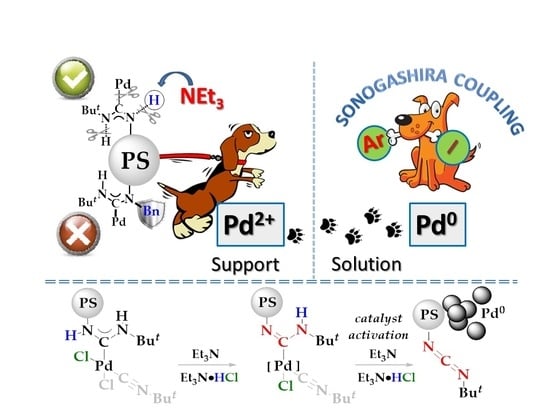
Polystyrene-Supported Acyclic Diaminocarbene Palladium Complexes in Sonogashira Cross-Coupling: Stability vs. Catalytic Activity
Abstract
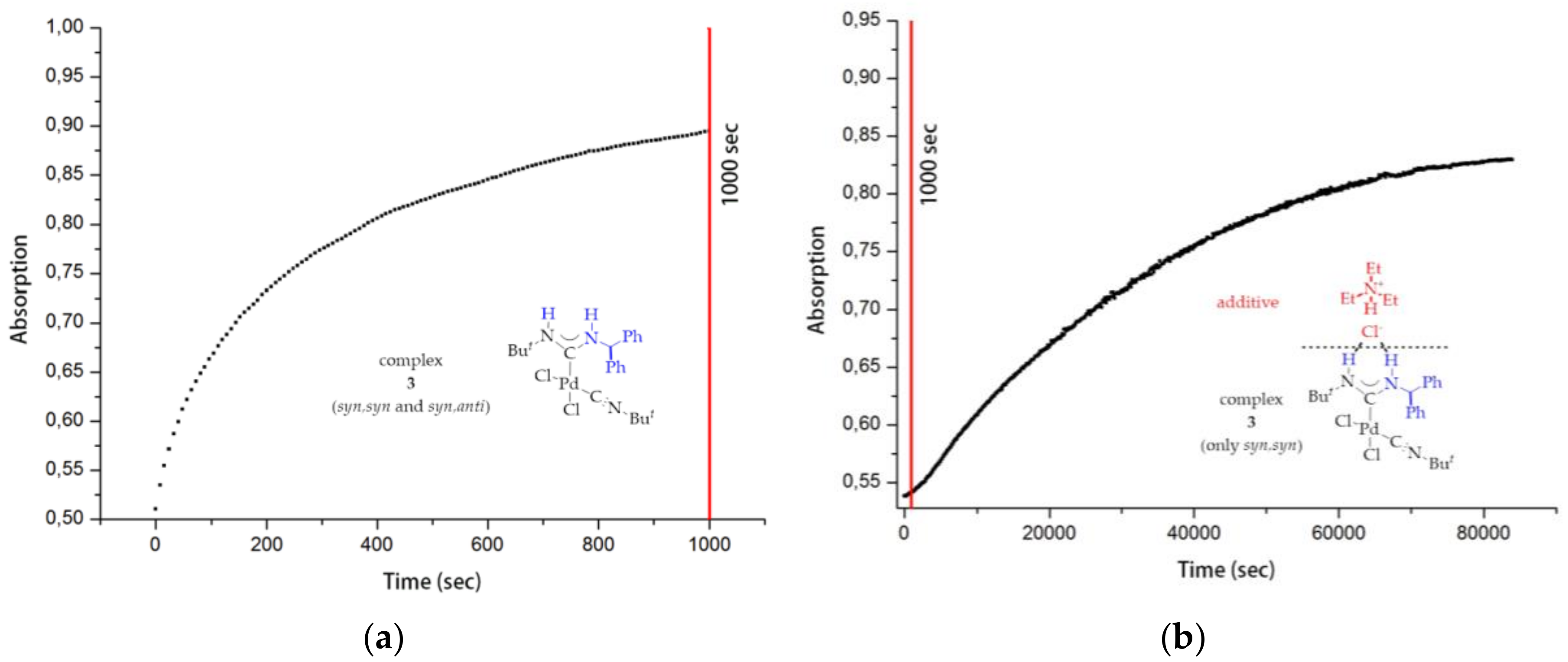
1. Introduction
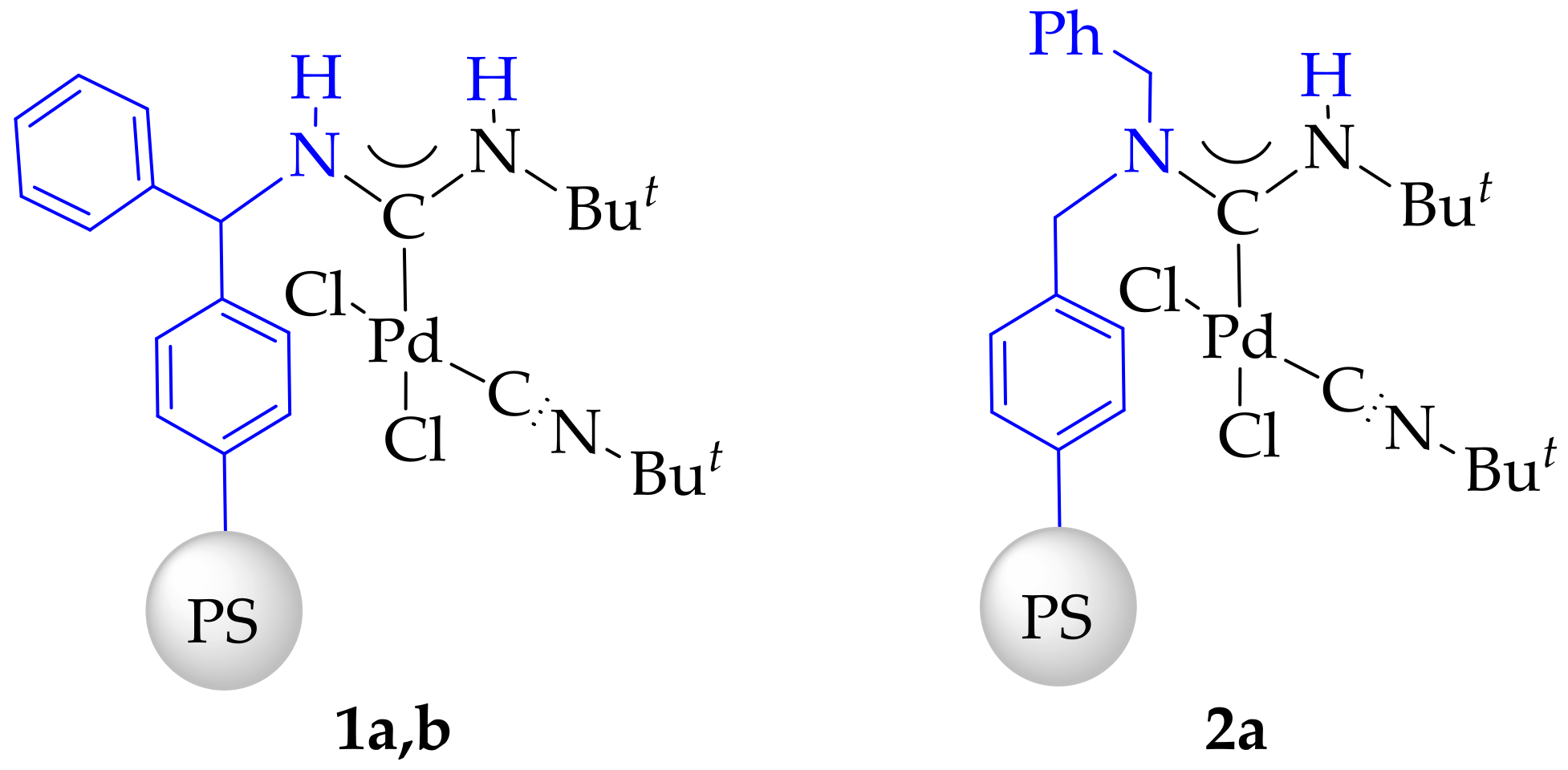
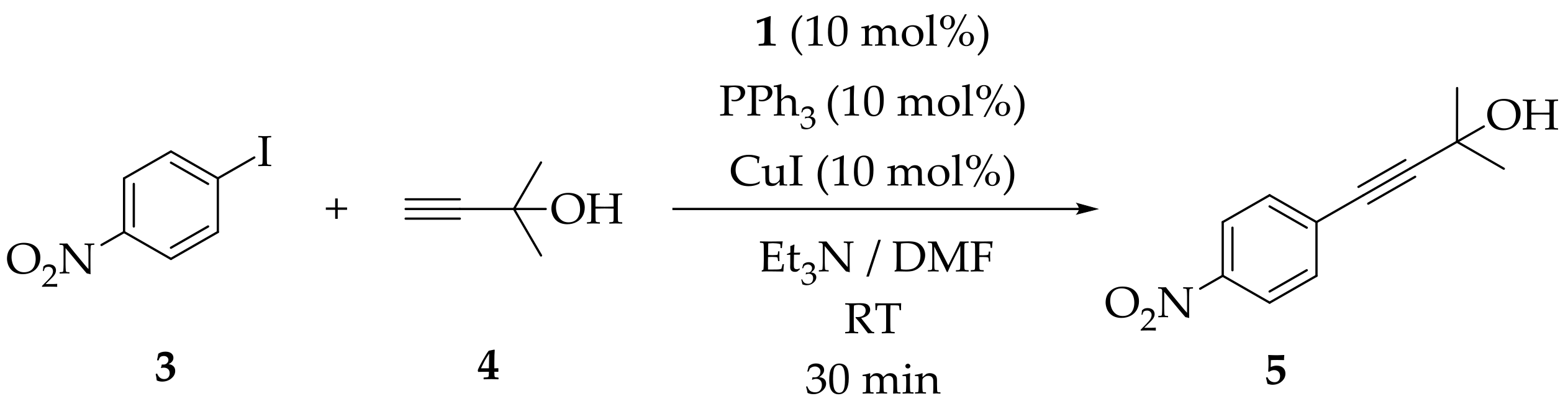
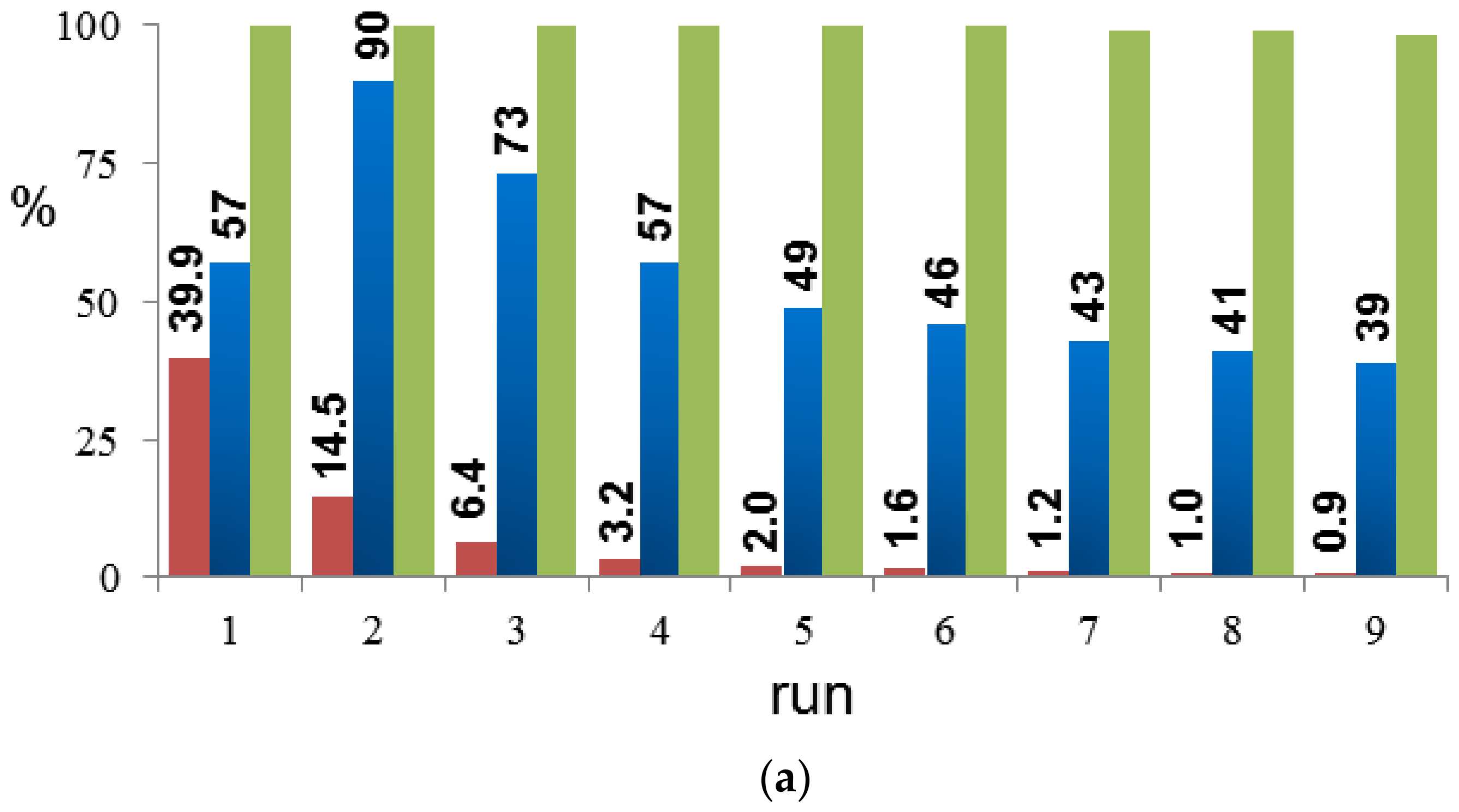
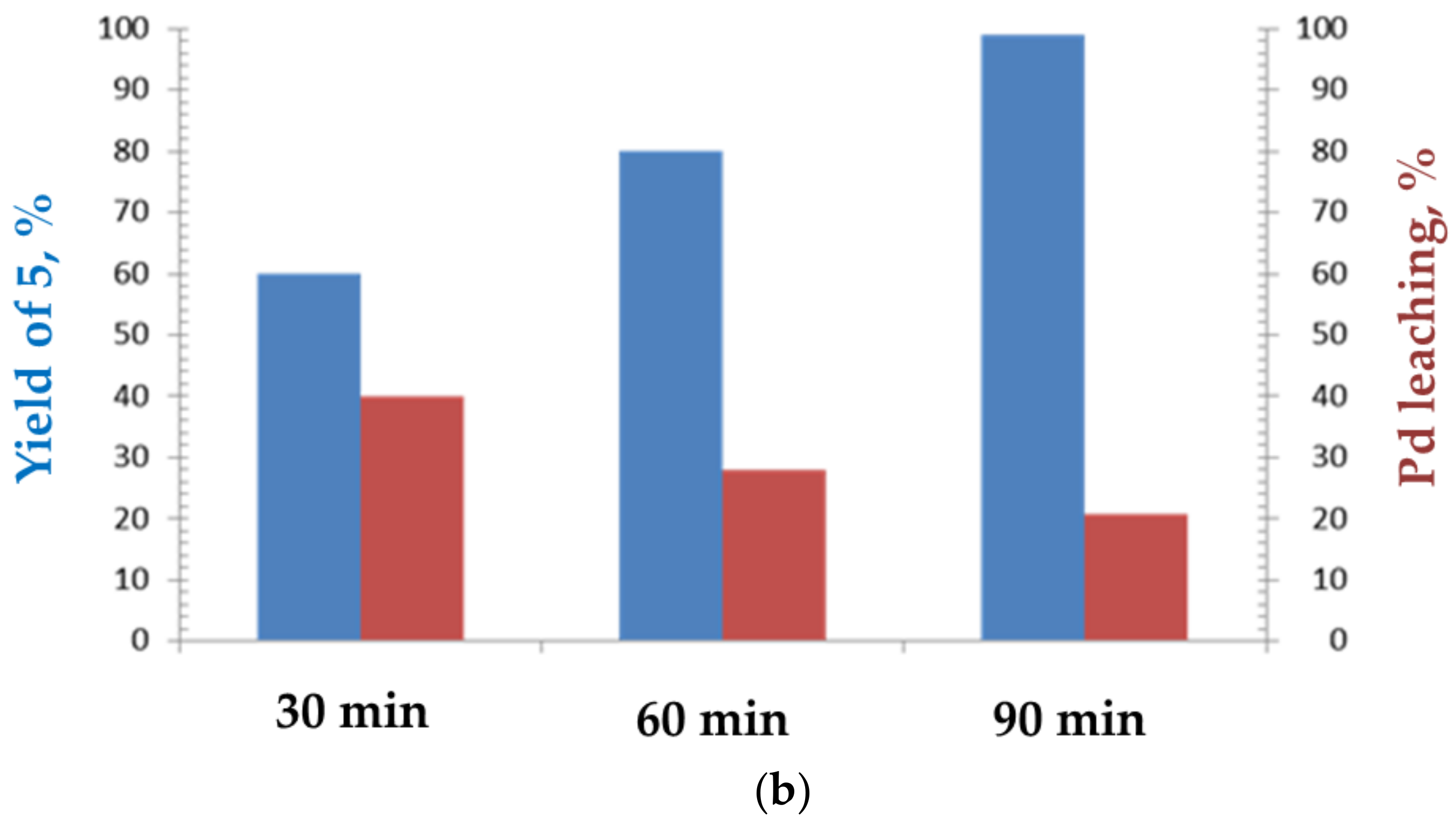
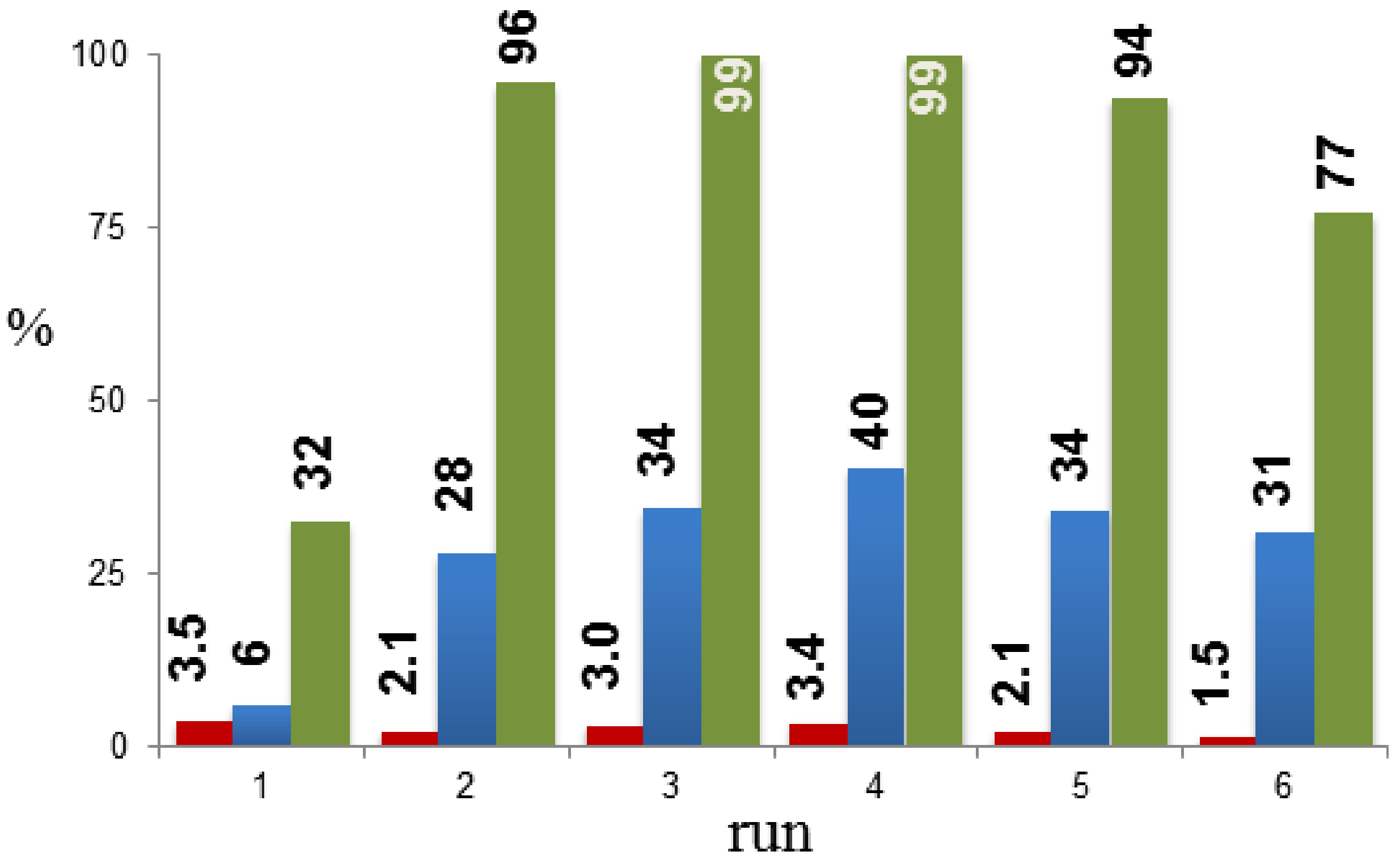
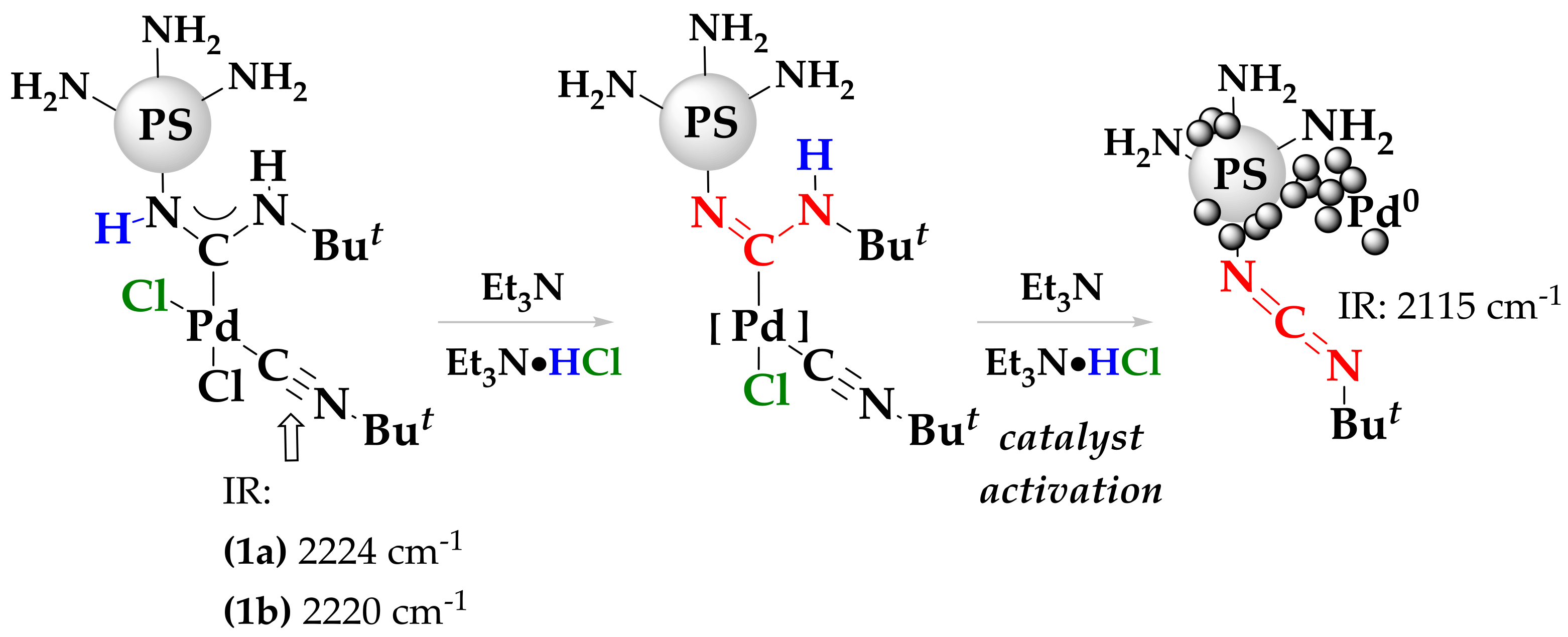
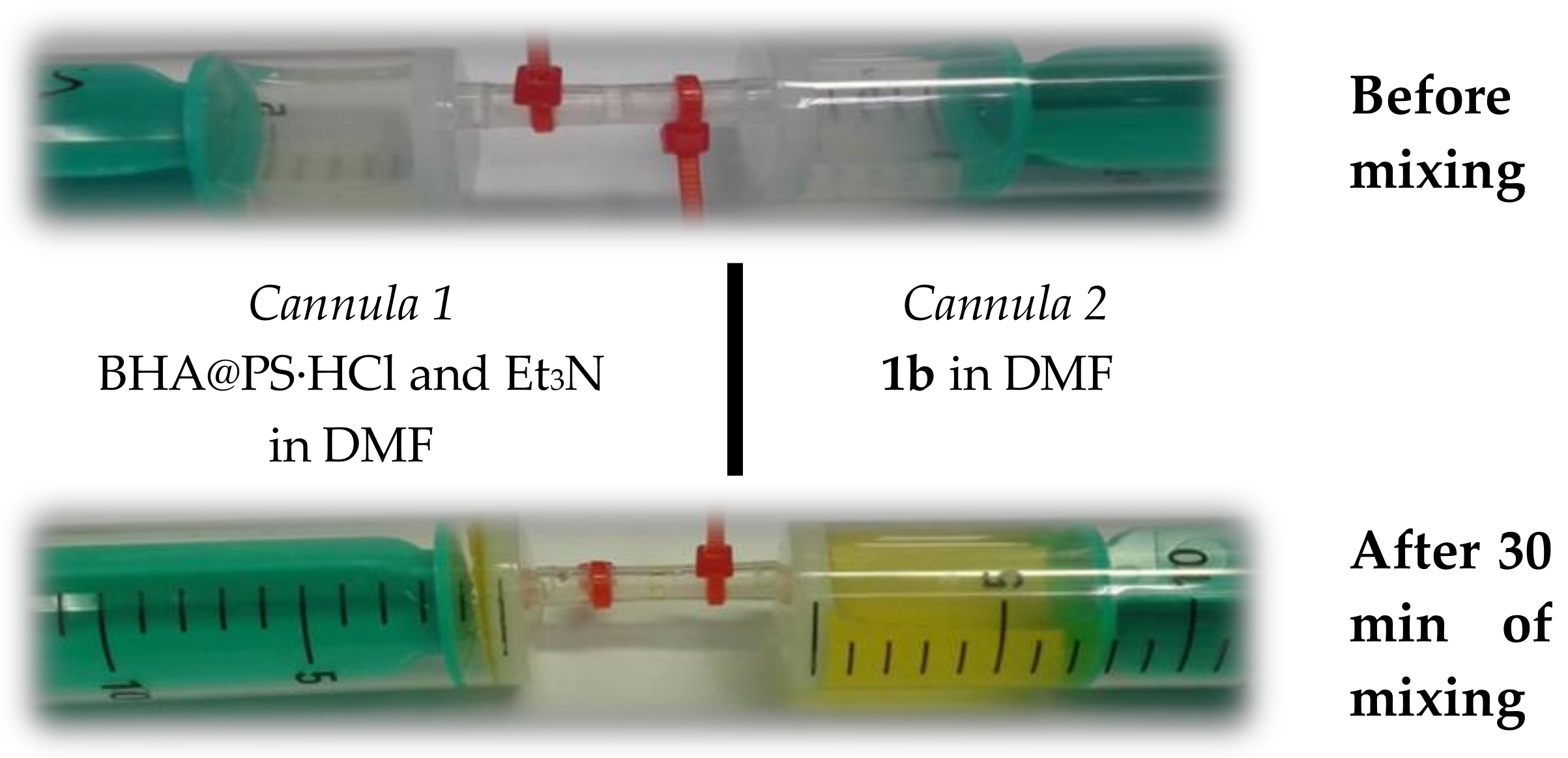
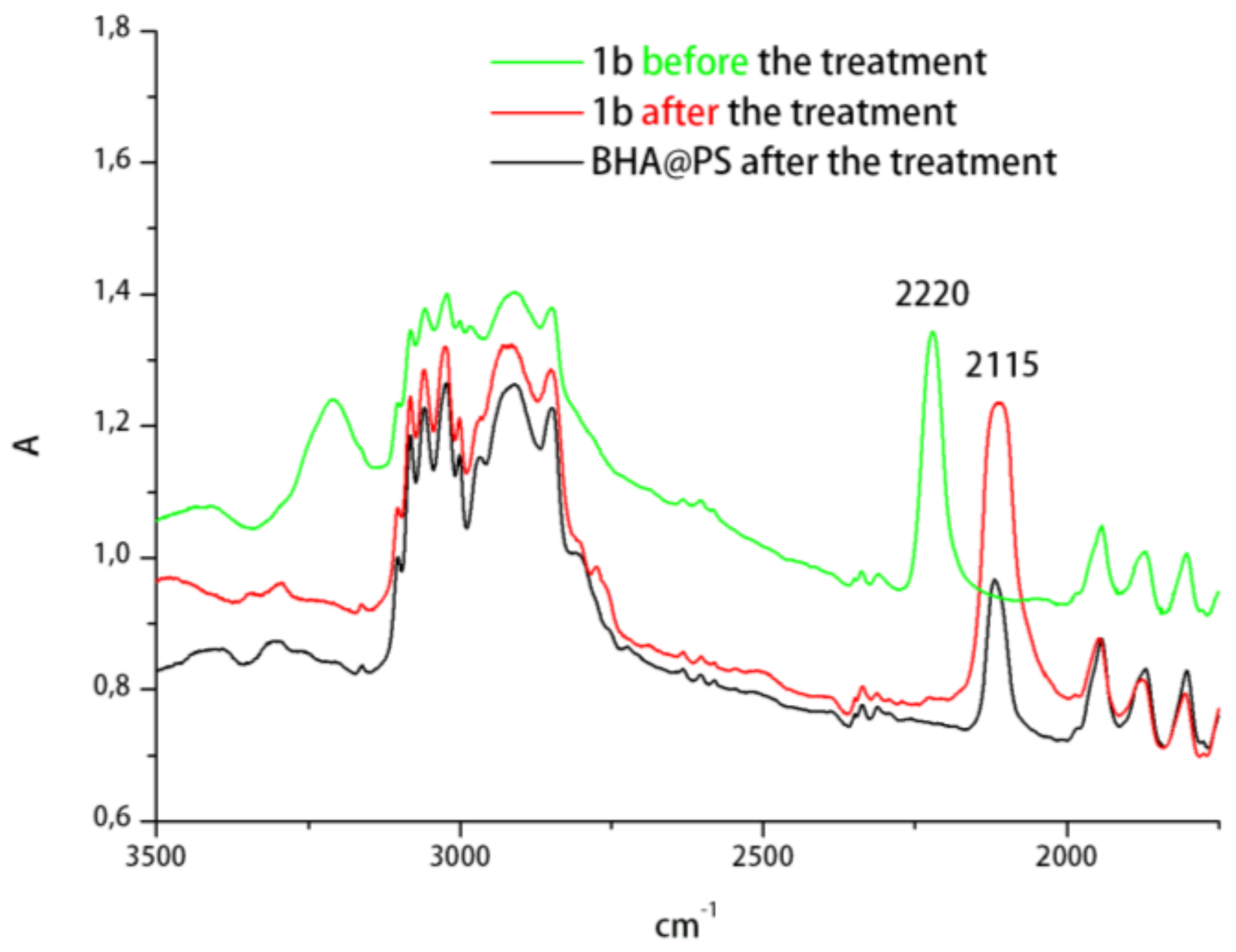
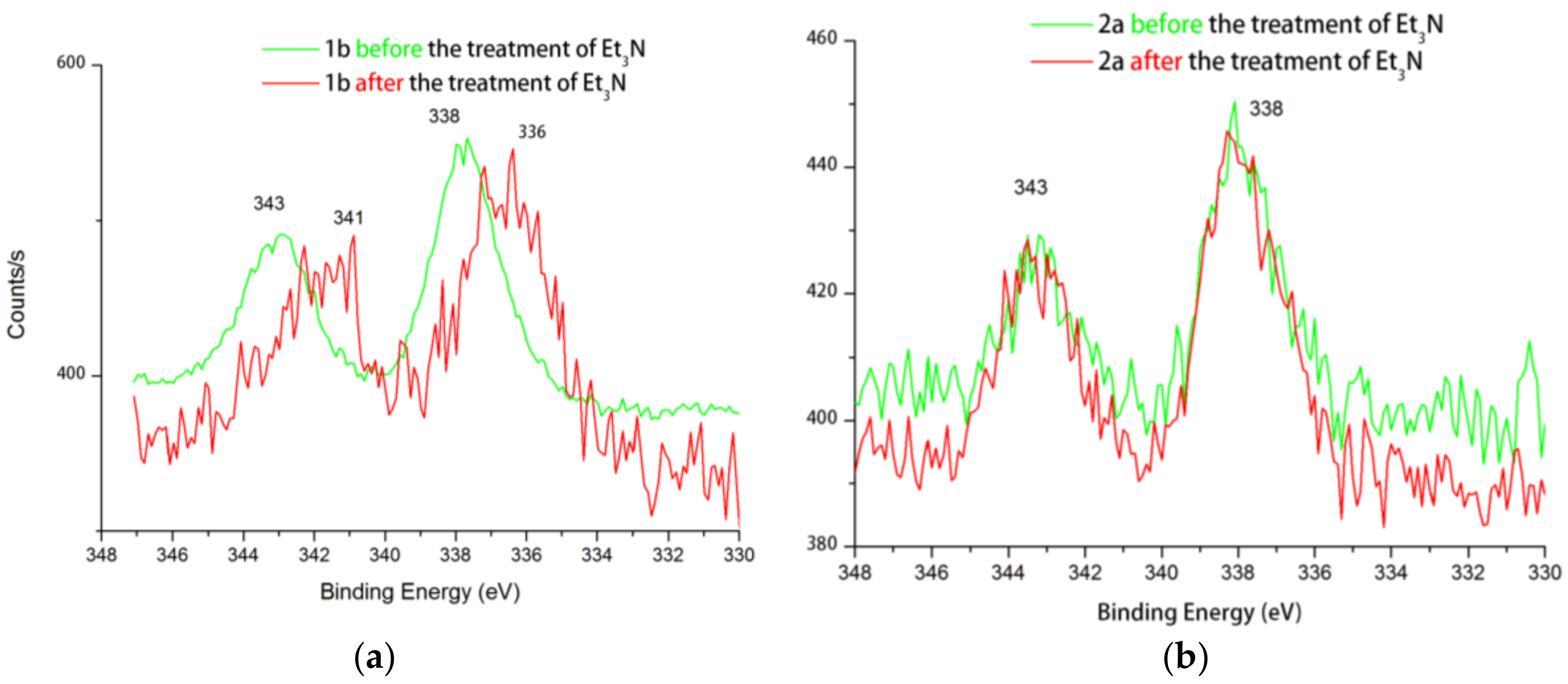
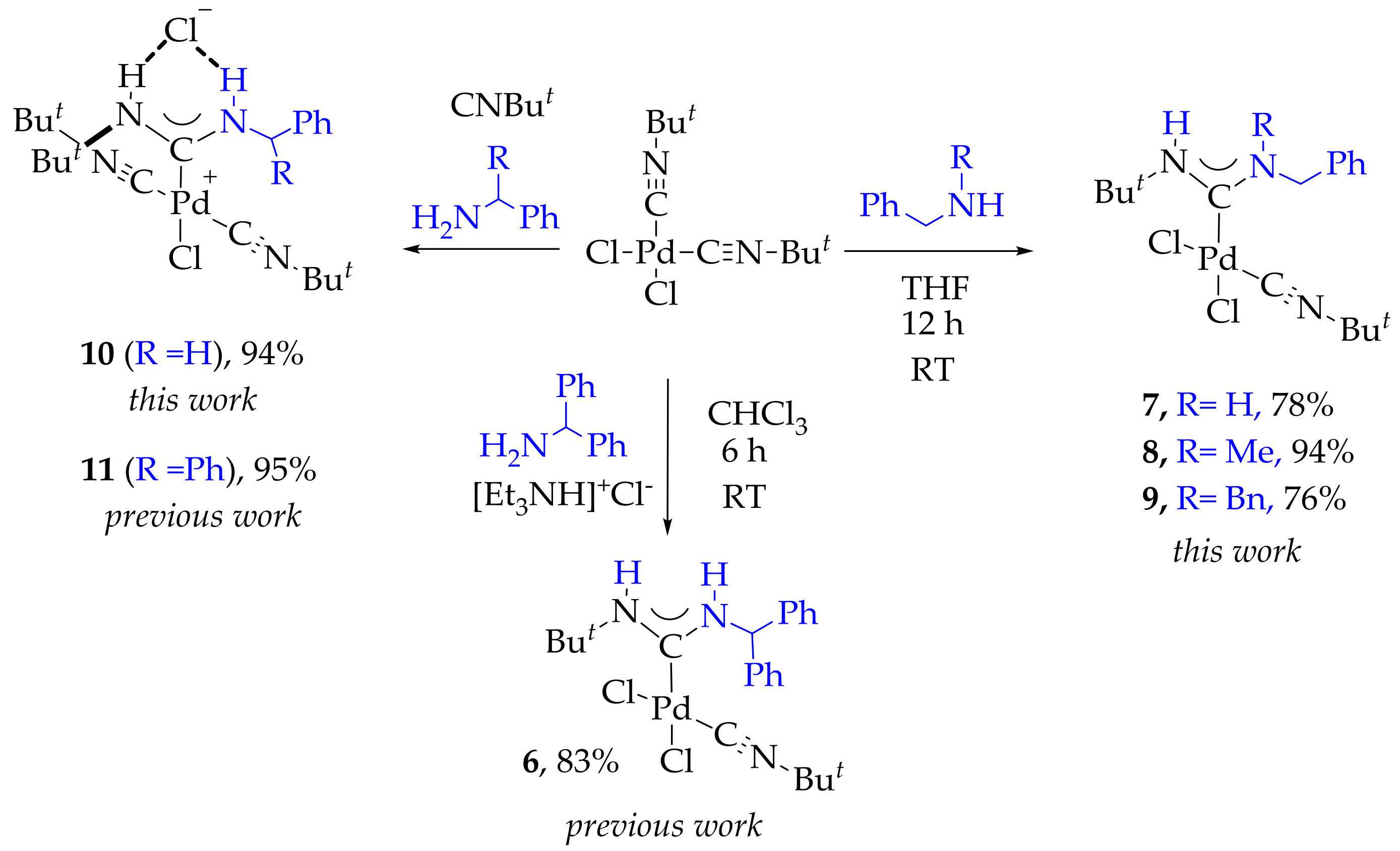
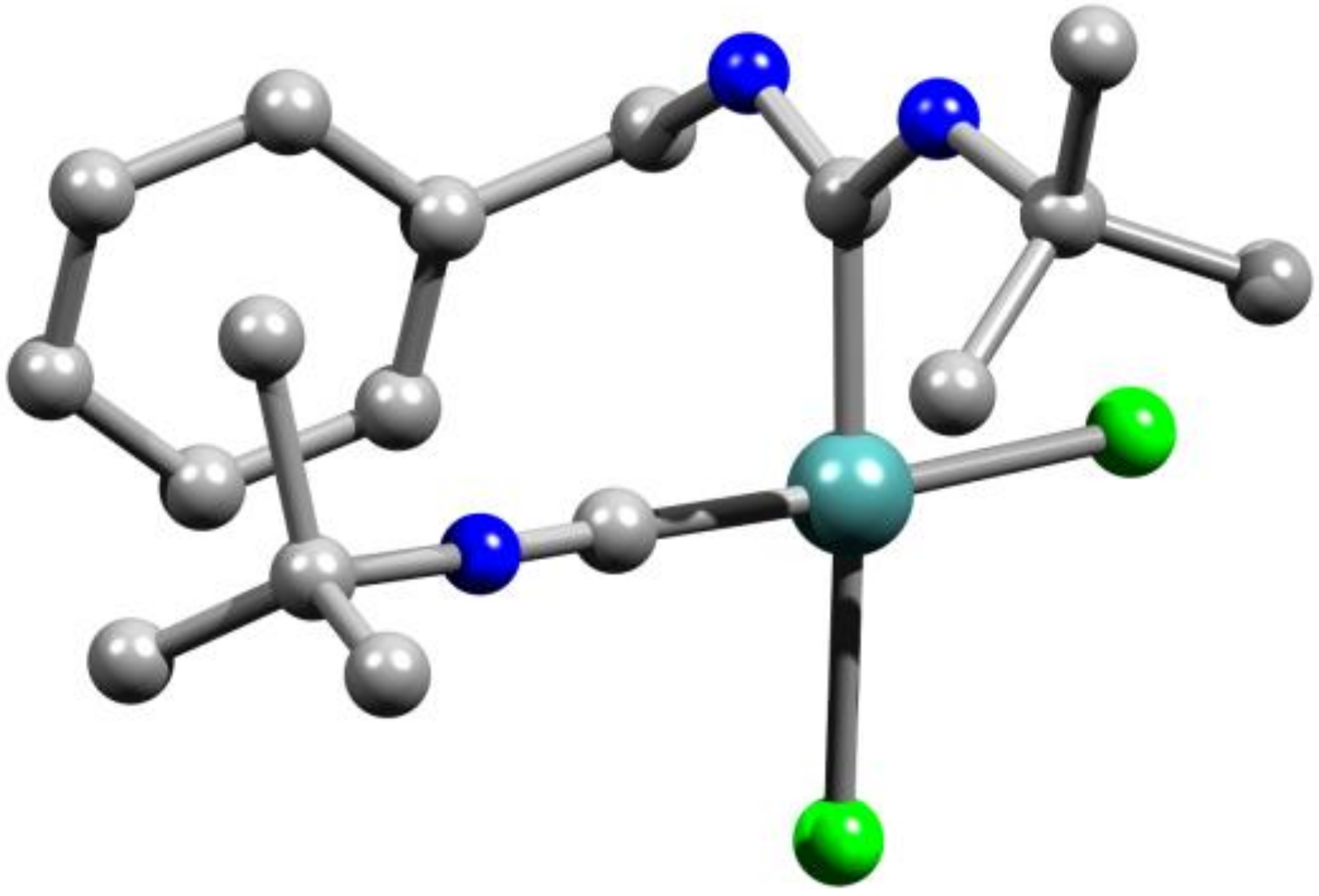
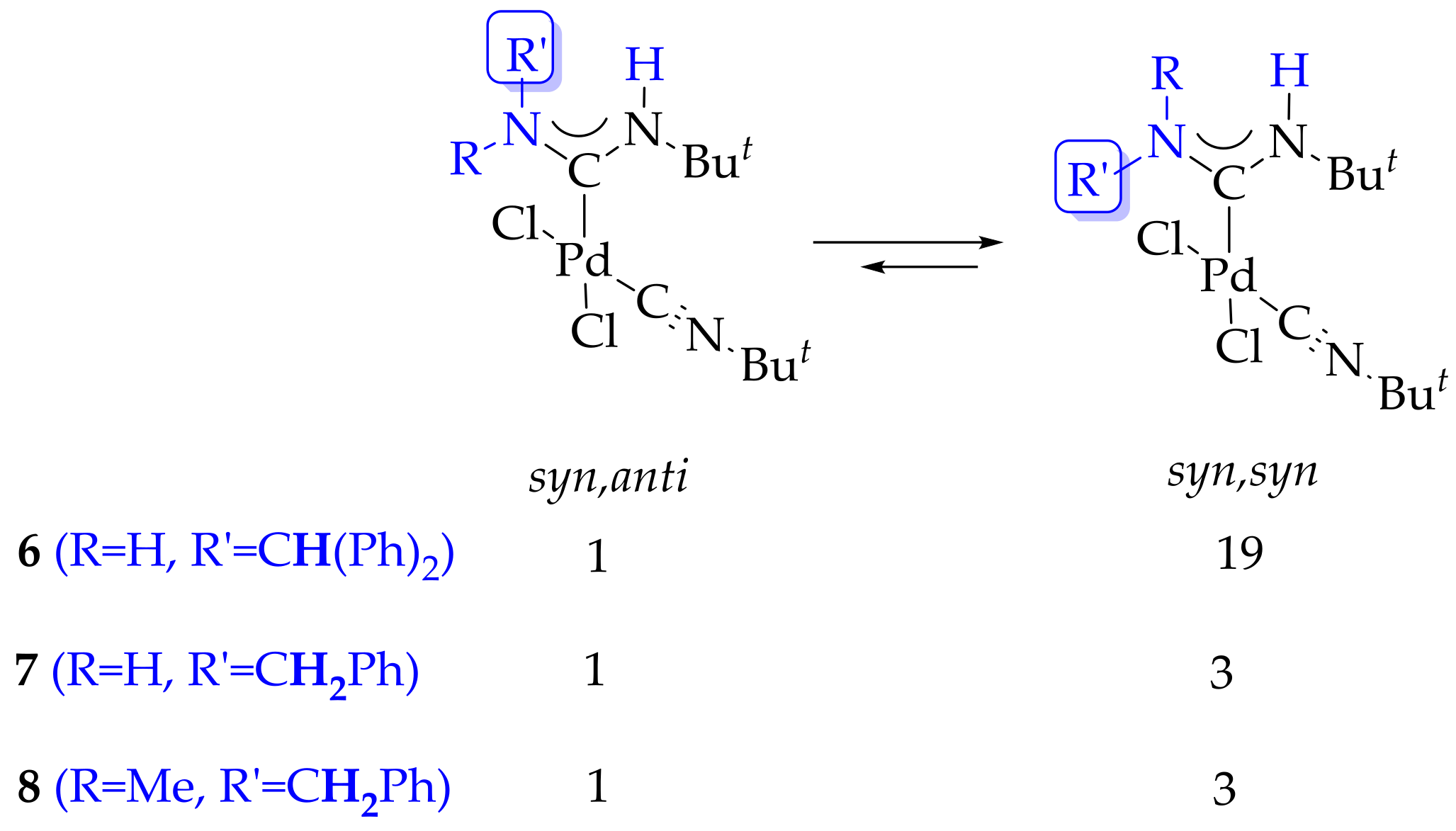
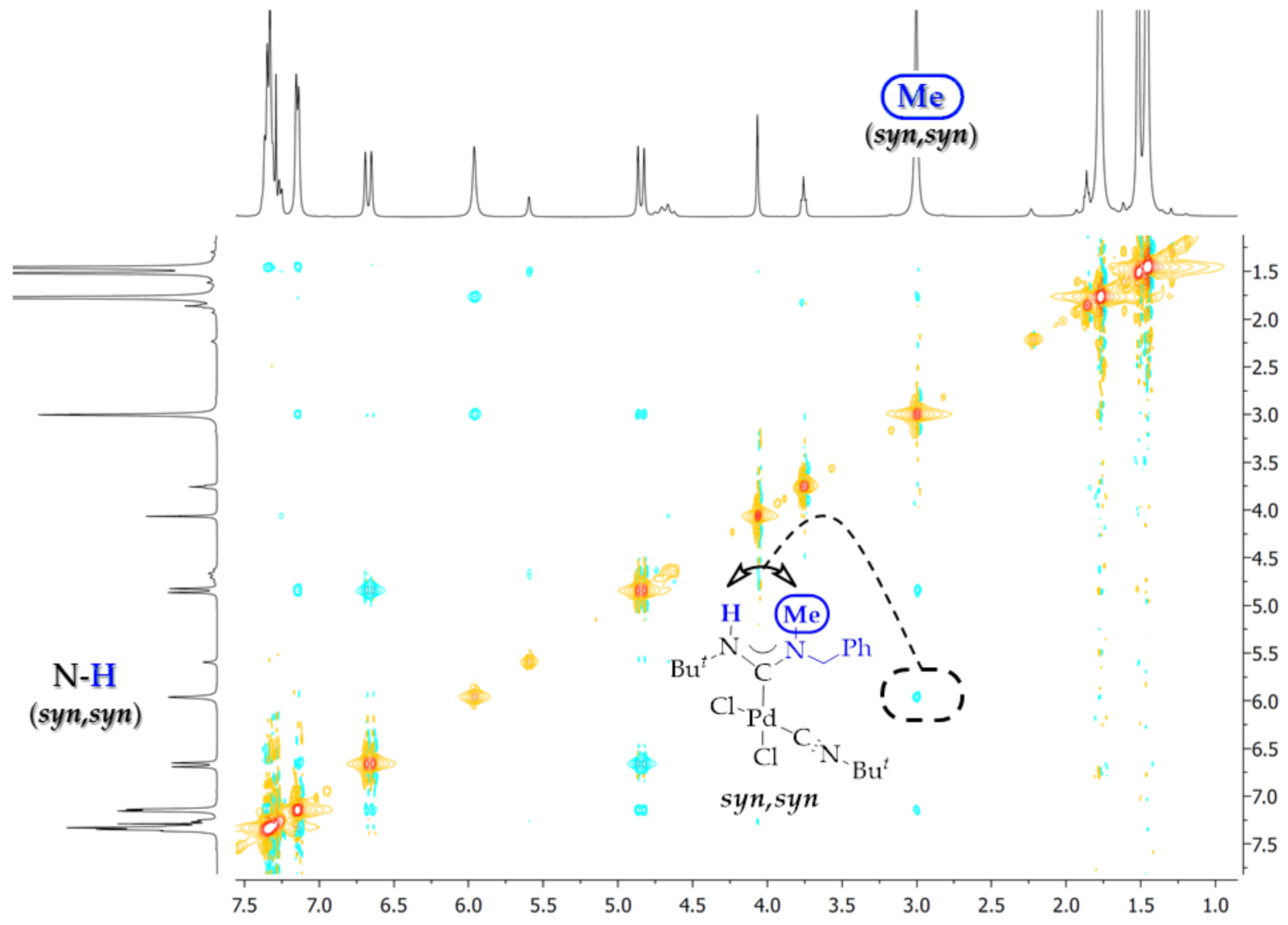
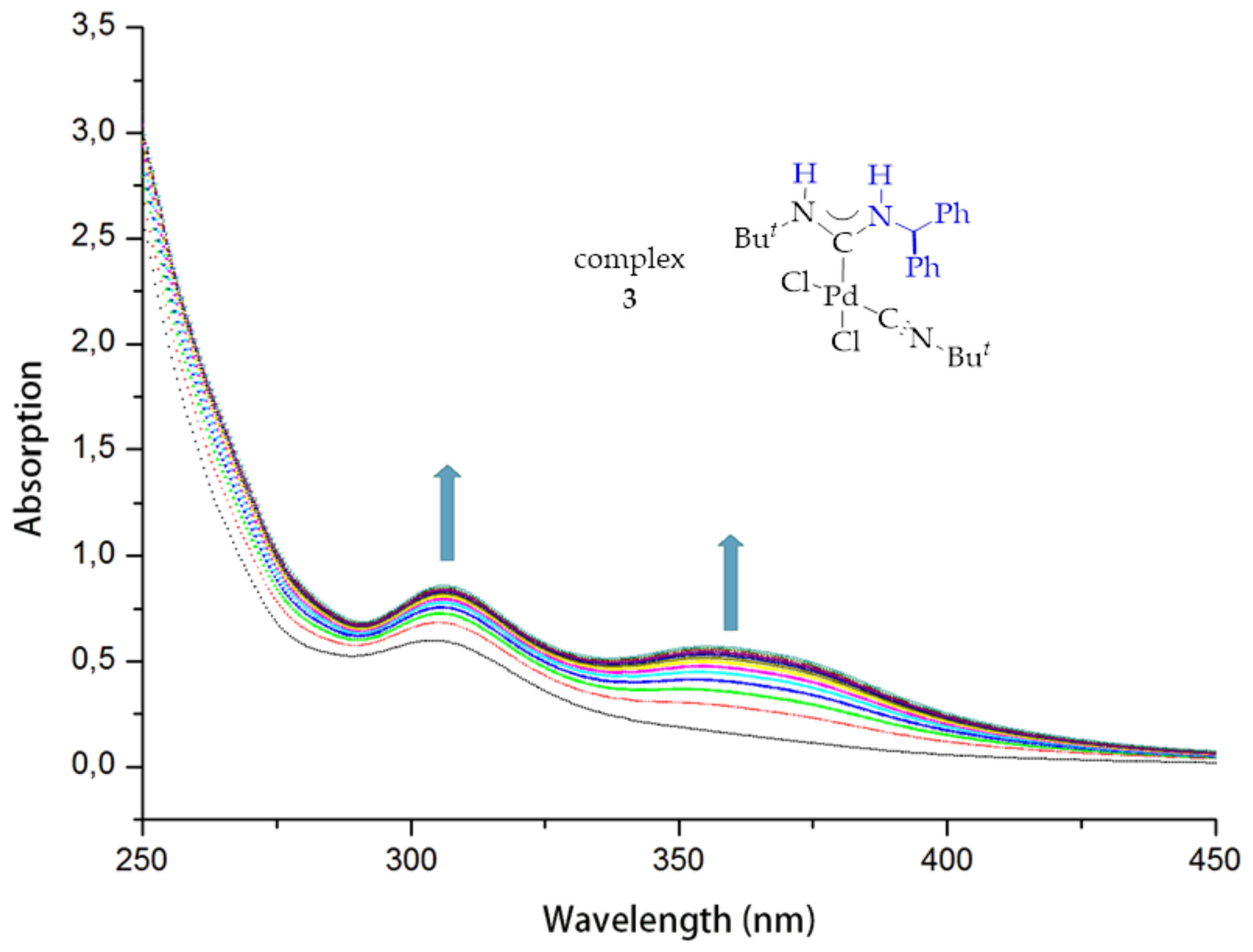
2. Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis of 7, 8 and 9
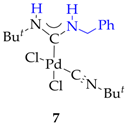

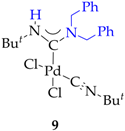

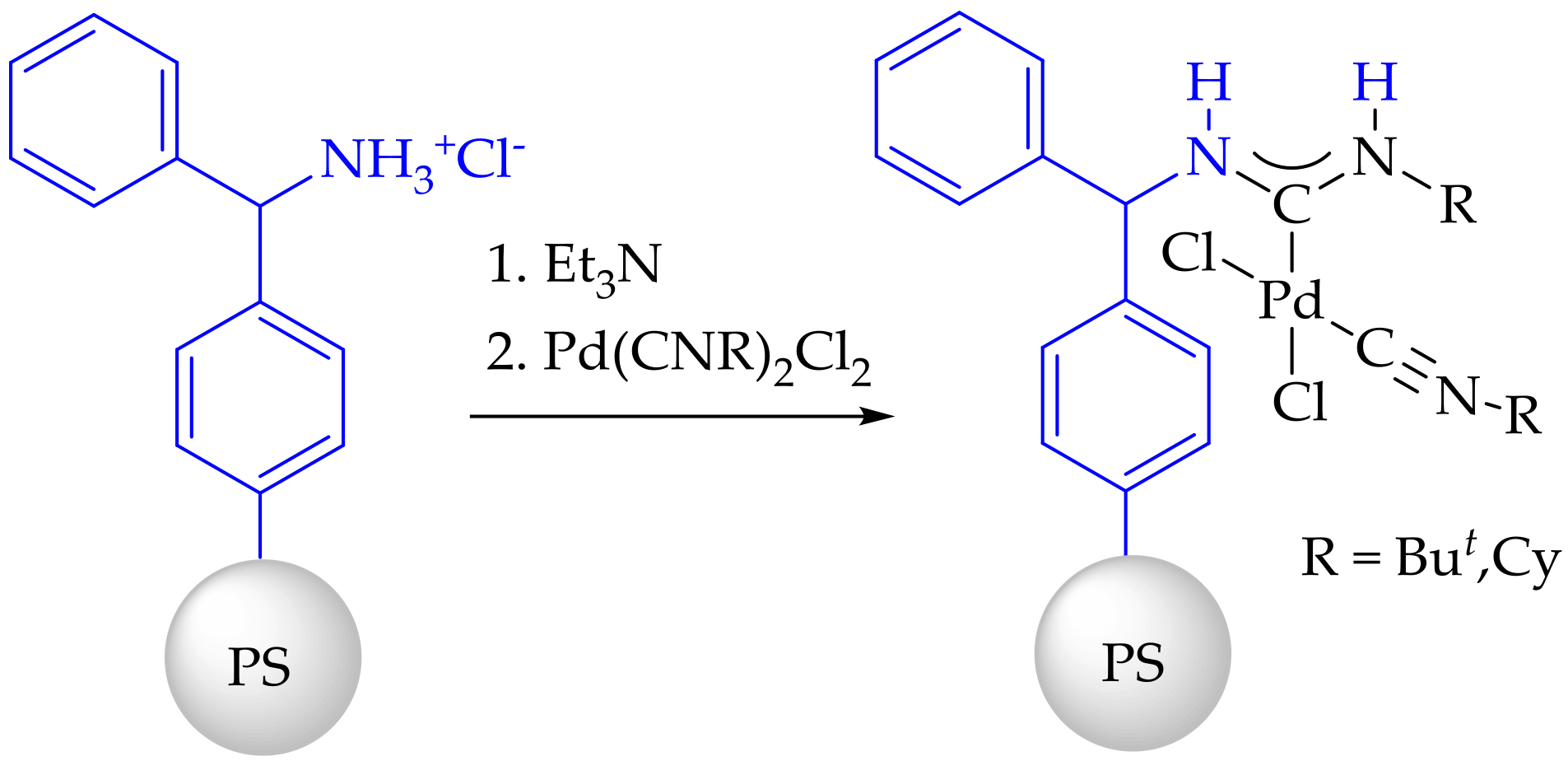
3.3. Synthesis and Characterization of Dibenzylamino-Functionalized Polystyrene (DBA@PS)
3.4. Synthesis and Characterization of Immobilized Acyclic Diaminocarbene Palladium (II) Complexes (1, 2)
- Complex 1a: 0.075 mmol[Pd]/g. Obtained from 39.7 mg of PdCl2(CNBut)2 and 1.5 g of polystyrene-benzhydrylamine resin (BHA@PS).
- Complex 1b: 0.481 mmol[Pd]/g. Obtained from 197.5 mg of PdCl2(CNBut)2 and 1.5 g of polystyrene-benzhydrylamine resin (BHA@PS).
- Complex 2: 0.475 mmol[Pd]/g. Obtained from 197.5 mg of PdCl2(CNBut)2 and 1.5 g of dibenzylamine resin (DBA@PS).
3.5. The General Procedure for the Sonogashira Reaction Using Heterogeneous Precatalysts:
3.6. Kinetic Studies of 6, 8 and 9 Decomposition
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jana, R.; Pathak, T.P.; Sigman, M.S. Advances in Transition Metal (Pd,Ni,Fe)-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions Using Alkyl-organometallics as Reaction Partners. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1417–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson Seechurn, C.C.C.; Kitching, M.O.; Colacot, T.J.; Snieckus, V. Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling: A Historical Contextual Perspective to the 2010 Nobel Prize. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5062–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, C.; Çalimsiz, S.; Hoi, K.H.; Mallik, D.; Sayah, M.; Organ, M.G. The Development of Bulky Palladium NHC Complexes for the Most-Challenging Cross-Coupling Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3314–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Johansson Seechurn, C.C.C.; Colacot, T.J. Development of Preformed Pd Catalysts for Cross-Coupling Reactions, Beyond the 2010 Nobel Prize. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1147–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, J.A.; Poyatos, M. Recent developments in the applications of palladium complexes bearing N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. Curr. Org. Chem. 2011, 15, 3309–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marion, N.; Nolan, S.P. Well-Defined N-Heterocyclic Carbenes−Palladium(II) Precatalysts for Cross-Coupling Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyarskiy, V.P.; Luzyanin, K.V.; Kukushkin, V.Y. Acyclic diaminocarbenes (ADCs) as a promising alternative to N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) in transition metal catalyzed organic transformations. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 2029–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyarskiy, V.P.; Luzyanin, K.V.; Kukushkin, V.Y. Palladium-(Acyclic Diaminocarbene) Species as Alternative to Palladium-(Nitrogen Heterocyclic Carbenes) in Cross-Coupling Catalysis. In Advances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 53, pp. 145–155. ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter, L.M. Catalysis with Acyclic Aminocarbene Ligands: Alternatives to NHCs with Distinct Steric and Electronic Properties. In N-Heterocyclic Carbenes; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; pp. 499–524. [Google Scholar]
- Michelin, R.A.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Guedes da Silva, M.F.C. Aminocarbene complexes derived from nucleophilic addition to isocyanide ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2001, 218, 75–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaughter, L.M. Acyclic Aminocarbenes in Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1802–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tskhovrebov, A.G.; Luzyanin, K.V.; Kuznetsov, M.L.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Balova, I.A.; Haukka, M.; Kukushkin, V.Y. Substituent R-Dependent Regioselectivity Switch in Nucleophilic Addition of N -Phenylbenzamidine to Pd II and Pt II Complexed Isonitrile RN≡C Giving Aminocarbene-Like Species. Organometallics 2011, 30, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzyanin, K.V.; Tskhovrebov, A.G.; Carias, M.C.; Guedes da Silva, M.F.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Kukushkin, V.Y. Novel Metal-Mediated (M = Pd, Pt) Coupling between Isonitriles and Benzophenone Hydrazone as a Route to Aminocarbene Complexes Exhibiting High Catalytic Activity (M = Pd) in the Suzuki-Miyaura Reaction. Organometallics 2009, 28, 6559–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, S.; de Vries, J.G.; Farina, V. Why Does Industry Not Use Immobilized Transition Metal Complexes as Catalysts? Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbet, J.P.; Mignani, G. Selected patented cross-coupling reaction technologies. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 2651–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, A. Efficient, Selective, and Recyclable Palladium Catalysts in Carbon−Carbon Coupling Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2251–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.; Han, B. Coupling Reactions with Supported Ionic Liquid Catalysts. In Supported Ionic Liquids; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; pp. 233–250. ISBN 9783527331246. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, R.; Lindhorst, A.C.; Groche, F.J.; Kühn, F.E. Immobilization of N-Heterocyclic Carbene Compounds: A Synthetic Perspective. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 1970–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganath, K.V.S.; Onitsuka, S.; Kumar, A.K.; Inanaga, J. Recent progress of N-heterocyclic carbenes in heterogeneous catalysis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 2161–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazin, C.S.J. Recent advances in the design and use of immobilised N-heterocyclic carbene ligands for transition-metal catalysis. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2009, 12, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, E.; Movassagh, B. Polystyrene-resin supported N-heterocyclic carbene-Pd(II) complex based on plant-derived theophylline: A reusable and effective catalyst for the Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction of arenediazonium tetrafluoroborate salts with arylboronic acids. J. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 822, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, E.; Movassagh, B. Synthesis of polystyrene-supported Pd(II)-NHC complex derived from theophylline as an efficient and reusable heterogeneous catalyst for the Heck-Matsuda cross-coupling reaction. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 418–419, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhryakov, K.V.; Mugemana, C.; Vu, K.B.; Rodionov, V.O. Palladium N-Heterocyclic Carbene Precatalyst Site Isolated in the Core of a Star Polymer. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 4826–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, S.N.; Kumbhar, A.S.; Mali, S.S.; Hong, C.K.; Salunkhe, R.S. A Merrifield resin supported Pd–NHC complex with a spacer(Pd–NHC@SP–PS) for the Sonogashira coupling reaction under copper- and solvent-free conditions. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, S.Z.; Qian, H.; Lin, Z.Y. A magnetically separable palladium catalyst containing a bulky N-heterocyclic carbene ligand for the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevanneshan, Z.; Moghadam, M.; Mirkhani, V.; Tangestaninejad, S.; Mohammadpoor-Baltork, I.; Rezaei, S. Suzuki–Miyaura C–C coupling reactions catalysed by a homogeneous and nanosilica supported palladium(II) N-heterocyclic carbene complex derived from 3,5-di(1-imidazolyl)pyridine. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 9729–9734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiaci, M.; Zarghani, M.; Khojastehnezhad, A.; Moeinpour, F. Preparation, characterization and first application of silica supported palladium-N-heterocyclic carbene as a heterogeneous catalyst for C–C coupling reactions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 15496–15501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Marefat, M.R.; Hasannia, M.; Akhavan, P.F.; Mansouri, F.; Artelli, Z.; Mohammadi, F.; Vali, H. Imidazolyl-Functionalized Ordered Mesoporous Polymer from Nanocasting as an Effective Support for Highly Dispersed Palladium Nanoparticles in the Heck Reaction. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 2508–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, M.P.; Copéret, C.; Thieuleux, C. Mesostructured Hybrid Organic–Silica Materials: Ideal Supports for Well-Defined Heterogeneous Organometallic Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1458–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhamifar, D.; Karimi, B.; Rastegar, J.; Banakar, M.H. Palladium-Containing Ionic Liquid-Based Ordered Mesoporous Organosilica: An Efficient and Reusable Catalyst for the Heck Reaction. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.M.; Yusoff, M.M.; Rahman, M.L. Mesoporous Silica MCM-41 Supported N -Heterocyclic Carbene-Pd Complex for Heck and Sonogashira Coupling Reactions. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2015, 62, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Olid, F.; Andrés, R.; de Jesús, E.; Flores, J.C.; Gómez-Sal, P.; Heuzé, K.; Vellutini, L. Magnetically recoverable catalysts based on mono- or bis-(NHC) complexes of palladium for the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction in aqueous media: Two NHC–Pd linkages are better than one. Dalt. Trans. 2016, 45, 11633–11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Chong, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, W. One-pot preparation of magnetic N-heterocyclic carbene-functionalized silica nanoparticles for the Suzuki–Miyaura coupling of aryl chlorides: Improved activity and facile catalyst recovery. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, N.; Gao, S.; Feng, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Graphene oxide supported N-heterocyclic carbene-palladium as a novel catalyst for the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 21863–21868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Raza, F.; Jeon, S.-J.; Kim, H.-I.; Kang, T.W.; Yim, D.; Kim, J.-H. Recyclable N-heterocyclic carbene/palladium catalyst on graphene oxide for the aqueous-phase Suzuki reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 3426–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahed, S.K.; Esmatpoursalmani, R.; Bazgir, A. N-Heterocyclic carbene palladium complex supported on ionic liquid-modified graphene oxide as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for Suzuki reaction. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 14586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widegren, J.A.; Finke, R.G. A review of the problem of distinguishing true homogeneous catalysis from soluble or other metal-particle heterogeneous catalysis under reducing conditions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2003, 198, 317–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.F.; Kurokhtina, A.A. Distinguishing between the homogeneous and heterogeneous mechanisms of catalysis in the Mizoroki-Heck and Suzuki-Miyaura reactions: Problems and prospects. Kinet. Catal. 2012, 53, 714–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabtree, R.H. Resolving heterogeneity problems and impurity artifacts in operationally homogeneous transition metal catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1536–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananikov, V.P.; Beletskaya, I.P. Toward the Ideal Catalyst: From Atomic Centers to a “Cocktail” of Catalysts. Organometallics 2012, 31, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astakhov, A.V.; Khazipov, O.V.; Chernenko, A.Y.; Pasyukov, D.V.; Kashin, A.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Khrustalev, V.N.; Chernyshev, V.M.; Ananikov, V.P. A New Mode of Operation of Pd-NHC Systems Studied in a Catalytic Mizoroki-Heck Reaction. Organometallics 2017, 36, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meijere, A.; Brase, S.; Oestreich, M. Metal-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions and More; De Meijere, A., Bräse, S., Oestreich, M., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; ISBN 9783527655588. [Google Scholar]
- Kashin, A.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Catalytic C–C and C–heteroatom bond formation reactions: In situ generated or preformed catalysts? Complicated mechanistic picture behind well-known experimental procedures. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 11117–11125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremin, D.B.; Ananikov, V.P. Understanding active species in catalytic transformations: From molecular catalysis to nanoparticles, leaching, “Cocktails” of catalysts and dynamic systems. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 346, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruttadauria, M.; Giacalone, F.; Noto, R. “Release and catch” catalytic systems. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtaka, A.; Okagaki, T.; Hamasaka, G.; Uozumi, Y.; Shinagawa, T.; Shimomura, O.; Nomura, R. Application of “Boomerang” Linear Polystyrene-Stabilized Pd Nanoparticles to a Series of C–C Coupling Reactions in Water. Catalysts 2015, 5, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliaro, M.; Pandarus, V.; Ciriminna, R.; Béland, F.; Demma Carà, P. Heterogeneous versus Homogeneous Palladium Catalysts for Cross-Coupling Reactions. ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, V.N.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Balova, I.A. Polystyrene-supported diaminocarbene complexes of palladium(II): Synthesis, characterization and application as a precatalyst in Sonogashira–Hagihara and Suzuki–Miyaura cross coupling. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2017, 86, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, V.N.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Korvinson, K.A.; Novikov, A.S.; Balova, I.A. Synthesis and Simple Immobilization of Palladium(II) Acyclic Diaminocarbene Complexes on Polystyrene Support as Efficient Catalysts for Sonogashira and Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling. Organometallics 2016, 35, 1684–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, V.N.; Korvinson, K.; Sorokoumov, V.N. Chiral acyclic diaminocarbene complexes of palladium(II) immobilized on a polymeric support as promising catalysts of the Suzuki reaction. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2016, 86, 2473–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyarskiy, V.P.; Bokach, N.A.; Luzyanin, K.V.; Kukushkin, V.Y. Metal-Mediated and Metal-Catalyzed Reactions of Isocyanides. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2698–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crociani, B.; Boschi, T.; Belluco, U. Synthesis and reactivity of novel palladium(II)-isocyanide complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1970, 9, 2021–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, A.S.K.; Lothschütz, C.; Böhling, C.; Rominger, F. From Isonitriles to Carbenes: Synthesis of New NAC− and NHC−Palladium(II) Compounds and Their Catalytic Activity. Organometallics 2011, 30, 2411–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tšupova, S.; Rudolph, M.; Rominger, F.; Hashmi, A.S.K. Synthesis and Properties of Hydrazino Amino Acyclic Carbenes of Gold(I), Platinum(II), Palladium(II) and Rhodium(III). Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 3999–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, A.; Rudolph, M.; Rominger, F.; Hashmi, A.S.K. An Alternative Approach to PEPPSI Catalysts: From Palladium Isonitriles to Highly Active Unsymmetrically Substituted PEPPSI Catalysts. Chem. A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 11065–11071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, D.; Wurm, T.; Graf, K.; Rudolph, M.; Rominger, F.; Hashmi, A.S.K. From Isonitriles to Unsaturated NHC Complexes of Gold, Palladium and Platinum. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, A.S.K.; Lothschuetz, C.; Boehling, C.; Hengst, T.; Hubbert, C.; Rominger, F. Carbenes Made Easy: Formation of Unsymmetrically Substituted N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes of Palladium(II), Platinum(II) and Gold(I) from Coordinated Isonitriles and their Catalytic Activity. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 3001–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Hirao, T.; Saegusa, T. Heterocycle syntheses by diaminocarbene—palladium(II) complex intermediates. J. Organomet. Chem. 1977, 131, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Hirao, T.; Ohta, N.; Saegusa, T. Synthesis of ketenimine via (N-alkylimino)acylpalladium complex intermediate. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 18, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Hirao, T.; Saegusa, T. Synthetic reactions by complex catalysts. XXXVII. Novel and versatile method of carbodiimide synthesis oxidation of carbene palladium(II) complex with silver oxide. J. Org. Chem. 1975, 40, 2981–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, A.; Roche, M.; Alami, M.; Messaoudi, S. 2-Aminobiphenyl Palladacycles: The “Most Powerful” Precatalysts in C–C and C–Heteroatom Cross-Couplings. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, S.; Kinzhalov, M.A.; Valishina, E.; Luzyanin, K.V.; Boyarskiy, V.P.; Buslaeva, T.M.; Haukka, M.; Kukushkin, V.Y. Application of palladium complexes bearing acyclic amino(hydrazido)carbene ligands as catalysts for copper-free Sonogashira cross-coupling. J. Catal. 2015, 329, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzhalov, M.A.; Boyarskiy, V.P.; Luzyanin, K.V.; Dolgushin, F.M.; Kukushkin, V.Y. Metal-mediated coupling of a coordinated isocyanide and indazoles. Dalt. Trans. 2013, 42, 10394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, S.; Tatsuno, Y.; Ataka, K. Univalent palladium complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971, 93, 6705–6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
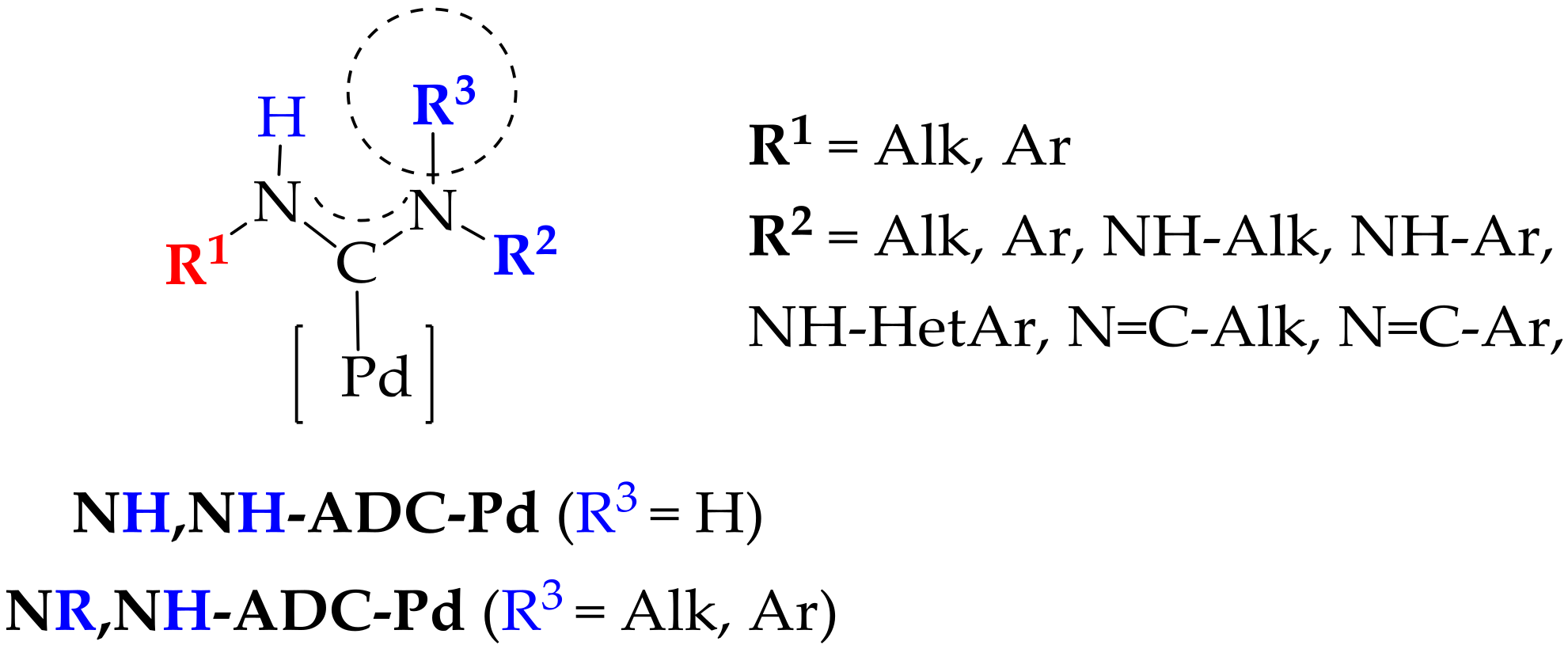
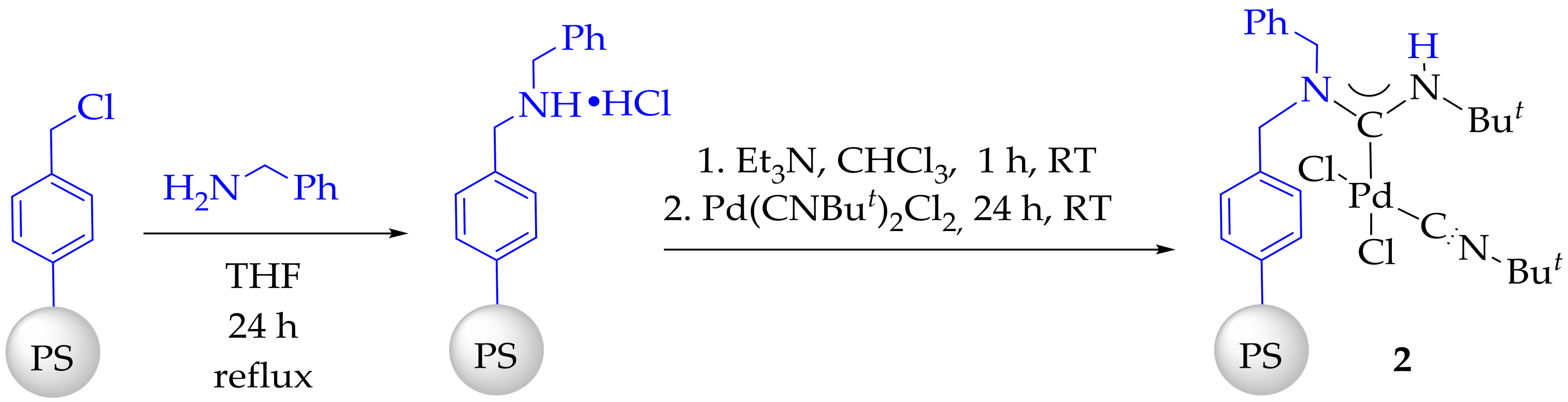
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mikhaylov, V.N.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Liakhov, D.M.; Tskhovrebov, A.G.; Balova, I.A. Polystyrene-Supported Acyclic Diaminocarbene Palladium Complexes in Sonogashira Cross-Coupling: Stability vs. Catalytic Activity. Catalysts 2018, 8, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040141
Mikhaylov VN, Sorokoumov VN, Liakhov DM, Tskhovrebov AG, Balova IA. Polystyrene-Supported Acyclic Diaminocarbene Palladium Complexes in Sonogashira Cross-Coupling: Stability vs. Catalytic Activity. Catalysts. 2018; 8(4):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040141
Chicago/Turabian StyleMikhaylov, Vladimir N., Viktor N. Sorokoumov, Denis Martin Liakhov, Alexander G. Tskhovrebov, and Irina A. Balova. 2018. "Polystyrene-Supported Acyclic Diaminocarbene Palladium Complexes in Sonogashira Cross-Coupling: Stability vs. Catalytic Activity" Catalysts 8, no. 4: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040141
APA StyleMikhaylov, V. N., Sorokoumov, V. N., Liakhov, D. M., Tskhovrebov, A. G., & Balova, I. A. (2018). Polystyrene-Supported Acyclic Diaminocarbene Palladium Complexes in Sonogashira Cross-Coupling: Stability vs. Catalytic Activity. Catalysts, 8(4), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040141