Enhanced Fracture Toughness and High-Temperature Strength of Directionally Solidified Mo-XC Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results & Discussion
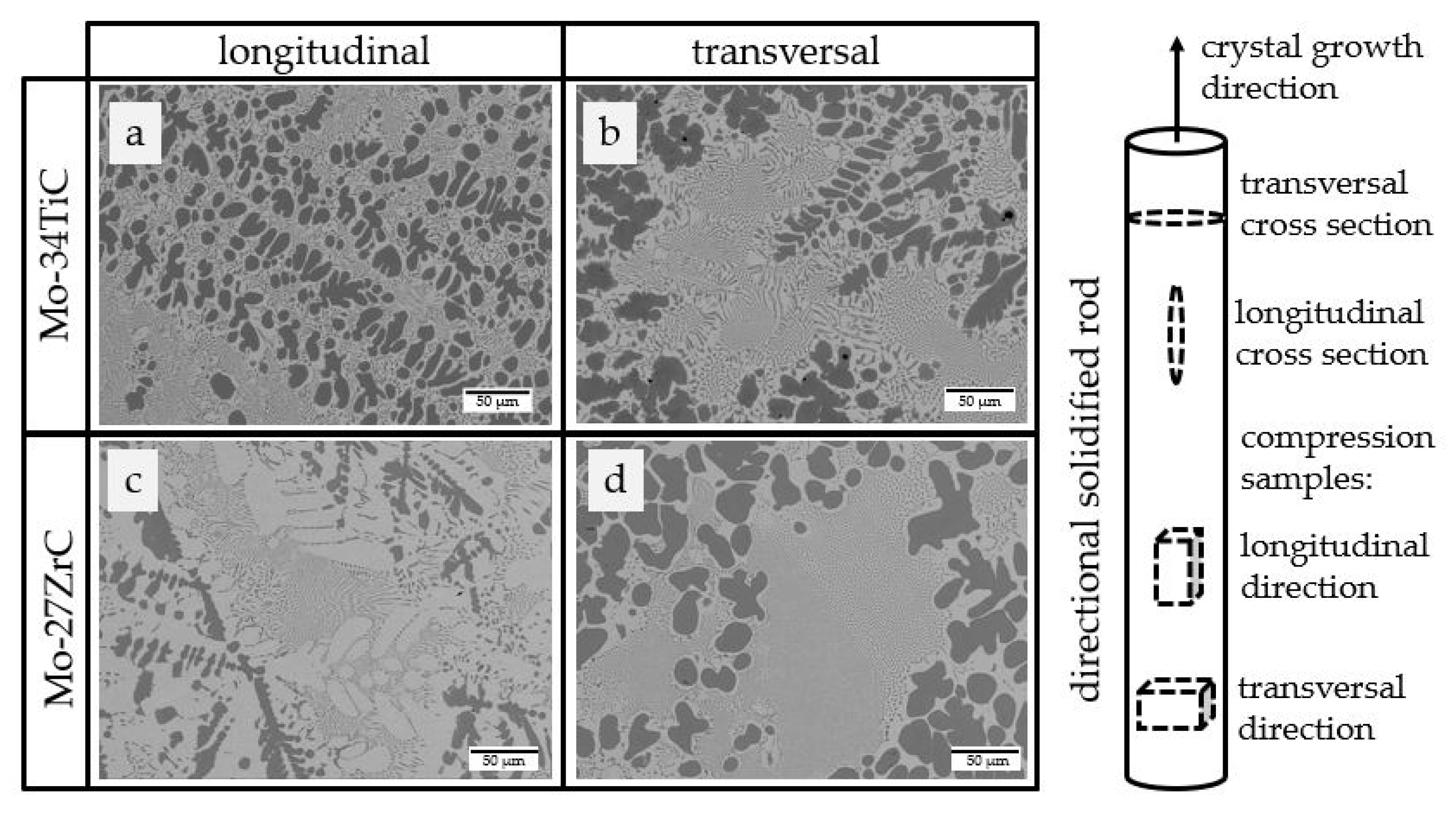
3.1. Microstructures
3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.2.1. Fracture Toughness
3.2.2. Compressive Strength
4. Conclusions
- The cross sections of Mo-34TiC and Mo-27ZrC show microstructures with eutectic colonies with preferred orientation as well as coarse dendritic regions;
- The fracture toughness of 26 MPa m1/2 for the Mo-27ZrC alloy is higher compared with Mo-34TiC (16 MPa m1/2), affected by the homogeneity and fraction of the Moss phase. The reasons for the comparatively high values are the high crack energy dissipation at the phase boundaries (testing the samples perpendicular to growth direction), the homogeneous distribution of the Moss phase and acceptable values for the oxygen content being similar to those shown in studies by Bolbut et al. [20]. This indicates that stable crack growth at an early stage of fracture resulted in a superior fracture performance of Mo-27ZrC;
- Uniaxial compression tests on longitudinal and transversal specimens displays anisotropic deformation behavior. A specimen in the transversal section shows higher yield stresses, whereas a specimen in the longitudinal section offers a decrease of strength with increasing temperatures; and
- A specimen tested in the transversal section shows a higher ductility between 400 °C and 800 °C. Both longitudinal samples show a plateau-like plastic strain at temperatures lower than 800 °C, while the potential of plasticity is higher in Mo-27ZrC. The longitudinal sample of Mo-34TiC seems to have a BDTT between 800 °C and 1000 °C.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heumüller, H. Refraktärmetalle—Schlüsselwerkstoffe für die Hightech-Industrie. World Metall.—ERZMETALL 2008, 61, 352–389. [Google Scholar]
- Cédat, D.; Rey, C.; Clavel, M.; Schmitt, J.H.; Le Flem, M.; Allemand, A. Microstructural characterization of a composite Mo reinforced by 25 at.% TiC. J. Nucl. Mater. 2009, 385, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohyama, A.; Igata, N. Surface radiation damage in Mo-TiC eutectic alloy and TiC bombarded by Ar+ and He+ Ions. J. Nucl. Mater. 1981, 103, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurishita, H.; Shiraishi, J.; Matsubara, R.; Yoshinaga, H. Measurement and Analysis of the Strength of Mo-TiC Composites in the Temperature Range 285 K-2270 K*. Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met. 1987, 28, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, Y. Strengths and ductility of Mo-TiC alloys after secondary recrystallization. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2003, 21, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Flem, M.; Allemand, A.; Urvoy, S.; Cédat, D.; Rey, C. Microstructure and thermal conductivity of Mo-TiC cermets processed by hot isostatic pressing. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 380, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedat, D.; Libert, M.; Le Flem, M.; Fandeur, O.; Rey, C.; Clavel, M.; Schmitt, J.-H. Experimental characterization and mechanical behaviour modelling of molybdenum-titanium carbide composite for high temperature applications. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2009, 27, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suzuki, T.; Nomura, N.; Yoshimi, K.; Hanada, S. Microstructure and Creep of Mo-ZrC In-situ Composite. Mater. Trans. JIM 2000, 41, 1164–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Nomura, N.; Hanada, S. Microstructures and fracture toughness of directionally solidifed Mo-ZrC eutectic composites. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2002, 3, 137–143. Available online: http://www.elsevier.com/locate/stam (accessed on 30 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Landwehr, S.E.; Hilmas, G.E.; Fahrenholtz, W.G.; Talmy, I.G. Processing of ZrC-Mo cermets for high-temperature applications, part I: Chemical interactions in the ZrC-Mo system. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 1998–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landwehr, S.E.; Hilmas, G.E.; Fahrenholtz, W.G.; Talmy, I.G.; Wang, H. Thermal properties and thermal shock resistance of liquid phase sintered ZrC-Mo cermets. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 115, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landwehr, S.E.; Hilmas, G.E.; Fahrenholtz, W.G.; Talmy, I.G.; DiPietro, S.G. Microstructure and mechanical characterization of ZrC-Mo cermets produced by hot isostatic pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 497, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohser-Wiedemann, R.; Weck, C.; Martin, U.; Müller, A.; Seifert, H.J. Spark plasma sintering of TiC particle-reinforced molybdenum composites. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater 2012, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takida, T.; Mabuchi, M.; Nakamura, M.; Igarashi, T.; Doi, Y.; Nagae, T. The Role of Dispersed Particles in Strengthening and Fracture Mechanisms in a Mo-ZrC Alloy Processed by Mechanical Alloying. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2000, A31, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takida, T.; Mabuchi, M.; Nakamura, M.; Igarashi, T.; Doi, Y.; Nagae, T. Mechanical properties of a ZrC-dispersed Mo alloy processed by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 276, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takida, T.; Kurishita, H.; Mabuchi, M.; Igarashi, T.; Doi, Y.; Nagae, T. Mechanical properties of fine-grained, sintered molybdenum alloys with dispersed particles developed by mechanical alloying. Mater. Trans. 2004, 45, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimi, K.; Nakamura, J.; Kanekon, D.; Yamamoto, S.; Maruyama, K.; Katsui, H.; Goto, T. High-Temperature Compressive Properties of TiC-Added Mo-Si-B Alloys. JOM 2014, 66, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, J.; Kanekon, D.; Yoshimi, K. Characterization of Mo/Mo2C interface in MoSiBTiC alloy. Mater. Lett. 2016, 180, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasemann, G.; Bogomol, I.; Schliephake, D.; Loboda, P.I.; Krüger, M. Microstructure and creep properties of a near-eutectic directionally solidified multiphase Mo–Si–B alloy. Intermetallics 2014, 48, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolbut, V.; Bogomol, I.; Bauer, C.; Krüger, M. Gerichtet erstarrte Mo-Zr-B-Legierungen: Directionally solidified Mo-Zr-B alloys. Materwiss Werksttech 2017, 48, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.; Betke, U.; Hoffmeister, M.; Krüger, M. Density Reduction of Mo-Si-B Alloys by Vanadium Alloying. JOM 2018, 70, 2574–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, D.; Heilmaier, M.; Schneibel, J.H.; Jéhanno, P.; Skrotzki, B.; Saage, H. The influence of silicon on the strength and fracture toughness of molybdenum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 463, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, H.-J. Werkstoffanalytische Verfahren; Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie: Leipzig, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, M.; Franz, S.; Saage, H.; Heilmaier, M.; Schneibel, J.; Jéhanno, P.; Böning, M.; Kestler, H. Mechanically alloyed Mo-Si-B alloys with a continuous α-Mo matrix and improved mechanical properties. Intermetallics 2008, 16, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, M.; Schliephake, D.; Jain, P.; Kumar, K.S. Effects of Zr Additions on the Microstructure and the Mechanical Behavior of PM Mo-Si-B Alloys. JOM 2013, 65, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.; Krüger, M. Impact of phase distribution on the fracture toughness of high temperature resistant Mo-Si-B alloys. Pract. Metallogr. 2015, 52, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Becker, J.; Breuer, D.; Bogomol, I.; Krüger, M. Enhanced Fracture Toughness and High-Temperature Strength of Directionally Solidified Mo-XC Alloys. Crystals 2022, 12, 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12111534
Becker J, Breuer D, Bogomol I, Krüger M. Enhanced Fracture Toughness and High-Temperature Strength of Directionally Solidified Mo-XC Alloys. Crystals. 2022; 12(11):1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12111534
Chicago/Turabian StyleBecker, Julia, Danio Breuer, Iurii Bogomol, and Manja Krüger. 2022. "Enhanced Fracture Toughness and High-Temperature Strength of Directionally Solidified Mo-XC Alloys" Crystals 12, no. 11: 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12111534
APA StyleBecker, J., Breuer, D., Bogomol, I., & Krüger, M. (2022). Enhanced Fracture Toughness and High-Temperature Strength of Directionally Solidified Mo-XC Alloys. Crystals, 12(11), 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12111534








