Anisotropy of Voltage Sensitivity of Bow-Tie Microwave Diodes Containing 2DEG Layer
Abstract
1. Introduction
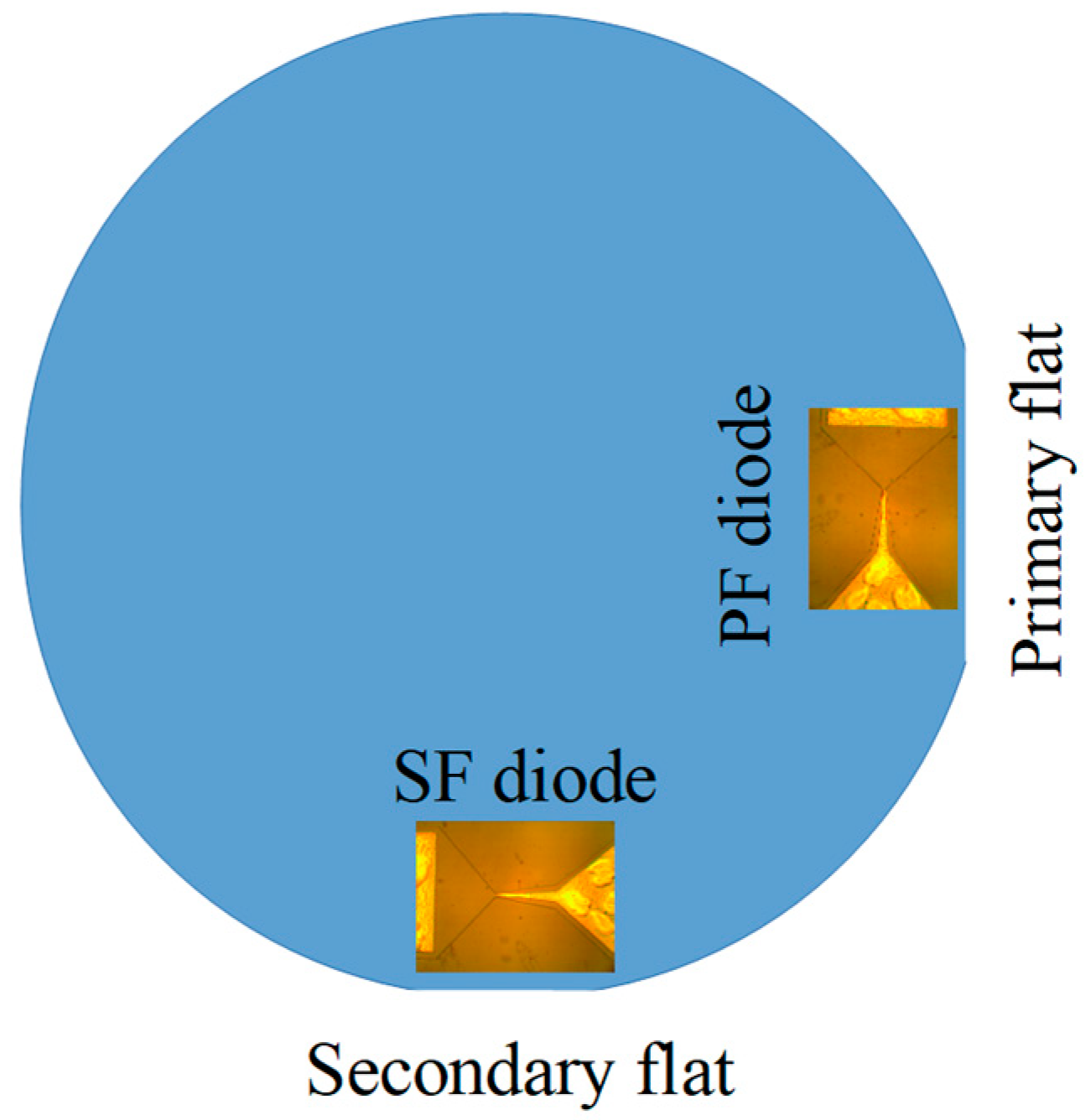
2. Samples and Methods
3. Results
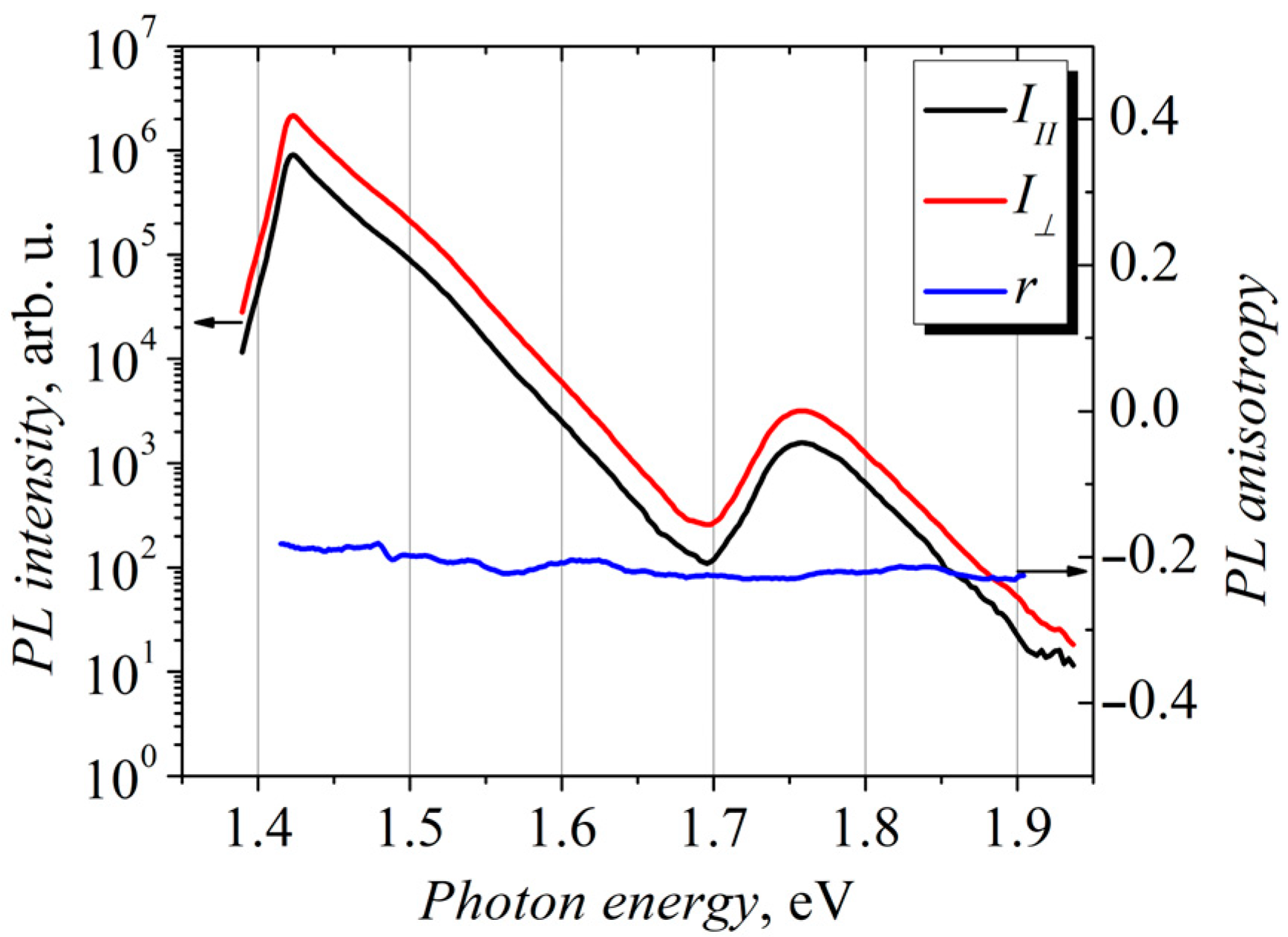
3.1. Photoluminescence Anisotropy of the Modulation-Doped GaAs/AlGaAs Structure
3.2. Voltage Sensitivity of the Bow-Tie Diodes
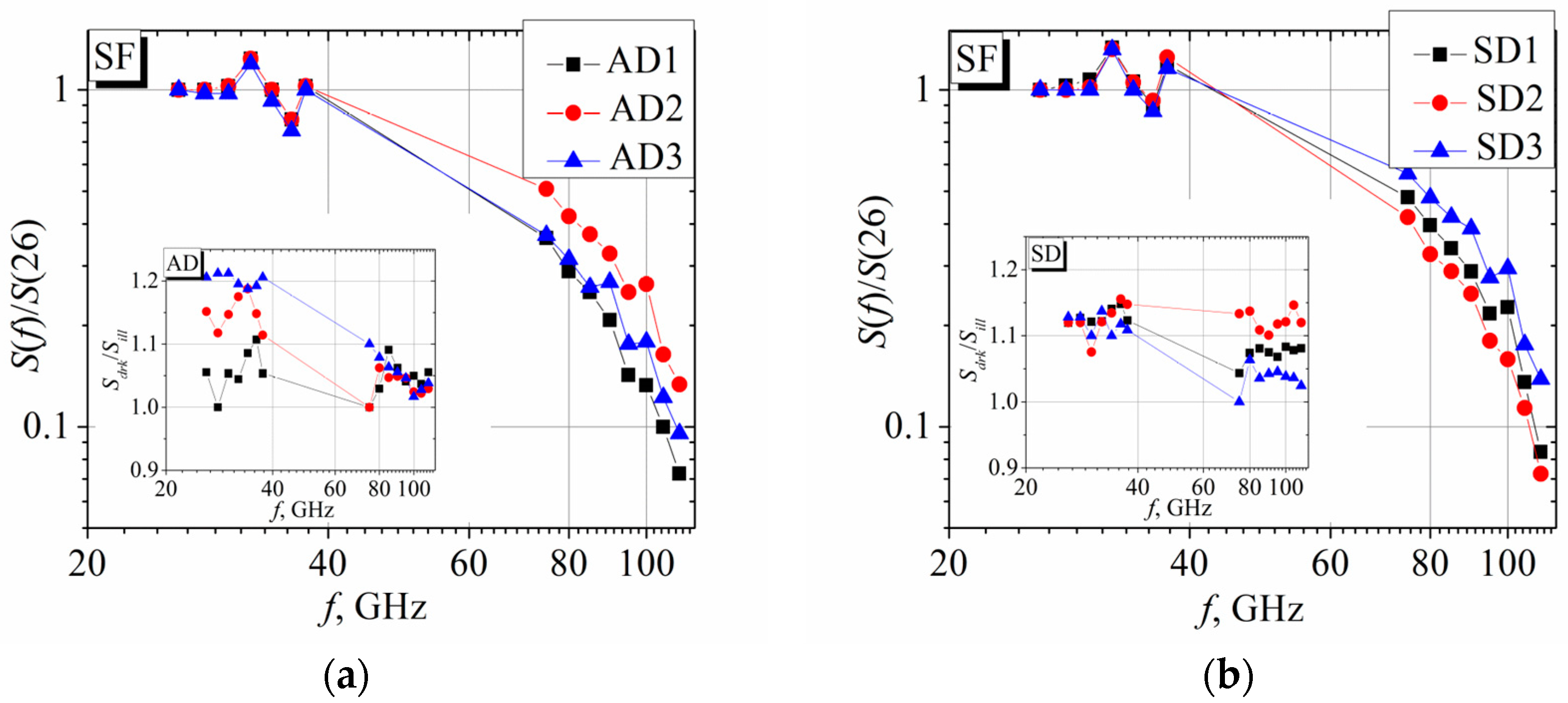
3.3. Frequency Dependence of the Voltage Sensitivity in Differently Oriented Bow-Tie Diodes
3.4. Influence of Illumination on the Electrical Properties of Bow-Tie Diodes
4. Conclusions
- In the dark, the microwave voltage sensitivity of the bow-tie diodes with their longitudinal axis oriented along the primary flat cut of GaAs(100) substrate (PF diodes) is higher for asymmetric bow-tie diodes than for symmetric ones, and vice versa. The voltage sensitivity of the diodes oriented perpendicular to this direction (SF diodes) is higher for symmetric diodes.
- Illumination affects the PF and SF diodes differently. If the voltage sensitivity of the PF bow-tie diodes increases when illuminated, the voltage sensitivity of the SF diodes decreases when exposed to light.
- Asymmetric PF diodes are several times more sensitive to microwave radiation than symmetric bow-tie diodes.
- The frequency dependence of the voltage sensitivity of the PF and SF diodes are similar in the Ka and W frequency ranges; a decrease in the voltage sensitivity with a time constant of several picoseconds is observed.
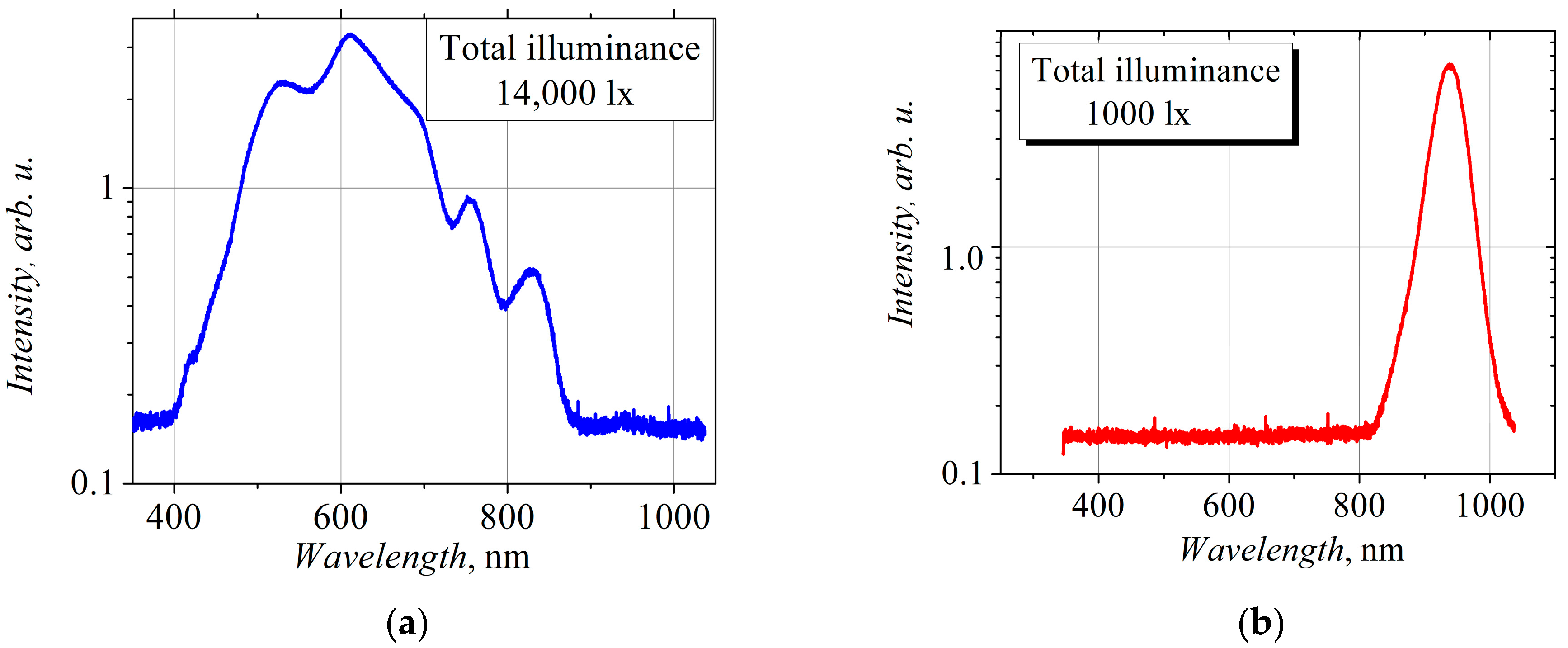
- When comparing the effects of the illumination of the diodes using white light and infrared radiation, in most cases, we observe a greater influence of the infrared red radiation on the voltage sensitivity of the diodes, while the resistance of the diodes changes more noticeably under white light illumination.
- Therefore, we attribute these changes in the electrical parameters of the bow-tie diodes under the influence of the illumination to the emission of electrons from the energy gap of the AlGaAs barrier layer into the conduction band.
- Finally, a comparison of the research results regarding bow-tie diodes oriented perpendicular to each other with respect to the crystallographic axes allows us to state that the nature of the voltage detected in the microwaves in the bow-tie diodes lies in the heating of electrons in both the AlGaAs barrier and the GaAs channel. The heating of electrons in the barrier layer determines the different detection properties of the diodes due to the redistribution of electrons in higher energy valleys.
- We hope this article will inspire further research into the anisotropic properties of bow-tie diodes, as some questions regarding the nature of the detected voltage remain unanswered. We also aim to initiate fruitful discussions on this topic.
- Further studies on bow-tie diodes based on modulation-doped semiconductor structures could be carried out by minimizing the influence of the doped barrier layer and, as an instrument, using a wider variety of light sources to modify the detection properties of bow-tie diodes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| Orientation | Diode | Illumination | Number of Measured Diodes | Smean, V/W | Smedian, V/W | StD, V/W | StD/Smean, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF | SD1 | white | 10 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.22 | 34 |
| dark | 10 | 0.40 | 0.38 | 0.18 | 46 | ||
| SD2 | white | 10 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.18 | 37 | |
| dark | 10 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 40 | ||
| SD3 | white | 11 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.11 | 27 | |
| dark | 11 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.08 | 27 | ||
| AD1 | white | 11 | 1.40 | 1.40 | 0.42 | 30 | |
| dark | 11 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 0.37 | 49 | ||
| AD2 | white | 11 | 0.80 | 0.74 | 0.26 | 32 | |
| dark | 11 | 0.51 | 0.44 | 0.32 | 62 | ||
| AD3 | white | 11 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.15 | 20 | |
| dark | 11 | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.13 | 25 | ||
| SF | SD1 | white | 9 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.25 | 40 |
| dark | 9 | 0.68 | 0.75 | 0.27 | 40 | ||
| SD2 | white | 9 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.04 | 9 | |
| dark | 9 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.05 | 9 | ||
| SD3 | white | 9 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 11 | |
| dark | 9 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 12 | ||
| AD1 | white | 11 | 0.32 | 0.44 | 0.40 | 126 | |
| dark | 11 | 0.34 | 0.47 | 0.39 | 116 | ||
| AD2 | white | 13 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.14 | 49 | |
| dark | 13 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 43 | ||
| AD3 | white | 18 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 33 | |
| dark | 18 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.11 | 31 |
| Orientation | Diode | Illumination | Number of Measured Diodes | R(0)mean, V/W | R(0)median, V/W | StD, V/W | StD/R(0)mean, % | Calculated, R(0) kΩ | (R(0)mean-Rcalc.)/R(0) calc.. % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF | SD1 | white | 11 | 11.8 | 11.87 | 0.54 | 4.6 | 11.35 | 4 |
| dark | 11 | 14.84 | 15.25 | 1.16 | 7.8 | 12.24 | 21 | ||
| SD2 | white | 9 | 9.58 | 9.59 | 0.14 | 1.5 | 9.36 | 2 | |
| dark | 9 | 12 | 12 | 0.32 | 2.7 | 10.1 | 19 | ||
| SD3 | white | 10 | 8.41 | 8.39 | 0.16 | 1.9 | 8.42 | 0 | |
| dark | 10 | 10.41 | 10.61 | 0.45 | 4.3 | 9.09 | 15 | ||
| AD1 | white | 10 | 4.42 | 4.43 | 0.14 | 3.2 | 3.1 | 43 | |
| dark | 10 | 5.48 | 5.49 | 0.26 | 4.7 | 3.34 | 64 | ||
| AD2 | white | 11 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 0.1 | 2.9 | 2.58 | 36 | |
| dark | 11 | 4.3 | 4.34 | 0.18 | 4.2 | 2.8 | 54 | ||
| AD3 | white | 11 | 3.1 | 3.11 | 0.05 | 1.6 | 2.32 | 34 | |
| dark | 11 | 3.8 | 3.82 | 0.1 | 2.6 | 2.52 | 51 | ||
| SF | SD1 | white | 8 | 11.25 | 11.15 | 0.47 | 4.17 | 11.35 | −10 |
| dark | 8 | 13.30 | 13.20 | 0.39 | 2.95 | 12.24 | 106 | ||
| SD2 | white | 9 | 9.70 | 9.60 | 0.20 | 2.06 | 9.36 | 34 | |
| dark | 9 | 11.28 | 11.30 | 0.32 | 2.83 | 10.1 | 118 | ||
| SD3 | white | 9 | 8.56 | 8.50 | 0.19 | 2.20 | 8.42 | 14 | |
| dark | 9 | 9.97 | 10.00 | 0.26 | 2.61 | 9.09 | 88 | ||
| AD1 | white | 10 | 3.73 | 3.75 | 0.11 | 2.89 | 3.1 | 63 | |
| dark | 10 | 4.41 | 4.50 | 0.19 | 4.42 | 3.34 | 107 | ||
| AD2 | white | 13 | 3.19 | 3.21 | 0.09 | 2.73 | 2.58 | 61 | |
| dark | 13 | 3.71 | 3.75 | 0.16 | 4.25 | 2.8 | 91 | ||
| AD3 | white | 18 | 2.83 | 2.92 | 0.27 | 9.66 | 2.32 | 51 | |
| dark | 18 | 3.29 | 3.36 | 0.32 | 9.85 | 2.52 | 77 |
Appendix C
References
- Jacoboni, C.; Reggiani, L. Bulk hot-electron properties of cubic semiconductors. Adv. Phys. 1979, 28, 493–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylord, T.K.; Rabson, T.A. Anisotropy in the Conductivity of N-Gallium Arsenide. Phys. Lett. A 1970, 33, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylord, T.K.; Rabson, T.A. Determination of Conduction Anisotropies in Semiconductors. Solid-State Electron. 1972, 15, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalevich, V.K.; Zakharchenya, B.P.; Fedorova, O.M. Strong anisotropy of the conduction-electron g-factor in GaAs/AlGaAs quantum wells. Phys. Solid State 1995, 37, 154–156. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/252641982 (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Cole, B.E.; Batty, W.; Imanaka, Y.; Shimamoto, Y.; Singleton, J.; Chamberlain, J.M.; Miura, N.; Henini, M.; Cheng, T. Effective-mass anisotropy in GaAs-(Ga,Al)As twodimensional hole systems: Comparison of theory and very high-field cyclotron resonance experiments. J. Phys. Candens. Mater 1995, 7, L675–L681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Koshiba, S.; Sakaki, H. Large conductance anisotropy in a novel two-dimensional electron system grown on vicinal (111)B GaAs with multiatomic steps. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 4093–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, F.; Lelarge, F.; Cavanna, A.; Laruelle, F.; Etienne, B. Enhancement of electron conductivity in GaAs/AlAs coupled quantum wires. Physica E 1998, 2, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.H.; Grahn, H.T.; Ploog, K.; Merlin, R. Giant Electropleochroism in GaAs-(Al, Ga) As Heterostructures: The Quantum-Well Pockels Effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 69, 973–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalygin, V.A.; Makhov, I.S.; Adamov, R.B.; Vinnichenko, M.Y.; Khvostikov, V.P.; Firsov, D.A. Electric-field-induced polarization anisotropy of interband photoluminescence in GaAs. J. Appl. Phys. 2024, 136, 195703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.; Klipstein, P.C.; Grey, R.; Hill, G. Rotation of the Conduction Band Valleys in AlAs due to XX-XY Mixing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 3693–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reker, T.; Im, H.; Bremme, L.E.; Choi, H.; Chung, Y.; Klipstein, P.C.; Shtrikman, H. Effective Mass Anisotropy of Γ Electrons in GaAs/AlGaAs Quantum Wells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 056403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vdovin, E.E.; Khanin, Y.N.; Dubrovskii, Y.V.; Main, P.C.; Eaves, L.; Henini, M.; Hill, G. Probing the effective mass anisotropy of G electrons in a GaAsÕ.AlGa.As quantum well. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 205305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balocchi, A.; Amand, T.; Wang, G.; Liu, B.L.; Renucci, P.; Duong, Q.H.; Marie, X. Electric field dependence of the spin relaxation anisotropy in (111) GaAs/AlGaAs quantum wells. New J. Phys. 2013, 15, 095016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckyanova, M.N.; Johnson, J.A.; Maznev, A.A.; Garg, J.; Jandl, A.; Bulsara, M.T.; Fitzgerald, E.A.; Nelson, K.A.; Chen, G. Anisotropy of the Thermal Conductivity in GaAs/AlAs Superlattices. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3973–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisodia, N.; Muduli, P.K. Enhancement of microwave detection sensitivity in un-biased perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions using voltage controlled magnetic anisotropy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 515, 167301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorudas, J.; Seliuta, D.; Minkevičius, L.; Janonis, V.; Subačius, L.; Pashnev, D.; Pralgauskaitė, S.; Matukas, J.; Ikamas, K.; Lisauskas, A.; et al. Terahertz bow-tie diode based on asymmetrically shaped AlGaN/GaN heterostructures. Lith. J. Phys. 2023, 63, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliuta, D.; Vyšniauskas, J.; Ikamas, K.; Lisauskas, A.; Kašalynas, I.; Reklaitis, A.; Valušis, G. Symmetric bow-tie diode for terahertz detection based on transverse hot-carrier transport. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 275106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valušis, G.; Lisauskas, A.; Yuan, H.; Knap, W.; Roskos, H.G. Roadmap of Terahertz Imaging 2021. Sensors 2021, 21, 4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ašmontas, S.; Anbinderis, M.; Čerškus, A.; Gradauskas, J.; Lučun, A.; Sužiedėlis, A. Microwave Bow-Tie Diodes on Bases of 2D Semiconductor Structures. Crystals 2024, 14, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sužiedėlis, A.; Ašmontas, S.; Gradauskas, J.; Čerškus, A.; Šilėnas, A.; Lučun, A. Impact of Buffer Layer on Electrical Properties of Bow-Tie Microwave Diodes on the Base of MBE-Grown Modulation-Doped Semiconductor Structure. Crystals 2025, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sužiedėlis, A.; Ašmontas, S.; Gradauskas, J.; Čerškus, A.; Anbinderis, M. Indirect measurement of electron energy relaxation time at room temperature in two dimensional heterostructured semiconductors. Materials 2022, 15, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawski, A. Fluorescence Anisotropy: Theory and Applications of Rotational Depolarization. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1993, 23, 459–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameloot, M.; vandeVen, M.; Acuña, A.U.; Valeur, B. Fluorescence anisotropy measurements in solution: Methods and reference materials (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 589–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharchenya, B.P.; Mirlin, D.N.; Perel’, V.I.; Reshina, I.I. Spectrum and polarization of hot-electron photoluminescence in semiconductors. Sov. Phys. Uspekhi 1982, 25, 143–166. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1070/PU1982v025n03ABEH004519 (accessed on 3 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Sužiedėlis, A.; Ašmontas, S.; Gradauskas, J.; Čerškus, A.; Požela, K.; Anbinderis, M. Competition between Direct Detection Mechanisms in Planar Bow-Tie Microwave Diodes on the Base of InAlAs/InGaAs/InAlAs Heterostructures. Sensors 2023, 23, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, P. The relationship of the D-X centre in AlxGa1-xAs and other III-V alloys with the conduction band structure. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 1988, 3, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canali, C.; Jacoboni, C.; Nava, F. Intervalley Diffusion of Hot Electrons in Germanium. Solid State Commun. 1978, 26, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sužiedėlis, A.; Ašmontas, S.; Kundrotas, J.; Nargelienė, V.; Gradauskas, J. Voltage sensitivity of a point-contact GaAs/AlGaAs heterojunction microwave detector. Phys. Scr. 2012, 85, 035702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartnagel, L.; Katilius, R.; Matulionis, A. Microwave Noise in Semiconductor Devices; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; 312p. [Google Scholar]
- Dargys, A.; Kundrotas, J. Handbook on Physical Properties if Ge, Si, GaAs and InP; Science and Encyclopedia Publishers: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1994; 264p, Available online: https://openlibrary.org/books/OL295382M/Handbook_on_physical_properties_of_Ge_Si_GaAs_and_InP (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Mooney, P.M. Deep donor levels(DX centers) inIII-V semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 67, R1–R26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conwell, E.M. High Field Transport in Semiconductors; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1967; 293p. [Google Scholar]








| Diode | PF Oriented Along the Primary Flat Cut | SF Oriented Along the Secondary Flat Cut | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Dark | Illuminated | In Dark | Illuminated | |
| Intervalley Relaxation Time , ps | ||||
| AD | 4.1 ± 0.6 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 3.7 ± 0.8 |
| SD | 3.1 ± 0.4 | 2.7 ± 0.5 | 3.6 ± 0.7 | 3.6 ± 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sužiedėlis, A.; Ašmontas, S.; Gradauskas, J.; Čerškus, A.; Lučun, A.; Anbinderis, M.; Zharchenko, I. Anisotropy of Voltage Sensitivity of Bow-Tie Microwave Diodes Containing 2DEG Layer. Crystals 2025, 15, 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040367
Sužiedėlis A, Ašmontas S, Gradauskas J, Čerškus A, Lučun A, Anbinderis M, Zharchenko I. Anisotropy of Voltage Sensitivity of Bow-Tie Microwave Diodes Containing 2DEG Layer. Crystals. 2025; 15(4):367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040367
Chicago/Turabian StyleSužiedėlis, Algirdas, Steponas Ašmontas, Jonas Gradauskas, Aurimas Čerškus, Andžej Lučun, Maksimas Anbinderis, and Ihor Zharchenko. 2025. "Anisotropy of Voltage Sensitivity of Bow-Tie Microwave Diodes Containing 2DEG Layer" Crystals 15, no. 4: 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040367
APA StyleSužiedėlis, A., Ašmontas, S., Gradauskas, J., Čerškus, A., Lučun, A., Anbinderis, M., & Zharchenko, I. (2025). Anisotropy of Voltage Sensitivity of Bow-Tie Microwave Diodes Containing 2DEG Layer. Crystals, 15(4), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15040367







