Co0.85Bi0.15Fe1.9X0.1O4 (X = Ce4+, Sm3+, Ho3+, and Er3+) Nanoparticles with Selective Anticancer Activity: A Structural and Morphological Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
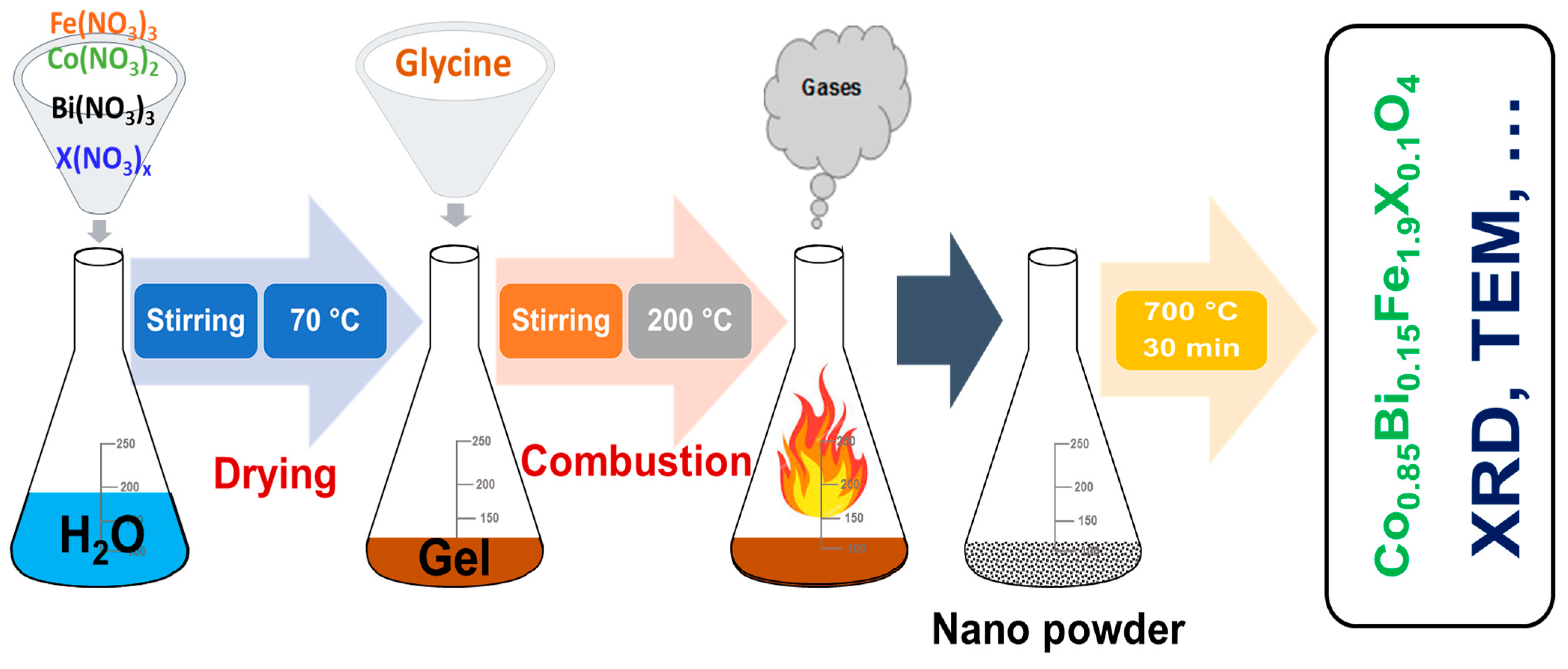
2.1. Synthesis Method
2.2. Characterizations
2.3. In Vitro Cancer Viability Analysis
2.3.1. Cell Culture
2.3.2. The Test Nanomaterials and Reagents
2.3.3. Cell Viability Assay
3. Results and Discussions
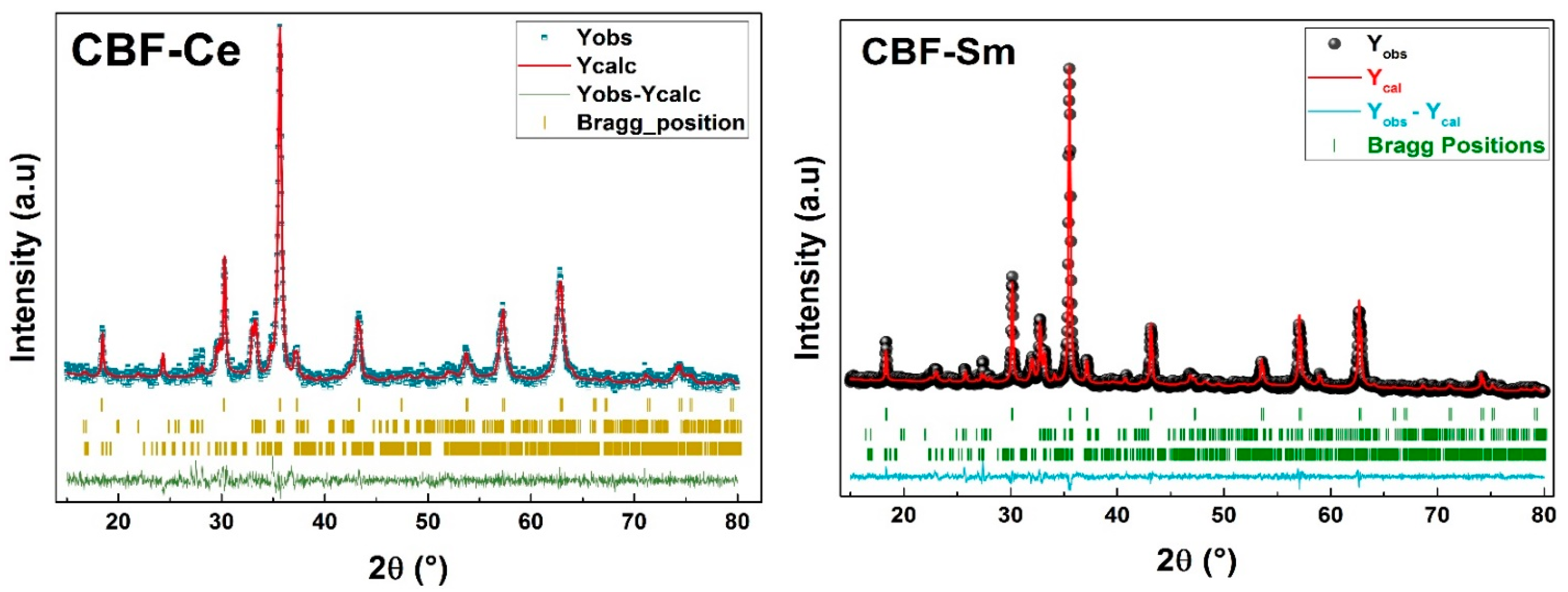
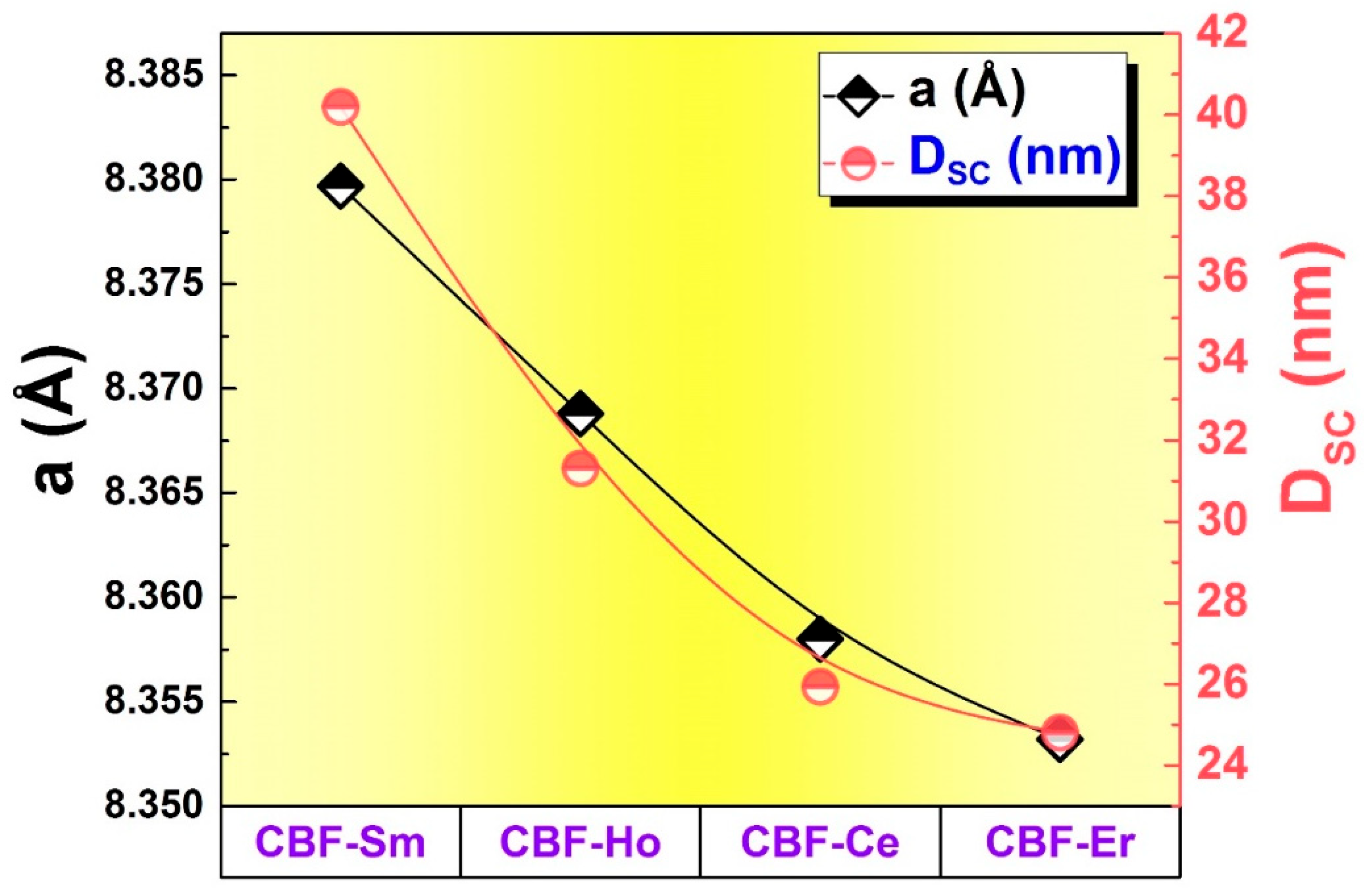
3.1. Structural Proprieties
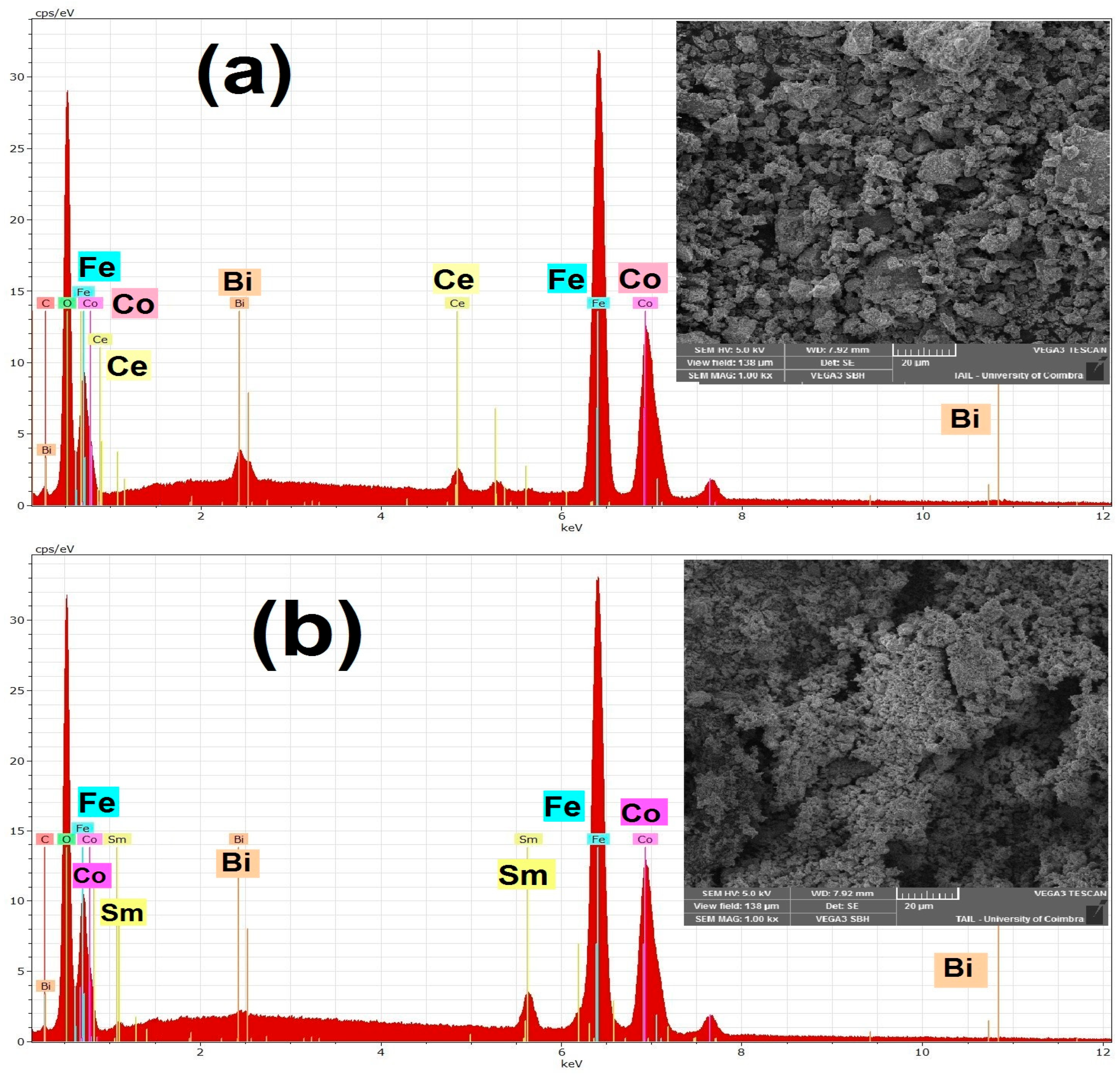
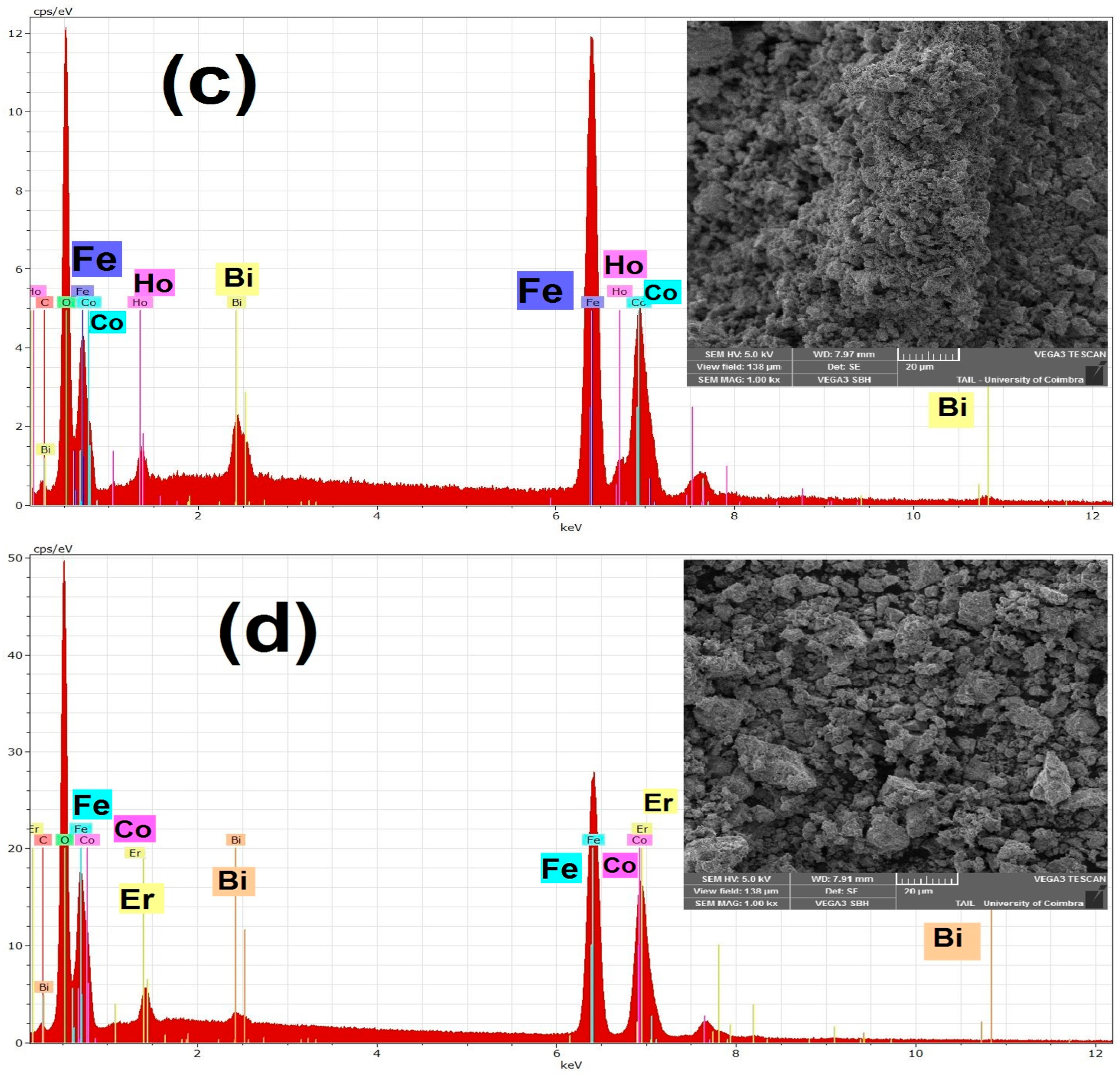
3.2. Morphological Study
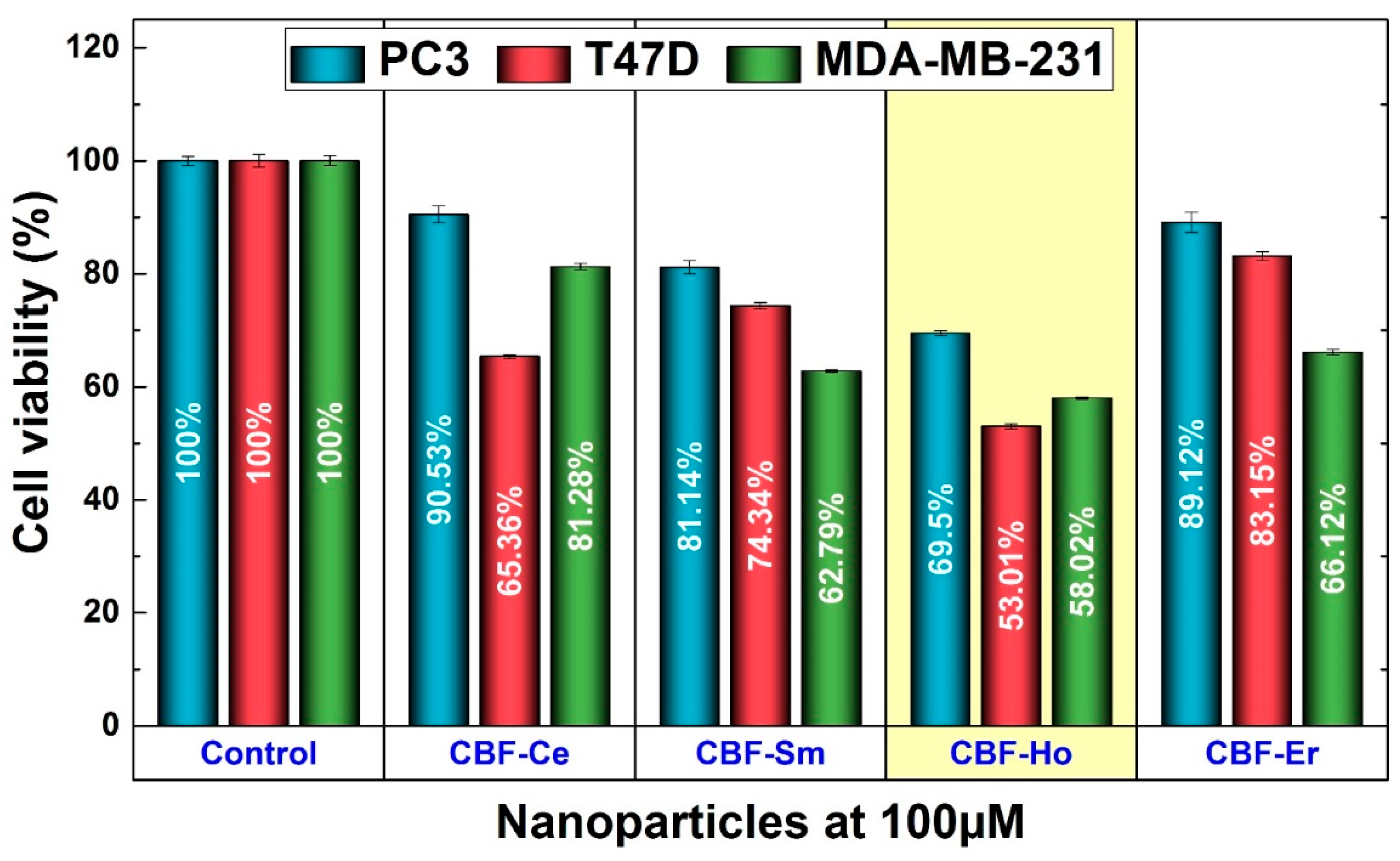
3.3. Cancer Cells Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ishaque, M.; Islam, M.; Khan, M.A.; Rahman, I.; Genson, A.; Hampshire, S. Structural, electrical and dielectric properties of yttrium substituted nickel ferrites. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2010, 405, 1532–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.F.; Valente, M. Magnesium ferrite nanoparticles inserted in a glass matrix—Microstructure and magnetic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.J.; Lee, W.; Oh, Y.S.; Lee, J.K. Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Catalyst Vehicle for Simple and Easy Recycling. New J. Chem. 2003, 27, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeete, Z.; Cheng, H.; Crew, E.; Lin, L.; Zhao, W.; Joseph, P.; Shan, S.; Cronk, H.; Luo, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Design of Functional Nanoparticles and Assemblies for Theranostic Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21752–21768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schuth, F. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Protection, Functionalization, and Application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P.; Giri, J.; Samanta, G.; Sarma, H.D.; Mishra, K.P.; Bellare, J.; Banerjee, R.; Bahadur, D. Comparative Evaluation of Heating Ability and Biocompatibility of Different Ferrite-based Magnetic Fluids for Hyperthermia Application. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2007, 81B, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, J.; Kumar, T.J.; Sundaram, P.K.; Baldev, R. Tunable Optical Filter. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2003, 14, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, J.P.; Wilhelm, C.; Servais, J.; Menager, C.; Bacri, J.C.; Gazeau, F. Size-sorted anionic iron oxide nanomagnets as colloidal mediators for magnetic hyperthermia. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2628–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrollahi, H.; Janghorban, K. Influence of additives on the magnetic proper-ties, microstructure and densification of Mn−Zn soft ferrites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2007, 141, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangmanee, M.; Maensiri, S. Nanostructures and magnetic properties of cobaltferrite (CoFe2O4) fabricated by electro spinning. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 97, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shobaky, G.A.; Turky, A.M.; Mostafa, N.Y.; Mohamed, S.K. Effect of preparation conditions on physicochemical, surface and catalytic properties of cobalt ferrite prepared by coprecipitation. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 493, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, A.; Saher, L.; Bejar, M.B.; Dhahri, E.; Graca, M.F.P.; Valente, M.A.; Sanguino, P.; Helguero, L.A.; Bachari, K.; Silva, A.M.; et al. CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite studies on permanent magnet application and cytotoxic effects on breast and prostate cancer cell lines. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, S.; Shokrollahi, H. Magnetic and structural properties of RE doped Co-ferrite (R = Nd, Eu, and Gd) nano-particles synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 345, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M.L.; Zhang, Z.J. Synthesis and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles doped with lanthanide ions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 3651–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, A.; Saher, L.; Bejar, M.B.; Dhahri, E.; Graca, M.F.P.; Valente, M.A.; Sanguino, P.; Helguero, L.A.; Bachari, K.; Silva, A.M.; et al. Synthesis and physico-chemical characterization of Bi-doped Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Cytotoxic effects against breast and prostate cancer cell lines. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2022, 137, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, S.K.; Jadhav, S.S.; Jadhav, V.V.; Patange, S.M.; Naushad, M.; Mane, R.S.; Kim, K.H. The structural and magnetic properties of dual phase cobalt ferrite. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2524–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.A. The Rietveld Method; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Ortega, A.; Lottini, E.; Fernandez, C.J.; Sangregorio, C. Exploring the magnetic properties of cobalt-ferrite nanoparticles for the development of a rare-earth-free permanent magnet. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 4048–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, R.; Chauhan, A.; Jasrotia, R.; Ijaz, M.F.; Batoo, K.M.; Verma, R. Bi-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding applications. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron 2025, 36, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toksha, B.G.; Shirsath, S.E.; Mane, M.L.; Patange, S.M.; Jadhav, S.S.; Jadhav, K.M. Autocombustion High-Temperature Synthesis, Structural, and Magnetic Properties of CoCrxFe2−xO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0). J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 20905–20912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashhash, A.; Bobrikov, I.; Yehia, M.; Kaiser, M.; Uyang, E. Neutron diffraction and Mössbauer spectroscopy studies for Ce doped CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 503, 166624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, M.M.; Mohamed, R.M.; El-Shall, H. Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Sm-substituted CoFe2O4 synthesized by citrate precursor method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 198, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahar, L.B.; Artus, M.; Ammar, S.; Smiri, L.S.; Herbst, F.; Vaulay, M.-J.; Richard, V.; Grenèche, J.-M.M.J.; Villain, F.; Fiévet, F. Magnetic properties of CoFe1.9RE0.1O4 nanoparticles (RE = La, Ce, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Ho) prepared in polyol. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 3242–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, F.B.; Benali, A.; Triki, M.; Dhahri, E.; Graça, M.P.F.; Valente, M.A. Effect of annealing temperature on structural, morphology and dielectric properties of La0.75Ba0.25FeO3 perovskite. Superlatt. Microstruct. 2018, 117, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D.R.; Jiang, N.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Vulcani, V.A.S.; Martins, A.; Machado, D.S.; Landers, R.; Camargo, P.H.C.; Pancotti, A. Employing Calcination as a Facile Strategy to Reduce the Cytotoxicity in CoFe2O4 and NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39830–39838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Chemical Formula | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| C0.85Bi0.15Fe1.9Ce0.1O4 | CBFO-Ce |
| C0.85Bi0.15Fe1.9Sm0.1O4 | CBFO-Sm |
| C0.85Bi0.15Fe1.9Ho0.1O4 | CBFO-Ho |
| C0.85Bi0.15Fe1.9Er0.1O4 | CBFO-Er |
| Χ2 | a (Å) | V (Å3) | DSC (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBFO-Ce | 1.360 | 8.3581 | 583.866 | 25.940 |
| CBFO-Sm | 1.503 | 8.3797 | 588.423 | 40.203 |
| CBFO-Ho | 1.218 | 8.3688 | 586.130 | 31.388 |
| CBFO-Er | 1.240 | 8.3532 | 582.847 | 24.810 |
| Cell Viability at 100 µM (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBF-Ce | CBF-Sm | CBF-Ho | CBF-Er | |
| MDA-MB-231 | 81.28 ± 0.57 | 62.79 ± 0.21 | 58.02 ± 0.24 | 66.12 ± 0.50 |
| PC3 | 90.53 ± 1.48 | 81.14 ± 1.14 | 69.50 ± 0.91 | 89.12 ± 1.76 |
| T47D | 65.36 ± 0.31 | 74.34 ± 0.58 | 53.01 ± 0.70 | 83.15 ± 0.77 |
| IC50 MDA (µM) | 102.730 ± 0.524 | |||
| IC50 PC3 (µM) | 166.892 ± 0.986 | |||
| IC50 T47D (µM) | 118.704 ± 0.635 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saher, L.; Benali, A.; Haddad, S.; Dhahri, E.; Graça, M.P.F.; Costa, B.F.O.; Helguero, L.A.; Silva, A.M.S. Co0.85Bi0.15Fe1.9X0.1O4 (X = Ce4+, Sm3+, Ho3+, and Er3+) Nanoparticles with Selective Anticancer Activity: A Structural and Morphological Approach. Crystals 2025, 15, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15050482
Saher L, Benali A, Haddad S, Dhahri E, Graça MPF, Costa BFO, Helguero LA, Silva AMS. Co0.85Bi0.15Fe1.9X0.1O4 (X = Ce4+, Sm3+, Ho3+, and Er3+) Nanoparticles with Selective Anticancer Activity: A Structural and Morphological Approach. Crystals. 2025; 15(5):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15050482
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaher, Liza, Adel Benali, Saoussen Haddad, Essebti Dhahri, Manuel P. F. Graça, Benilde F. O. Costa, Luisa A. Helguero, and Artur M. S. Silva. 2025. "Co0.85Bi0.15Fe1.9X0.1O4 (X = Ce4+, Sm3+, Ho3+, and Er3+) Nanoparticles with Selective Anticancer Activity: A Structural and Morphological Approach" Crystals 15, no. 5: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15050482
APA StyleSaher, L., Benali, A., Haddad, S., Dhahri, E., Graça, M. P. F., Costa, B. F. O., Helguero, L. A., & Silva, A. M. S. (2025). Co0.85Bi0.15Fe1.9X0.1O4 (X = Ce4+, Sm3+, Ho3+, and Er3+) Nanoparticles with Selective Anticancer Activity: A Structural and Morphological Approach. Crystals, 15(5), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15050482










