Role of Strain Reversal in Microstructure and Texture of Pure Al during Non-Monotonic Simple Shear Straining
Abstract
:1. Introduction
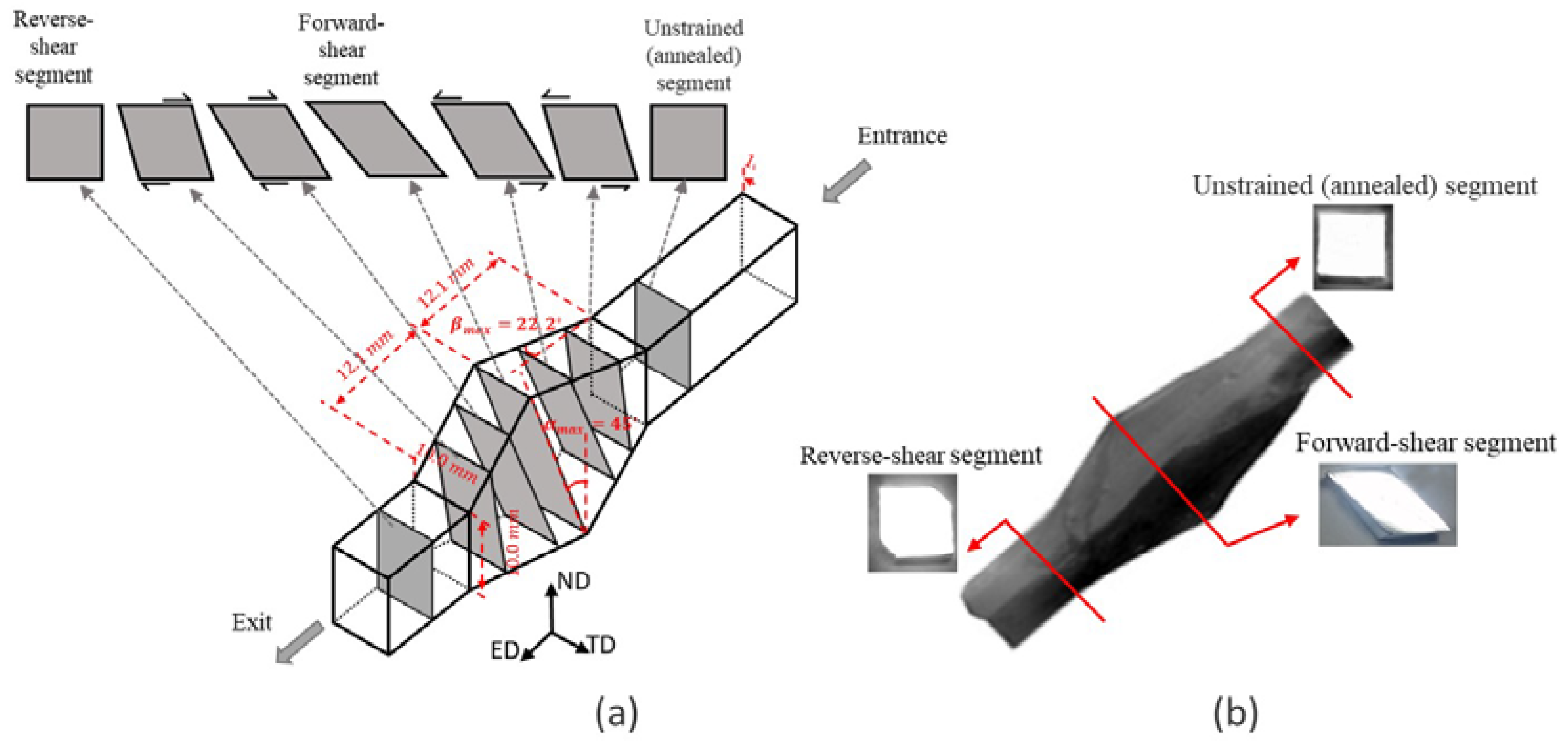
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
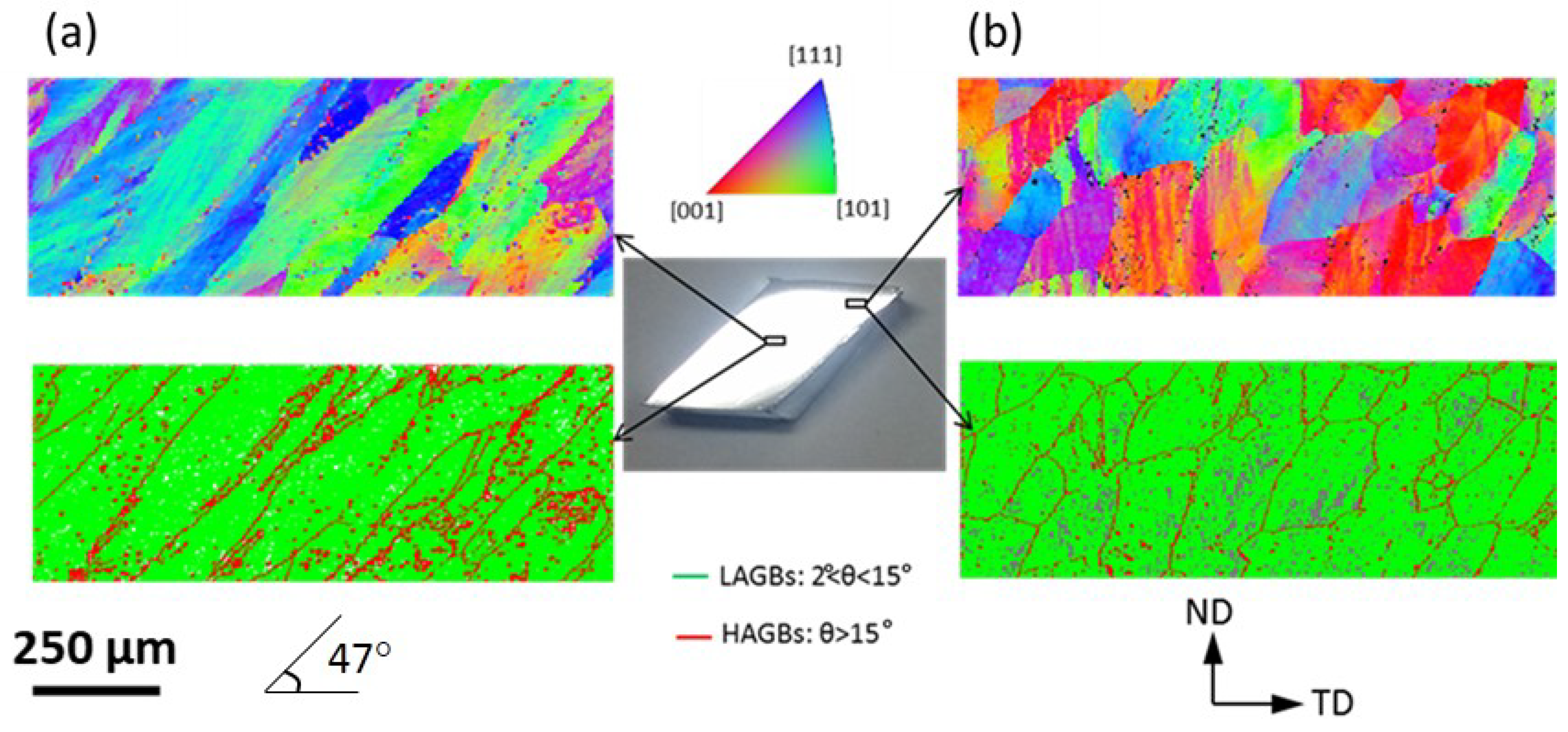
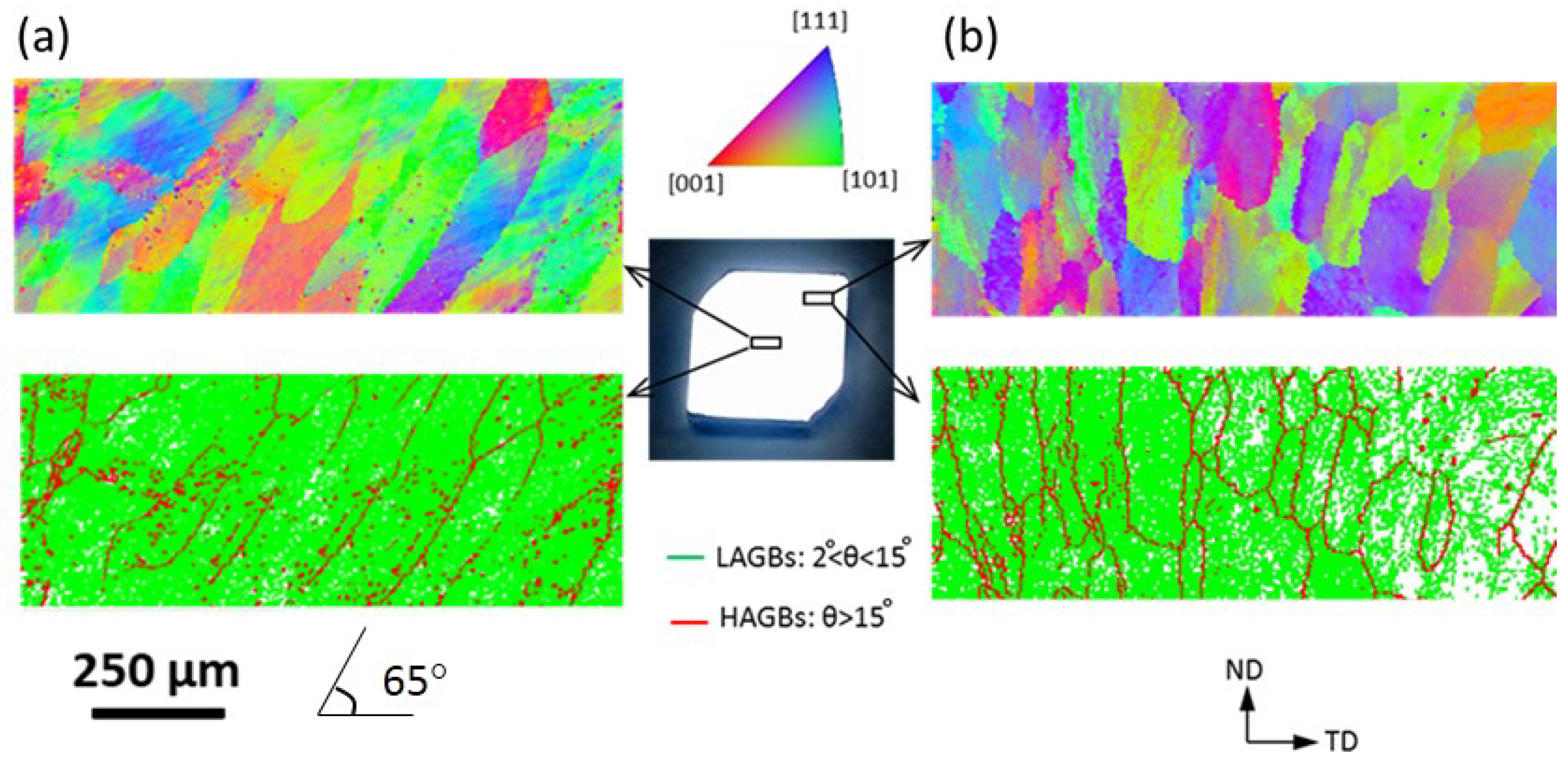
3.1. EBSD Characterisation
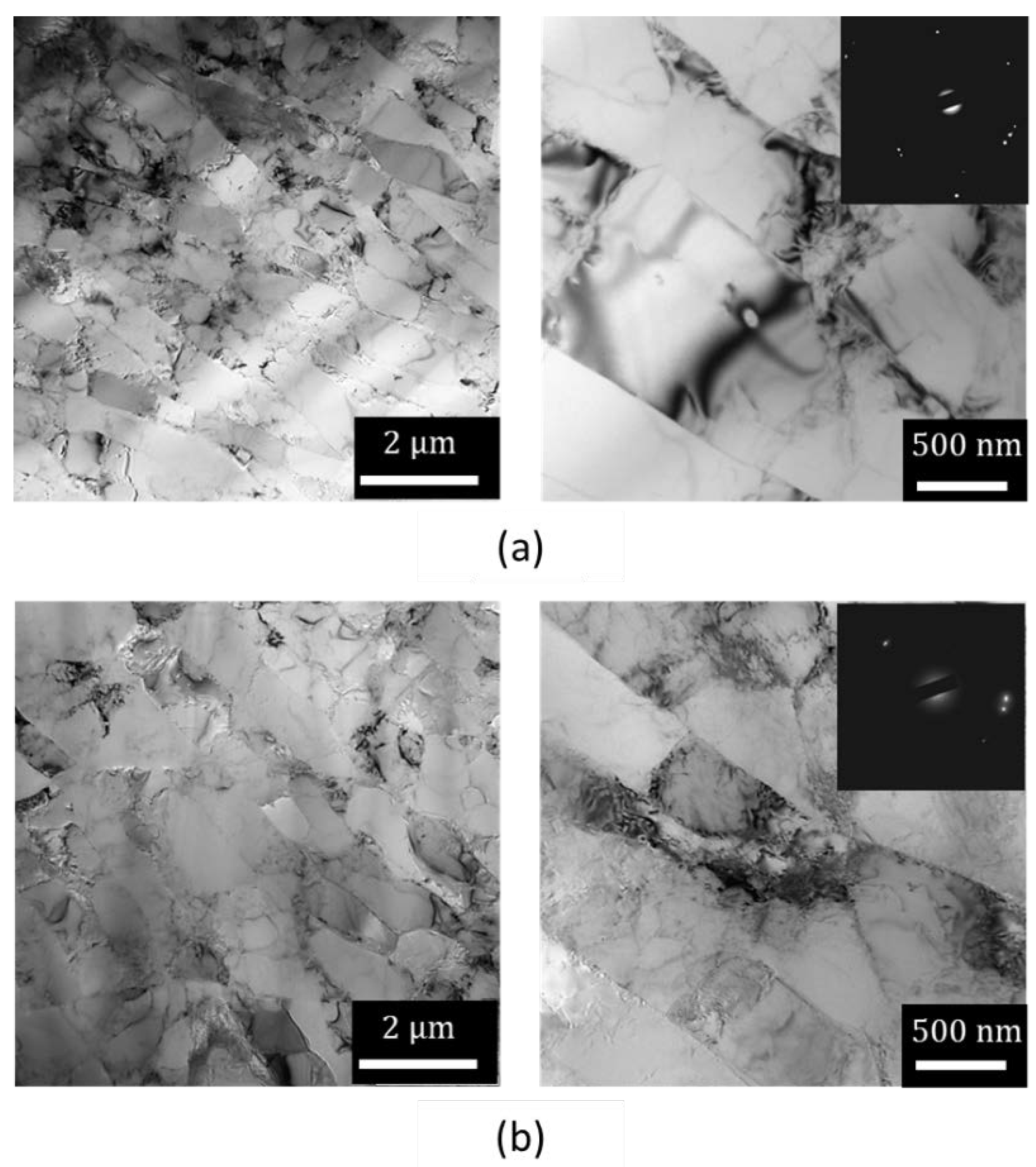
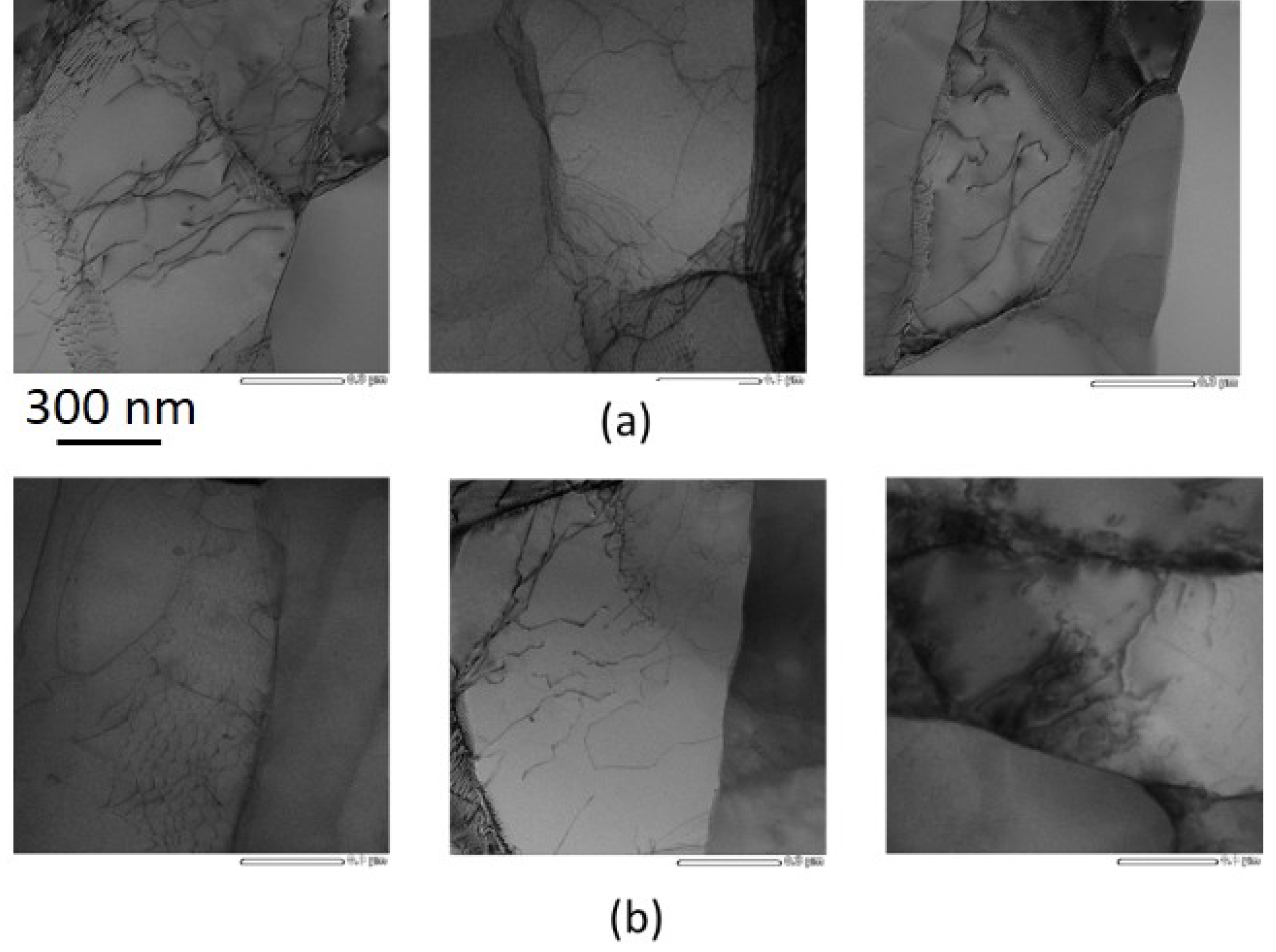
3.2. TEM/STEM Characterisation
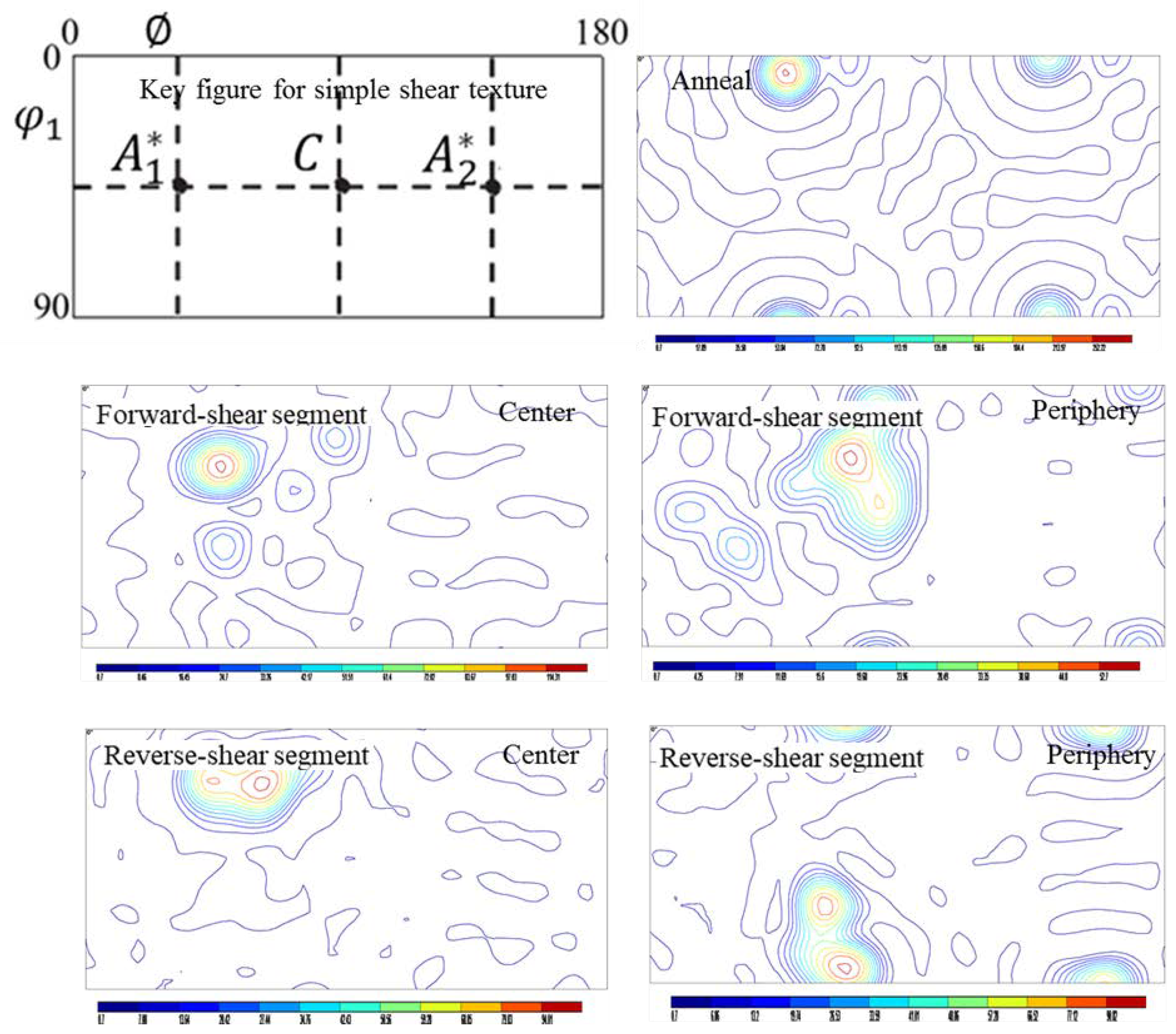
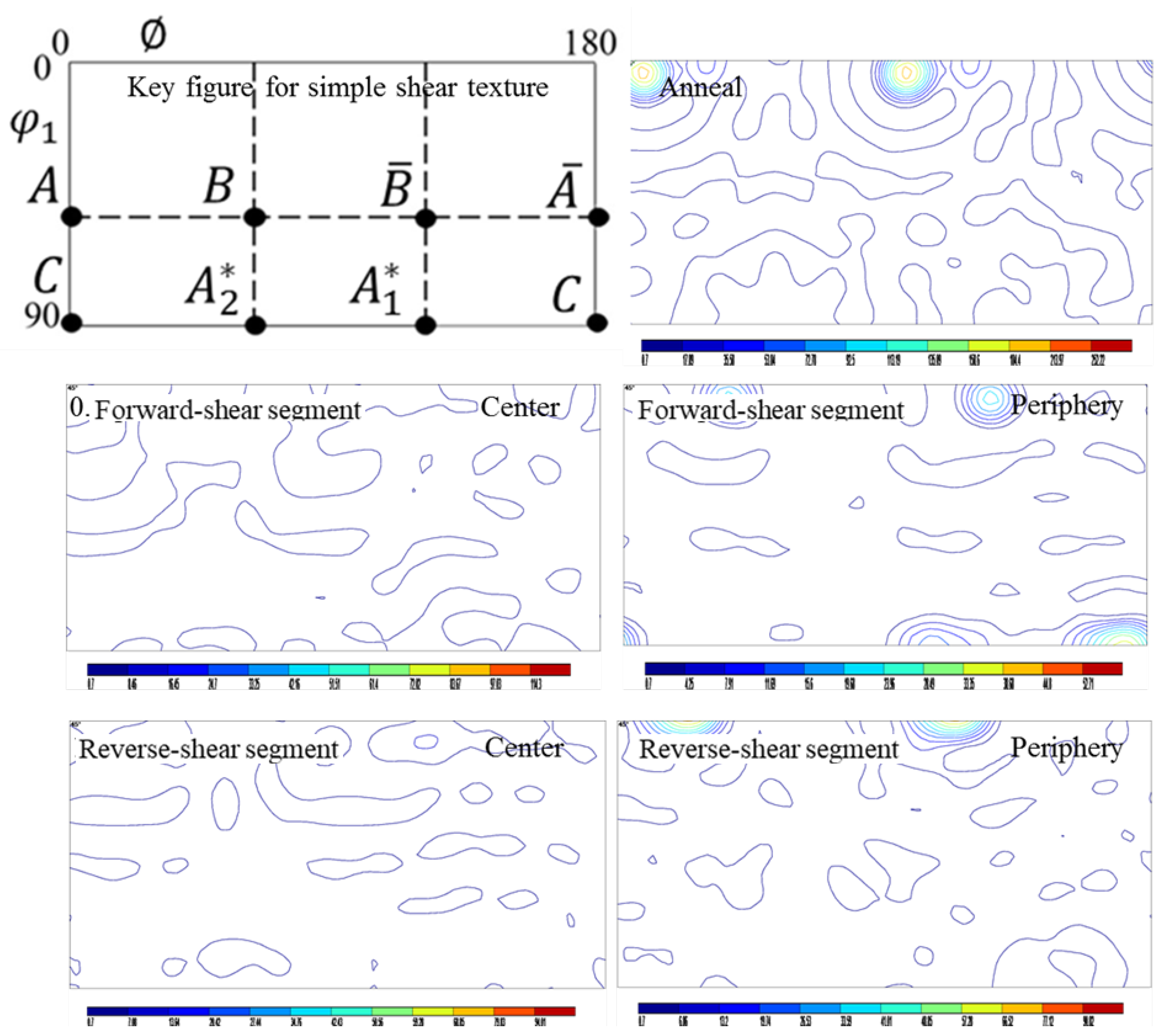
3.3. Texture Evaluation
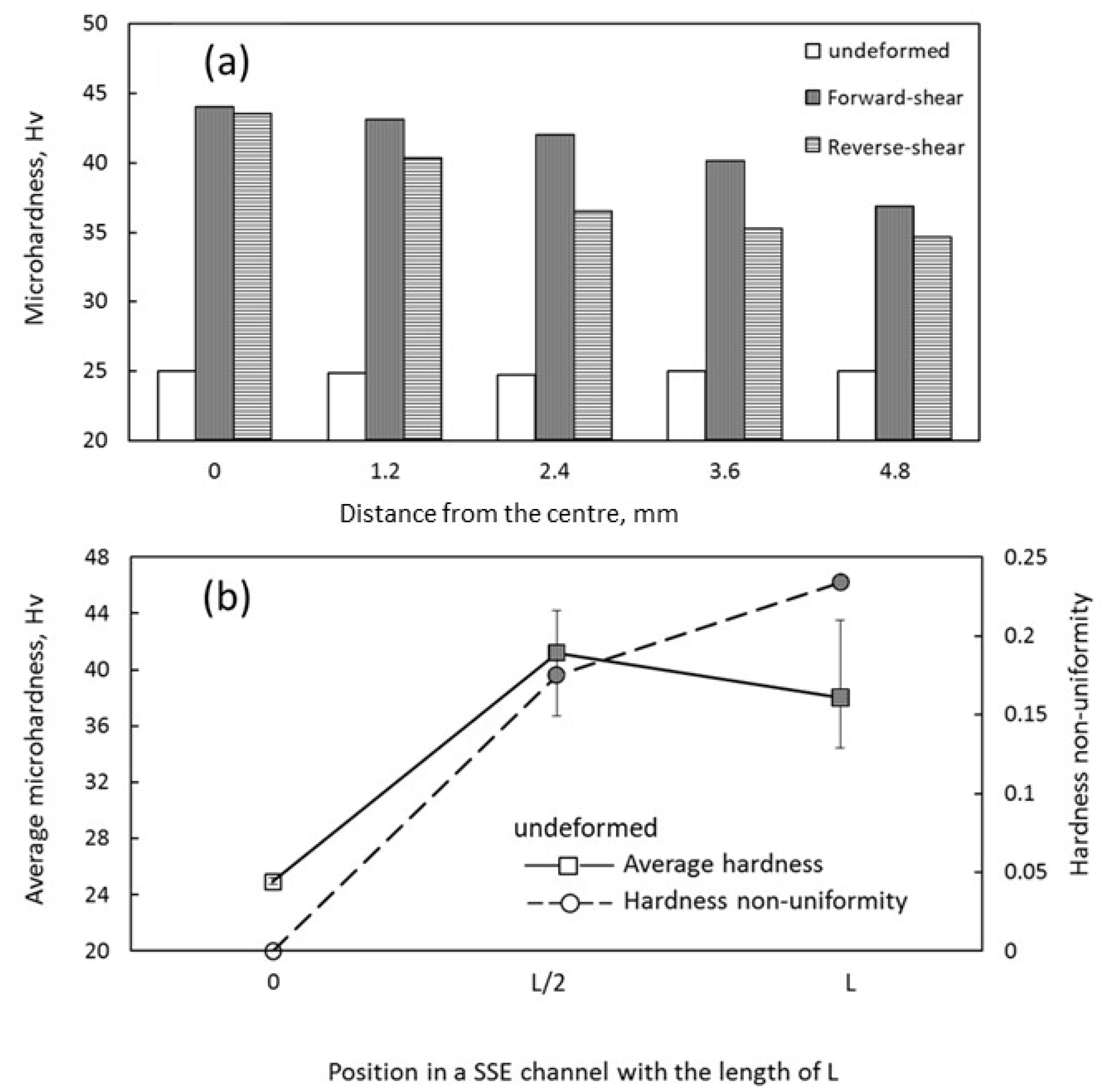
3.4. Hardness Investigation
4. Discussion
4.1. Grain’s Elongation Angle
4.2. Grain Size
4.3. Dislocation Density
4.4. Texture Evolution
4.5. Hardness
5. Conclusions
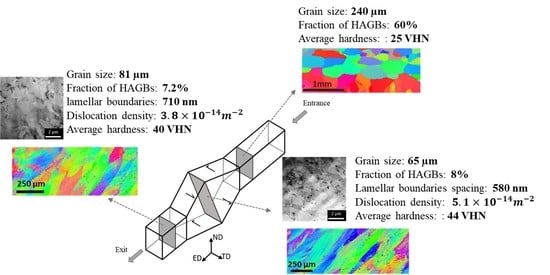
- Application of a single cycle of SSE caused the large and equiaxed grain structure to replace with fully elongated grains at the centre and less elongated ones at the samples’ surface.
- The grain size decreased from 240 µm at the initial stage to 65 µm and 83 µm at the central and peripheral regions respectively, after reaching the highest forward shear strain. Interestingly, after a full reversion of the strain, the grain size was 81 µm and 98 µm at the central and surface peripheral regions.
- The fraction of HAGBs on the centre and periphery of the reverse-shear segment was 7.2% and 11.5%, showing a decrease in comparison to that of forward-shear segment, which was 8% and 15% respectively.
- TEM image characterized a structure with lamellar boundaries before and after strain reversal, with a higher number of LAGBs in the forward-shear-segment. The dislocation density decreased from 5.1 × 10−14 m−2 in the forward-shear segment to 3.8 × 10−14 m−2 in the reverse-shear segment due to the strain reversal.
- The hardness of the initial sample rose from 25 VHN to 42 VHN by applying of the forward shear and decreased to 36 VHN after strain reversal. Additionally, the hardness distribution inhomogeneity increased by changing the direction of the shear.
- The cube texture was diminished and/or replaced with the simple shear texture in the forward-shear segment and restored to some extent in the reverse-shear segment.
- Strain reversal resulted in the increase in the grain size, reduction in the dislocation density, hardness and mean misorientation angle, and restoring the texture in the reverse-shear segment. This behaviour was contributed to a kind of Bauschinger effect that affected the microstructure and mechanical properties during strain reversal.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
References
- Meyers, M.A.; Chawla, K.K. Mechanical Behavior of Materials; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hosford, W.F. Mechanical Behavior of Materials; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rauch, E.F.; Gracio, J.J.; Barlat, F. Work-hardening model for polycrystalline metals under strain reversal at large strains. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 2939–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Rauch, E.F.; Teodosiu, C. Work-hardening behavior of mild steel under stress reversal at large strains. Int. J. Plast. 1992, 8, 839–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, D.; Todaka, Y.; Umemoto, M.; Tsuji, N. Role of strain reversal in grain refinement by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 499, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, H.; Ikeda, T.; Uenoya, T.; Vinogradov, A.; Hashimoto, S. Reversible nature of shear bands in copper single crystals subjected to iterative shear of ECAP in forward and reverse directions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 2602–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, D.; Bhattacharjee, P.P.; Todaka, Y.; Umemoto, M.; Tsuji, N. Texture evolution in pure aluminum subjected to monotonous and reversal straining in high-pressure torsion. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.F.; Tóth, L.S.; Davies, C.H.J. Effect of strain reversal on texture and grain refinement in route C equal channel angular pressed copper. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.F.; Tóth, L.S. The origin of strain reversal texture in equal channel angular pressing. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 5749–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, F.; Fang, X.; Li, Z.; Sun, Z.; Hou, J.; Cao, J. Effect of strain reversal on the stress-induced martensitic transformation and tensile properties of a metastable β titanium alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 784, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzagorta, J.L.; Jorge-Badiola, D.; Gutiérrez, I. Effect of the strain reversal on austenite–ferrite phase transformation in a Nb-microalloyed steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Muszka, K.; Wynne, B.P.; Palmiere, E.J. Influence of strain reversal on dynamic transformation in microalloyed steels deformed above the Ae3 temperature. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 12427–12444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Muszka, K.; Wynne, B.P.; Palmiere, E.J. On the interactions between strain path reversal and dynamic recrystallisation in 316L stainless steel studied by hottorsion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 568, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Badiola, D.; Gutiérrez, I. Study of the strain reversal effect on the recrystallization and strain-induced precipitation in a Nb-microalloyed steel. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcadet, S.J.; Mohr, D. Effect of compression–tension loading reversal on the strain to fracture of dual phase steel sheets. Int. J. Plast. 2015, 72, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, F.; Paul, J.D.H.; Staron, P.; Oehring, M.; Kolednik, O.; Predan, J.; Fischer, F.D. The effect of residual stresses and strain reversal on the fracture toughness of TiAl alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 709, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, P.D.; Semiatin, S.L. The effect of strain-path reversal on cavitation during hot torsion of Ti-6Al-4V. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 3697–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y. Direct observation of twinning–detwinning–retwinning on magnesium single crystal subjected to strain-controlled cyclic tension–compression in [0 0 0 1] direction. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2011, 91, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toribio, J.; Kharin, V.; Ayaso, F.-J.; Lorenzo, M.; González, B.; Matos, J.-C.; Aguado, L. Analysis of the Bauschinger Effect in Cold Drawn Pearlitic Steels. Metals 2020, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Li, F.; Mao, X.; Yuan, S.; Wang, J. Effect of strain reversal on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy under cyclic torsion deformation. Procedia Eng. 2017, 207, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; He, Y.; Dunstan, D.J.; Zhang, B.; Gan, Z.; Hu, P.; Ding, H. Anomalous Plasticity in the Cyclic Torsion of Micron Scale Metallic Wires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 244301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Li, F.; Cao, J.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, C. Vickers microhardness and microstructure relationship of Ti-6Al-4V alloy under cyclic forward-reverse torsion and monotonic torsion loading. Mater. Des. 2017, 114, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, M.; Langdon, T.G. The significance of strain reversals during processing by high-pressure torsion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 498, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, N.; Starink, M.J. Microstructure development and hardening during high pressure torsion of commercially pure aluminium: Strain reversal experiments and a dislocation based model. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 2581–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawasaki, M.; Ahn, B.; Langdon, T.G. Significance of strain reversals in a two-phase alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 7008–7016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardis, N.; Ebrahimi, R. Deformation behavior in Simple Shear Extrusion (SSE) as a new severe plastic deformation technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 527, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardis, N.; Ebrahimi, R. Different processing routes for deformation via simple shear extrusion (SSE). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 6153–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, A.; Bagherpour, E.; Ebrahimi, R. Circular Simple Shear Extrusion as an Alternative to Simple Shear Extrusion Technique. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Mech. Eng. 2020, 44, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tork, N.B.; Pardis, N.; Ebrahimi, R. Investigation on the feasibility of room temperature plastic deformation of pure magnesium by simple shear extrusion process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 560, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, R.; Rezvani, A.; Bagherpour, E. Circular simple shear extrusion as an alternative for simple shear extrusion technique for producing bulk nanostructured materials. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 15, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherpour, E.; Qods, F.; Ebrahimi, R.; Miyamoto, H. Microstructure quantification of ultrafine grained pure copper fabricated by simple shear extrusion (SSE) technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 674, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali, M.; Limouei, M.B.; Balali, M. Study on Optimization of Parameters Affecting Simple Shear Extrusion of Pure Copper to Fabricate Fine Grain Structure. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2018, 71, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherpour, E.; Qods, F.; Ebrahimi, R.; Miyamoto, H. Nanostructured pure copper fabricated by simple shear extrusion (SSE): A correlation between microstructure and tensile properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 679, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat Tork, N.; Saghafian, H.; Razavi, S.H.; Al-Fadhalah, K.J.; Ebrahimi, R.; Mahmudi, R. Microstructure and texture characterization of Mg–Al and Mg–Gd binary alloys processed by simple shear extrusion. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherpour, E.; Mortezaei, S.; Ebrahimi, R.; Miyamoto, H.; Qods, F. On the Production of Severely Deformed Workpieces in Large Scales: A Step towards Industrialization. JOM 2019, 71, 4424–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagherpour, E.; Qods, F.; Ebrahimi, R.; Miyamoto, H. Microstructure evolution of pure copper during a single pass of simple shear extrusion (SSE): Role of shear reversal. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 666, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherpour, E.; Qods, F.; Ebrahimi, R.; Miyamoto, H. Texture Changes during Simple Shear Extrusion (SSE) Processing of Pure Copper. Mater. Trans. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagherpour, E.; Qods, F.; Ebrahimi, R.; Miyamoto, H. Microstructure and Texture Inhomogeneity after Large Non-Monotonic Simple Shear Strains: Achievements of Tensile Properties. Metals 2018, 8, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagherpour, E.; Reihanian, M.; Ebrahimi, R. Processing twining induced plasticity steel through simple shear extrusion. Mater. Des. 2012, 40, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, R.K. The determination of dislocation densities in thin films. Philos. Mag. A J. Theor. Exp. Appl. Phys. 1961, 6, 1183–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, Y.; Mitsuhara, M.; Hata, S.; Nakashima, H.; Tsuji, N. Quantification of internal dislocation density using scanning transmission electron microscopy in ultrafine grained pure aluminium fabricated by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 528, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardal, A.; Lie, K. Measuring the Thickness of Aluminium Alloy Thin Foils Using Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy. Mater. Charact. 2000, 44, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahmer, D.M.; Polvorosa, R.; López de Lacalle, L.N.; Alonso-Pinillos, U.; Abate, G.; Riu, F. Alternatives for Specimen Manufacturing in Tensile Testing of Steel Plates. Exp. Tech. 2016, 40, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestens, L.A.I.; Pirgazi, H. Texture formation in metal alloys with cubic crystal structures. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Beyerlein, I.J.; Bourke, M.A.M. Texture formation during equal channel angular extrusion of fcc and bcc materials: Comparison with simple shear. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 394, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; Yakou, T.; Karashima, S. Deformation behaviour and dislocation structures upon stress reversal in polycrystalline aluminium. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1975, 20, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaka, Y.; Umemoto, M.; Yamazaki, A.; Sasaki, J.; Tsuchiya, K. Effect of Strain Path in High-Pressure Torsion Process on Hardening in Commercial Purity Titanium. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, T.; Yakou, T.; Kocks, U.F. Forward and reverse rearrangements of dislocations in tangled walls. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1986, 81, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryk, H.; Stupkiewicz, S. A quantitative model of grain refinement and strain hardening during severe plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 444, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Beyerlein, I.J.; Alexander, D.J.; Vogel, S.C. Texture evolution during equal channel angular extrusion: Effect of initial texture from experiment and simulation. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrasse, S.; Segal, V.M.; Kalidindi, S.R.; Alford, F. Texture evolution during equal channel angular extrusion: Part I. Effect of route, number of passes and initial texture. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 368, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, H.; Fushimi, J.; Mimaki, T.; Vinogradov, A.; Hashimoto, S. The Effect of the Initial Orientation on Microstructure Development of Copper Single Crystals Subjected to Equal-Channel Angular Pressing. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 503–504, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwas, S.; Arruffat-Massion, R.; Tóth, L.S.; Eberhardt, A.; Fundenberger, J.-J.; Skrotzki, W. Evolution of crystallographic texture during equal channel angular extrusion of copper: The role of material variables. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gazder, A.A.; Beyerlein, I.J.; Davies, C.H.J.; Pereloma, E.V. Microstructure and texture evolution during equal channel angular extrusion of interstitial-free steel: Effects of die angle and processing route. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.A.; Lebensohn, R.A.; Wenk, H.R.; Kumar, A. Stacking fault energy and microstructure effects on torsion texture evolution. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2000, 456, 921–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwas, S.; Tóth, L.S.; Fundenberger, J.-J.; Grosdidier, T.; Skrotzki, W. Texture Evolution in FCC Metals during Equal Channel Angular Extrusion (ECAE) as a Function of Stacking Fault Energy. Solid State Phenom. 2005, 105, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Al | Si | Mn | Mg | Zn | Ti | Fe | v |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99.27 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.03 |
| Notation | Euler Angles (°) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35.26/215.26 | 45 | 0/90 | ||
| 125.26 | 90 | 45 | ||
| 144.74 | 45 | 0/90 | ||
| 54.74/234.74 | 90 | 45 | ||
| 0 | 35.26 | 45 | ||
| 180 | 35.26 | 45 | ||
| 0/120/240 | 54.74 | 45 | ||
| 60/180 | 54.74 | 45 | ||
| 90/270 | 45 | 0/90 | ||
| 0/180 | 90 | 45 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bagherpour, E.; Reihanian, M.; Ebrahimi, R.; Qods, F.; Miyamoto, H. Role of Strain Reversal in Microstructure and Texture of Pure Al during Non-Monotonic Simple Shear Straining. Crystals 2020, 10, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100926
Bagherpour E, Reihanian M, Ebrahimi R, Qods F, Miyamoto H. Role of Strain Reversal in Microstructure and Texture of Pure Al during Non-Monotonic Simple Shear Straining. Crystals. 2020; 10(10):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100926
Chicago/Turabian StyleBagherpour, Ebad, Mohsen Reihanian, Ramin Ebrahimi, Fathallah Qods, and Hiroyuki Miyamoto. 2020. "Role of Strain Reversal in Microstructure and Texture of Pure Al during Non-Monotonic Simple Shear Straining" Crystals 10, no. 10: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100926
APA StyleBagherpour, E., Reihanian, M., Ebrahimi, R., Qods, F., & Miyamoto, H. (2020). Role of Strain Reversal in Microstructure and Texture of Pure Al during Non-Monotonic Simple Shear Straining. Crystals, 10(10), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100926