallography [54]. The authors performed their study on the TTR mutant V30M, obtaining high-resolution crystal complexes structurally very similar to that already reported in literature for wt-TTR [83,84]. The crystals of V30M-TTR in complex with compounds 7, 8, and 9 belonged to the space group P21212 with a dimer in the asymmetric unit. The symmetric operation generates the tetramer with the two T4-BPs that form a channel that crosses the whole protein [54].
Compound 7, as revealed by the electron density maps, exhibited dual binding modes with the V30M mutant, as it did with wt-TTR [54,84]. In the first, known as the “canonical binding mode”, the resorcinic ring is located in the outer binding pocket with its hydroxyl groups oriented toward Lys15/15′, while the phenolic ring resides in the inner binding pocket with its hydroxy moiety pointing toward Ser117/117′ (Figure 6A, ligand in yellow). In the second mode, compound 7 is flipped. The resorcinol ring is inserted into the inner binding pocket with its hydroxy moieties oriented toward Ser117/117′, while the phenolic ring is positioned in the outer cavity (Figure 6A, ligand in green). This dual binding behavior was also observed for compound 8 (ligand in lime in Figure 6B and ligand in light pink in Figure 6C) [54].
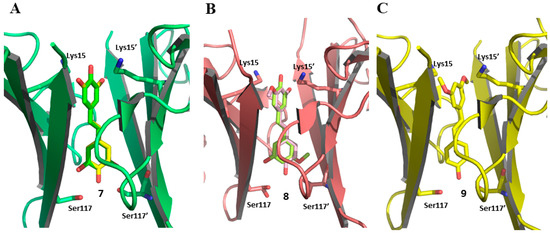
Figure 6.
Binding modes of resveratrol (7), pinostilbene (8), and pterostilbene (9) in complex with V30M-TTR. (A) Dual binding modes of compound 7, highlighted by coloring the ligand in yellow and green (pdb code 8w72); (B) Dual binding modes of compound 8, highlighted by coloring the ligand in lime and light pink (pdb code 8w45); (C) Binding mode of compound 9 (pdb code 8W76).
Regarding compound 9, only the “canonical binding mode” was observed. The aromatic ring bearing the methoxy groups is located in the outer cavity, while the phenolic ring is positioned deep within the T4-BSs (Figure 6C, ligand in yellow) [54].
According to the authors, these encouraging results highlight the potential of resveratrol derivatives for the development of novel therapeutic approaches in which resveratrol analogies could be used as a supplement during the ATTR treatment.
4. Other Natural Stabilizers from Various Sources
Omega-3 poly-unsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are recognized to have multiple positive effects on human health, such as the reduction of blood pressure and of hypertriglyceridemia [85,86]. Within this class of molecules are eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) (10) (Figure 7) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (11) (Figure 7), which naturally occur, for example, in oil from fish [87].
Figure 7.
Molecular structures of eicosapentaenoic acid (10) and docosahexaenoic acid (11).
These molecules were already known for their interesting properties (such as their antioxidant activity); however, more recently, they have also been investigated for their capability of preventing the misfolding of the TTR protein [87,88,89]. To perform the study, compounds 10 and 11 were purchased from an appropriate supplier; all the following tests were performed in triplicate (n = 3). The turbidimetric assay on wt-TTR showed that 10 and 11 can effectively inhibit the amyloid fibril formation (the percentage of fibril formation was 40% and 36%, respectively). In addition, further studies on wt-TTR using thioflavin T fluorescence spectroscopy revealed that 11 has a similar efficacy to diflunisal in reducing the amyloid β-sheet content (42% vs. 54% for 11 and diflunisal, respectively), while 10 is much less active (22%). According to the authors, these results might depend on the fact that small protofibrils can be clearly detected only using the thioflavin T assay and not the turbidimetric one. In order to clarify the mechanism of action of these molecules, an ANS displacement biding assay on wt-TTR was also carried out, and the results revealed that both 10 and 11 can bind to the TTR-binding sites with an IC50 of 13.0 ± 0.08 µM and 12.1 ± 0.07 µM, respectively. This interaction likely leads to a stabilization of the TTR tetramer and justifies the inhibition of the amyloid fibril formation. In light of this, the authors have suggested the use of these molecules in association with appropriate drugs for the treatment of ATTR [87].
Another source of natural compounds that has been investigated for new natural TTR inhibitors is Santalum album L., a plant that has been traditionally exploited to produce perfumes [90,91]. In particular, this plant contains two natural sesquiterpenes, α-santalol (12) (Figure 8) and β-santalol (13) (Figure 8), that have recently attracted attention for their activity in ATTR [90].
Figure 8.
Chemical structures of α-santalol (12) and β-santalol (13).
In their study, Mohankumar at al. purified compounds 12 and 13 from sandalwood (Santalum album L.) oil [90]. Both compounds were proven to be capable of inhibiting the aggregation of both wt-TTR (EC50 values were 36.7 ± 1.2 µM and 31.1 ± 2.4 µM for 12 and 13, respectively) and V30M-TTR (EC50 values were 44.3 ± 3.5 µM and 34.5 ± 2.8 µM for 12 and 13, respectively) under acidic conditions, albeit, in both cases, less effectively than tolcapone (EC50 values were 4.6 ± 0.5 µM and 4.8 ± 0.7 µM for wt-TTR and V30M-TTR, respectively). Notably, these results were obtained from four independent biological replicates, each performed in triplicate. In addition, the capability of these compounds to stabilize the TTR protein was verified using a urea-induced denaturation assay on wt-TTR and V30M-TTR. Moreover, in in vivo experiments on C. elegans worms expressing wt-TTR and V30M-TTR (both at full-length and fused with a fluorescent protein), both 12 and 13 were proven to be capable of inhibiting the formation of TTR aggregates as effectively as tolcapone. Noteworthy, the compounds were more effective as the worms grew older, and a synergistic effect was observed when they were administrated together each at its half optimal dose (16 μM and 8 μM for 12 and 13, respectively) [90].
5. Conclusions
ATTR is a complex disease caused by the dissociation and consequent misfolding of the TTR protein, which results in the deposition of TTR-derived fibrils in different areas of the body. One of the currently available therapeutic strategies for managing this disease consists of the administration of TTR-stabilizing drugs, the purpose of which is to avoid fibril formation. However, despite their proven clinical benefits, these therapeutics are not resolutive, making further research in this field essential. In this scenario, dietary supplements containing natural compounds capable of stabilizing the TTR protein could contribute to the therapeutic action of the drugs used in therapy, thus representing a new helpful tool in the clinical management of this disease. In light of this, here, we reported the natural compounds with such activity that have most recently been reported (years 2020–2025) in the literature as transthyretin stabilizers. Their therapeutic potential in the treatment of ATTR has been described, and the available crystallographic data elucidating their binding mode to TTR have been illustrated. Overall, the use of natural compounds in the form of dietary supplements appears to be a promising strategy for improving the clinical management of the ATTR disorder. However, additional research is needed to determine its feasibility and its actual therapeutic effectiveness. Hopefully, this review will help shed some light on these issues and assist future researchers in designing new and improved protocols for treating this disease.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.M., L.C., and S.N.; software, L.C.; writing—original draft preparation, C.M. and L.C.; writing—review and editing, C.M., L.C., and S.N.; funding acquisition, S.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Italian Ministry of University and Research (MUR) “A comprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in Cardiomyocyte dysfunction Induced by transthyretin Amyloid aggregates: evaluation Of NEw stabilizers of transthyretin misfolding” (CIAONE) CIAONE, PRIN: 2022KJB3B7, CUP I53D23004260006.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ATTR | transthyretin amyloidosis |
| DHA | docosahexaenoic acid |
| EPA | eicosapentaenoic acid |
| PUFAs | poly-unsaturated fatty acids |
| T4 | thyroxine |
| RBP | retinol binding protein |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| Aβ | amyloid-β |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| T4-BP | thyroxine-binding pocket |
| wt-TTR | wild-type TTR |
| mTTR | mutant TTR |
| TTR | transthyretin |
References
- Hung, H.-C.; Joshipura, K.J.; Jiang, R.; Hu, F.B.; Hunter, D.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Colditz, G.A.; Rosner, B.; Spiegelman, D.; Willett, W.C. Fruit and Vegetable Intake and Risk of Major Chronic Disease. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.H. Dietary Antioxidants in Disease Prevention. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1996, 13, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Schluesener, H. Natural Polyphenols against Neurodegenerative Disorders: Potentials and Pitfalls. Ageing Res. Rev. 2012, 11, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, M.; Naz, M.; Jawaid, T.; Arif, M. Natural Products and Their Active Principles Used in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Review. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2019, 19, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.; Rizvi, S. Current Understanding of Dietary Polyphenols and Their Role in Health and Disease. CNF 2009, 5, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortore, G.; Orlandini, E.; Braca, A.; Ciccone, L.; Rossello, A.; Martinelli, A.; Nencetti, S. Targeting Different Transthyretin Binding Sites with Unusual Natural Compounds. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.; Saraiva, M.J.; Almeida, M.R. Natural Polyphenols Inhibit Different Steps of the Process of Transthyretin (TTR) Amyloid Fibril Formation. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2424–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Kosaka, Y.; Mizuguchi, M. Inhibitory Activities of Propolis and Its Promising Component, Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester, against Amyloidogenesis of Human Transthyretin. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 8928–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.; Saraiva, M.J.; Almeida, M.R. Uncovering the Neuroprotective Mechanisms of Curcumin on Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintas, A.; Vaz, D.C.; Cardoso, I.; Saraiva, M.J.; Brito, R.M. Tetramer Dissociation and Monomer Partial Unfolding Precedes Protofibril Formation in Amyloidogenic Transthyretin Variants. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 27207–27213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipe, J.D.; Benson, M.D.; Buxbaum, J.N.; Ikeda, S.-I.; Merlini, G.; Saraiva, M.J.M.; Westermark, P. Amyloid Fibril Proteins and Amyloidosis: Chemical Identification and Clinical Classification International Society of Amyloidosis 2016 Nomenclature Guidelines. Amyloid 2016, 23, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, I.; Goldsbury, C.S.; Müller, S.A.; Olivieri, V.; Wirtz, S.; Damas, A.M.; Aebi, U.; Saraiva, M.J. Transthyretin Fibrillogenesis Entails the Assembly of Monomers: A Molecular Model for in Vitro Assembled Transthyretin Amyloid-like Fibrils. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 317, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, G.; Richardson, S.J. The Evolution of Gene Expression, Structure and Function of Transthyretin. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997, 116, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, S.; Rask, L.; Peterson, P. Studies on Thyroid Hormone-Binding Proteins. II. Binding of Thyroid Hormones, Retinol-Binding Protein, and Fluorescent Probes to Prealbumin and Effects of Thyroxine on Prealbumin Subunit Self Association. J. Biol. Chem. 1975, 250, 8554–8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, H.M.; Newcomer, M.E. The Structure of Human Retinol-Binding Protein (RBP) with Its Carrier Protein Transthyretin Reveals an Interaction with the Carboxy Terminus of RBP. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 2647–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauder, A.J.; Dickson, P.W.; Aldred, A.R.; Schreiber, G.; Mendelsohn, F.A.; Hudson, P. Synthesis of Transthyretin (Pre-Albumin) mRNA in Choroid Plexus Epithelial Cells, Localized by in Situ Hybridization in Rat Brain. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1986, 34, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martone, R.L.; Herbert, J.; Dwork, A.; Schon, E.A. Transthyretin Is Synthesized in the Mammalian Eye. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 151, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermark, G.T.; Westermark, P. Transthyretin and Amyloid in the Islets of Langerhans in Type-2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2008, 2008, 429274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, B.; Li, H.; Richard, K.; Mortimer, R. Synthesis of Thyroid Hormone Binding Proteins Transthyretin and Albumin by Human Trophoblast. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 6714–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemi, M.; Gaiteiro, C.; Ribeiro, C.A.; Santos, L.M.; Gomes, J.R.; Oliveira, S.M.; Couraud, P.-O.; Weksler, B.; Romero, I.; Saraiva, M.J.; et al. Transthyretin Participates in Beta-Amyloid Transport from the Brain to the Liver- Involvement of the Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1? Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, L.; Fruchart-Gaillard, C.; Mourier, G.; Savko, M.; Nencetti, S.; Orlandini, E.; Servent, D.; Stura, E.A.; Shepard, W. Copper Mediated Amyloid-β Binding to Transthyretin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, L.; Camodeca, C.; Tonali, N.; Barlettani, L.; Rossello, A.; Fruchart Gaillard, C.; Kaffy, J.; Petrarolo, G.; La Motta, C.; Nencetti, S.; et al. New Hybrid Compounds Incorporating Natural Products as Multifunctional Agents against Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-H.; Jung, E.S.; Sohn, J.-H.; Hong, H.J.; Hong, H.S.; Kim, J.W.; Na, D.L.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.; Ha, H.J.; et al. Human Serum Transthyretin Levels Correlate Inversely with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 25, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, J.A.; Benson, M.D. Transthyretin: A Review from a Structural Perspective. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1491–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtczak, A.; Cody, V.; Luft, J.R.; Pangborn, W. Structure of Rat Transthyretin (rTTR) Complex with Thyroxine at 2.5 Å Resolution: First Non-Biased Insight into Thyroxine Binding Reveals Different Hormone Orientation in Two Binding Sites. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2001, 57, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lill, M.A.; Danielson, M.L. Computer-Aided Drug Design Platform Using PyMOL. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2011, 25, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz, M.A.; Coelho, T.; Bellotti, V.; Fernandez-Arias, M.I.; Mallaina, P.; Obici, L. A Narrative Review of the Role of Transthyretin in Health and Disease. Neurol. Ther. 2020, 9, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Naharro, A.; Hawkins, P.N.; Fontana, M. Cardiac Amyloidosis. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, s30–s35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.A.; Benson, M.D.; Dyck, P.J.; Grogan, M.; Coelho, T.; Cruz, M.; Berk, J.L.; Plante-Bordeneuve, V.; Schmidt, H.H.J.; Merlini, G. Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy of Transthyretin Amyloidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 2451–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, I.; González-Duarte, A.; Obici, L.; Schmidt, H.H.-J.; Simoneau, D.; Ong, M.-L.; Amass, L. “Red-Flag” Symptom Clusters in Transthyretin Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2016, 21, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plante-Bordeneuve, V. Transthyretin Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy: An Update. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrahina, V.; Grittner, U.; Beetz, C.; Skripuletz, T.; Juenemann, M.; Krämer, H.H.; Hahn, K.; Rieth, A.; Schaechinger, V.; Patten, M.; et al. Hereditary Transthyretin-Related Amyloidosis Is Frequent in Polyneuropathy and Cardiomyopathy of No Obvious Aetiology. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.R.; Futema, M.; Akhtar, M.M.; Lorenzini, M.; Pittman, A.; Syrris, P.; Elliott, P.M. Prevalence of TTR Variants Detected by Whole-Exome Sequencing in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Amyloid 2019, 26, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, L.; Tonali, N.; Shepard, W.; Nencetti, S.; Orlandini, E. Physiological Metals Can Induce Conformational Changes in Transthyretin Structure: Neuroprotection or Misfolding Induction? Crystals 2021, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chompoopong, P.; Mauermann, M.L.; Siddiqi, H.; Peltier, A. Amyloid Neuropathy: From Pathophysiology to Treatment in Light-Chain Amyloidosis and Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Ann. Neurol. 2024, 96, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekijima, Y.; Sousa, L. Pathogenesis, Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Management of CNS Complications in Hereditary ATTR Amyloidosis. Amyloid 2025, 32, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manganelli, F.; Fabrizi, G.M.; Luigetti, M.; Mandich, P.; Mazzeo, A.; Pareyson, D. Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis Overview. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, C.; Ciccone, L.; Orlandini, E.; Rossello, A.; Nencetti, S. A Snapshot of the Most Recent Transthyretin Stabilizers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, J.P.; Costa-Rodrigues, D.; Gales, L. Inhibitors of Transthyretin Amyloidosis: How to Rank Drug Candidates Using X-Ray Crystallography Data. Molecules 2024, 29, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruberg, F.L.; Grogan, M.; Hanna, M.; Kelly, J.W.; Maurer, M.S. Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2872–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, M. Transthyretin: Its Function and Amyloid Formation. Neurochem. Int. 2022, 155, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, F.A.; Judge, D.P.; Ebede, B.; Li, H.; Stewart, M.; Amass, L.; Sultan, M.B. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Tafamidis for the Treatment of Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloid Polyneuropathy: Results up to 6 Years. Amyloid 2017, 24, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurwitz, J.H.; Maurer, M.S. Tafamidis-A Pricey Therapy for a Not-So-Rare Condition. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.S.; Schwartz, J.H.; Gundapaneni, B.; Elliott, P.M.; Merlini, G.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Grogan, M.; Witteles, R.; Damy, T.; et al. Tafamidis Treatment for Patients with Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A. Acoramidis: First Approval. Drugs 2025, 85, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.; Saint Croix, G.R.; Lacy, S.; Fattouh, M.; Barillas-Lara, M.I.; Behrooz, L.; Mechanic, O. The Use of Diflunisal for Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Review. Heart Fail. Rev. 2022, 27, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschöpe, C.; Elsanhoury, A. Treatment of Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy: The Current Options, the Future, and the Challenges. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damy, T.; Garcia-Pavia, P.; Hanna, M.; Judge, D.P.; Merlini, G.; Gundapaneni, B.; Patterson, T.A.; Riley, S.; Schwartz, J.H.; Sultan, M.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Tafamidis Doses in the Tafamidis in Transthyretin Cardiomyopathy Clinical Trial (ATTR-ACT) and Long-Term Extension Study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penchala, S.C.; Connelly, S.; Wang, Y.; Park, M.S.; Zhao, L.; Baranczak, A.; Rappley, I.; Vogel, H.; Liedtke, M.; Witteles, R.M.; et al. AG10 Inhibits Amyloidogenesis and Cellular Toxicity of the Familial Amyloid Cardiomyopathy-Associated V122I Transthyretin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9992–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulawa, C.E.; Connelly, S.; DeVit, M.; Wang, L.; Weigel, C.; Fleming, J.A.; Packman, J.; Powers, E.T.; Wiseman, R.L.; Foss, T.R.; et al. Tafamidis, a Potent and Selective Transthyretin Kinetic Stabilizer That Inhibits the Amyloid Cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9629–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, L.; Tonali, N.; Nencetti, S.; Orlandini, E. Natural Compounds as Inhibitors of Transthyretin Amyloidosis and Neuroprotective Agents: Analysis of Structural Data for Future Drug Design. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1145–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Mizuguchi, M. Inhibition of the Amyloidogenesis of Transthyretin by Natural Products and Synthetic Compounds. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.M.; Connelly, S.; Fearns, C.; Powers, E.T.; Kelly, J.W. The Transthyretin Amyloidoses: From Delineating the Molecular Mechanism of Aggregation Linked to Pathology to a Regulatory-Agency-Approved Drug. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 421, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Kusaka, K.; Mizuguchi, M.; Nabeshima, Y.; Fujiwara, S. Resveratrol Derivatives Inhibit Transthyretin Fibrillization: Structural Insights into the Interactions between Resveratrol Derivatives and Transthyretin. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 15511–15523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, H.; Isoguchi, A.; Okada, M.; Masuda, T.; Misumi, Y.; Tsutsui, C.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ichiki, Y.; Sawashita, J.; Ueda, M.; et al. Glavonoid, a Possible Supplement for Prevention of ATTR Amyloidosis. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silano, V.; Coppens, P.; Larrañaga-Guetaria, A.; Minghetti, P.; Roth-Ehrang, R. Regulations Applicable to Plant Food Supplements and Related Products in the European Union. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binns, C.W.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, A.H. Problems and Prospects: Public Health Regulation of Dietary Supplements. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2018, 39, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, L. Review on the Structures and Activities of Transthyretin Amyloidogenesis Inhibitors. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1057–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Kelly, J.W. A Competition Assay to Identify Amyloidogenesis Inhibitors by Monitoring the Fluorescence Emitted by the Covalent Attachment of a Stilbene Derivative to Transthyretin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raksat, A.; Maneerat, W.; Rujanapun, N.; Andersen, R.J.; Pyne, S.G.; Laphookhieo, S. Antibacterial and Inhibitory Activities against Nitric Oxide Production of Coumaronochromones and Prenylated Isoflavones from Millettia extensa. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2343–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raksat, A.; Maneerat, W.; Andersen, R.J.; Pyne, S.G.; Laphookhieo, S. Antibacterial Prenylated Isoflavonoids from the Stems of Millettia extensa. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máximoa, P.; Lourenço, A.; Savluchinske Feio, S.; Roseiro, J.C. A New Prenylisoflavone from Ulex Jussiaei. Z. Für Naturforsch. C 2002, 57, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thanh Luan, N.N.; Okada, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Suzuki, M.; Nabeshima, Y.; Mizuguchi, M.; Toyooka, N. Divergent Total Synthesis of Isoflavone Natural Products and Their Potential as Therapeutic Agents for TTR Amyloidosis. J. Nat. Prod. 2024, 87, 2604–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, T.; Kosaka, Y.; Mizuguchi, M. Crystal Structures of Human Transthyretin Complexed with Glabridin. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Choe, S.S.; Jang, H.; Kim, J.; Jeong, H.W.; Jo, H.; Jeong, K.-H.; Tadi, S.; Park, M.G.; Kwak, T.H.; et al. AMPK Activation with Glabridin Ameliorates Adiposity and Lipid Dysregulation in Obesity. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Mae, T.; Kitano, M.; Sakamoto, Y.; Ikematsu, H.; Nakagawa, K. Licorice Flavonoid Oil Effects Body Weight Loss by Reduction of Body Fat Mass in Overweight Subjects. J. Health Sci. 2006, 52, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, M.; Mimaki, Y.; Honda, S.; Tanaka, H.; Yokota, S.; Mae, T. Phenolics from Glycyrrhiza Glabra Roots and Their PPAR-γ Ligand-Binding Activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulusoy, H.G.; Sanlier, N. A Minireview of Quercetin: From Its Metabolism to Possible Mechanisms of Its Biological Activities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3290–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, L.; Tonali, N.; Fruchart-Gaillard, C.; Barlettani, L.; Rossello, A.; Braca, A.; Orlandini, E.; Nencetti, S. Antioxidant Quercetin 3-O-Glycosylated Plant Flavonols Contribute to Transthyretin Stabilization. Crystals 2022, 12, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianci, M.; Folli, C.; Zonta, F.; Florio, P.; Berni, R.; Zanotti, G. Structural Evidence for Asymmetric Ligand Binding to Transthyretin. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowska, A.M.; Camangi, F.; Braca, A. Quali-Quantitative Analysis of Flavonoids of Cornus mas L. (Cornaceae) Fruits. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzi, A.M.; Giacomelli, C.; De Leo, M.; Russo, L.; Camangi, F.; De Tommasi, N.; Braca, A.; Martini, C.; Trincavelli, M.L. Cornus Sanguinea Fruits: A Source of Antioxidant and Antisenescence Compounds Acting on Aged Human Dermal and Gingival Fibroblasts. Planta Med. 2021, 87, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.M.T.R.; de Almeida Silva, V.; Palmieri, L.d.C.; Oliveira, M.C.B.R.; Foguel, D.; Polikarpov, I. Identification of a Novel Ligand Binding Motif in the Transthyretin Channel. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolado, I.; Nieto, J.; Saraiva, M.J.M.; Arsequell, G.; Valencia, G.; Planas, A. Kinetic Assay for High-Throughput Screening of In Vitro Transthyretin Amyloid Fibrillogenesis Inhibitors. J. Comb. Chem. 2005, 7, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, R.; Coleman, C.; Ionescu-Zanetti, C.; Carter, S.A.; Krishna, V.; Grover, R.K.; Roy, R.; Singh, S. Mechanism of Thioflavin T Binding to Amyloid Fibrils. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 151, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Khan, S.; Rahman, S.; Singh, L.R. The Extracellular Protein, Transthyretin Is an Oxidative Stress Biomarker. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.D.; Minamino, N.; Takao, T. Free Thiol of Transthyretin in Human Plasma Most Accessible to Modification/Oxidation. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 10785–10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frozza, R.L.; Bernardi, A.; Hoppe, J.B.; Meneghetti, A.B.; Matté, A.; Battastini, A.M.O.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Salbego, C. Neuroprotective Effects of Resveratrol Against Aβ Administration in Rats Are Improved by Lipid-Core Nanocapsules. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 47, 1066–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walle, T.; Hsieh, F.; DeLegge, M.H.; Oatis, J.E.; Walle, U.K. High Absorption but Very Low Bioavailability of Oral Resveratrol in Humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollár, P.; Hotolová, H. Biological effects of resveratrol and other constituents of wine. Ceska Slov. Farm. 2003, 52, 272–281. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Sang, S. Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics of Resveratrol and Pterostilbene. BioFactors 2018, 44, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.; Mohandas, S.; Ganesan, K.; Xu, B.; Ramkumar, K.M. New Insights into Dietary Pterostilbene: Sources, Metabolism, and Health Promotion Effects. Molecules 2022, 27, 6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchettini, J.C.; Klabunde, T.; Petrassi, H.M.; Oza, V.B.; Raman, P.; Kelly, J.W. Rational Design of Potent Human Transthyretin Amyloid Disease Inhibitors. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, A.; Zhang, J.; Derbyshire, D.; Wu, X.; Konradsson, P.; Hammarström, P.; Von Castelmur, E. Transthyretin Binding Mode Dichotomy of Fluorescent Trans-Stilbene Ligands. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musazadeh, V.; Kavyani, Z.; Naghshbandi, B.; Dehghan, P.; Vajdi, M. The Beneficial Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Controlling Blood Pressure: An Umbrella Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 985451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arca, M.; Borghi, C.; Pontremoli, R.; De Ferrari, G.M.; Colivicchi, F.; Desideri, G.; Temporelli, P.L. Hypertriglyceridemia and Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Their Often Overlooked Role in Cardiovascular Disease Prevention. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, L.; Nencetti, S.; Rossello, A.; Barlettani, L.; Tonali, N.; Nieri, P.; Orlandini, E. Omega-3 PUFAs as a Dietary Supplement in Senile Systemic Amyloidosis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meital, L.T.; Windsor, M.T.; Perissiou, M.; Schulze, K.; Magee, R.; Kuballa, A.; Golledge, J.; Bailey, T.G.; Askew, C.D.; Russell, F.D. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Decrease Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Macrophages from Patients with Small Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppedisano, F.; Macrì, R.; Gliozzi, M.; Musolino, V.; Carresi, C.; Maiuolo, J.; Bosco, F.; Nucera, S.; Caterina Zito, M.; Guarnieri, L.; et al. The Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties of n-3 PUFAs: Their Role in Cardiovascular Protection. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohankumar, A.; Kalaiselvi, D.; Thiruppathi, G.; Muthusaravanan, S.; Vijayakumar, S.; Suresh, R.; Tawata, S.; Sundararaj, P. Santalol Isomers Inhibit Transthyretin Amyloidogenesis and Associated Pathologies in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 924862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuttan, R.; Panikkar, B.; Binitha, P.P. Amino Acids in Sandal (Santalum Album L) with Special Reference to Cis-4-Hydroxy-l-Proline and Sym. Homospermidine. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).