Abstract
2,2-Bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)-1,1-diphenylethanol (HL) is a heteroscorpionate ligand capable of coordinating metal ions through two nitrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. We report a base free synthetic route to metal complexes of L and explore the resulting structural diversity. Notably, complex composition varies substantially depending on the metal ion, including dinuclear molybdenum species and distinct coordination behavior with silicon and copper. The isolated compounds include the dinuclear, oxygen-bridged complexes (LMoO2)2O and (LMoO)(μ-O)2, as well as the mononuclear complexes LTi(NMe2)3, LZrCl3, LGeCl3, LWO2Cl, LCu(acetate)2H, and LSiMe2Cl. Single crystal X-ray diffraction reveals that the bulky complex structures generate cavities in the crystal lattice, frequently occupied by solvent molecules. The titanium, zirconium, molybdenum, tungsten, and germanium complexes exhibit octahedral coordination, while structural peculiarities are observed for copper and silicon. The copper(II) complex shows a distorted octahedral geometry with one elongated ligand bond; the silicon complex is pentacoordinated in the solid state. Additional characterization includes melting points, NMR, and IR spectroscopy. The developed synthetic strategy provides a straightforward and versatile route to heteroscorpionate metal complexes.
1. Introduction
Trispyrazolylborates and polypyrazolylalkanes have been used for a long time as ligands in transition metal chemistry [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. The focus of research has shifted since 2000 to so-called heteroscorpionates [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. These ligands coordinate at a metal ion via two pyrazolate groups, and the third functional group, which might be, for instance, an alcoholate, thiolate, or carboxy group. Review articles are available for a broader overview of the available heteroscorpionate ligands [12,13,15]. Such ligands can be considered as structural models mimicking the active sites of metalloenzymes [21]. Heteroscorpionate complexes have been described as excellent initiators for ring-opening polymerization [22,23,24,25,26] and show catalytic activity in the different transformations of organic substrates [13,27,28] and in carbon dioxide fixation [29,30,31]. Biological activities (antimicrobial, antioxidant, in vitro cytotoxicity) have been observed mainly for heteroscorpionate-copper(II) complexes [32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39].
2,2-bis(3,5-dimethyl-pyrazol-1-yl)-1,1-diphenylethanol (1) has previously been employed by several research groups for the synthesis of transition metal complexes (Scheme 1). Complexes of molybdenum, tungsten, and various rare-earth metals bearing this ligand have been reported in the literature [40,41,42,43,44]. Structurally related heteroscorpionate ligands have also been widely utilized for metal coordination [9,10,11,45,46,47,48,49]. Conventional synthetic approaches for heteroscorpionate complexes typically involve deprotonation of the ligand-using bases such as NaH, NaOMe, or KOtBu, followed by reaction with metal halides [41,42,50].
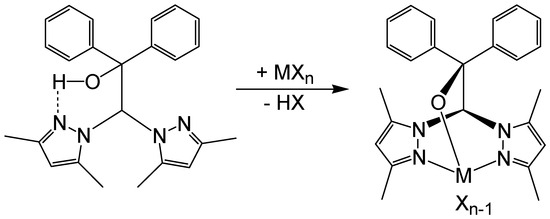
Scheme 1.
General reaction scheme of ligand 1 (left) with metal derivatives MXn and typical coordination mode with a metal ion (right).
In an effort to streamline this process, we recently demonstrated that a tungsten complex of 1 could be obtained simply by mixing solutions of the ligand and WOCl4 in tetrahydrofuran. After standing for several weeks, the complex crystallized directly from the reaction mixture and was isolated in high yield without further purification [51]. Encouraged by this result, we sought to investigate whether this base-free synthesis could be extended to other metal ions. In this case study, we explore the coordination behavior of 1 with selected metal ions, including titanium and zirconium (early transition metals), molybdenum (in two different complexes), copper (a late transition metal), and silicon and germanium (main group elements). In the following sections, we will present and discuss the crystal structures of the compounds obtained and draw conclusions from the experience gained.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
All reactions were carried out under argon using the Schlenk technique [52,53]. NMR spectra were recorded in CDCl3 or DMSO-d6 with TMS as internal standard either on a BRUKER DPX 400 spectrometer at 400.13, 100.61, and 79.49 MHz for 1H, 13C, and 29Si NMR spectra or on a BRUKER AVANCE III 500 MHz spectrometer at 500.13, 125.76, and 99.36 MHz for 1H, 13C, and 29Si NMR spectra, respectively. IR spectra were recorded on a Nicolet 380 FT-IR by Thermo. Melting points were measured using a Polytherm A hot stage microscope from Wagner and Munz with an attached 52II thermometer from Fluke.
2.2. Syntheses
The ligand 2,2-bis(3,5-dimethyl-pyrazol-1-yl)-1,1-diphenylethanol was prepared according to a reported method [43]. For the synthesis of heteroscorpionate, complexes of 1 used the general method A described below. Deviations from this method are described in the text of the individual experiments.
2.2.1. General Method A
Ligand 1 was dissolved in dry, oxygen-free THF (30 mL) to yield a colorless solution. This solution was added to an equimolar solution of the respective metal compound in THF under inert conditions. The resulting mixture was left to stand at room temperature for several weeks, during which crystalline products typically formed at the bottom of the Schlenk tube. In some cases, the mixture was stored in a refrigerator to promote crystallization (for details, see individual experiments).
One crystal was selected for a single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The remaining product was isolated by concentrating the solution to one-third of its volume under reduced pressure, followed by refrigerated storage for one week. The resulting product was collected by filtration, washed with n-hexane, and dried in vacuo.
Note: Drying in vacuo primarily removes solvent molecules from the crystal lattice. Therefore, product yields are reported for solvent-free molecular compositions.
2.2.2. Titanium Complex 2
Compound 2 was synthesized according to method A using 1.93 g (5 mmol) 1 and 1.12 g (5 mmol) titaniumtetrakis(dimethylamide) in 60 mL THF. After mixing both components, the solution turned red. Standing at room temperature does not give any solid product after six weeks. Therefore, the Schlenk vessel was stored at 5 °C in the refrigerator for seven months. Orange-colored crystals of 2 were isolated after that time. A total of 1.95 g (61.2% yield).
m.p. 160 °C (decomposition).
1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 1.75 (THF), 1.98 (s, 6H, pz-CH3), 2.12 (s, 6H, pz-CH3), 2.21 (s, 18 H, NMe2), 3.6 (THF), 5.67 (s, 2H, pz-H), 6.99 (s, 1H, –CH–C), 7.15–7.22 (m, 5H, Ph-H), 7.36–7.39 (m, 5H, Ph-H). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 10.8 (pz-CH3), 13.9 (pz-CH3), 38.9 (NMe2), 25.6, 67.5 (THF), 71.3 (–CH–C–O), 81.6 (–CH–C–O), 105.6 (pz-C), 126.9 (Ph-C), 127.4 (Ph-Cpara), 128.0 (Ph-C), 140.9 (Ph-Cipso), 144.7 (pz-C), 146.6 (pz-C). The NMR spectra show additional signals for NMe2 groups as an impurity.
IR ν [cm−1] = 3059.5 (w), 2959.3 (w), 2917.9 (w), 2834.2 (m), 2797.2 (m), 2792.6 (m), 2749.2 (s), 1560.3 (m), 1488.7 (w), 1460.2 (w), 1446.4 (s), 1419.2 (w), 1389.9 (m), 1322.4 (w), 1309.2 (w), 1254.3 (m), 1236.2 (m), 1175.0 (w), 1143.7 (m), 1114.9 (w), 1073.8 (m), 1036.7 (w), 969.9 (w), 945.8 (m), 903.6 (m), 838.1 (w), 820.6 (w), 793.1 (m), 714.5 (vs), 701.0 (vs), 690.4 (vs), 664.1 (m), 635.3 (m), 624.6 (w), 613.5 (w), 549.4 (m), 478.9 (m).
The experiment was repeated using similar starting quantities to determine whether a faster synthesis of compound 2 was possible. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 48 h. Subsequently, the solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to a volume of 50 mL and left to stand overnight at 5 °C in a refrigerator. An orange-colored powder formed, which was isolated by filtration and dried under vacuum, affording the same product in 64% yield.
2.2.3. Zirconium Complex 3
Compound 3 was synthesized according to method A using 1.19 g (3.1 mmol) 1 and 1.16 g (3.1 mmol) ZrCl4.2(THF) in 220 mL THF. The solution was left standing at room temperature for three months. During that time, the solution turned cloudy, but no precipitate was formed. The solution was filtrered. The volume of the solution was reduced in vacuo to 80 mL. Storage in the refrigerator at 5 °C for six months gave very small colorless prisms of 3.
A total of 1.28 g (71.0% yield).
m.p. 310 °C (decomposition).
1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 1.91 (s, 6H, pz-CH3), 1.98 (s, 6H, pz-CH3), 5.67 (s, 2H, pz-H), 6.99 (s, 1H, –CH–C), 7.15–7.39 (m, 10H, Ph-H). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 10.8 (pz-CH3), 13.9 (pz-CH3), 71.2 (–CH–C–O), 81.6 (–CH–C–O), 105.6 (pz-C), 126.9 (Ph-C), 127.4 (Ph-Cpara), 128.0 (Ph-C), 140.9 (pz-C), 144.7 (Ph-Cipso), 146.6 (pz-C). The NMR spectra show traces of THF and further impurities.
IR ν [cm−1] = 3133.5 (w), 3060.9 (w), 2922.5 (w), 1769.7 (m), 1722.8 (m), 1598.5 (w), 1553.6 (s), 1491.5 (w), 1449.0 (s), 1414.4 (w), 1386.4 (w), 1372.6 (m), 1341.8(w), 1301.8 (m), 1239.3 (m), 1184.7 (m), 1137.6 (w), 1116.2 (w), 1107.1 (w), 1078.3 (m), 1047.1 (m), 1033.6 (m), 1001.1 (w), 986.1 (w), 927.3 (w), 908.0 (s), 830.7 (w), 809.7 (s), 750.6 (s), 712.8 (vs), 706,0 (vs), 695.1 (vs), 663.5 (w), 647.7 (w), 634.5 (m), 626.1 (m).
The experiment was repeated using similar starting quantities to develop a faster synthesis of compound 3 without using a base, such as NaH or NaOMe. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 48 h. Afterward, the solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to a volume of 50 mL and left to stand overnight at 5 °C in the refrigerator. A white powder was obtained by filtration and subsequent drying under vacuum, affording the same product in 68% yield.
2.2.4. Molybdenum Complexes 4 and 5
Compounds 4 and 5 were synthesized according to method A using 2 g (5.2 mmol) 1 and 1.37 g (5.2 mmol) molybdenum hexacarbonyl in 90 mL THF. The solution did not show any sign of product formation after six weeks (clear solution, no precipitate or crystals). Therefore, the Schlenk tube was flushed with air and left standing again. After an additional eight weeks of waiting, a crystalline material was formed inside the vessel. Two types of crystals were produced from this reaction batch: brown prisms 4 and colorless, knife-shaped crystals 5. It turned out that these were different products. Crystal structure analyses of both compounds were performed. In total, 1.85 g of product was isolated (yield assumed for pure 5 as product would be 68.2%). Compound 4 decomposes around 320 °C, and compound 5 decomposes above 330 °C. No melting was observed.
1H-NMR (CDCl3): δ 1.85 (THF), 2.01 (s, 6H, pz-CH3), 2.02 (s, 6H, pz-CH3), 3.76 (THF), 5.76, 5.94 (s, 2H, pz-H), 6.98, 6.99 (s, 1H, –CH–C), 7.15–7.40 (m, 10H, Ph-H). 13C-NMR (CDCl3): δ 11.1, 11.2 (pz-CH3), 13.3, 14.3 (pz-CH3), 25.6, 68.5 (THF), 70.4, 70.8 (–CH–C–O), 81.9, 83.5 (–CH–C–O), 106.3, 107.1 (pz-C), 126.4, 126.5 (Ph-C), 127.0 (Ph-Cpara), 127.5, 127.8 (Ph-C), 139.6, 140.7 (pz-C), 144.1, 144.8 (Ph-Cipso), 147.1, 152.6 (pz-C). The NMR spectra show various impurities due to the complex reaction process.
IR ν [cm−1] = 3367.6 (w), 3131.7 (m), 3091.8 (w), 3057.6 (m), 3020.9 (w), 2924.6 (m), 2867.3 (m), 2010.6 (w), 1890.1 (m), 1826.4 (w), 1767.8 (vs), 1655.1, (w), 1597.1 (w), 1560.7 (vs), 1463.1 (s), 1447.8 (s), 1417.9 (s), 1389.6 (s), 1320.0 (s), 1261.1 (s), 1180.7 (s), 1141.8 (w), 1118.4 (m), 1074.3 (s), 1045.5 (s), 988.0 (m), 929.6 (s), 897.0 (s), 832.7 (m), 754.3 (s), 694.9 (s), 659.7 (m), 634.3 (s), 590.1 (w), 507.9 (m), 473.1 (m), 440.7 (w), 404.7 (m)
2.2.5. Pseudopolymorph of the Tungsten Complex 6
The tungsten complex 6, which we have published earlier, was solved in pyridine and treated with triphenylphosphine. The aim of this procedure was to reduce the tungsten complex to an oxidation state of +4 and to obtain the pyridine adduct. This failed. A crystalline pseudopolymorph of 6 was obtained instead. That means that no real reaction took place, and the compound 6 was instead recrystallized from pyridine.
Compound 6 was obtained from 0.59 g (0.9 mmol) LWO2Cl, 0.26 g (0.99 mmol) PPh3, and 30 mL pyridine. A total of 0.45 g (77.8% yield).
m.p. 354 °C (decomposition).
1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 2.36 (s, 6H, pz-CH3), 2.43 (s, 6H, pz-CH3), 6.03 (s, 2H, pz-H), 5.76 (s, 1H, -CH-C), 7.21–8.93 (m, 10H, Ph-H). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 11.2 (pz-CH3), 14.6 (pz-CH3), 71.4 (-CH-C-O), 87.7 (-CH-C-O), 107.8 (pz-C), 126.0 (Ph-C), 128.0 (Ph-Cpara), 128.5 (Ph-C), 142.1 (Ph-Cipso), 142.8 (pz-C), 152.6 (pz-C). The NMR spectra show a signal for water in the 1H NMR at 3.73 ppm, which stems from the DMSO-d6, and further impurities.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3129.9 (m), 3068.1 (m), 2972.3 (s), 2861.7 (m), 1965.6 (w), 1904.3 (w), 1599.6 (m), 1585.9 (w), 1557.5 (s), 1490.4 (m), 1462.2 (s), 1446.9 (s), 1416.3 (s), 1381.3 (s), 1311.2 (s), 1255.9 (s), 1185.6 (s), 1141.5 (m), 1118.9 (s), 1075.2 (s), 1048.9 (s), 1001.8 (m), 987.2 (m), 960.2 (w), 948.1 (vs), 906.7 (vs), 838.2 (w), 803.5 (m), 753.2 (s), 713.3 (s), 695.9 (m), 663.0 (w), 645.4 (w), 632.8 (m), 626.7 (m), 592.6 (w), 558.8 (m), 513.9 (w), 480.4 (m), 411.2 (m).
2.2.6. Copper Complex 7
Compound 7 was synthesized according to method A using 2 g (5.2 mmol) of 1 and 1.04 g (5.2 mmol) of copper(II)-acetate-hydrate in 110 mL THF. Blue crystals formed after four weeks standing at room temperature, 2.13 g (72.1% yield).
m.p. 88 °C.
Remark: NMR spectra of the copper(II) complex were recorded. There are missing signals and substantial line broadening of the remaining signals due to the paramagnetic character of this complex. Therefore, the spectra are only shown in the Supporting Information.
IR ν [cm−1] = 3123.7 (w), 3089.6 (w), 3059.8 (w), 2977.3 (s), 2858.8 (s), 2506.7 (vw), 1590.7 (s), 1562.3 (s), 1492.1 (m), 1459.7 (s), 1446.9 (s), 1387.9 (s), 1332.7 (s), 1311.9 (s), 1244.6 (s), 1171.9 (s), 1138.8 (w), 1103.3 (m), 1063.4 (s), 1046.6 (s), 1000.8 (m), 948.1 (w), 916.7 (m), 888.6 (m), 834.8 (s), 814.1 (m), 757.1 (vs), 709.6 (s), 684.6 (s), 665.7 (s), 633.2 (s), 619.1 (m), 543.8 (m), 512.2 (w), 489.3 (m), 451.4 (w).
2.2.7. Silicon Complex 8
Compound 8 was synthesized via a modified procedure designed to remove the generated hydrogen chloride by forming an ammonium salt. Dichlorodimethylsilane (0.774 g, 0.72 mL, 6.0 mmol) was dissolved in 40 mL of THF, and triethylamine (0.76 g, 0.9 mL, 6.6 mmol) was added dropwise via syringe. A solution of ligand 1 (2.3 g, 6.0 mmol) in 80 mL of THF was then added dropwise to the reaction mixture under constant stirring. The mixture was stirred for 24 h at room temperature.
The resulting triethylammonium chloride precipitate was removed by filtration. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, and the residue was extracted with 200 mL of 1,2-dimethoxyethane (DME) to dissolve the product, leaving behind the residual triethylammonium chloride. The solution was filtered and stored in a refrigerator for three weeks, yielding colorless crystals suitable for X-ray crystallography.
The remaining product was isolated by concentrating the mother liquor to one-third of its original volume under reduced pressure, followed by refrigerated storage for one week. The resulting product was collected by filtration, washed with n-hexane, and dried in vacuo to yield 2.01 g of compound 8 (70.0%).
m.p. 195–198 °C.
1H-NMR (CDCl3): δ 0.02 (s, 6H, Si-CH3), 1.96 (s, 6H, pz-CH3), 2.11 (s, 6H, pz-CH3), 3.31 (s, CH3, DME), 3.46 (s, CH2, DME), 5.68 (s, 2H, pz-H), 7.20 (s, 1H, –CH–C), 7.1–7.16 (m, 5H, Ph-H), 7.35–7.37 (m, 5H, Ph-H).
13C-NMR (CDCl3): δ 0.01 (Si-CH3), 10.7 (pz-CH3), 11.6 (pz-CH3), 58.0 (CH3, DME), 70.8 (CH2, DME), 73.4 (–CH–C–O), 81.1 (–CH–C–O), 106.1 (pz-C), 125.2 (Ph-C), 126.3 (Ph-Cpara), 127.0 (Ph-C), 141.8 (Ph-Cipso), 142.0 (pz-C), 145.6 (pz-C).
29Si-NMR δ −21.9.
29Si CP MAS NMR δiso −31.70, with δ11 67.87, δ22 −65.23, δ33 −97.75, Ω 165.62, κ −0.61 [data in the Herzfeld-Berger convention: Ω = δ11 − δ33 and κ = 3(δ22 − δiso)/Ω.].
IR ν [cm−1] = 3246.3 (m), 3058.7 (w), 2962.8 (m), 2919.9 (w), 1570.3 (vs), 1560.7 (s), 1491.6 (m), 1458.2 (s), 1450.5 (s), 1419.5 (m), 1380.0 (m), 1366.5 (m), 1340.5 (w), 1313.4 (w), 1260.7 (vs), 1179.2 (m), 1153.8 (w), 1097.0 (s), 1063.3 (s), 1032.4 (s), 974.2 (m), 909.7 (w), 868.9 (m), 806.1 (vs), 752.0 (s), 717.1 (m), 696.6 (vs), 669.5 (s), 660.4 (m), 624.7 (m), 540.4 (w), 506.2 (w), 472.2 (w), 464.5 (w), 440.1 (w).
2.2.8. Germanium Complex 9
Compound 9 was synthesized according to method A using 3.25 g of (8.4 mmol) 1 and 1.8 g (8.4 mmol) of GeCl4 in 200 mL of THF. A first batch of reaction product formed within 24 h of standing at room temperature. The white precipitate was filtered off; it is a powder unsuitable for crystal structure analysis. The filtered solution was stored in the refrigerator at 5 °C for 10 months. After that time, very small colorless needles of 9 formed. These were isolated and analyzed, 3.7 g (78.0% yield).
m.p. 303 °C (decomposition).
1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 1.92 (s, 6H, pz-CH3), 2.0 (s, 6H, pz-CH3), 5.70 (s, 2H, pz-H), 7.01 (s, 1H, –CH–C), 7.21–7.97 (m, 10H, Ph-H). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 10.8 (pz-CH3), 13.8 (pz-CH3), 55.4 (–CH–C–O), 67.5 (–CH–C–O), 105.7 (pz-C), 126.8 (Ph-C), 126.9 (Ph-Cpara), 128.0 (Ph-C), 143.2 (pz-C), 144.6 (Ph-Cipso), 146.8 (pz-C). The NMR spectra show signals for THF and some further impurities.
IR ν [cm−1] = 3135.7 (w), 3057.2 (w), 2925.8 (w), 1769.7 (m), 1555.5 (s), 1487.3 (w), 1460.0 (s), 1446.4 (s), 1414.3 (w), 1381.6 (m), 1373.0 (m), 1316.3 (m), 1303.2 (m), 1254.5 (m), 1203.3 (w), 1181.4 (m), 1156.8 (w), 1116.2 (w),1140.8 (w), 1114.1 (w), 1072.8 (m), 1051.7 (s), 1032.1 (m), 988.3 (w), 951.6 (w), 926.8 (w), 906.8 (s), 859.0 (w), 839.7 (w), 815.8 (m) 808.5 (m), 752.8 (vs), 709.1 (vs), 707,0 (vs), 656.7 (w), 641.5 (w), 630.6 (m), 624.0 (m), 616.8 (w).
2.3. Single Crystal Structure Determination
Data collection of complexes 2 and 4–8 was performed on a STOE IPDS-2T image plate diffractometer (STOE & Cie GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany), while data collection of 3 and 9 was performed on a STOE STADIVARI (STOE & Cie GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany) due to the very small crystal edge lengths of less than 0.1 mm. Both diffractometers are equipped with a low-temperature device with Mo-Kα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å) using ω and φ scans. Software for data collection is: X-AREA, cell refinement: X-AREA, and data reduction: X-RED [54]. Preliminary structure models were derived using direct methods [55], and the structure was refined using full-matrix least-squares calculations based on F2 for all reflections using SHELXL (Universität Göttingen, Göttingen, German) [56]. The hydrogen atoms were included in the structure models in calculated positions and were refined as constrained to the bonding atoms.
The crystal structure of 2 contains one molecule of THF in the asymmetric unit. The atoms of this solvent molecule have enlarged displacement ellipsoids. Resolution of these displacement ellipsoids in two disordered positions led to severe problems in refinement. Therefore, the THF molecule was refined without disorder.
The crystals of compounds 4 and 5 contain two molecules of THF in the asymmetric unit each. The THF molecules are heavily disordered and were treated with split atom models in compound 4 using DELU, SIMU, and SAME instructions. This approach was not fruitful in the crystal structure of 5. Therefore, the THF molecules were removed with the SQUEEZE procedure [57,58,59]. The total potential solvent accessible volume treated in that way is 1104 Å3 for a unit cell volume of 3257.47 Å3, i.e., 33.9%.
The crystal structure of 7 contains a total potential solvent accessible volume of 129 Å3 for a unit cell volume of 2387.85 Å3, i.e., 5.4%. Therein, diffuse residual electron density with about three electrons is present. This was removed from the final refinement with the SQUEEZE procedure.
The crystal structure of 7 was initially solved and refined in space group Ia. PLATON ADDSYMM (Utrecht University, Utrecht, Netherlands)proposed to use the conventional setting Ic, which was performed. Unfortunately, the Checkcif routine does not recognize this setting and generates an alert level A. The crystals of compound 7 contain two molecules of THF in the asymmetric unit. One THF molecule is nearly circularly disordered around its position (40:60) and was treated with a split atom model using SIMU, DELU, and SAME instructions. One of the dimethylpyrazolyl units is disordered (39:61) and was refined with a split atom model using ISOR instructions.
The crystals of compound 8 contain one molecule of 1,2-dimethoxyethane (DME) per molecule of 8. One oxygen atom of DME is heavily disordered in at least two positions (59:41; SAME and SADI instructions), and it was difficult to develop an appropriate split-atom model for this solvent molecule. Several alerts in the Checkcif data are caused by this disorder.

Table 1.
Crystallographic data from data collection and refinement processes for 2–5.

Table 2.
Crystallographic data from data collection and refinement processes for 6–9.
3. Results and Discussion
The preparative protocol developed by us is aimed at a simple and robust approach. Reaction time was not a major factor for us. We were mainly interested in crystals suitable for single X-ray diffraction and were, therefore, willing to accept long reaction times. A general reaction scheme is shown in Scheme 1. The following substrates were reacted with the ligand 1: titanium tetrakis(dimethylamide), zirconium tetrachloride THF adduct (ZrCl4.2THF), molybdenum hexacarbonyl, copper(II) acetate, dichlorodimethylsilane, and germanium tetrachloride. These reactions were carried out to see whether the synthesis principle is generally applicable and works with different metals and main group elements of the periodic table. Furthermore, the previously obtained complex cis-[2,2-bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)-1,1-diphenylethanolato]chloridodioxidotungsten(VI) [51] was dissolved in pyridine and treated with triphenylphosphine. This procedure aimed to reduce the tungsten complex to an oxidation state of +4 and to obtain the pyridine adduct.
The NMR spectra of the obtained products show mainly the signals of 1 and, in some cases, solvent molecules (see experimental section). This information is sparse and is not sufficient to reliably derive the structures of the reaction products. Single crystal structure analyses were, therefore, carried out on the crystalline products. These will be discussed in the next section.
3.1. Molecular Structures
The titanium(IV) complex 2 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/n with the complex molecule and one molecule of THF in the asymmetric unit (Figure 1). The composition of this complex is LTi(NMe2)3. It is an octahedral titanium complex. The tridentate ligand is coordinated in a facial coordination mode. The other three coordination sites are occupied by the dimethylamino groups.
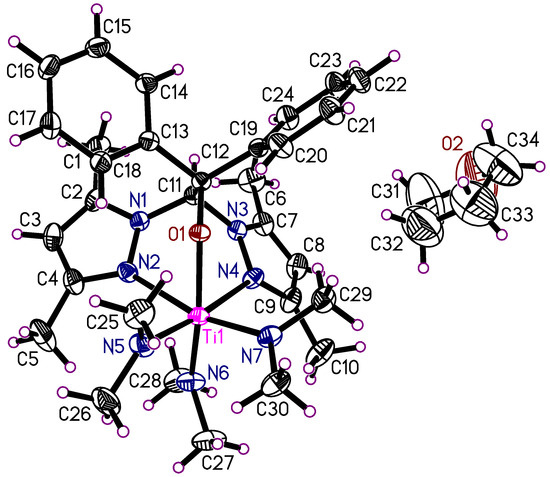
Figure 1.
Asymmetric unit of the crystal structure of 2 showing the atomic numbering scheme. The thermal ellipsoids of the non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Two comparable titanium complexes 2a and 2b (see Scheme 2) were described in the chemical literature [48,60]. Therein, three dimethylamino groups are bound to the titanium atom. The other three coordination sites in the coordination sphere of the titanium atom are occupied by two different heteroscorpionate ligands (see Scheme 2). This demonstrates the high structural variability of the heteroscorpionate ligands.
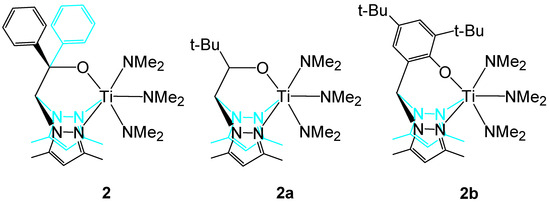
Scheme 2.
Heteroscorpionate-tris(dimethylamino)–titanium(IV) complex 2 (this work); 2a and 2b from literature [48,60].
The Ti-X bond lengths in 2, 2a, and 2b are very similar (see Table 3). The atomic radius for the octahedral coordinated titanium was given as 1.36 Å [61]. Together with the atomic radii for oxygen (0.66 Å) and nitrogen (0.70 Å), the expected values for Ti-O bonds are 2.02 Å and for Ti-N bonds 2.06 Å. The observed Ti-O bond lengths in 2-2b are somewhat shorter than the expected value. Striking differences are found in the Ti-N bond lengths. The bonds to the pyrazolyl groups are substantially longer than expected [2.337 (2) to 2.444 (2) Å]. In turn, the Ti-N bond lengths to the dimethylamino groups are shorter than expected [1.915 (6) to 1.965 (2) Å]. This is probably caused by the three dimethylamino groups at the titanium atoms in these types of complexes, which are able to donate electron density to the titanium atoms via their free electron pairs at the nitrogen atoms. This, in turn, elongates the distances to the tridentate ligand. The short Ti-N distances hint at partial double bond interactions of the titanium atoms with the dimethylamino nitrogen atoms.

Table 3.
Selected bond lengths in 2, 2a, and 2b. All values are in Å (values for 2a and 2b are taken from the literature [48,60]. Equivalent bonds are shown in the same line).
Several intramolecular interactions, such as C-H···π, π···π, C-H···O, and C-H···N, can influence the molecular structure. In here, C-H···π are absent while the aromatic rings form a kind of π-stacking between an imidazole and a phenyl ring with a distance of 3.9 Å. Furthermore, the aromatic rings, in particular the hydrogen atoms, interact with the oxygen atoms in intramolecular C-H···O contacts of 2.38 and 2.47 Å. The tridendate coordination of the oxygen atom is fulfilled with a hydrogen atom of the adjacent methyl group C25 (2.46 Å). Furthermore, the amine nitrogen atoms interact with the adjacent methyl groups in C-H···N interactions (2.46–2.66 Å). The orientation of the ligands at the titanium atom is, therefore, influenced by several intramolecular interactions.
The zirconium(IV) complex 3 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with one product molecule of the composition LZrCl3 in the asymmetric unit (Figure 2). The complex shows the expected octahedral coordination geometry. The tridentate ligand occupies three facial positions, three chlorine atoms, and the other three positions in the coordination polyhedron. The chlorine atom Cl2 is in trans position to O1 and features a longer bond length of 2.444 (1) Å than the other two chlorine atoms [2.410 (1) Å for Zr1-Cl1 and 2.426 (1) Å for Zr1-Cl3]. This molecular arrangement is influenced by intramolecular Caryl-H···O (2.68 and 2.71 Å) and Cmethyl-H···Cl (2.75–2.79 Å) interactions. Intramolecular interactions of the aryl units are not observed.
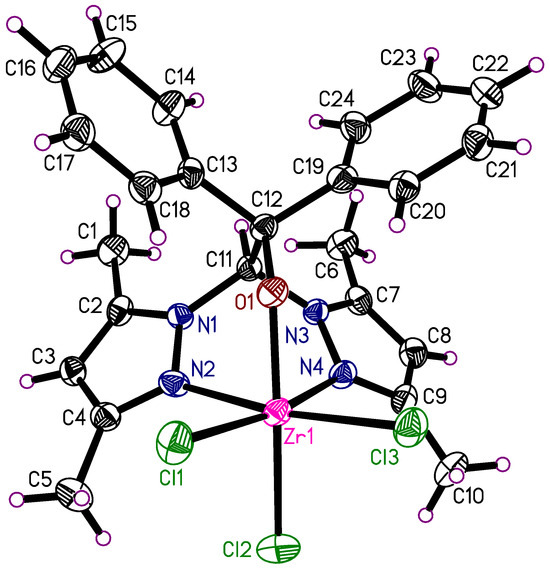
Figure 2.
Molecular structure of 3. The thermal ellipsoids of the non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Crystal structures of heteroscorpionate–zirconium complexes are very rare in the literature. There is only one comparable complex designated here as 3a (Scheme 3) [50]. This binuclear complex features Zr-Cl bonds with similar lengths of 2.476 (3) and 2.449 (3) Å as in compound 3 with 2.410 (1) to 2.444 (1) Å. The bond lengths to the heteroscorpionate ligands are also similar in both complexes. However, complex 3a is an oxygen-bridged dimer with a different heteroscorpionate ligand and has heptacoordinated zirconium atoms. Some differences between the two complexes are, therefore, to be expected.
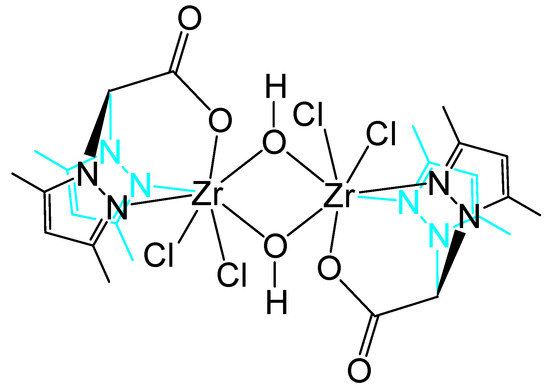
Scheme 3.
Binuclear heteroscorpionate–zirconium(IV) complex 3a from the literature [50].
The dinuclear molybdenum(V) complex 4 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with the half complex molecule and two molecules of THF in the asymmetric unit (Figure 3). The THF molecules are heavily disordered, each in two positions with site occupation factors of 0.59/0.41 and 0.84/0.16. It was possible to develop a suitable split atom model for these. The whole complex molecule is generated by an inversion center, which is situated in the middle of the rectangle formed by the atoms Mo1-O2-Mo1A-O2A (Figure 4). The composition of the complex is LMo(O)(μ-O)2(O)MoL with both molybdenum atoms in an oxidation state of +5. The Mo1-Mo1A distance in 4 is 2.5600(9) Å, which indicates a Mo-Mo single bond resulting from a d1-d1 interaction. Comparable compounds feature Mo-Mo-bond lengths of 2.541 to 2.690 Å [62].
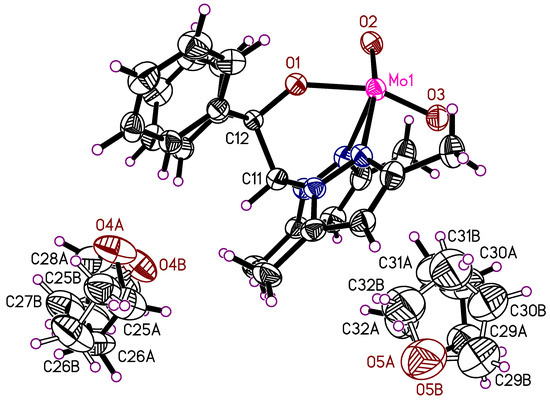
Figure 3.
Asymmetric unit of the crystal structure of 4. The atomic numbering scheme for the heteroscorpionate ligand is the same as in the other structures. The thermal ellipsoids of the non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
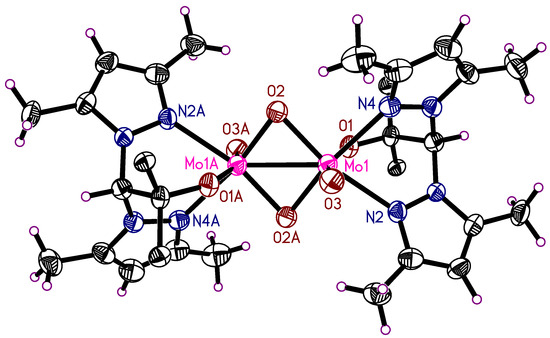
Figure 4.
Molecular structure of 4 showing the dimeric feature of the Mo complex. The THF guest molecules are omitted for clarity. The thermal ellipsoids of the non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
There are crystal structures of two binuclear heteroscorpionate complexes of molybdenum(V) in the literature (Scheme 4). One is formed with the bis(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)acetato [63], the other one with the tris(pyrazol-1-yl)methanesulfonato ligand [64]. The latter one could also coordinate via three nitrogen atoms from the pyrazolyl groups, but prefers in this complex a coordination as a heteroscorpionate ligand with N,N,O-coordination mode.
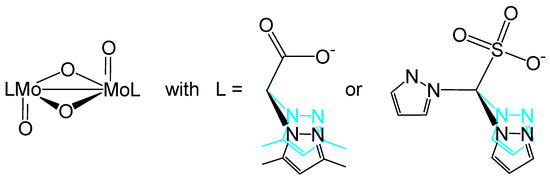
Scheme 4.
Dinuclear heteroscorpionate–molybdenum(V) complexes from the literature [63,64].
The molecular structure shows several intramolecular C-H···O interactions of different methyl groups in the range of 2.31–2.63 Å being co-responsible for the molecular arrangement. The aryl units do not interact in intramolecular stacking interactions, but in C-H···π contacts of 2.7 and 3.0 Å with the pyrazolyl ring representing the π-unit.
The dinuclear molybdenum(VI) complex 5 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P2/c with the half complex molecule and two molecules of THF in the asymmetric unit (Figure 5). The phenyl groups of the heteroscorpionate ligand are disordered, each in two positions (0.89/0.11 and 0.58/0.42) using suitable split atom models. The THF molecules are heavily disordered. It was not possible to develop a suitable split-atom model for these. The THF molecules were removed from the final refinement with the SQUEEZE procedure. The whole complex molecule is generated by a two-fold rotation axis, which goes through the central oxygen atom O4 (Figure 6). The composition of the complex is LMo(O)2(μ-O)(O)2MoL. Again, the molecular structure is influenced by intramolecular C-H···O interactions (2.22–2.69 Å) and is comparable to the observed interactions of compound 4. Intramolecular contacts of the π-units present in 5 are not observed.
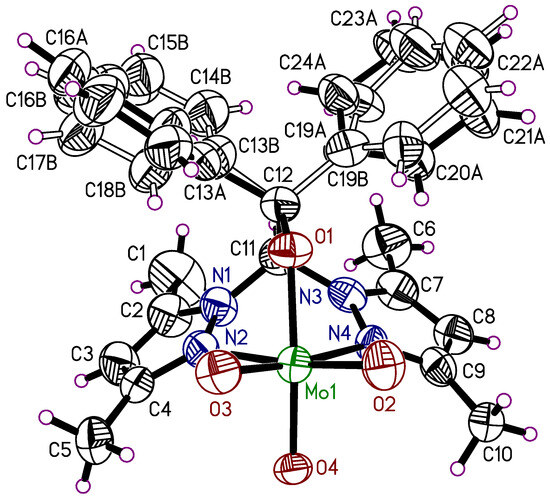
Figure 5.
Asymmetric unit of the crystal structure of 5. Heavily disordered THF molecules have been removed from the final refinement. The thermal ellipsoids of the non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
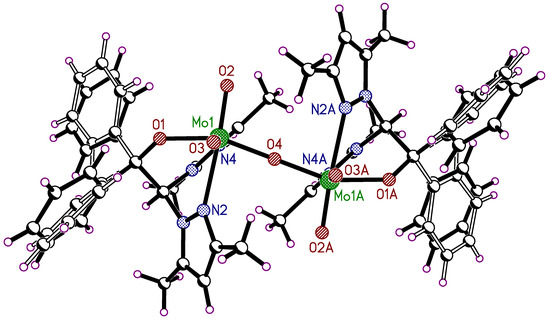
Figure 6.
Molecular structure of 5 showing the dimeric feature of the Mo complex.
Compound 5 was already described in the chemical literature. The crystal structure obtained by Hoffmann, Tran, and Carrano contains one molecule of methylene chloride in the asymmetric unit [41] and represents a pseudopolymorph of the crystal structure described here. This pseudopolymorph crystallized in the orthorhombic space group Pba2. The same type of dinuclear molybdenum(VI) complex was also isolated with the bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)acetate ligand [65].
The comparison of the bond lengths of complexes 4 and 5 is only possible to a limited extent due to the different bridging modes of the dimeric complexes. The bond lengths to the tridentate ligand are very similar in both complexes (Table 4). The bridging oxygen atoms O2 and O2A in 4 have longer Mo-O bond lengths (1.951 and 1.945 Å) than the bridging bond Mo1-O4 in 5 (1.890 Å). The terminal bonds Mo1-O3 in 4 and Mo1-O2 and Mo1-O3 in 5 are, in turn, almost identical.

Table 4.
Selected bond lengths in 4 and 5. All values in Å.
The mononuclear tungsten(VI) complex 6 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with the complex molecule in the asymmetric unit (Figure 7). The composition of this complex is LW(O)2Cl. The isolated complex 6 represents a pseudopolymorph of the previously published tungsten complex, which crystallized in the monoclinic space group Pc with one molecule of THF in the asymmetric unit [51]. Coordination geometry, bond lengths, and angles of 6 are very similar to this previously isolated complex. Several complexes of the type LM(O)2Cl with L = heteroscorpionate ligand and M = Mo, W have been discribed in the chemical literature [40,41,42,66].
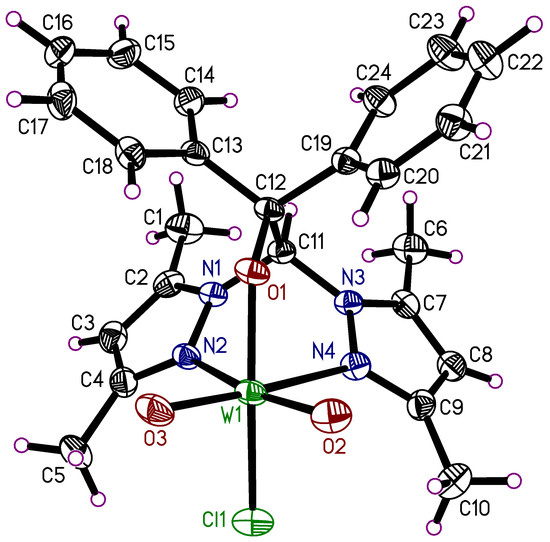
Figure 7.
Molecular structure of 6. The thermal ellipsoids of the non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
As in compound 3, the ortho aryl hydrogen atoms interact with the adjacent oxygen atom in intramolecular Caryl-H···O (2.65 and 2.69 Å) interactions. Since the chlorine atoms (as present in 3) are substituted with O2 and O3, the methyl groups form intramolecular Cmethyl-H···O (2.49 and 2.57 Å) contacts instead of C-H···Cl interactions. Again, contacts of the aryl units are absent within a molecule.
The copper(II) complex 7 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group Ic with the complex molecule (Figure 8) and two molecules of THF in the asymmetric unit (Figure 9). One of the THF molecules is disordered in two positions (40.3/59.7%), and was treated with a split atom model (Figure 9). The composition of the complex is (HL)Cu(acetate)2. In this complex, the heteroscorpionate ligand unusually still has a hydrogen atom on O1, showing an intramolecular interaction with O5 (O1-H1O···O5: 2.556(5) Å, 166(6)°). One of the acetate groups is bound to the central copper atom via the atoms O2 and O3 (Cu1-O2: 1.944(5) Å; Cu1-O3: 2.557(4) Å), while O2 shows an additional intramolecular interaction to H5C (C5-H5C···O2: 3.146(7) Å). The second acetate group is coordinated to the copper atom only via the O4 atom since O5 interacts in the mentioned hydrogen bond to O1 and an additional interaction to H20 (C20-H20···O5: 3.075(6) Å). One dimethylpyrazolyl group interacts only in the mentioned C5-H5···O2 intramolecular contact. The second dimethylpyrazolyl group shows no intramolecular contacts due to the disorder in two positions (39.7/60.3%), and gives an intramolecular contact to O3 only in the main disorder part (C10B-H10E···O3: 2.482 Å). The aryl units in 7 show intramolecular π stacking interactions (3.99 Å) between adjacent pyrazolyl moieties as well as intramolecular C-H···π contacts with the disordered pyrazolyl rings (2.8 and 2.9 Å).
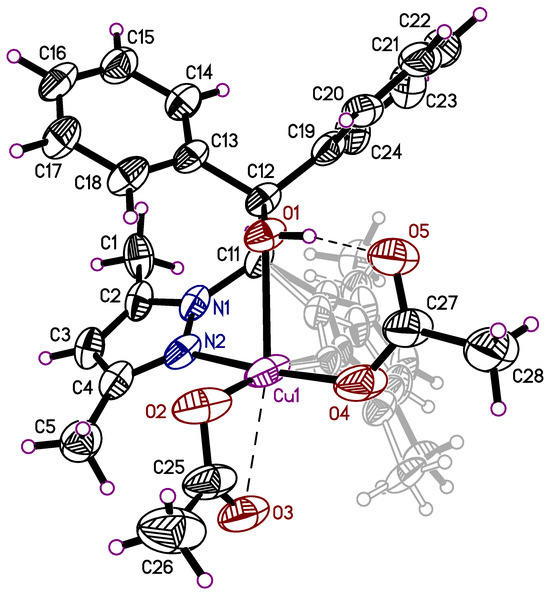
Figure 8.
Molecular structure of 7, the two THF guest molecules are omitted for clarity and shown in Figure 9. The thermal ellipsoids of the non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level (the disordered dimethylpyrazolyl group behind the acetate group is shown in grey, allowing better visibility of the acetate coordination).
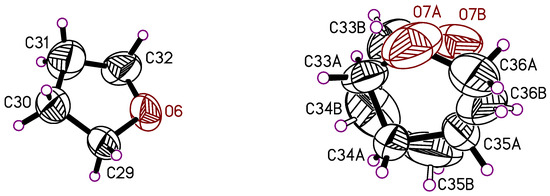
Figure 9.
THF molecules, which are present in the crystal structure of 7. The thermal ellipsoids of the non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
The oxygen atom O3 is significantly further away from the copper atom than the oxygen atom O2. If we, therefore, initially ignore the interaction with O3, we can consider the complex to be fivefold coordinated. The parameter τ from Addison et al. has proven useful for analyzing the coordination geometry of fivefold coordinated complexes [67]. The largest bond angle β and the second largest angle α at the central atom are used to calculate this parameter with τ = (β − α)/60°. If τ = 0, it is a perfect square pyramid, while τ = 1 indicates a perfect trigonal bipyramid. The largest bond angle is O4-Cu1-N2 with 174.7(2)°, and the second largest is O2-Cu1-N4A with 171.6(6)°. The parameter τ calculated from these is 0.05. That means the copper complex is a nearly perfect square pyramid. However, the long-distance interaction Cu1…O3 [2.557(4) Å] supplements the coordination sphere to an octahedron with one elongated axis.
This distorted and, compared to the other transition metal complexes presented here, unusual coordination geometry of the copper complex is due to the d9 configuration of the Cu2+ ion. This leads to a Jahn–Teller distortion of the complex [68]. Copper(II) complexes can adopt many different coordination geometries. A square-pyramidal fivefold coordinated complex with an additional coordination to a sixth more distant ligand is not uncommon [69,70].
The copper(II) ions seem to prefer hexacoordination with two heteroscorpionate ligands and yields mainly complexes of the type L2Cu, as can be seen from a number of such complexes in the literature [36,71,72,73,74,75,76].
The silicon(IV) complex 8 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with the silicon complex (Figure 10) and one molecule of 1,2-dimethoxyethane in the asymmetric unit (Figure 11). One oxygen atom of the solvent molecule is disordered. The composition of the complex is (L)Si(Me)2Cl. The central silicon atom is bound to two methyl groups, one chlorine atom, and the oxygen atom O1 of the heteroscorpionate ligand. Furthermore, there is an interaction between N2 from one of the dimethylpyrazolyl groups and the silicon atom, making the silicon atom pentacoordinate. This is in contrast to the other structures presented in this paper. Herein, the heteroscorpionate ligand coordinates only via one nitrogen atom at the central silicon atom. Furthermore, the N2 atom shows intramolecular C-H···N interactions to the methyl groups coordinated at the central silicon atom (2.49–2.57 Å). The coordination geometry can also be characterized with the parameter τ (see above). The largest bond angle at the silicon atom is Cl1-Si1-N2 with 175.15°, and the second largest is O1-Si1-C25 with 122.28 (9)°, which gives a value of τ = 0.88 and corresponds to a distorted trigonal bipyramid. The atoms N2 and Cl1 are in axial position, and the atoms O1, C25, and C26 are in the equatorial plane.
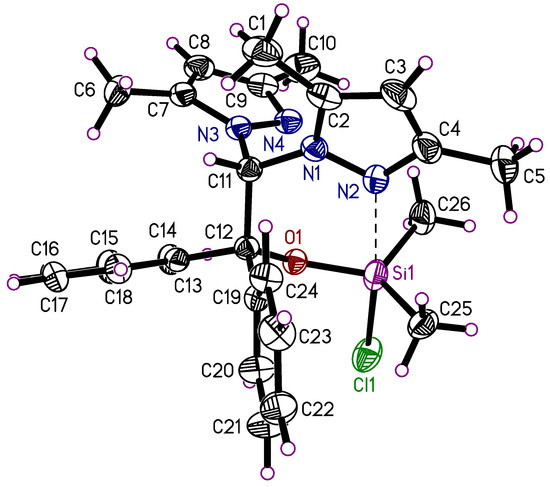
Figure 10.
Molecular structure of 8, the DME guest molecule is omitted for clarity and shown in Figure 11. The thermal ellipsoids of the non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
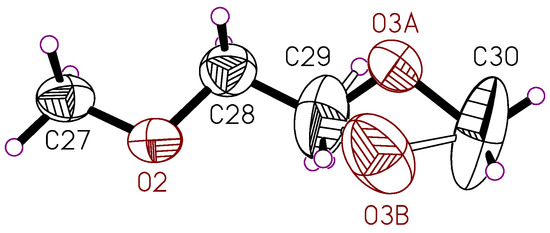
Figure 11.
1,2-dimethoxyethane molecule, which is present in the crystal structure of 8. The thermal ellipsoids of the non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Within the complex molecule 8, C-H···π contacts between the aryl rings and the pyrazolyl groups (2.77 and 2.86 Å) complete the intramolecular interactions influencing the molecular structure.
There are no comparable heteroscorpionate complexes of silicon in the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD version 5.45 update on March 2024) [77]. However, various 3,5-dimethylpyrazole complexes of silicon have already been described in the literature [78,79].
The germanium(IV) complex 9 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group Cc with one product molecule of the composition LGeCl3 in the asymmetric unit (Figure 12 top). The complex shows the expected octahedral coordination geometry and is directly comparable with the zirconium complex 3 since both complexes have the same composition as LMCl3. A fitting plot of both molecules is shown in Figure 12 (bottom) with the atoms Ge/Zr, N2, N4, and O1 as reference points. There is an R.M.S. deviation of all atoms of the structures of 0.14 Å. The overall geometries of both complexes are very similar. The phenyl group C13-C18 has a slightly differing orientation in both complexes. The shorter atomic radius of germanium is also visible in the fitting plot. These bond length differences are further substantiated in Table 5. The difference in the atomic radii of zirconium and germanium is 0.26 Å. The differences in the bond lengths fluctuate around this value, but tend to be somewhat smaller than expected.
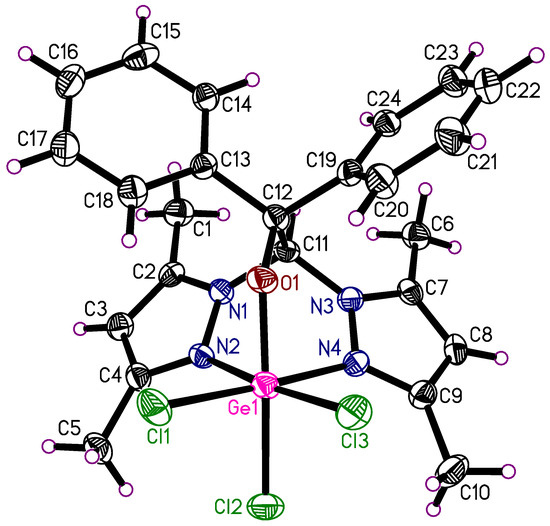
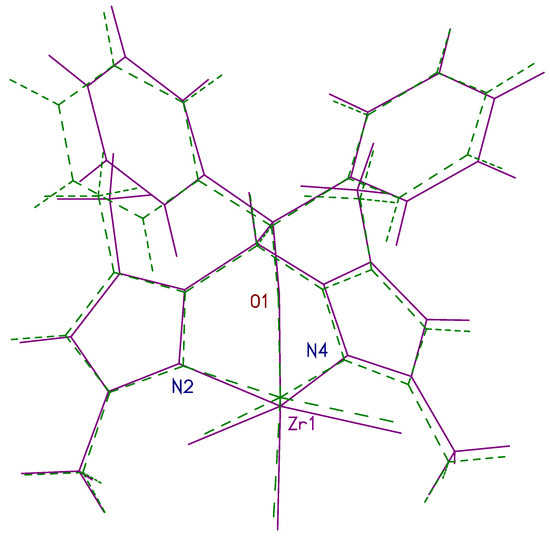
Figure 12.
Molecular structure of 9 (top). The thermal ellipsoids of the non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level. Molecule fitting of 3 and 9 (bottom; dashed lines—germanium complex 3; full lines—zirconium complex 9).

Table 5.
Selected bond lengths in 3 and 9 and differences between these (all values in Å). The atomic radii in the last line are taken from [61].
As expected, the molecular structure of 9 is similar to 3 and is influenced by identical intramolecular C-H···Cl and C-H···O contacts. The lengths in 9 are shorter in contrast to 3. While the C-H···Cl contacts are 2.62 and 2.63 Å, the C-H···O contacts are about 2.30 and 2.33 Å. As in 3, the aryl units do not take part in intramolecular interaction to form the molecular arrangement.
3.2. Discussion of the Outcome of the Reactions
Simplified structural formulas of the complexes under discussion are shown in Scheme 5. The deprotonated ligand (L) usually occupies three coordination sites at the metal complexes investigated here (coordinating atoms are marked in red in the figure). Exceptions are the copper complex 7, where the ligand is still protonated, and the silicon complex 8, where the heteroscorpionate ligand acts as a bidentate ligand. The compounds 2–6 and 9 reach hexacoordination for the central atoms. In the case of compounds 4 and 5, dimeric oxygen-bridged complexes were obtained.
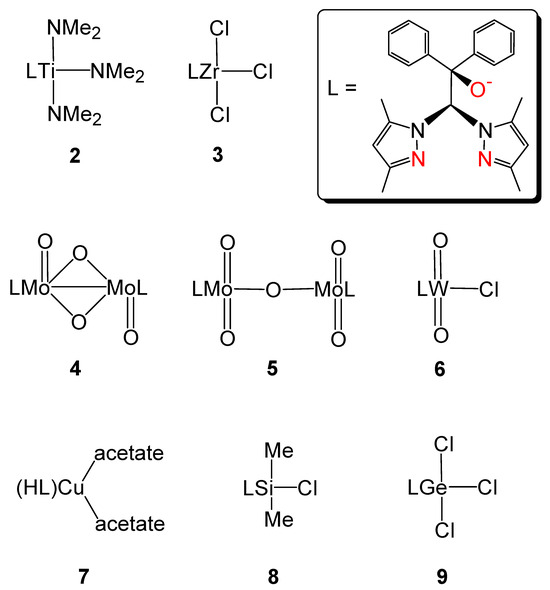
Scheme 5.
Structurally characterized compounds in this paper with L = 2,2-bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)-1,1-diphenylethanolat.
Molybdenum hexacarbonyl showed no signs of reaction with the ligand even after a six-week waiting period. It is known from the literature that molybdenum hexacarbonyl can be oxidized and complexed by oxidation with oxygen or suitable oxidants in the presence of chelating ligands [64,80,81]. We made use of this knowledge by flushing the reaction vessel with air. The reaction mixture then became opaque within a few days, and after eight weeks, two different crystalline products could be identified from the reaction mixture. These are the molybdenum(V) complex 4 and the molybdenum(VI) complex 5, both of which are present as binuclear oxygen-bridged dimers. Similar oxygen-bridged molybdenum complexes of both types are described in the literature [41,63]. The reaction equations in Scheme 6 describe the formation of these compounds. Future investigations will focus on the selective synthesis of both complexes, but this was outside the scope of this work.
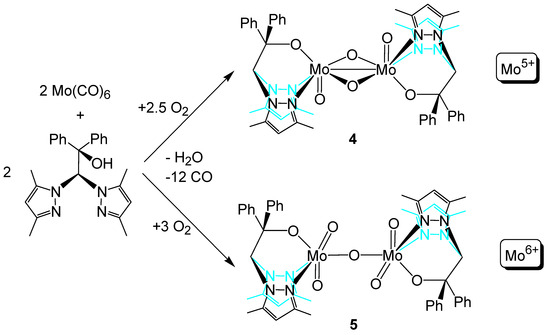
Scheme 6.
Formation of oxygen-bridged complexes 4 and 5.
To be honest, the heteroscorpionate complex of tungsten presented here (6) originates from a failed experiment. It was shown in the literature that it is possible to reduce the analogous heteroscorpionate complex of molybdenum(VI) to a molybdenum(IV) complex by reducing the thetriphenylphophine in the presence of pyridine as an additional neutral ligand (Scheme 7) [40,41]. Our aim was to reduce the previously published tungsten(VI) complex to the tungsten(IV) complex using the same method. This failed. Instead, a crystalline pseudopolymorph of 6 was obtained. That means no real reaction took place, and the compound was instead recrystallized from pyridine.
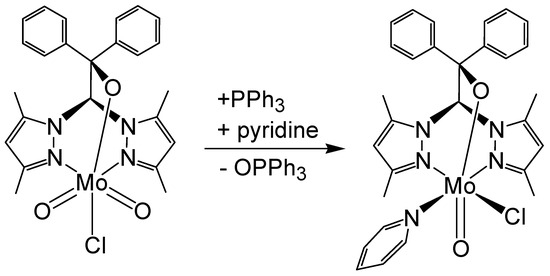
Scheme 7.
Reduction of a heteroscorpionate–molybdenum(VI) complex with triphenylphosphine in the presence of pyridine after [41].
Compounds 7 and 8 show special features regarding the coordination of the central atoms. In the copper complex 7, the coordination of the central atom is generated by the three atoms (N, N, and O) from the heteroscorpionate ligand and two oxygen atoms of the acetate groups, thereby forming a pentagonal pyramidal copper complex (Scheme 8). Additionally, there is a long-distance interaction between a second oxygen atom from one of the acetate groups with the central atom.
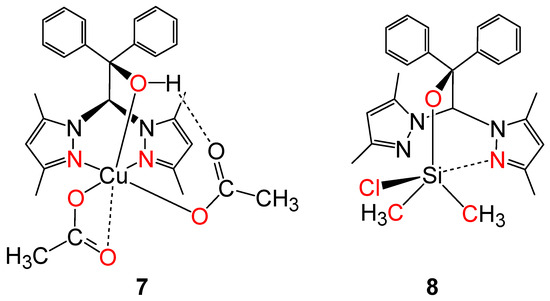
Scheme 8.
Coordination of the central atoms in compounds 7 and 8.
In the silicon complex 8, the heteroscorpionate ligand coordinates only via the oxygen atom and one of the dimethylpyrazolyl nitrogen atoms to the silicon atom. Additionally, a chlorine atom and two methyl groups are bound to the silicon atom. It results in a pentacoordination of the silicon atom in the solid-state structure (Scheme 8). Furthermore, there is a discrepancy between the NMR chemical shift in the solid state and in the solution. A chemical shift of δiso = −31.70 ppm is observed in the 29Si solid state NMR spectrum, including typical values of the 29Si NMR tensor components for a pentacoordinate complex (see Experimental section). In contrast to that, the 29Si NMR the spectrum in the solution features a chemical shift of δ = −21.9 ppm. That means the complex in the solution is tetracoordinated.
4. Conclusions
We aimed to develop a simple and robust synthetic method for heteroscorpionate complexes without using bases such as NaH, NaOMe, or KtOBu. Simple mixing of the heteroscorpionate ligand with suitable metal-containing reagents proved successful, yielding the desired complexes in moderate to good yields as single crystals suitable for X-ray crystallography. The batch products obtained via this simplified workup procedure contain several impurities, as evidenced by the NMR data (see Supporting Information). Additional recrystallization steps may, therefore, be required. A further drawback of this approach is the extended time needed to obtain single crystals in some cases. We demonstrated that the reaction time could be significantly reduced by stirring the reaction mixture for 48 h, followed by the standard workup procedure. However, this modified method did not produce crystalline material, but rather a powder-like product.
Several surprising results were obtained from the syntheses performed. In the case of the reaction of Mo(CO)6, a mixture of two reaction products was formed, which is problematic for the further use of these molybdenum complexes. However, the two molybdenum complexes isolated give insight into the structural diversity of these heteroscorpionate complexes. A new pseudopolymorph of the previously described tungsten complex 6 was obtained. The copper complex 7 and the silicon complex 8 show some structural peculiarities in the molecular structures (discussion see previous section).
The heteroscorpionate ligand 1 is ideal as a tridentate ligand in facial coordination and stabilizes, thereby, octahedral complexes. Furthermore, 1 is able to adopt from other coordination modes.
The combination of phenyl and 1,3-dimethylpyrazolyl groups in the heteroscorpionate ligand leads to a high degree of three-dimensional order of the metal complexes derived therefrom and gives usual crystals of good quality. However, the spatially demanding substituents on the ligand cause the inclusion of solvent molecules in the crystal lattice. The refinement of these solvent molecules causes considerable problems for some of the structures discussed here.
The syntheses carried out prove that it is possible to produce metal complexes with this heteroscorpionate ligand using the base-free synthesis method developed by us. This method for the preparation of heteroscorpionate complexes is widely applicable, as we were able to show using examples of complex compounds of various transition metal ions and main group element derivatives.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cryst15100865/s1, Figure S1. 1H NMR spectrum of 2 in DMSO-d6 (400.13 MHz at 298 K). Figure S2. 13C NMR spectrum of 2 in DMSO-d6 (100.62 MHz at 298 K). Figure S3. 1H NMR spectrum of 3 in DMSO-d6 (500.13 MHz at 298 K). Figure S4. 13C NMR spectrum of 3 in DMSO-d6 (125.77 MHz at 298 K). Figure S5. 1H NMR spectrum of 4 and 5 in CDCl3 (400.13 MHz at 298 K). Figure S6. 13C NMR spectrum of 4 and 5 in CDCl3 (100.61 MHz at 298 K). Figure S7. 1H NMR spectrum of 6 in DMSO-d6 (400.13 MHz at 298 K). Figure S8. 13C NMR spectrum of 6 in DMSO-d6 (100.62 MHz at 298 K). Figure S9. 1H NMR spectrum of 7 in CDCl3 (500.13 MHz at 298 K). Figure S10. 13C NMR spectrum of 7 in CDCl3 (125.76 MHz at 298 K). Figure S11. 29Si NMR spectrum of 8 in CDCl3 (79.49 MHz at 298 K). Figure S12. 1H NMR spectrum of 8 in CDCl3 (400.13 MHz at 298 K). Figure S13. 13C NMR spectrum of 8 in CDCl3 (100.61 MHz at 298 K). Figure S14. 1H NMR spectrum of 9 in DMSO-d6 (500.13 MHz at 298 K). Figure S15. 13C NMR spectrum of 9 in DMSO-d6 (125.76 MHz at 298 K). checkCIF/PLATON report: bg813_5_checkcif, bg891_5_publ_checkcif. bg892sq_2_checkcif, BG892_54_checkcif. bg903_3_sq_checkcif. BG939_03_checkcif. BG943_02_checkcif. BG950_1_checkcif.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, U.B. and B.G.; Methodology, U.B.; Validation, U.B. and A.S.; Formal analysis, U.B. and A.S.; Investigation, U.B., B.G. and A.S.; Data curation, U.B., B.G. and A.S.; Writing—original draft, U.B.; Writing—review & editing, U.B. and A.S.; Visualization, U.B.; Supervision, U.B.; Project administration, U.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Crystallographic datasets for the structures 2–9 are available through the Cambridge Structural Database with deposition numbers CCDC 2448688-2448695. These data can be obtained free of charge via https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/ (accessed on 14 August 2025).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank TU Bergakademie Freiberg (Freiberg, Germany) for financial support. The authors gratefully acknowledge the help from Beate Kutzner and Erica Brendler (Institute for Analytical Chemistry, TU Bergakademie Freiberg) for NMR measurements, and Katrin Fuchs for analysis of NMR spectra and IR measurements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Trofimenko, S. Boron-Pyrazole Chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 1842–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimenko, S. Boron-Pyrazole Chemistry. I. Pyrazaboles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 3165–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimenko, S. Recent advances in poly(pyrazolyl)borate (scorpionate) chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 943–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimenko, S. Scorpionates: The Coordination Chemistry of Poly(pyrazolyl)borate Ligands; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli, P.M.B.; Cowan, J.A.; Schultz, A.J.; Koetzle, T.F.; Yap, G.P.A.; Trofimenko, S. Low-temperature neutron structure determinations of a series of scorpionate complexes of molybdenum containing BHMo agostic bonds. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 890, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharbani, D.; Deb, D.K.; Mawnai, I.L.; Kurbah, S.D.; Sarkar, B.; Rymmai, E.K. Pyrazole cleavage of tris(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)borate with Ruthenium(II) complexes: Synthesis, structural characterization and DFT studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1133, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshma, G.; Nakul, S.; Mahitha, P.M.; Kulkarni, N.V.; Senthurpandi, D.; Yamijala, S.S.R.K.C.; Brennessel, W.W.; Jones, W.D. Synthesis and molecular structure of half-sandwich ruthenium(II) complexes containing pyrazolyl ligands: Solvent induced geometrical change in κ2-scorpionate supported complex. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1251, 132005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, A.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Antinolo, A.; Tejeda, J.; Lara-Sanchez, A. Heteroscorpionate ligands based on bis(pyrazol-1-yl)methane: Design and coordination chemistry. Dalton Trans. 2004, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, A.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Antinolo, A.; Tejeda, J.; Lara-Sanchez, A.; Sanchez-Barba, L.F.; Sanchez-Molina, M.; Franco, S.; Lopez-Solera, M.I.; Rodriguez, A.M. Design of new heteroscorpionate ligands and their coordinative ability toward Group 4 transition metals; an efficient synthetic route to obtain enantiopure ligands. Dalton Trans. 2006, 4359–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, E.; Haas, T.; Burzlaff, N. Synthesis and Transition Metal Complexes of Novel N,N,O Scorpionate Ligands Suitable for Solid Phase Immobilisation. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 2006, 4989–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, E.; Türkoglu, G.; Wolf, M.; Zenneck, U.; Burzlaff, N. Novel N,N,O Scorpionate Ligands and Transition Metal Complexes Thereof Suitable for Polymerisation. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 2008, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, A.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Lara-Sanchez, A.; Tejeda, J.; Sanchez-Barba, L.F. Recent Advances in the Design and Coordination Chemistry of Heteroscorpionate Ligands Bearing Stereogenic Centres. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 2008, 5309–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, A.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Lara-Sanchez, A.; Sanchez-Barba, L.F. Metal complexes with heteroscorpionate ligands based on the bis(pyrazol-1-yl)methane moiety: Catalytic chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 1806–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinari, C.; Pettinari, R.; Marchetti, F. Chapter Four—Golden Jubilee for Scorpionates: Recent Advances in Organometallic Chemistry and Their Role in Catalysis. Adv. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 65, 175–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrano, C.J. A Family of Homo- and Heteroscorpionate Ligands: Applications to Bioinorganic Chemistry. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2016, 2377–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Počkaj, M.; Kitanovski, N. A Novel Tetranuclear Silver Compound with bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)acetate: A Simple Synthesis Yielding Complex Crystal Structure. Acta Chim. Slov. 2018, 65, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, K.; Kuboniwa, A.; Tan, S.L.; Tiekink, E.R.T. Structural and Hirshfeld Surface Analysis of Thallium(I) and Indium(III) Complexes of a Soft Scorpionate Ligand. Crystals 2023, 13, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SShatokhin, S.; Tuskaev, V.A.; Gagieva, S.C.; Rybalkina, E.Y.; Pozdnyakov, D.I.; Melnikova, E.K.; Denisov, G.L.; Zubkevich, S.V.; Oganesyan, E.T. Synthesis, structural characterization, antioxidant and cytotoxic activity towards human cancer cell lines and computational studies of new Ni(II), Co(II) and Pd(II) complexes with 3-[bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)methyl]chromen-4-one derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1241, 130706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzegai, W.; Reil, M.; Burzlaff, N. Bis(4-carboxylpyrazol-1-yl)acetic acid: A scorpionate ligand for complexes with improved water solubility. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 6839–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflock, S.; Langer, F.; Reil, M.; Strinitz, L.; Lorenz, R.; Hübner, E.G.; Burzlaff, N. p-Block metal complexes with bis(pyrazol-1-yl)acetato ligands. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 3902–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzlaff, N. Tripodal N, N, O-ligands for metalloenzyme models and organometallics. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 60, 101–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Garcés, A.; Fajardo, M.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Otero, A.; Antiñolo, A.; Tejeda, J.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; López-Solera, M.I. Well-Defined Alkyl Heteroscorpionate Magnesium Complexes as Excellent Initiators for the ROP of Cyclic Esters. Organometallics 2007, 26, 6403–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cui, D. Heteroscorpionate Rare-Earth Metal Zwitterionic Complexes: Syntheses, Characterization, and Heteroselective Catalysis on the Ring-Opening Polymerization of rac-Lactide. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 11520–11526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, S.; Navarro, M.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; Garcés, A.; Castro-Osma, J.A.; Rodríguez, A.M. Efficient Production of Poly(Cyclohexene Carbonate) via ROCOP of Cyclohexene Oxide and CO2 Mediated by NNO-Scorpionate Zinc Complexes. Polymers 2020, 12, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, A.; Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Otero, A.; Fernández, I.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; Rodríguez, A.M. Organo-Aluminum and Zinc Acetamidinates: Preparation, Coordination Ability, and Ring-Opening Polymerization Processes of Cyclic Esters. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 12132–12142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Martínez de Sarasa Buchaca, M.; de la Cruz-Martínez, F.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Rodríguez, A.M.; Rodríguez-Diéguez, A.; Castro-Osma, J.A.; Otero, A.; et al. Versatile organoaluminium catalysts based on heteroscorpionate ligands for the preparation of polyesters. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 7471–7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.; Otero, A.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; Castro-Osma, J.A.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Rodríguez, A.M. Heteroscorpionate Rare-Earth Catalysts for the Hydroalkoxylation/Cyclization of Alkynyl Alcohols. Organometallics 2016, 35, 1802–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cruz-Martínez, F.; Martínez de Sarasa Buchaca, M.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Rodríguez, A.M.; Castro-Osma, J.A.; Lara-Sánchez, A. Zinc-Catalyzed Hydroalkoxylation/Cyclization of Alkynyl Alcohols. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 5322–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, M.; Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Garcés, A.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Fernández, I.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; Rodríguez, A.M. Bimetallic scorpionate-based helical organoaluminum complexes for efficient carbon dioxide fixation into a variety of cyclic carbonates. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 3265–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Baeza, J.; Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; Sobrino, S.; Martínez-Ferrer, J.; Garcés, A.; Navarro, M.; Rodríguez, A.M. NNC-Scorpionate Zirconium-Based Bicomponent Systems for the Efficient CO2 Fixation into a Variety of Cyclic Carbonates. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 12422–12430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cruz-Martínez, F.; de Sarasa Buchaca, M.M.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Rodríguez, A.M.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; Castro-Osma, J.A.; Lara-Sánchez, A. Heteroscorpionate Rare-Earth Catalysts for the Low-Pressure Coupling Reaction of CO2 and Cyclohexene Oxide. Organometallics 2021, 40, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, S.; Mahendiran, D.; Selvan, D.A.; Rahiman, A.K. Bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane-based heteroscorpionate metal(II) complexes: Theoretical, antimicrobial, antioxidant, in vitro cytotoxicity and c-Met tyrosine kinase studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1196, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, S.; Mahendiran, D.; Rahiman, A.K. Theoretical, antimicrobial, antioxidant, in vitro cytotoxicity, and cyclin-dependent kinase 2 inhibitor studies of metal(II) complexes with bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane-based heteroscorpionate ligands. J. Coord. Chem. 2019, 72, 2015–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, S.; Mahendiran, D.; Viswanathan, V.; Velmurugan, D.; Rahiman, A.K. Heteroscorpionate-based heteroleptic copper(II) complexes: Antioxidant, molecular docking and in vitro cytotoxicity studies. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, 2351–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellei, M.; Gandin, V.; Cimarelli, C.; Quaglia, W.; Mosca, N.; Bagnarelli, L.; Marzano, C.; Santini, C. Syntheses and biological studies of nitroimidazole conjugated heteroscorpionate ligands and related Cu(I) and Cu(II) complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2018, 187, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellei, M.; Gandin, V.; Marchio, L.; Marzano, C.; Bagnarelli, L.; Santini, C. Syntheses and biological studies of Cu(II) complexes bearing bis(pyrazol-1-yl)- and bis(triazol-1-yl)-acetato heteroscorpionate ligands. Molecules 2019, 24, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellei, M.; Bagnarelli, L.; Luciani, L.; Del Bello, F.; Giorgioni, G.; Piergentili, A.; Quaglia, W.; De Franco, M.; Gandin, V.; Marzano, C.; et al. Synthesis and Cytotoxic Activity Evaluation of New Cu(I) Complexes of Bis(pyrazol-1-yl) Acetate Ligands Functionalized with an NMDA Receptor Antagonist. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellei, M.; Santini, C.; Bagnarelli, L.; Battocchio, C.; Iucci, G.; Venditti, I.; Meneghini, C.; Amatori, S.; Sgarbossa, P.; Marzano, C.; et al. Exploring the Antitumor Potential of Copper Complexes Based on Ester Derivatives of Bis(pyrazol-1-yl)acetate Ligands. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellei, M.; Santini, C.; Bagnarelli, L.; Caviglia, M.; Sgarbossa, P.; De Franco, M.; Zancato, M.; Marzano, C.; Gandin, V. Novel Silver Complexes Based on Phosphanes and Ester Derivatives of Bis(pyrazol-1-yl)acetate Ligands Targeting TrxR: New Promising Chemotherapeutic Tools Relevant to SCLC Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.T.; Einwaechter, S.; Chohan, B.S.; Basu, P.; Carrano, C.J. Isomerization and Oxygen Atom Transfer Reactivity in Oxo−Mo Complexes of Relevance to Molybdoenzymes. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 7573–7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.T.; Tran, B.L.; Carrano, C.J. Oxidation-state and metal-ion dependent stereoisomerization in oxo molybdenum and tungsten complexes of a bulky alkoxy heteroscorpionate ligand. Dalton Trans. 2006, 3822–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, B.L.; Carrano, C.J. Synthesis and characterization of heteroscorpionate dioxo-tungsten(VI) complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2007, 360, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cui, D.; Trifonov, A.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Heteroscorpionate Rare-Earth Metal Dialkyl Complexes and Catalysis on MMA Polymerization. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2010, 2861–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvortsov, G.G.; Cherkasov, A.V.; Fukin, G.K.; Trifonov, A.A. Yttrium complexes containing heteroscorpionate ligands [(3,5-But2C3HN2)2CHC(Ph)2O]− and [o-Me2NC6H4CH2C(NCy)2]−. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2016, 65, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampier, S.; Burzlaff, N. Heteroscorpionate complexes based on bis(3,5-di-tert-butylpyrazol-1-yl)dithioacetate. Acta Cryst. C 2013, 69, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trofimenko, S.; Jové, F.; Yap, G.P.A. An unusual bis-heteroscorpionate complex with anomalous ligands: [tris(3,4-dibromo-5-phenylpyrazolyl)hydroborato][hydrotris(3-neopentylpyrazolyl)borato]nickel(II). Acta Cryst. C 2016, 72, 802–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, A.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Antinolo, A.; Tejeda, J.; Lara-Sanchez, A.; Sanchez-Barba, L.F.; Sanchez-Molina, M.; Franco, S.; Lopez-Solera, M.I.; Rodriguez, A.M. Highly Diastereoselective Nucleophilic Addition to Myrtenal. Straightforward Synthesis of an Enantiopure Scorpionate Ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 8475–8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, A.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Tejeda, J.; Lara-Sanchez, A.; Sanchez-Molina, M.; Franco, S.; Lopez-Solera, I.; Rodriguez, A.M. On the Search for NNO-Donor Enantiopure Scorpionate Ligands and Their Coordination to Group 4 Metals. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 5540–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagunas-Simón, B.; González-Montiel, S.; Salazar-Pereda, V.; Vásquez-Pérez, J.M.; Cruz-Borbolla, J. An structural study of Pt•••Hδ–C(sp3) anagostic interaction in heteroscorpionate complexes. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1300, 137289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, A.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Antiñolo, A.; Tejeda, J.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; Sánchez-Barba, L.; Fernández-López, M.; López-Solera, I. New Complexes of Zirconium(IV) and Hafnium(IV) with Heteroscorpionate Ligands and the Hydrolysis of Such Complexes To Give a Zirconium Cluster. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, U.; Schwarzer, A.; Günther, B. The heteroscorpionate ligand 2,2-bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)-1,1-diphenylethanol and an easy preparation of its tungsten complex. Acta Cryst. C 2019, 75, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, S.; Dehnert, J. Eine rationelle anaerobe Arbeitsmethode. Z. Chem. 1964, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, U. Inertgastechnik; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoe&Cie. X-RED and X-AREA; Stoe&Cie: Darmstadt, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. Single crystal structure validation with the program PLATON. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A. PLATON SQUEEZE: A tool for the calculation of the disordered solvent contribution to the calculated structure factors. Acta Crystallogr. C 2015, 71, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A. checkCIF validation ALERTS: What they mean and how to respond. Acta Crystallogr. E 2020, 76, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milione, S.; Bertolasi, V.; Cuenca, T.; Grassi, A. Titanium Complexes Bearing a Hemilabile Heteroscorpionate Ligand: Synthesis, Reactivity, and Olefin Polymerization Activity. Organometallics 2005, 24, 4915–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauling, L. Die Natur der Chemischen Bindung; Verlag Chemie: Weinheim/Bergstr, Germany, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Aguado, R.; Escribano, J.; Pedrosa, M.R.; De Cian, A.; Sanz, R.; Arnáiz, F.J. Binuclear oxomolybdenum(V) chlorides: Molecular structure of Mo2O4Cl2(DMF)4 and Mo2O4Cl2(bipy)2·DMF. Polyhedron 2007, 26, 3842–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitanovski, N.; Golobič, A.; Čeh, B. Synthesis and structural characterization of mono- and dinuclear Mo(V)-oxo-complexes containing bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)acetate anion as ligand. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2011, 14, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinoi, C.; da Silva, M.F.C.G.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Smoleński, P.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Poli, R.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Molybdenum Complexes Bearing the Tris(1-pyrazolyl)methanesulfonate Ligand: Synthesis, Characterization and Electrochemical Behaviour. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2010, 2415–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitanovski, N.; Golobič, A.; Čeh, B. Syntheses and structural characterization of two novel oxygen bridged dinuclear Mo-complexes containing bdmpza as ligand, trans-[Mo2O5(bdmpza)2] and trans-[Mo2O3(NCS)2(bdmpza)2]·4CH3CN. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2006, 9, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, B.S.; Chohan, B.S.; Hoffman, J.T.; Einwächter, S.; Carrano, C.J. A Family of Dioxo−Molybdenum(VI) Complexes of N2X Heteroscorpionate Ligands of Relevance to Molybdoenzymes. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 7800–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addison, A.W.; Rao, T.N.; Reedijk, J.; van Rijn, J.; Verschoor, G.C. Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopic properties of copper(II) compounds containing nitrogen-sulphur donor ligands; the crystal and molecular structure of aqua [1,7-bis (N-methylbenzimidazol-2′-yl)-2,6-dithiaheptane]-copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans 1984, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G. Anorganische Chemie, 4th ed.; Verlag Chemie: Weinheim, Germany, 1982; p. 828. [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway, B.J. Copper(II). In Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry; Wilkinson, G., Gillard, R.D., McCleverty, J.A., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; Volume 5, pp. 594–650. [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway, B.J.; Billing, D.E. The electronic properties and stereochemistry of mono-nuclear complexes of the copper(II) ion. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1970, 5, 143–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, V.; Thilagar, P.; Senapati, T. Transition Metal-Assisted Hydrolysis of Pyrazole-Appended Organooxotin Carboxylates Accompanied by Ligand Transfer. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 2007, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkoglu, G.; Ulldemolins, C.P.; Müller, R.; Hübner, E.; Heinemann, F.W.; Wolf, M.; Burzlaff, N. Bis(3,5-dimethyl-4-vinylpyrazol-1-yl)acetic Acid: A New Heteroscorpionate Building Block for Copolymers that Mimic the 2-His-1-carboxylate Facial Triad. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2010, 2962–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkoglu, G.; Heinemann, F.W.; Burzlaff, N. Transition metal complexes bearing a 2,2-bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)propionate ligand: One methyl more matters. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 4678–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlevčar, B.; Gamez, P.; de Gelder, R.; Driessen, W.L.; Reedijk, J. Unprecedented Change of the Jahn−Teller Axis in a Centrosymmetric CuII Complex Induced by Lattice Water Molecules—Crystal and Molecular Structures of Bis[bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)acetato]copper(II) and Its Dihydrate. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 2003, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quillian, B.; Lynch, W.E.; Padgett, C.W.; Lorbecki, A.; Petrillo, A.; Tran, M. Syntheses and Crystal Structures of Copper(II) Bis(pyrazolyl)acetic Acid Complexes. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2019, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlevčar, B.; Počkaj, M.; Kitanovski, N. IR analysis of the carboxylate forms in structurally determined [CuII(κ3-L)2] species isolated from different acidic solutions. Maced. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2015, 34, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, C.R.; Bruno, I.J.; Lightfoot, M.P.; Ward, S.C. The Cambridge Structural Database. Acta Cryst. B 2016, 72, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitto, F.; Kraushaar, K.; Böhme, U.; Brendler, E.; Wagler, J.; Kroke, E. Chlorosilanes and 3,5-Dimethylpyrazole: Multinuclear Complexes, Acetonitrile Insertion and 29Si NMR Chemical-Shift Anisotropy Studies. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 2954–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitto, F.; Brendler, E.; Böhme, U.; Wagler, J.; Kroke, E. 3,5-Dimethylpyrazolyl-Substituted Di- and Trisiloxanes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2016, 4207–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.C.; Neves, P.; Figueiredo, S.; Fernandes, J.A.; Valente, A.A.; Paz, F.A.A.; Pillinger, M.; Lopes, A.D.; Gonçalves, I.S. Tris(pyrazolyl)methane molybdenum tricarbonyl complexes as catalyst precursors for olefin epoxidation. J. Mol. Cat. A Chem. 2013, 370, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.A. Structural studies of some chromium and molybdenum complexes of 5,6-benzoquinoline. J. Coord. Chem. 2006, 59, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).