Abstract
New iridium(III)-bipyridonate complexes having cyclopentadienyl ligands with a series of alkyl substituents were synthesized for the purpose of tuning the catalytic activity for acceptorless dehydrogenation reactions. A comparison of the catalytic activity was performed for the reaction of alcoholic substrates such as 1-phenylethanol, 2-octanol, and benzyl alcohol. The 1-t-butyl-2,3,4,5-tetramethylcyclopentadienyl iridium complex exhibited the best performance, which surpassed that of the 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl (Cp*) iridium catalyst in the dehydrogenation reaction of alcohols. The catalytic activity in the dehydrogenation of 2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline was also examined. The highest efficiency was obtained in the reaction catalyzed by the same t-butyl-substituted cyclopentadienyl iridium complex.
1. Introduction
Dehydrogenation of small organic molecules without using external oxidants (i.e., acceptorless dehydrogenation) is an attractive transformation reaction from the viewpoint of excellent atomic efficiency [1,2,3,4]. Avoidance of the use of harmful oxidants without generating stoichiometric amounts of waste (other than hydrogen gas) meets the requirements of green chemistry. Moreover, the resulting hydrogen gas can be used as a promising energy carrier owing to its high weight energy density and carbon neutrality. These characteristics make the significance of acceptorless dehydrogenation much greater in the field of organic synthesis as well as energy science [4,5,6,7,8,9]. Owing to the catalytic activity of ruthenium complexes in dehydrogenation reactions of alcohols [10,11], considerable efforts have been made to improve catalytic systems with the development of complexes such as pincer-type ruthenium or iridium complexes with non-innocent behavior of the pincer ligands (Scheme 1a) [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Recently, a catalytic system has been applied to the dehydrogenation reaction of N-heterocyclic compounds for use in hydrogen storage (Scheme 1b) [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. The search for a highly efficient catalytic dehydrogenation system remains a challenging task. Our research group has consistently studied the catalytic activity of pentamethylcyclopentadienyl (Cp*) iridium complexes for the hydrogen transfer process of alcoholic substrates [31,32,33,34,35]. By combining hydroxypyridine or dihydroxybipyridine derivatives as non-innocent ligands, the Cp* iridium complex shows an extremely high catalytic activity in acceptorless dehydrogenation reactions of alcoholic substrates and N-heterocyclic compounds (Scheme 1c) [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47]. Theoretical studies suggest that the spectator Cp* ligand contributes to the stabilization of catalytically active species and to the milder electron-population change on the iridium center during the reaction, which decreases the overall reaction barrier [48].
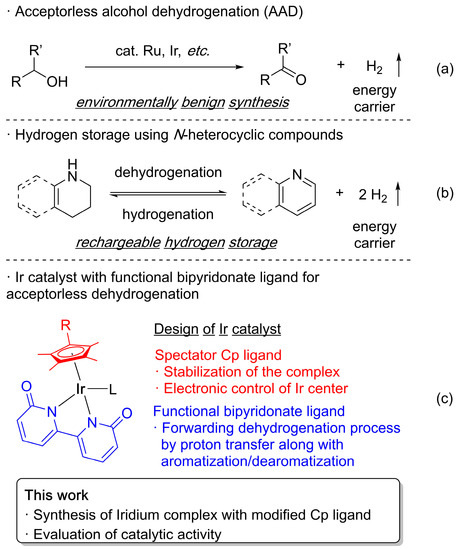
Scheme 1.
Acceptorless dehydrogenation of alcohols (a) and N-heterocyclic compounds (b) and design of the iridium catalyst bearing Cp and bipyridonate ligand (c).
In general, a cyclopentadienyl (Cp) ligand donates six electrons to a metal center with tridentate coordination mode, which results in stable complexes that are widely used as catalysts. The incorporation of substituents on the Cp ring allows both electronic and steric perturbation on the Cp metal complexes [49,50,51]. Well-modified Cp ligands have been used to improve the potential catalytic activity and reaction selectivity of transition metal complexes [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61]. Thus, a systematic study of the modified Cp-ligated iridium complex should provide significant insight for the development of a more active catalytic system for acceptorless dehydrogenation reactions. Herein, we synthesized a series of bipyridonate-coordinated iridium(III) complexes bearing Cp ligands with various alkyl substituents to reveal the trend of catalytic activity in the dehydrogenation of alcohols and 2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline (Scheme 1c). The 1-tert-butyl-2,3,4,5-tetramethylcyclopentadienyl iridium complex exhibited higher activity.
2. Results
On the basis of our previous studies, in which Cp* iridium complexes exhibited excellent catalytic activity [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47], we attempted to modify one methyl group in the Cp* ligand to hydrogen, ethyl, isopropyl, and t-butyl groups in order to improve the catalytic properties (Scheme 2). A series of cyclopentadienyl-ligated iridium dichloride dimers 1a–1e were synthesized by the reaction of iridium trichloride with parent cyclopentadiene derivatives [62,63,64]. The structure of novel complex 1e was successfully identified by X-ray crystallographic analysis. The coordination reactions of 1a–1e with 6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine in methanol at 60 °C gave cationic complexes 2a–2e, which were converted into neutral aquo complexes 3a–3e by treatment with NaOtBu in water. The structures of cationic bipyridine complexes 2 and neutral bipyridonate complexes 3 were fully characterized by 1H and 13C NMR and elemental analysis. X-ray crystallographic analysis could be performed for 2a and 2e to provide unambiguous structural information (Figure 1, details are indicated in the Supplementary Materials). The t-butyl group of 2e is located at the trans position to the chloro ligand probably owing to its steric demand. Complexes 2a and 2e showed similar structural parameters around the iridium center.
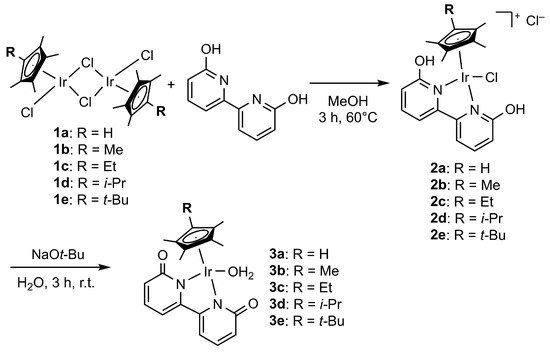
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of bipyridonate iridium complexes with a Cp ligand bearing a series of alkyl groups.
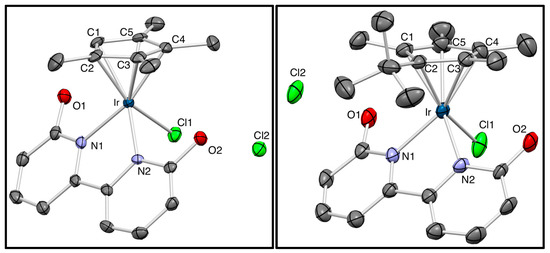
Figure 1.
ORTEP illustrations of complexes 2a (left) and 2e (right) at the 50% probability level: Solvent molecules and hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity.
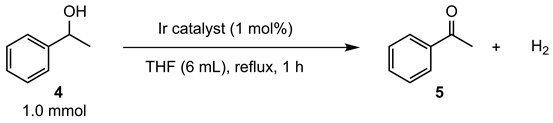
After obtaining a series of iridium catalysts (3), their catalytic activities in the dehydrogenation of 1-phenylethanol (4), which is a model substrate that we previously studied in detail, were investigated (Table 1). To ensure full solubility of iridium complexes, reactions were performed in THF under reflux conditions. The yield of the dehydrogenated product acetophenone (5) after 1 h was determined by gas chromatography (GC) analysis to evaluate initial catalytic activity. In the presence of tetramethylcyclopentadienyl complex 3a, the dehydrogenation reaction proceeded to give acetophenone in 35% yield (Table 1, entry 1). Cp* complex 3b, ethyltetramethylcyclopentadienyl complex 3c, and isopropyltetramethylcyclopentadienyl complex 3d exhibited higher catalytic activities than 3a to produce 5 in similar yields (Table 1, entries 2–4). The t-butyltetramethylcyclopentadienyl complex 3e exhibited the highest catalytic activity (Table 1, entry 5). Although the differences in catalytic activity between 3b–3d were not large, the observed trend indicated that a stronger electron-donating cyclopentadienyl ligand leads up to higher catalytic activity. This conclusion is based on the observation that 3a was least active while 3e showed the highest catalytic activity. After 24 h, the complete conversion of the starting alcohol was achieved, which suggests that the obtained results originated only from the catalytic activity and not from the deactivation of catalysts.

Table 1.
Catalytic activity of iridium complexes (3) in the dehydrogenation of 4.
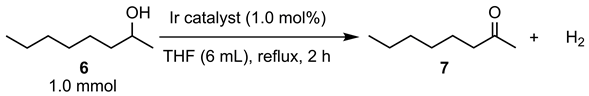
The catalytic abilities of iridium complexes (3) were also examined in the dehydrogenation reaction of 2-octanol (6) as an aliphatic alcohol in refluxing THF (Table 2). Catalyst 3a exhibited the lowest catalytic activity to give 2-octanone (7) with an 18% yield after 2 h (Table 2, entry 1). Catalyst 3b exhibited moderate performance and produced a dehydrogenated product with a 49% yield (Table 2, entry 2). The highest catalytic ability was achieved by 3e, which produced 7 with a 57% yield (Table 2, entry 3). The trend of catalytic ability is consistent with that of the dehydrogenation reaction of 1-phenylethanol (4), which is shown in Table 1.

Table 2.
Catalytic activity of iridium complexes (3) in the dehydrogenation of 6.
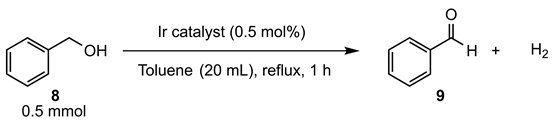
However, compared with the dehydrogenation of secondary alcohols, no significant difference in catalytic activity was observed for the primary alcohol (Table 3). The reactions were performed under more diluted conditions than those for secondary alcohols to suppress undesired side reactions, such as self-condensation, leading to ester product. Dehydrogenation reaction of benzyl alcohol (8) in refluxing toluene was carried out in the presence of 0.5 mol% of iridium catalyst to produce benzaldehyde (9). Catalyst 3a exhibited a slightly lower performance compared with catalyst 3b and 3e (Table 3, entries 1–3). Catalysts 3b and 3e showed similar catalytic activities.

Table 3.
Catalytic activity of iridium complexes 3a, 3b, and 3e in the dehydrogenation of 8.
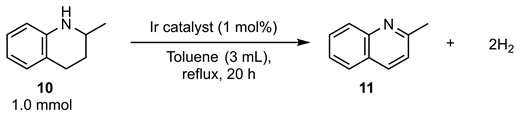
We have previously reported that the dehydrogenation of a cyclic amine, which leads to aromatized N-heterocycles, is also catalyzed by the same iridium complex used for the dehydrogenation of alcoholic substrates [45,46,47]. Hence, we also examined the catalytic activity of a series of iridium complexes (3) in the dehydrogenation of 2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline (10) as a model substrate (Table 4). Considering the relatively slower reaction rate for the dehydrogenation of cyclic amines than that of alcohols, the reactions were performed under toluene reflux conditions for 20 h. Catalyst 3a exhibited moderate catalytic activity to produce the dehydrogenated product 2-methylquinoline (11) with a 55% yield (Table 4, entry 1). Catalyst 3b exhibited high performance with a 91% yield (Table 4, entry 2). The reactions in the presence of catalysts 3c and 3d were somehow significantly less effective than the reaction catalyzed by 3b (Table 4, entries 3 and 4). Similar to the dehydrogenation of alcoholic substrates, the highest catalytic ability was achieved by catalyst 3e (Table 4, entry 5).

Table 4.
Catalytic activity of iridium complexes (3) in the dehydrogenation of 10.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on JEOL ECX-500 (500 MHz) and ECS-400 (400 MHz) spectrometers (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). 1H and 13C NMR spectra of each isolated products are shown in Supplementary Materials. Gas chromatography (GC) analyses were performed on a GC-4000Plus (GL-Science, Tokyo, Japan) with a capillary column (InertCap for Amines and InertCap Pure WAX). Elemental analyses were carried out at the Microanalysis Center of Kyoto University. Melting points were measured by a Yanaco MP-500D (Yanaco Group, Kyoto, Japan) in air. Dehydrated solvent was used in the reaction. HCp*Ethyl(5-ethyl-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclopentadiene) [65], HCp*iPr(5-isopropyl-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclopentadiene) [64,65], HCp*tBu(5-tert-butyl-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclopentadiene) [66], (Cp*Ir(6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine)Cl)Cl (2b) [67], Cp*Ir(2.2′-bipyridine-6,6′-dionato)H2O (3b) [40], and 6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine [68] were prepared according to the literature method. All other reagents are commercially available and were used as received (FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corp., Osaka, Japan); (Nacalai Tesque, Kyoto, Japan); (Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan).
3.2. Procedures for the Synthesis of (CpRIrCl2)2
3.2.1. (η5-C5Me4H)IrCl2)2 (CAS: 835614-43-2) (1a)
Under an atmosphere of argon, IrCl3·5H2O (998.2 mg, 2.57 mmol) was placed in a 50-mL two-neck flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. Methanol (19.7 mL) and 1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclopentadiene (1271.3 mg, 10.37 mmol) [69] were added, and the mixture was stirred for 48 h at 90 °C. After cooling to r.t., orange precipitate was filtered with a glass filter, washed with Et2O (15 mL), and then dried under vacuum to give the title compound as an orange solid (355.5 mg, 0.463 mmol, 36%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, r.t.) δ 5.24 (s, 2H, CpH), 1.66 (s, 12H, CpCH3), 1.61 (s, 12H, CpCH3). 13C NMR (100.5 MHz, CDCl3, r.t.) δ 92.1 (s, CpC), 86.4(s, CpC), 68.0 (s, CpC), 11.1 (s, CpCH3), 9.4 (s, CpCH3).
3.2.2. (Cp*EthylIrCl2)2 (CAS: 2050480-26-5) (1c)
Under an atmosphere of argon, IrCl3·5H2O (645.6 mg, 1.66 mmol) was placed in a 50-mL two-neck flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. Methanol (13.0 mL) and 5-ethyl-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclopentadiene [65] (996.3 mg, 6.63 mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred for 72 h at 90 °C. After cooling to r.t., the solvent was slightly removed by vacuum and orange precipitate was filtered with a glass filter, washed with Et2O (15 mL), and then dried under vacuum to give the title compound as an orange solid (458.2 mg, 0.519 mmol, 77%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, r.t.) δ 2.13 (q, 4H, J = 7.6 Hz, CH2), 1.58 (s, 12H, CpCH3), 1.56 (s, 12H, CpCH3), 1.05 (t, 6H, J = 7.6 Hz, CH3). 13C NMR (100.5 MHz, CDCl3, r.t.) δ 89.2 (s, CpC), 86.6 (s, CpC), 86.2 (s, CpC), 17.7 (s, CH2), 11.8 (s, CH3), 9.4 (s, CpCH3), 9.2 (s, CpCH3).
3.2.3. (Cp*iPrIrCl2)2 (CAS: 1621315-48-7) (1d)
Under an atmosphere of argon, IrCl3·5H2O (840.2 mg, 2.16 mmol) was placed in a 50-mL two-neck flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. Methanol (16.6 mL) and 5-isopropyl-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclopentadiene [64,65] (1440.7 mg, 8.77 mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred for 48 h at 90 °C. After cooling to r.t., orange precipitate was filtered with a glass filter, washed with Et2O (20 mL), and then dried under vacuum to give the title compound as an orange solid (783.8 mg, 0.919 mmol, 85%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, r.t.) δ 2.46 (sept, 2H, J = 7.2 Hz, CH), 1.66 (s, 12H, CpCH3), 1.58 (s, 12H, CpCH3), 1.26 (d, 12H, J = 7.2 Hz, CH3). 13C NMR (100.5 MHz, CDCl3, r.t.) δ 90.4 (s, CpC), 86.3 (s, CpC), 86.1 (s, CpC), 25.3 (s, CH), 20.7 (s, CH(CH3)2), 10.4 (s, CpCH3), 9.6 (s, CpCH3).
3.2.4. (Cp*tBuIrCl2)2 (1e)
Under an atmosphere of argon, IrCl3·5H2O (546.5 mg, 1.41 mmol) was placed in a 50-mL two-neck flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. Methanol (11.1 mL) and 5-tert-butyl-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclopentadiene [66] (1010.0 mg, 5.66 mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred for 144 h at 90 °C. After cooling to r.t., orange precipitate was filtered with a glass filter, washed with Et2O (10 mL), and then dried under vacuum to give an orange solid (276.8 mg, 0.314 mmol, 45%). M.P. (decomp.) > 277.6 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, r.t.) δ 1.79 (s, 12H, CpCH3), 1.61 (s, 12H, CpCH3), 1.37 (s, 18H, C(CH3)3). 13C NMR (100.5 MHz, CDCl3, r.t.) δ 92.1 (s, CpC), 87.4 (s, CpC), 84.8 (s, CpC), 33.8 (s, CMe3), 30.9 (s, C(CH3)3), 13.3 (s, CpCH3), 10.1 (s, CpCH3). Anal. Calcd for C26H42Cl4Ir2: C, 35.45; H, 4.81. Found: C, 35.05; H, 4.69.
3.3. Procedures for the Synthesis of (CpRIr(6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine)Cl)Cl
3.3.1. ((η5-C5Me4H)Ir(6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine)Cl)Cl (2a)
Under an atmosphere of argon, ((η5-C5Me4H)IrCl2)2 (1a) (49.8 mg, 0.065 mmol), 6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine (24.4 mg, 0.130 mmol), and methanol (1.1 mL) were placed in a 10-mL two-neck test tube flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. The mixture was stirred for 3 h at 60 °C. After cooling to r.t., the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was dried under vacuum to give the title compound as a yellow solid (59.3 mg, 0.1036 mmol, 80%). M.P. (decomp.) > 344.9 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD, r.t.) δ 7.99 (t, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, aromatic), 7.93 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, aromatic), 7.12 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, aromatic), 5.87 (s, CpH), 1.73 (s, Cp(CH)3), 1.68 (s, Cp(CH)3). 13C NMR (100.5 MHz, CD3OD, r.t.) δ 165.4 (s, aromatic), 156.1 (s, aromatic), 143.3 (s, aromatic), 116.4 (s, aromatic), 113.9 (s, aromatic), 92.3 (s, CpC), 91.9 (s, CpC), 77.3 (s, CpC), 10.7 (s, CH3), 10.0 (s, CH3). Anal. Calcd for C19H21Cl2IrN2O2: C, 39.86; H, 3.70; N, 4.89. Found: C, 39.69; H, 3.68; N, 4.77.
3.3.2. (Cp*EthylIr(6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine)Cl)Cl (2c)
Under an atmosphere of argon, (Cp*EthylIrCl2)2 (1c) (106.1 mg, 0.13 mmol), 6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine (48.7 mg, 0.26 mmol), and methanol (2.0 mL) were placed in a 10-mL two-neck test tube flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. The mixture was stirred for 3 h at 60 °C. After cooling to r.t., the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was dried under vacuum to give the title compound as a yellow solid (121 mg, 0.201 mmol, 78%). M.P. (decomp.) > 344.7 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD, r.t.) δ 7.97 (t, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, aromatic), 7.89 (d, 2H, J = 7.8 Hz, aromatic), 7.07 (d, 2H, J = 8.2 Hz, aromatic), 2.12 (q, 2H, J = 7.6 Hz, CH2), 1.67 (s, 6H, Cp(CH)3), 1.66 (s, 6H, Cp(CH)3), 1.05 (t, 3H, J = 8.0 Hz, CH3). 13C NMR (100.5 MHz, CD3OD, r.t.) δ 164.1 (s, aromatic), 154.5 (s, aromatic), 142.0 (s, aromatic), 114.8 (s, aromatic), 112.7 (s, aromatic), 91.2 (s, CpC), 89.6 (s, CpC), 88.9 (s, CpC), 17.3 (s, CH2), 11.0 (s, CH3), 8.4 (s, CpCH3), 8.3 (s, CpCH3). Anal. Calcd for C21H25Cl2IrN2O2: C, 42.00; H, 4.20; N, 4.66. Found: C, 41.90; H, 4.38; N, 4.53.
3.3.3. (Cp*iPrIr(6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine)Cl)Cl (2d)
Under an atmosphere of argon, (Cp*iPrIrCl2)2 (1d) (101.6 mg, 0.12 mmol), 6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine (44.8 mg, 0.24 mmol), and methanol (2.0 mL) were placed in a 10-mL two-neck test tube flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. The mixture was stirred for 3 h at 60 °C. After cooling to r.t., the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was dried under vacuum to give the title compound as a yellow solid (121.3 mg, 0.197 mmol, 83%). M.P. (decomp.) > 342.3 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD, r.t.) δ 7.97 (t, 2H, J = 7.6 Hz, aromatic), 7.90 (d, 2H, J = 7.8 Hz, aromatic), 7.08 (d, 2H, J = 8.2 Hz, aromatic), 2.38 (sept, 1H, J = 7.6 Hz, CH), 1.79 (s, 6H, CpCH3), 1.73 (s, 6H, CpCH3), 0.99 (d, 6H, J = 7.2 Hz, CH3). 13C NMR (100.5 MHz, CD3OD, r.t.) δ 165.5 (s, aromatic), 156.1 (s, aromatic), 143.4 (s, aromatic), 116.1 (s, aromatic), 114.1 (s, aromatic), 98.2 (s, CpC), 88.3 (s, CpC), 86.9 (s, CpC), 26.8 (s, CH), 20.5 (s, CH3), 11.6 (s, CpCH3), 9.4 (s, CpCH3). Anal. Calcd for C22H27Cl2IrN2O2: C, 43.00; H, 4.43; N, 4.56. Found: C, 42.60; H, 4.74; N, 4.42.
3.3.4. (Cp*tBuIr(6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine)Cl)Cl (2e)
Under an atmosphere of argon, (Cp*tBuIrCl2)2 (1e) (36.3 mg, 0.04 mmol), 6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine (15.7 mg, 0.08 mmol), and methanol (0.7 mL) were placed in a 10-mL two-neck test tube flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. The mixture was stirred for 3 h at 60 °C. After cooling to r.t., the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was dried under vacuum to give the title compound as a yellow solid (44.2 mg, 0.0703 mmol, 86%). M.P. (decomp.) > 344.6 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD, r.t.) δ 7.99 (t, 2H, J = 7.6 Hz, aromatic), 7.94 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, aromatic), 7.08 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, aromatic), 1.88 (s, 6H, CpCH3), 1.82 (s, 6H, CpCH3), 0.93 (s, 9H, CH3). 13C NMR (100.5 MHz, CD3OD, r.t.) δ 165.4 (s, aromatic), 156.2 (s, aromatic), 143.5 (s, aromatic), 116.1 (s, aromatic), 114.2 (s, aromatic), 101.8 (s, CpC), 88.9 (s, CpC), 84.4 (s, CpC), 34.3 (s, CMe3), 30.3 (s, CH3), 15.0 (s, CpCH3), 9.6 (s, CpCH3).
3.4. Procedures for the Synthesis of CpRIr(2.2′-bipyridine-6,6′-dionato)H2O
3.4.1. (η5-C5Me4H)Ir(2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-dionato)H2O (3a)
Under an atmosphere of argon, ((η5-C5Me4H)IrCl2)2 (1a) (203.8 mg, 0.27 mmol), 6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine (99.8 mg, 0.53 mmol), and methanol (6.4 mL) were placed in a 30-mL two-neck round flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. The mixture was stirred for 3 h at 60 °C. After cooling to r.t., the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was dried under vacuum overnight to give a yellow solid. Sodium tert-butoxide (102.6 mg, 1.07 mmol) and degassed H2O (9.3 mL) were added to the same flask and stirred for 3 h at r.t. After the reaction, the precipitate was filtered by cannulation through glass filter under argon atmosphere and dried under vacuum. CH2Cl2 (35 mL) was added to dissolve the solid. Solution was collected in flask, and the solvent was evaporated. CH2Cl2 (1 mL) was added, followed by the addition of hexane (15 mL) for reprecipitation. The resulting solid was filtered with glass filter and washed with H2O (10 mL), affording the title compound as a green yellow solid (158.3 mg, 0.306 mmol, 57%) after drying under vacuum. M.P. (decomp.) > 288.9 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD, r.t.) δ 7.45 (br t, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, aromatic), 6.71 (br d, 2H, J = 7.2 Hz, aromatic), 6.51 (br d, 2H, J = 6.8 Hz aromatic), 5.85 (br s, 1H, CpH), 1.72 (br s, 6H, CpCH3), 1.52 (br s, 6H, CpCH3). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD, 60 °C) δ 7.23 (t, 2H, , J = 12 Hz, aromatic), 6.92 (d, 2H, J = 9.0 Hz, aromatic), 6.64 (br, 2H, aromatic), 5.60 (br, 1H, CpH), 1.59 (s, 6H, CpCH3), 1.43 (s, 6H, CpCH3). 13C NMR (100.5 MHz, CD3OD, 60 °C) δ 171.4 (s, aromatic), 157.7 (s, aromatic), 139.7 (s, aromatic), 118.5 (s, aromatic), 107.5 (s, aromatic), 92.0 (s, CpC), 88.7 (s, CpC), 74.4 (s, CpC), 10.7 (s, CpCH3), 9.9 (s, CpCH3). Anal. Calcd for C19H21IrN2O3: C, 44.09; H, 4.09; N, 5.41. Found: C, 43.84; H, 3.96; N, 5.39.
3.4.2. Cp*EthylIr(2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-dionato)H2O (3c)
Under an atmosphere of argon, (Cp*EthylIrCl2)2 (1c) (198.2 mg, 0.24 mmol), 6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine (90.4 mg, 0.48 mmol), and methanol (5.8 mL) were placed in a 30-mL two-neck round flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. The mixture was stirred for 3 h at 60 °C. After cooling to r.t., the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was dried under vacuum overnight to give a yellow solid. Sodium tert-butoxide (92.3 mg, 0.96 mmol) and degassed H2O (8.4 mL) were added to the same flask and stirred for 3 h at r.t. After the reaction, the precipitate was filtered by cannulation through glass filter under argon atmosphere and dried under vacuum. CH2Cl2 (35 mL) was added to dissolve the solid. Solution was collected in flask, and the solvent was evaporated. CH2Cl2 (1 mL) was added, followed by the addition of hexane (15 mL) for reprecipitation. The resulting solid was filtered with glass filter and washed with H2O (8 mL). The title compound was obtained as a green yellow solid (141.3 mg, 0.259 mmol, 57%) after drying under vacuum. M.P. (decomp.) > 272.3 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD, 60 °C) δ 7.42 (t, 2H, J = 6.5 Hz, aromatic), 6.90 (d, 2H, J = 6.5 Hz, aromatic), 6.52 (br s, 2H, aromatic), 1.95 (br s, 2H, CH2), 1.47 (s, 12H, CpCH3), 0.93 (br s, 3H, CH3). 13C NMR (100.5 MHz, CD3OD, 60 °C) δ 171.3 (s, aromatic), 157.2 (s, aromatic), 139.5 (s, aromatic), 118.3 (s, aromatic), 106.7 (s, aromatic), 90.0 (s, CpC), 88.2 (s, CpC, two peaks may be overlapped), 18.7 (s, CH), 11.9 (s, CH3), 9.7 (s, CpCH3, two peaks may be overlapped). Anal. Calcd for C21H25IrN2O3: C, 46.23; H, 4.62; N, 5.13. Found: C, 46.13; H, 4.56; N, 5.11.
3.4.3. Cp*iPrIr(2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-dionato)H2O (3d)
Under an atmosphere of argon, (Cp*iPrIrCl2)2 (1d) (159.3 mg, 0.19 mmol), 6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine (70.8 mg, 0.38 mmol), and methanol (4.4 mL) were placed in a 30-mL two-neck round flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. The mixture was stirred for 3 h at 60 °C. After cooling to r.t., the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was dried with vacuum overnight to give a yellow solid. Sodium tert-butoxide (71.8 mg, 0.75 mmol) and degassed H2O (6.6 mL) were added to the same flask and stirred for 3 h at r.t. After the reaction, the precipitate was filtered by cannulation through glass filter under argon atmosphere and dried under vacuum. CHCl3 (35 mL) was added to dissolve the solid. The solution was collected in flask, and solvent was evaporated. CHCl3 (1 mL) was added, followed by the addition of hexane (10 mL) for reprecipitation. The resulting solid was filtered with glass filter and washed with H2O (8 mL). Title compound was obtained as a green yellow solid (87 mg, 0.155 mmol, 42%) after drying under reduced pressure. M.P. (decomp.) > 274.7 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD, r.t.) δ 7.43 (t, 2H, J = 7.6 Hz, aromatic), 6.93 (d, 2H, J = 6.0 Hz, aromatic), 6.42 (d, 2H, J = 7.2 Hz, aromatic), 2.16 (br sept, 1H, J = 3.6 Hz CH), 1.83 (br s, 6H, CpCH3), 1.71 (br s, 6H, CpCH3), 0.94 (br d, 6H, J = 6.4 Hz, CH3). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD, 60 °C) δ 7.40 (t, 2H, J = 10.5 Hz, aromatic), 6.88 (d, 2H, J = 9.0 Hz, aromatic), 6.43 (br s, 2H, J = 11.0 Hz, aromatic), 2.22 (sept, 1H, J = 9.0 Hz, CH), 1.77 (s, 6H, CpCH3), 1.70 (s, 6H, CpCH3), 0.97 (d, 6H, J = 9.0 Hz, CH3). 13C NMR (100.5 MHz, CD3OD, 60 °C) δ 171.2 (s, aromatic), 157.6 (s, aromatic), 139.6 (s, aromatic), 118.2 (s, aromatic), 106.4 (s, aromatic), 94.5 (s, CpC), 89.0 (s, CpC), 81.5 (s, CpC), 26.8 (s, CH), 20.1 (s, CH3), 11.2 (s, CpCH3), 9.7 (s, CpCH3). Anal. Calcd for C22H27IrN2O3: C, 47.21; H, 4.86; N, 5.01. Found: C, 47.41; H, 4.98; N, 4.90.
3.4.4. Cp*tBuIr(2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-dionato)H2O (3e)
Under an atmosphere of argon, (CptBuIrCl2)2 (1e) (146.5 mg, 0.17 mmol), 6,6′-dihydroxy-2,2′-bipyridine (63.2 mg, 0.34 mmol), and methanol (4.0 mL) were placed in a 30-mL two-neck round flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. The mixture was stirred for 3 h at 60 °C. After cooling to r.t., the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and dried under vacuum overnight to give a yellow solid. Sodium tert-butoxide (65.5 mg, 0.68 mmol) and degassed H2O (6.6 mL) were added to the same flask and stirred for 3 h at r.t. After the reaction, the precipitate was filtered by cannulation through glass filter under argon atmosphere and dried under vacuum. CHCl3 (55 mL) was added to dissolve the solid. The solution was collected in flask, and solvent was evaporated. CHCl3 (1 mL) was added, followed by the addition of hexane (15 mL) for reprecipitation. The resulting solid was filtered with glass filter and washed with H2O (10 mL). The title compound was obtained as a green yellow solid (121.1 mg, 0.211 mmol, 63.6%) after drying under vacuum. M.P. (decomp.) > 280.2 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD, r.t.) δ 7.43 (t, 2H, J = 7.6 Hz, aromatic), 6.96 (d, 2H, J = 6.8 Hz, aromatic), 6.43 (br d, 2H, J = 4.8 Hz), 1.93 (s, CpCH3), 1.80 (s, CpCH3), 0,90 (s, CH3), 13C NMR (100.5 MHz, CD3OD, r.t.) δ 170.7 (s, aromatic), 157.8 (s, aromatic), 140.0 (s, aromatic), 118.1 (s, aromatic), 106.8 (s, aromatic), 100.2 (s, CpC), 90.6 (s, CpC), 74.5 (s, CpC), 33.7 (s, CH), 29.8 (s, CH3), 14.8 (s, CpCH3), 10.1 (s, CpCH3), Anal. Calcd for C23H29IrN2O3: C, 48.15; H, 5.10; N, 4.88. Found: C, 48.36; H, 5.15; N, 4.90.
3.5. Investigation of Catalytic Activity in Dehydrogenation of 1-Phenylethanol (4)
Under an atmosphere of argon, Ir catalyst (1.0 mol%), THF (6.0 mL), and 1-phenylethanol (4) (1.0 mmol) were placed in a 50-mL two-neck round flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. It was stirred for 1 h at 106 °C (oil bath temperature) under reflux. After the reaction, THF (24 mL) and undecane (internal standard) were added and stirred. Conversion and yield were determined by GC. Average of three runs is shown.
3.6. Investigation of Catalytic Activity in Dehydrogenation of Benzyl alcohol (6)
Under an atmosphere of argon, Ir catalyst (0.5 mol%), toluene (20 mL), and benzylalcohol (6) (0.5 mmol) were placed in a 50-mL two-neck round flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. It was stirred for 1 h at 131 °C (oil bath temperature) under reflux. After the reaction, toluene (10 mL) and biphenyl (internal standard) were added and stirred. Conversion and yield were determined by GC.
3.7. Investigation of Catalytic Activity in Dehydrogenation of 2-Octanol (8)
Under an atmosphere of argon, Ir catalyst (1.0 mol%), THF (6 mL), and 2-octanol (8) (1.0 mmol) were placed in a 30-mL two-neck round flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. It was stirred at 131 °C (oil bath temperature) under reflux. After the reaction, toluene (14 mL) and biphenyl (internal standard) were added and stirred. Conversion and yield were determined by GC.
3.8. Investigation of Catalytic Activity in Dehydrogenation of 2-MeTHQ (10)
Under an atmosphere of argon, Ir catalyst (1.0 mol%), toluene (3 mL), and 2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline (10) (1.0 mmol) were placed in a 30-mL two-neck round flask equipped with a Dimroth condenser and three-way cock. It was stirred for 20 h at 131 °C (oil bath temperature) under reflux. After the reaction, toluene (14 mL) and undecane (internal standard) were added and stirred. Conversion and yield were determined by GC.
3.9. X-ray Crystallographic Analyses
Crystallographic data of 1e was collected on a Rigaku/R Axis Rapid diffractometer with CrystalClear (Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan). Crystallographic data of 2a and 2e were collected on a Rigaku/Saturn 70 CCD diffractometer and processed with CrystalClear (Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan). Calculations for 1e were performed with the CrystalStructure software package (Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan). Calculations for 2a and 2e were performed with the Olex2 software package (Ver. 1.2.10, OlexSys Ltd., Durham, UK). Details are indicated in the Supplementary Materials.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, we successfully synthesized new iridium complexes (1–3) having cyclopentadienyl ligands with various alkyl substituents. The t-butyl-substituted cyclopentadienyl complex 3e exhibited a slightly higher catalytic activity than other complexes in the dehydrogenation of alcohols and 2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline. This study provides systematic information on the effect of substituents on the cyclopentadienyl ligand in a catalytic dehydrogenation reaction. However, the reason for the better catalytic performance of 3e is unclear. Computational studies on the relationship between the effect of the cyclopentadienyl ligand on iridium complexes and their catalytic activity are ongoing.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4344/9/10/846/s1, detailed description of experimental procedures, 1H and 13C NMR data of the isolated products with spectral charts; the cif and checkcif output files for 1e, 2a, and 2e.
Author Contributions
J.J. performed the experiments, analyzed the results, and wrote the draft of the manuscript. T.S. supported the analysis of the experimental results and the writing of the manuscript. K.F. guided the research, designed the experiments, and wrote the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by The Research Grant against Global Warming of the Ichimura Foundation for New Technology. This work was also financially supported by JSPS KAKENHI grant numbers JP18H04255, JP19H02715, and JP19H05053.
Acknowledgments
We thank Shigeyoshi Sakaki for the suggestive discussion on the design of the iridium complexes.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Friedrich, A.; Schneider, S. Acceptorless Dehydrogenation of Alcohols: Perspectives for Synthesis and H2 Storage. ChemCatChem 2009, 1, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunanathan, C.; Milstein, D. Applications of Acceptorless Dehydrogenation and Related Transformations in Chemical Synthesis. Science 2013, 341, 1229712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabtree, R.H. Homogeneous Transition Metal Catalysis of Acceptorless Dehydrogenative Alcohol Oxidation: Applications in Hydrogen Storage and to Heterocycle Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9228–9246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiki, S.M.A.H.; Toyao, T.; Shimizu, K. Acceptorless dehydrogenative coupling reactions with alcohols over heterogeneous catalysts. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 2933–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trincado, M.; Banerjee, D.; Grützmacher, H. Molecular catalysts for hydrogen production from alcohols. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2464–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Pan, Q.; Xu, J.; Fang, T. Current situation and prospect of hydrogen storage technology with new organic liquid. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 17442–17451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordakis, K.; Tang, C.; Vogt, L.K.; Junge, H.; Dyson, P.J.; Beller, M.; Laurenczy, G. Homogeneous Catalysis for Sustainable Hydrogen Storage in Formic Acid and Alcohols. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 372–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakko-Saksa, P.T.; Cook, C.; Kiviaho, J.; Repo, T. Liquid organic hydrogen carriers for transportation and storing of renewable energy—Review and discussion. J. Power Sources 2018, 396, 803–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modisha, P.M.; Ouma, C.N.M.; Garidzirai, R.; Wasserscheid, P.; Bessarabov, D. The Prospect of Hydrogen Storage Using Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 2778–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A.; Robinson, S.D. Catalytic dehydrogenation of primary and secondary alcohols by Ru(OCOCF3)2(CO)(PPh3)2. J. Organomet. Chem. 1975, 87, C52–C53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A.; Robinson, S.D. Complexes of the platinum metals. 7. Homogeneous ruthenium and osmium catalysts for the dehydrogenation of primary and secondary alcohols. Inorg. Chem. 1977, 16, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligthart, G.B.W.L.; Meijer, R.H.; Donners, M.P.J.; Meuldijk, J.; Vekemans, J.A.J.M.; Hulshof, L.A. Highly sustainable catalytic dehydrogenation of alcohols with evolution of hydrogen gas. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 1507–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gandelman, M.; Shimon, L.J.W.; Rozenberg, H.; Milstein, D. Electron-Rich, Bulky Ruthenium PNP-Type Complexes. Acceptorless Catalytic Alcohol Dehydrogenation. Organometallics 2004, 23, 4026–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, G.R.A.; Williams, J.M.J. Oxidant-free oxidation: Ruthenium catalyzed dehydrogenation of alcohols. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 8233–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Buijtenen, J.; Meuldijk, J.; Vekemans, J.A.J.M.; Hulshof, L.A.; Kooijman, H.; Spek, A.L. Dinuclear Ruthenium Complexes Bearing Dicarboxylate and Phosphine Ligands. Acceptorless Catalytic Dehydrogenation of 1-Phenylethanol. Organometallics 2006, 25, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, A.M.; Rauchfuss, T.B.; Wilson, S.R. Coordination Chemistry of a Model for the GP Cofactor in the Hmd Hydrogenase: Hydrogen-Bonding and Hydrogen-Transfer Catalysis. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, A.M.; Rauchfuss, T.B.; Gray, D.L. Organoiridium Pyridonates and Their Role in the Dehydrogenation of Alcohols. Organometallics 2010, 29, 6763–6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratta, W.; Bossi, G.; Putignano, E.; Rigo, P. Pincer and Diamine Ru and Os Diphosphane Complexes as Efficient Catalysts for the Dehydrogenation of Alcohols to Ketones. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 3474–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prades, A.; Peris, E.; Albrecht, M. Oxidations and Oxidative Couplings Catalyzed by Triazolylidene Ruthenium Complexes. Organometallics 2011, 30, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Balaraman, E.; Leitus, G.; Milstein, D. Electron-Rich PNP- and PNN-Type Ruthenium(II) Hydrido Borohydride Pincer Complexes. Synthesis, Structure, and Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Alcohols and Hydrogenation of Esters. Organometallics 2011, 30, 5716–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, S.; Shaposhnikov, I.; Cohen, S.; Gelman, D. Ligand–Metal Cooperation in PCP Pincer Complexes: Rational Design and Catalytic Activity in Acceptorless Dehydrogenation of Alcohols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3533–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gülcemal, S.; Gülcemal, D.; Whitehead, G.F.S.; Xiao, J. Acceptorless Dehydrogenative Oxidation of Secondary Alcohols Catalysed by Cp*IrIII-NHC Complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 10513–10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabtree, R.H. Hydrogen storage in liquid organic heterocycles. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moores, A.; Poyatos, M.; Luo, Y.; Crabtree, R.H. Catalysed low temperature H2 release from nitrogen heterocycles. New J. Chem. 2006, 30, 1675–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tonks, I.; Belli, J.; Jensen, C.M. Dehydrogenation of N-ethyl perhydrocarbazole catalyzed by PCP pincer iridium complexes: Evaluation of a homogenous hydrogen storage system. J. Organomet. Chem. 2009, 694, 2854–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Belli, J.; Jensen, C.M. Homogeneous dehydrogenation of liquid organic hydrogen carriers catalyzed by an iridium PCP complex. Faraday Discuss. 2011, 151, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Brennessel, W.W.; Jones, W.D. A Molecular Iron Catalyst for the Acceptorless Dehydrogenation and Hydrogenation of N-Heterocycles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8564–8567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Chakraborty, S.; Yuan, H.; Jones, W.D. Acceptorless, Reversible Dehydrogenation and Hydrogenation of N-Heterocycles with a Cobalt Pincer Catalyst. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6350–6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manas, M.G.; Sharninghausen, L.S.; Crabtree, R.H. Iridium catalyzed reversible dehydrogenation e Hydrogenation of quinoline derivatives under mild conditions. J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 792, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivancos, Á.; Beller, M.; Albrecht, M. NHC-Based Iridium Catalysts for Hydrogenation and Dehydrogenation of N-Heteroarenes in Water under Mild Conditions. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Yamaguchi, R. Cp*Ir Complex-Catalyzed Hydrogen Transfer Reactions Directed toward Environmentally Benign Organic Synthesis. Synlett 2005, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Enoki, Y.; Yamaguchi, R. Cp*Ir-catalyzed N-alkylation of amines with alcohols. A versatile and atom economical method for the synthesis of amines. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 1943–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, R.; Fujita, K.; Yamaguchi, R. Multialkylation of Aqueous Ammonia with Alcohols Catalyzed by Water-Soluble Cp*Ir–Ammine Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15108–15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, R.; Fujita, K.; Yamaguchi, R. N-Alkylation of Amines with Alcohols Catalyzed by a Water-Soluble Cp*Iridium Complex: An Efficient Method for the Synthesis of Amines in Aqueous Media. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Furukawa, S.; Morishima, N.; Shimizu, M.; Yamaguchi, R. N-Alkylation of Aqueous Ammonia with Alcohols Leading to Primary Amines Catalyzed by Water-Soluble N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes of Iridium. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1993–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K. Development and Application of New Iridium Catalysts for Efficient Dehydrogenative Reactions of Organic Molecules. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Tanino, N.; Yamaguchi, R. Ligand-Promoted Dehydrogenation of Alcohols Catalyzed by Cp*Ir Complexes. A New Catalytic System for Oxidant-Free Oxidation of Alcohols. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Yoshida, T.; Imori, Y.; Yamaguchi, R. Dehydrogenative Oxidation of Primary and Secondary Alcohols Catalyzed by a Cp*Ir Complex Having a Functional C,N-Chelate Ligand. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2278–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, R.; Fujita, K.; Yamaguchi, R. Dehydrogenative Oxidation of Alcohols in Aqueous Media Using Water-Soluble and Reusable Cp*Ir Catalysts Bearing a Functional Bipyridine Ligand. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3643–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, R.; Fujita, K.; Yamaguchi, R. Cooperative Catalysis by Iridium Complexes with a Bipyridonate Ligand: Versatile Dehydrogenative Oxidation of Alcohols and Reversible Dehydrogenation–Hydrogenation between 2-Propanol and Acetone. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12790–12794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Tamura, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Onoda, M.; Yamaguchi, R. Dehydrogenative Oxidation of Alcohols in Aqueous Media Catalyzed by a Water-Soluble Dicationic Iridium Complex Bearing a Functional N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligand without Using Base. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 7226–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Kobayashi, D.; Shimizu, M.; Fujita, K. Synthesis of a series of iridium complexes bearing substituted 2-pyridonates and their catalytic performance for acceptorless dehydrogenation of alcohols under neutral conditions. J. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 843, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Wang, H.; Shimbayashi, T.; Fujita, K. Dehydrogenative Transformation of Alcoholic Substrates in Aqueous Media Catalyzed by an Iridium Complex Having a Functional Ligand with α-Hydroxypyridine and 4,5-Dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl Moieties. Catalysis 2018, 8, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Ikeda, C.; Takahashi, Y.; Fujita, K. Homogeneous Catalytic System for Reversible Dehydrogenation−Hydrogenation Reactions of Nitrogen Heterocycles with Reversible Interconversion of Catalytic Species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8410–8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Yamaguchi, R. Homogeneous Perdehydrogenation and Perhydrogenation of Fused Bicyclic N-Heterocycles Catalyzed by Iridium Complexes Bearing a Functional Bipyridonate Ligand. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4829–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Wada, T.; Shiraishi, T. Reversible Interconversion between 2,5-Dimethylpyrazine and 2,5-Dimethylpiperazine by Iridium-Catalyzed Hydrogenation/Dehydrogenation for Efficient Hydrogen Storage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 10886–10889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoda, M.; Nagano, Y.; Fujita, K. Iridium-catalyzed dehydrogenative lactonization of 1,4-butanediol and reversal hydrogenation: New hydrogen storage system using cheap organic resources. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Sakaki, S.; Fujita, K.; Sano, H.; Yamaguchi, R. Efficient Catalyst for Acceptorless Alcohol Dehydrogenation: Interplay of Theoretical and Experimental Studies. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, C.G.; Kossler, D.; Cramer, N. Asymmetric Catalysis Powered by Chiral Cyclopentadienyl Ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3935–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piou, T.; Rovis, T. Electronic and Steric Tuning of a Prototypical Piano Stool Complex: Rh(III) Catalysis for C–H Functionalization. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, L.D.; Lindall, C.M.; Masters, A.F.; Clentsmith, G.K.B. Penta-arylcyclopentadienyl complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1733–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piou, T.; Romanov-Michailidis, F.; Momanova-Michaelides, M.; Jackson, K.E.; Semakul, N.; Taggart, T.D.; Newell, B.S.; Rithner, C.D.; Paton, R.S.; Rovis, T. Correlating Reactivity and Selectivity to Cyclopentadienyl Ligand Properties in Rh(III)-Catalyzed C–H Activation Reactions: An Experimental and Computational Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1296–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Jeong, J.; Chang, S. [4+2] or [4+1] Annulation: Changing the Reaction Pathway of a Rhodium-Catalyzed Process by Tuning the Cp Ligand. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2408–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, S.; Shibata, Y.; Tanaka, K. Fulvene Synthesis by Rhodium(I)-Catalyzed [2+2+1] Cycloaddition: Synthesis and Catalytic Activity of Tunable Cyclopentadienyl Rhodium(III) Complexes with Pendant Amides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 3590–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyster, T.K.; Rovis, T. An improved catalyst architecture for rhodium(III) catalyzed C–H activation and its application to pyridine synthesis. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1606–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyster, T.K.; Rovis, T. Pyridine synthesis from oximes and alkynes via rhodium(III) catalysis: Cp* and Cpt provide complementary selectivity. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11846–11848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, R.; Shibata, Y.; Yamada, T.; Tanaka, K. Aerobic Oxidative Olefination of Benzamides with Styrenes Catalyzed by a Moderately Electron-Deficient CpRh(III) Complex with a Pendant Amide. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 2501–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Shibata, Y.; Kawauchi, S.; Yoshizaki, S.; Tanaka, K. Formal Lossen Rearrangement/[3+2] Annulation Cascade Catalyzed by a Modified Cyclopentadienyl RhIII Complex. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 5723–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Shibata, Y.; Tanaka, K. Functionalized Cyclopentadienyl Ligands and Their Substituent Effects on a Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Oxidative [4+2] Annulation of Indole- and Pyrrole-1-Carboxamides with Alkynes. Asian. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 7, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasawa, J.; Shibata, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Tanaka, K. Synthesis of Functionalized (η5-Indenyl)rhodium(III) Complexes and Their Application to C–H Bond Functionalization. Chem. Asian. J. 2018, 13, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piou, T.; Rovis, T. Rh(III)-Catalyzed Cyclopropanation Initiated by C–H Activation: Ligand Development Enables a Diastereoselective [2+1] Annulation of N-Enoxyphthalimides and Alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11292–11295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahr, A.; Nürnberg, O.; Werner, H. Halfsandwich-Type Complexes of Iridium with Tetramethylcyclopentadienyl as Ligand. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2003, 629, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, T.; Fairhurst, G.; Chalk, C.D.; Tabatabaian, K.; White, C. Ethyltetramethylcyclopentadienyl Complexes of Cobalt, Rhodium, Iridium and Ruthenium. Transit. Met. Chem. 1978, 3, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.M.; McGeagh, M.; Peña, D.D.; Merola, J.S. Extending the range of pentasubstituted cyclopentadienyl compounds: The synthesis of a series of tetramethyl(alkyl or aryl)cyclopentadienes (Cp*R), their iridium complexes and their catalytic activity for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. Polyhedron 2014, 84, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.C.; Ressegue, E.; Merola, J.S. Rapid Access to Derivatized, Dimeric, Ring-Substituted Dichloro(cyclopentadienyl)rhodium(III) and Iridium(III) Complexes. Organometallics 2016, 35, 4014–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Plooy, K.E.; du Toit, J.; Levendis, D.C.; Coville, N.J. Multiply substituted cyclopentadienyl metal complexes: I. Solid-state and solution conformational studies on (η5-C5Me4R)Fe( CO)(L) I(R = H, tBu). J. Organomet. Chem. 1996, 508, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePasquale, J.; Nieto, I.; Reuther, L.E.; Herbst-Gervasoni, C.J.; Paul, J.J.; Mochalin, V.; Zeller, M.; Thomas, C.M.; Addison, A.W.; Papish, E.T. Iridium Dihydroxybipyridine Complexes Show That Ligand Deprotonation Dramatically Speeds Rates of Catalytic Water Oxidation. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 9175–9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemoto, T.; Nagayoshi, M.; Adachi, K.; Tomizawa, G. Synthesis, Properties, and Reactivity of N,N′-Difluorobipyridinium and Related Salts and Their Applications as Reactive and Easy-To-Handle Electrophilic Fluorinating Agents with High Effective Fluorine Content. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 3379–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, M.D.; Simpson, P.V.; Gupta, V.; Fu, J.; Moxey, G.J.; Schwich, T.; Criddle, A.L.; Petrie, S.; MacLellan, J.G.; Batten, S.R.; et al. Syntheses of Pentanuclear Group 6 Iridium Clusters by Core Expansion of Tetranuclear Clusters with Ir(CO)2(η5-C5Me4R) (R = H, Me). Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 11256–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).