Molecular Dynamics Study of Nanoscratching Behavior of Water-Film-Covered GaN (0001) Surface Using Spherical Diamond Abrasive
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nanoindentation Properties
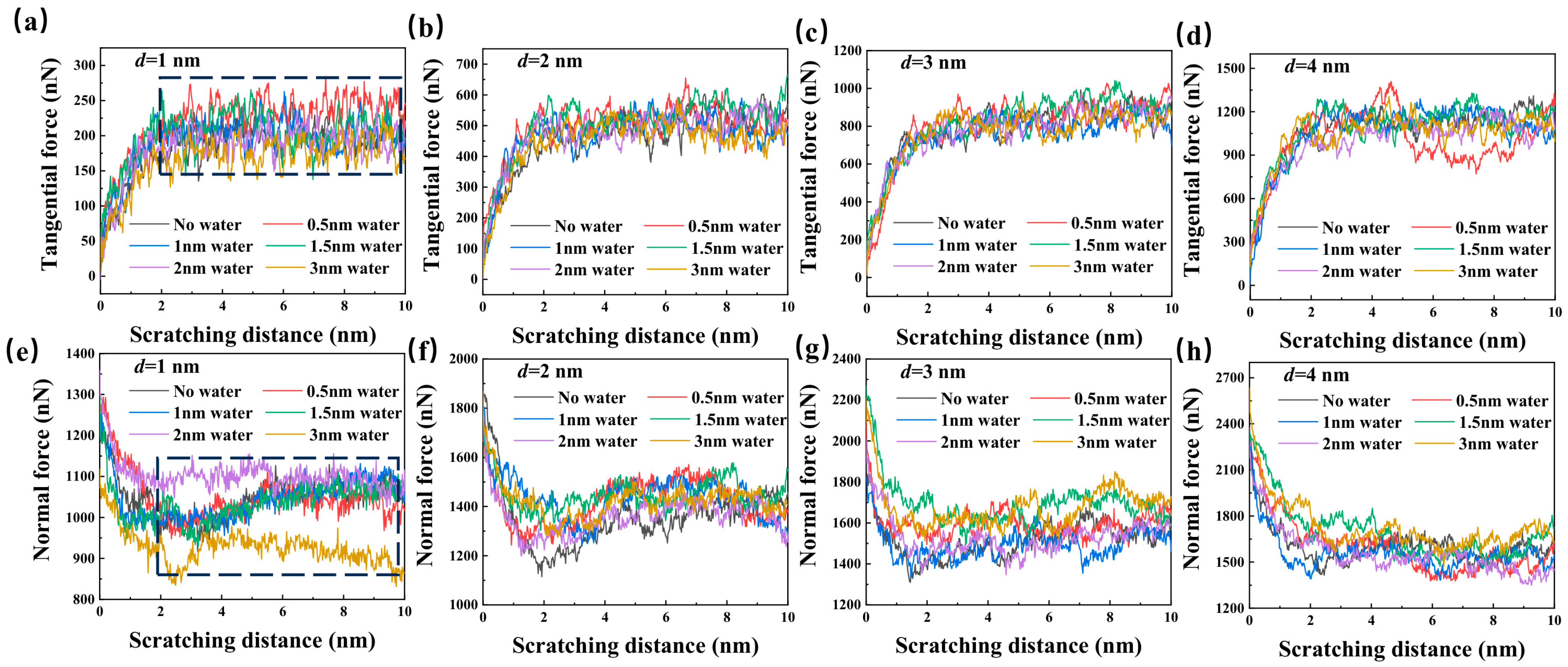
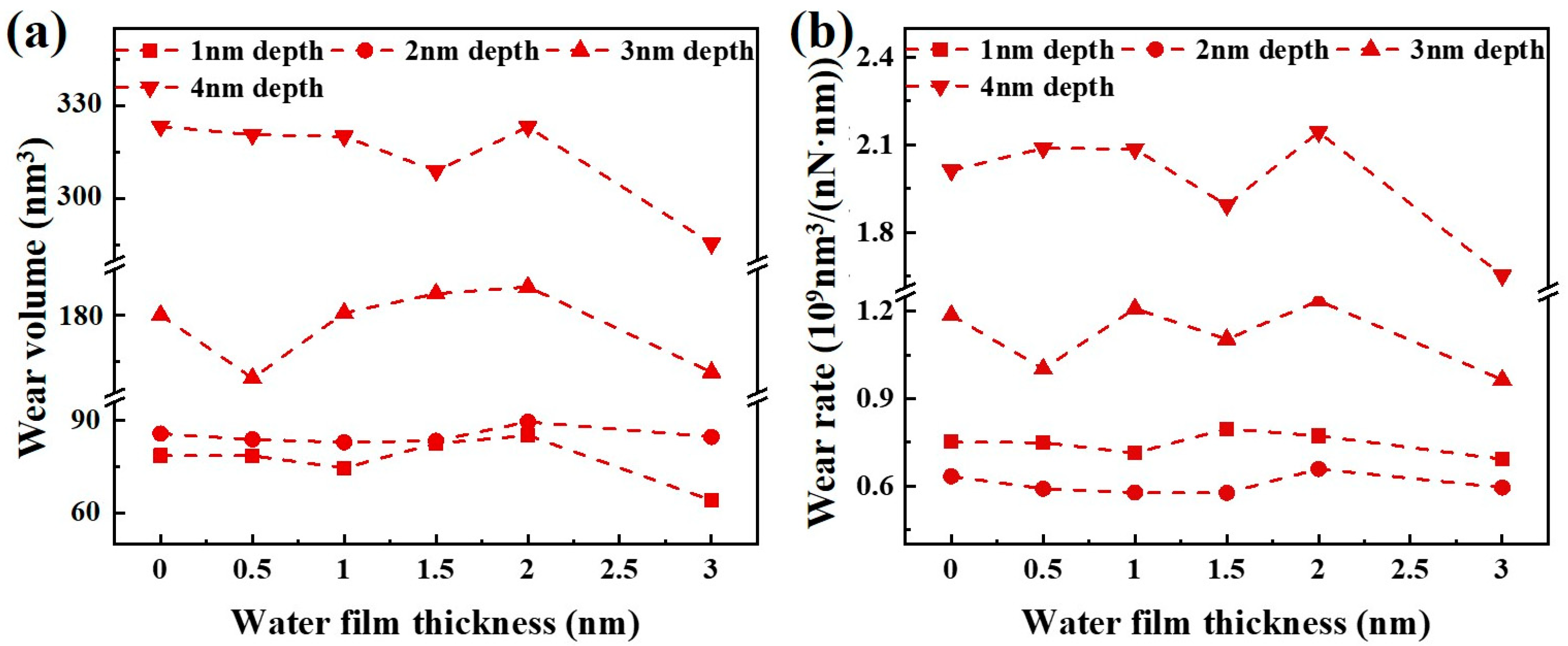
3.2. Nanotribological Performance
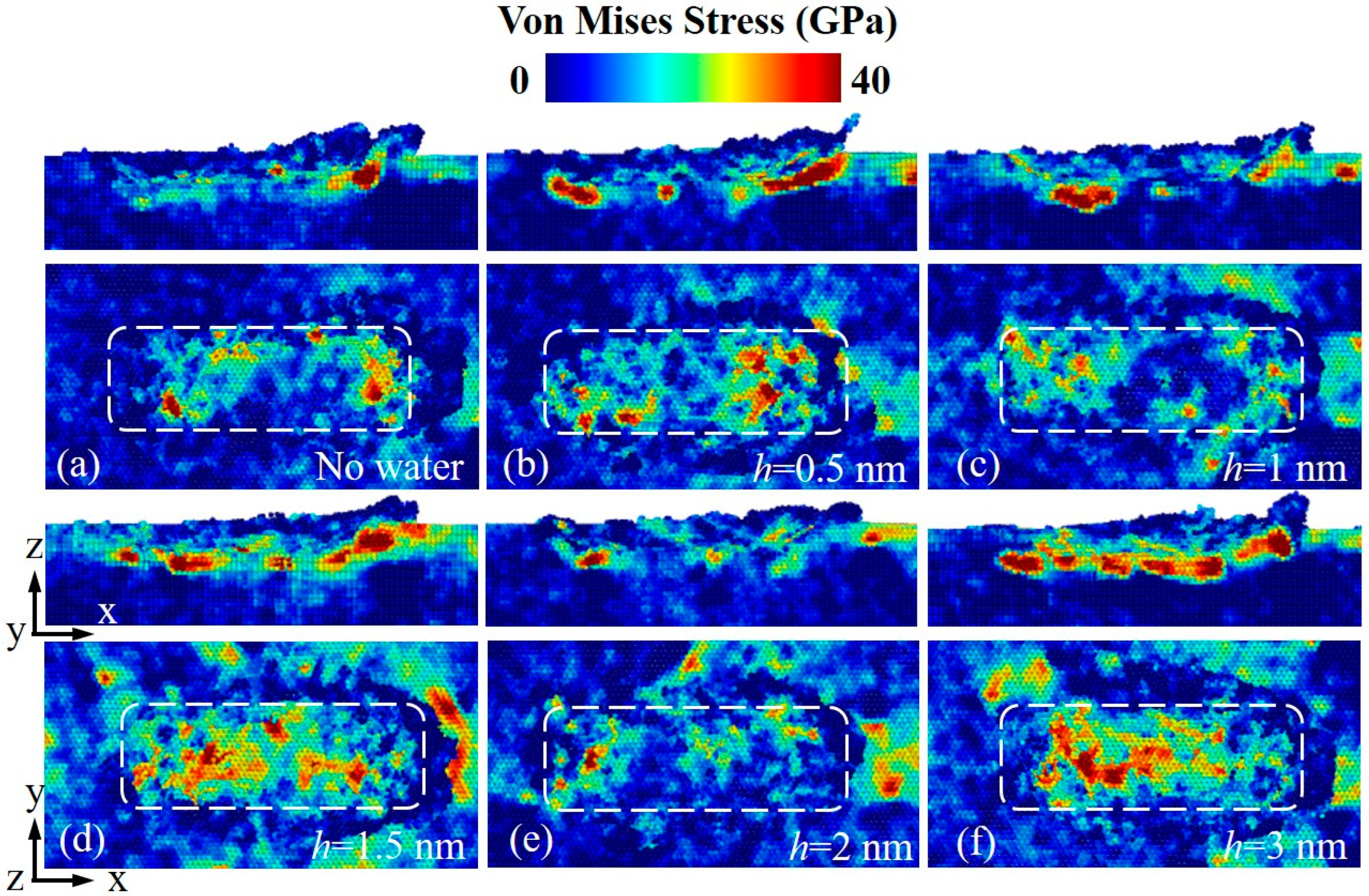
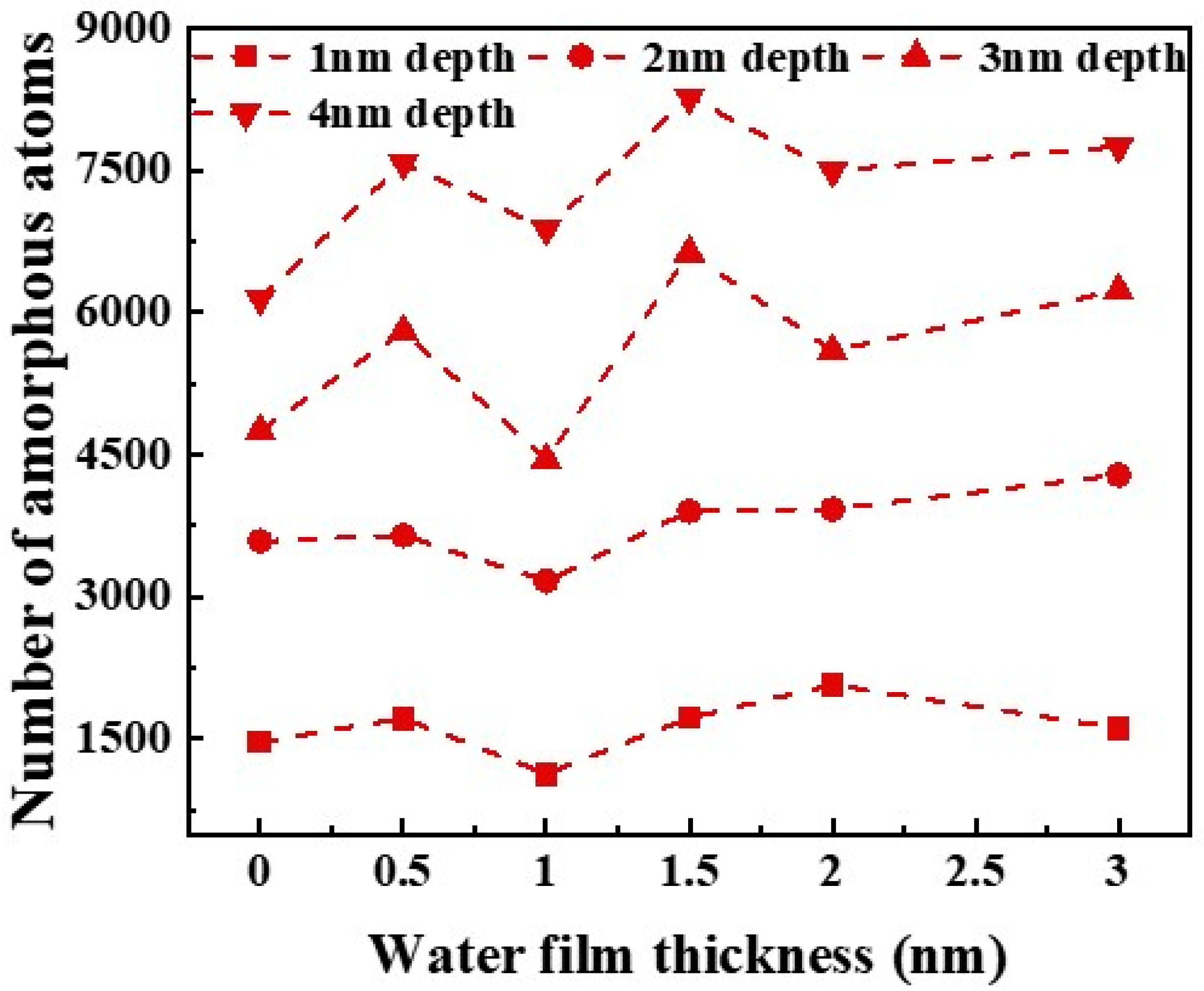
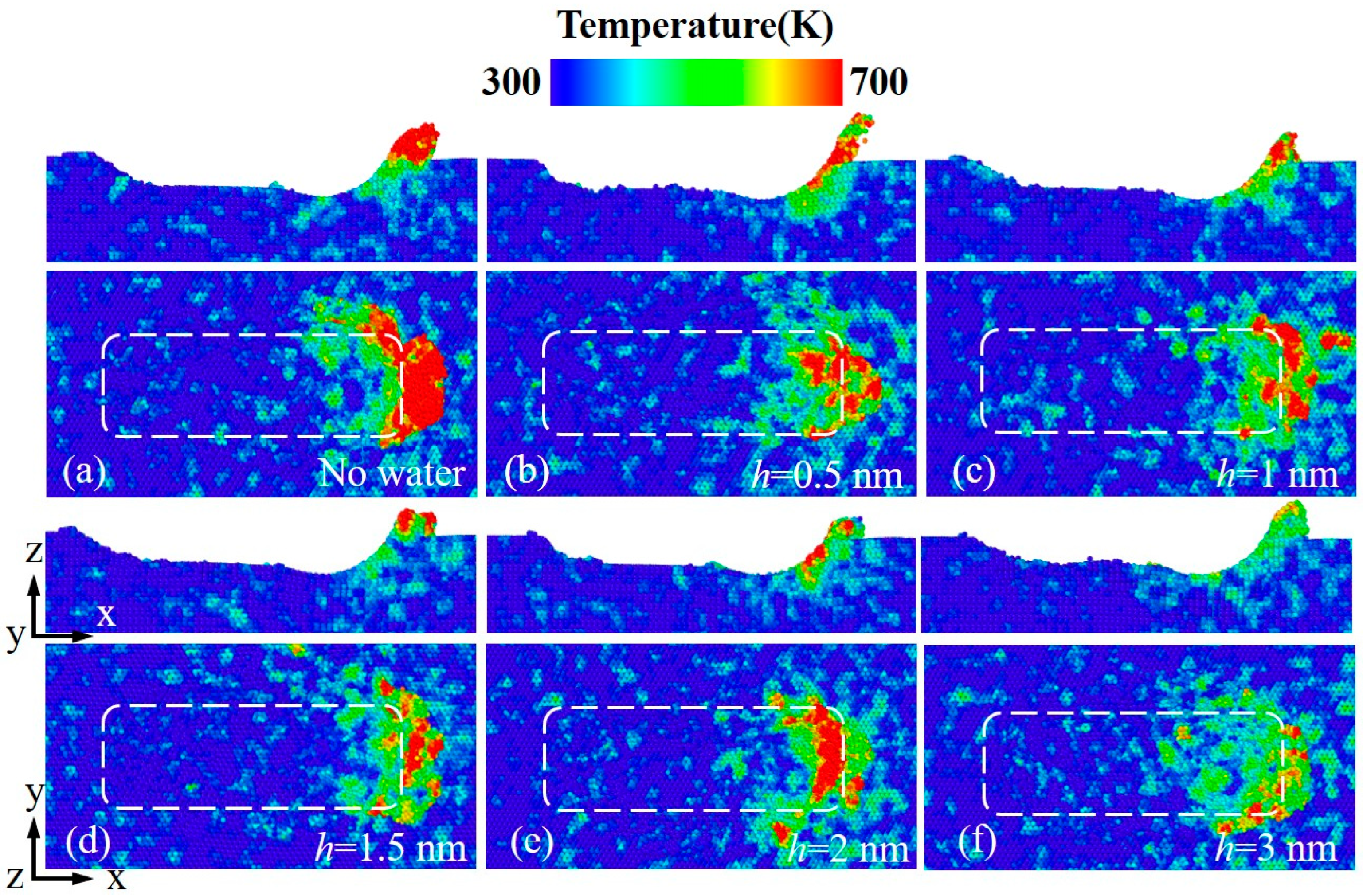
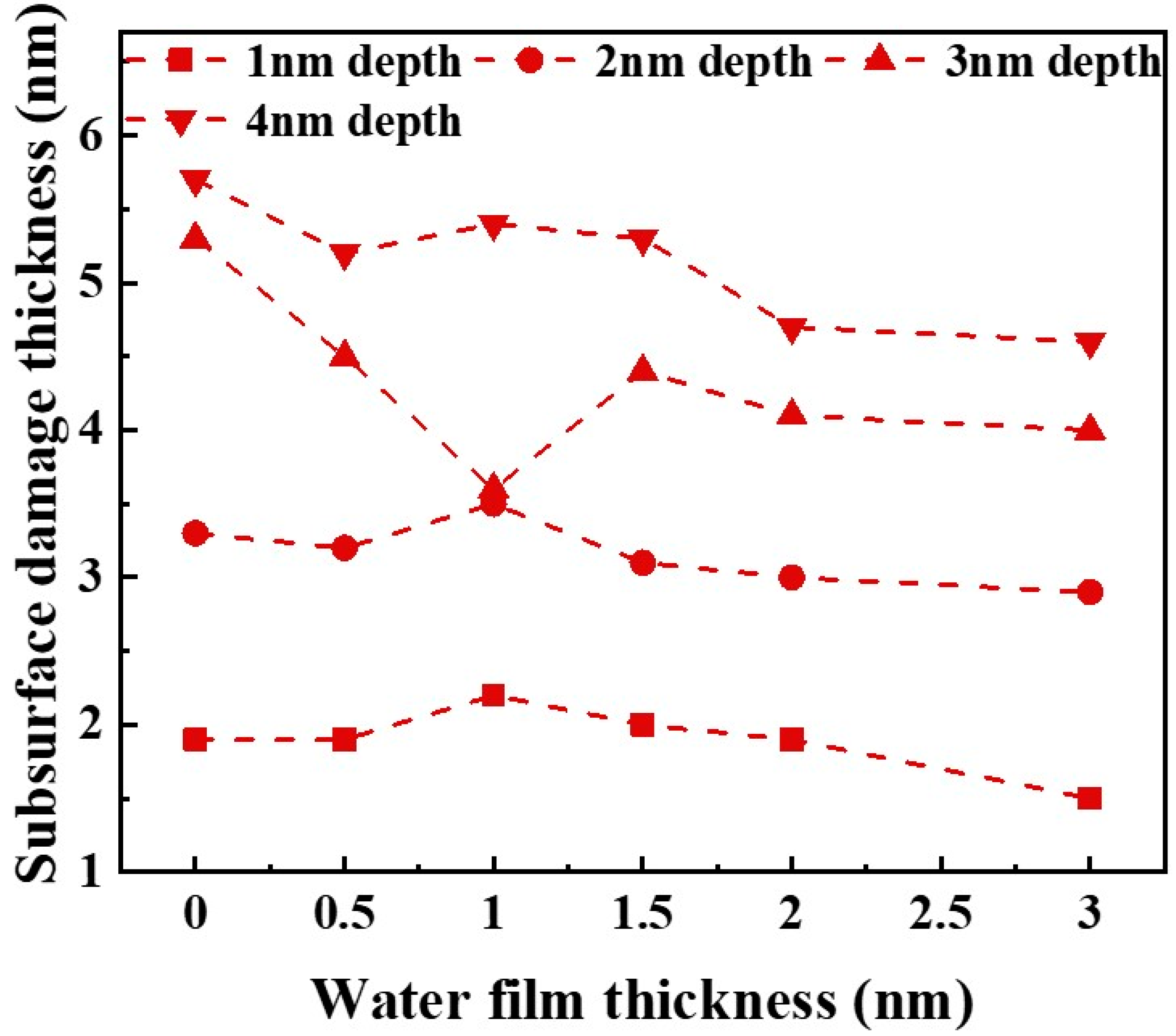
3.3. Subsurface Lattice Damage
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The tangential and normal forces exhibited no significant variation trend with increasing water film thickness from 0 to 3 nm, attributed to the competing effects of lubrication and movement obstruction of the water molecules during scratching. A 3 nm thick water film achieved the lowest friction coefficient under most scratching depth conditions. The water film influenced material plastic flow and chip formation, thereby mitigating the surface pile-up of GaN during scratching. In addition, the wear volume demonstrated a non-monotonic trend: it initially decreased, then increased, and subsequently decreased again as water film thickness rose from 0 to 3 nm, and it reached its minimum value at 3 nm water film thickness due to the enhanced lubrication and the heat absorption of the water film.
- (2)
- Water-film-covered GaN surfaces covered with water film exhibited a thinner subsurface damage layer compared to bare GaN workpiece, with the thickness of the damage layer monotonically decreasing as water film thickness increased. Nevertheless, the water film failed to inhibit the nucleation and propagation of the dislocations during scratching, and hence the water-film-covered GaN workpieces exhibited more dislocations than the bare GaN workpiece. This study can enhance the understanding of water film effects on the water-mediated nanotribological and ultra-precision machining processes of GaN.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wheeler, J.M.; Niederberger, C.; Tessarek, C.; Christiansen, S.; Michler, J. Extraction of plasticity parameters of GaN with high temperature, in situ micro-compression. Int. J. Plast. 2013, 40, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, T. Recent development of vertical GaN power devices. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, SB0805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Jia, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q. A review on the GaN-on-Si power electronic devices. Fundam. Res. 2022, 2, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Lai, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, B. GaN Power Integration for High Frequency and High Efficiency Power Applications: A Review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 15529–15542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Ge, L.; Liu, Z.; Xu, M.; Peng, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Xie, X.; et al. Research Progress in Capping Diamond Growth on GaN HEMT: A Review. Crystals 2023, 13, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, A.S.A.; Nirmal, D. A survey of Gallium Nitride HEMT for RF and high power applications. Superlattices Microstruct. 2017, 109, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Huang, H.; Zhu, X.; Kang, R. Surface integrity and removal mechanism of silicon wafers in chemo-mechanical grinding using a newly developed soft abrasive grinding wheel. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 63, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Imanishi, M.; Murakami, K.; Yoshimura, M. Recent progress of Na-flux method for GaN crystal growth. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, SC0803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, Z.; Yuan, S.; Guo, X.; Kang, R.; Guo, D. Study on subsurface damage mechanism of gallium nitride in nano-grinding. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2021, 128, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, J.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Effects of surface texturing on nanotribological properties and subsurface damage of monocrystalline GaN subjected to scratching investigated using molecular dynamics simulation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 539, 148277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Vaudo, R.P.; Brandes, G.R. Fabrication of GaN wafers for electronic and optoelectronic devices. Opt. Mater. 2003, 23, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyher, J.L.; Müller, S.; Grzegory, I.; Porowski, S. Chemical polishing of bulk and epitaxial GaN. J. Cryst. Growth 1997, 182, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.C.; Kim, J.; Singh, R.K.; Arjunan, A.C.; Lee, H. Evaluation of subsurface damage inherent to polished GaN substrates using depth-resolved cathodoluminescence spectroscopy. Thin Solid Film. 2018, 660, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y. Molecular dynamics study of the removal mechanism of SiC in a fixed abrasive polishing in water lubrication. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 24961–24974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Bian, D. Nanoscratch of aluminum in dry, water and aqueous H2O2 conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 464, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Ni, Z.; An, W. Nanoscale friction and wear properties of silicon wafer under different lubrication conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 282, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Knaggs, M.; Goel, G.; Zhou, X.W.; Upadhyaya, H.M.; Thakur, V.K.; Kumar, V.; Bizarri, G.; Tiwari, A.; Murphy, A.; et al. Horizons of modern molecular dynamics simulation in digitalized solid freeform fabrication with advanced materials. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 18, 100356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Li, S.; Chai, P.; Lan, K.; Yu, R. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Single-Crystal 4H-SiC Nano Scratching with Different Scratching Directions of the Tool. Crystals 2023, 13, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Luo, X.; Agrawal, A.; Reuben, R.L. Diamond machining of silicon: A review of advances in molecular dynamics simulation. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2015, 88, 131–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Jiao, Z.; Huang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Yin, C.; Wang, H.; Pinto, H.C.; Greiner, C.; Liu, W. Wear-resistant CrCoNi nanocrystalline film via friction-driven surface segregation. Acta Mater. 2024, 279, 120299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Dong, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Han, S.; Yin, C.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, W. Enhancing tribocorrosion resistance of VCoNi alloys in artificial seawater via nitrogen alloying. Corros. Sci. 2025, 243, 112600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Feng, H.; Li, J.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, L. Nanoscale sliding friction behavior on Cu/Ag bilayers influenced by water film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 545, 148957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, W.; Zhu, F. Polishing process of 4H-SiC under different pressures in a water environment. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 133, 109710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, T. Molecular dynamics study of the effect of water lubrication three-body polishing sapphire. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hua, D.; Zhou, Q.; Li, S.; Eder, S.J.; Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, W. Effect of a water film on the material removal behavior of Invar during chemical mechanical polishing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 616, 156490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Liu, P. Molecular dynamics study on the mechanism of AFM-based nanoscratching process with water-layer lubrication. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 346, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.W.; Huang, Y.F.; Gan, D.; Xu, J.Y.; Li, H.; Wang, G.; Meng, S.; Chen, X.L. Wetting behavior of water on silicon carbide polar surfaces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 28033–28039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yang, L.H.; Gan, Y.; Chen, Q. The Influence of Sliding Speed on the Friction Behavior of Silica Surface. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 3384–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Chen, J.; Fang, L.; Sun, K.; Sun, J.; Han, J. Atomistic scale nanoscratching behavior of monocrystalline Cu influenced by water film in CMP process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béré, A.; Serra, A. On the atomic structures, mobility and interactions of extended defects in GaN: Dislocations, tilt and twin boundaries. Philos. Mag. 2006, 86, 2159–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Deng, S.; Shang, F.; Wan, Q.; Yan, Y. Dependence of tribological behavior of GaN crystal on loading direction: A molecular dynamics study. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 075108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Fang, Q.; Li, J. Molecular dynamics simulations for nanoindentation response of nanotwinned FeNiCrCoCu high entropy alloy. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 465701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Wu, H. Interface-governed nanometric machining behaviour of Cu/Ag bilayers using molecular dynamics simulation. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 1341–1353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. The effect of rough surface on nanoscale high speed grinding by a molecular dynamics simulation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2015, 98, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohamey, Y.M.; Abdel Magied, A.M.; Salah El Din, L.A.; Mohamed, R.A. MRI is it complementary or mandatory to ultrasound in classification of different congenital anomalies of female reproductive tract? Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2018, 49, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Parameters Name | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Radius of Diamond Abrasive, R (nm) | 4 | |
| Water film | Density, ρ (g/cm3) | 1 |
| Thickness, h (nm) | 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, and 3 | |
| Size of GaN workpiece (nm3) | 30 × 20 × 15 | |
| Scratching depth, d (nm) | 1, 2, 3, and 4 | |
| Scratching distance, L (nm) | 10 | |
| Scratching velocity, v (m/s) | 40 | |
| Scratching direction | [1-210] crystal orientation | |
| Potential | Type | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| GaN | SW potential | Refs. [30,31] |
| C-N | 6-12 LJ | ε = 0.0037235 eV, δ = 0.33677 nm |
| O-Ga | 6-12 LJ | ε =0.0084843 eV, δ = 0.34721 nm |
| O-N | 6-12 LJ | ε = 0.0037321 eV, δ = 0.31479 nm |
| O-C | 6-12 LJ | ε = 0.0041369 eV, δ = 0.32531 nm |
| C-Ga | 6-12 LJ | ε = 0.0084646 eV, δ = 0.36919 nm |
| O-O | 12-12 LJ | ε = 0.0041499 eV, δ = 0.30332 nm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, J.; Feng, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J. Molecular Dynamics Study of Nanoscratching Behavior of Water-Film-Covered GaN (0001) Surface Using Spherical Diamond Abrasive. Crystals 2025, 15, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15050428
Yin J, Feng S, Liu Y, Guo J. Molecular Dynamics Study of Nanoscratching Behavior of Water-Film-Covered GaN (0001) Surface Using Spherical Diamond Abrasive. Crystals. 2025; 15(5):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15050428
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Jiaqin, Shuaicheng Feng, Yang Liu, and Jian Guo. 2025. "Molecular Dynamics Study of Nanoscratching Behavior of Water-Film-Covered GaN (0001) Surface Using Spherical Diamond Abrasive" Crystals 15, no. 5: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15050428
APA StyleYin, J., Feng, S., Liu, Y., & Guo, J. (2025). Molecular Dynamics Study of Nanoscratching Behavior of Water-Film-Covered GaN (0001) Surface Using Spherical Diamond Abrasive. Crystals, 15(5), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15050428







