Peptide–Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates as Artificial Carbonic Anhydrase Mimics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
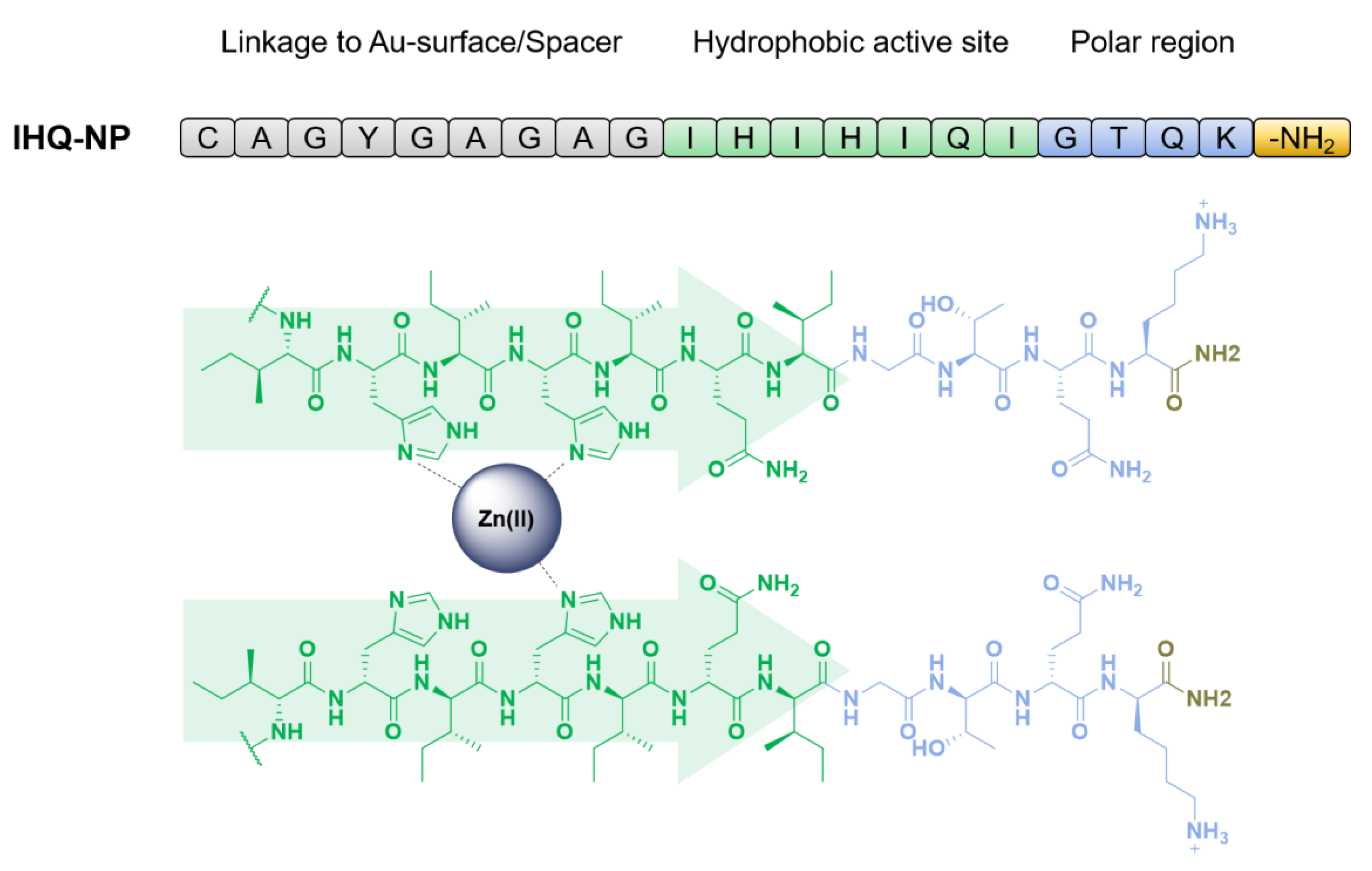
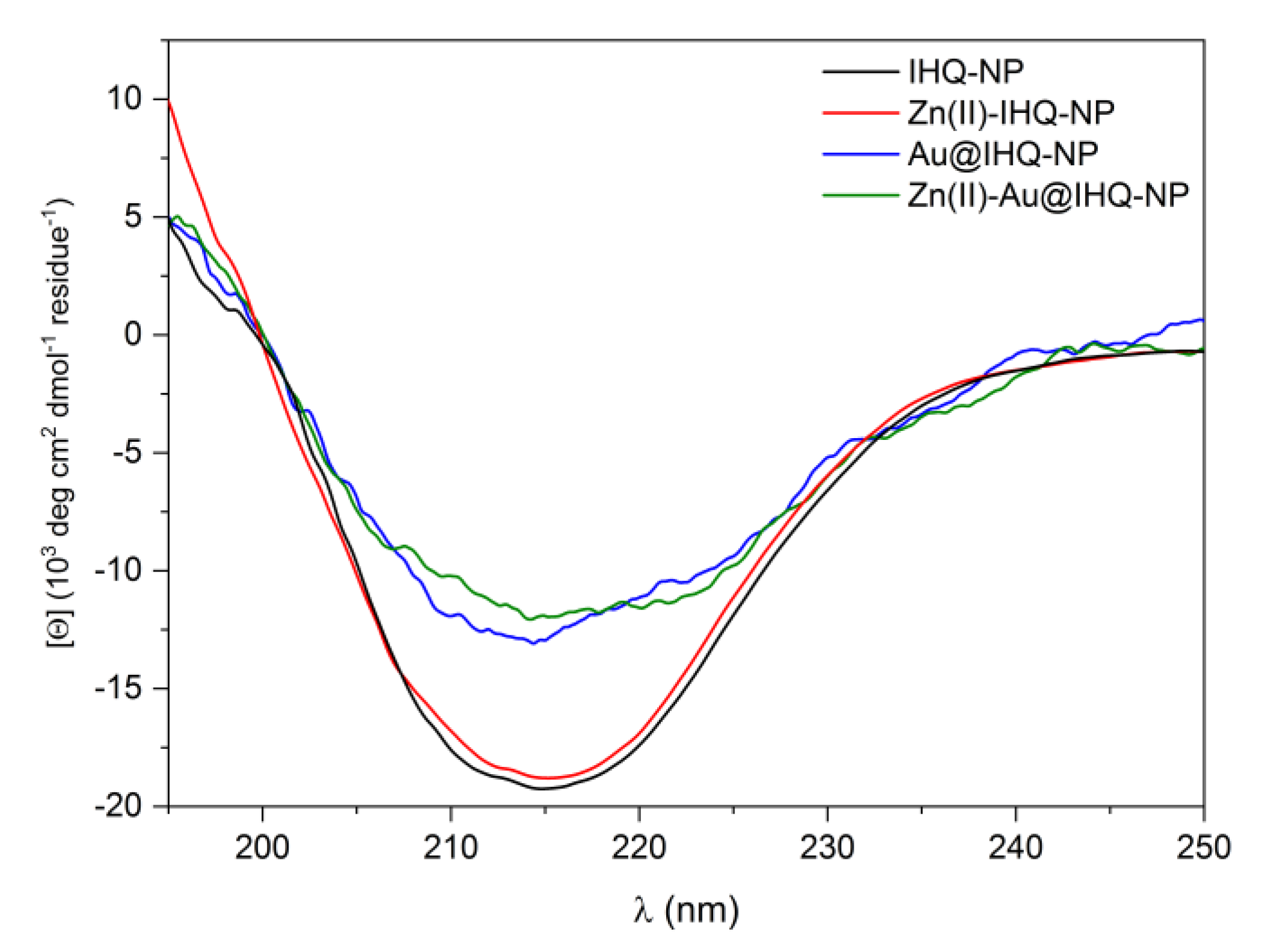
2.1. Peptide Design
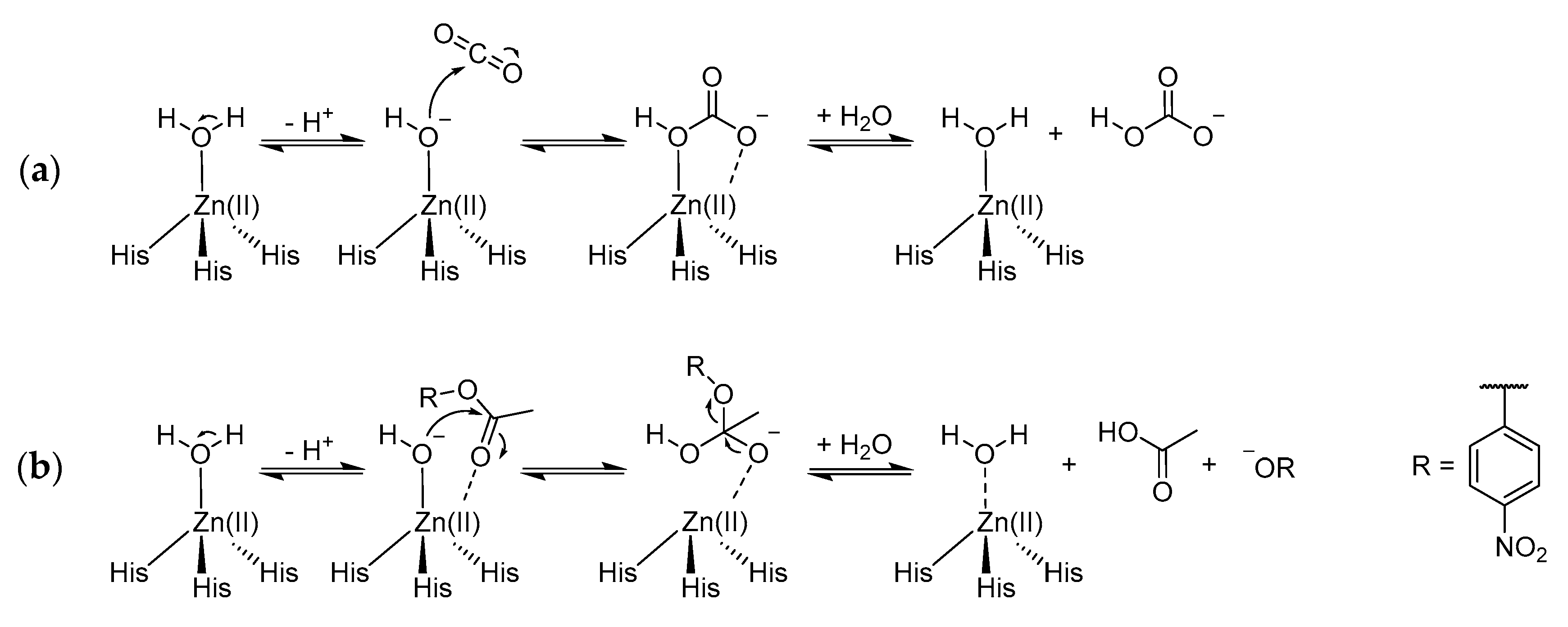
2.2. Esterase Activity
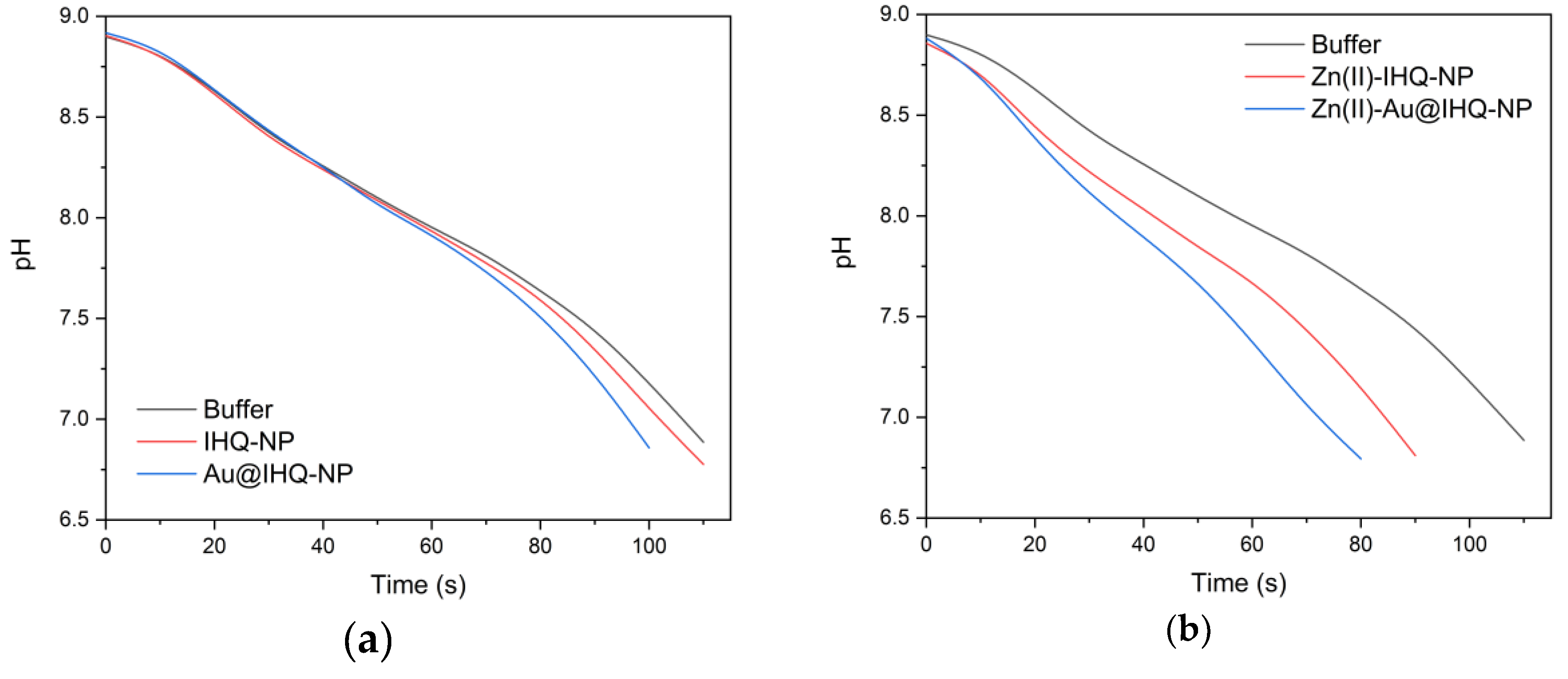
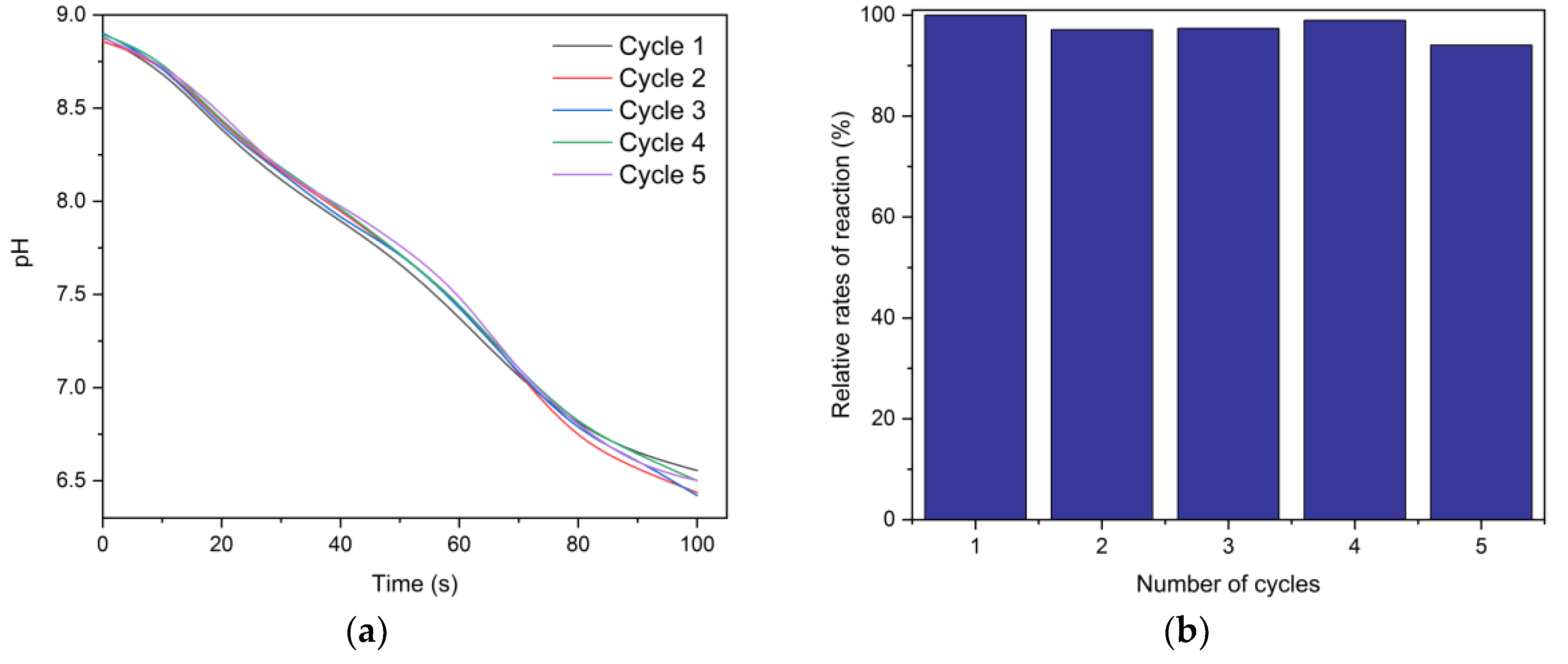
2.3. Carbonic Anhydrase Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Peptide Synthesis
3.2. Peptide Stock Solution
3.3. Synthesis of Au@IHQ-NP
3.4. Esterase Activity
3.5. Carbonic Anhydrase Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pasquato, L.; Pengo, P.; Scrimin, P. Nanozymes: Functional Nanoparticle-Based Catalysts. Supramol. Chem. 2005, 17, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Wei, H. Nanozymes in Bionanotechnology: From Sensing to Therapeutics and Beyond. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Catalytically Active Nanomaterials: Artificial Enzymes of Next Generation. Nanosci. Technol. 2017, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E. Nanomaterials with Enzyme-like Characteristics (Nanozymes): Next-Generation Artificial Enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6060–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Nano-Gold as Artificial Enzymes: Hidden Talents. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4200–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquato, L.; Pengo, P.; Scrimin, P. Functional Gold Nanoparticles for Recognition and Catalysis. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 3481–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengo, P.; Polizzi, S.; Pasquato, L.; Scrimin, P. Carboxylate-Imidazole Cooperativity in Dipeptide-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles with Esterase-like Activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1616–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengo, P.; Baltzer, L.; Pasquato, L.; Scrimin, P. Substrate Modulation of the Activity of an Artificial Nanoesterase Made of Peptide-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczak, D.J.; Koksch, B. Peptide-Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates as Sequential Cascade Catalysts. ChemCatChem 2018, 4324–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczak, D.J.; Heier, J.L.; Schade, B.; Koksch, B. Catalytic Activity of Peptide-Nanoparticle Conjugates Regulated by a Conformational Change. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3557–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczak, D.J.; Scholz, J.; Koksch, B. Tuning the Catalytic Activity and Substrate Specificity of Peptide-Nanoparticle Conjugates. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 5665–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, K.A.; Huang, C.; Fierke, C.A. Function and Mechanism of Zinc Metalloenzymes. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1437S–1446S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zastrow, M.L.; Pecoraro, V.L. Designing Hydrolytic Zinc Metalloenzymes. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 957–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christianson, D.W.; Fierke, C.A. Carbonic Anhydrase: Evolution of the Zinc Binding Site by Nature and by Design. Acc. Chem. Res. 1996, 29, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, C.D.; Habibzadegan, A.; Gill, S.; Mckenna, R. Carbonic Anhydrases and Their Biotechnological Applications. Biomolecules 2013, 3, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boone, C.D.; Gill, S.; Habibzadegan, A.; McKenna, R. Carbonic Anhydrase: An Efficient Enzyme with Possible Global Implications. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.K.J.; Stevens, G.W.; Caruso, F.; Kentish, S.E. The Use of Carbonic Anhydrase to Accelerate Carbon Dioxide Capture Processes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjafari, P.; Asghari, K.; Mahinpey, N. Investigating the Application of Enzyme Carbonic Anhydrase for CO2 Sequestration Purposes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufo, C.M.; Moroz, Y.S.; Moroz, O.V.; Stöhr, J.; Smith, T.A.; Hu, X.; DeGrado, W.F.; Korendovych, I.V. Short Peptides Self-Assemble to Produce Catalytic Amyloids. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Un, C.; Song, H.; Sankara, B.; Gruner, S.M.; Park, S.; Mckenna, R. Tracking Solvent and Protein Movement during CO2 Release in Carbonic Anhydrase II Crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5257–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulski, R.L.; Silverman, D.N. Proton Transfer in Catalysis and the Role of Proton Shuttles in Carbonic Anhydrase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2010, 1804, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colangelo, E.; Chen, Q.; Davidson, A.M.; Paramelle, D.; Sullivan, M.B.; Volk, M.; Levy, R. Experimental and Computational Investigation of the Structure of Peptide Monolayers on Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2017, 33, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, C.P.; Middleton, D.A.; Volk, M.; Lévy, R. Amyloid-Derived Peptide Forms Self-Assembled Monolayers on Gold Nanoparticle with a Curvature-Dependent β-Sheet Structure. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1416–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uda, N.R.; Seibert, V.; Stenner-Liewen, F.; Müller, P.; Herzig, P.; Gondi, G.; Zeidler, R.; van Dijk, M.; Zippelius, A.; Renner, C. Esterase Activity of Carbonic Anhydrases Serves as Surrogate for Selecting Antibodies Blocking Hydratase Activity. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zastrow, M.L.; Peacock, A.F.A.; Stuckey, J.A.; Pecoraro, V.L. Hydrolytic Catalysis and Structural Stabilization in a Designed Metalloprotein. Nat. Chem. 2011, 4, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.M.; Tawfik, D.S. Directed Evolution of the Promiscuous Esterase Activity of Carbonic Anhydrase II. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 5444–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, L.; Gabrielli, L.; Sun, X.; De Biasi, F.; Rastrelli, F.; Mancin, F.; De Vivo, M. Nanoparticle-Based Receptors Mimic Protein-Ligand Recognition. Chem 2017, 3, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, C.A.; Liu, K.; Sarma, M.; Parkin, S.R.; Remias, J.E.; Brandewie, C.M.; Odom, S.A.; Liu, K. Improving Carbon Capture from Power Plant Emissions with Zinc- and Cobalt-Based Catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 3620–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, R.A.; Miller, D.A.; Parkin, S.R.; Liu, K.; Remias, J.E.; Yang, Y.; Lightstone, F.C.; Liu, K.; Lippert, C.A.; Odom, S.A. Carbonic Anhydrase Mimics for Enhanced CO 2 Absorption in an Amine-Based Capture Solvent. Dalt. Trans. 2016, 45, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, G.M.; Stringer, J.; Brandvold, D.K.; Simsek, F.A.; Medina, M.-G.; Egeland, G. Development of Integrated System for Biomimetic CO2 Sequestration Using the Enzyme Carbonic Anhydrase. Energy Fuels 2001, 15, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, D.M.; Portugal, A.F.; Lozano, A.E.; de la Campa, J.G.; de Abajo, J. New Liquid Absorbents for the Removal of CO2 from Gas Mixtures. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizaki, K.; Kanakubo, M.; Nanjo, H.; Shimizu, S.; Onoda, M.; Fujioka, Y. 13C NMR Studies on the Dissolution Mechanisms of Carbon Dioxide in Amine-Containing Aqueous Solvents at High Pressures toward an Integrated Coal Gasification Combined Cycle−Carbon Capture and Storage Process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evjen, S.; Fiksdahl, A.; Pinto, D.D.D.; Knuutila, H.K. New Polyalkylated Imidazoles Tailored for Carbon Dioxide Capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2018, 76, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Atwater, M.; Wang, J.; Huo, Q. Extinction Coefficient of Gold Nanoparticles with Different Sizes and Different Capping Ligands. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 58, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
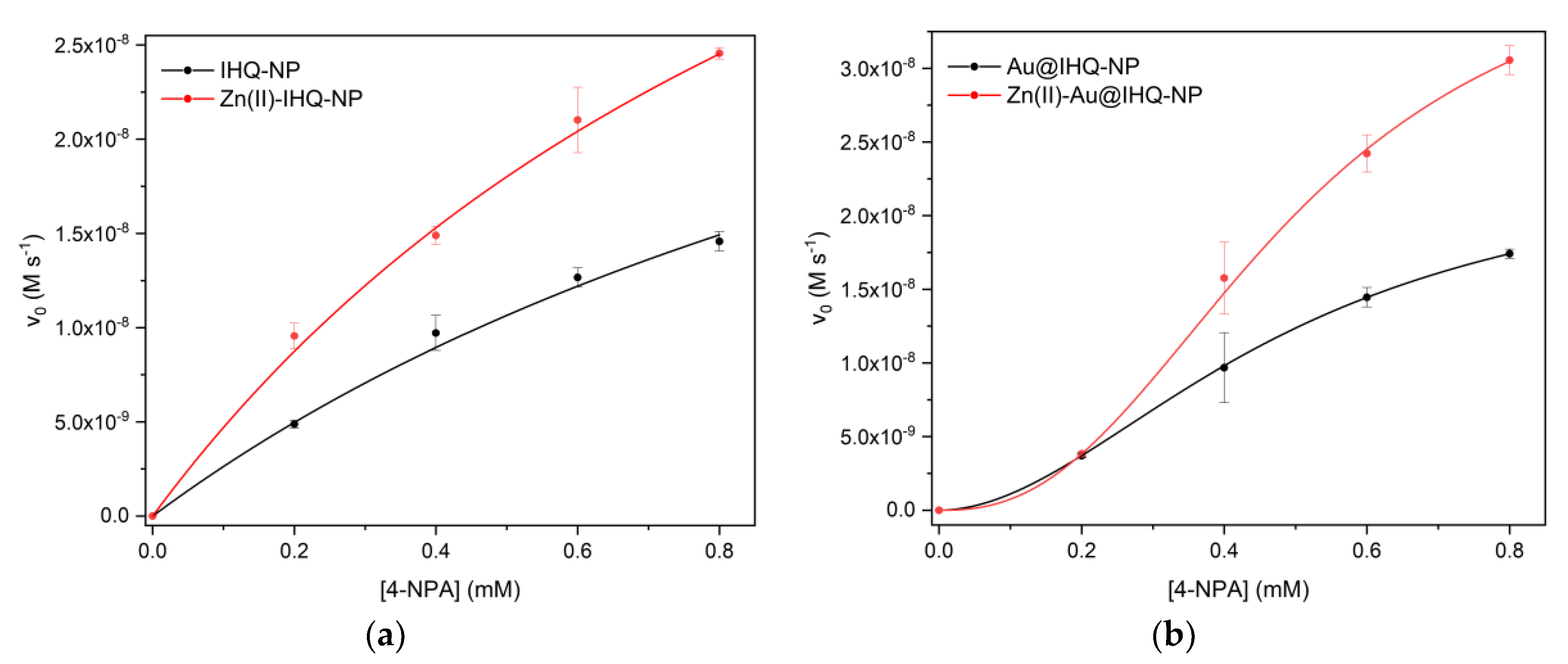
| Catalyst | kcat (10−3 s−1) | KM (mM) | kcat/KM (M−1 s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IHQ-NP 1 | 4.49 ± 0.68 | 1.61 ± 0.27 | 2.79 ± 0.98 |
| Zn(II)-IHQ-NP 1 | 10.53 ± 0.72 | 1.21 ± 0.20 | 8.69 ± 1.47 |
| Au@IHQ-NP 2 | 2.41 ± 0.02 | 0.49 ± 0.06 | 4.95 ± 0.61 |
| Zn(II)-Au@IHQ-NP 2 | 7.97 ± 0.41 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 16.06 ± 1.78 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mikolajczak, D.J.; Koksch, B. Peptide–Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates as Artificial Carbonic Anhydrase Mimics. Catalysts 2019, 9, 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110903
Mikolajczak DJ, Koksch B. Peptide–Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates as Artificial Carbonic Anhydrase Mimics. Catalysts. 2019; 9(11):903. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110903
Chicago/Turabian StyleMikolajczak, Dorian J., and Beate Koksch. 2019. "Peptide–Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates as Artificial Carbonic Anhydrase Mimics" Catalysts 9, no. 11: 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110903
APA StyleMikolajczak, D. J., & Koksch, B. (2019). Peptide–Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates as Artificial Carbonic Anhydrase Mimics. Catalysts, 9(11), 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110903




