Photorefractive Effect in NLC Cells Caused by Anomalous Electrical Properties of ITO Electrodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. ITO Electrode as the SPR Effect Source in the Pure NLC Cells
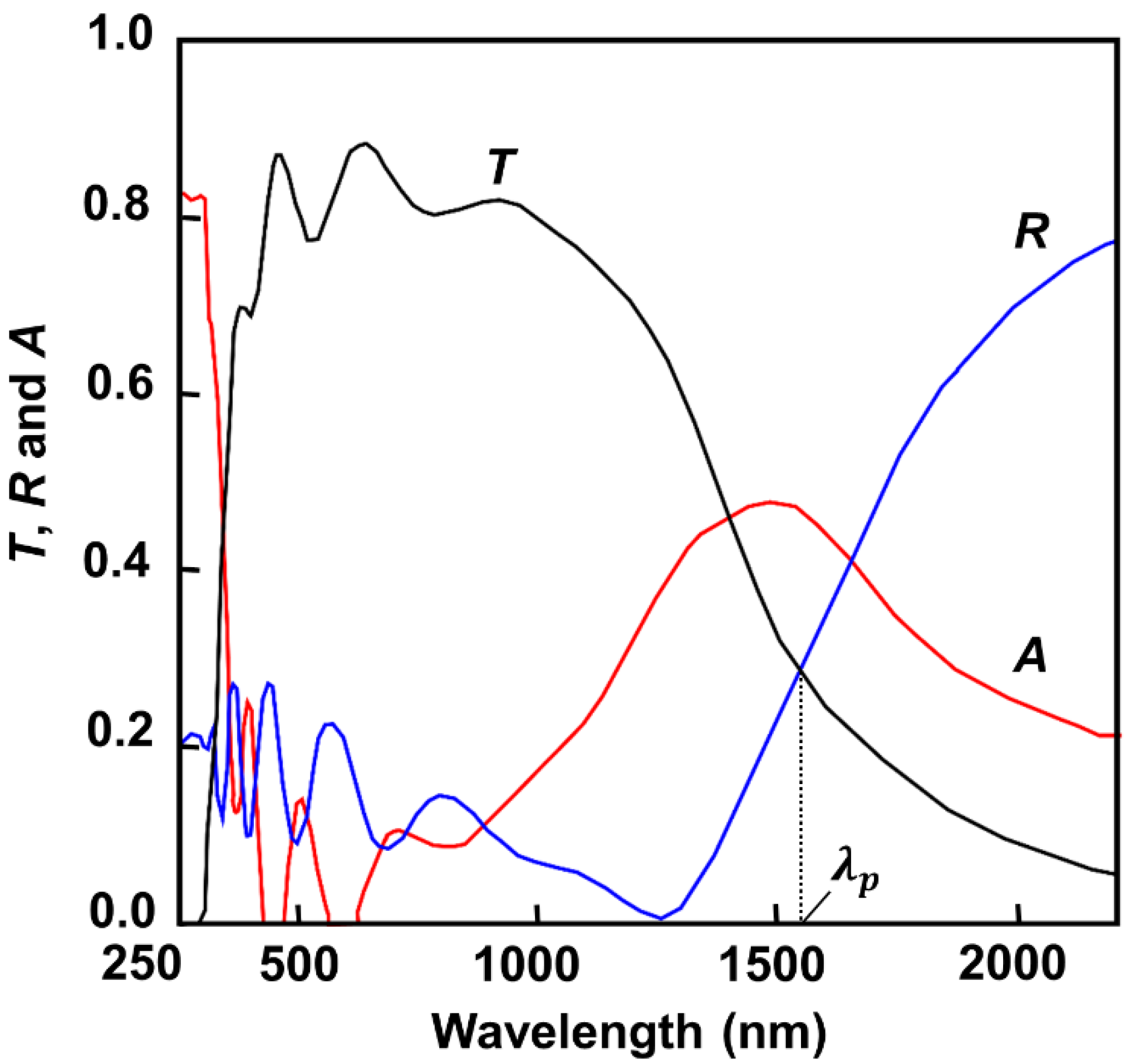
2.1. Opto-Electronic Behavior of the ITO Thin Films
2.2. Frequency-Dependent Conductivity of ITO Thin Film
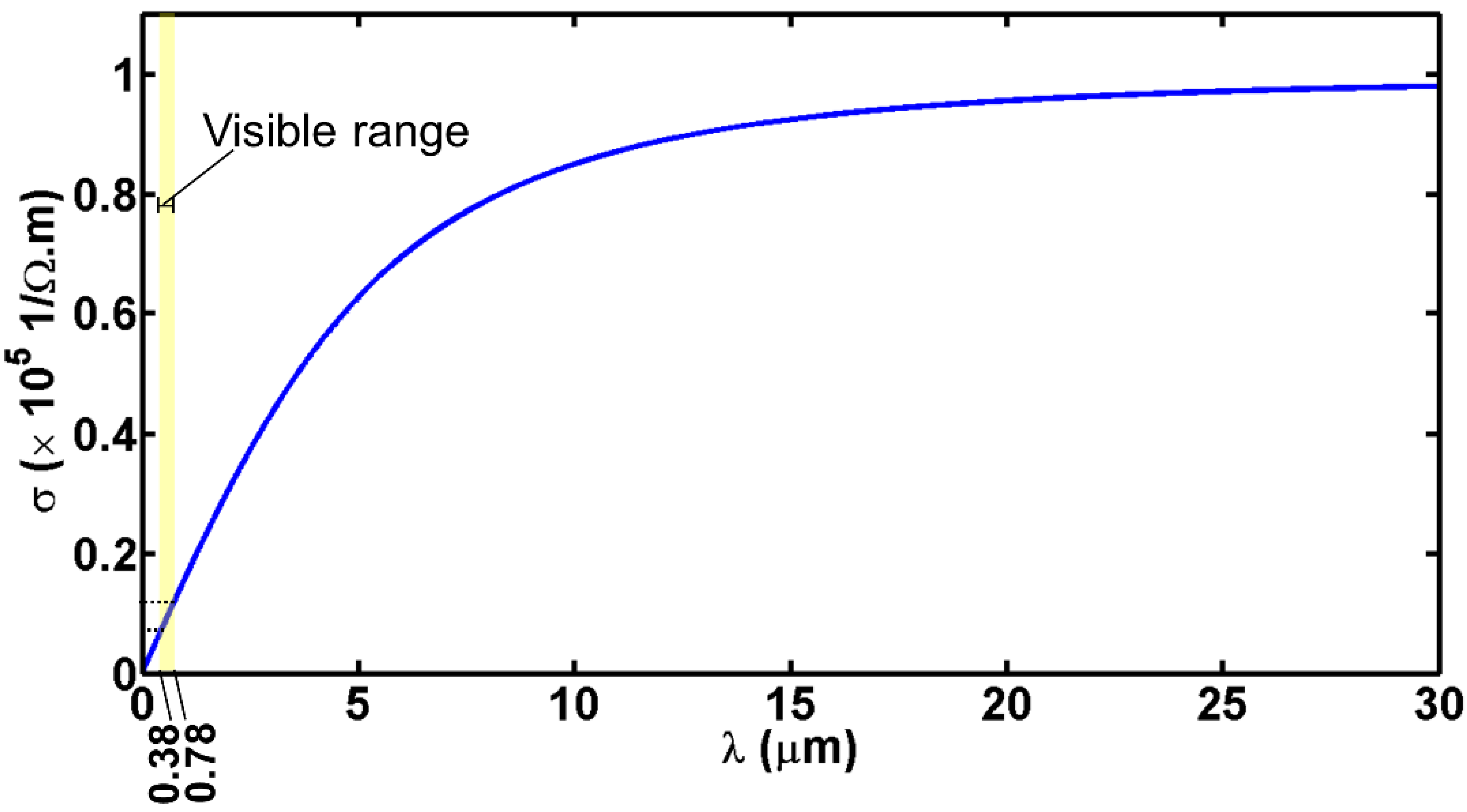
2.3. ITO Conductivity in Very Low DC Operating Regime
3. A Brief Review of the Self-Action of a Visible Light Beam in the NLC Cells Biased with a DC Electric Field
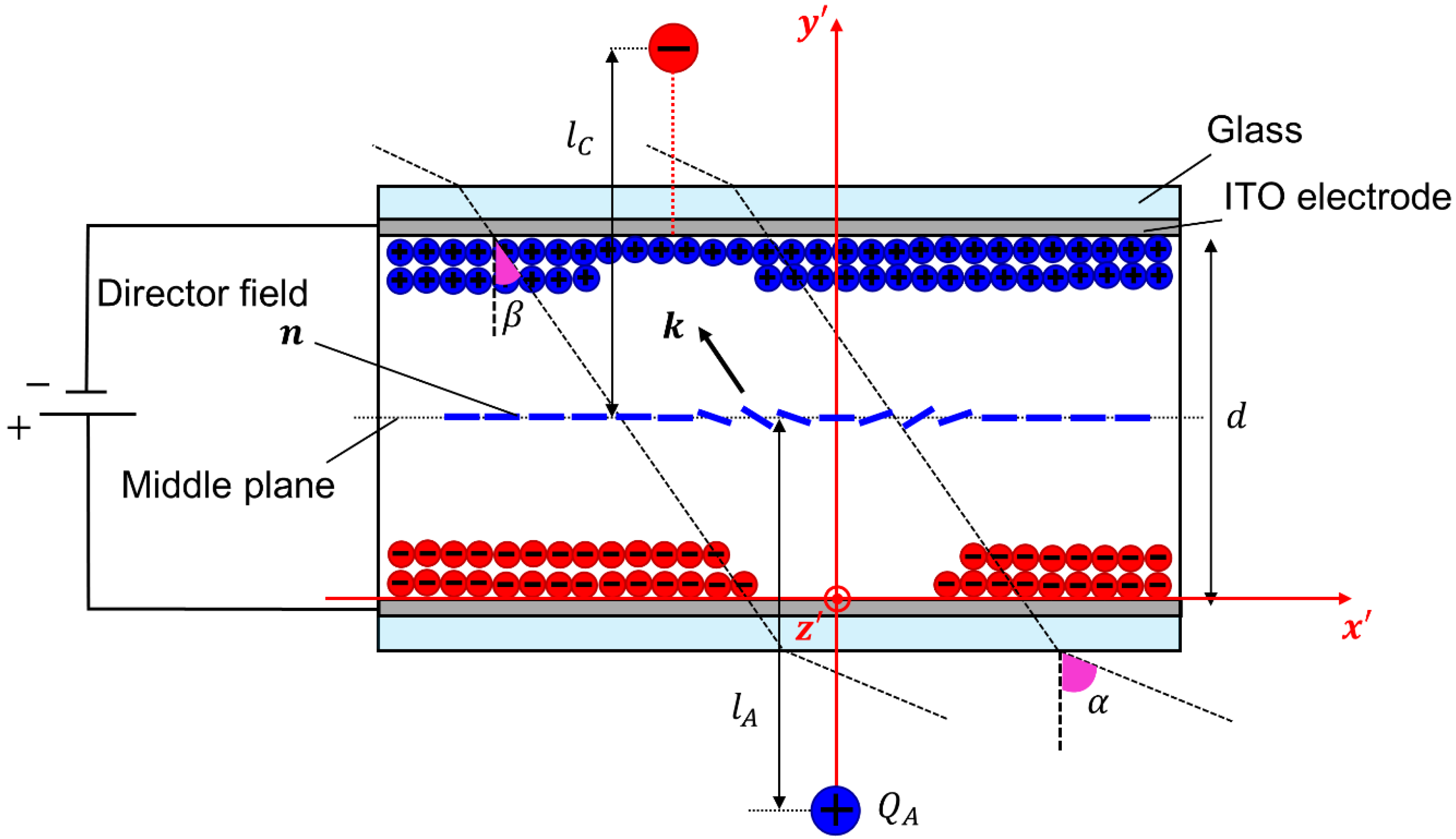
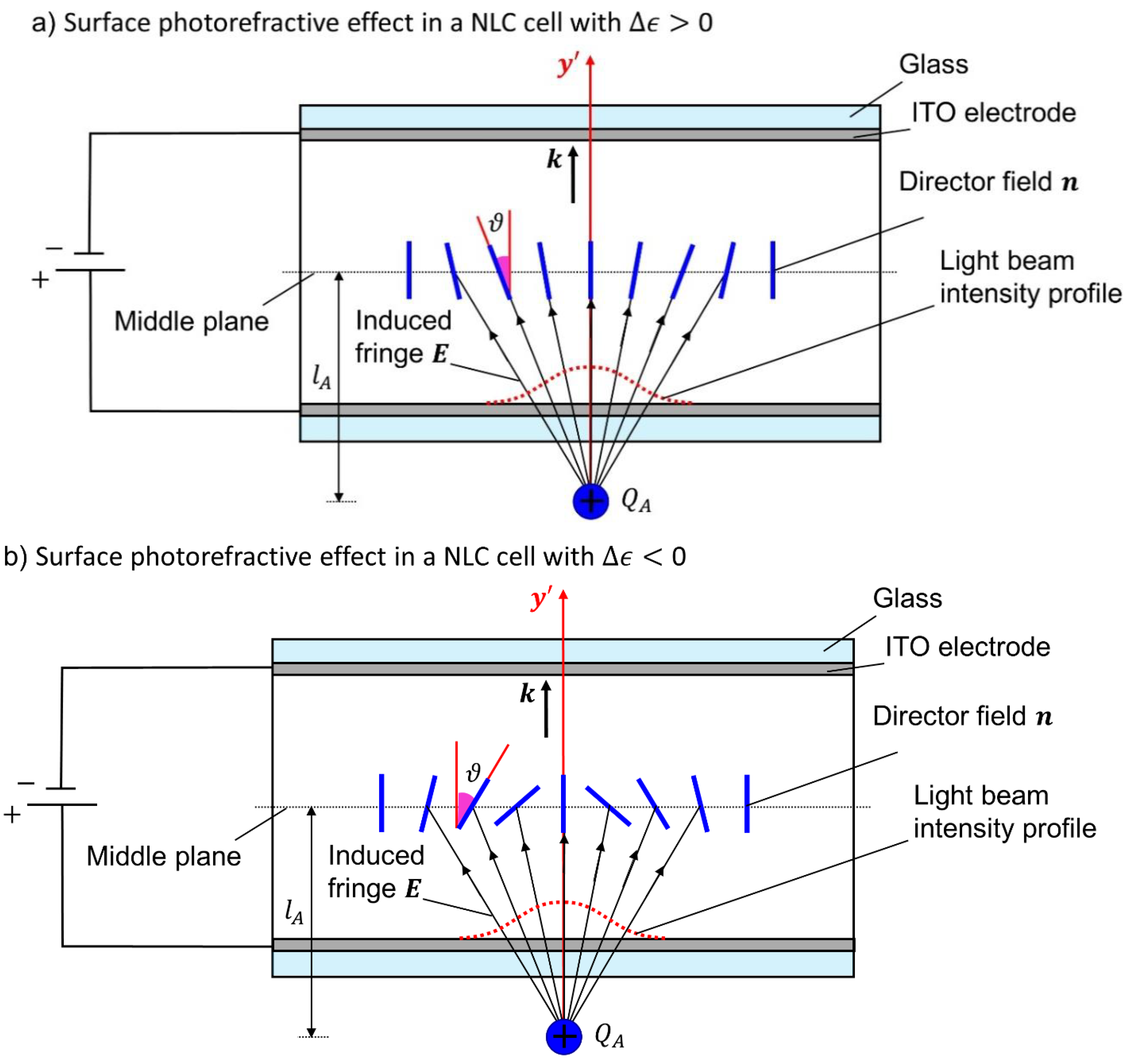
3.1. The SPR Effect Manifested in the Formation of the Aberration Patterns
3.2. Generation of Optical Vortices in the NLC Context Due to the SPR Effect
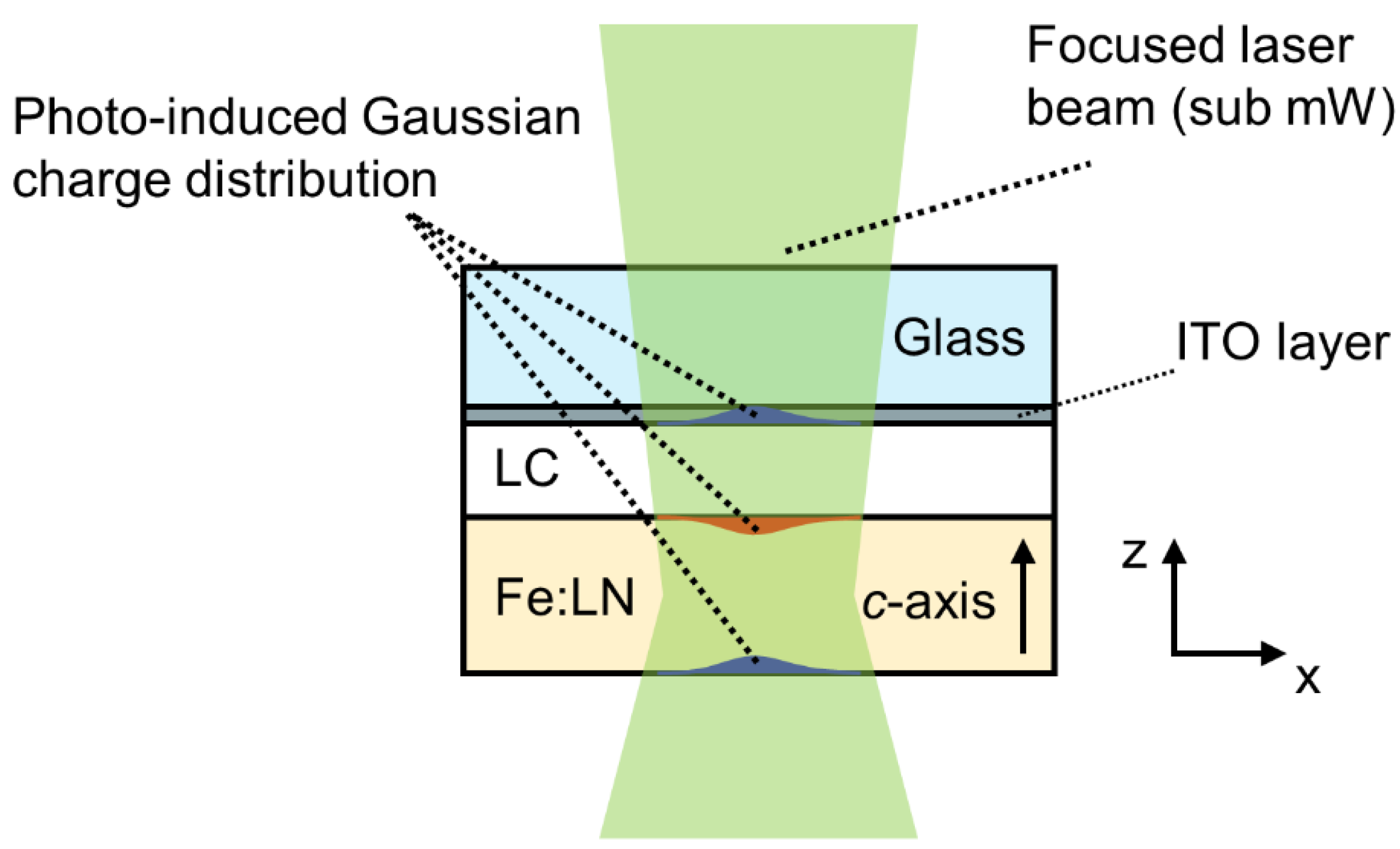
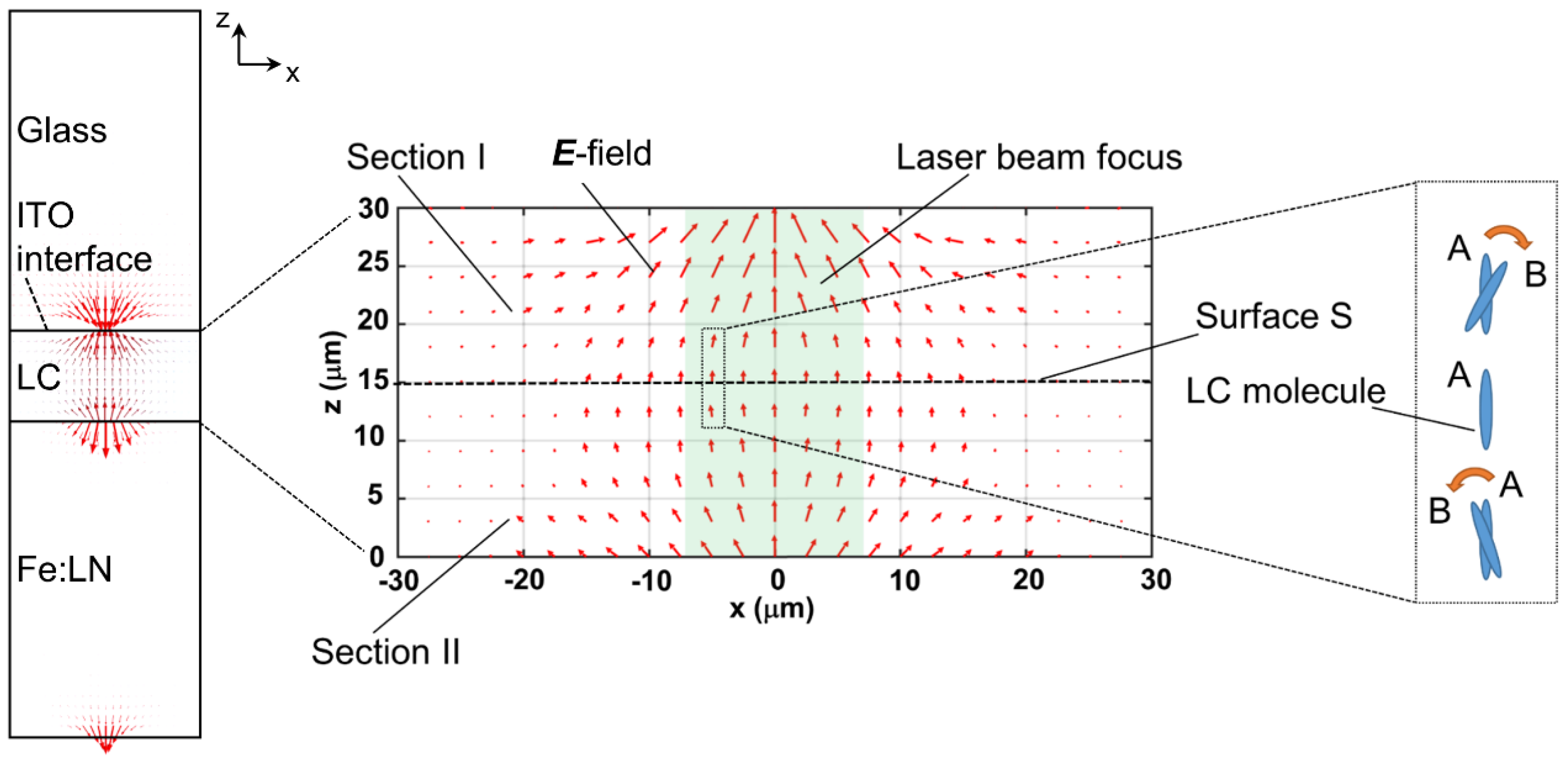
3.3. SPR Effect-Assisted Formation of Umbilical Defects in an NLC Cell Made from a Photo-Responsive Substrate
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ballman, A.A. Growth of Piezoelectric and Ferroelectric Materials by the CzochraIski Technique. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1965, 48, 112–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassau, K.; Levinstein, H.; LoIacono, G. Ferroelectric lithium niobate. 2. Preparation of single domain crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1966, 27, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yariv, A.; Yeh, P. Optical Waves in Crystals; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1984; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Zolot’Ko, A.S.; Budagovsky, I.A.; Kitaeva, V.F.; Ochkin, V.N.; Shakun, A.V.; Smayev, M.P.; Barnik, M.I. Orientational Interaction of a Light Beam and NLCs Subjected to External DC Field. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2006, 454, 407–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budagovsky, I.A.; Zolot’Ko, A.S.; Smayev, M.P.; Barnik, M.I. Self-action of a light beam in nematic liquid crystals in the presence of a DC electric field. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 2010, 111, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudenko, E.V.; Sukhov, A.V. Optically induced spatial charge separation in a nematic and the resultant orientational nonlinearity. JETP 1994, 105, 1621–1634. [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko, E.V.; Sukhov, A.V. Photoinduced electrical conductivity and photorefraction in a nematic liquid crystal. JETP Lett. 1994, 59, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko, E.V.; Sukhov, A.V. Photorefractive Effect in Nematic Liquid Crystals: Ion-Diffusion Approach. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. Sci. Technol. Sect. A. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1996, 282, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Montemezzani, G.; Günter, P. Orientational photorefractive effect in nematic liquid crystal with externally applied fields. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 1709–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ostroverkhov, V.; Singer, K.D.; Reshetnyak, V.; Reznikov, Y. Electrically controlled surface diffraction gratings in nematic liquid crystals. Opt. Lett. 2000, 25, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliusi, P.; Cipparrone, G. Extremely sensitive light-induced reorientation in nondoped nematic liquid crystal cells due to photoelectric activation of the interface. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 9116–9122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, I.; Chen, K.; Williams, Y. Orientational Photorefractive Effect in Undoped and CdSe Nanorods-Doped Nematic Liquid Crystal—Bulk and Interface Contributions. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2006, 12, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budagovsky, I.A.; Zolot’Ko, A.S.; Lobanov, A.N.; Smayev, M.P.; Tskhovrebov, A.M.; Averyushkin, A.S.; Barnik, M.I. Study of the photocurrent in liquid crystal cells exhibiting the photorefractive effect. Bull. Lebedev Phys. Inst. 2010, 37, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibpourmoghadam, A.; Wolfram, L.; Jahanbakhsh, F.; Mohr, B.; Reshetnyak, V.Y.; Lorenz, A. Tunable Diffraction Gratings in Copolymer Network Liquid Crystals Driven with Interdigitated Electrodes. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2019, 1, 2574–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouskova, E.; Reznikov, Y.; Shiyanovskii, S.; Su, L.; West, J.; Kuksenok, O.; Francescangeli, O.; Simoni, F. Photo-orientation of liquid crystals due to light-induced desorption and adsorption of dye molecules on an aligning surface. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 051709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budagovsky, I.A.; Ochkin, V.N.; Smayev, M.P.; Zolot’Ko, A.S.; Bobrovsky, A.Y.; Boiko, N.I.; Lysachkov, A.I.; Shibaev, V.P.; Barnik, M.I. Interaction of light with a NLC–dendrimer system. Liq. Cryst. 2009, 36, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibpourmoghadam, A.; Jiao, L.; Reshetnyak, V.; Evans, D.R.; Lorenz, A. Optical manipulation and defect creation in a liquid crystal on a photoresponsive surface. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 96, 022701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibpourmoghadam, A.; Jiao, L.; Omairat, F.; Evans, D.R.; Lucchetti, L.; Reshetnyak, V.; Lorenz, A. Confined photovoltaic fields in a photo-responsive liquid crystal test cell. In Liquid Crystals XXI; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10361, p. 1036112. [Google Scholar]
- Habibpourmoghadam, A. Theoretical Prediction of Umbilics Creation in Nematic Liquid Crystals with Positive Dielectric Anisotropy. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 21459–21468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neaman, D.A. Semiconductor Physics and Devices; IRWIN: Chicago, IL, USA, 2003; Chapter 10; p. 457. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, S.; Banerjee, R.; Basu, N.; Batabyal, A.K.; Barua, A.K. Properties of tin doped indium oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 1983, 54, 3497–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohhata, Y.; Shinoki, F.; Yoshida, S. Optical properties of r.f. reactive sputtered tin-doped In2O3 films. Thin Solid Films 1979, 59, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, E. Anomalous Optical Absorption Limit in InSb. Phys. Rev. 1954, 93, 632–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, S.-C.; Chang, C.-F. Fabrication and Characterization of Indium Tin Oxide Films. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2017, 15, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, M.; Kaczmarek, D.; Domaradzki, J.; Wojcieszak, D.; Song, S.; Placido, F. Influence of thickness on transparency and sheet resistance of ITO thin films. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Advanced Semiconductor Devices and Microsystems, Smolenice, Slovakia, 25–27 October 2010; pp. 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Gilmore, C.M.; PiquéA; Horwitz, J.; Mattoussi, H.; Murata, H.; Kafafi, Z.; Chrisey, D. Electrical, optical, and structural properties of indium–tin–oxide thin films for organic light-emitting devices. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 6451–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Cameron, D.C. Investigation of annealing effects on sol–gel deposited indium tin oxide thin films in different atmospheres. Thin Solid Films 2002, 420, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, H.; Ueda, K. Transparent conductive oxides. In Springer Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Farhan, M.S.; Zalnezhad, E.; Bushroa, A.; Sarhan, A.A.D. Electrical and optical properties of indium-tin oxide (ITO) films by ion-assisted deposition (IAD) at room temperature. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 14, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Lau, S.P.; Sun, Z.; Shi, X.; Tay, B.K.; Tan, H. Structural and electrical properties of copper thin films prepared by filtered cathodic vacuum arc technique. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 138, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.P.; Porch, A.; Jones, M.O.; Morgan, D.V.; Perks, R.M. Basic materials physics of transparent conducting oxides. Dalton Trans. 2004, 19, 2995–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, A.F.; Regel, A.R. Non-crystalline, amorphous and liquid electronic semiconductors. Prog. Semicond. 1960, 4, 237–291. [Google Scholar]
- Heeger, A.J. The Critical Regime of the Metal-Insulator Transition in Conducting Polymers: Experimental Studies. Phys. Scr. 2002, 2002, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, N.F.; Davis, E.A. Electronic Processes in Non-Cyrstalline Materials; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, D.K.; Kumar, K.U.; Subrahmanyam, A. Metal-insulator transition in tin doped indium oxide (ITO) thin films: Quantum correction to the electrical conductivity. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 15109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-J.; Li, Z.-Q. Electronic conduction properties of indium tin oxide: Single-particle and many-body transport. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 343201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, T.S. The Interpretation of the Properties of Indium Antimonide. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. B 1954, 67, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.C.C.; Goodenough, J.B. X-ray photoemission spectroscopy studies of Sn-doped indium-oxide films. J. Appl. Phys. 1977, 48, 3524–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamberg, I.; Granqvist, C.G.; Berggren, K.F.; Sernelius, B.E.; Engström, L. Band-gap widening in heavily Sn-doped In2O3. Phys. Rev. B. 1984, 30, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamberg, I.; Granqvist, C.G. Evaporated Sn-doped In2O3 films: Basic optical properties and applications to energy-efficient windows. J. Appl. Phys. 1986, 60, R123–R160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizzardi, M.; Bonfadini, S.; Moscardi, L.; Kriegel, I.; Scotognella, F.; Criante, L. Large scale indium tin oxide (ITO) one dimensional gratings for ultrafast signal modulation in the visible spectral region. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 6881–6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Körber, C.; Wachau, A.; Säuberlich, F.; Gassenbauer, Y.; Harvey, S.P.; Proffit, D.E.; Mason, T.O. Transparent Conducting Oxides for Photovoltaics: Manipulation of Fermi Level, Work Function and Energy Band Alignment. Materials 2010, 3, 4892–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hichou, A.; Kachouane, A.; Bubendorff, J.L.; Addou, M.; Ebothe, J.; Troyon, M.; Bougrine, A. Effect of substrate temperature on electrical, structural, optical and cathodoluminescent properties of In2O3-Sn thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 2004, 458, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matino, F.; Persano, L.; Arima, V.; Pisignano, D.; Blyth, R.I.R.; Cingolani, R.; Rinaldi, R. Electronic structure of indium-tin-oxide films fabricated by reactive electron-beam deposition. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 085437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-S.; Choi, W.C.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, C.K.; Min, S.-K. Characterization of the oxidized indium thin films with thermal oxidation. Thin Solid Films 1996, 279, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palik, E.D. Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Porch, A.; Morgan, D.V.; Perks, R.M.; Jones, M.O.; Edwards, P.P. Electromagnetic absorption in transparent conducting films. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 4734–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Park, J.; Kang, J.-H.; Yuan, H.; Cui, Y.; Hwang, H.Y.; Brongersma, M.L. Quantification and impact of nonparabolicity of the conduction band of indium tin oxide on its plasmonic properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 181117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Papadakis, G.; Burgos, S.P.; Chander, K.; Kriesch, A.; Pala, R.; Peschel, U.; Atwater, H.A. Nanoscale Conducting Oxide PlasMOStor. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 6463–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-W.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Yu, P.-C.; Shieh, J.-M.; Pan, C.-L. Frequency-Dependent Complex Conductivities and Dielectric Responses of Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films from the Visible to the Far-Infrared. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2010, 46, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.; Castellón, E. Transparent Conductive Materials: Materials, Synthesis, Characterization, Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Neelakanta, P.S. Handbook of Electromagnetic Materials: Monolithic and Composite Versions and Their Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bechstedt, F. Many-Body Approach to Electronic Excitations; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. Solid State Technology Branch of Nasa Lewis Research Center Fourth Annual Digest; NASA Technical Memorandum V. 105752; Lewis Research Center: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, S. Microelectronics and Optoelectronics Technology. Laxmi Publications Pvt. Ltd: New Delhi, India, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi, C. Basic Semiconductor Physics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; Volume 9, pp. 443–510. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, K.F. The Physics of Semiconductors: With Applications to Optoelectronic Devices; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pagliusi, P.; Cipparrone, G. Surface-induced PR-like effect in pure liquid crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafemina, J.P. Photoconduction in polyimide. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1989, 159, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolot’ko, A.S.; Kitaeva, V.F.; Sobolev, N.N.; Sukhorukov, A.P. Self-focusing of laser radiation in the course of the Fréedericksz transition in the nematic phase of a liquid crystal. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 1981, 81, 933–941. [Google Scholar]
- Budagovsky, I.A.; Ochkin, V.N.; Smayev, M.P.; Zolot’ko, A.S.; Barnik, M.I. Asymmetric aberrational patterns at light beam self-action in nematic liquid crystals. In ICONO 2007: Coherent and Nonlinear Optical Phenomena, Proceedings of the SPIE; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; Volume 6729, p. 67293E. [Google Scholar]
- Zel’dovich, B.Y.; Tabiryan, N.V. Orientational optical nonlinearity of liquid crystals. Sov. Phys. Uspekhi 1985, 28, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaeva, V.F.; Zolot’ko, A.S.; Barnik, M.I. Orientational optical nonlinearity of absorbing nematic liquid crystals. Mol. Mater. 2000, 12, 271–293. [Google Scholar]
- Zolot’ko, A.S.; Kitaeva, V.F.; Kroo, N.; Sobolev, N.N.; Sukhorukov, A.P.; Csillag, L. Nature of the aberration pattern formed as the result of self-focusing of a light beam caused by reorientation of the director in liquid crystals. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 1982, 83, 1368–1375, [J. Exp. Theor. Phys (Sov. Phys. JETP), 83 (4), 786 (1982)]. [Google Scholar]
- Brasselet, E. Tunable Optical Vortex Arrays from a Single Nematic Topological Defect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 087801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapini, A. Umbilics: Static properties and shear-induced displacements. J. Phys. 1973, 34, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basistiy, I.V.; Soskin, M.S.; Vasnetsov, M.V. Optical wavefront dislocations and their properties. Opt. Commun. 1995, 119, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahagan, K.T.; Swartzlander, J.G.A.; Jr., G.A.S. Optical vortex trapping of particles. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahagan, K.T.; Swartzlander, G.A. Simultaneous trapping of low-index and high-index microparticles observed with an optical-vortex trap. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1999, 16, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, F.; Anzolin, G.; Umbriaco, G.; Bianchini, A.; Barbieri, C. Overcoming the Rayleigh Criterion Limit with Optical Vortices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 163903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Foo, G.; Johnson, E.G.; Swartzlander, G.A., Jr. Experimental Verification of an Optical Vortex Coronagraph. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 053901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.; Courtial, J.; Padgett, M.; Vasnetsov, M.V.; Pas’Ko, V.; Barnett, S.M.; Franke-Arnold, S. Free-space information transfer using light beams carrying orbital angular momentum. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 5448–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, A.; Vaziri, A.; Weihs, G.; Zeilinger, A. Entanglement of the orbital angular momentum states of photons. Nature 2001, 412, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budagovsky, I.A.; Shvetsov, S.A.; Zolot’Ko, A.S. Optical vortex generation in homeotropic NLCs in the presence of DC electric field. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 637, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budagovsky, I.A.; Zolot’Ko, A.S.; Smayev, M.P.; Shvetsov, S.A. Formation of the light beam with wavefront screw dislocation at the photorefractive effect in nematic liquid crystal. Bull. Lebedev Phys. Inst. 2015, 42, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budagovsky, I.A.; Zolot’Ko, A.S.; Shvetsov, S.A. On the formation of vortex light beams at the surface photorefractive effect in NLC. Bull. Lebedev Phys. Inst. 2016, 43, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravets, N.; Podoliak, N.; Kaczmarek, M.; Brasselet, E. Self-induced liquid crystal q-plate by photoelectric interface activation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 061101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.E.; Grier, D.G. Structure of Optical Vortices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 133901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleev, I.D.; Swartzlander, J.G.A.; Jr., G.A.S. Composite optical vortices. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2003, 20, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.M.; Padgett, M. Orbital angular momentum: Origins, behavior and applications. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2011, 3, 161–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Burzynski, R.; Ghosal, S.; Casstevens, M.K. PR polymers and composites. Adv. Mater. 1996, 8, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenbaum, E.; Diest, K.; Atwater, H.A. Unity-Order Index Change in Transparent Conducting Oxides at Visible Frequencies. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2111–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melikyan, A.; Lindenmann, N.; Walheim, S.; Leufke, P.M.; Ulrich, S.; Ye, J.; Vincze, P.; Hahn, H.; Schimmel, T.; Koos, C.; et al. Surface plasmon polariton absorption modulator. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 8855–8869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Shim, E.; Zhu, A.Y.; Zhu, H.; Reed, J.C.; Cubukcu, E. Voltage tuning of plasmonic absorbers by indium tin oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 221102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorger, V.J.; Lanzillotti-Kimura, N.D.; Ma, R.-M.; Zhang, X. Ultra-compact silicon nanophotonic modulator with broadband response. Nanophotonics 2012, 1, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrucci, L. Generation of Helical Modes of Light by Spin-to-Orbital Angular Momentum Conversion in Inhomogeneous Liquid Crystals. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2008, 488, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habibpourmoghadam, A. Photorefractive Effect in NLC Cells Caused by Anomalous Electrical Properties of ITO Electrodes. Crystals 2020, 10, 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100900
Habibpourmoghadam A. Photorefractive Effect in NLC Cells Caused by Anomalous Electrical Properties of ITO Electrodes. Crystals. 2020; 10(10):900. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100900
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabibpourmoghadam, Atefeh. 2020. "Photorefractive Effect in NLC Cells Caused by Anomalous Electrical Properties of ITO Electrodes" Crystals 10, no. 10: 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100900
APA StyleHabibpourmoghadam, A. (2020). Photorefractive Effect in NLC Cells Caused by Anomalous Electrical Properties of ITO Electrodes. Crystals, 10(10), 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100900




