Ru–Pd Bimetallic Catalysts Supported on CeO2-MnOX Oxides as Efficient Systems for H2 Purification through CO Preferential Oxidation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
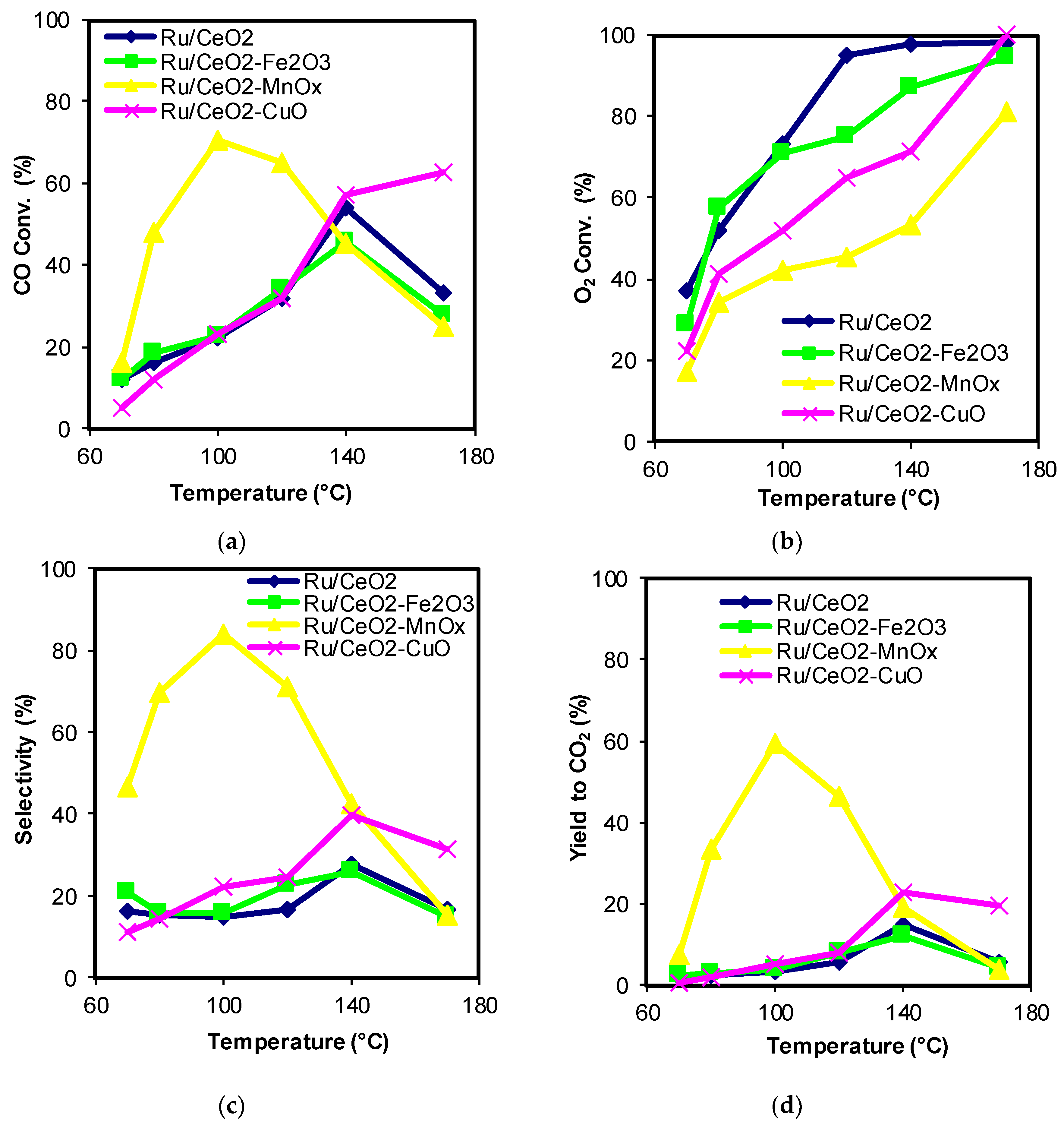
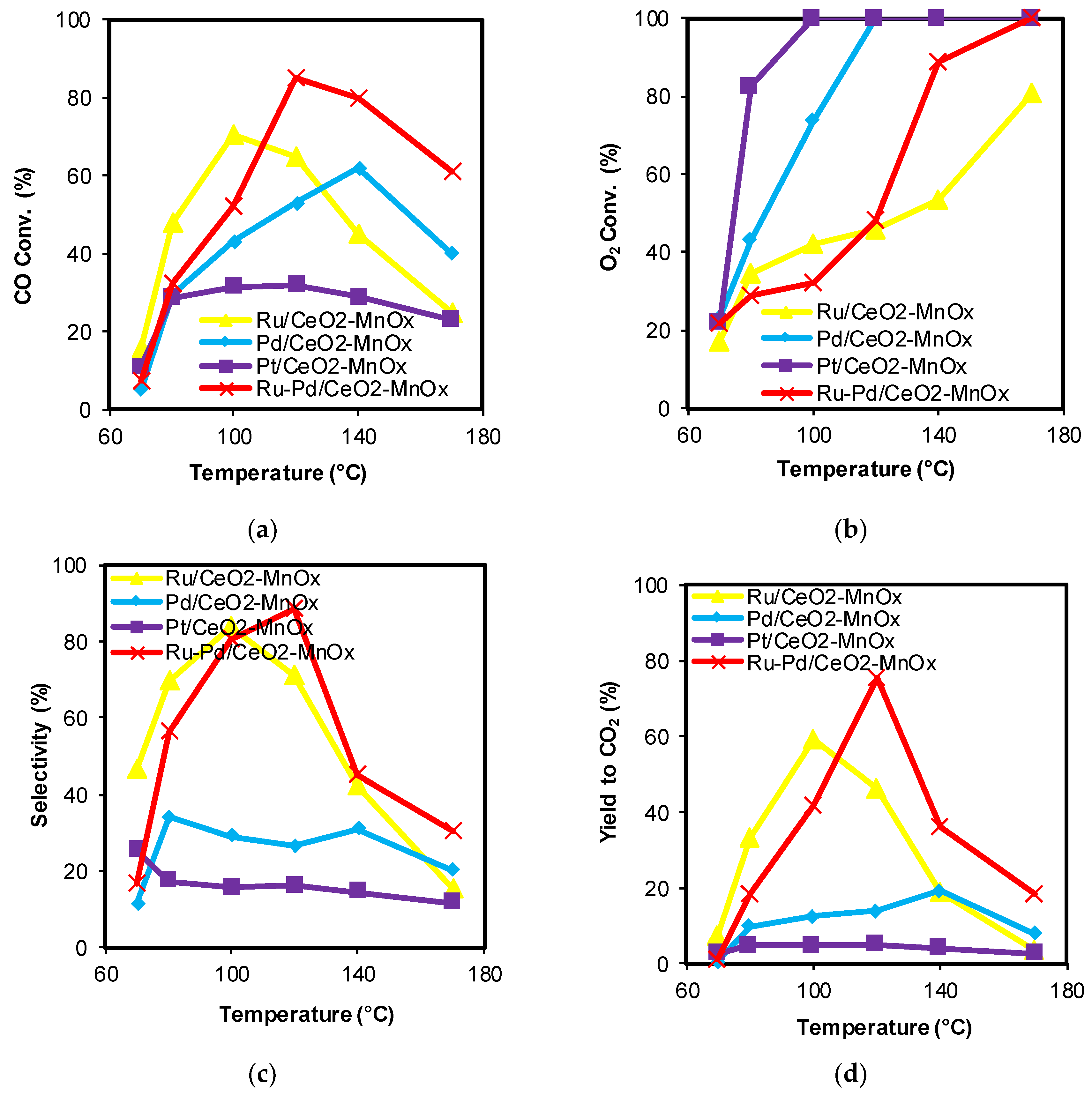
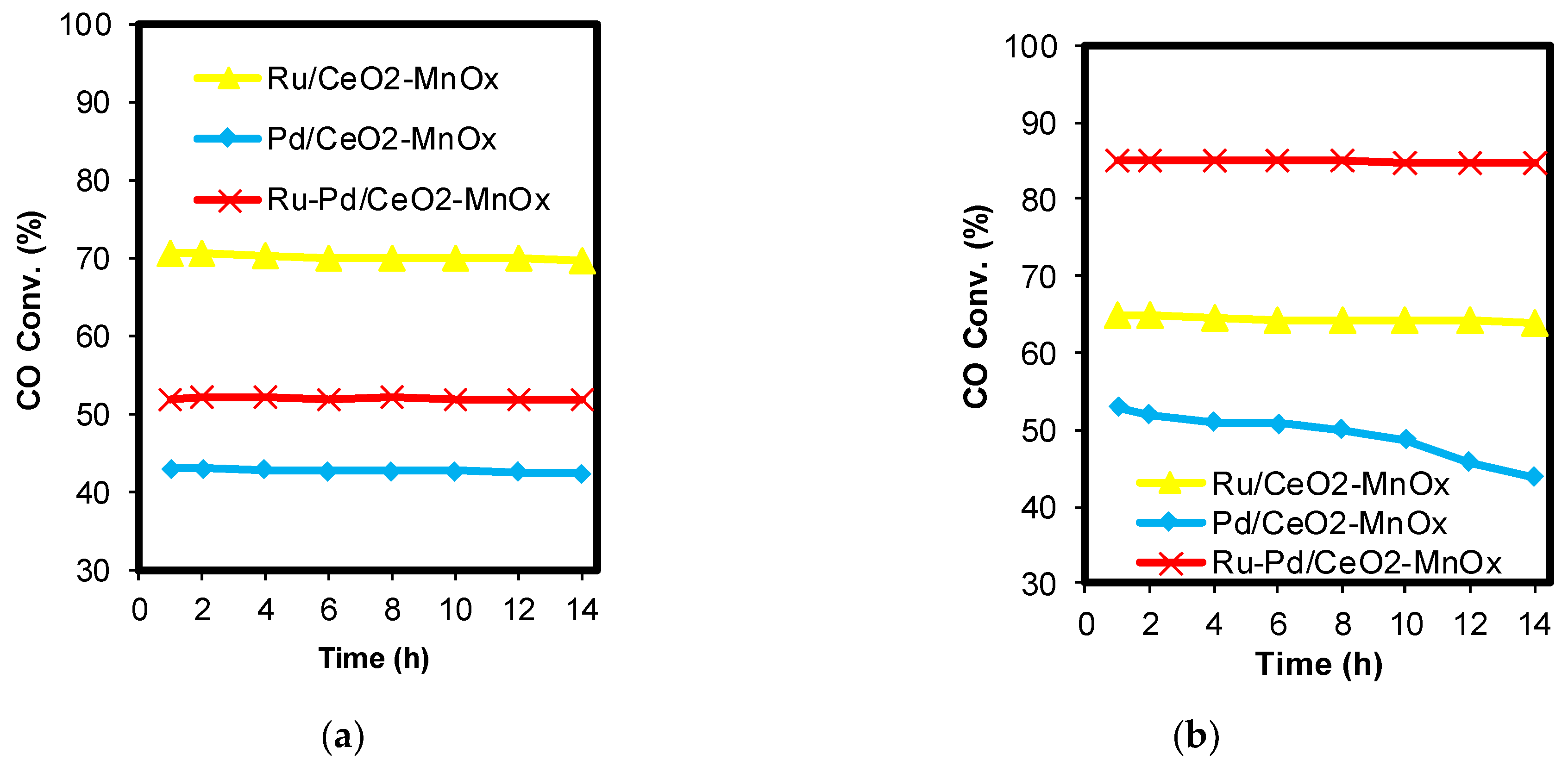
2.1. Catalytic Activity
2.2. Catalysts Characterization
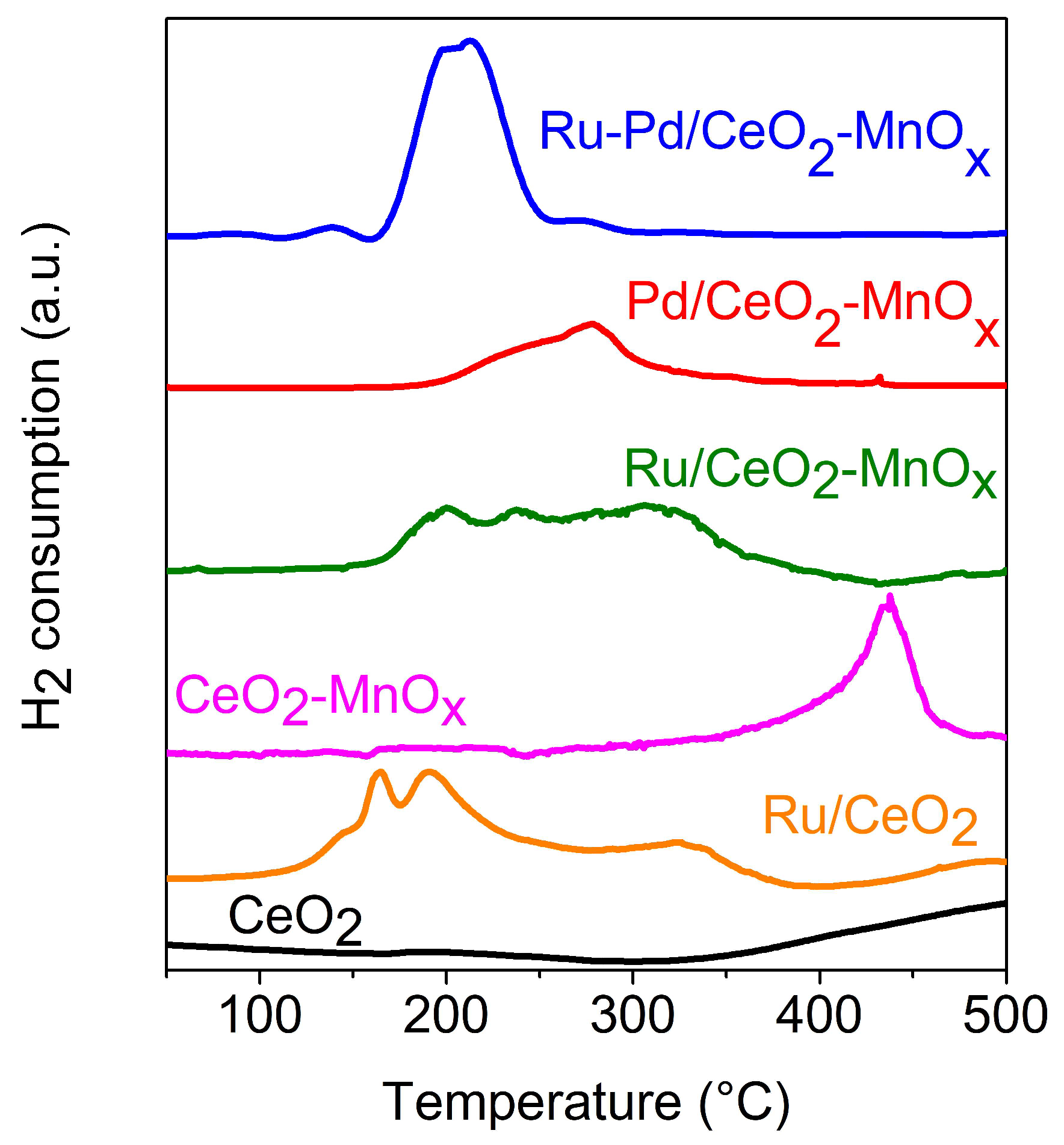
2.2.1. Temperature Programmed Reduction (H2-TPR)
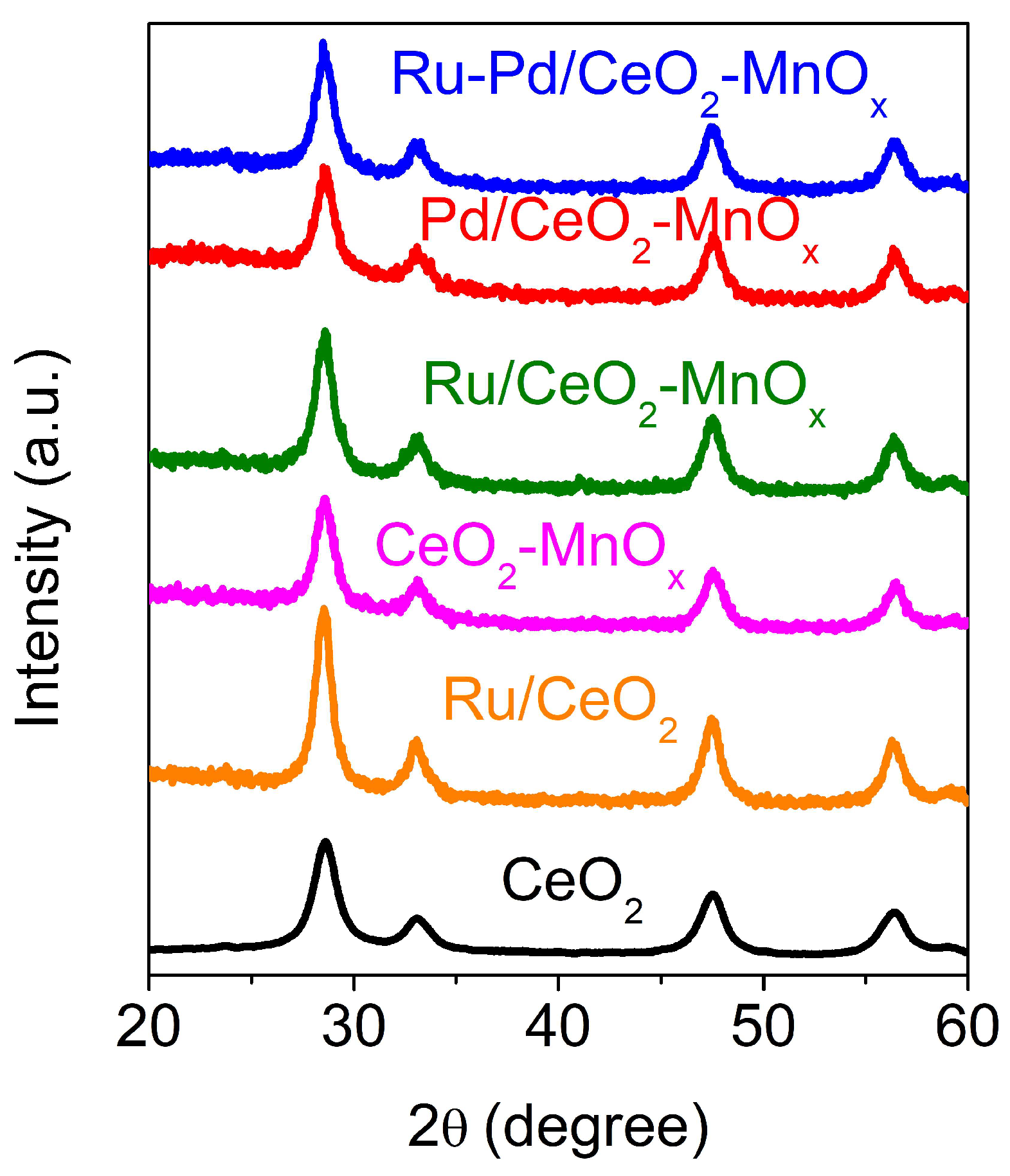
2.2.2. Structural and Textural Properties
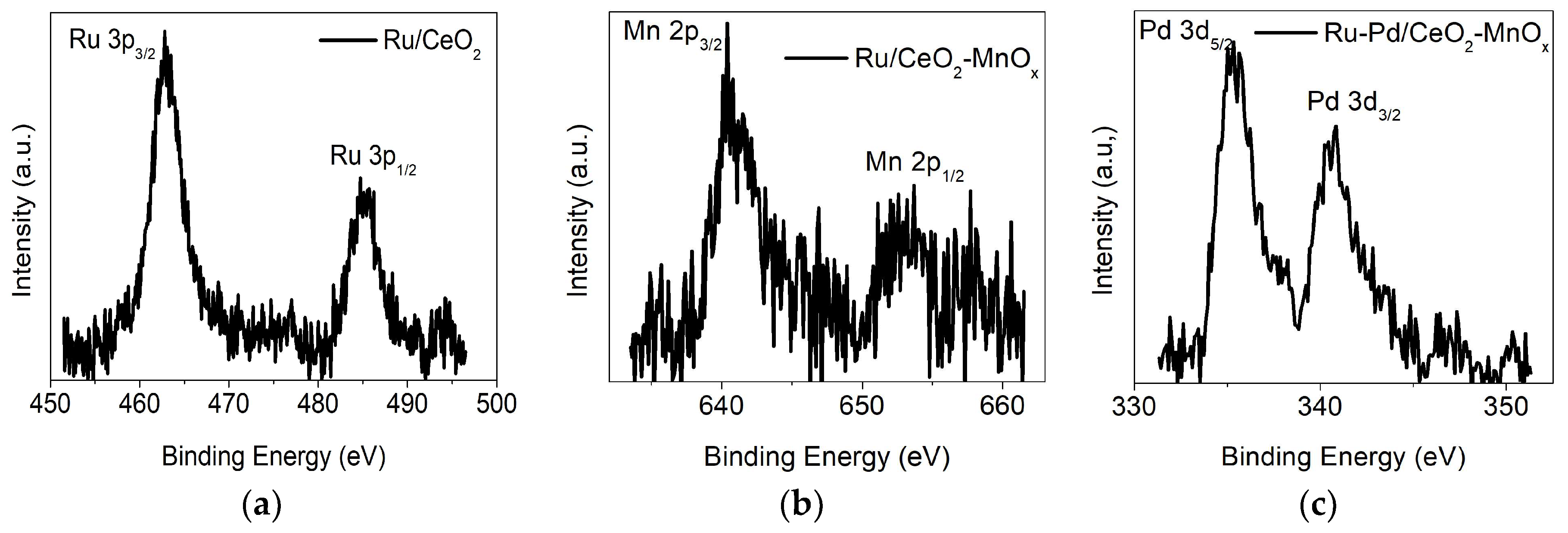
2.2.3. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Measurements
3. Discussion
- (a)
- Reactants’ adsorption on the Ru surface:CO(g) + Ru → COad-Ru
O2(g) + Ru → O2(g)-Ru - (b)
- Oxygen dissociation:O2(g)-Ru → Oad-Ru
- (c)
- CO2 formation:COad-Ru + Oad-Ru → CO2(g)-Ru
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Catalyst Preparation
4.2. Catalytic Performance Test
O2 conversion (%) = (([O2]in − [O2]out)/[O2]in) × 100
Selectivity (%) = (0.5 × [CO2]out/([O2]in − [O2]out)) × 100
CO2 yield (%) = (Selectivity * CO conversion)/100
4.3. Catalysts’ Characterization
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.J.; Jo, M.J.; Nam, S.Y. A review of polymer-nanocomposite electrolyte membranes for fuel cell application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connel, M.; Kolb, G.; Schelhaas, K.; Schuerer, J.; Tiemann, D.; Ziogas, A.; Hessel, V. The development and evaluation of microstructured reactors for the water gas shift and preferential oxidation reactions in the 5 kW range. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 2317–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.D.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.C. Recent progress in selective CO removal in a H2-rich stream. Catal. Today 2009, 139, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S. Overview of Pd-based membranes for producing pure hydrogen and state of art at ENEA laboratories. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 12650–12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, A.; Zhang, T. Recent Advances in Preferential Oxidation of CO Reaction over Platinum Group Metal Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, R.; Crisafulli, C.; Condorelli, G.G.; Lupo, F.; Scirè, S. Au–Ag/CeO2 and Au–Cu/CeO2 Catalysts for Volatile Organic Compounds Oxidation and CO Preferential Oxidation. Catal. Lett. 2015, 145, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.S.; Morfin, F.; Aouine, M.; Bosselet, F.; Rousset, J.L.; Piccolo, L. Trends in the CO oxidation and PROX performances of the platinum-group metals supported on ceria. Catal. Today 2015, 253, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño, F.; Descorme, C.; Duprez, D. Noble metal catalysts for the preferential oxidation of carbon monoxide in the presence of hydrogen (PROX). Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2004, 54, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Park, E.D.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, D.; Lee, K.H. Preferential CO oxidation over supported noble metal catalysts. Catal. Today 2009, 146, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciré, S.; Fiorenza, R.; Gulino, A.; Cristaldi, A.; Riccobene, P.M. Selective oxidation of CO in H2-rich stream over ZSM5 zeolites supported Ru catalysts: An investigation on the role of the support and the Ru particle size. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 520, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.; Wu, G.; Dai, W.; Guan, N.; Li, L. Ru/TiO2 for the preferential oxidation of CO in H2-rich stream: Effects of catalyst pre-treatments and reconstruction of Ru sites. Fuel 2015, 143, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, R.; Crisafulli, C.; Scirè, S. H2 purification through preferential oxidation of CO over ceria supported bimetallic Au-based catalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 19390–19398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirè, S.; Crisafulli, C.; Riccobene, P.M.; Patanè, G.; Pistone, A. Selective oxidation of CO in H2-rich stream over Au/CeO2 and Cu/CeO2 catalysts: An insight on the effect of preparation method and catalyst pretreatment. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 417–418, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, L.; Petrova, P.; Pantaleo, G.; Zanella, R.; Sobczak, J.W.W.; Lisowski, W.; Kaszkur, Z.; Munteanu, G.; Yordanova, I.; Liotta, L.F.; et al. Alumina supported Au/Y-doped ceria catalysts for pure hydrogen production via PROX. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; Wei, M.; Zhao, X.; Ning, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Q.; Bao, X. Active Phase of FeOx/Pt Catalysts in Low-Temperature CO Oxidation and Preferential Oxidation of CO Reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 10398–10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, A.; Kimura, J.; Oshio, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Ichikawa, M. Preferential Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide Catalyzed by Platinum Nanoparticles in Mesoporous Silica. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10120–10125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luengnaruemitchai, A.; Srihamat, K.; Pojanavaraphan, C.; Wanchanthuek, R. Activity of Au/Fe2O3–TiO2 catalyst for preferential CO oxidation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 13443–13445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, L.; Petrova, P.; Pantaleo, G.; Zanella, R.; Liotta, L.F.; Georgiev, V.; Boghosian, S.; Kaszkur, Z.; Sobczak, J.W.; Lisowski, W.; et al. Gold catalysts supported on Y-modified ceria for CO-free hydrogen production via PROX. Appl. Catal. B. Environ. 2016, 188, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Arias, A.; Gamarra, D.; Hungría, A.B.; Fernández-García, M.; Munuera, G.; Hornés, A.; Bera, P.; Conesa, J.C.; Cámara, A.L. Characterization of Active Sites/Entities and Redox/Catalytic Correlations in Copper-Ceria-Based Catalysts for Preferential Oxidation of CO in H2-Rich Streams. Catalysts 2013, 3, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M. The role of Copper-Ceria interactions in catalysis science: Recent theoretical and experimental advances. Appl. Catal. B. Environ. 2016, 198, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, J.; Qian, K.; Huang, W.; Luo, M. A comparative study of formaldehyde and carbon monoxide complete oxidation on MnOx–CeO2catalyst. J. Rare Earths 2009, 27, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delimaris, D.; Ioannides, T. VOC oxidation over MnOx–CeO2 catalysts prepared by a combustion method. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 84, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xingyi, W.; Qian, K.; Dao, L. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over MnOx–CeO2 mixed oxide catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 86, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, G.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y. Catalytic removal of benzene over CeO2–MnOx composite oxides prepared by hydrothermal method. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 138, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Prasad, R. A Review on Preferential Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide in Hydrogen Rich Gases. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2011, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Chu, W.; Dai, X.; Pitchon, V. Bimetallic Au–Cu supported on ceria for PROX reaction: Effects of Cu/Au atomic ratios and thermal pretreatments. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 142–143, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovarelli, A.; Fornasiero, P. Catalysis by Ceria and Related Materials, 2nd ed.; Graham, J.H., Ed.; Catalytic Science Series; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cecilia, J.A.; Arango-Díaz, A.; Franco, F.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Storaro, L.; Moretti, E.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. CuO-CeO2 supported on montmorillonite-derived porous clay heterostructures (PCH) for preferential CO oxidation in H2-rich stream. Catal. Today 2015, 253, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlich, M.J.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Behm, R.J. Kinetics of the Selective Low-Temperature Oxidation of CO in H2-Rich Gas over Au/α-Fe2O3. J. Catal. 1999, 182, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.M.; Kahlich, M.J.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Behm, R.J. Correlation between CO surface coverage and selectivity/kinetics for the preferential CO oxidation over Pt/γ-Al2O3 and Au/α-Fe2O3: An in-situ DRIFTS study. J. Power Sources 1999, 84, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisafulli, C.; Scirè, S.; Maggiore, R.; Minicò, S.; Galvagno, S. CO2 reforming of methane over Ni–Ru and Ni–Pd bimetallic catalysts. Catal. Lett. 1999, 59, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xin, Q.; Shen, W. Carbon monoxide oxidation over CuO/CeO2 catalysts. Catal. Today 2004, 93, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Patel, A.; Rudolph, V.; Zhu, Z. Catalytic performance of Ru nanoparticles supported on different mesoporous silicas for preferential oxidation of CO in H2-rich atmosphere. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 447–448, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, L.; Pantaleo, G.; Ivanova, I.; Maximova, A.; Zanella, R.; Kaszkur, Z.; Venezia, A.M.; Andreeva, D. Preferential oxidation of CO in H2 rich stream (PROX) over gold catalysts supported on doped ceria: Effect of preparation method and nature of dopant. Catal. Today 2010, 158, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.B.; Luo, J.Y.; Meng, M.; Wang, G.; He, J.J. Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of highly active catalyst Au/MnOx–CeO2 used for the preferential oxidation of CO in H2-rich stream. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 3743–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobe, E.R.; de Boer, B.A.; Geus, J.W. The reduction and oxidation behaviour of manganese oxides. Catal. Today 1999, 47, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, R.; Scirè, S.; Venezia, A.M. Carbon supported bimetallic Ru-Co catalysts for H2 production through NaBH4 and NH3BH3 hydrolysis. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Qin, Z.; Shan, W.; Shen, W.; Wang, J. Pd/CeO2–TiO2 catalyst for CO oxidation at low temperature: A TPR study with H2 and CO as reducing agents. J. Catal. 2004, 225, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, H.W.; Graham, G.W.; Chun, W.; McCabe, R.W.; Cuif, J.P.; Deutsch, S.E.; Touret, O. Characterization of model automotive exhaust catalysts: Pd on ceria and ceria–zirconia supports. Catal. Today 1999, 50, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakova, T.; Boccuzzi, F.; Manzoli, M.; Sobczak, J.W.; Idakiev, V.; Andreeva, A. A comparative study of nanosized IB/ceria catalysts for low-temperature water-gas shift reaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 298, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, M.; Uto, M.; Kurogi, D.; Kijima, T. MnOx−CeO2 Binary Oxides for Catalytic NOx Sorption at Low Temperatures. Sorptive Removal of NOx. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 3158–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollimore, D.; Heal, G.R. An improved method for the calculation of pore size distribution from adsorption data. J. Appl. Chem. 1964, 14, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirè, S.; Riccobene, P.M.; Crisafulli, C. Ceria supported group IB metal catalysts for the combustion of volatile organic compounds and the preferential oxidation of CO. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 101, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Jiang, N.; Li, Y.; Xu, D.; Qiu, G. Synthesis and Characterization of Y-Doped Mesoporous CeO2 Using A Chemical Precipitation Method. J. Rare Earths 2007, 25, 428–433. [Google Scholar]
- Natile, M.M.; Boccaletti, G.; Glisenti, A. Properties and Reactivity of Nanostructured CeO2 Powders: Comparison among Two Synthesis Procedures. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 6272–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosynek, M.P.; Magnuson, D.T. Infrared study of carbon dioxide adsorption on lanthanum sesquioxide and trihydroxide. J. Catal. 1977, 48, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, A. Molecular Spectroscopy of Oxide Catalyst Surfaces; Sheppard, N.T., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Sakata, Y.; Arai, T.; Domen, K.; Maruya, K.I.; Onishi, T. Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide adsorption on cerium oxide studied by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Part 1.—Formation of carbonate species on dehydroxylated CeO2, at room temperature. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1989, 85, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayssilov, G.N.; Mihaylov, M.; Petkov, P.S.; Hadjiivanov, K.I.; Neyman, K.M. Reassignment of the Vibrational Spectra of Carbonates, Formates, and Related Surface Species on Ceria: A Combined Density Functional and Infrared Spectroscopy Investigation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 23435–23454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, A.; Mineo, P.; Scamporrino, E.; Vitalini, D.; Fragalà, I. Spectroscopic and Microscopic Characterization and Behavior of an Optical pH Meter Based on a Functional Hybrid Monolayer Molecular System: Porphyrin Molecules Covalently Assembled on a Molecularly Engineered Silica Surface. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 2404–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, A.; Condorelli, G.G.; Mineo, P.; Fragalà, I. An x-ray photoelectron spectra and atomic force microscopy characterization of silica substrates engineered with a covalently assembled siloxane monolayer. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulino, A.; Gupta, T.; Mineo, P.; van der Boom, M.E. Selective NOx optical sensing with surface-confined osmium polypyridyl complexes. Chem. Commun. 2007, 46, 4878–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, M.; Okal, J. Synthesis and structure characterization of Ru nanoparticles stabilized by PVP or γ-Al2O3. J. Mater. Res. Bull. 2008, 43, 3111–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, A.; Egdell, R.G.; Fragalà, I. Low-temperature stabilisation of tetragonal zirconia by antimony. J. Mater. Chem. 1996, 11, 1805–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motiei, L.; Lahav, M.; Gulino, A.; Iron, M.A.; van der Boom, M.E. Electrochemical Characteristics of a Self-Propagating Molecular-Based Assembly. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 14283–14286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkesson, B. ESCA studies on the charge distribution in some dinitrogen complexes of rhenium, iridium, ruthenium, and osmium. Acta Chem. Scand. 1973, 27, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militello, M.C.; Simko, S.J. Elemental Palladium by XPS. Surf. Sci. Spectra 1994, 3, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, C.J. Recommended Auger parameters for 42 elemental solids. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2012, 185, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulm, H.; Hohlneicher, G.; Freund, H.-J.J. Charge distribution in some ternary vintl phases as studied by v-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Less Common Met. 1986, 115, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Anpo, M. Ordered Mesoporous CeO2 Synthesized by Nanocasting from Cubic Ia3d Mesoporous MCM-48 Silica: Formation, Characterization and Photocatalytic Activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 17809–17813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, A.; Dapporto, P.; Rossi, P.; Fragalà, I. Synthesis and Characterization of Liquid MOCVD Precursors for Thin Films of Cadmium Oxide. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 4955–4962. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Sayari, A.; Adnot, A.; Larachi, F. Composition–activity effects of Mn–Ce–O composites on phenol catalytic wet oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 32, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Shen, W. MnOx-CeO2 mixed oxide catalysts for complete oxidation of formaldehyde: Effect of preparation method and calcination temperature. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 62, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solsona, B.; Hutchigns, G.J.; García, T.; Taylor, S.H. Improvement of the catalytic performance of CuMnOx catalysts for CO oxidation by the addition of Au. New J. Chem. 2004, 28, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Cole, K.J.; Taylor, S.H.; Crudace, M.J.; Hutchigns, G.J. Copper manganese oxide catalysts for ambient temperature carbon monoxide oxidation: Effect of calcination on activity. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 305, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, F.; Trunfio, G.; Negro, J.; Fazio, B.; Spadaro, L. Basic Evidence of the Molecular Dispersion of MnCeOx Catalysts Synthesized via a Novel “Redox-Precipitation” Route. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, O.H.; Centeno, M.A.; Arzamendi, G.; Gandía, L.M.; Romero-Sarria, F.; Odriozola, J.A. Iron-modified ceria and Au/ceria catalysts for Total and Preferential Oxidation of CO (TOX and PROX). Catal. Today 2010, 157, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirè, S.; Minicò, S.; Crisafulli, C.; Satriano, C.; Pistone, A. Catalytic combustion of volatile organic compounds on gold/cerium oxide catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 40, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doornkamp, C.; Ponec, V. The universal character of the Mars and Van Krevelen mechanism. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 162, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, I.; Antonini, M.; Galletti, C.; Saracco, G.; Specchia, V. Selective CO-oxidation over Ru-based catalysts in H2-rich gas for fuel cell applications. Top. Catal. 2004, 30, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, X.C.; Ouyang, L.; Yang, X.-Y.; Mao, W.; Su, J.; Han, Y.-F. Mechanistic study of preferential CO oxidation on a Pt/NaY zeolite catalyst. J. Catal. 2012, 287, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.Y.; Alexeev, O.S.; Amiridis, M.D. Preferential oxidation of CO under excess H2 conditions over Ru catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 286, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, P.S.; Colussi, S.; Di Benedetto, A.; Landi, G.; Lisi, L.; Llorca, J.; Trovarelli, A. CO preferential oxidation under H2-rich streams on copper oxide supported on Fe promoted CeO2. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 506, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, Q.; Ma, H.; Li, Z.M. Preferential oxidation of CO and its subsequent methanation in H2-rich gas over CuO-NiO/CeO2 catalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 4646–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Park, E.D.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, D. Selective CO removal in a H2-rich stream over supported Ru catalysts for the polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC). Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 366, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayoglu, S.; Nilekar, A.U.; Mavrikakis, M.; Eichhorn, B. Ru–Pt core–shell nanoparticles for preferential oxidation of carbon monoxide in hydrogen. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozdnyakova, O.; Teschner, D.; Wootsch, A.; Kröhnert, J.; Steinhauer, B.; Sauer, H.; Toth, L.; Jentoft, F.C.; Knop-Gericke, A.; Paál, Z.; et al. Preferential CO oxidation in hydrogen (PROX) on ceria-supported catalysts, part I: Oxidation state and surface species on Pt/CeO2 under reaction conditions. J. Catal. 2006, 237, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.M.; Laguna, O.H.; López-Cartes, C.; Centeno, M.A. Synthesis and characterization of Rh/MnO2-CeO2/Al2O3 catalysts for CO-PrOx reaction. Mol. Catal. 2017, 440, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Bao, T.; Li, Y.; Min, X.; Zhao, D.; Muhammad, T. The supported CeO2/Co3O4–MnO2/CeO2 catalyst on activated carbon prepared by a successive-loading approach with superior catalytic activity and selectivity for CO preferential oxidation in H2-rich stream. Catal. Comm. 2014, 48, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.H.; Sasirekha, N.; Chen, Y.W.; Wang, W.J. Preferential Oxidation of CO in H2 Stream over Au/MnO2−CeO2 Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 4927–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecilia, J.A.; Arango-Diaz, A.; Marrero-Jerez, J.; Nunez, P.; Moretti, E.; Storaro, L.; Rodiguez-Castellon, E. Catalytic Behaviour of CuO-CeO2 Systems Prepared by Different Synthetic Methodologies in the CO-PROX Reaction under CO2-H2O Feed Stream. Catalysts 2017, 7, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, D.; Grant, J.T. Surface Analysis by Auger and X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; IM Publications: Chichester, UK; Surface Spectra Ltd.: Manchester, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gulino, A. Structural and electronic characterization of self-assembled molecular nanoarchitectures by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1479–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Catalysts | CeO2 Size by XRD (nm) * | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Mean Pore Diameter (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2 | 10 | 107 | 2.9 | 0.129 |
| Ru/CeO2 | 9.0 | 108 | 2.7 | 0.131 |
| CeO2-MnOx | 8.5 | 119 | 2.1 | 0.137 |
| Ru/CeO2-MnOx | 8.8 | 118 | 2.2 | 0.133 |
| Pd/CeO2-MnOx | 8.7 | 118 | 2.3 | 0.132 |
| Ru-Pd/CeO2-MnOx | 8.2 | 123 | 1.8 | 0.139 |
| Catalysts | Metals Loading (wt %) | Support | Space Velocity (GHSV) | Gas Mixture (vol. %) | CO Conversion (%) | CO2 Selectivity (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ru/CeO2-MnOx | 1 | CeO2-5wt%MnOx | 0.39 molCO h−1 gcat−1 | 1 CO, 1 O2, 88 H2, rest He | 41 (80 °C) 72 (100 °C) 65 (120 °C) | 70 (80 °C) 84 (100 °C) 71 (120 °C) | this work |
| Ru–Pd/CeO2-MnOx | 0.5–0.5 | CeO2-5wt%MnOx | 0.39 molCO h−1 gcat−1 | 1 CO, 1 O2, 88 H2, rest He | 32 (80 °C) 52 (100 °C) 85 (120 °C) | 56 (80 °C) 81 (100 °C) 88 (120 °C) | this work |
| Pt/CeO2 | 1 | CeO2 | not reported | 1 CO, 1 O2, rest H2 | 65 (80 °C) 70 (100 °C) 60 (120 °C) | 72 (80 °C) 68 (100 °C) 61 (120 °C) | [78] |
| Rh/MnO2-CeO2/Al2O3 | 1 | 10 wt %MnO2, 40 wt %CeO2, 50 wt %Al2O3 | 60,000 cm3 h−1 gcat−1 | 1 CO, 1 O2, 50 H2, rest N2 | 15 (80 °C) 20 (100 °C) 38 (120 °C) | 57 (80 °C) 55 (100 °C) 50 (120 °C) | [79] |
| CeO2/Co3O4-MnO2/CeO2 | - | 27.5 wt %Co on activated carbon 8:1 Co/Mn and Co/Ce (atom. ratio) | 15,000 mL h−1 gcat−1 | 1 CO, 1 O2, 50 H2, rest Ar | 82 (80 °C) 100 (100 °C) 100 (120 °C) | 85 (80 °C) 80 (100 °C) 70 (120 °C) | [80] |
| Au/MnO2-CeO2 | 1 | 0.5MnO2 0.5CeO2 (atom. ratio) | not reported | 1.33 CO, 1.33 O2, 65.33 H2, rest He | 90 (80 °C) 88 (100 °C) 86 (120 °C) | 50 (80 °C) 47 (100 °C) 45 (120 °C) | [81] |
| CuO/CeO2 | 6 | PMMA as template | 22,000 h−1 | 1.25 CO, 1.25 O2, 50% H2, rest He | 92 (80 °C) 96 (100 °C) 97 (120 °C) | 82 (80 °C) 80 (100 °C) 78 (120 °C) | [82] |
| Au-Ag/CeO2 | 1–1 | CeO2 | 0.39 molCO h−1 gcat−1 | 1 CO, 1 O2, 88 H2, rest He | 90 (80 °C) 76 (100 °C) 50 (120 °C) | 73 (80 °C) 44 (100 °C) 30 (120 °C) | [12] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fiorenza, R.; Spitaleri, L.; Gulino, A.; Scirè, S. Ru–Pd Bimetallic Catalysts Supported on CeO2-MnOX Oxides as Efficient Systems for H2 Purification through CO Preferential Oxidation. Catalysts 2018, 8, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8050203
Fiorenza R, Spitaleri L, Gulino A, Scirè S. Ru–Pd Bimetallic Catalysts Supported on CeO2-MnOX Oxides as Efficient Systems for H2 Purification through CO Preferential Oxidation. Catalysts. 2018; 8(5):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8050203
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiorenza, Roberto, Luca Spitaleri, Antonino Gulino, and Salvatore Scirè. 2018. "Ru–Pd Bimetallic Catalysts Supported on CeO2-MnOX Oxides as Efficient Systems for H2 Purification through CO Preferential Oxidation" Catalysts 8, no. 5: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8050203
APA StyleFiorenza, R., Spitaleri, L., Gulino, A., & Scirè, S. (2018). Ru–Pd Bimetallic Catalysts Supported on CeO2-MnOX Oxides as Efficient Systems for H2 Purification through CO Preferential Oxidation. Catalysts, 8(5), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8050203









