Photocatalytic Water Disinfection under Solar Irradiation by d-Glucose-Modified Titania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of d-Glucose-Modified TiO2
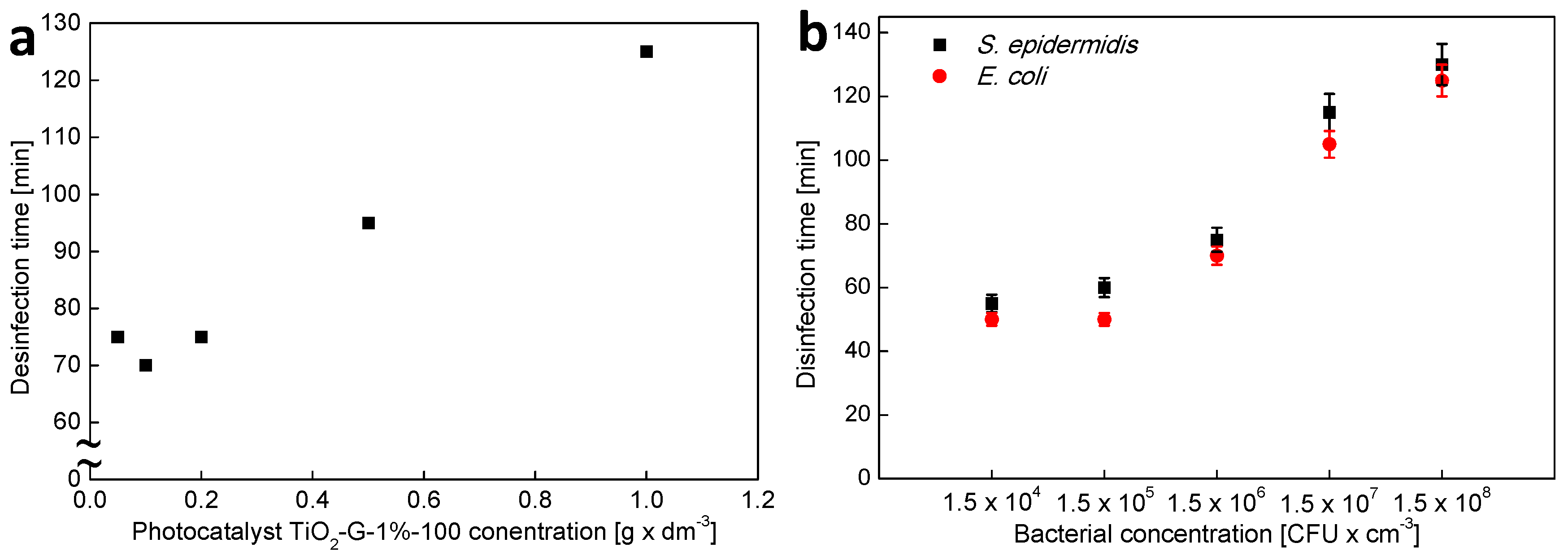
2.2. Dose-Dependent Photocatalytic Inactivation of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus epidermidis
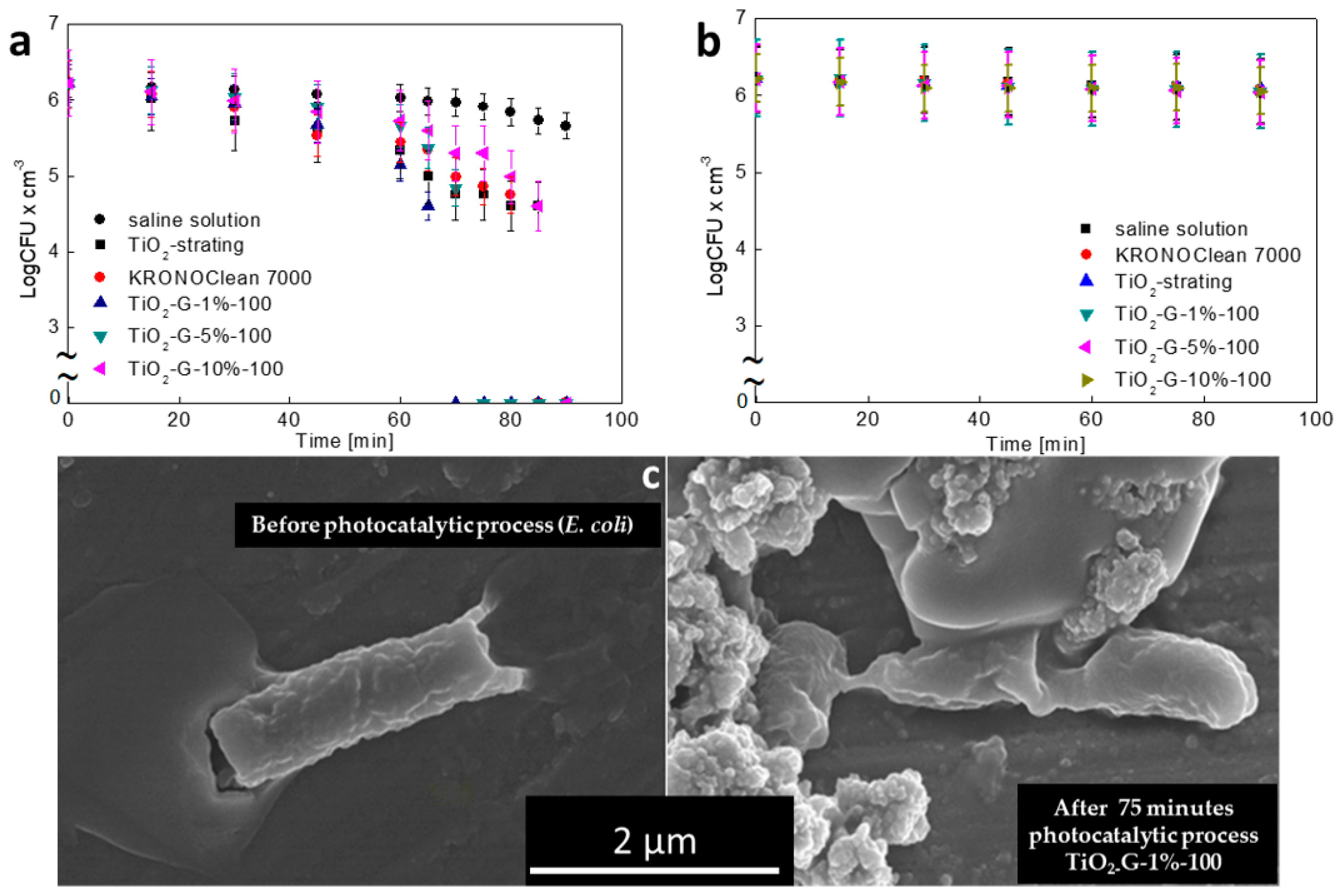
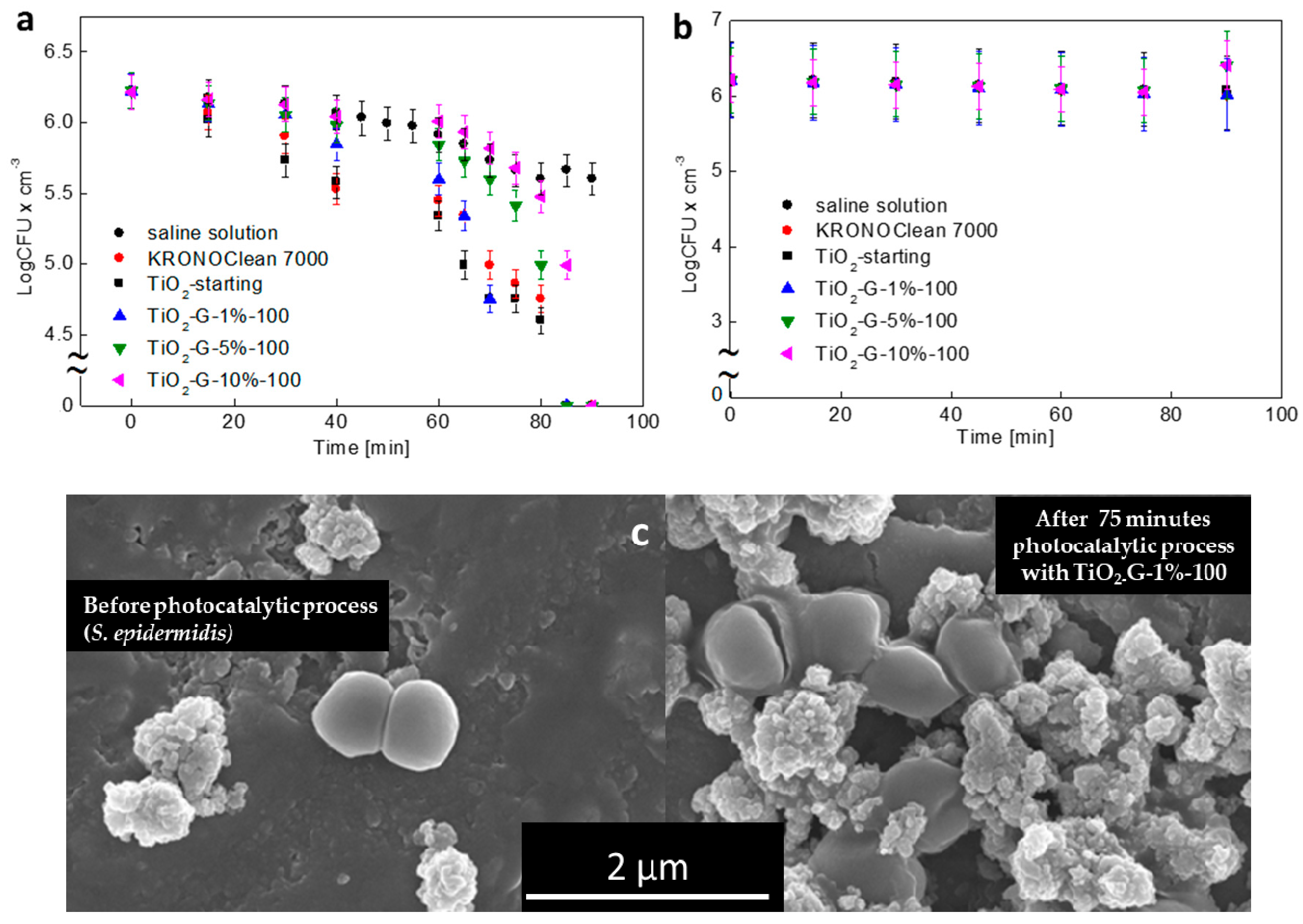
2.3. Influenece of d-Glucose Content, Used for TiO2 Modification at 100 °C, on Disinfection Properties
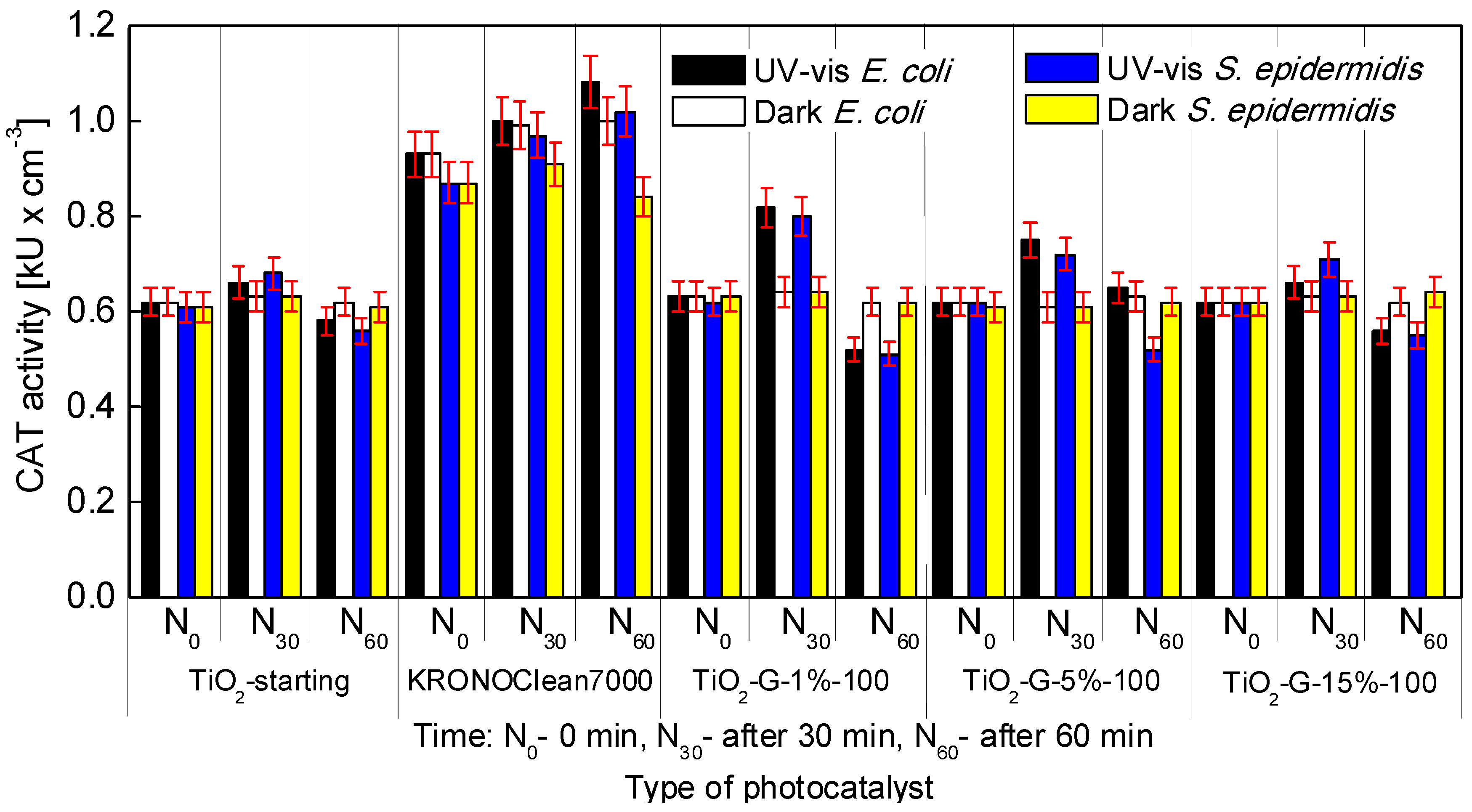
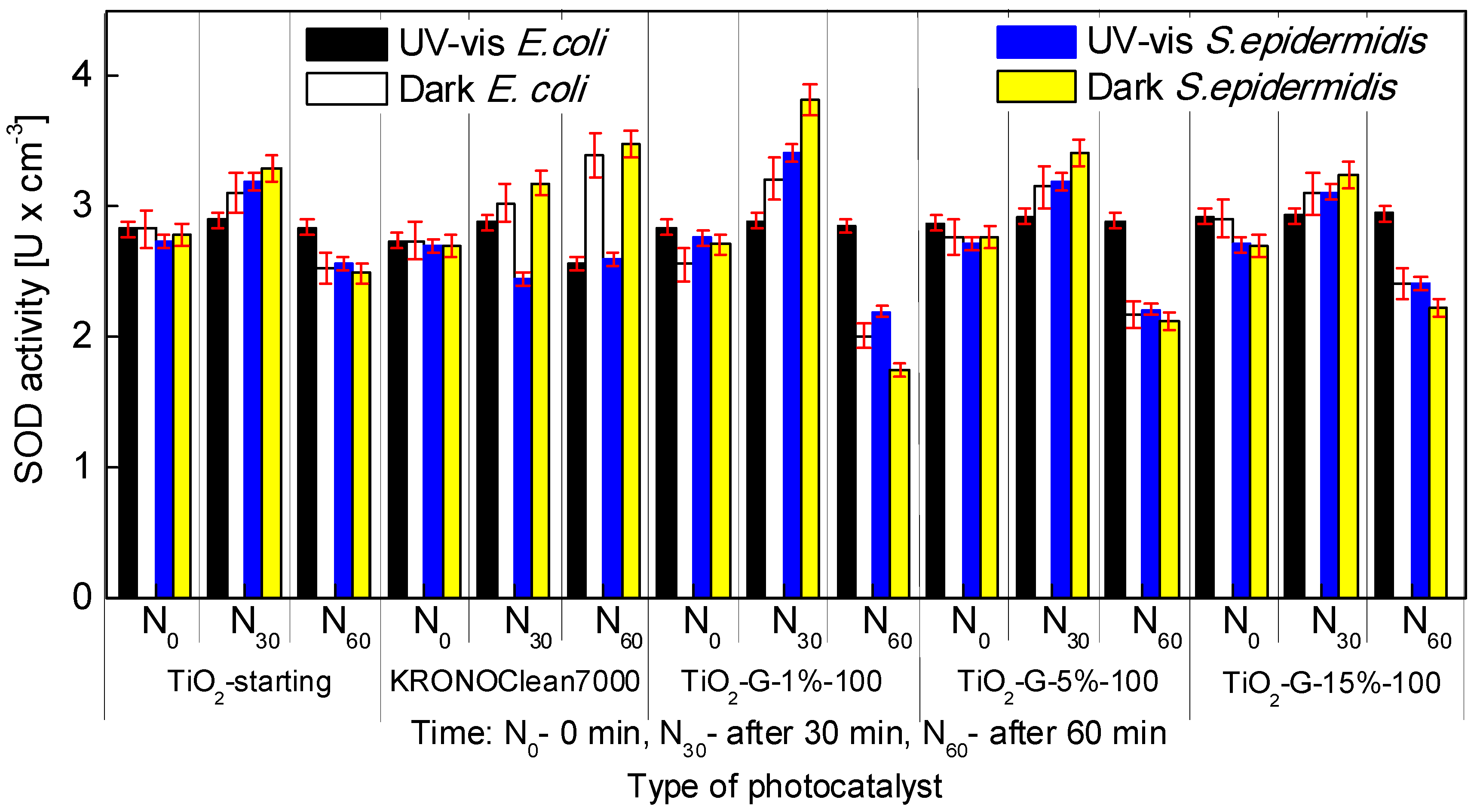
2.4. Influenece of d-Glucose Content, Used for TiO2 Modification at 100 °C, on Enzymatic Activity
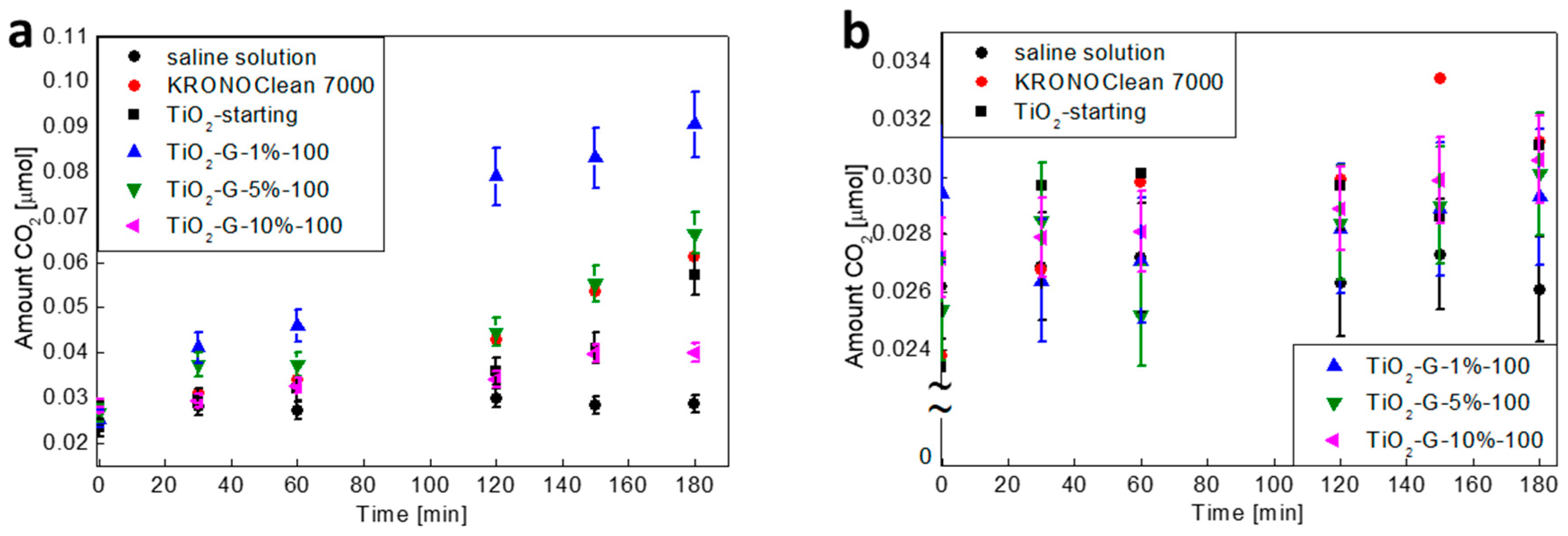
2.5. Influenece of d-Glucose Content, Used for TiO2 Modification at 100 °C, on Bacteria Mineralization
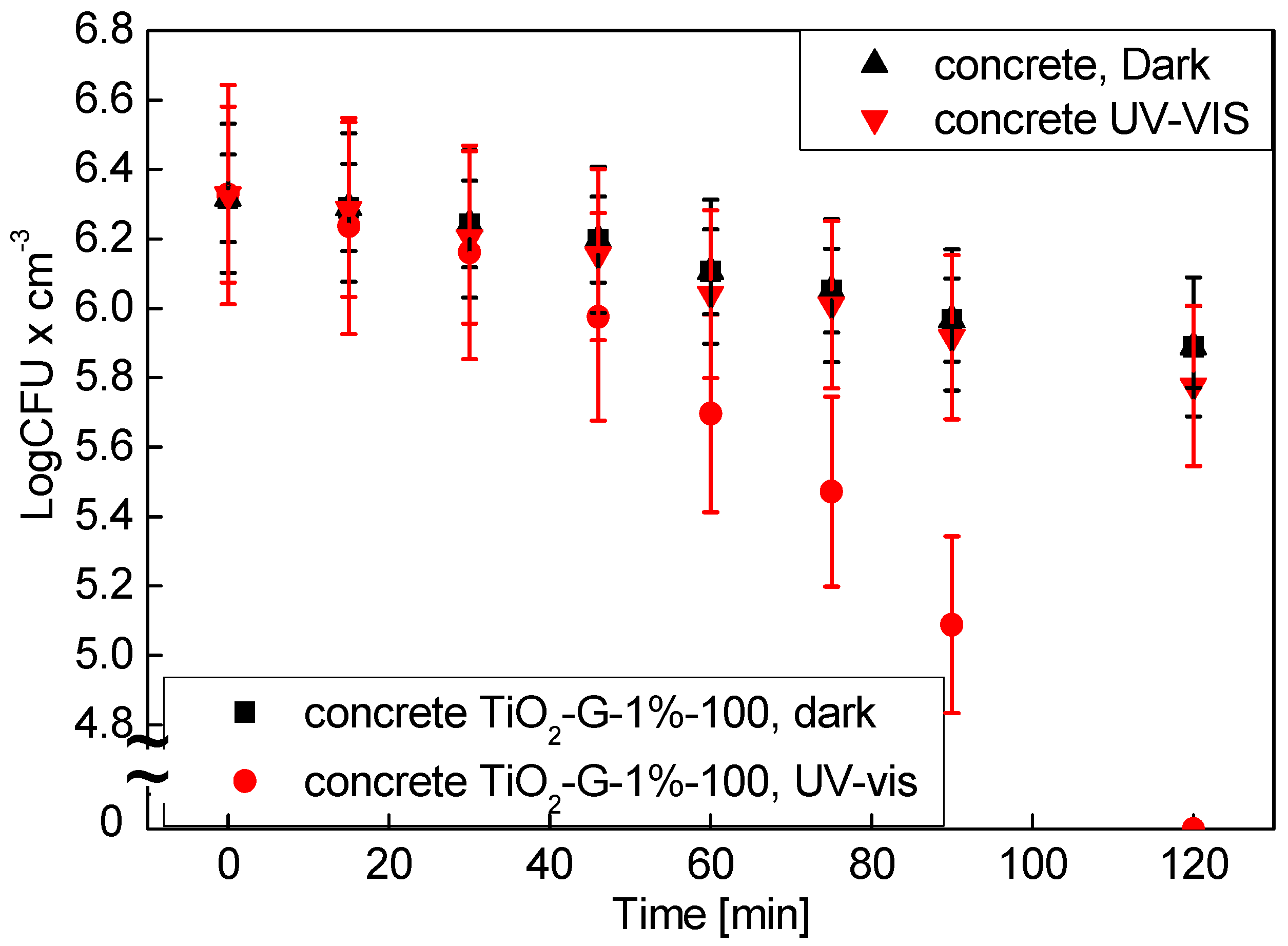
2.6. Commercialization of Antimicrobial Photocatalysts for Building Materials
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of C/TiO2
4.2. Characterisation of Photocatalyst
4.3. Antimicrobial Properties of Dispersed C/TiO2
4.4. Antimicrobial Properties of Employed in Concrete TiO2-G-1%-100
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rengifo-Herrera, J.A.; Mielczarski, E.; Mielczarski, J.; Castillo, N.C.; Kiwi, J.; Pulgarin, C. Escherichia coli inactivation by N, S co-doped commercial TiO2 powders under UV and visible light. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 84, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, E.; Mahaney, O.O.P.; Abe, R.; Ohtani, B. Visible-light-induced photocatalysis through surface plasmon excitation of gold on titania surfaces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Han, C.; Pelaez, M.; Zhu, D.; Liao, S.; Likodimos, V.; Ioannidis, N.; Kontos, A.G.; Falaras, P.; Dunlop, P.S.M.; et al. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic evaluation of visible light activated c-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 294003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asahi, R.; Morikawa, T.; Irie, H.; Ohwaki, T. Nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide as visible-light-sensitive photocatalyst: Designs, developments, and prospects. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9824–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asahi, R.; Morikawa, T.; Ohwaki, T.; Aoki, K.; Taga, Y. Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium oxides. Science 2001, 293, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanivelu, K.; Im, J.-S.; Lee, Y.-S. Carbon doping of TiO2 for visible light photo catalysis—A review. Carbon Lett. 2007, 8, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Nishikawa, T.; Ohtani, B.; Chen, A. Synthesis and characterization of carbon-doped TiO2 nanostructures with enhanced visible light response. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 4530–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Dong, F.; Zhao, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Guan, B. The fabrication and characterization of novel carbon doped TiO2 nanotubes, nanowires and nanorods with high visible light photocatalytic activity. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 235701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J. Carbon-deposited TiO2: Synthesis, characterization, and visible photocatalytic performance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Yang, S.; Shi, J.; Niu, C. Highly crystallized C-doped mesoporous anatase TiO2 with visible light photocatalytic activity. Catalysts 2016, 6, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawski, A.W.; Janus, M.; Tryba, B.; Inagaki, M.; Kałucki, K. TiO2-anatase modified by carbon as the photocatalyst under visible light. Rendus Rendu Chim. 2006, 9, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, S.; Kisch, H. Daylight photocatalysis by carbon-modified titanium dioxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 4908–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janus, M.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Kusiak-Nejman, E.; Morawski, A.W. Disinfection of E. coli by carbon modified TiO2 photocatalysts. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2012, 38, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanag, A.; Rokicka, P.; Kusiak-Nejman, E.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Morawski, A.W. TiO2/glucose nanomaterials with enhanced antibacterial properties. Mater. Lett. 2016, 185, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanag, A.; Rokicka, P.; Kusiak-Nejman, E.; Kapica-Kozar, J.; Wrobel, R.J.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Morawski, A.W. Antibacterial properties of TiO2 modified with reduced graphene oxide. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Inactivated properties of activated carbon-supported TiO2 nanoparticles for bacteria and kinetic study. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, J.G.; Cui, W.; Zhang, Z. Degradative and disinfective properties of carbon-doped anatase-rutile TiO2 mixtures under visible light irradiation. Catal. Today 2013, 207, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-S.; Kau, J.-H.; Huang, H.-H.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Wu, W.-S.; Chang, H.-H. Antibacterial properties of visible-light-responsive carbon-containing titanium dioxide photocatalytic nanoparticles against anthrax. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzybowska, B.; Słoczyński, J.; Grabowski, R.; Samson, K.; Gressel, I.; Wcisło, K.; Gengembre, L.; Barbaux, Y. Effect of doping of TiO2 support with altervalent ions on physicochemical and catalytic properties in oxidative dehydrogenation of propane of vanadia–titania catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 230, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- örsi, F. Kinetic studies on the thermal decomposition of glucose and fructose. J. Therm. Anal. 1973, 5, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimestad, R.; Vågen, I.M. Thermal stability of glucose and other sugar aldoses in normal phase high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Coruña 2006, 1118, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siuzdak, K.; Sawczak, M.; Klein, M.; Nowaczyk, G.; Jurga, S.; Cenian, A. Preparation of platinum modified titanium dioxide nanoparticles with the use of laser ablation in water. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 15199–15206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska-Jurek, A.; Kowalska, E.; Sobczak, J.W.; Lisowski, W.; Ohtani, B.; Zaleska, A. Preparation and characterization of monometallic (au) and bimetallic (ag/au) modified-titania photocatalysts activated by visible light. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 101, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Janczarek, M.; Endo, M.; Balčytis, A.; Nitta, A.; Mendez Medrano, M.G.; Colbeau-Justin, C.; Juodkazis, S.; Ohtani, B.; Kowalska, E. Noble metal-modified faceted anatase titania photocatalysts: Octahedron versus decahedron. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 237, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltrusaitis, J.; Schuttlefield, J.; Zeitler, E.; Grassian, V.H. Carbon dioxide adsorption on oxide nanoparticle surfaces. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleisch, T.H.; Mains, G.J. Reduction of copper oxides by uv radiation and atomic hydrogen studied by xps. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1982, 10, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Self-accumulated ag nanoparticles on mesoporous TiO2 thin film with high bactericidal activities. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 3676–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, N.; Chenakin, S. Xps characterization of Au/TiO2 catalysts: Binding energy assessment and irradiation effects. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 391, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossnagel, S.M.; Sites, J.R. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of ion beam sputter deposited SiO2, TiO2, and Ta2O5. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 1984, 2, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, H.; Soloviev, A.; Li, Z.; Søgaard, E.G. Xps and ftir investigation of the surface properties of different prepared titania nano-powders. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 246, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Q. Effect of surface structure on photocatalytic activity of TiO2 thin films prepared by sol-gel method. Thin Solid Films 2000, 379, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonnen, J.; Kilvington, S.; Kehoe, S.C.; Al-Touati, F.; McGuigan, K.G. Solar and photocatalytic disinfection of protozoan, fungal and bacterial microbes in drinking water. Water Res. 2005, 39, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maletić, M.; Vukčević, M.; Kalijadis, A.; Janković-Častvan, I.; Dapčević, A.; Laušević, Z.; Laušević, M. Hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2/carbon composites and their application for removal of organic pollutants. Arab. J. Chem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Lee, S.-H.; Choi, W. Glucose–TiO2 charge transfer complex-mediated photocatalysis under visible light. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 162, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z. One-step “green” synthetic approach for mesoporous c-doped titanium dioxide with efficient visible light photocatalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 16717–16723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, J. Heterogeneous photocatalysis: Fundamentals and applications to the removal of various types of aqueous pollutants. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Chung, H.; Choi, W.; Yoon, J. Linear correlation between inactivation of E. coli and OH radical concentration in TiO2 photocatalytic disinfection. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benabbou, A.K.; Derriche, Z.; Felix, C.; Lejeune, P.; Guillard, C. Photocatalytic inactivation of escherischia coli. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 76, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Singh, S.S.; Shanker, R.; Dhawan, A. Engineered ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and dna damage leading to reduced viability of escherichia coli. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1872–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanag, A.; Morawski, A.W.; Kapica-Kozar, J.; Kusiak-Nejman, E. Photocatalytic performance of thermally prepared TiO2/C photocatalysts under artificial solar light. Micro Nano Lett. 2016, 11, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Li, H.; Hong, W.; Fan, S.; Zhu, L. The effect of carbon content on the structure and photocatalytic activity of nano-bi2wo6 powder. Powder Technol. 2013, 247, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacem, M.; Bru-Adan, V.; Goetz, V.; Steyer, J.P.; Plantard, G.; Sacco, D.; Wery, N. Inactivation of escherichia coli by TiO2-mediated photocatalysis evaluated by a culture method and viability-qpcr. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2016, 317, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, J.; Ma, S.; Liu, G.; Yang, K.; Tong, M.; Lin, D. Toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to escherichia coli: Effects of particle size, crystal phase and water chemistry. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clogston, J.D.; Patri, A.K. Zeta potential measurement. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 697, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadwan, M.H.; Abed, H.N. Data supporting the spectrophotometric method for the estimation of catalase activity. Data Brief 2016, 6, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marklund, S.; Marklund, G. Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1974, 47, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Rokicka, P.; Janus, M.; Kusiak Najman, E.; Morawski, A.W. Method for Testing Antibacterial Properties of Materials Made from Cements Containing Titanium Dioxide. Patent Number 416,872, 19 April 2016. [Google Scholar]

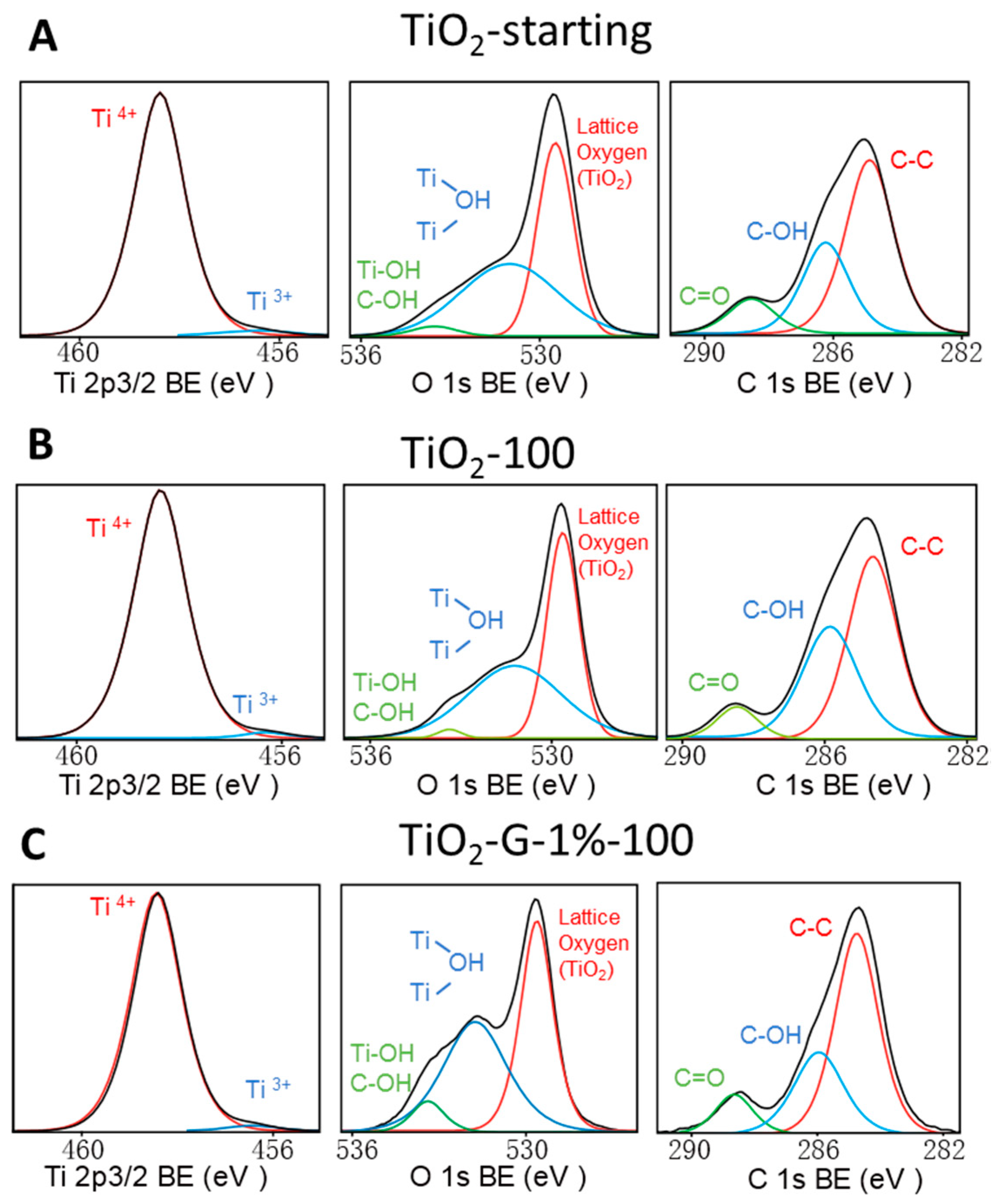

| Sample Name | Anatase Content [%] a | Anatase Crystallite Size [nm] | SBET [m2/ g] | Carbon Content (wt %) | Zeta Potential ζ [mV] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starting TiO2 | 95.0 | 11.0 | 312 | 0.0 | −24.13 |
| KRONOClean7000 | 100.0 | 11.0 | 242 | 0.96 | −17.71 |
| TiO2-G-1%-100 | 97.8 | 11.7 | 268 | 0.59 | −13.49 |
| TiO2-G-5%-100 | 97.6 | 11.4 | 252 | 2.23 | −25.28 |
| TiO2-G-10%-100 | 97.6 | 11.2 | 214 | 4.49 | −26.49 |
| TiO2-G-1%-150 | 98.0 | 16.0 | 155 | 0.49 | −17.04 |
| TiO2-G-5%-150 | 98.1 | 13.4 | 206 | 2.10 | −20.24 |
| TiO2-G-10%-150 | 97.8 | 11.4 | 195 | 3.91 | −23.70 |
| TiO2-G-1%-200 | 98.0 | 21.8 | 87 | 0.29 | −16.80 |
| TiO2-G-5%-200 | 97.9 | 17.2 | 120 | 1.90 | −18.72 |
| TiO2-G-10%-200 | 97.9 | 17.3 | 110 | 3.37 | −23.34 |
| Sample name | Content (at. %) | Ratio | ||||||||
| Ti 2p3/2 | O 1s | C 1s | O/Ti | C/Ti | ||||||
| Starting TiO2 | 17.71 | 43.95 | 38.34 | 2.5 | 2.2 | |||||
| TiO2-100 | 15.05 | 43.3 | 41.65 | 2.9 | 2.8 | |||||
| TiO2-G-1%-100 | 12.1 | 36.06 | 51.84 | 3.0 | 4.3 | |||||
| Fraction of oxidation states | ||||||||||
| Sample name | Ti 2p3/2 (%) | O 1s (%) | C 1s (%) | |||||||
| Ti4+ | Ti3+ | TiO2 | =Oa | -OHb | C-C | C-OH | C=O | |||
| Starting TiO2 | 97.9 | 2.1 | 47.2 | 50.0 | 2.8 | 58.7 | 30.1 | 11.2 | ||
| TiO2-100 | 98.1 | 1.9 | 45.0 | 53.6 | 1.4 | 54.7 | 37.2 | 8.1 | ||
| TiO2-G-1%-100 | 97.8 | 2.2 | 46.0 | 47.2 | 6.8 | 61.5 | 28.5 | 10.0 | ||
| Photocatalyst TiO2-G-1%-100 Concentration [g × dm3] | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | - | SI | SI | * | *** |
| 0.1 | SI | - | SI | * | *** |
| 0.2 0.5 | * | * | * | - | *** |
| 1.0 | *** | *** | *** | *** | - |
| Initial concentration of E. coli [CFU × cm3] | 1.5 × 104 | 1.5 × 105 | 1.5 × 106 | 1.5 × 107 | 1.5 × 108 |
| 1.5 × 104 | - | SI | SI | ** | *** |
| 1.5 × 105 | SI | - | SI | ** | *** |
| 1.5 × 106 | SI | SI | - | ** | *** |
| 1.5 × 107 | ** | ** | ** | - | * |
| 1.5 × 108 | *** | *** | *** | * | - |
| Initial concentration of S. epidermidis [CFU × cm3] | 1.5 × 104 | 1.5 × 105 | 1.5 × 106 | 1.5 × 107 | 1.5 × 108 |
| 1.5 × 104 | - | SI | SI | ** | *** |
| 1.5 × 105 | SI | - | SI | ** | *** |
| 1.5 × 106 | SI | SI | - | ** | *** |
| 1.5 × 107 | ** | ** | ** | - | * |
| 1.5 × 108 | *** | *** | *** | * | - |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Rokicka, P.; Wang, K.; Endo, M.; Morawski, A.W.; Kowalska, E. Photocatalytic Water Disinfection under Solar Irradiation by d-Glucose-Modified Titania. Catalysts 2018, 8, 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8080316
Markowska-Szczupak A, Rokicka P, Wang K, Endo M, Morawski AW, Kowalska E. Photocatalytic Water Disinfection under Solar Irradiation by d-Glucose-Modified Titania. Catalysts. 2018; 8(8):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8080316
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkowska-Szczupak, Agata, Paulina Rokicka, Kunlei Wang, Maya Endo, Antoni Waldemar Morawski, and Ewa Kowalska. 2018. "Photocatalytic Water Disinfection under Solar Irradiation by d-Glucose-Modified Titania" Catalysts 8, no. 8: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8080316
APA StyleMarkowska-Szczupak, A., Rokicka, P., Wang, K., Endo, M., Morawski, A. W., & Kowalska, E. (2018). Photocatalytic Water Disinfection under Solar Irradiation by d-Glucose-Modified Titania. Catalysts, 8(8), 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8080316










