Highly Active TiO2 Microspheres Formation in the Presence of Ethylammonium Nitrate Ionic Liquid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The BET Surface Area and SEM Analysis
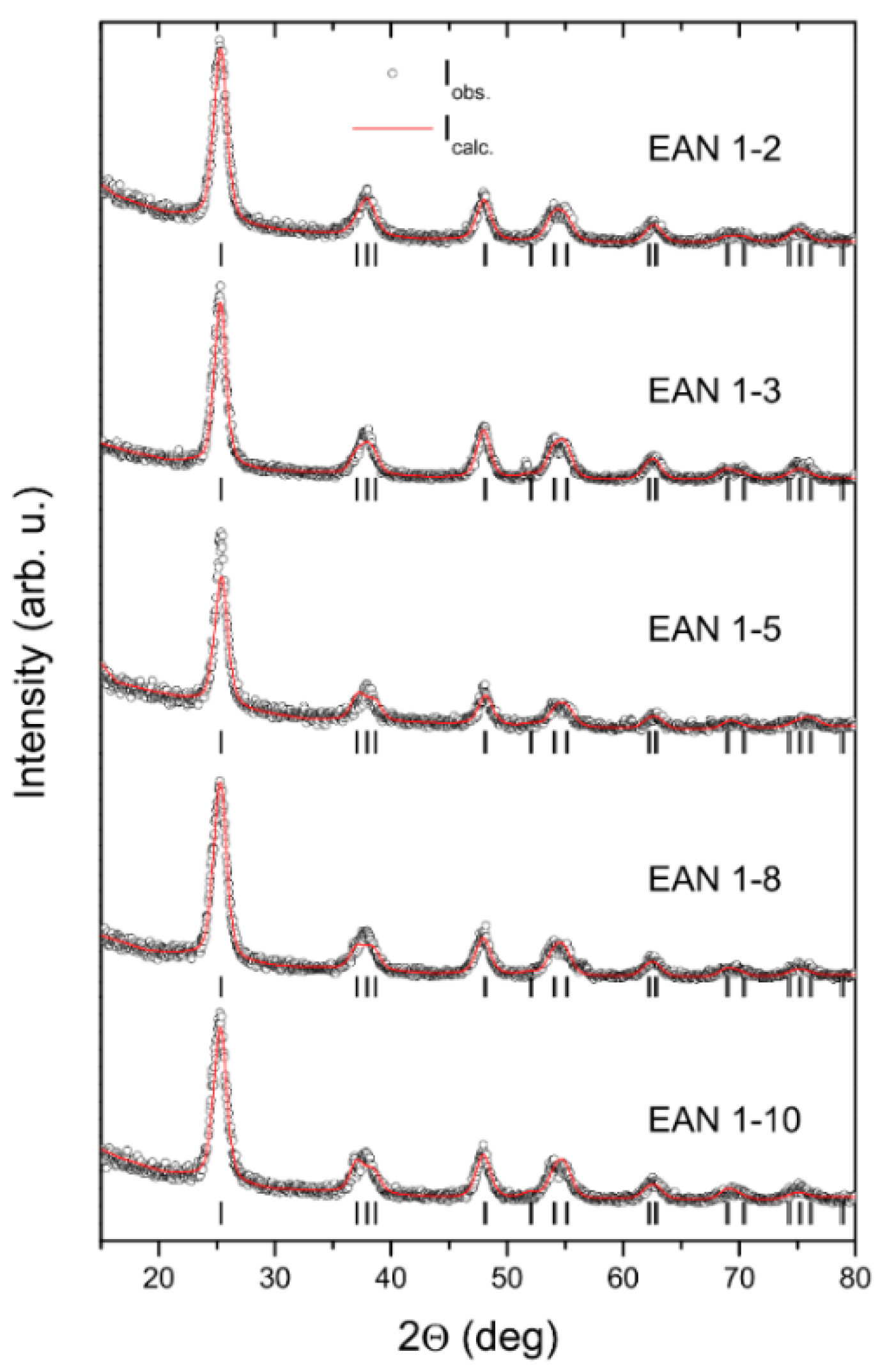
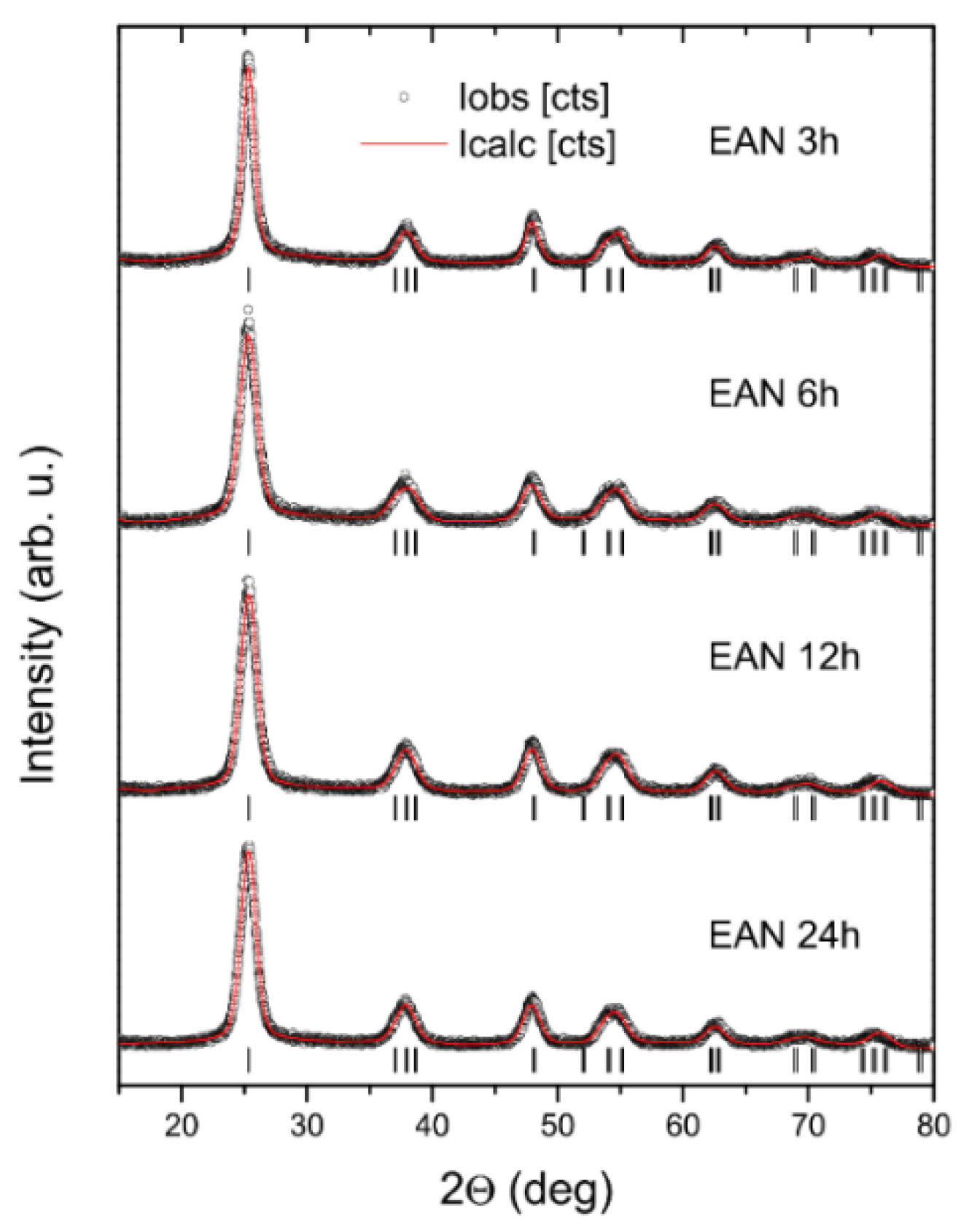
2.2. XRD Analysis
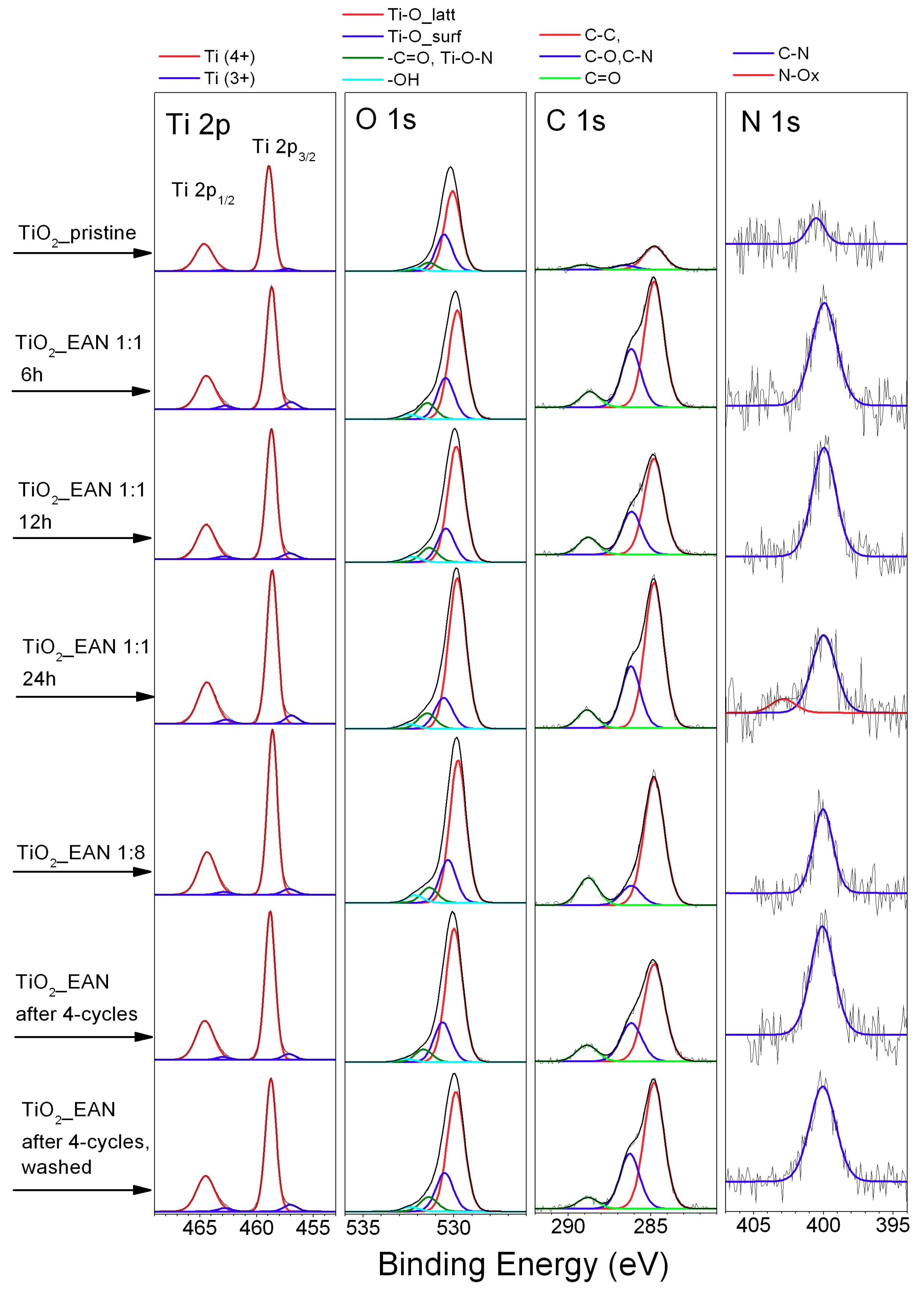
2.3. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Analysis
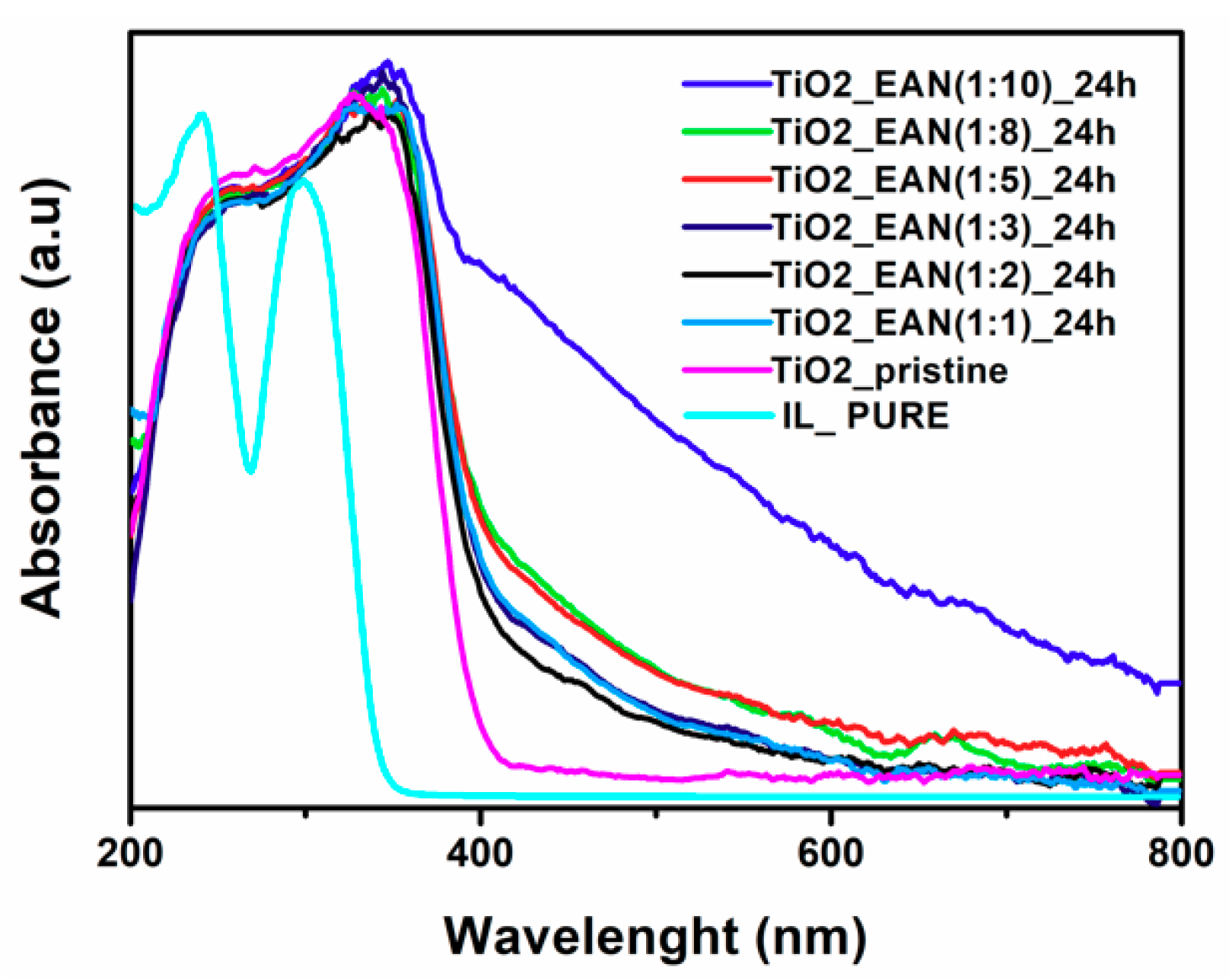
2.4. UV-VIS Spectrum
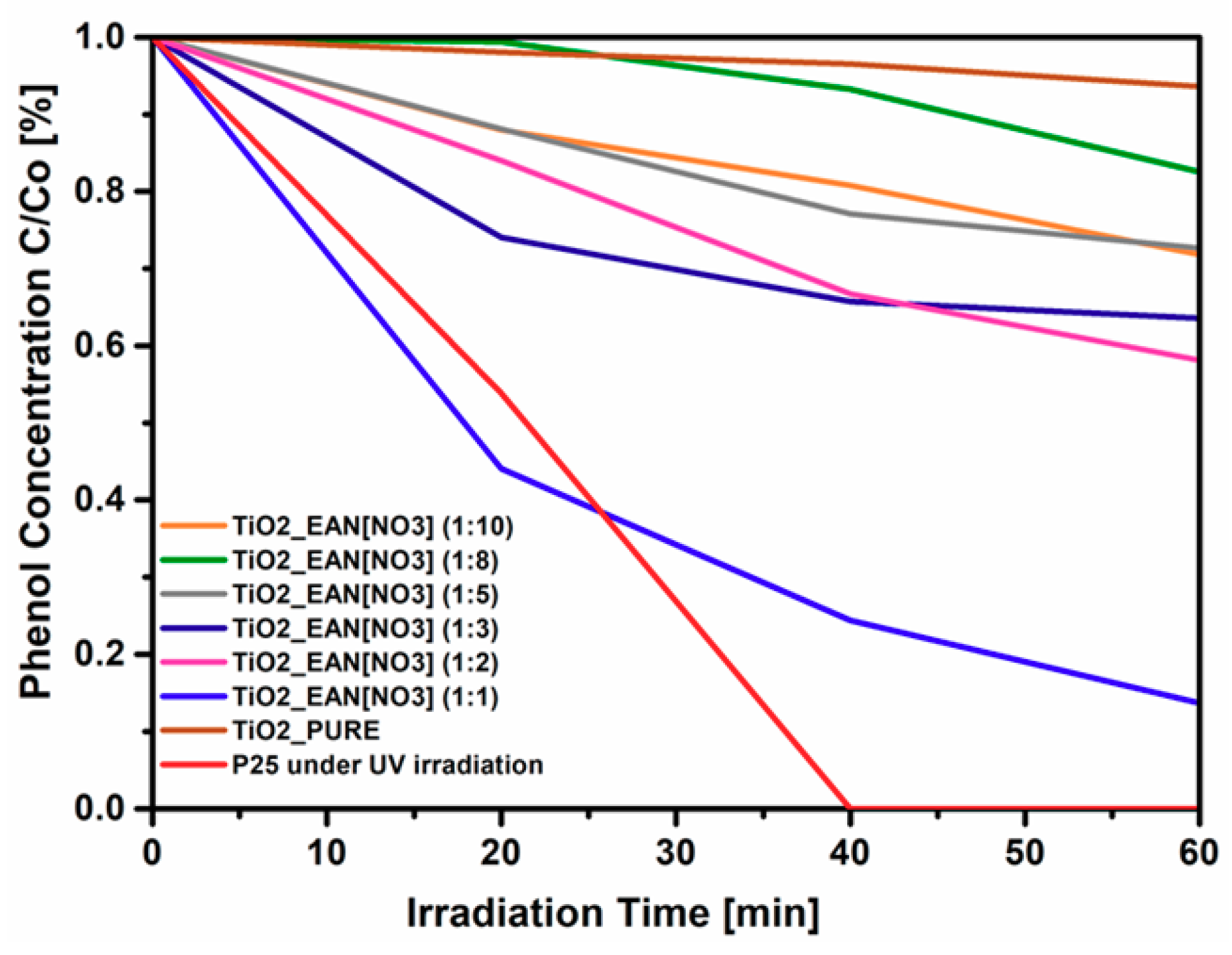
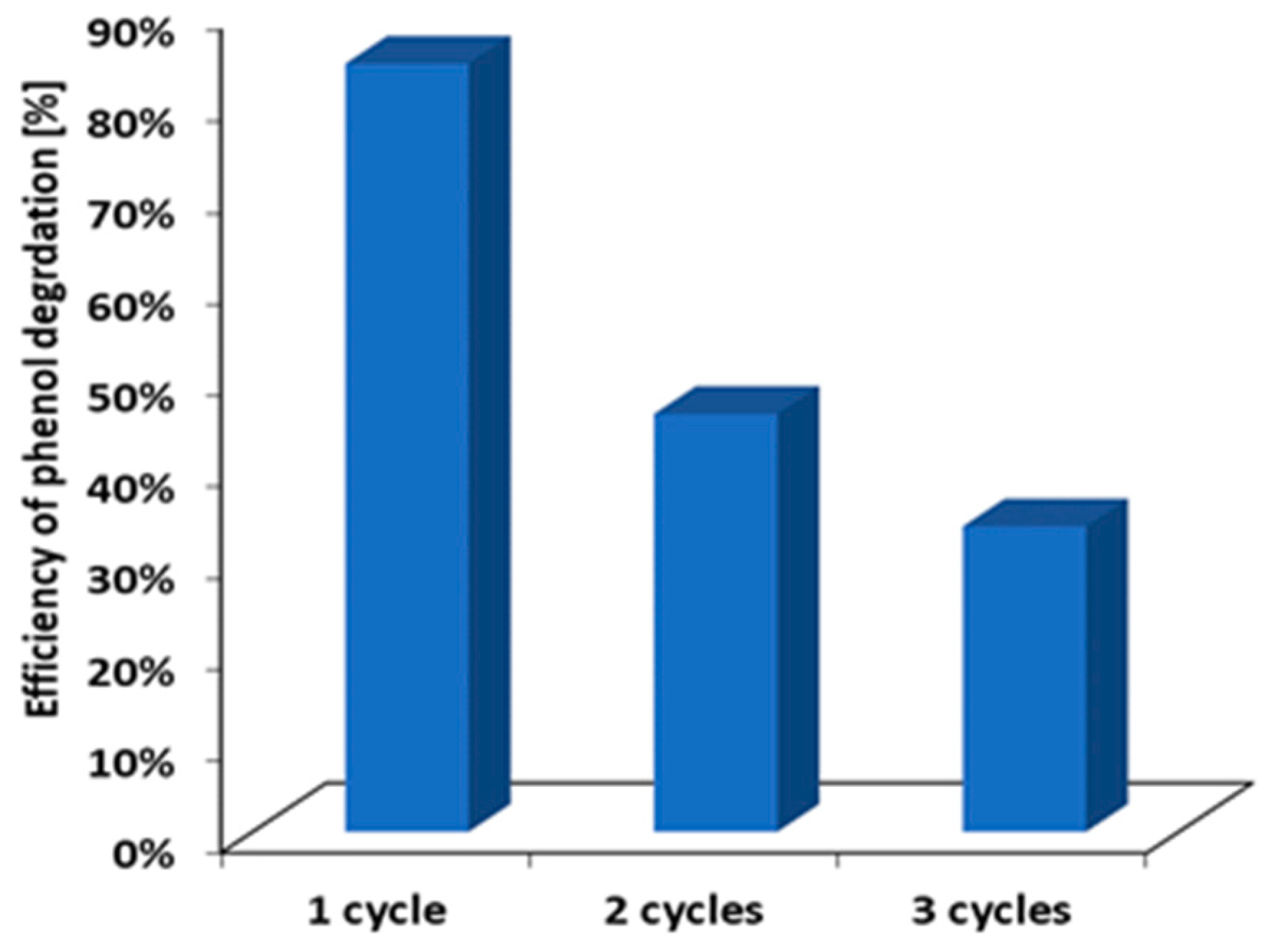
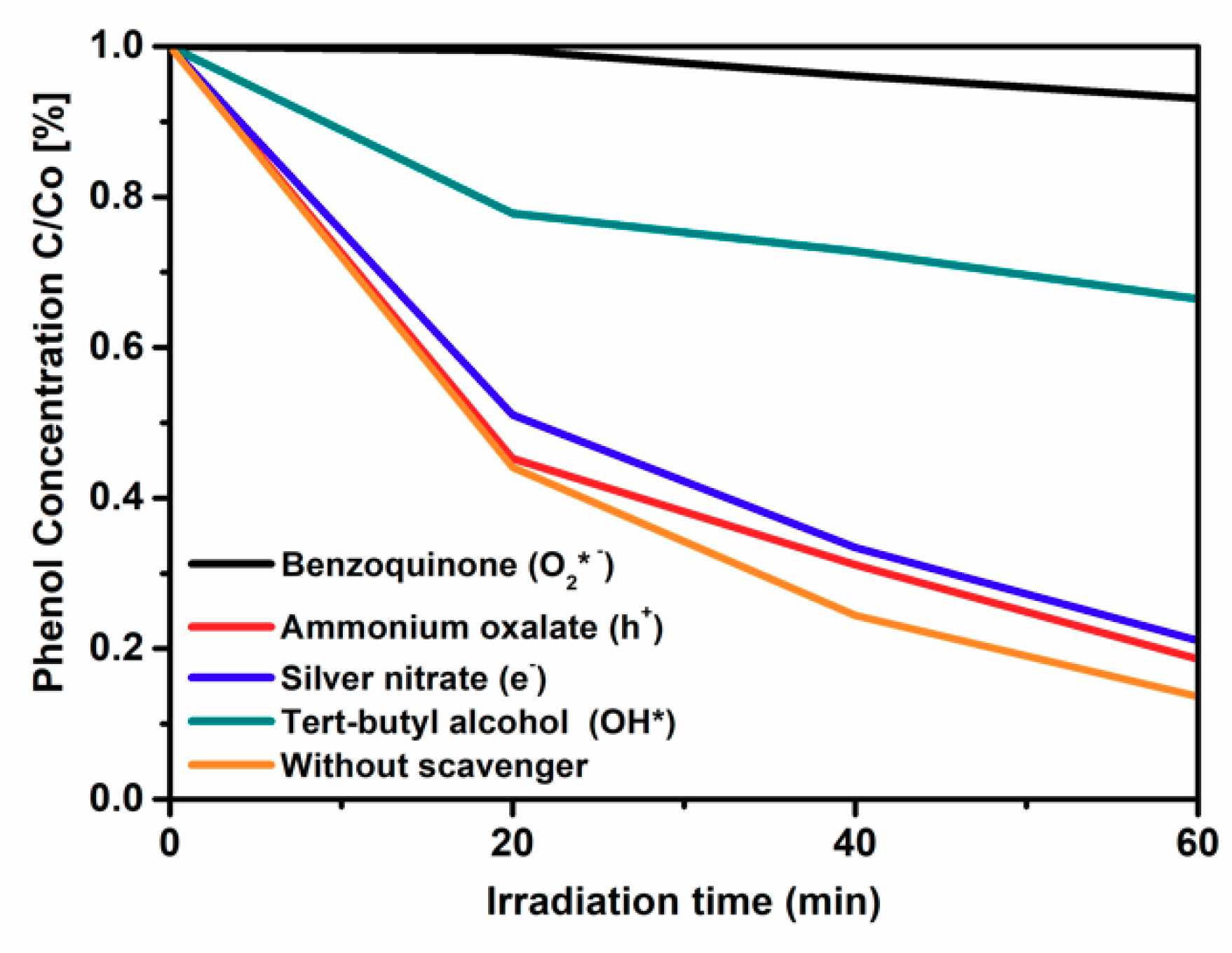
2.5. Photocatalytic Activity of IL–TiO2 in Phenol Decomposition Model Reaction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of IL-Assisted TiO2 Particles
3.3. Surface Properties Characterization
3.4. Evaluation of Photocatalytic Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffmann, M.R.; Martin, S.T.; Choi, W.; Bahnemann, D.W. Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Rao, T.N.; Tryk, D.A. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2000, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaez, M.; Nolan, N.T.; Pillai, S.C.; Seery, M.K.; Falaras, P.; Kontos, A.G.; Dunlop, P.S.M.; Hamilton, J.W.J.; Byrne, J.A.; O’Shea, K.; et al. A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 125, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M.A.; Dulay, M.T. Heterogeneous photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, T.L.; Yates, J.T. Surface science studies of the photoactivation of TiO2 new photochemical processes. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4428–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Xue, Z.; Xue, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Hao, J. Ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of morphology-controlled TiO2 particles with efficient photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 81108–81114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R.; Bansal, V. Ionic liquid mediated synthesis of nitrogen, carbon and fluorine-codoped rutile TiO2 nanorods for improved UV and visible light photocatalysis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ouyang, S.; Liu, L.; Reunchan, P.; Umezawa, N.; Ye, J. Recent advances in TiO2-based photocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 12642–12661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, D.; Yu, C.; Yin, Y.; Dai, H.; Shao, G. A sol–gel route to synthesize SiO2/TiO2 well-ordered nanocrystalline mesoporous photocatalysts through ionic liquid control. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 3065–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alammar, T.; Noei, H.; Wang, Y.; Mudring, A.-V. Mild yet phase-selective preparation of TiO2 nanoparticles from ionic liquids—A critical study. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8045–8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.; Breternitz, J.; Groh, M.F.; Ruck, M. Ionic liquids as crystallisation media for inorganic materials. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 4874–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.; Majeed, J.; Dey, K.K.; Ayyub, P.; Tyagi, A.K.; Bharadwaj, S.R. Effect of Mo-Incorporation in the TiO2 Lattice: A mechanistic basis for photocatalytic dye degradation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 15946–15962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Feng, X.; An, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J. Ionic Liquid Assisted Chemical Strategy to TiO2 Hollow Nanocube Assemblies with Surface-Fluorination and Nitridation and High Energy Crystal Facet Exposure for Enhanced Photocatalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 10283–10295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gindri, I.M.; Frizzo, C.P.; Bender, C.R.; Tier, A.Z.; Martins, M.A.P.; Villetti, M.A.; Machado, G.; Rodriguez, L.C.; Rodrigues, D.C. Preparation of TiO2 nanoparticles coated with ionic liquids: A supramolecular approach. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 11536–11543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łuczak, J.; Paszkiewicz, M.; Krukowska, A.; Malankowska, A.; Zaleska-Medynska, A. Ionic liquids for nano-and microstructures preparation. Part 1: Properties and multifunctional role. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 230, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszkiewicz, M.; Łuczak, J.; Lisowski, W.; Patyk, P.; Zaleska-Medynska, A. The ILs-assisted solvothermal synthesis of TiO2 spheres: The effect of ionic liquids on morphology and photoactivity of TiO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 184, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Singh, V. Current status and future challenges in ionic liquids, functionalized ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvent-mediated synthesis of nanostructured TiO2: A review. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 2844–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wender, H.; Feil, A.F.; Diaz, L.B.; Ribeiro, C.S.; Machado, G.J.; Migowski, P.; Weibel, D.E.; Dupont, J.; Teixeira, S.R. Self-organized TiO2 nanotube arrays: Synthesis by anodization in an ionic liquid and assessment of photocatalytic properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M. Enhanced and suppressed effects of ionic liquid on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2. Adsorption 2013, 19, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, P.C.; Marr, A.C. Ionic liquid gel materials: Applications in green and sustainable chemistry. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-M.; Lee, C.-Y. A salt-assisted approach for the pore-size-tailoring of the ionic-liquid-templated TiO2 photocatalysts exhibiting high activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 132, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.W.; Finger, P.H.; Mignoni, M.L.; Emmerich, D.J.; Mendes, F.M.T.; Amorim, S.; Pergher, S.B.C. TiO2-TON zeolite synthesis using an ionic liquid as a structure-directing agent. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 213, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Gong, L.; Song, H.; Liu, Y.; Yin, D. Ionic liquid of [Bmim]+Cl− for the preparation of hierarchical nanostructured rutile titania. J. Solid State Chem. 2007, 180, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołąbiewska, A.; Paszkiewicz-Gawron, M.; Sadzińska, A.; Lisowski, W.; Grabowska, E.; Zaleska-Medynska, A.; Łuczak, J. Fabrication and photoactivity of ionic liquid–TiO2 structures for efficient visible-light-induced photocatalytic decomposition of organic pollutants in aqueous phase. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.-C.; Ho, S.-Y.; Lin, Y.-P.; Lai, Y.-C.; Liang, W.-C.; Chen-Yang, Y.-W. Effect of π–π stacking of water miscible ionic liquid template with different cation chain length and content on morphology of mesoporous TiO2 prepared via sol–gel method and the applications. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 131, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Gan, Y.; Liu, L.; Ju, M. Microwave-assisted ionic liquid synthesis of Ti3+ self-doped TiO2 hollow nanocrystals with enhanced visible-light photoactivity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 191, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczak, J.; Paszkiewicz-Gawron, M.; Długokęcka, M.; Lisowski, W.; Grabowska, E.; Makurat, S.; Rak, J.; Zaleska-Medynska, A. Visible light photocatalytic activity of ionic liquid-TiO2 spheres: Effect of the ionic liquid’s anion structure. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 4377–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ko, K.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Illas, F. Single oxygen vacancies of (TiO2) 35 as a prototype reduced nanoparticle: Implication for photocatalytic activity. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 23755–23762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Cheng, G.F. Synthesis of Bi2Se3 Nanosheets by Microwave Heating Using an Ionic Liquid. Cryst. Growth Des. 2006, 6, 2174–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, H.; Sallard, S.B.; Djerdj, I.; Antonietti, M.; Smarsly, B.M. Toward a Low-Temperature Sol−Gel Synthesis of TiO2(B) Using Mixtures of Surfactants and Ionic Liquids. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 3502–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, Y.L.; Tripathi, A.K.; Singh, V.K.; Balo, L.; Gupta, H.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, R.K. Preparation and properties of titania based ionogels synthesized using ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium thiocyanate. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 220, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Xiao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.-M.; Wu, Q.; Sun, K. Covalently functionalized TiO2 with ionic liquid: A high-performance catalyst for photoelectrochemical water oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 166, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, T.N.; Nagaraju, G.; Dupont, J. Photocatalytic activity of Li-doped TiO2 nanoparticles: Synthesis via ionic liquid-assisted hydrothermal route. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 78, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liang, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, M. Hydrothermal synthesis of mesostructured nanocrystalline TiO2 in an ionic liquid–water mixture and its photocatalytic performance. Solid State Sci. 2009, 11, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, S.K.; Kaur, N.; Singh, V. Fabrication of phase and morphology controlled pure rutile and rutile/anatase TiO2 nanostructures in functional ionic liquid/water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ohno, T.; Nishijima, K.; Abe, R.; Ohtani, B. Is methylene blue an appropriate substrate for a photocatalytic activity test? A study with visible-light responsive Titania. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 429, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, B. Photocatalysis A to Z—What we know and what we do not know in a scientific sense. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2010, 11, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.-T.; Wang, X.-J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.-X.; Hao, Y.-J.; Liu, R.-H.; Zhao, D.-S. Ionic-liquid-assisted synthesis of high-visible-light-activated N–B–F-tri-doped mesoporous TiO2 via a microwave route. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 144, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhoseini, F.; Salabat, A. Ionic liquid based microemulsion method for the fabrication of poly (methyl methacrylate)–TiO2 nanocomposite as a highly efficient visible light photocatalyst. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12536–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, K.J.A.; Viswanathan, B. Effect of surface area, pore volume and particle size of P25 titania of the phase transformation of anatase to rutile. Indian J. Chem. 2009, 48A, 1378–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Djerdj, I.; Tonejc, A.M. Structural investigations of nanocrystalline TiO2 samples. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 413, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumkin, A.V.; Kraut-Vass, A.; Gaarenstroom, S.W.; Powell, C.J. NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database, NIST Standard Reference Database 20, Version 4.1. 2012. Available online: http://srdata.nist.gov/xps/ (accessed on 25 March 2013).
- Hu, X.; Zhang, T.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.; Yan, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y. Fabrication of carbon-modified TiO2 nanotube arrays and their photocatalytic activity. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 4579–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, M.; Inagaki, M.; Tryba, B.; Toyoda, M.; Morawski, A.W. Carbon-modified TiO2 photocatalyst by ethanol carbonisation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 63, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusiak-Nejman, E.; Janus, M.; Grzmil, B.; Morawski, A.W. Methylene Blue decomposition under visible light irradiation in the presence of carbon-modified TiO2 photocatalysts. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2011, 226, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kong, J.; Jia, H.; Wang, Z. Synthesis and characterization of carbon modified TiO2 nanotube and photocatalytic activity on methylene blue under sunlight. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 344, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-N.; Wang, H.-L.; Wang, X.-K.; Jiang, W.-F. Facile synthesis of tunable carbon modified mesoporous TiO2 for visible light photocatalytic application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 412, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.-P.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Chang, L.; Wang, H.-L. In-situ one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of carbon-TiO2 nanocomposites and their photocatalytic applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6114–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Long, M.; Cai, W.; Chen, C.; Wu, Y. Low temperature hydrothermal synthesis of N-doped TiO2 photocatalyst with high visible-light activity. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 502, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolat, D.; Quici, N.; Kusiak-Nejman, E.; Morawski, A.W.; Puma, G.L. One-step, hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen, carbon co-doped titanium dioxide (N, CTiO2) photocatalysts. Effect of alcohol degree and chain length as carbon dopant precursors on photocatalytic activity and catalyst deactivation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 115, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Cai, L.; Huang, L.; Yu, H.; Wang, H. Preparation of nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide with visible-light photocatalytic activity using a facile hydrothermal method. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2008, 69, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
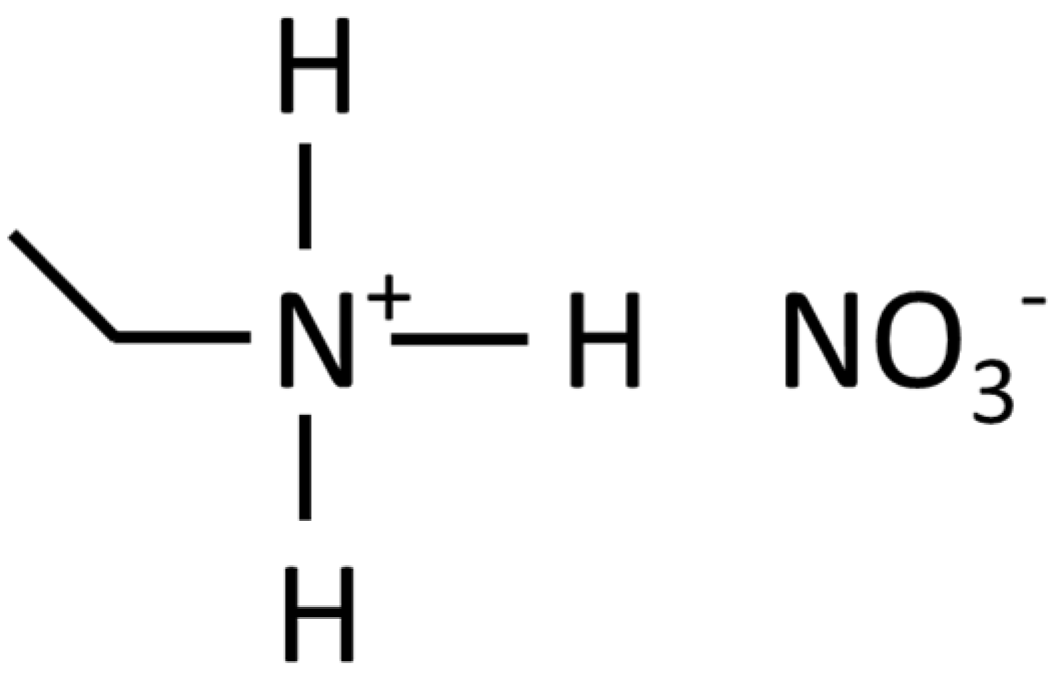

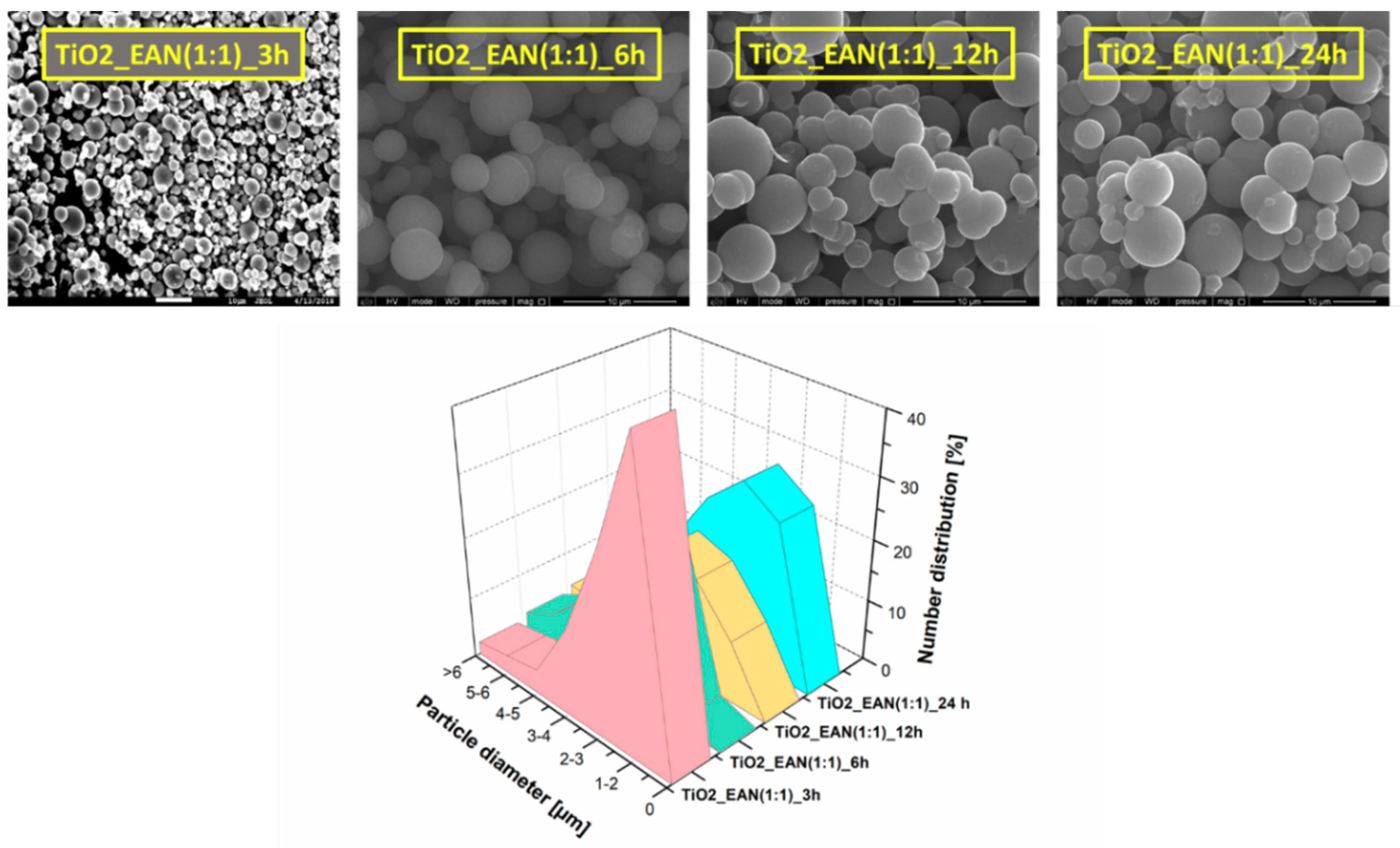

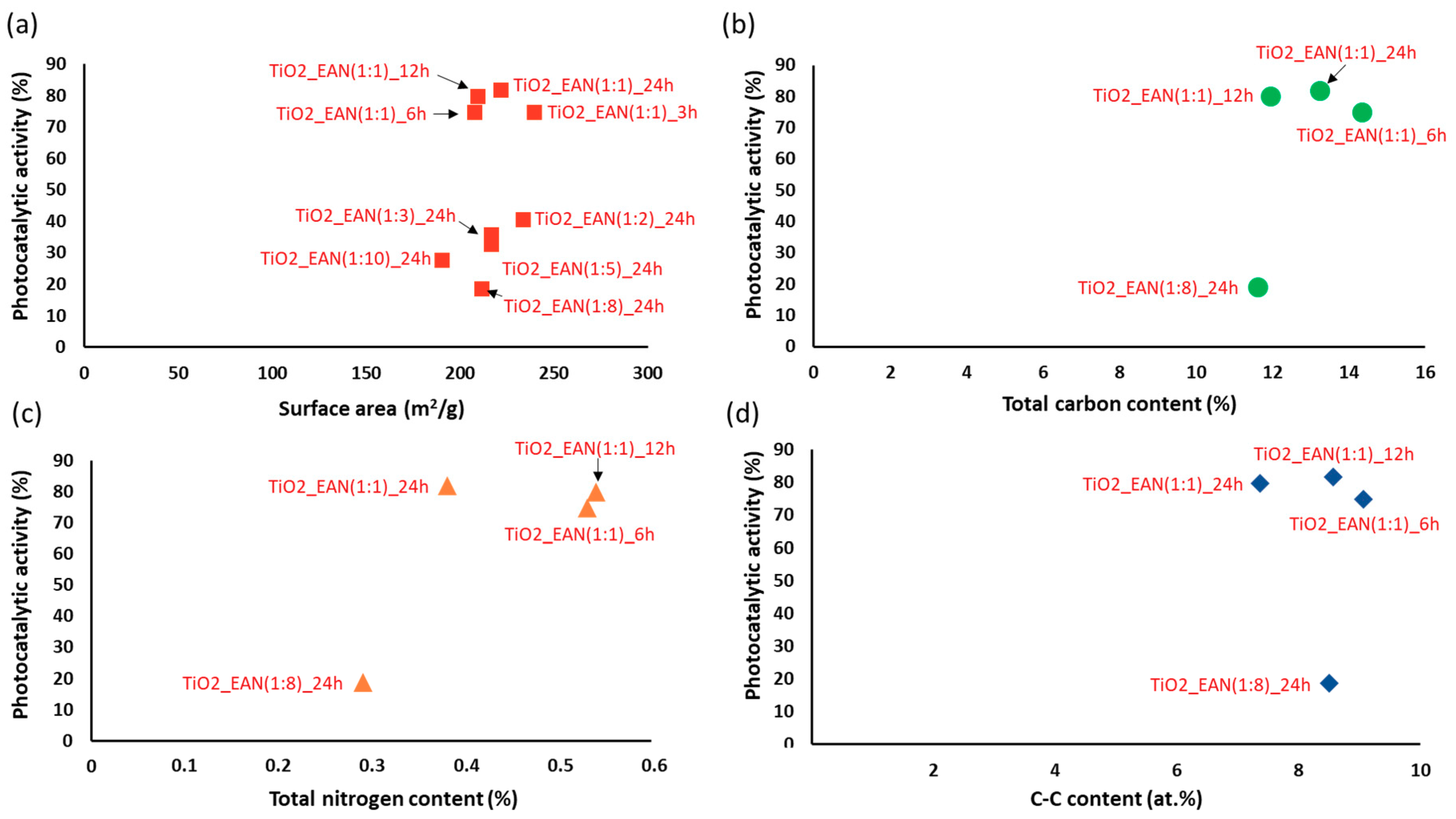
| Sample | Time of the Synthesis | Molar Ratio (IL:TBOT) | Specific Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3·g−1) | Phenol Degradation Efficiency under 60 min of VIS Irradiation (%) | Rate of Phenol Degradation under Visible Light (λ > 420) [µmol·dm−3·min−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2_pristine | 24 | - | 184 | 0.069 | 7 | 0.18 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:10)_24h | 24 | 1:10 | 190 | 0.093 | 28 | 1.01 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:8)_24h | 24 | 1:8 | 211 | 0.102 | 19 | 0.55 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:5)_24h | 24 | 1:5 | 216 | 0.105 | 33 | 1.11 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:3)_24h | 24 | 1:3 | 216 | 0.105 | 36 | 1.17 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:2)_24h | 24 | 1:2 | 233 | 0.113 | 41 | 1.32 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:1)_24h | 24 | 1:1 | 221 | 0.108 | 82 | 3.12 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:1)_3h | 3 | 1:1 | 239 | 0.12 | 75 | 2.28 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:1)_6h | 6 | 1:1 | 207 | 0.101 | 75 | 2.38 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:1)_12h | 12 | 1:1 | 209 | 0.102 | 80 | 2.53 |
| Sample | a (Å) | c (Å) | d (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2_EAN(1:1)_3h | 3.8051(3) | 9.554(2) | 65 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:1)_6h | 3.7907(7) | 9.504(3) | 50 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:1)_12h | 3.7892(6) | 9.507(3) | 55 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:1)_24h | 3.7890(6) | 9.502(3) | 60 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:2)_24h | 3.7899(7) | 9.499(3) | 55 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:3)_24h | 3.7926(8) | 9.506(4) | 60 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:5)_24h | 3.7814(11) | 9.472(6) | 65 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:8)_24h | 3.7953(9) | 9.483(5) | 55 |
| TiO2_EAN(1:10)_24h | 3.7942(12) | 9.476(7) | 55 |
| Sample Label | ∑ Ti (at. %) | Ti 2p3/2 Fraction (%) | ∑ O (at. %) | O 1s Fraction (%) | ∑ C (at. %) | C 1s Fraction (%) | ∑ N (at. %) | N 1s Fraction (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti(4+) 458.7 ± 0.1 eV | Ti(3+) 457.0 ± 0.1 eV | Ti-Olatt 529.9 ± 0.1 eV | Ti-Osurf 530.5 ± 0.1 eV | –Ti–O–N, –C=O 531.5 ± 0.1 eV | –OH 532.4 ± 0.1 eV | “A” C–C 284.8 eV | “B” C–OH, C–N 286.2 ± 0.1 eV | “C” –C=O, 288.9 ± 0.1 eV | N–C 399.9 ± 0.1 eV | N–Ox 402.8 ± 0.1 eV | |||||
| TiO2_pristine | 29.44 | 97.59 | 2.41 | 66.27 | 62.35 | 28.60 | 6.59 | 2.46 | 4.15 | 72.27 | 13.46 | 14.27 | 0.14 | 100 | 0 |
| TiO2_EAN 1:1_6h | 23.15 | 93.37 | 6.63 | 61.97 | 63.55 | 24.13 | 9.54 | 2.78 | 14.35 | 63.03 | 29.19 | 7.78 | 0.53 | 100 | 0 |
| TiO2_EAN 1:1_12h | 24.00 | 94.06 | 5.94 | 63.51 | 68.33 | 19.89 | 8.50 | 3.28 | 11.94 | 61.53 | 27.49 | 10.99 | 0.54 | 100 | 0 |
| TiO2_EAN 1:1_24h | 23.37 | 93.64 | 6.36 | 63.00 | 74.56 | 15.33 | 7.72 | 2.39 | 13.24 | 64.56 | 27.42 | 8.02 | 0.38 | 84.89 | 5.11 |
| TiO2_EAN 1:8_24h | 24.32 | 95.44 | 4.56 | 63.80 | 68.52 | 20.58 | 7.25 | 3.65 | 11.61 | 73.05 | 11.18 | 15.77 | 0.29 | 100 | 0 |
| TiO2_EAN_4-cycles | 24.61 | 94.47 | 4.78 | 63.77 | 70.46 | 21.06 | 6.75 | 1.73 | 11.14 | 64.12 | 25.22 | 10.66 | 0.49 | 100 | 0 |
| TiO2_EAN_4-cycles (washed) | 23.53 | 93.10 | 6.13 | 62.35 | 67.42 | 21.84 | 8.15 | 2.59 | 13.64 | 65.63 | 28.52 | 5.84 | 0.48 | 100 | 0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gołąbiewska, A.; Checa-Suárez, M.; Paszkiewicz-Gawron, M.; Lisowski, W.; Raczuk, E.; Klimczuk, T.; Polkowska, Ż.; Grabowska, E.; Zaleska-Medynska, A.; Łuczak, J. Highly Active TiO2 Microspheres Formation in the Presence of Ethylammonium Nitrate Ionic Liquid. Catalysts 2018, 8, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8070279
Gołąbiewska A, Checa-Suárez M, Paszkiewicz-Gawron M, Lisowski W, Raczuk E, Klimczuk T, Polkowska Ż, Grabowska E, Zaleska-Medynska A, Łuczak J. Highly Active TiO2 Microspheres Formation in the Presence of Ethylammonium Nitrate Ionic Liquid. Catalysts. 2018; 8(7):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8070279
Chicago/Turabian StyleGołąbiewska, Anna, Micaela Checa-Suárez, Marta Paszkiewicz-Gawron, Wojciech Lisowski, Edyta Raczuk, Tomasz Klimczuk, Żaneta Polkowska, Ewelina Grabowska, Adriana Zaleska-Medynska, and Justyna Łuczak. 2018. "Highly Active TiO2 Microspheres Formation in the Presence of Ethylammonium Nitrate Ionic Liquid" Catalysts 8, no. 7: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8070279
APA StyleGołąbiewska, A., Checa-Suárez, M., Paszkiewicz-Gawron, M., Lisowski, W., Raczuk, E., Klimczuk, T., Polkowska, Ż., Grabowska, E., Zaleska-Medynska, A., & Łuczak, J. (2018). Highly Active TiO2 Microspheres Formation in the Presence of Ethylammonium Nitrate Ionic Liquid. Catalysts, 8(7), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8070279








