Effect of Process Conditions on Particle Size and Shape in Continuous Antisolvent Crystallisation of Lovastatin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Experimental Solubility Measurements
2.2.2. Induction Time Measurements
2.2.3. Antisolvent Crystallisation of Lovastatin
2.2.4. Offline Analysis of Dry Powder Samples
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Optical Microscopy
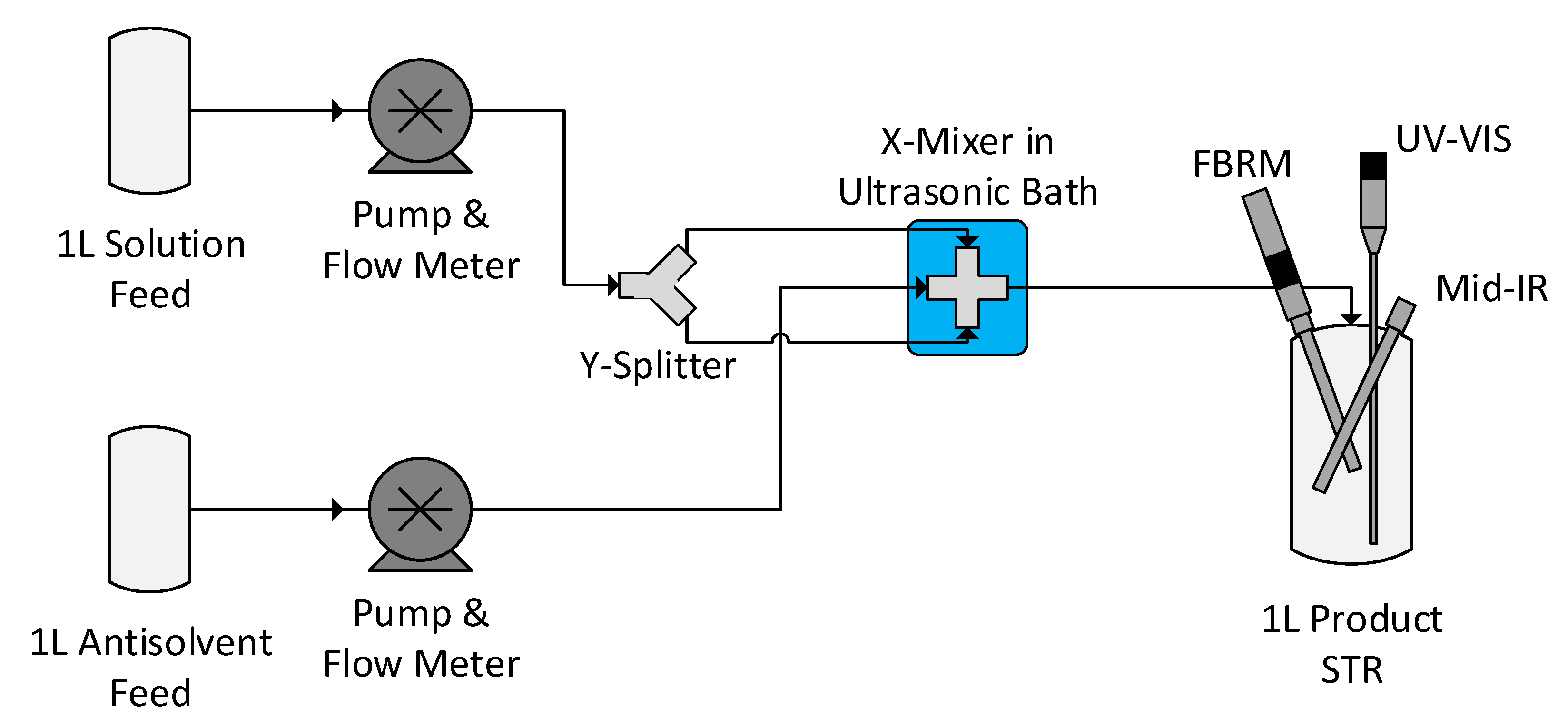
2.2.5. Online Process Analytical Technology (PAT) Monitoring
3. Results and Discussion
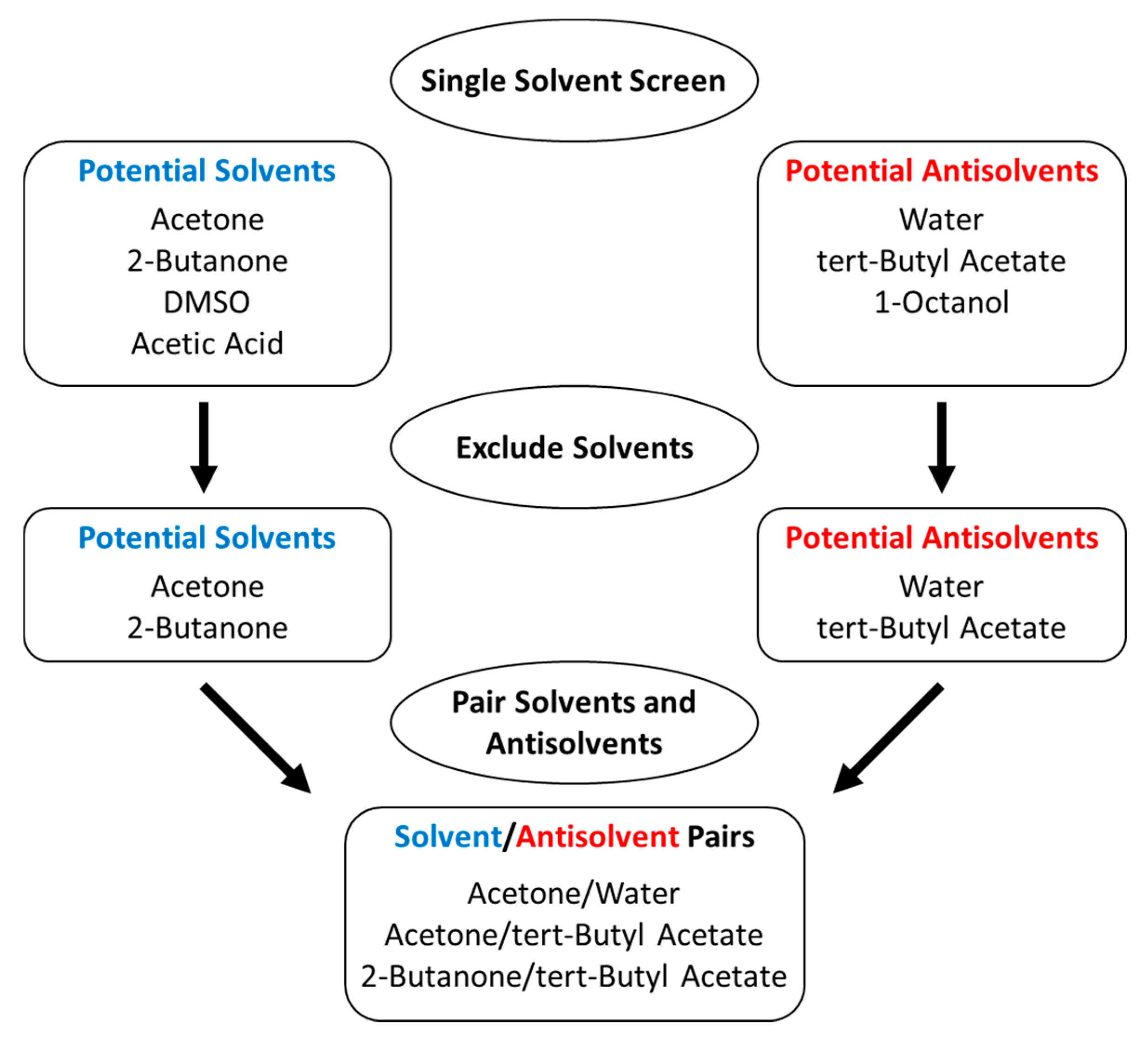
3.1. Literature Solvent/Antisolvent Screen
3.2. Experimental Solubility Measurements
3.3. Induction Time Measurements
3.4. Antisolvent Crystallisation of Lovastatin
3.4.1. Experimental Conditions
3.4.2. Process Overview
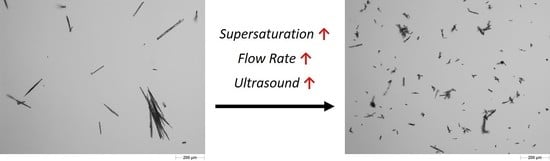
3.4.3. Particle Size and Shape
3.4.4. Yield and Solid Recovery
3.4.5. Online PAT Monitoring
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plumb, K. Continuous processing in the pharmaceutical industry—Changing the mind set. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2005, 83, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenberg, C.; Scholl, J.; Vicum, L.; Mazzotti, M.; Brozio, J. Experimental characterization and multi-scale modeling of mixing in static mixers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 4135–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenberg, C.; Mazzotti, M. Experimental characterization and multi-scale modeling of mixing in static mixers. Part 2. Effect of viscosity and scale-up. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 4286–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, A.; Lemenand, T.; Della Valle, D.; Peerhossaini, H. Static mixers: Mechanisms, applications, and characterization methods—A review. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 205–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.A.; Schacht, U.; Svoboda, V.; Edwards, D.P.; Florence, A.J.; Pulham, C.R.; Sefcik, J.; Oswald, L.D.H. Rapid Continuous Antisolvent Crystallization of Multicomponent Systems. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svoboda, V.; MacFhionnghaile, P.; McGinty, J.; Connor, L.E.; Oswald, I.D.H.; Sefcik, J. Continuous Cocrystallization of Benzoic Acid and Isonicotinamide by Mixing-Induced Supersaturation: Exploring Opportunities between Reactive and Antisolvent Crystallization Concepts. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 1902–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacFhionnghaile, P.; Svoboda, V.; McGinty, J.; Nordon, A.; Sefcik, J. Crystallization Diagram for Antisolvent Crystallization of Lactose: Using Design of Experiments To Investigate Continuous Mixing-Induced Supersaturation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 2611–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramakers, L.A.I.; McGinty, J.; Beckmann, W.; Levilain, G.; Lee, M.; Wheatcroft, H.; Houson, I.; Sefcik, J. Investigation of Metastable Zones and Induction Times in Glycine Crystallization across Three Different Antisolvents. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 4935–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, N.E.B.; Schacht, U.; Raval, V.; McGlone, T.; Sefcik, J.; Florence, A.J. Seeded Crystallization of beta-L-Glutamic Acid in a Continuous Oscillatory Baffled Crystallizer. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGinty, J.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Price, C.; ter Horst, J.H.; Sefcik, J. Chapter 1 Nucleation and Crystal Growth in Continuous Crystallization. In The Handbook of Continuous Crystallization; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, S.; Morris, G.; Hao, H.X.; Barrett, M.; Glennon, B. In-situ monitoring and characterization of plug flow crystallizers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 77, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kamaraju, V.K.; Hou, G.Y.; Power, G.; Donnellan, P.; Glennon, B. Kinetic identification and experimental validation of continuous plug flow crystallisation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 133, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, Y.E.D.; Tung, H.H.; Braatz, R.D. Effect of jet velocity on crystal size distribution from antisolvent and cooling crystallizations in a dual impinging jet mixer. Chem. Eng. Process. 2015, 97, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.; Dalvi, S.V.; Dave, R.N. Controlled liquid antisolvent precipitation using a rapid mixing device. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 5669–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenberg, C.; Mazzotti, M. Continuous Precipitation of L-Asparagine Monohydrate in a Micromixer: Estimation of Nucleation and Growth Kinetics. AIChE J. 2011, 57, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, M.; Mukai, K.; Cork, D.; Mae, K. Continuous crystallization using a sonicated tubular system for controlling particle size in an API manufacturing process. Chem. Eng. Process. 2016, 102, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, M.; Alund, B.L.; Rasmuson, A.C. Reaction crystallization kinetics of benzoic add. AIChE J. 2001, 47, 1544–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandin, A.F.; Mangin, D.; Nallet, V.; Klein, J.P.; Bossoutrot, J.M. Kinetics identification of salicylic acid precipitation through experiments in a batch stirred vessel and a T-mixer. Chem. Eng. J. 2001, 81, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.N.; Bigam, G.; Chan, J.K.; Hogg, A.M.; Nakashima, T.T.; Vederas, J.C. Biosynthesis of The Hypocholesterolemic Agent Mevinolin by Aspergillus-Terreus—Determination of the Origin of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen-Atoms by C-13-Nmr and Mass-Spectrometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 3694–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, A.W.; Chen, J.; Kuron, G.; Hunt, V.; Huff, J.; Hoffman, C.; Rothrock, J.; Lopez, M.; Joshua, H.; Harris, E.; et al. Mevinolin—A Highly Potent Competitive Inhibitor of Hydroxymethylglutaryl-Coenzyme-a Reductase and a Cholesterol-Lowering Agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 3957–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, M.I.; Oliveira, M.A.; Gomes, E.C.L.; Mussel, W.N.; Castro, W.V.; Soares, C.D.V. Thermal characterization of lovastatin in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 106, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javernik, S.; Kreft, S.; Strukelj, B.; Vrecer, F. Oxidation of lovastatin in the solid state and its stabilization with natural antioxidants. Pharmazie 2001, 56, 738–740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turner, T.D.; Hatcher, L.E.; Wilson, C.C.; Roberts, K.J. Habit Modification of the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Lovastatin Through a Predictive Solvent Selection Approach. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1779–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatcher, L.E.; Li, W.; Payne, P.; Benyahia, B.; Rielly, C.D.; Wilson, C.C. Tuning Morphology in Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients: Controlling the Crystal Habit of Lovastatin through Solvent Choice and Non-Size-Matched Polymer Additives. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 5854–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, K.C.L.; Mulinari, F.; Franco, O.L.; Soares, M.S.F.; Magalhaes, B.S.; Parachin, N.S. Lovastatin production: From molecular basis to industrial process optimization. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 648–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.K.; Fujiwara, M.; Braatz, R.D. Modelling and control of combined cooling and antisolvent crystallization processes. J. Process. Control 2008, 18, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, Z.Q.; Chai, J.; Xu, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Qian, G.; Zhou, X.G. Nucleation kinetics of lovastatin in different solvents from metastable zone widths. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 133, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.A.; Davey, R.J. Concerning the crystal morphologies of the alpha and beta polymorphs of p-aminobenzoic acid. Crystengcomm 2015, 17, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmback, X.; Rasmuson, A.C. Size and morphology of benzoic acid crystals produced by drowning-out crystallisation. J. Cryst. Growth 1999, 198, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; Rosbottom, I.; Marziano, I.; Hammond, R.B.; Roberts, K.J. Crystal Morphology and Interfacial Stability of RS-Ibuprofen in Relation to Its Molecular and Synthonic Structure. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 3088–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rimez, B.; Conte, J.; Lecomte-Norrant, E.; Cognet, P.; Gourdon, C.; Scheid, B. Continuous-Flow Tubular Crystallization To Discriminate between Two Competing Crystal Polymorphs. 2. Antisolvent Crystallization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 6440–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sypek, K.; Burns, I.S.; Florence, A.J.; Sefcik, J. In Situ Monitoring of Stirring Effects on Polymorphic Transformations during Cooling Crystallization of Carbamazepine. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 4821–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Variankaval, N.; Cote, A.S.; Doherty, M.F. From form to function: Crystallization of active pharmaceutical ingredients. AIChE J. 2008, 54, 1682–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovette, M.A.; Doherty, M.F. Needle-Shaped Crystals: Causality and Solvent Selection Guidance Based on Periodic Bond Chains. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 3341–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.F.; Chen, C.; Zhu, P.; Xia, H.M.; Shi, J.Y.; Yan, F.Y.H.; Shen, R.Q. Passive Micromixer Platform for Size- and Shape-Controllable Preparation of Ultrafine HNS. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 16709–16718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, K.; Hudson, S.P.; Rasmuson, A.C. Stepwise Use of Additives for Improved Control over Formation and Stability of Mefenamic Acid Nanocrystals Produced by Antisolvent Precipitation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, T.B.; Rasmuson, A.C.; Hudson, S.P. Size and Shape Control of Micron-Sized Salicylic Acid Crystals during Antisolvent Crystallization. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Q.; Shan, J.H.; Chen, D.; Li, H.Z. Tuning the Crystal Habits of Organic Explosives by Antisolvent Crystallization: The Case Study of 2,6-dimaino-3,5-dinitropyrazine-1-oxid (LLM-105). Crystals 2019, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.; Koo, J.Y.; Choi, H.C. Additive-Free Morphology Control of Organic Polyhedral Molecular Crystals by the Antisolvent Molecular Geometry: From Rod, Disk, to Cube. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 7239–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Song, H.P.; Leng, Y. Rapid determination of lovastatin in the fermentation broth of Aspergillus terreus using dual-wavelength UV spectrophotometry. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurtz, S.S.; Wikingss, A.E.; Camin, D.L.; Thompson, A.R. Refractive index and density of acetone-water solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nti-Gyabaah, J.; Chmielowski, R.; Chan, V.; Chiew, Y.C. Solubility of lovastatin in a family of six alcohols: Ethanol, 1-propanol, 1-butanol, 1-pentanol, 1-hexanol, and 1-octanol. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 359, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nti-Gyabaah, J.; Chiew, Y.C. Solubility of lovastatin in ethyl acetate, propyl acetate, isopropyl acetate, butyl acetate, sec-butyl acetate, isobutyl acetate, tert-butyl acetate, and 2-butanone, between (285 and 313) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2008, 53, 2060–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Gong, J.B.; Wang, J.K. Solubility of lovastatin in acetone, methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate, and butyl acetate between 283 K and 323 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2005, 50, 1389–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Conference of Harmonisation Expert Working Group. Impurities: Guideline for Residual solvents Q3C(R5); International Conference on Harmonisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gillian, J.M.; Kirwan, D.J. Quasi-emulsion precipitation of pharmaceuticals. 1. Conditions for formation and crystal nucleation and growth behavior. Cryst. Growth Des. 2006, 6, 2214–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, J.K. Solubility of lovastatin in acetone plus water solvent mixtures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2008, 53, 1335–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.C.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, J.T. Investigation of Oiling-Out Phenomenon of Small Organic Molecules in Crystallization Processes: A Review. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 7855–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimaladevi, P.; Supriya, S.; Srinivasan, K. The role of ultrasound in controlling the liquid-liquid phase separation and nucleation of vanillin polymorphs I and II. J. Cryst. Growth 2018, 484, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.G.; Altimimi, F.; Gong, J.B.; Bao, Y.; Wang, J.K.; Rohani, S. Ultrasonic Irradiation and Seeding To Prevent Metastable Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation and Intensify Crystallization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 2628–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Experiment Label | Ultrasound | Solution: Antisolvent Flow Ratio | Total Flow Rate (g/min) | Pre-Nucleation Supersaturation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp 1 | Off | 1:1 | 200 | 13.7 |
| Exp 2 | Off | 1:1 | 400 | 13.7 |
| Exp 3 | Off | 2:1 | 200 | 5.20 |
| Exp 4 | Off | 3:1 | 200 | 2.65 |
| Exp 5 | On | 1:1 | 200 | 13.7 |
| Exp 6 | On | 1:1 | 400 | 13.7 |
| Exp 7 | On | 2:1 | 200 | 5.20 |
| Exp 8 | On | 3:1 | 200 | 2.65 |
| Experiment Label | Final Solution Concentration (g/kg Solvent) | Yield (%) | Solid Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exp 1 | 11.27 | 75.12 | 81.29 |
| Exp 2 | 7.26 | 84.05 | 90.95 |
| Exp 3 | 21.37 | 64.43 | 86.04 |
| Exp 4 | 27.97 | 58.13 | 96.16 |
| Exp 5 | 20.33 | 54.72 | 60.11 |
| Exp 6 | 13.70 | 69.70 | 75.42 |
| Exp 7 | 21.80 | 63.69 | 85.06 |
| Exp 8 | 31.63 | 52.46 | 95.55 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McGinty, J.; Chong, M.W.S.; Manson, A.; Brown, C.J.; Nordon, A.; Sefcik, J. Effect of Process Conditions on Particle Size and Shape in Continuous Antisolvent Crystallisation of Lovastatin. Crystals 2020, 10, 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100925
McGinty J, Chong MWS, Manson A, Brown CJ, Nordon A, Sefcik J. Effect of Process Conditions on Particle Size and Shape in Continuous Antisolvent Crystallisation of Lovastatin. Crystals. 2020; 10(10):925. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100925
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcGinty, John, Magdalene W. S. Chong, Andrew Manson, Cameron J. Brown, Alison Nordon, and Jan Sefcik. 2020. "Effect of Process Conditions on Particle Size and Shape in Continuous Antisolvent Crystallisation of Lovastatin" Crystals 10, no. 10: 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100925
APA StyleMcGinty, J., Chong, M. W. S., Manson, A., Brown, C. J., Nordon, A., & Sefcik, J. (2020). Effect of Process Conditions on Particle Size and Shape in Continuous Antisolvent Crystallisation of Lovastatin. Crystals, 10(10), 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100925