An Overview on Zeolite Shaping Technology and Solutions to Overcome Diffusion Limitations
Abstract
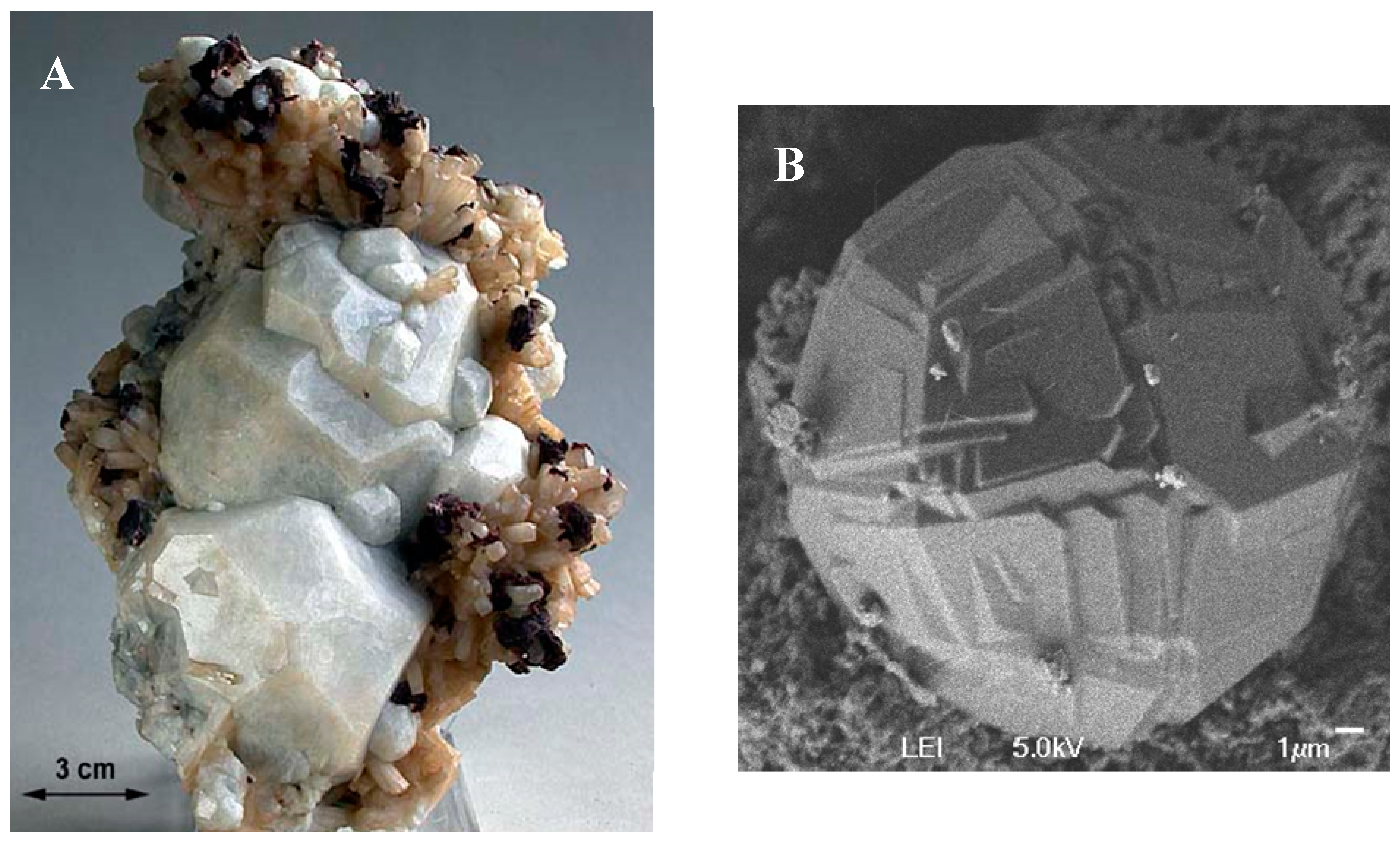
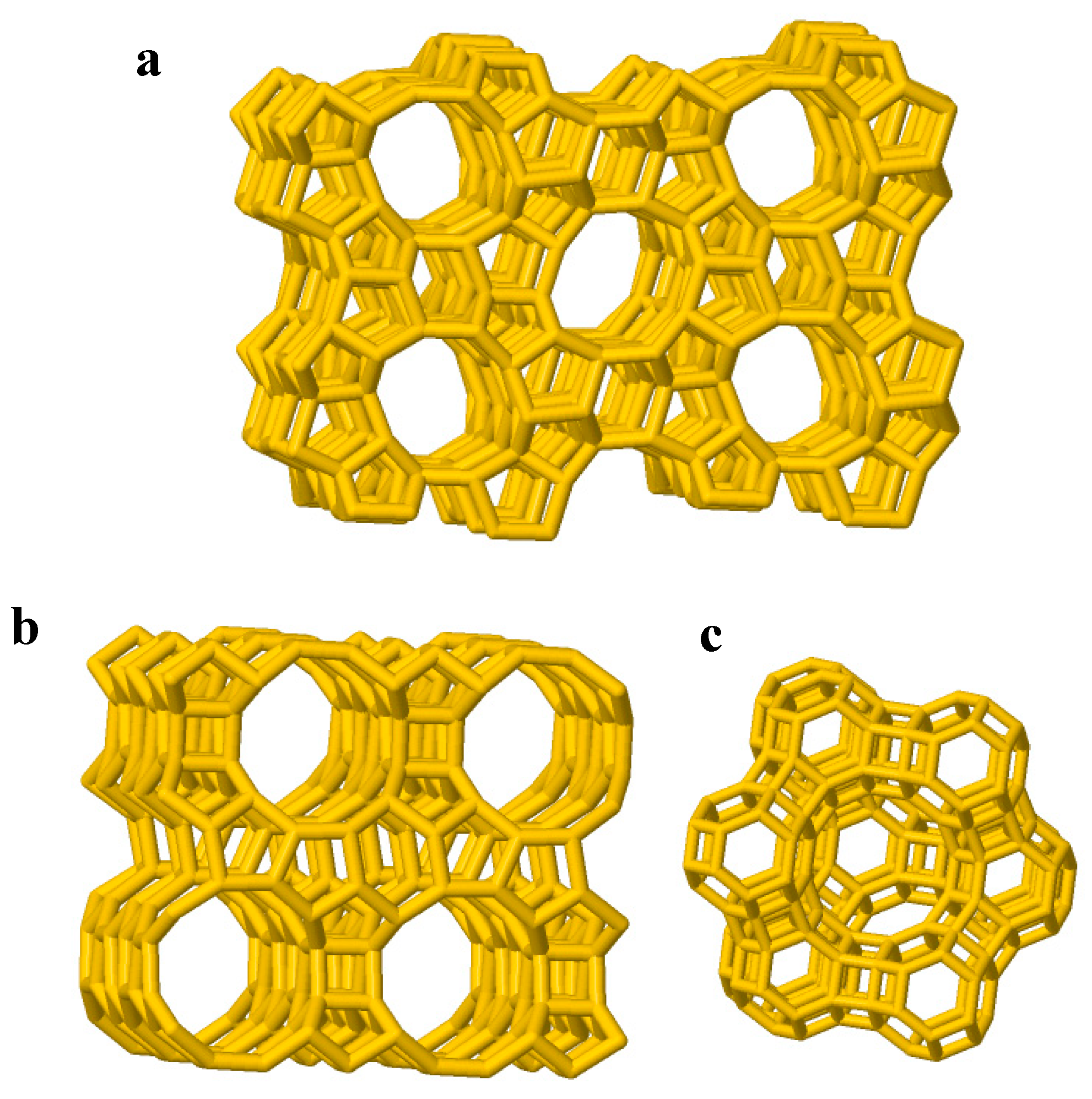
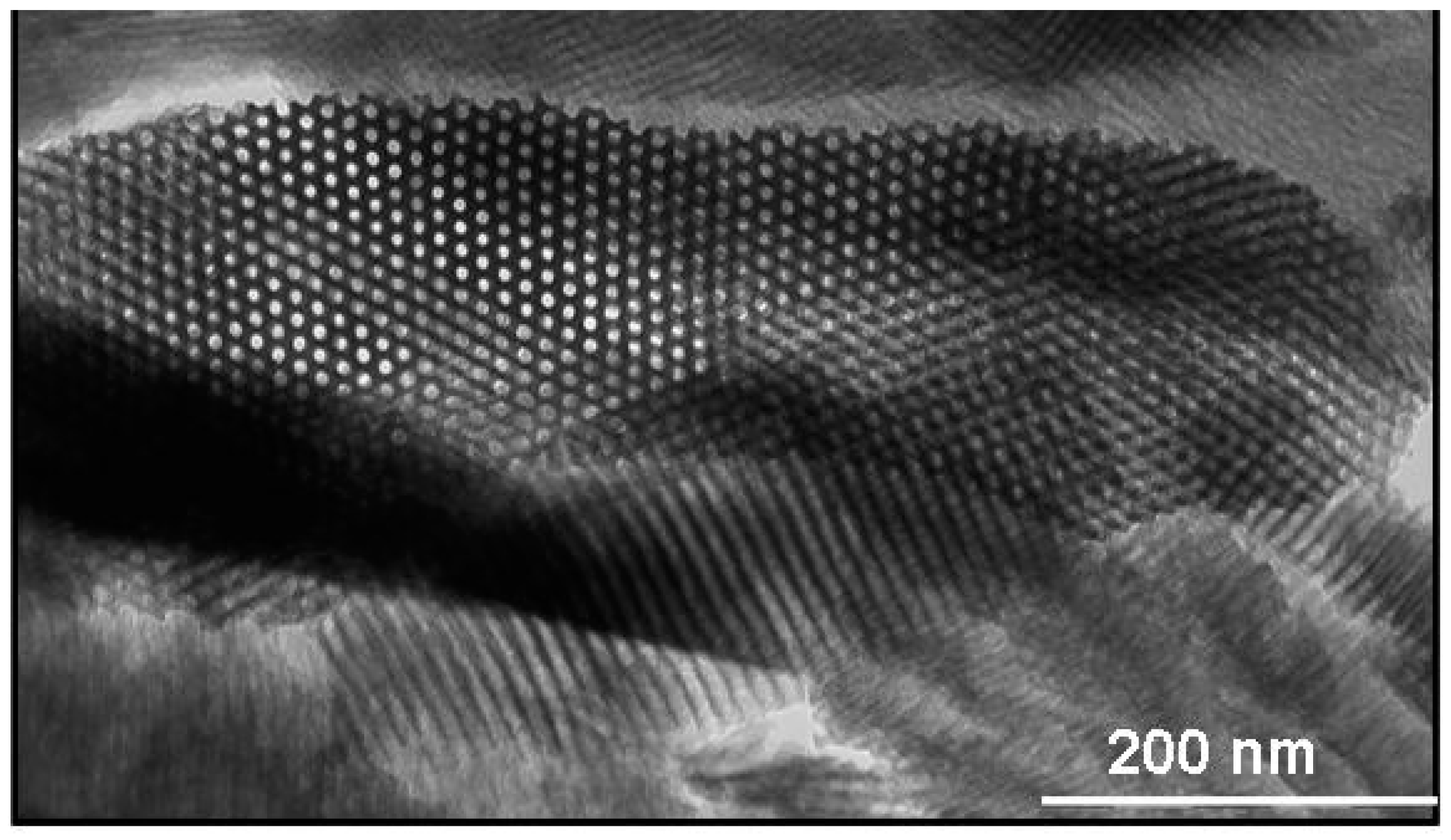
1. Zeolite Properties
2. Applications of Zeolites
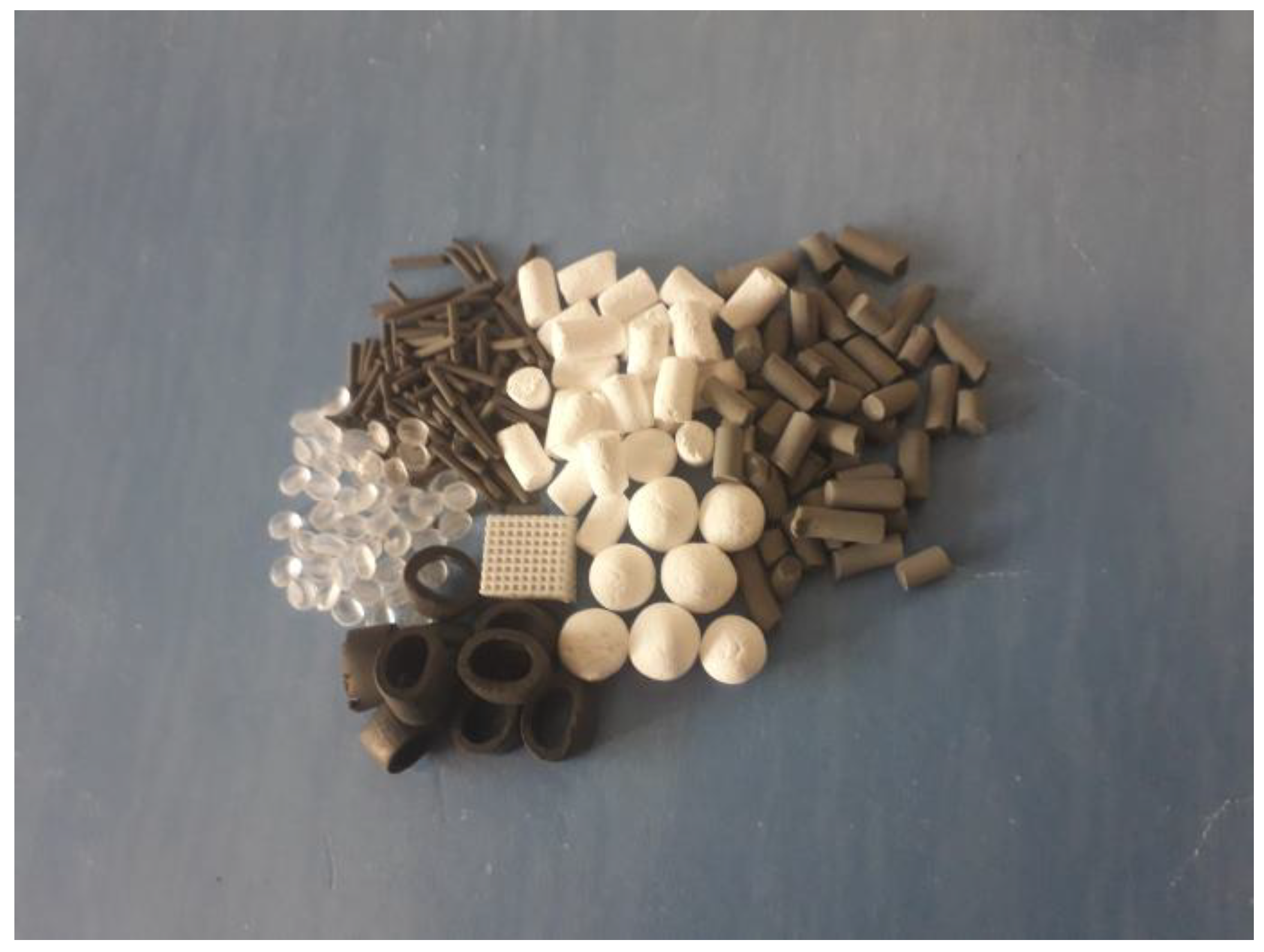
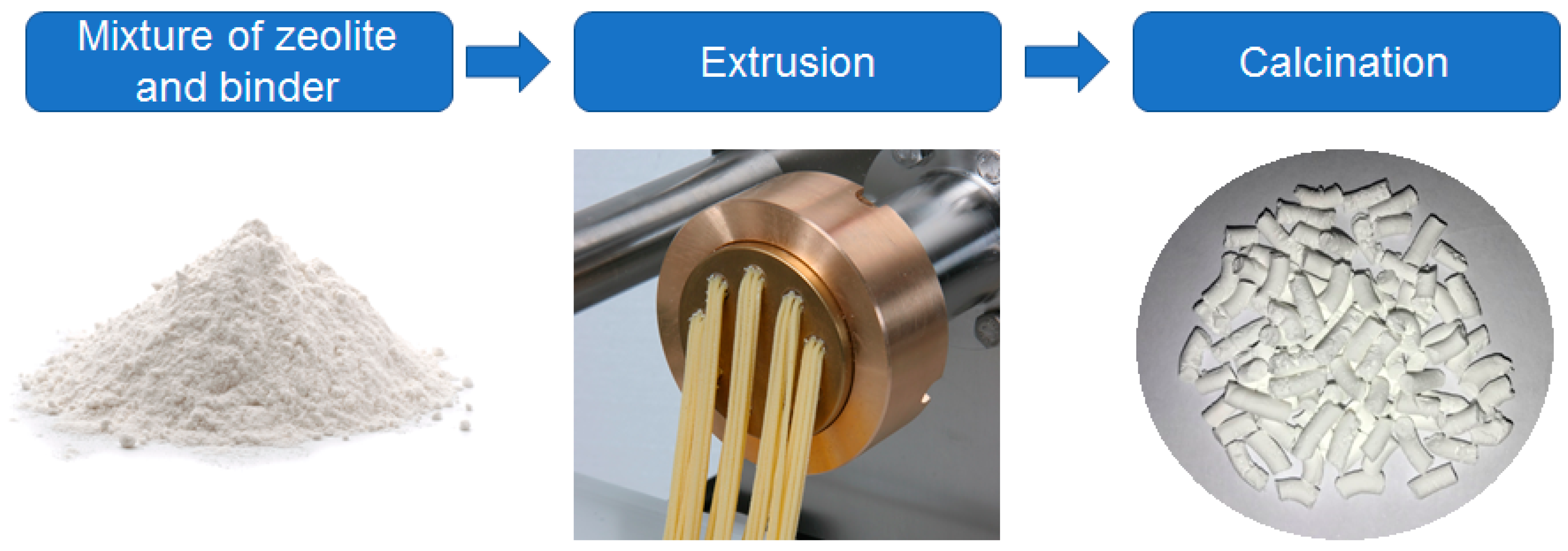
3. Strategies to Produce Zeolite Bodies
3.1. Silica and Alumina Binders
3.2. New Binder Systems
4. Hierarchical Aluminas as a Solution for Diffusion Limitations
4.1. Ordered Mesoporous Aluminas
4.2. Disordered Mesoporous Aluminas
4.3. Macrostructured Aluminas
5. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cronstedt, A.F. Rön Och Beskrifning om en Obekant Bärg Art, Som Kallas Zeolites; Akad.Handl.Stockholm: Tokyo, Japan, 1756; Volume 18, pp. 120–130. [Google Scholar]
- Colella, C.; Gualtieri, A.F. Cronstedt’s zeolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 105, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewenstein, W. The distribution of aluminum in the tetrahedra of silicates and aluminates. Am. Mineral. 1954, 39, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Losch, P.; Boltz, M.; Soukup, K.; Song, I.H.; Yun, H.S.; Louis, B. Binderless zeolite coatings on macroporous α-SiC foams. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 188, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, G.; Knözinger, H.; Schüth, F.; Weitkamp, J. Physical Properties—Microporosity. In Handbook Heterogeneous Catalysis, 2nd ed.; Wiley VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; Volume 1, p. 729. [Google Scholar]
- Baerlocher, C.; McCusker, L.B. Database of Zeolite Structures. Available online: http://www.iza-structure.org/databases/ (accessed on 16 January 2018).
- Perego, C.; Bassi, G.; Girotti, G. Extruded Catalyst Based on Silica/Alumina Gel. European Patent 0 665 055 A1, 23 January 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, P.; Garwood, W. Catalytic Composition from Reaction of High Silica Zeolites with Binder. U.S. Patent 4,563,435, 23 June 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.; Berndt, H.; Lohse, U.; Wolf, U. Effect of Si:Al ratio and type of binder on the catalytic properties of HZSM-5 catalysts. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1993, 89, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Alkhawaldeh, A.; Anthony, R.G. Investigation on acidity of zeolites bound with silica and alumina. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2002, 143, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Guo, J.; Meng, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Effects of colloidal silica binder on catalytic activity and adhesion of HZSM-5 coatings for structured reactors. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 22, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Ihm, S.K. Influence of catalyst binders on the acidity and catalytic performance of HZSM-5 zeolites for methanol-to-propylene (MTP) process: Single and binary binder system. Top. Catal. 2010, 53, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasture, M.W.; Niphadkar, P.S.; Bokade, V.V.; Joshi, P.N. On the catalytic performance in isopropylation of benzene over H/β zeolite catalysts: Influence of binder. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Liu, J. Influence of alumina binder content on catalytic performance of Ni/HZSM-5 for hydrodeoxygenation of cyclohexanone. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Kong, X.; Chen, L. Influence of binder on catalytic performance of Ni/HZSM-5 for hydrodeoxygenation of cyclohexanone. Catal. Commun. 2014, 45, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Uriarte, P.; Gamero, M.; Ateka, A.; Diaz, M.; Aguayo, A.T.; Bilbao, J. Effect of the acidity of HZSM-5 zeolite and the binder in the DME transformation to olefins. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; He, L.; Shang, S. Study on aluminum phosphate binder and related Al2O3–SiC ceramic coating. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 348, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, Y.W.; Viswanadham, N.; Jun, K.W.; Bae, W.J. Novel aluminophosphate (AlPO) bound ZSM-5 extrudates with improved catalytic properties for methanol to propylene (MTP) reaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 374, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiding, J.; Patcas, F.C.; Kraushaar-Czarnetzki, B. Extrusion of zeolites: Properties of catalysts with a novel aluminium phosphate sintermatrix. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 328, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiding, J.; Kraushaar-Czarnetzki, B. Novel extruded fixed-bed MTO catalysts with high olefin selectivity and high resistance against coke deactivation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 391, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, G.T.; Meirer, F.; Mertens, M.M.; Bons, A.J.; Weiss, B.M.; Stevens, P.A.; de Smit, E.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Binder Effects in SiO2-and Al2O3-Bound Zeolite ZSM-5-Based Extrudates as Studied by Microspectroscopy. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowes, E. Extrusion of Silica-Rich Solids. U.S. Patent 4,582,815, 15 April 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.; Mihut, C.; Simmons, M. Method of Forming Zeolite Shaped Body with Silica Binder. U.S. Patent 9,180,441 B2, 10 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Keville, K.; Timken, H.; Ware, R. Method for Preparing Catalysts Comprising Zeolites Extruded with an Alumina Binder. U.S. Patent 5,500,109, 19 March 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Plee, D. Zeolite Granules with Zeolitic Binder. U.S. Patent 5,132,260, 21 July 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Timken, H. Method for Preparing Titania-Bound Zeolite Catalysts. U.S. Patent 5,430,000, 4 July 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Verduijn, J. Process for Producing Substantially Binder-Free Zeolit. U.S. Patent 5,460,769, 24 October 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Shen, B.; Liu, J. N-Paraffins adsorption with 5A zeolites: The effect of binder on adsorption equilibria. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 64, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J. Ultrahigh mechanically stable hierarchical mordenite zeolite monolith: Direct binder-/template-free hydrothermal synthesis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 138, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasra, R.V.; Tyagi, B.; Badheka, Y.M.; Choudary, V.N.; Bhat, T.S.G. Effect of clay binder on sorption and catalytic properties of zeolite pellets. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 3263–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorado, F.; Romero, R.; Caizares, P. Hydroisomerization of n-butane over Pd/HZSM-5 and Pd/Hβ with and without binder. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 236, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucas, A.; Valverde, J.L.; Sánchez, P.; Dorado, F.; Ramos, M.J. Influence of the binder on the n-octane hydroisomerization over palladium-containing zeolite catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 8217–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, P.; Dorado, F.; Fúnez, A.; Jiménez, V.; Ramos, M.J.; Valverde, J.L. Effect of the binder content on the catalytic performance of beta-based catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 273, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, K.; Mirmohammadi, S.J. Preparation of 5A zeolite monolith granular extrudates using kaolin: Investigation of the effect of binder on sieving/adsorption properties using a mixture of linear and branched paraffin hydrocarbons. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 106, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uphade, B.; Gopal, S. Zeolite-Binder Catalyst Composition. U.S. Patent 2010/0029999 A1, 4 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, D.W.; Cho, S. Effect of base binder, flash calcined hydrotalcite, in MFI zeolite granule: Catalytic activity over 1-butene isomerization and MTO reaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 502, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazer-Bachi, D.; Harbuzaru, B.; Lecolier, E. Zeolite Formed by Extrusion and Pelleting with a Hydraulic Binder Having Improved Mechanical Properties and Process and Preparing Same. U.S. Patent 2016/0288109A1, 18 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, S.; Sachse, A.; Galarneau, A. Challenges and strategies in the synthesis of mesoporous alumina powders and hierarchical alumina monoliths. Materials 2012, 5, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trueba, M.; Trasatti, S.P. γ-Alumina as a support for catalysts: A review of fundamental aspects. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 17, 3393–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Coombs, N.; Sokolov, I.; Ozin, G.A. Free-standing and oriented mesoporous silica films grown at the air-water interface. Nature 1996, 381, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Fan, H.; Stump, A.; Ward, T.L.; Rieker, T.; Brinker, C.J. Aerosol-assisted self-assembly of mesostructured spherical nanoparticles. Nature 1999, 398, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Guo, F.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, H. Self-assembly synthesis of organized mesoporous alumina by precipitation method in aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 93, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Yin, A.X.; Luo, C.; Sun, L.D.; Zhang, Y.W.; Duan, W.T.; Liu, H.C.; Yan, C.H. Facile synthesis for ordered mesoporous γ-aluminas with high thermal stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, S.M.; Vinu, A.; Pikus, S.; Jaroniec, M. Adsorption and structural properties of ordered mesoporous alumina synthesized in the presence of F127 block polymer. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 385, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wan, Z.; Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, D. A facile synthesis strategy for structural property control of mesoporous alumina and its effect on catalysis for biodiesel production. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Yang, J.; Li, Q.; Tu, B.; Zhao, D. Synthesis of ordered mesoporous alumina with large pore sizes and hierarchical structure. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 143, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Xu, S.; Lü, J.; Yan, X.; Hu, L.; Xue, Q. Facile synthesis of ordered mesoporous γ-alumina monoliths via polymerization-based gel-casting. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 138, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejenaru, N.; Lancelot, C.; Blanchard, P.; Lamonier, C.; Rouleau, L.; Payen, E.; Dumeignil, F.; Royer, S. Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic performances of novel CoMo hydrodesulfurization catalysts supported on mesoporous aluminas. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic applications of mesoporous γ-alumina from boehmite sol. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 111, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulvio, P.F.; Brosey, R.I.; Jaroniec, M. Synthesis of mesoporous alumina from boehmite in the presence of triblock copolymer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Mesoporous γ-alumina formed through the surfactant-mediated scaffolding of peptized pseudoboehmite nanoparticles. Langmuir 2010, 26, 10063–10067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Mesostructured γ-Al2O3 with a lathlike framework morphology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 41, 12294–12301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleta, R.; Alphonse, P.; Pin, L.; Gressier, M.; Menu, M.-J. An efficient route to aqueous phase synthesis of nanocrystalline γ-Al2O3 with high porosity: From stable boehmite colloids to large pore mesoporous alumina. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, L.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of mesoporous alumina using a recyclable methylcellulose template. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 142, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.S.; Licea, Y.E.; Huang, X.; Willinger, M.; Louis, B.; Pereira, M.M. Improving textural properties of γ-alumina by using second generation biomass in conventional hydrothermal method. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 207, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Lal, B.; Singh, A.; Saxena, A.K.; Dangwal, V.S.; Sharma, L.D.; Dhar, G.M. Control of mesoporosity in alumina. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2001, 8, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Song, J.; Xu, X.; He, M.; Wang, Q.; Yan, L. Peptization Mechanism of Boehmite and Its Effect on the Preparation of a Fluid Catalytic Cracking Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 10029–10034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Bodart, P.; Pruski, M.; Shanks, B.H. Characterization of mesoporous alumina molecular sieves synthesized by nonionic templating. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2002, 52, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.B.; Jiao, W.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; He, M.Y. CTAB-directed synthesis of mesoporous γ-alumina promoted by hydroxy polyacids. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 132, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.B.; Xue, T.; Jiao, W.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; He, M.Y. CTAB-directed synthesis of mesoporous γ-alumina promoted by hydroxy carboxylate: The interplay of tartrate and CTAB. Solid State Sci. 2011, 13, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, A.P.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, Y.H.; Yang, C.M.; Du, H. A facile rout to synthesis lamellate structure mesoporous alumina using polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG, molecular weight = 6000) as structure directing agent. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 159, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Mesoporous γ-alumina synthesized by hydro-carboxylic acid as structure-directing agent. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 92, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Xiao, T.; Yan, Z.; Sun, X.; Sloan, J.; González-Cortés, S.L.; Alshahrani, F.; Green, M.L.H. Synthesis of mesoporous alumina with highly thermal stability using glucose template in aqueous system. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 91, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacquin, J.P.; Dhainaut, J.; Duprez, D.; Royer, S.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. An efficient route to highly organized, tunable macroporous− mesoporous alumina. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 12896–12897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-L.; Duan, W.-T.; Yuan, Q.; Li, Z.-X.; Duan, H.-H.; Yan, C.-H. Hierarchical γ-Al2O3 monoliths with highly ordered 2D hexagonal mesopores in macroporous walls. Chem. Commun. 2009, 6174–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokudome, Y.; Fujita, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Miura, K.; Hirao, K. Synthesis of monolithic Al2O3 with well-defined macropores and mesostructured skeletons via the sol-gel process accompanied by phase separation. Chem. Mater. 2007, 13, 3393–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokudome, Y.; Nakanishi, K.; Kanamori, K.; Fujita, K.; Akamatsu, H.; Hanada, T. Structural characterization of hierarchically porous alumina aerogel and xerogel monoliths. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 338, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wei, Q.; Ling, R.; An, F.; Mu, G.; Huang, Y. Synthesis of macro-mesoporous alumina with yeast cell as bio-template. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 165, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reference | Catalyst | Binder | SBET (m2/g) | Mechanical Strength (kg/cm2) | Influence in Acidity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [7] | Amorphous silica/alumina | AlO(OH) | 608 | 249 (10 wt % binder) | |
| [9] | ZSM-5 | SiO2 or AlO(OH) | Acidity maintained with SiO2, but decreased with AlO(OH) | ||
| [11] | ZSM-5 | SiO2 | 210–350 | Decreased | |
| [12] | ZSM-5 | SiO2 or AlO(OH) or AlPO | 320–450 | 1.4 (10 wt % SiO2)—4.8 (20 wt % AlPO) | Decreased |
| [13] | BEA | Al2O3 | 400–500 | Increased | |
| [14] | ZSM-5 | Al2O3 | 235–275 | Decreased | |
| [15] | ZSM-5 | Al2O3 or SiO2 or kaolin | 200–260 | Decreased | |
| [16] | ZSM-5 | Al2O3 | 200–300 | Decreased | |
| [18] | ZSM-5 | AlPO | 315–370 | Decreased | |
| [19] | ZSM-5 | AlPO | 81 (25 wt % binder)—907 (75 wt % binder) | Maintained after ion-exchange | |
| [21] | ZSM-5 | SiO2 or Al2O3 | 350 | Decreased |
| Reference | Zeolite | Binder | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| [25] | A, X and Y | Siliceous earth | |
| [26] | ZSM-5 | Titania | √ Lower binder activity |
| [27,29] | Several | Binder-free | √ Adsorption properties similar to zeolite powder √ No evidence of pore blocking |
| [30,31,32,33] | X, Y, MOR, BEA, ZSM-5 | Bentonite and attapulgite | × Solid-state ion-exchange of Na+, Mg2+: decrease in Brønsted acid site density |
| [36] | MFI | Hydrotalcite | √ Preservation of the acidity √ Crush strength similar to commercial MFI granules |
| [37] | Several | Hydraulic binders (cements, plaster, aluminates, …) | √ High mechanical strength √ High thermal resistance |
| Reference | Al Source | Template | Surface Area (m²/g) | Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [42] | Aluminum salts | Polyethylene glycol 1540 | 300 | 6 |
| [43,45,47,48] | Aluminum isopropoxide; aluminum titert-butoxide | Pluronic P123 | 261–434 | 2.9–9.5 |
| [44,53] | Aluminum isopropoxide | Pluronic F127 | 338–450 | 8–14 |
| [46] | Aluminum isopropoxide | Pluronic P123 + trimethylbenzene | 309 | 7.5 |
| [49,50] | Boehmite | Pluronic P123 | 300–339 | 11–16 |
| [51] | Boehmite | Tergitol | 321 | 15 |
| [54] | Aluminum chloride + sodium aluminate | Methylcellulose | 315 | 8 |
| [55] | Bayerite | Sugar cane bagasse | 209 | 7.8 |
| [58] | Aluminum tri-sec-butoxide | Pluronic 64L | 470 | 11 |
| [59,60] | Aluminum nitrate | CTAB + hydroxylpolyacids | 400 | 6.2 |
| [61] | Sodium aluminate + aluminum sulphate | PEG 6000 | 280 | 12 |
| [62] | Boehmite | Hydro-carboxylic acids | 380 | 27 |
| Reference | Al Source | Method | Surface Area (m²/g) | Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [38] | Aluminum tri-sec-butoxide | Sol-gel | 338 | 11 |
| [63] | Aluminum isopropoxide | Glucose templating | 422 | 5.1 |
| [48] | Aluminum tri-sec-butoxide | Sol-gel | 349 | 10.7 |
| Reference | Al Source | Template | Surface Area (m²/g) | Pore Diameter (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [64] | Aluminium isopropoxide | Latex spheres | 249 | 0.3 |
| [65] | Aluminium isopropoxide | Polyurethane foam | 300 | 600 |
| [66,67] | Aluminium chloride | Poly(ethylene oxide) | 511 | 0.4–1.8 |
| [68] | Aluminium nitrate | Yeast | 340 | 1.5–3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bingre, R.; Louis, B.; Nguyen, P. An Overview on Zeolite Shaping Technology and Solutions to Overcome Diffusion Limitations. Catalysts 2018, 8, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040163
Bingre R, Louis B, Nguyen P. An Overview on Zeolite Shaping Technology and Solutions to Overcome Diffusion Limitations. Catalysts. 2018; 8(4):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040163
Chicago/Turabian StyleBingre, Rogéria, Benoît Louis, and Patrick Nguyen. 2018. "An Overview on Zeolite Shaping Technology and Solutions to Overcome Diffusion Limitations" Catalysts 8, no. 4: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040163
APA StyleBingre, R., Louis, B., & Nguyen, P. (2018). An Overview on Zeolite Shaping Technology and Solutions to Overcome Diffusion Limitations. Catalysts, 8(4), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040163





