The Influence of Different Foaming Agents on the Properties and Foaming Mechanisms of Foam Ceramics from Quartz Tailings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation of Foam Ceramics
2.3. Characterization of Materials
3. Results and Discussion
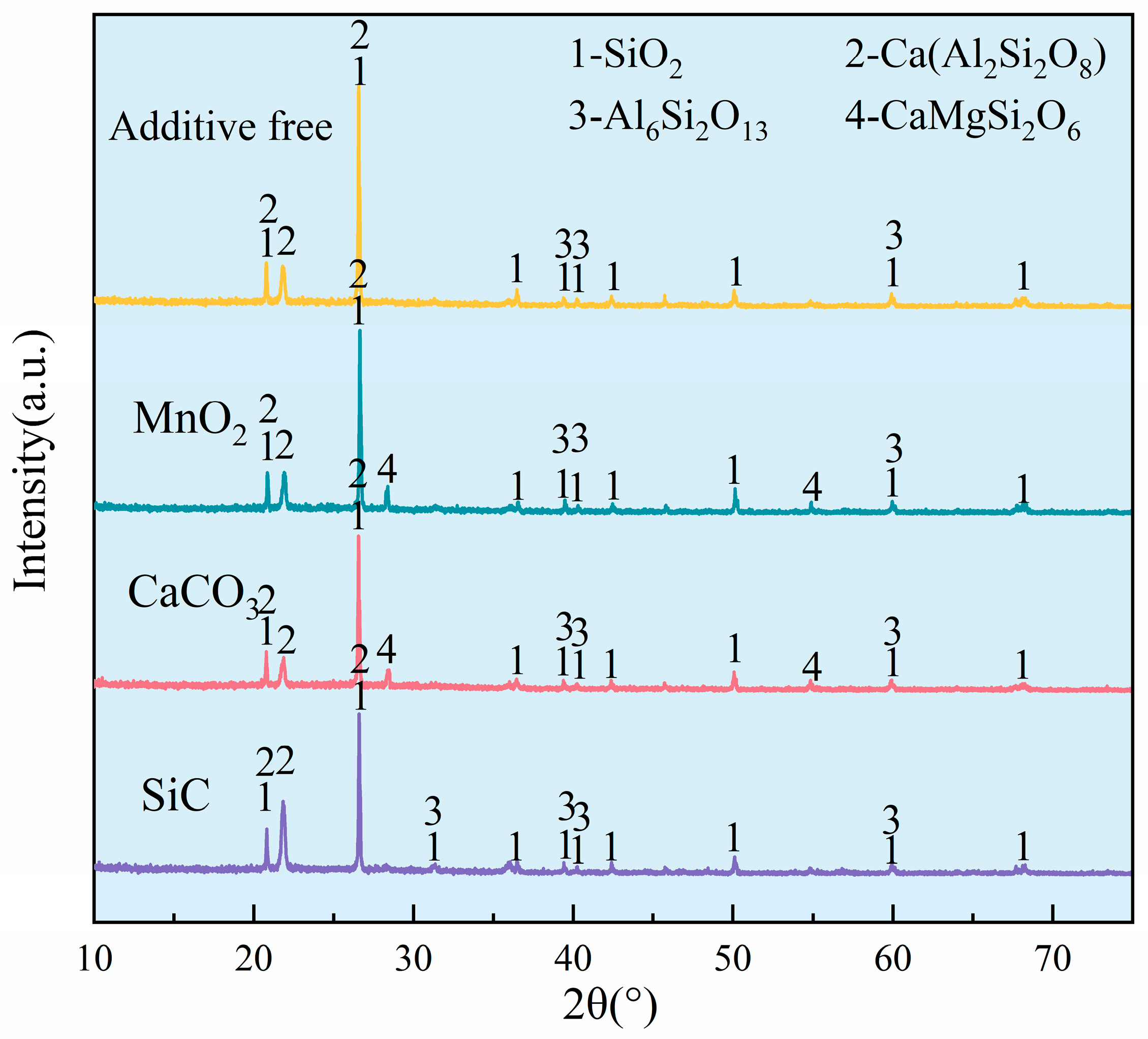
3.1. Phase Evolution
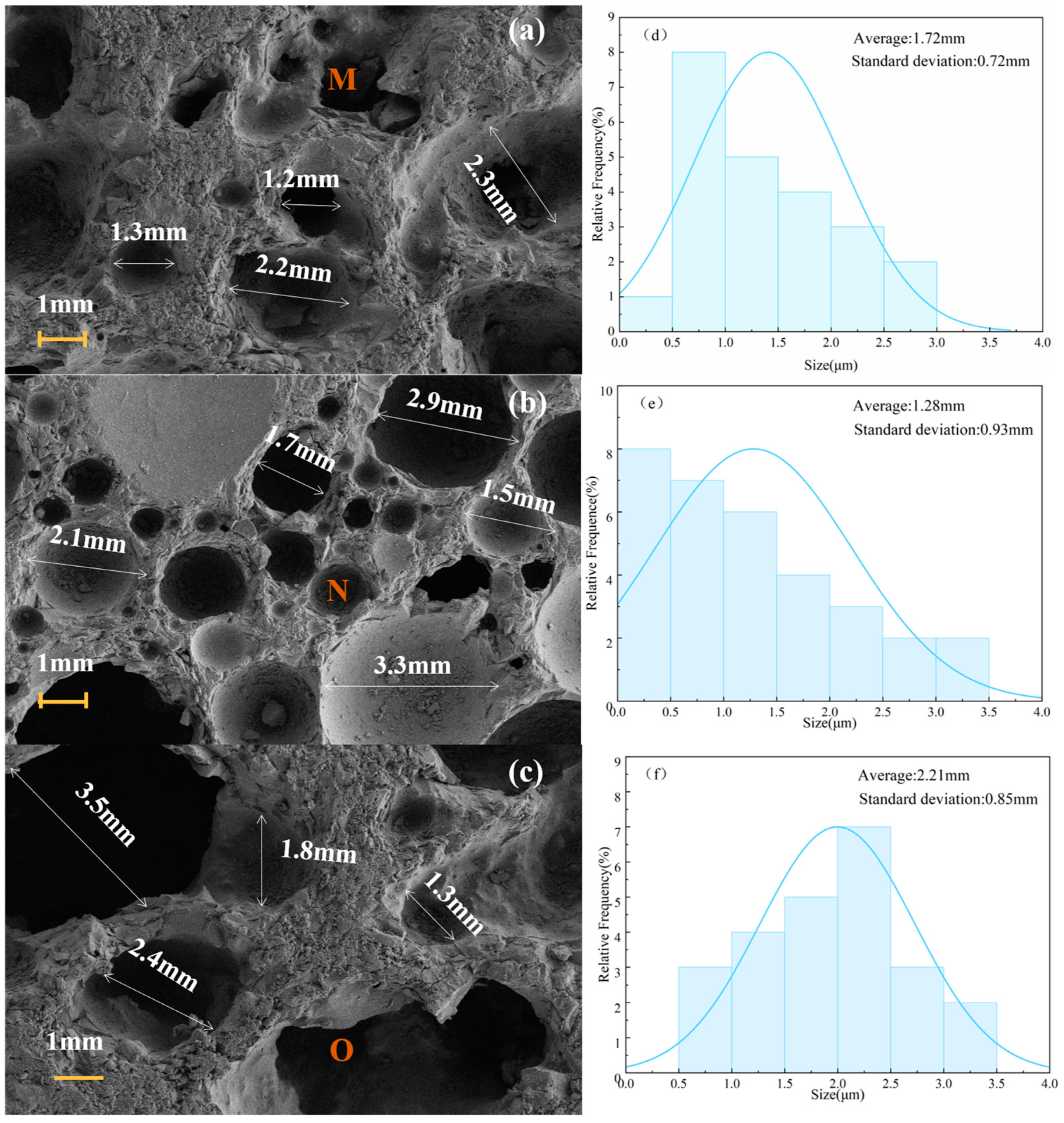
3.2. Microscopic Morphology and Pore Size Analysis
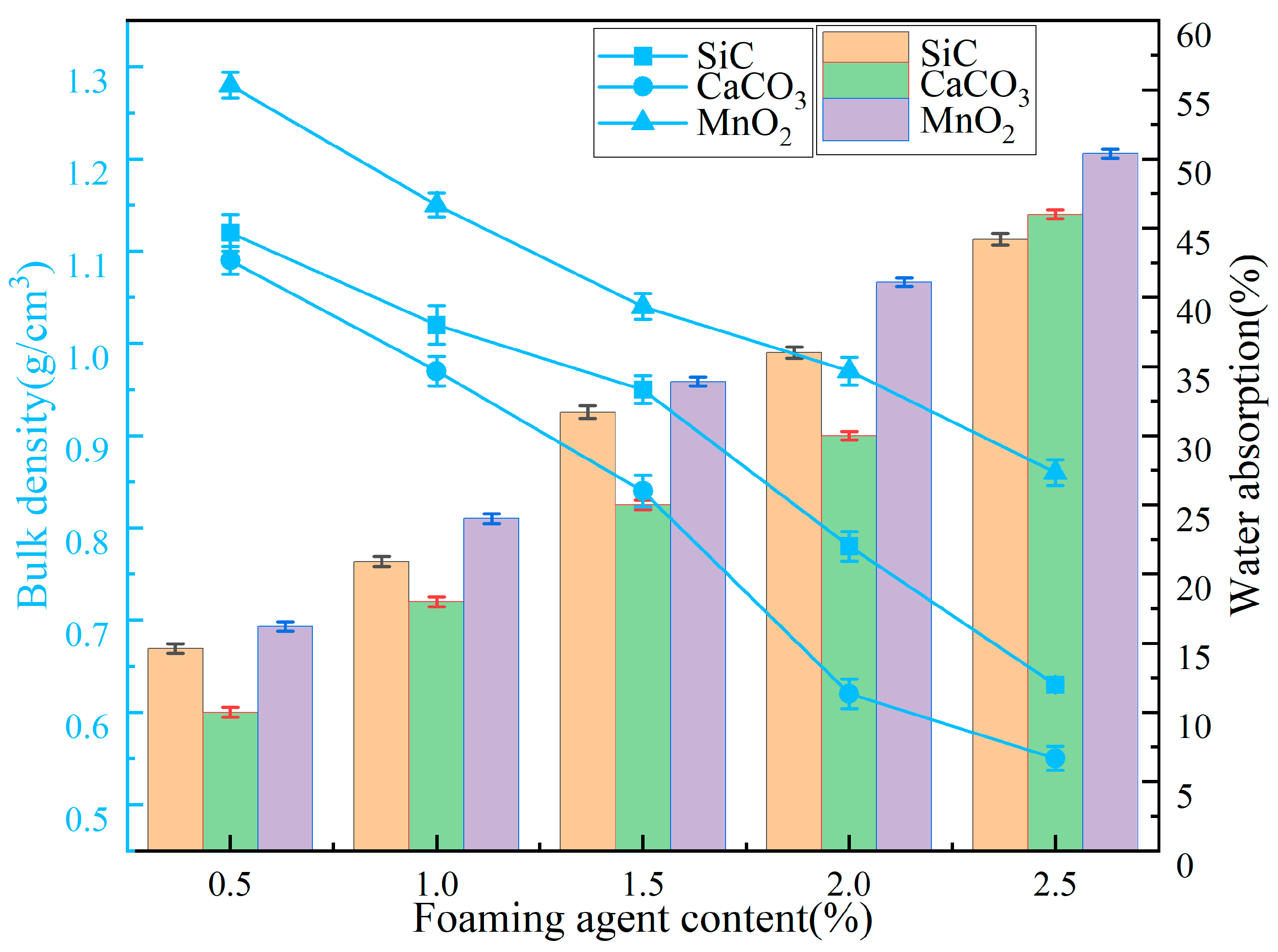
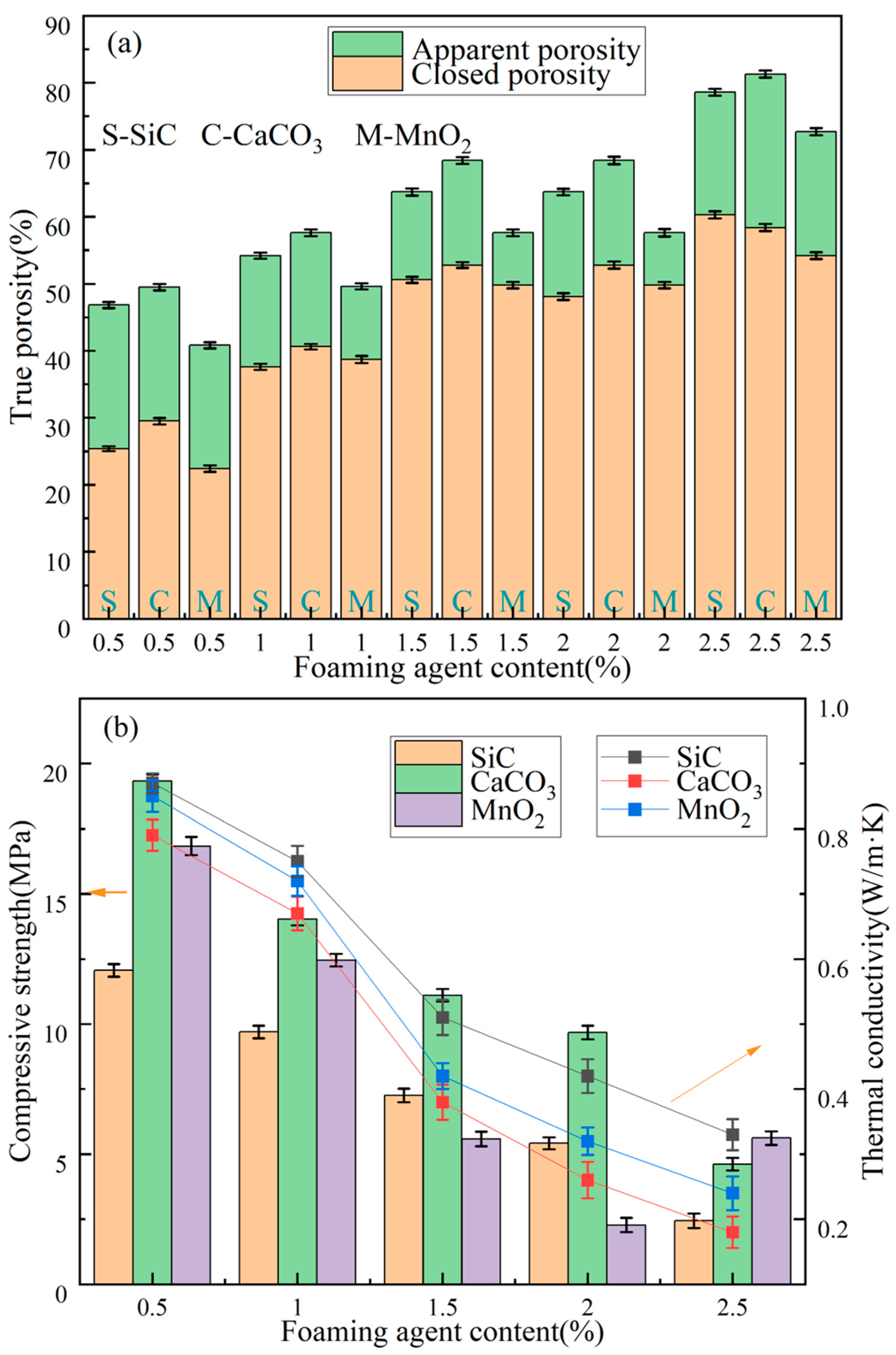
3.3. Analysis of Materials Properties
3.4. Foaming Mechanism

3.4.1. Foaming Mechanism of SiC
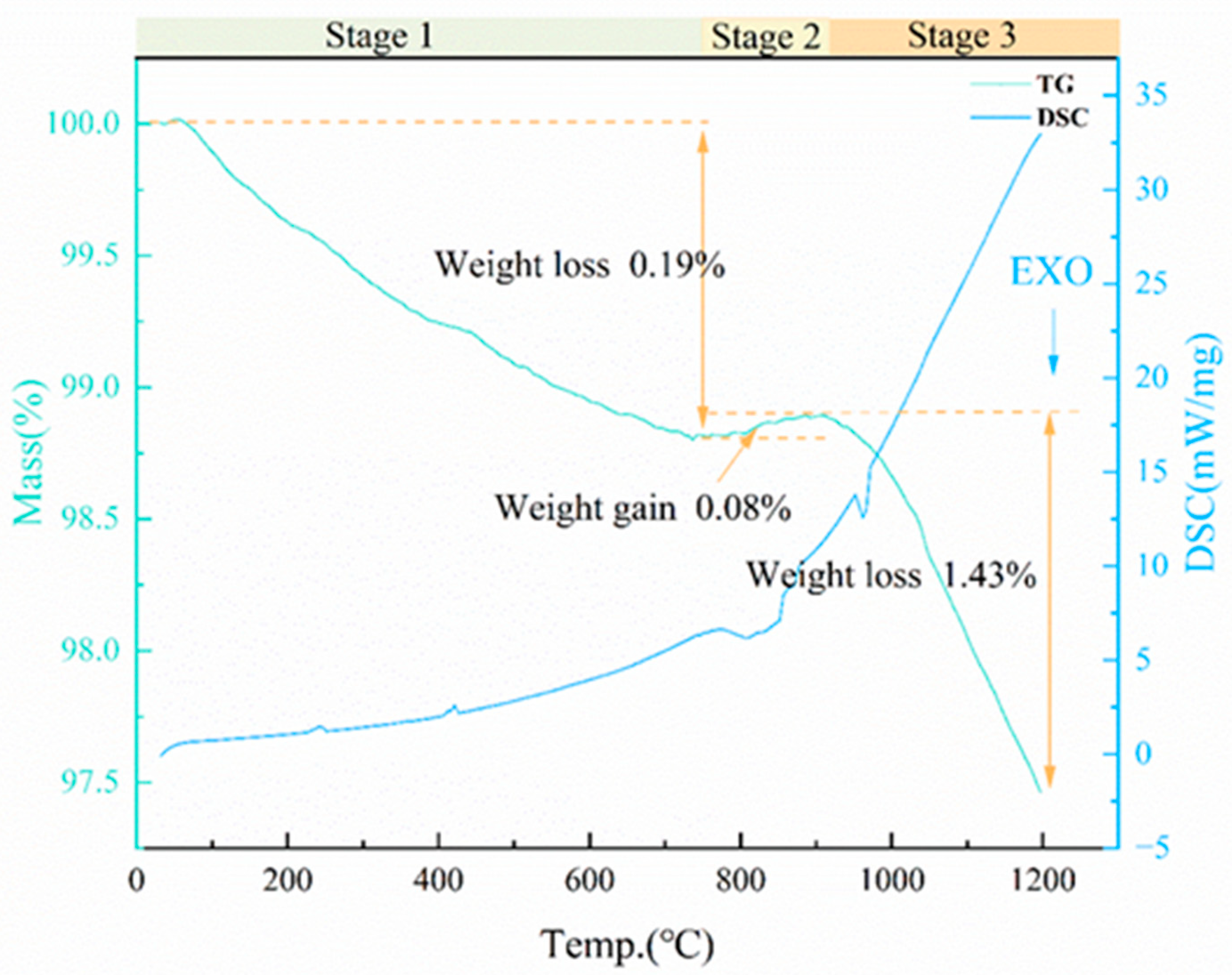
3.4.2. Foaming Mechanism of CaCO3
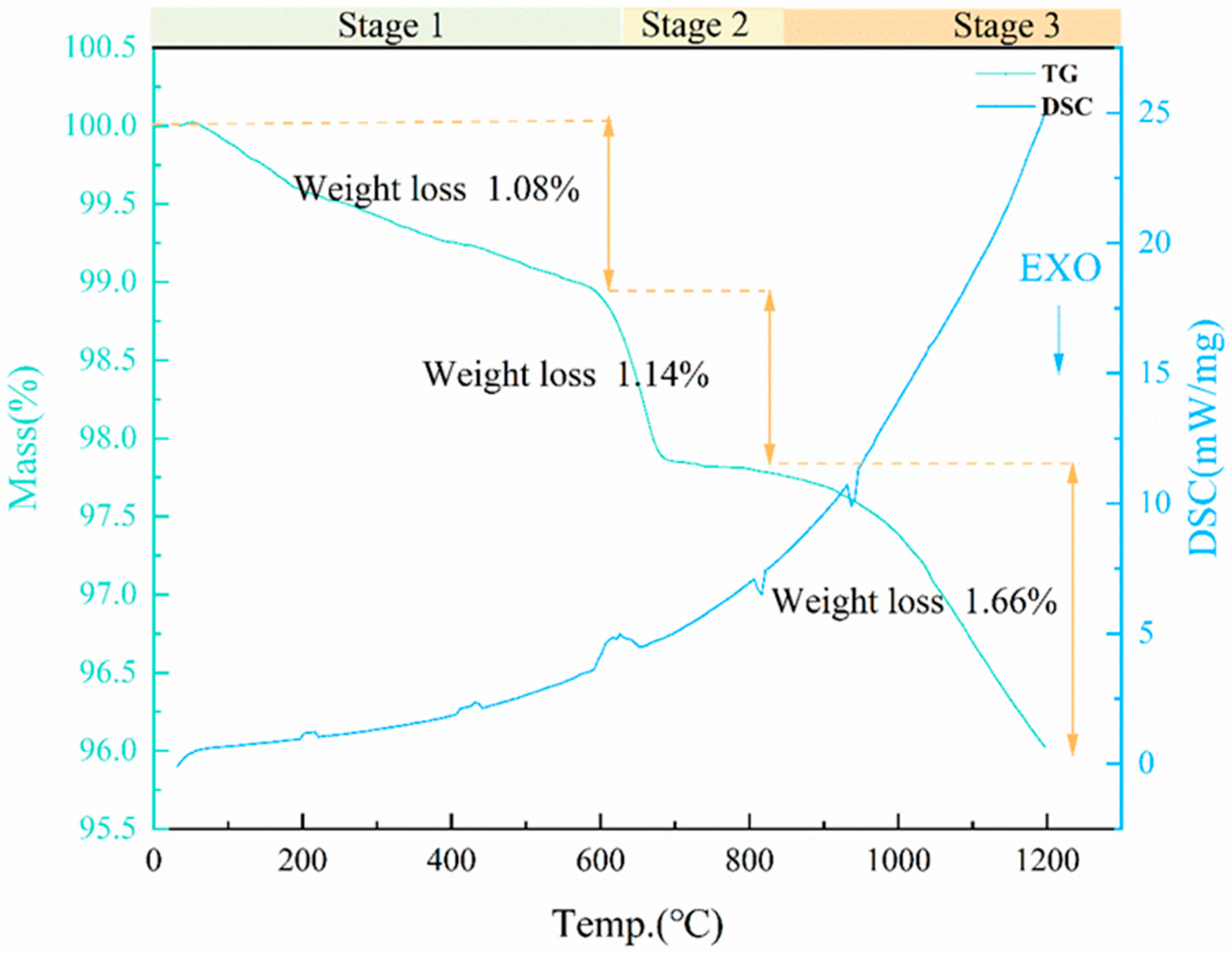
3.4.3. Foaming Mechanism of MnO2
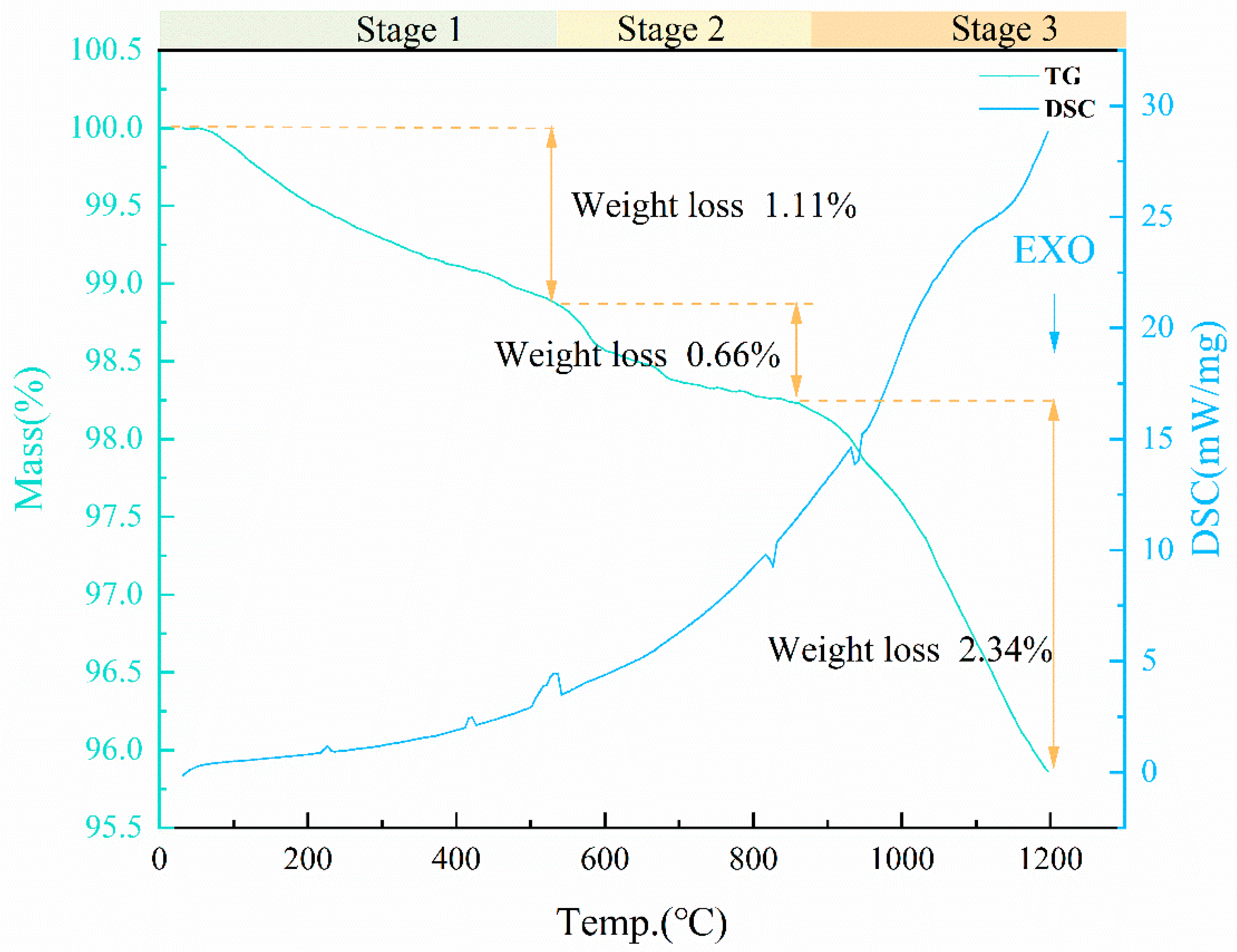
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TG-DSC | Thermogravimetric-differential scanning calorimetry |
References
- Zhou, J.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, L. Preparation, pore structure and properties of uniformly porous glass-ceramics sintered from granite powder using SiC@SiO2 foaming agent. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 52379–52387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; Kim, T.; Sahajwalla, V.; Hajimohammadi, A. Early age structural build-up and pore stability in raw foam at ambient conditions: Implications for the final properties of glass-ceramic foam. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 428, 136369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ren, B.; Yu, X.; Kang, S.; Shi, J.; Zhou, K. Ultralight corundum-mullite-zirconia composite ceramic foams prepared by triphasic nanoparticle stabilized foams with improved thermal shock resistance. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 10543–10550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zheng, W.; Li, G.; Yan, Z.; Yan, W.; Liang, Z.; Liu, P. Removal behavior of Al–Ti–Oinclusions in aluminum deoxidized molten steel containing titanium by microporous magnesium foam ceramic filters. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 4503–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Yang, J. Ultra-high strength ZTA ceramic foams with large amounts of intragranular structures resulting from dual-phase sol. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 15230–15239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ye, Z.; Jiao, H.; Zhao, K.; Yan, Z. Al2O3 porous ceramics with high strength by protein foaming method. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liang, J.; Fu, C.; Zeng, B.; Huang, M.; Yang, G.; Luo, X.; An, D.; Wei, S.; Xie, Z.; et al. Waste recycling of coal fly ash: A novel approach to prepare hierarchically porous coal fly ash/Al2O3 ceramic composite with high porosity and high strength templated by emulsion-assisted self-assembly. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 18588–18595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, G.; Li, C.; Liu, K. Preparation and characterization of SiO2–Al2O3–MgO–CaO–based ceramic foams mainly from Ca–Mg–rich molybdenum tailings. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 21839–21847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Liang, J.; Jiang, W.; Liu, J.; Jiang, F.; Feng, G.; Lao, X.; Tang, H.; Wang, T. Preparation of high strength foam ceramics from sand shale and steel slag. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 9256–9262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzawy, E.M.A.; El-Bassyouni, G.T.; Abd El-Shakour, Z.A.; Nabawy, B.S. Manufacture of low thermal conductivity anorthite ceramic foam using silica fume, aluminum slag, and limestone. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 7977–7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.; Sun, H.; Peng, T.; Liu, L.; Ding, W.; Liu, B.; Wang, C. Recycling of extracted titanium slag and gold tailings for preparation of self-glazed ceramic foams. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 23415–23427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, T.; Naskar, M.K.; Chakraborty, A.; Roy, P.K.; Chakraborty, S. Preparation of high-strength waste-derived eco-friendly ceramic foam as face brick and its estimation of building energy consumption for thermal insulation. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 88, 109043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Sun, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, X. Influence of SiC particle size and dosage on the pore structure and properties of foamed ceramics derived from coal bottom ash. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1020, 179399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Zhou, R.; Liu, H.; Huo, Y.; Wang, Y. Preparation of coal gangue based foamed ceramics with SiC as blowing agent and study on its thermal insulation performance. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 31680–31690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Du, R.; Zhao, H.; Xi, C.; He, Z.; Wang, P.; Han, L.; Zhang, S. Sustainable foam ceramic insulator manufactured from coal gangue and K-feldspar washed waste. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 12305–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liang, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Cui, Z.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, C. Preparation of lightweight foam glass-ceramics from copper slag tailings: Secondary aluminum slag as pore-forming agent. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 43699–43709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, H.; Peng, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Q. Production of glass-ceramics from MSW-fly ash and Dexing copper mine-tailing: Crystallization kinetics, structure, properties and immobilization of heavy metals. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 35428–35437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; Hajimohammadi, A.; Sahajwalla, V. Powder sintering and gel casting methods in making glass foam using waste glass: A review on parameters, performance, and challenges. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 1494–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Dai, L.; Yao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Preparation and Properties of Coal Gangue-Based High Strength Ceramic Foams. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 52, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, T.; Sun, H.; Peng, T.; Chen, Y. Preparation and characterization of ceramic foams mainly containing extracted titanium residues and silica tailings. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, F.; Li, W.; Jian, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J. Mullite ceramic foams with tunable pores from dual-phase sol nanoparticle-stabilized foams. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Su, Z.; Ma, Z.; Yu, W. Design and performance of a foamed ceramic prepared by sintering using boron carbide as a foaming agent. J. Alloys Compd. Commun. 2024, 4, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, L.; Jensen, L.R.; Yue, Y.; Østergaard, M.B. Crystallinity dependence of thermal and mechanical properties of glass-ceramic foams. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 44, 7936–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Song, Y.; Huang, H.; Yang, Y.; Shen, D.; Geng, H.; Ruan, J.; Gu, F. Preparation of foam glass ceramics from hazardous waste vitrification slag with the addition of Na2CO3. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 133225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.W.; Liang, Y.P.; Xu, J.; Meng, X.Y.; Zhu, J.T.; Cao, S.Y.; Wei, M.Y.; Zhang, R.X.; Yang, J.L.; Gao, F. Rare-earth-niobate high-entropy ceramic foams with enhanced thermal insulation performance. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 116, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Gao, W.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Fu, Y.; Kong, X. Recycling of Silicomanganese Slag and Fly Ash for Preparation of Environment-Friendly Foamed Ceramics. Materials 2023, 16, 6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Xia, Z.; Jiang, C.; Dong, Y.; Lan, Z. Effect of Various Foaming Agents on Ceramic Foam from Solid Waste. Crystals 2025, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Sun, D.; Lv, C. Foaming mechanism and performance of closed–pore foamed ceramics prepared using calcium carbonate as a foaming agent. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 29162–29173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Jiang, F.; Guo, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.; Qin, R. Interface characterization and mechanical property of an aluminum matrix syntactic foam with multi-shelled hollow sphere structure. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 18821–18833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Qian, D.; Xing, Y. A novel and clean utilization of multiple solid wastes to produce foam glass-ceramic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 370, 130711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; He, G.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Duan, Y.; Yuan, G.; Fu, H. Synergistic preparation and properties of ceramic foams from wolframite tailings and high-borosilicate waste glass. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 457, 139367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, X.; Chen, D.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Shao, Y. Fabrication of SiC-Al2O3 foam ceramic and its application in fluoride-containing water. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 2268–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Zhou, H.; Cai, L.; Jiang, Q.; Ke, S. Production of high value-added foamed glass-ceramics from high-titanium blast furnace slag and waste glass with the addition of SiC. Ceram. Int. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Galan, I.; Glasser, F.P.; Andrade, C. Calcium carbonate decomposition. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 111, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.P.; Tseng, P.W.; Huang, K.J.; Chen, Y.J. Foam glass production from waste bottle glass using silicon cutting waste of loose abrasive slurry sawing as foaming agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 383, 131344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, T.; Chen, B.; Wen, J.; Yang, G. Integrated Utilization of Vanadium-Titanium Magnetite Tailings for Synthesis of Lightweight Foamed Ceramics: Effect of Chemical Composition on the Properties and Phase Evolution. J. Sustain. Metall. 2022, 8, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.-L.; Feng, K.-Q.; Cai, L.-P.; Cai, J.-W.; Zhang, Z.-Y. Effect of TiO2 on crystallization and microstructure of foam glass ceramics prepared by high titanium blast furnace slag. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 11006–11017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Ruan, M.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, G.; Cai, J.; Zhao, T.; Fu, Q. Integrated utilization of recycled waste concrete powder waste glass power for preparation of foam ceramics. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.M.; Bunnori, N.M.; Ramesh, S.; Tan, C.Y.; Mo, K.H. Alkali activation of waste glass and aluminium dross for self-foaming glass ceramics production. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 6365–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lv, X.; Xiang, L. Review of the State of Impurity Occurrences and Impurity Removal Technology in Phosphogypsum. Materials 2023, 16, 5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fan, X. Preparation of gypsum with high purity and whiteness from phosphogypsum for CO2 mineral sequestration. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gol’tsman, B.M.; Yatsenko, E.A. Modern Methods for Foaming of Glass and Silicate Raw Materials: Review and Analysis. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2022, 56, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, M.; Chen, B.; Chen, C. The influence of temperature and SiC content on the recycling of iron ore tailings for the preparation of value-added foam ceramics. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 23, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Hu, N.; Ye, Y.; Chen, G. The foaming mechanism and properties of SiO2–Al2O3–CaO-based foamed ceramics with varied foaming agents. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 32448–32457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.R.; König, J.; Iversen, N.; Østergaard, M.B.; Yue, Y. The foaming mechanism of glass foams prepared from the mixture of Mn3O4, carbon and CRT panel glass. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 2839–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.R.; König, J.; Yue, Y. The mechanism of foaming and thermal conductivity of glasses foamed with MnO2. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2015, 425, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
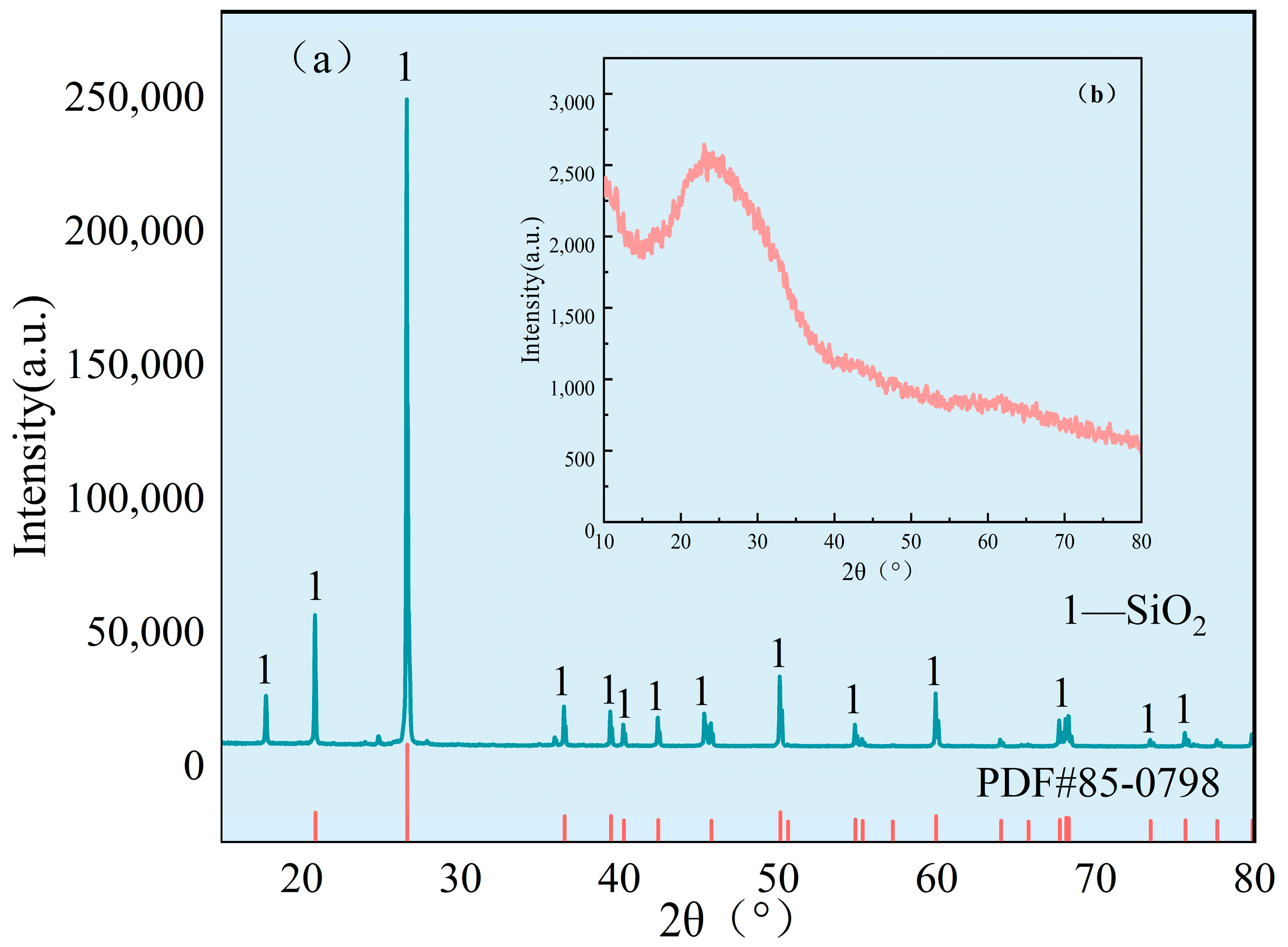
| Composition | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Na2O | MgO | Fe2O3 | CaO | TiO2 | K2O | Cr2O3 | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz tailing | 6.76 | 86.20 | 0.25 | 0.76 | 0.52 | 3.65 | 0.54 | 0.96 | - | 0.36 |
| Glass powder | 1.18 | 65.25 | 15.69 | 4.84 | 0.10 | 11.46 | 0.65 | 0.35 | 0.03 | 0.45 |
| Quartz Sand Tailing | Waste Glass Powder | SiC | CaCO3 | MnO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 59.5 | 40 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 |
| 59 | 40 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 58.5 | 40 | 1.5 | 0 | 0 |
| 58 | 40 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 57.5 | 40 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 |
| 59.5 | 40 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 |
| 59 | 40 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 58.5 | 40 | 0 | 1.5 | 0 |
| 58 | 40 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 57.5 | 40 | 0 | 2.5 | 0 |
| 59.5 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 59 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 58.5 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 1.5 |
| 58 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 57.5 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 |
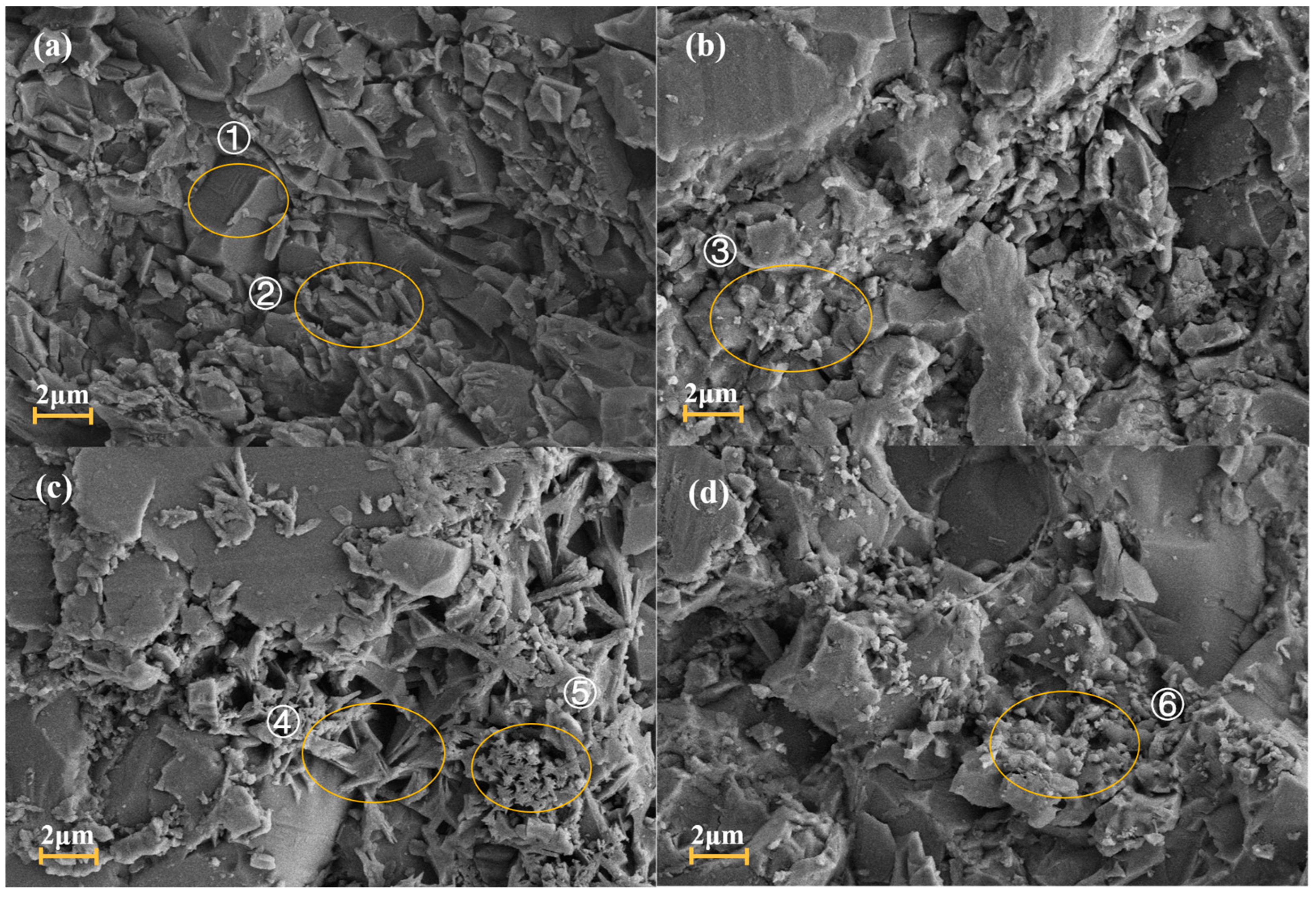
| Region | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | K | Ca | Fe | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ① | 49.71 | - | 0.86 | 3.19 | 42.74 | 0.24 | 2.83 | 0.17 | 0.26 |
| ② | 42.76 | 0.13 | 0.67 | 19.18 | 20.44 | 0.39 | 16.28 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| ③ | 45.46 | 0.26 | 1.43 | 37.26 | 12.85 | 0.43 | 1.98 | 0.16 | 0.17 |
| ④ | 43.45 | 0.07 | 0.48 | 20.46 | 18.62 | 0.26 | 16.29 | 0.24 | 0.13 |
| ⑤ | 43.37 | 0.23 | 11.64 | 1.31 | 25.36 | 0.43 | 17.20 | 0.25 | 0.21 |
| ⑥ | 45.57 | 0.16 | 1.03 | 37.77 | 12.36 | 0.27 | 2.35 | 0.34 | 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, H.; Zhang, J. The Influence of Different Foaming Agents on the Properties and Foaming Mechanisms of Foam Ceramics from Quartz Tailings. Crystals 2025, 15, 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070606
Gao H, Zhang J. The Influence of Different Foaming Agents on the Properties and Foaming Mechanisms of Foam Ceramics from Quartz Tailings. Crystals. 2025; 15(7):606. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070606
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Huiyang, and Jie Zhang. 2025. "The Influence of Different Foaming Agents on the Properties and Foaming Mechanisms of Foam Ceramics from Quartz Tailings" Crystals 15, no. 7: 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070606
APA StyleGao, H., & Zhang, J. (2025). The Influence of Different Foaming Agents on the Properties and Foaming Mechanisms of Foam Ceramics from Quartz Tailings. Crystals, 15(7), 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15070606






