Strain Rate and Temperature Effects on Tensile Properties of Polycrystalline Cu6Sn5 by Molecular Dynamic Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
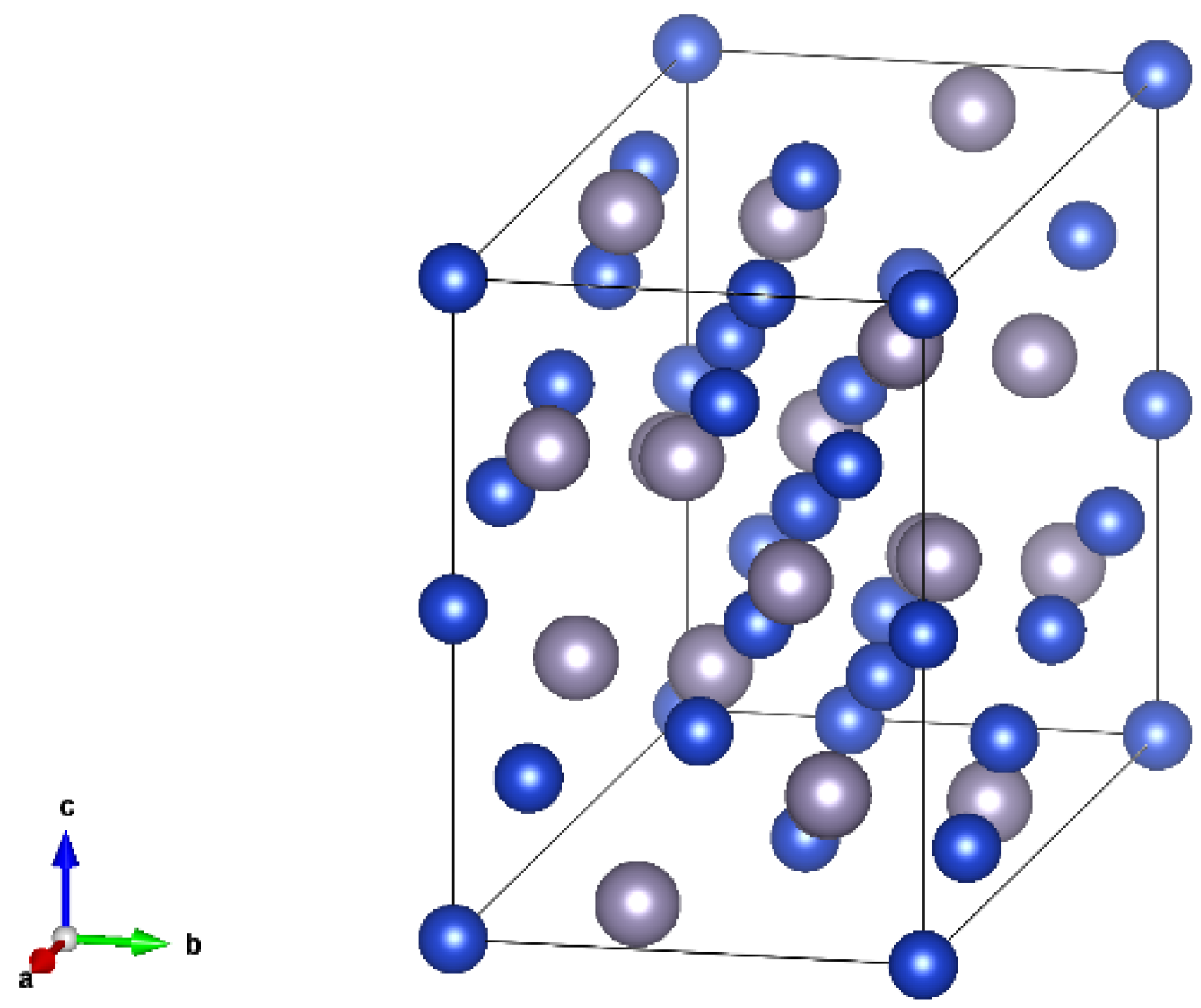
2.1. Structure of Cu6Sn5 Unit Cell
2.2. Modified Embedded Atom Method (MEAM) Potential
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Details of the MD Simulation
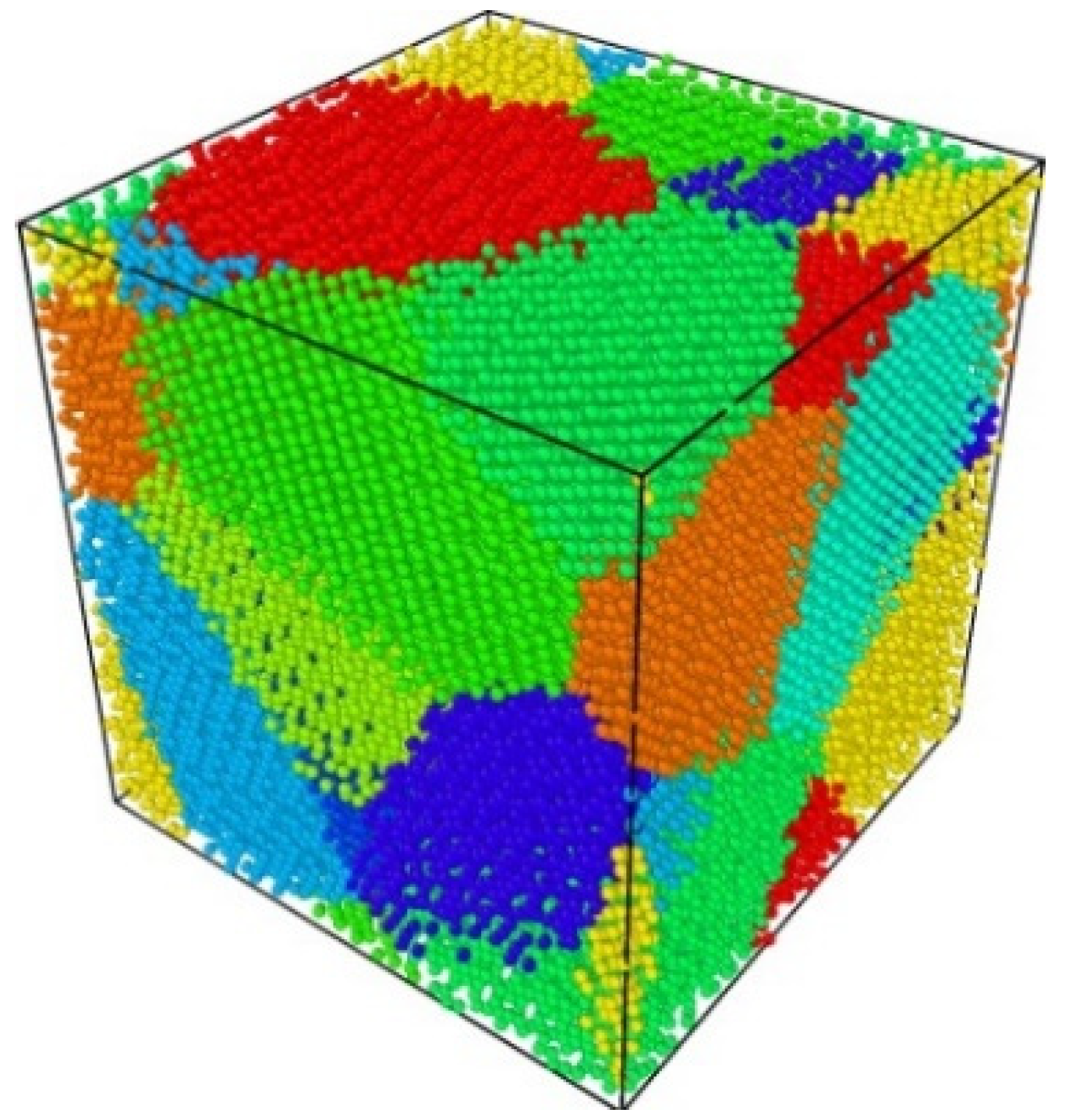
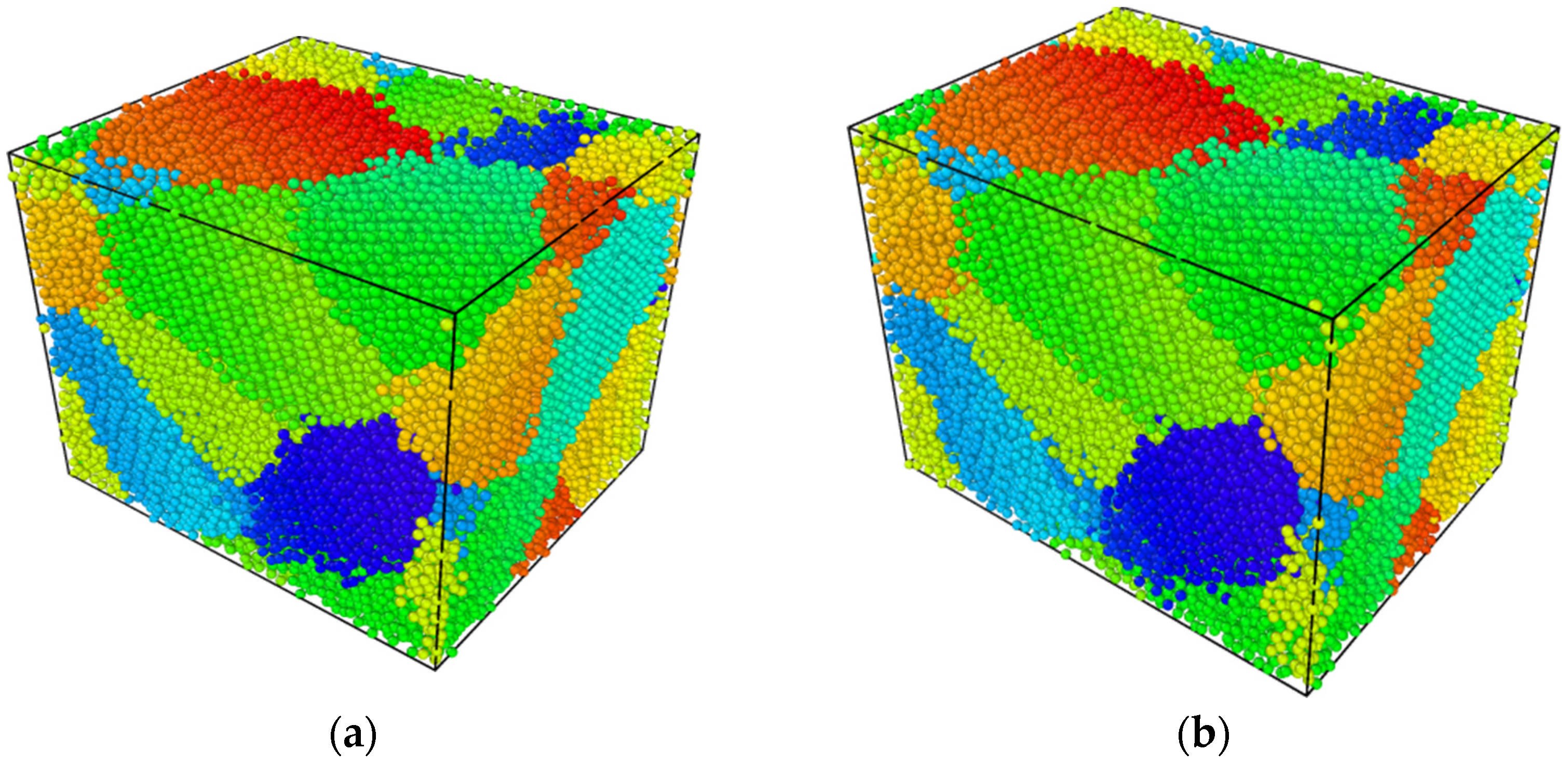
3.1.1. Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline Structures of Cu6Sn5
3.1.2. Validation of the MEAM Potential
3.1.3. Simulation Setting
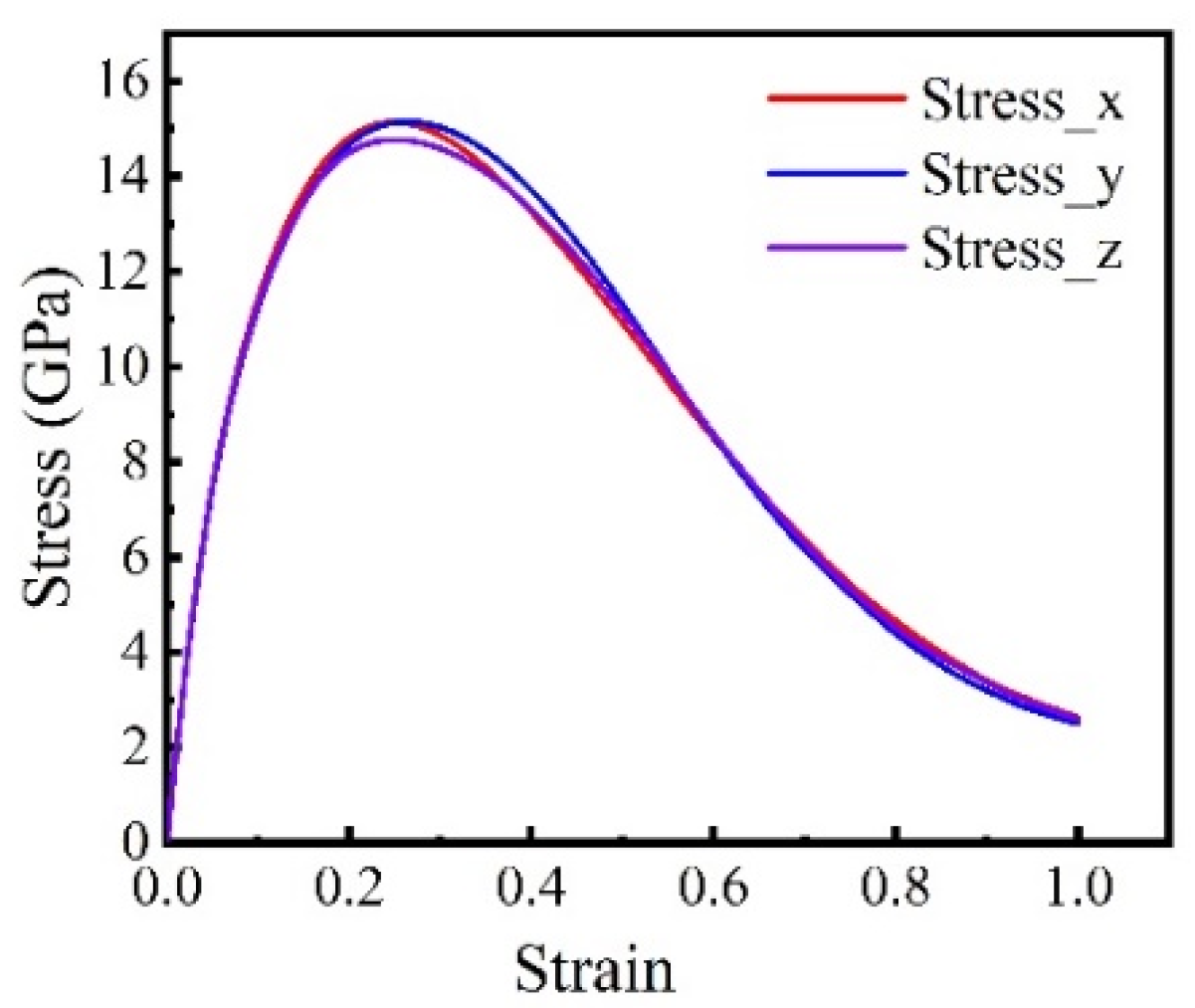
3.2. Isotropic Analysis of Tensile Properties of Polycrystals
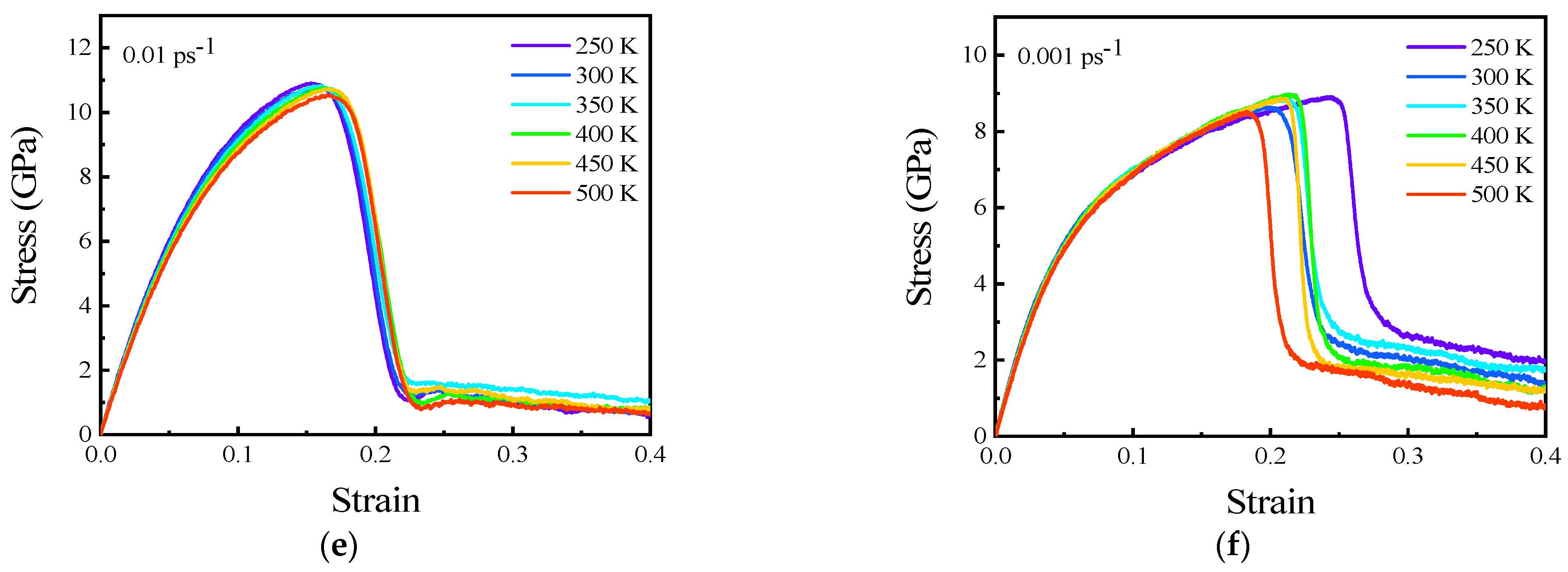
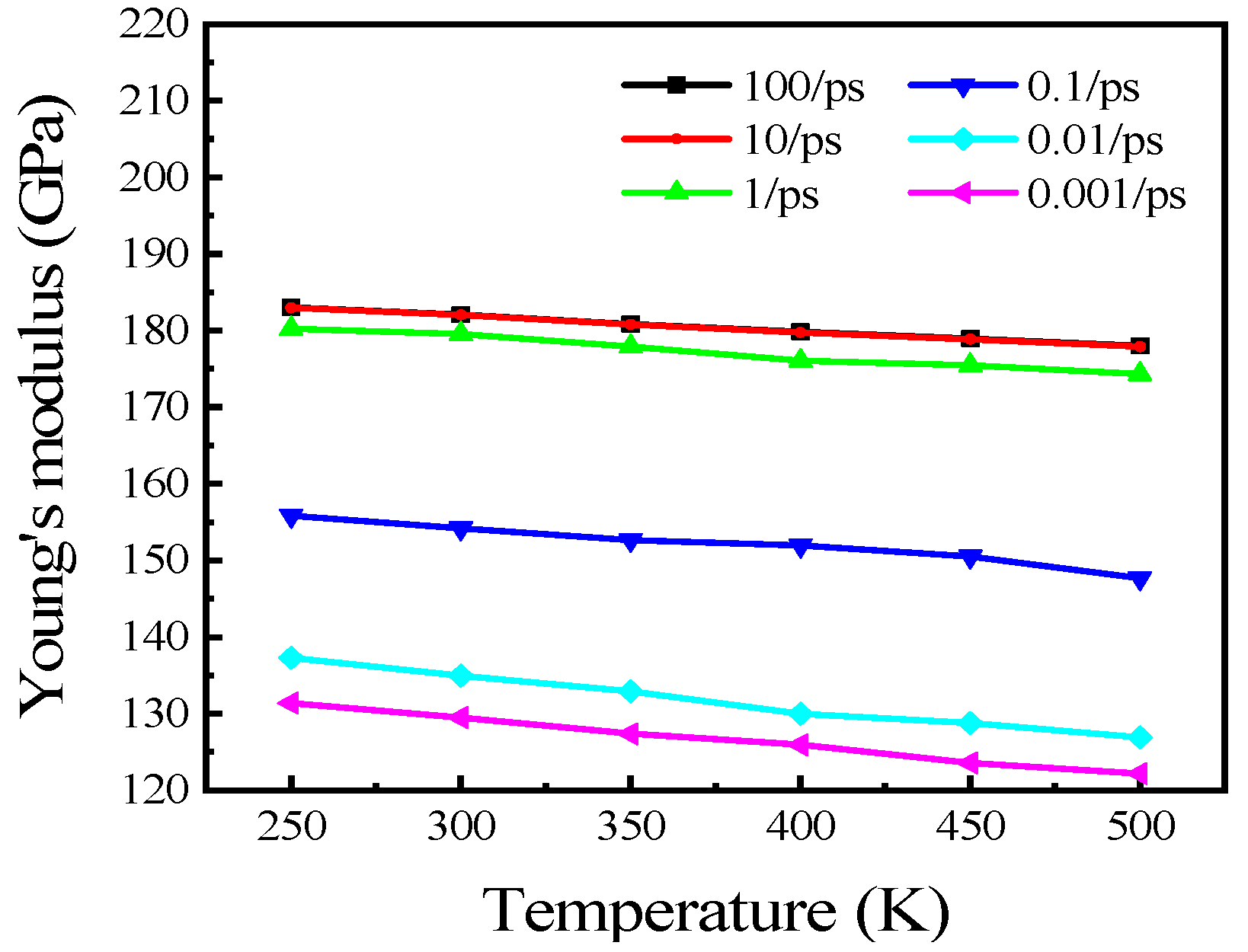
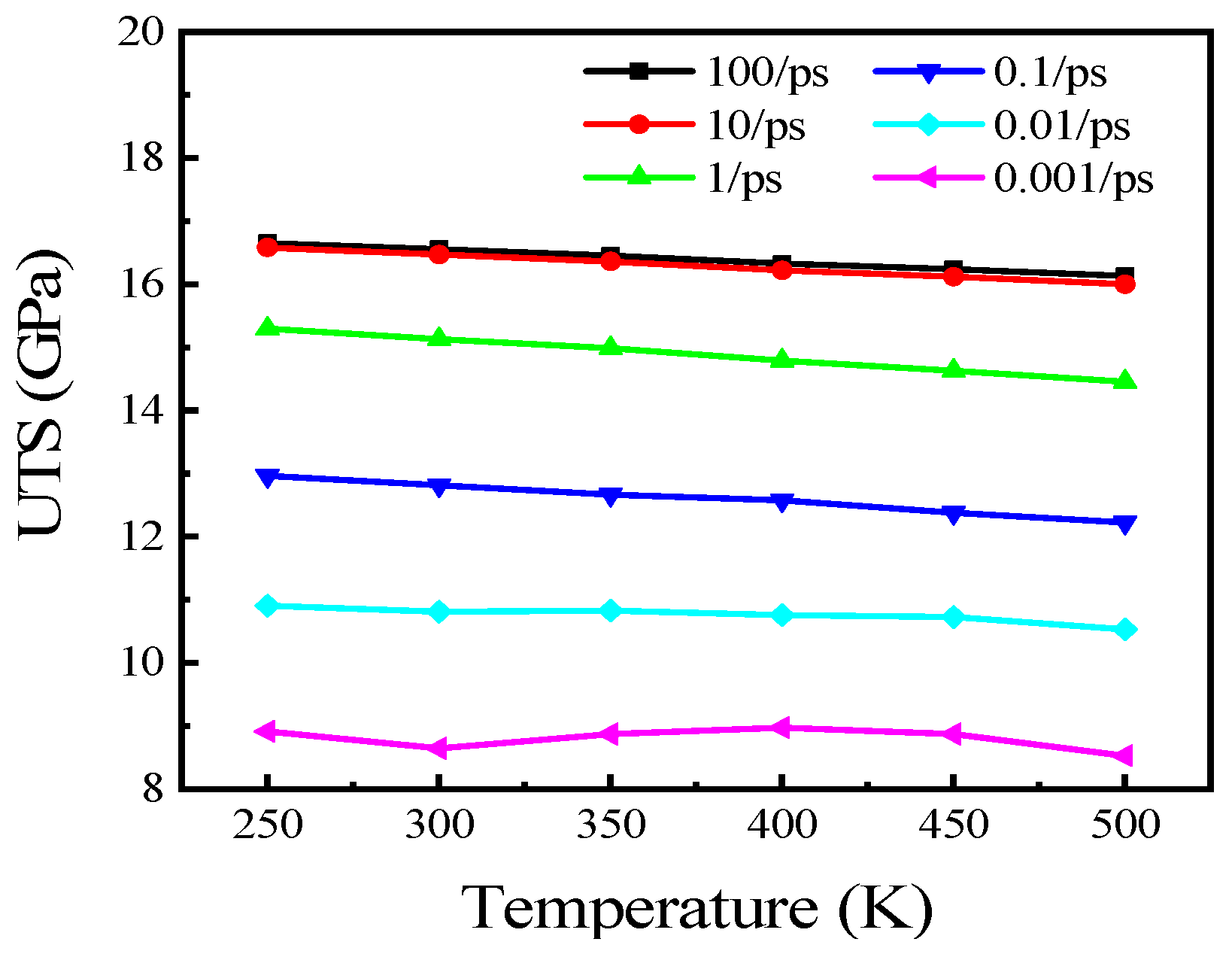
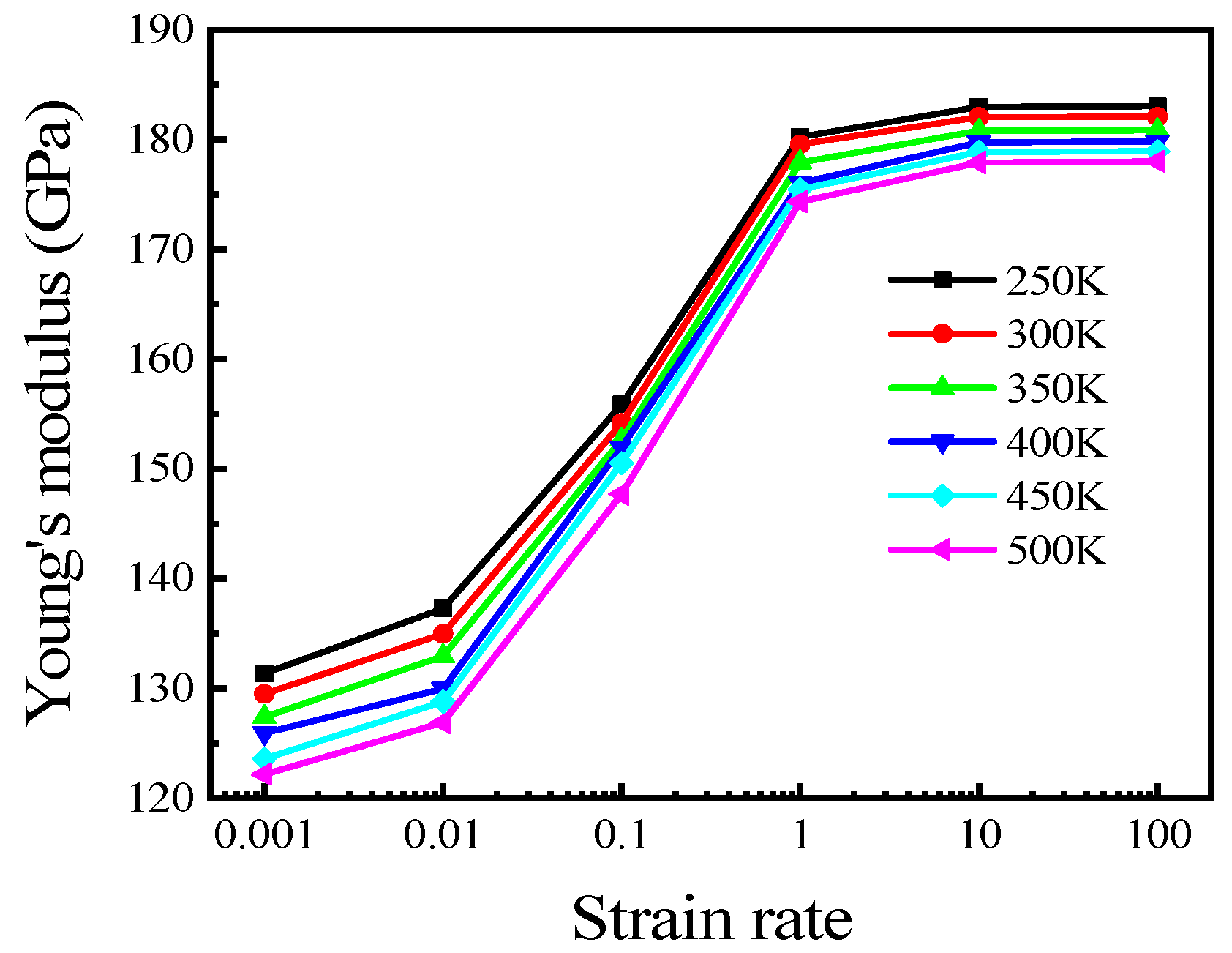
3.3. Temperature Effect on Tensile Properties of Polycrystalline Cu6Sn5
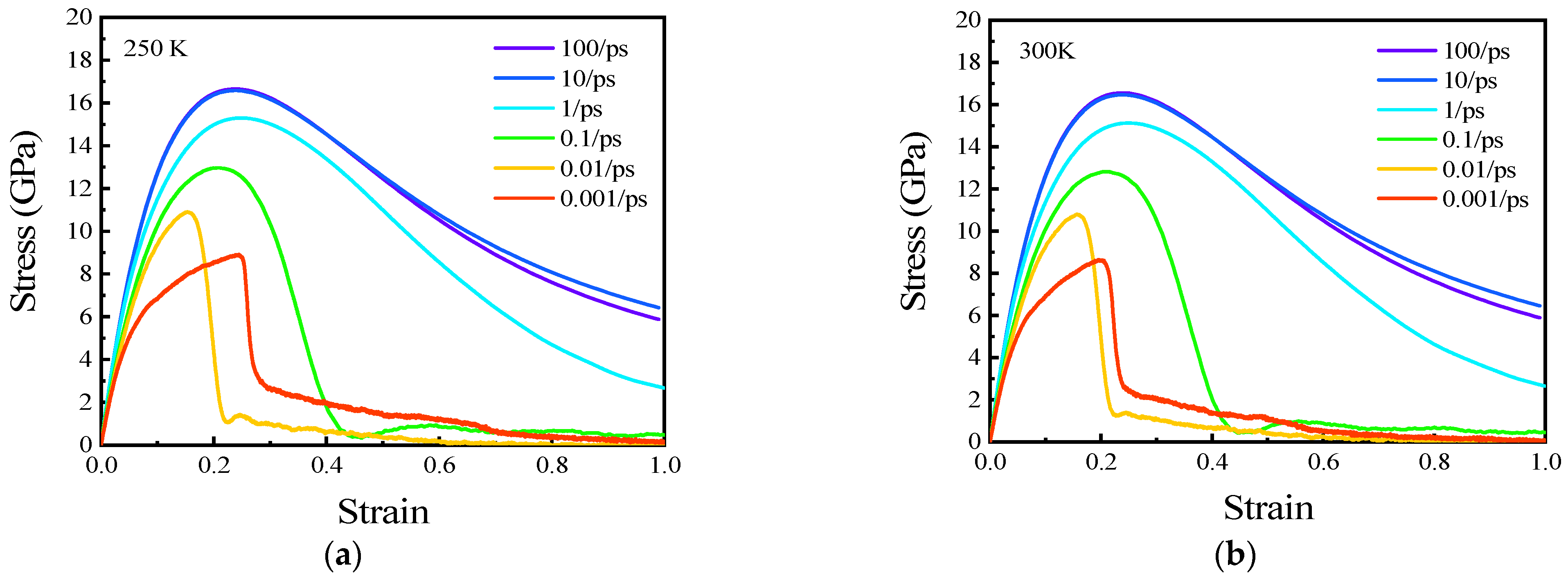
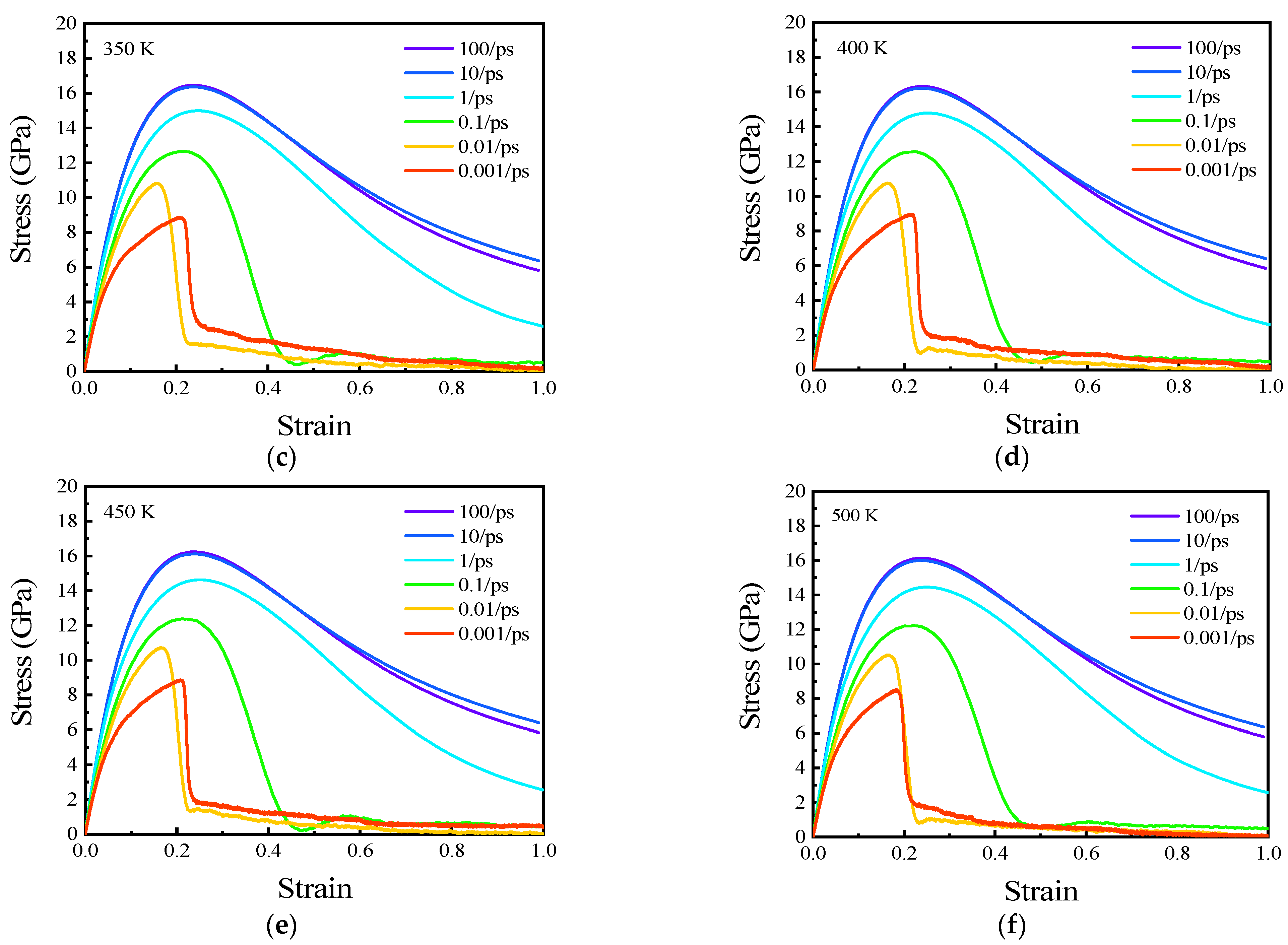
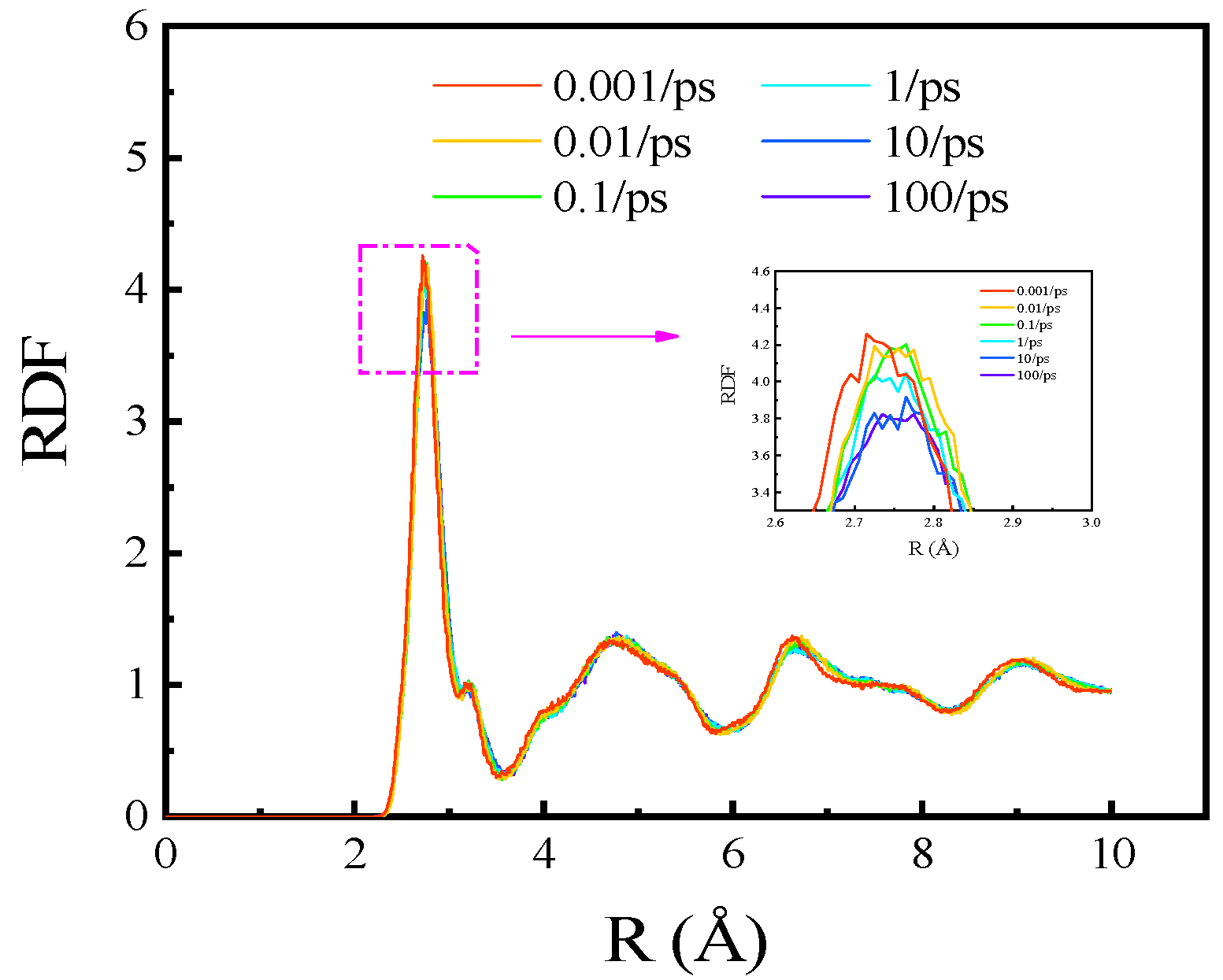
3.4. High Strain Rate Effects on Tensile Properties of Polycrystalline Cu6Sn5
3.5. Low Strain Rate Effects on Tensile Properties of Polycrystalline Cu6Sn5
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Young’s modulus and UTS decreased approximately linearly when the temperature increased from 250 to 500 K at high strain rates. The effect of temperature was relatively small compared with that of strain rate. The effect of temperature on mechanical properties was approximately negative linear, while the effect of strain rate on mechanical properties was approximately exponential with high strain rates.
- (2)
- The strain rate affected the deformation characteristics of the IMC. When it ranged from 0.001 to 100 ps−1, the elastic deformation was the dominant deformation in the stretching process. On the other hand, with a decrease in the strain rate, the plastic deformation was gradually more significant. When the strain rate was between 0.00001 and 0.0005 ps−1, the plastic deformation characteristics gradually appeared.
- (3)
- The strain rate affected the tensile strength of the IMC. At high strain rates (from 0.001 to 1 ps−1), Young’s modulus and UTS decreased with decreasing strain rate, and they exhibited exponential relationships with the strain rate. At low strain rates (from 0.00001 to 0.0005 ps−1), the relation between the UTS and strain rate was quadratic.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, H.; Hu, X.; Li, S.; Wan, Y.; Li, Q. Shear strength and fracture surface analysis of lead-free solder joints with high fraction of IMCs. Vacuum 2020, 180, 109611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Xiong, M.Y.; Sun, L. Structure and properties of Sn-Cu lead-free solders in electronics packaging. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2019, 20, 421–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, M.Y.; Zhang, L. Interface reaction and intermetallic compound growth behavior of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder joints on different substrates in electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 54, 1741–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, T.; Keer, L.M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X. Shear strength and fracture behavior of reflowed Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu/Cu solder joints under various strain rates. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 690, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Sun, F.; Guo, M. Investigation of Elevated Temperature Mechanical Properties of Intermetallic Compounds in the Cu-Sn System Using Nanoindentation. J. Electron. Packag. 2020, 142, 021004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.F.; Cheng, H.C.; Chen, W.H. Molecular dynamics calculations and nanoindentation testing of the strain-rate and size dependent material properties of Cu3Sn IMC. In Proceedings of the 2010 5th International Microsystems Packaging Assembly and Circuits Technology Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–22 October 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.S.; Yang, X.X.; Yuan, G.Z.; Li, Z.G.; Shu, X.F. Mechanical properties of intermetallic compounds at the Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/Cu joint interface using nanoindentation. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Hu, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, Q. Effect of Cu additions on mechanical properties of Ni3Sn4-based intermetallic compounds: First-principles calculations and nano-indentation measurements. Vacuum 2019, 164, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, A.; Rahman, A.; Chia, P.Y. Nanoindentation creep on Cu3Sn, Cu6Sn5 and (Cu, Ni)6Sn5 intermetallic compounds grown in electrodeposited multilayered thin film. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, V.M.F.; Johnston, C.; Grant, P.S. Nanomechanical characterization of Sn–Ag–Cu/Cu joints—Part 1: Young’s modulus, hardness and deformation mechanisms as a function of temperature. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 2460–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.Z.M.S.; Chia, P.Y.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A. Mechanical properties of intermetallic compounds in electrodeposited multilayered thin film at small scale by nanoindentation. Mater. Lett. 2015, 147, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Pan, K.L.; Zhang, J.; Gong, Y.B. Effect of In-Doping on Mechanical Properties of Cu6Sn5-Based Intermetallic Compounds: A First-Principles Study. J. Electron. Mater. 2021, 50, 4164–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wu, P. The Structural, Elastic and Electronic Properties of Ni3−xCuxSn4 (x = 0, 0.5, 1 and 1.5) Intermetallic Compounds via Ab Initio Calculations. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 4533–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, J. The effect of pressure and orientation on Cu-Cu3Sn interface reliability under isothermal ageing and monotonic traction via molecular dynamics investigation. Mater. Des. 2018, 149, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Hsu, Q.C. Study on Bonding and Shear Flow Phenomena of Shear Probe Test for BGA Solder Joint in Nano-Scale Analysis. In Proceedings of the ASME 2016 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 11–17 November 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.C.; Yu, C.F.; Chen, W.H. Size, Temperature, and Strain-Rate Dependence on Tensile Mechanical Behaviors of Ni3Sn4Intermetallic Compound Using Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 214510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Qu, J. Calculating the diffusivity of Cu and Sn in Cu3Sn intermetallic by molecular dynamics simulations. Mater. Lett. 2012, 73, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Yu, C.F.; Cheng, H.C.; Lu, S.T. Crystal size and direction dependence of the elastic properties of Cu3Sn through molecular dynamics simulation and nanoindentation testing. Microelectron. Reliab. 2012, 52, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Wang, W.L.; Wei, B. First-principle and molecular dynamics calculations for physical properties of Ni-Sn alloy system. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2015, 99, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.F.; Ladani, L. Local shear stress-strain response of Sn-3.5Ag/Cu solder joint with high fraction of intermetallic compounds: Experimental analysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 680, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, F.; An, T.; Chen, N. Strain Rate Effects and Rate-Dependent Constitutive Models of Lead-Based and Lead-Free Solders. J. Appl Mech 2009, 77, 011008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.C.; Yu, C.F.; Chen, W.H. Strain- and strain-rate-dependent mechanical properties and behaviors of Cu3Sn compound using molecular dynamics simulation. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 3103–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.T. High-rate squeezing process of bulk metallic glasses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.T.; Yang, L.Q. Damage mechanisms of bulk metallic glasses under high-rate compression. Int. J. Impact. Eng. 2017, 106, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Fan, J.; Nam, V.B.; Rabczuk, T. A nanoscale study of the negative strain rate dependency of the strength of metallic glasses by molecular dynamics simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 26552–26557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plimpton, S. Fast Parallel Algorithms for Short-range Molecular-Dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baskes, M.I. Modified Embedded-Atom Potentials for Cubic Materials and Impurities. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 46, 2727–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, A.K.; Stenberg, L.; Lidin, S. The superstructure of domain-twinned η′-Cu6Sn5. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B 1994, 50, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, J.F.; Ravelo, R.; Baskes, M.I. Morphology and dynamics of 2D Sn-Cu alloys on (100) and (111) Cu surfaces. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2000, 8, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirel, P. Atomsk: A tool for manipulating and converting atomic data files. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2015, 197, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.T.S.; Tan, V.B.C.; Lim, K.M. First-principles calculations of structural and mechanical properties of Cu6Sn5. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Asta, M. Phase stability, phase transformations, and elastic properties of Cu6Sn5: Ab initio calculations and experimental results. J. Mater. Res. 2005, 20, 3102–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Yooseob, S.; Wenbin, W.; Shruti, R.; George, Z.V.; Jeffrey, W.K. Order in polycrystalline plasticity deformation fields: Short-range intermittency and long-range persistency. Int. J. Plast. 2020, 128, 102674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Qi, Y.; Cagin, T.; Samwer, K.; Johnson, W.L.; Goddard, W.A. Strain rate induced amorphization in metallic nanowires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 2900–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M. A new look at the atomic level virial stress: On continuum-molecular system equivalence. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2003, 459, 2347–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Elements | Ec (eV) | A | r0 (Å) | α | β(0) | β(1) | β(2) | β(3) | t(1) | t(2) | t(3) | ρ0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 3.4 | 1.07 | 2.657 | 5.11 | 3.634 | 2.20 | 6.00 | 2.20 | 3.14 | 2.49 | 2.95 | 1 |
| Sn | 3.84 | 1 | 3.176 | 6.20 | 6.20 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 12.5 | 8.0 | −0.38 | 1 |
| Cu6Sn5 | 4.03 | 2.907 | 5.38 |
| (Cu, Cu, Cu) | (Cu, Cu, Sn) | (Cu, Sn, Cu) | (Sn, Sn, Sn) | (Sn, Cu, Sn) | (Sn, Sn, Cu) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmin | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.29 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Cmax | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 4.43 | 2.8 | 2.8 |
| Stiffness Constants (GPa) | C11 | C22 | C33 | C12 | C13 | C23 | C44 | C55 | C66 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our MD | 144.52 | 160.15 | 133.29 | 52.25 | 55.10 | 68.07 | 40.91 | 46.26 | 43.67 |
| Lee et al. [31] | 156.4 | 165.2 | 155.8 | 62.2 | 69.4 | 60.6 | 42.3 | 51.9 | 48.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Pan, K.; Zhang, J.; Gong, Y. Strain Rate and Temperature Effects on Tensile Properties of Polycrystalline Cu6Sn5 by Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Crystals 2021, 11, 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111415
Huang W, Pan K, Zhang J, Gong Y. Strain Rate and Temperature Effects on Tensile Properties of Polycrystalline Cu6Sn5 by Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Crystals. 2021; 11(11):1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111415
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Wei, Kailin Pan, Jian Zhang, and Yubing Gong. 2021. "Strain Rate and Temperature Effects on Tensile Properties of Polycrystalline Cu6Sn5 by Molecular Dynamic Simulation" Crystals 11, no. 11: 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111415
APA StyleHuang, W., Pan, K., Zhang, J., & Gong, Y. (2021). Strain Rate and Temperature Effects on Tensile Properties of Polycrystalline Cu6Sn5 by Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Crystals, 11(11), 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111415





