Rapid Synthesis of Highly Crystalline ZnO Nanostructures: Comparative Evaluation of Two Alternative Routes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
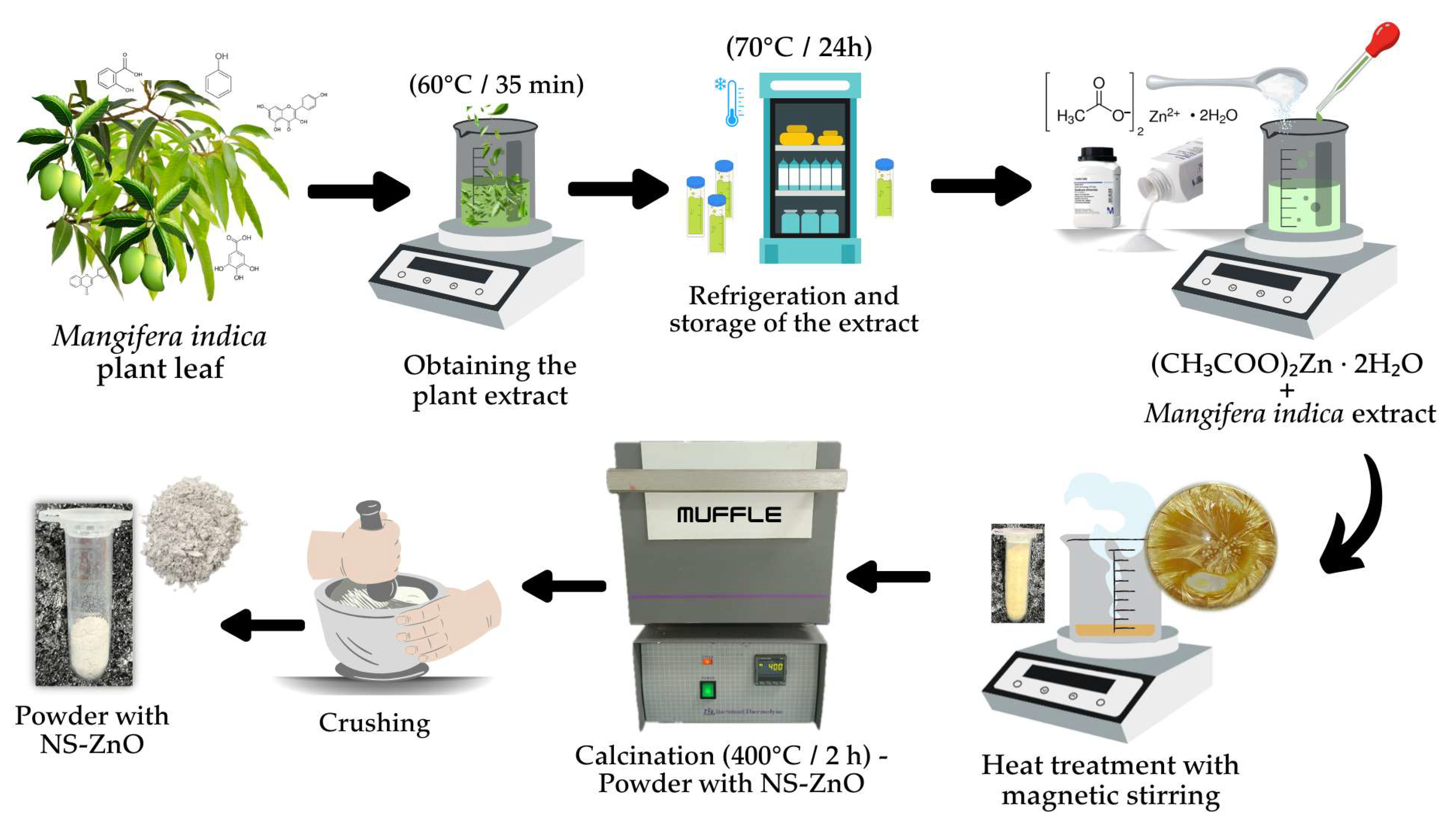
2.1. Rapid NS-ZnO Synthesis (Route 1)
2.2. NS-ZnO Synthesis (Route 2)
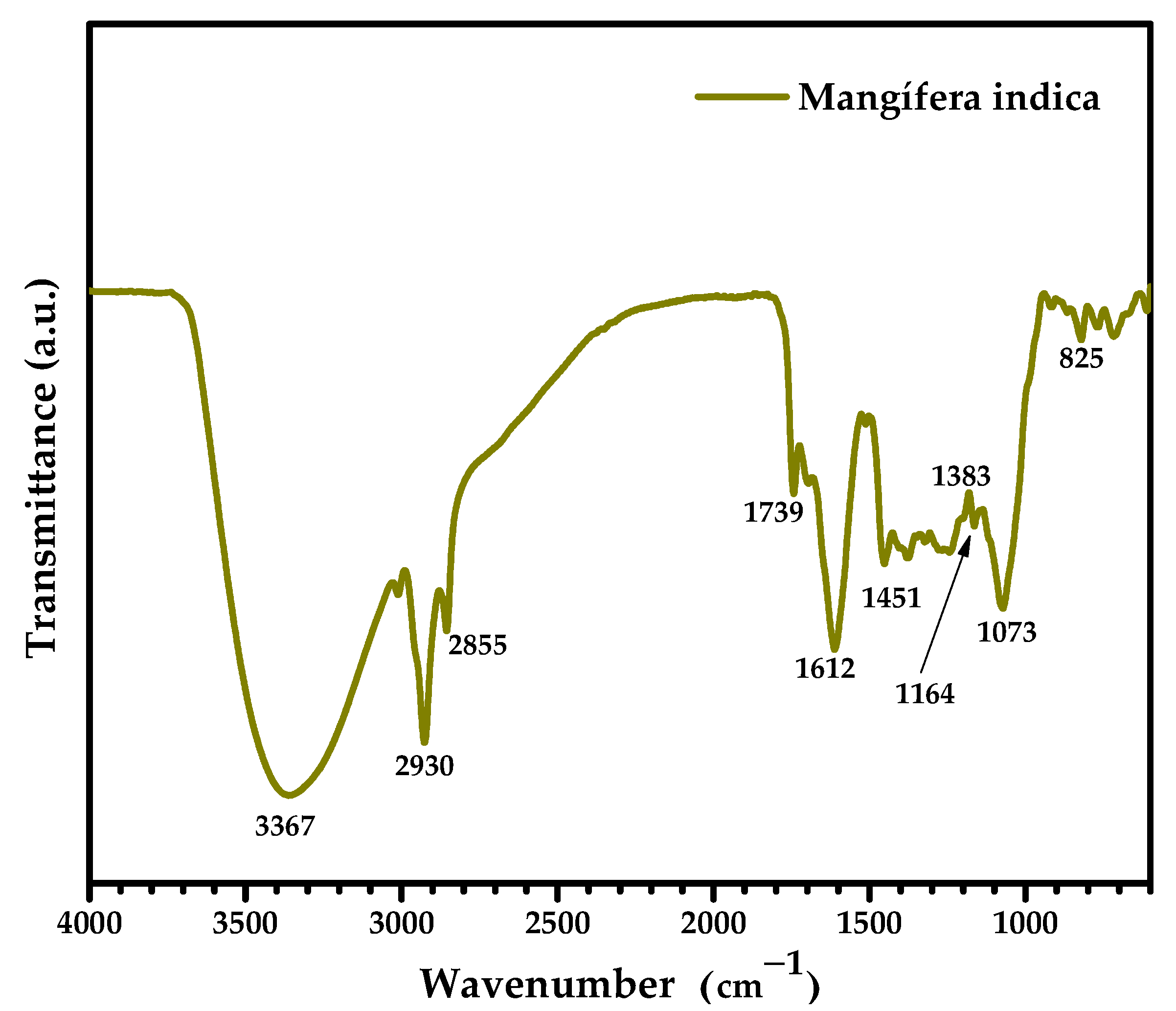
2.2.1. Preparation of Plant Extract
2.2.2. Physical-Green Synthesis of NS-ZnO
2.3. Characterization of NS-ZnO
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Analysis
3.2. Raman Spectroscopy Analysis
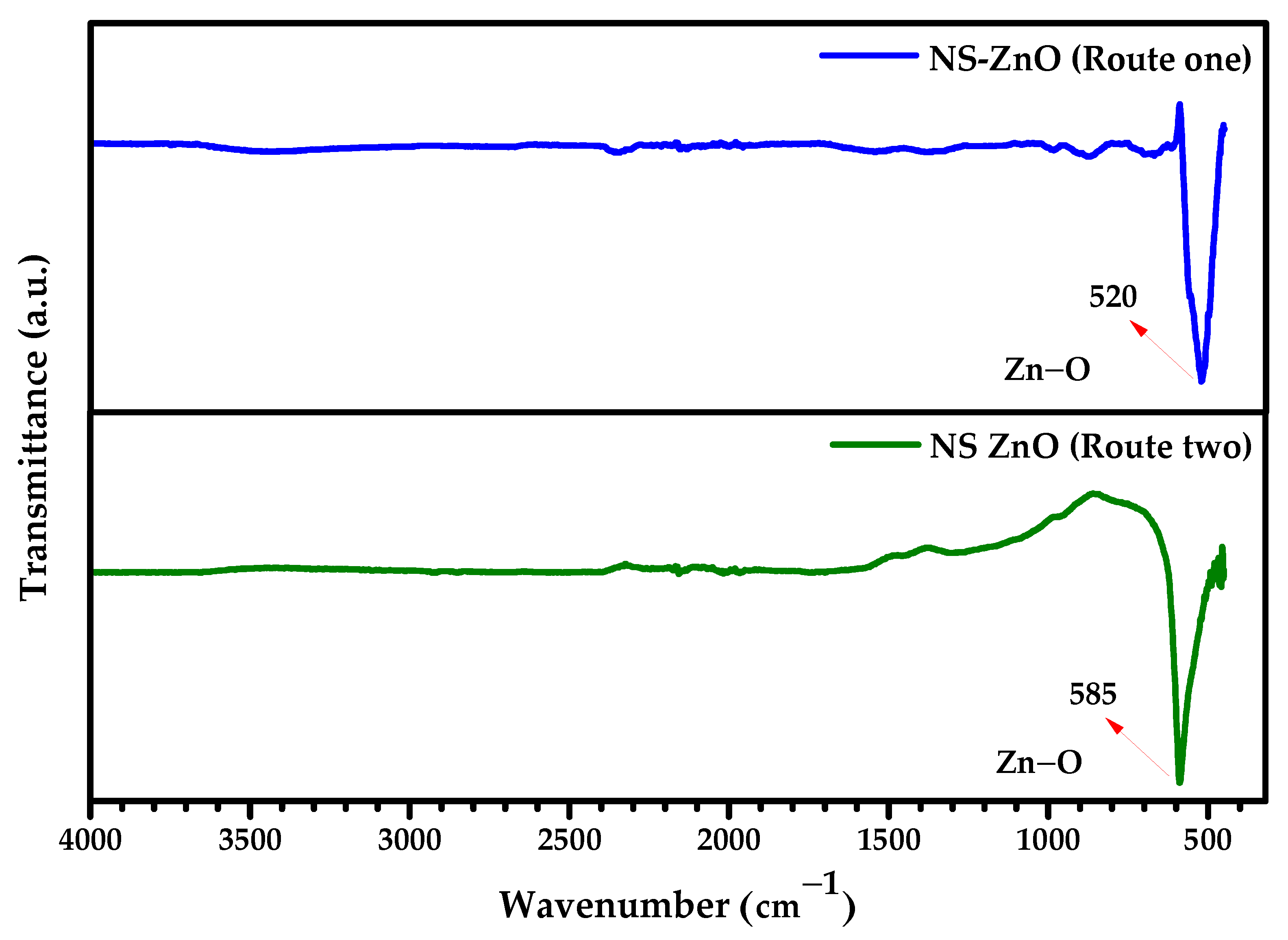
3.3. FTIR Analysis
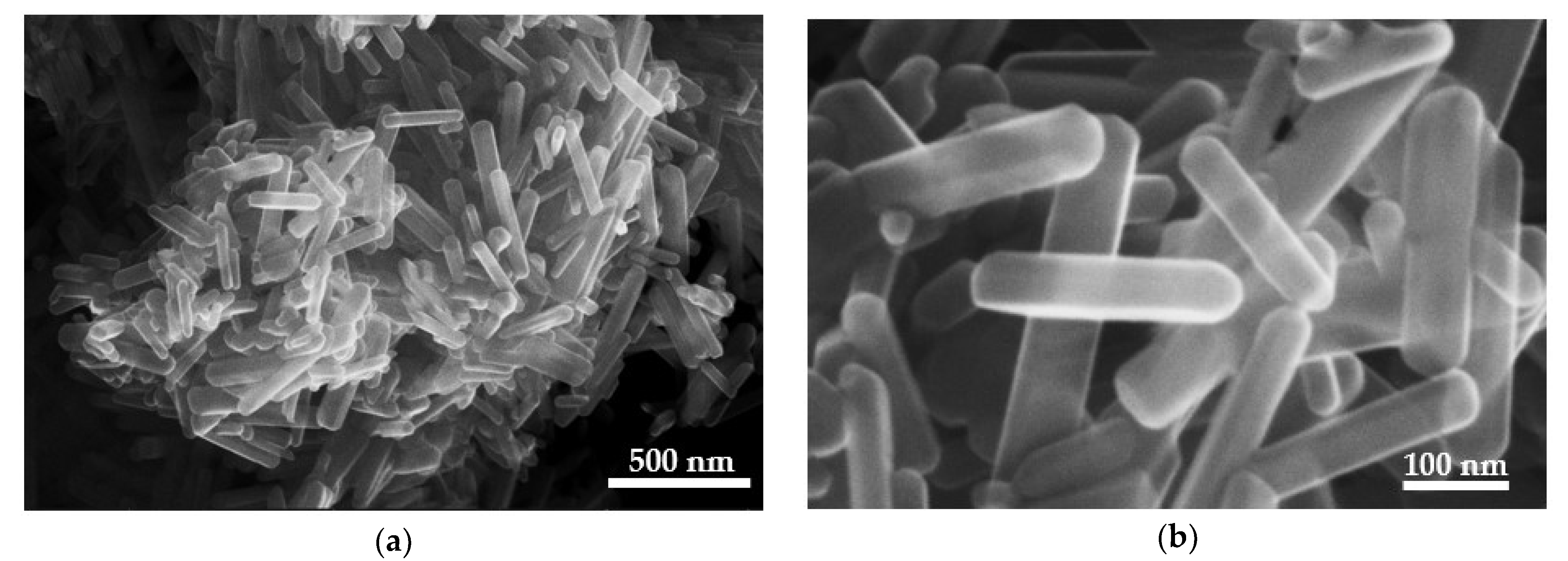
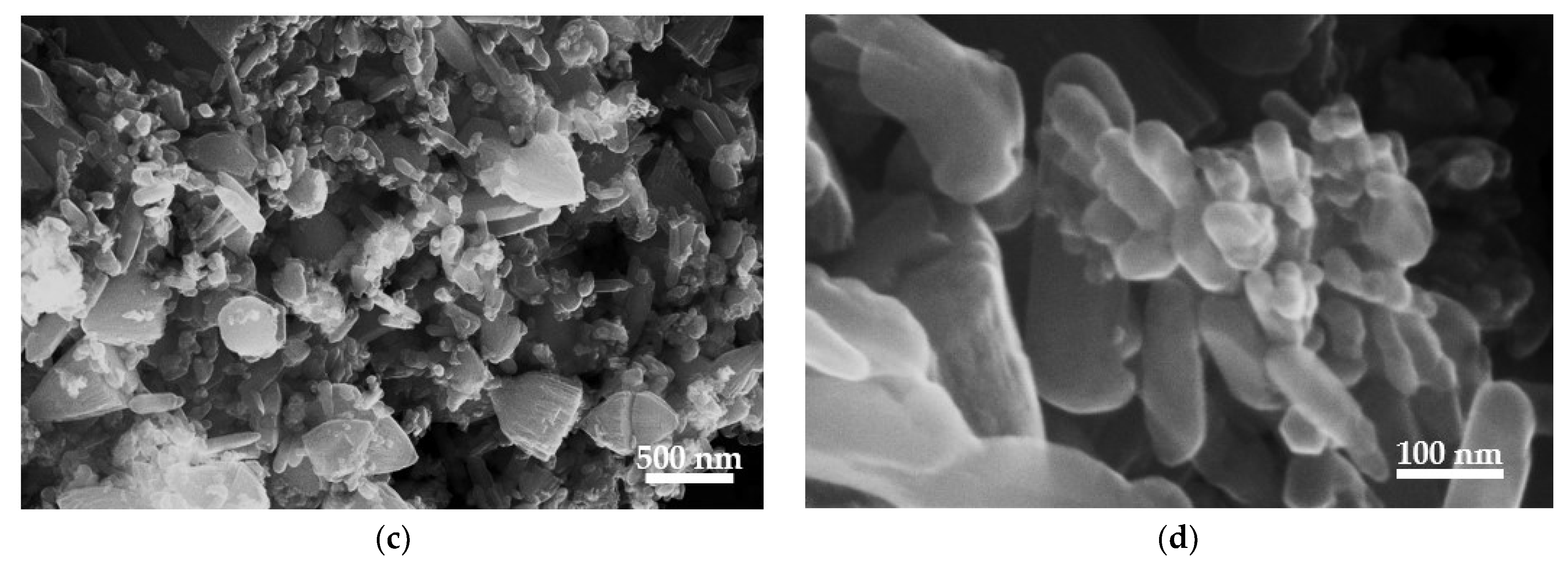
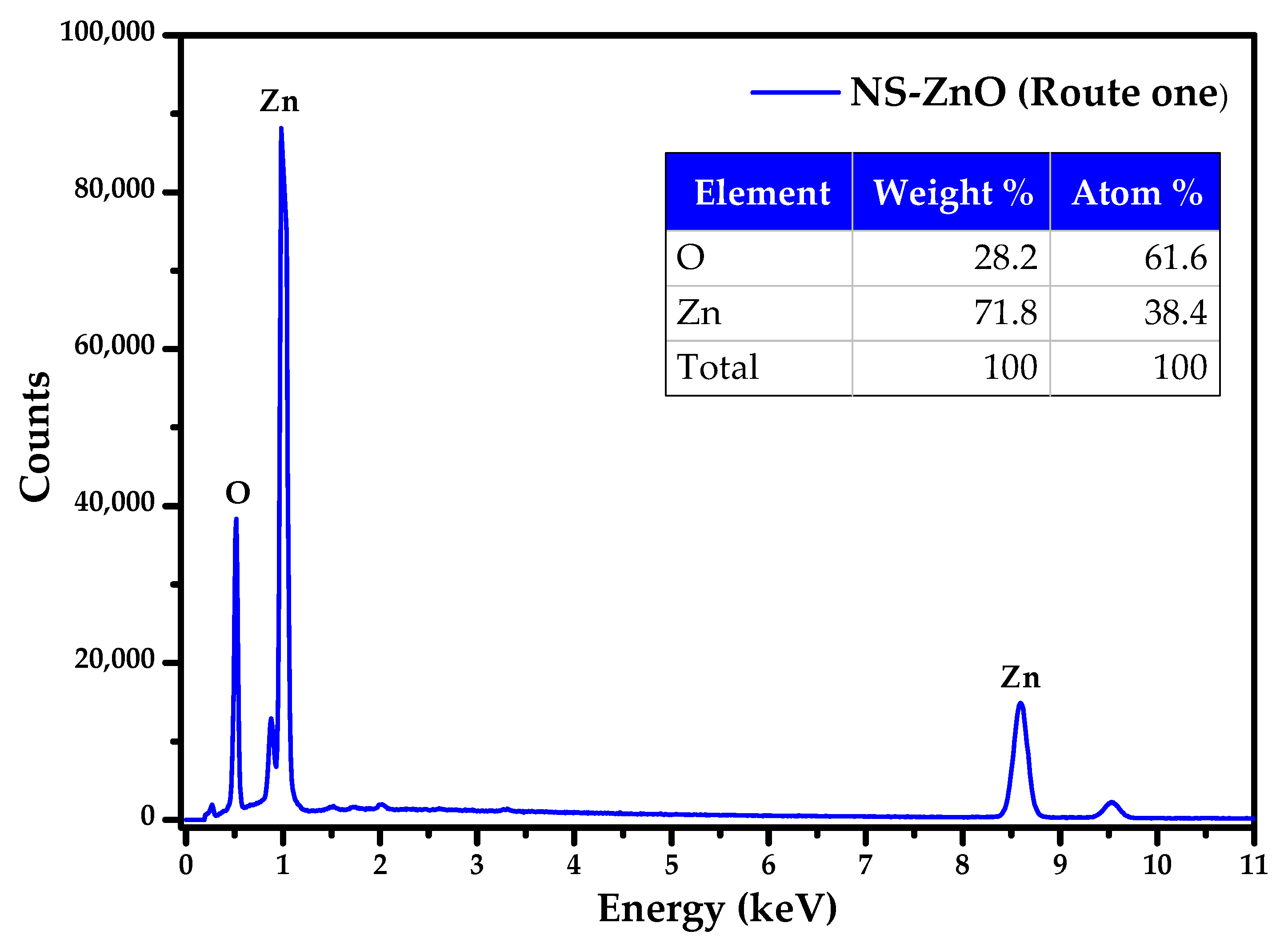
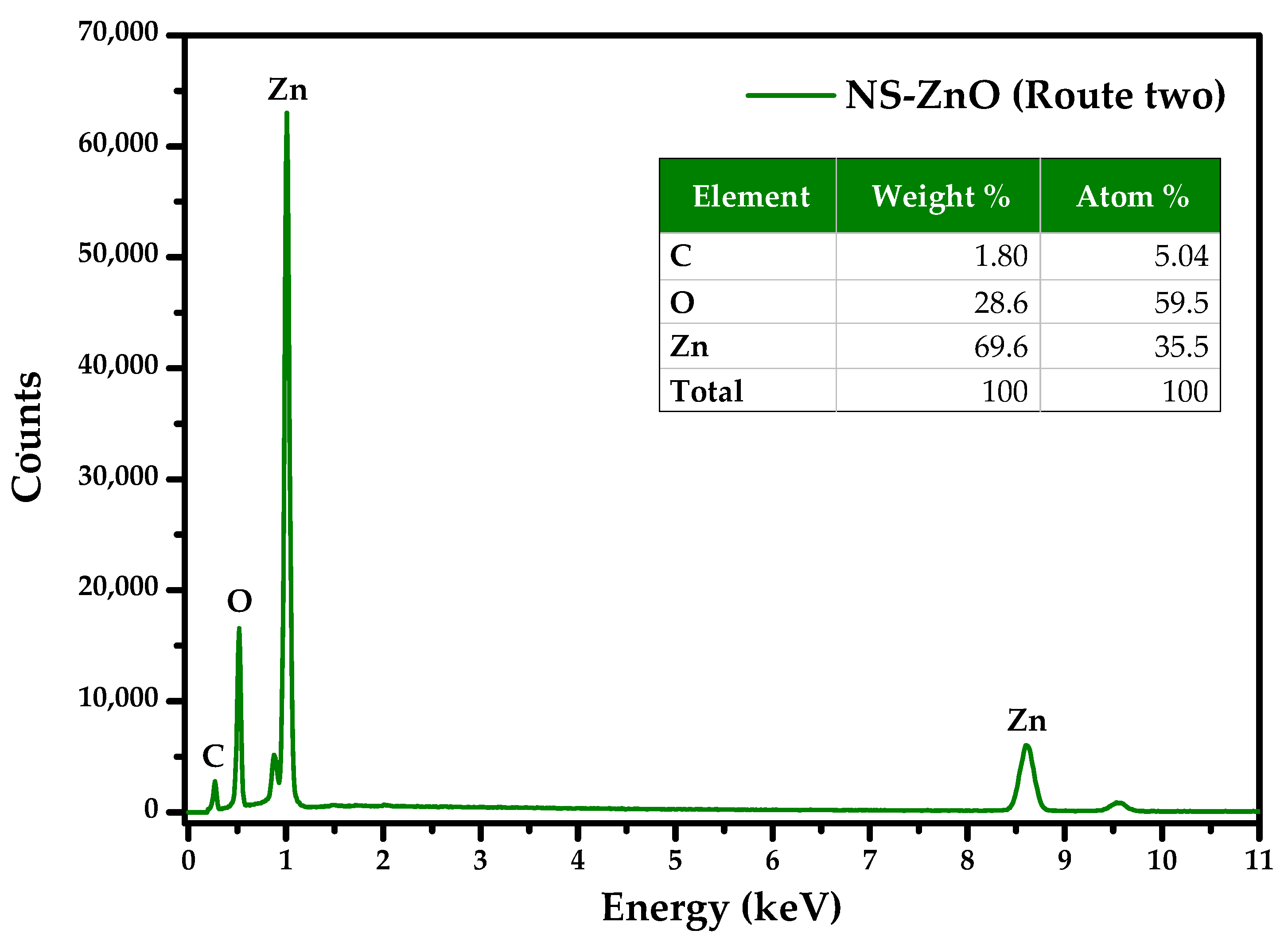
3.4. FE-SEM and EDS Analysis
3.5. UV-Vis Absorption Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borysiewicz, M.A. ZnO as a Functional Material, a Review. Crystals 2019, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, R.; Basak, A.; Maity, P.C.; Badhulika, S. ZnO Nano-Structured Based Devices for Chemical and Optical Sensing Applications. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorbiun, M.; Shayegan Mehr, E.; Ramazani, A.; Taghavi Fardood, S. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide and Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Extract of Oak Fruit Hull (Jaft) and Comparing Their Photocatalytic Degradation of Basic Violet 3. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2018, 12, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, L.; Fang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, L.; Xie, L.; Zhao, H. One-Dimensional Zinc Oxide Nanomaterials for Application in High-Performance Advanced Optoelectronic Devices. Crystals 2018, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Perez, J.E.; Almaral-Sanchez, J.L.; Hurtado-Macias, A.; Cortez-Valadez, M.; Borquez-Mendívil, A.; García-Grajeda, B.A.; Mendivil-Escalante, J.M.; Flores-Valenzuela, J. Structural and chemical analysis of Zn ion exchange in thermally modified zelite A4. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quím. 2024, 23, Mat24264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnati, P.; Haque, A.; Taufique, M.F.N.; Ghosh, K. A Systematic Study on the Structural and Optical Properties of Vertically Aligned Zinc Oxide Nanorods Grown by High Pressure Assisted Pulsed Laser Deposition Technique. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yao, C.; Gan, J.; Jiang, K.; Hu, Z.; Lin, J.; Xu, N.; Sun, J.; Wu, J. ZnO Colloids and ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized by Pulsed Laser Ablation of Zinc Powders in Water. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 109, 104918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, M.S.; Verma, H.; Akhani, S.B.; Pathak, J.; Joshi, U.; Joshi, A.; Prakash, C.; Kaur, K.; Oza, A. Photoluminescence and Antibacterial Performance of Sol–Gel Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 3472–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumaya, M.U.; Maria, K.H.; Toma, F.T.Z.; Zubair, M.A.; Chowdhury, M.T. Effect of Stabilizer Content in Different Solvents on the Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using the Chemical Precipitation Method. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittaya, L.; Chalad, C.; Sirimahachai, U. Green Synthesis and Biological Activities of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Ampelocissus martini Rhizome Extract. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202304671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Nath, B.C.; Phukon, P.; Kalita, A.; Dolui, S.K. Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayswal, S.; Moirangthem, R.S. Thermal decomposition route to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic application. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 2009, 020023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motelica, L.; Oprea, O.-C.; Vasile, B.-S.; Ficai, A.; Ficai, D.; Andronescu, E.; Holban, A.M. Antibacterial Activity of Solvothermal Obtained ZnO Nanoparticles with Different Morphology and Photocatalytic Activity against a Dye Mixture: Methylene Blue, Rhodamine B and Methyl Orange. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josun, J.; Sharma, P.; Kumar Garg, V. Optical and Structural Behavior of Hydrothermally Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles at Various Temperatures with NaOH Molar Ratios. Results Opt. 2024, 14, 100601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, J.A.A.; Guerrero, A.; Romero, A. Efficient and Sustainable Synthesis of Zinc Salt-Dependent Polycrystal Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Comprehensive Assessment of Physicochemical and Functional Properties. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagrán, Z.; Anaya-Esparza, L.M.; Velázquez-Carriles, C.A.; Silva-Jara, J.M.; Ruvalcaba-Gómez, J.M.; Aurora-Vigo, E.F.; Rodríguez-Lafitte, E.; Rodríguez-Barajas, N.; Balderas-León, I.; Martínez-Esquivias, F. Plant-Based Extracts as Reducing, Capping, and Stabilizing Agents for the Green Synthesis of Inorganic Nanoparticles. Resources 2024, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Seedi, H.R.; El-Shabasy, R.M.; Khalifa, S.A.M.; Saeed, A.; Shah, A.; Shah, R.; Iftikhar, F.J.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Omri, A.; Hajrahand, N.H.; et al. Metal Nanoparticles Fabricated by Green Chemistry Using Natural Extracts: Biosynthesis, Mechanisms, and Applications. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 24539–24559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.; Singh, P.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, P.; Bhankar, V.; Kumar, K. Plant-Mediated Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Their Applications: A Review. Mater. Res. Bull. 2023, 163, 112233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharissova, O.V.; Dias, H.V.R.; Kharisov, B.I.; Pérez, B.O.; Pérez, V.M.J. The Greener Synthesis of Nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, L.M.; Tai, L.T.; Dat, N.M.; Hai, N.D.; An, H.; Nam, N.T.H.; Thi Thu Hanh, T.; Hieu, N.H. Non-Metallic X (X = C, N, S, and P) Co-Doped Copper Oxide Derived from Mangifera indica Leaf Extract: Synthesis, Characterization, Density Functional Theory Simulation of Structure, and Photoactivities. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 687, 133393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.U.H.; Gul, N.S.; Mehmood, F.; Sabahat, S.; Muhammad, N.; Rahim, A.; Iqbal, J.; Khasim, S.; Salam, M.A.; Khan, T.M.; et al. Green Synthesis of Lead Oxide Nanoparticles for Photo-Electrocatalytic and Antimicrobial Applications. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1175114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saputra, I.S.; Nurfani, E.; Fahmi, A.G.; Saputro, A.H.; Apriandanu, D.O.B.; Annas, D.; Yulizar, Y. Effect of Secondary Metabolites from Several Leaf Extracts on the Green Synthesized-ZnO Nanoparticles. Vacuum 2024, 227, 113434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Biron, D.S.; dos Santos, V.; Bergmann, C.P. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide obtained by combining zinc nitrate with sodium hydroxide in polyol medium. Mater. Res. 2020, 23, e20200080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, M.; Kumar, S.; Gaur, J.; Kaushal, S.; Dalal, J.; Singh, G.; Misra, M.; Ahlawat, D.S. Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Justicia Adhatoda for Photocatalytic Degradation of Malachite Green and Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 2958–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, A.L. The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindu, P.; Thomas, S. Estimation of lattice strain in ZnO nanoparticles: X-ray peak profile analysis. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2014, 8, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghani, G.M.; Ahmed, A.B.; Al-Zubaidi, A.B. Synthesis, Characterization, and the Influence of Energy of Irradiation on Optical Properties of ZnO Nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullity, B.D.; Stock, S.R. Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 2nd ed.; Assison-Wesley Publishing Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Elmahaishi, M.F.; Azis, R.S.; Ismail, I.; Mustaffa, M.S.; Abbas, Z.; Matori, K.A.; Muhammad, F.D.; Saat, N.K.; Nazlan, R.; Ibrahim, I.R.; et al. Structural, Electromagnetic and Microwave Properties of Magnetite Extracted from Mill Scale Waste via Conventional Ball Milling and Mechanical Alloying Techniques. Materials 2021, 14, 7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Jangir, L.K.; Rathore, K.S.; Kumar, M.; Awasthi, K. Morphology-Dependent Structural and Optical Properties of ZnO Nanostructures. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2019, 125, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Jiménez, J.P.; Horta-Piñeres, S.D.; Castillo, S.J.; Izquierdo, J.L.; Avila, D.A. Ultra-Thin Films of CdS Doped with Silver: Synthesis and Modification of Optical, Structural, and Morphological Properties by the Doping Concentration Effect. Coatings 2025, 15, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, D.; Thomas, B.; Sudheep, N.M.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Zinc oxide nanoflowers decorated with Mangifera indica leaf extract phytochemicals as superior surface catalyst over commercial zinc oxide nanoparticles in the reduction of p-nitrophenol to p-aminophenol. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2025, 468, 116520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Chen, B.; Shanmugam, R.; Rathi, M.A.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M. Green synthesis, characterization and bioactivity of Mangifera indica seed-wrapped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Molecules 2023, 28, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-darwesh, M.Y.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Mohammed, M.A. A Review on Plant Extract Mediated Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmochowska, A.; Czajkowska, J.; Jędrzejewski, R.; Stawiński, W.; Migdał, P.; Fiedot-Toboła, M. Pectin Based Banana Peel Extract as a Stabilizing Agent in Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahakis, N.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Chapman, H.N. 3D nanocrystallography and the imperfect molecular lattice. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2024, 75, 483–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq Mohamed, M.J.; Gondal, M.A. Nanostructured Defects-Rich Black-ZnO/Biowaste-Derived Carbon Composites for Efficient Visible Light-Driven Hydrogen Generation: A Study on the Role of C–Zn@C–O–Zn Interface. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 92, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingshirn, C. ZnO: From Basics towards Applications. Phys. Status Solidi B Basic Res. 2007, 244, 3027–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yin, P.-G.; Wang, N.; Guo, L. Photoluminescence and Raman Scattering of ZnO Nanorods. Solid State Sci. 2009, 11, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Zhong, H.M.; Li, Z.F.; Lu, W. Raman Study for E2 Phonon of ZnO in Zn1−xMnxO Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 086105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, V.M.A.; Costa, T.G.; Chaves, A.S.; Fazzio, A.; Miwa, R.H. On the vibrational properties of transition metal doped ZnO: Surface, defect, and bandgap engineering. Acta Mater. 2023, 259, 119258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damen, T.C.; Porto, S.P.S.; Tell, B. Raman Effect in Zinc Oxide. Phys. Rev. 1966, 142, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorjeva, L.; Millers, D.; Łojkowski, W.; Strachowski, T. Luminescence and FTIR Spectroscopy of ZnO Nanocrystals. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 514–516, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Liu, A.; Liu, M.; Ma, Y.; Wei, J.; Man, B. Synthesis, Characterization and Optical Properties of Flower-like ZnO Nanorods by Non-Catalytic Thermal Evaporation. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 492, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, S.; Dutta, J. Hydrothermal Growth of ZnO Nanostructures. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2009, 10, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandeira, M.; Giovanela, M.; Roesch-Ely, M.; Devine, D.M.; da Silva Crespo, J. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Review of the Synthesis Methodology and Mechanism of Formation. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 15, 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimalraj, S.; Ashokkumar, T.; Saravanan, S. Biogenic gold nanoparticles synthesis mediated by Mangifera indica seed aqueous extracts exhibits antibacterial, anticancer and anti-angiogenic properties. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafton, A.B.; Cheatum, C.M. Two-dimensional infrared study of the CD and CO stretching vibrations in strongly hydrogen-bonded complexes. Chem. Phys. 2018, 512, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, J.; Yon, J.; Henry, C.; Kholghy, M.R. Approximating the van Der Waals Interaction Potentials between Agglomerates of Nanoparticles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2023, 34, 104269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, F.d.C.G.; Cervantes, J.L.; López, A.S.; Sifuentes, P.; Ramírez, E.; Pérez, G.; Díaz, J.C.; Díaz, L.L. Sol–gel/hydrothermal synthesis of well-aligned ZnO nanorods. Bol. Soc. Esp. Ceram. Vidr. 2023, 62, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Neeraj, S.; Natarajan, S.; Rao, C.N.R. Transformations of Two-Dimensional Layered Zinc Phosphates to Three-Dimensional and One-Dimensional Structures. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Ahmad, N.; Briscoe, J.; Zhang, D.-W.; Krause, S. Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors Using ZnO Nanorods as the Sensor Substrate for Bioanalytical Applications. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8708–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, P.P.; Silva, C.C.; Ramirez, M.A.; Biasotto, G.; Foschini, C.R.; Simões, A.Z. Multifunctional Environmental Applications of ZnO Nanostructures Synthesized by the Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 542, 148723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Kumar Kar, A. Influence of Oxygen-Related Surface Adsorbates on the Growth of Low Dimensional Nanostructures and Enhanced Luminescence Due to Superoxide Charge-Transfer States in ZnO for Application in Optoelectronic Devices. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 859, 157793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qin, J.; Hao, R.; Wang, L.; Shen, X.; Yu, R.; Limpanart, S.; Ma, M.; Liu, R. Carbon-Doped ZnO Nanostructures: Facile Synthesis and Visible Light Photocatalytic Applications. J. Phys. Chem. C Nanomater. Interfaces 2015, 119, 20544–20554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xue, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X. A facile route for the preparation of ZnO/C composites with high photocatalytic activity and adsorption capacity. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 4478–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Ma, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z. Facile synthesis of ZnO–C nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Jang, J.-W.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, K.-H. Carbon-Doped ZnO Nanostructures Synthesized Using Vitamin C for Visible Light Photocatalysis. CrystEngComm 2010, 12, 3929–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Porta, F.A.; Andrés, J.; Vismara, M.V.G.; Graeff, C.F.O.; Sambrano, J.R.; Li, M.S.; Varela, J.A.; Longo, E. Correlation between structural and electronic order-disorder effects and optical properties in ZnO nanocrystals. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 10164–10174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clament Sagaya Selvam, N.; Vijaya, J.J.; Kennedy, L.J. Effects of Morphology and Zr Doping on Structural, Optical, and Photocatalytic Properties of ZnO Nanostructures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 16333–16345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Asady, Z.M.; AL-Hamdani, A.H.; Hussein, M.A. Study the optical and morphology properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2213, 020061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.A.; Lv, R.; Gai, S.; Parchur, A.K.; Solanki, P.R.; Thakur, A.; Ansari, Z.A.; Dhayal, M.; Yang, P.; Nazeeruddin, M.; et al. ZnO nanostructures—Future frontiers in photocatalysis, solar cells, sensing, supercapacitor, fingerprint technologies, toxicity, and clinical diagnostics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 515, 215942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Younis, S.A.; Kim, K.-H.; Dong, F. Anisotropic ZnO nanostructures and their nanocomposites as an advanced platform for photocatalytic remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, P.; Peng, H.; Sun, B.; Lan, J.; Wan, J.; Fei, Y.; Ye, X.; Qu, S.; Ye, G.; He, Y.; et al. Modulation of ZnO Nanostructure for Efficient Photocatalytic Performance. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

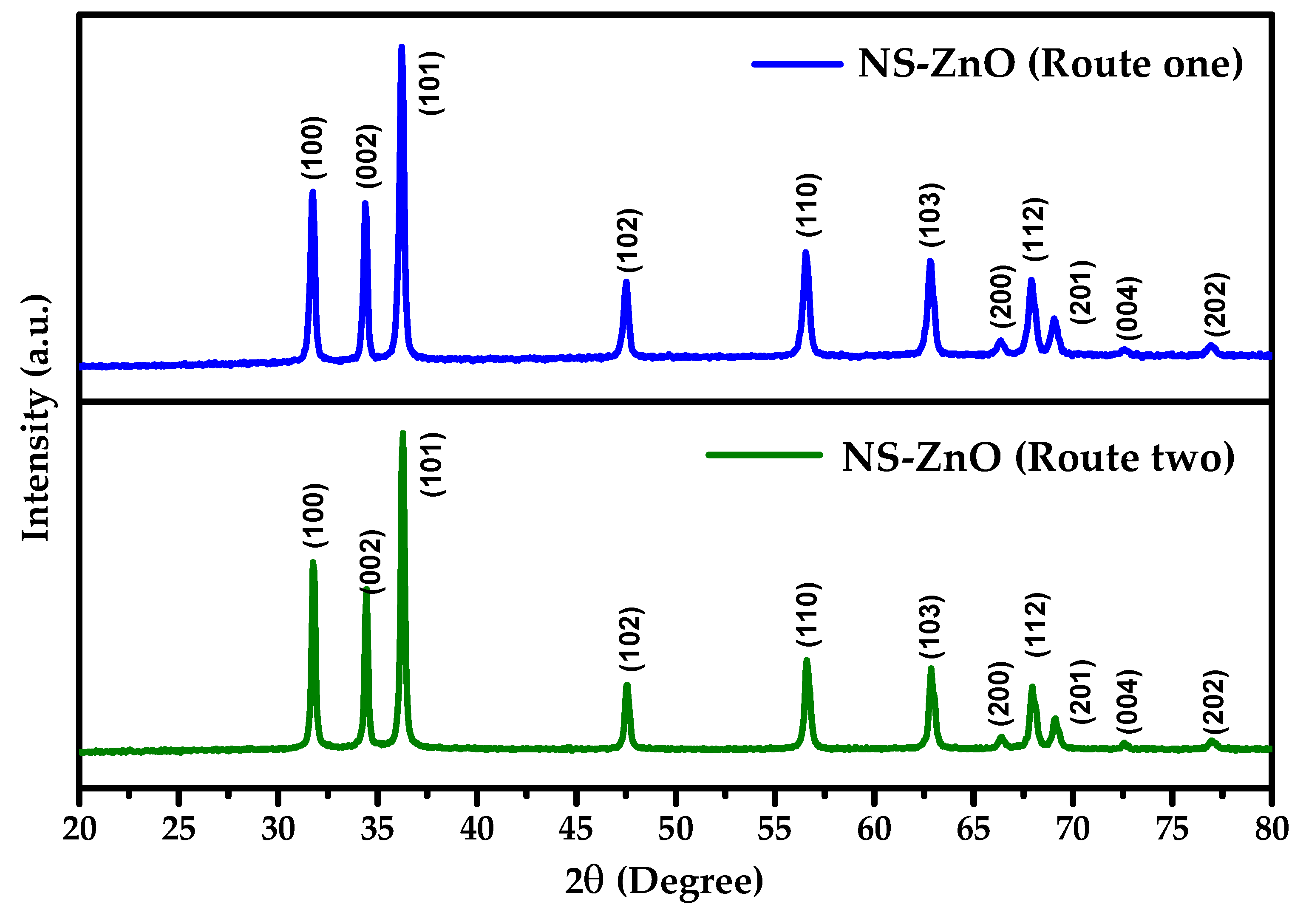



| ZnO Samples Name | Lattice Constants | Cell Volume (Å)3 | Crystallite Size (nm) | Crystallinity Index (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Å) | (Å) | ||||
| NS ZnO (route 1) | 3.2530 | 5.2110 | 47.75 | 30 | 86.9 |
| NS ZnO (route 2) | 3.2487 | 5.2040 | 47.56 | 35 | 91.6 |
| ICDD (#79-0205) | 3.2417 | 5.1875 | 47.21 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-Duarte, E.V.; Molina-Jiménez, J.P.; Avila, D.A.; Torres, C.O.; Horta-Piñeres, S.D. Rapid Synthesis of Highly Crystalline ZnO Nanostructures: Comparative Evaluation of Two Alternative Routes. Crystals 2025, 15, 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070640
Ruiz-Duarte EV, Molina-Jiménez JP, Avila DA, Torres CO, Horta-Piñeres SD. Rapid Synthesis of Highly Crystalline ZnO Nanostructures: Comparative Evaluation of Two Alternative Routes. Crystals. 2025; 15(7):640. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070640
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-Duarte, Emely V., Juan P. Molina-Jiménez, Duber A. Avila, Cesar O. Torres, and Sindi D. Horta-Piñeres. 2025. "Rapid Synthesis of Highly Crystalline ZnO Nanostructures: Comparative Evaluation of Two Alternative Routes" Crystals 15, no. 7: 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070640
APA StyleRuiz-Duarte, E. V., Molina-Jiménez, J. P., Avila, D. A., Torres, C. O., & Horta-Piñeres, S. D. (2025). Rapid Synthesis of Highly Crystalline ZnO Nanostructures: Comparative Evaluation of Two Alternative Routes. Crystals, 15(7), 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070640










