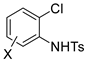
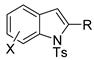
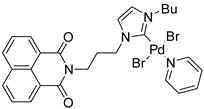
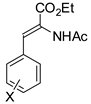
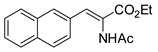
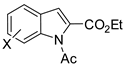
Abstract
Indole is the most frequently found heterocyclic core structures in pharmaceuticals, natural products, agrochemicals, dyes and fragrances. For about 150 years, chemists were absorbed in finding new and easier synthetic strategies to build this nucleus. Many books and reviews have been written, but the number of new syntheses that appear in the literature, make necessary continuous updates. This reviews aims to give a comprehensive overview on indole synthesis catalyzed by transition metals appeared in the literature in the years 2016 and 2017.
1. Introduction
The name indole arose from its first preparation: the reaction of the indigo dye with oleum, carried out by Baeyer [1]. It has an intense fecal odor, but at very low concentrations, it has a flowery smell and therefore it is used in perfumery.
Indole is one of the ubiquitous heterocyclic systems found in nature. In fact, it is present in the structures of different dyes, fragrances, pharmaceuticals, and agricultural chemicals [2]. Therefore, the synthesis of the indole nucleus and its functionalization is a key field in heterocyclic chemistry and has attracted the attention of synthetic organic chemists for over a century and a half. In this time frame, many synthetic strategies appeared in the literature, the most famous being the Bartoli, the Bischler–Möhlau, the Fischer, the Fukuyama, the Gassman, the Hemetsberger, the Larock, the Leimgruber–Batcho, the Madelung, the Nenitzescu, and the Reissert indole synthesis [3].
Moreover, transition metal catalyzed cross-coupling reactions involving C–H activation are an alternative strategy to the traditional synthetic protocol and have recently increased importance for the construction of C–C and C–N bonds [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14].
With this plethora of books and reviews on indole, was another review needed? The answer is “yes”, because in the last two years many and many other transition metal catalyzed reactions appeared in the literature and the aim of this paper is to give a comprehensive overview on this topic. The wide interest in the synthesis of this heterocycle was also demonstrated by the many papers appeared during the preparation of this review some of them has been added in the conclusion section.
We decided to give importance to the metal catalyst, thus every metal has its section.
The most frequently encountered reactions are enhanced by directing groups placed on the nitrogen atom. Some of them remain in the final product, other are eliminated somewhere during the reaction pathway. They are called “traceless directing groups”. A typical C–H activation reaction with traceless directing group contemplates a 1,2-migratory insertion-generated intermediate. The migration allows the extrusion of a proton from the benzene group, which remains as a freely available electrophile until being sequestered in the last stage, by the directing group removed as a nucleophile (Scheme 1).
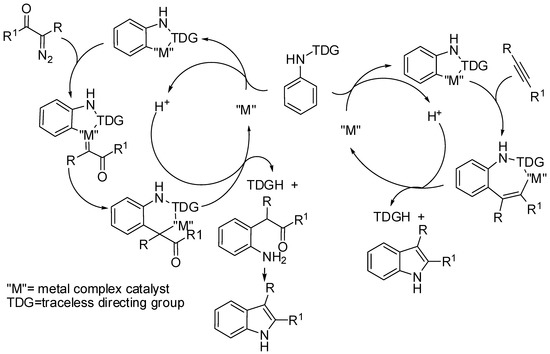
Scheme 1.
Accepted mechanism for C–H activation reaction with traceless directing group.
In the reactions described in this review involving 1-aryl-2-alkylalkynes the formation of the sole regioisomer with the aryl group in the 2-position is generally observed. The regioselectivity is caused by the favored coupling of aryl moiety with alkyne at the less hindered site (alkyl-containing carbon). Moreover, the reaction of meta-substituted aryl-nitrones, -nitrosamines, -hydrazines, and -ureas led to the prevalent or exclusive formation of the 6-substituted indole regioisomer. Preference for 6-substituted indole over 4-substituted one is very likely due to stereochemical aspects.
Owing to the easy availability of the starting materials, another widely used protocol for the construction of indoles is the cross-dehydrogenative coupling reactions of N-aryl enamines or imines discovered independently, but concomitantly, by Hartwig, Buchwald, and Miura [15,16,17]. It is surely the most used method starting from easily available anilines and carbonyl derivatives. In the time range covered by this review many examples will be encountered.
2. Cobalt
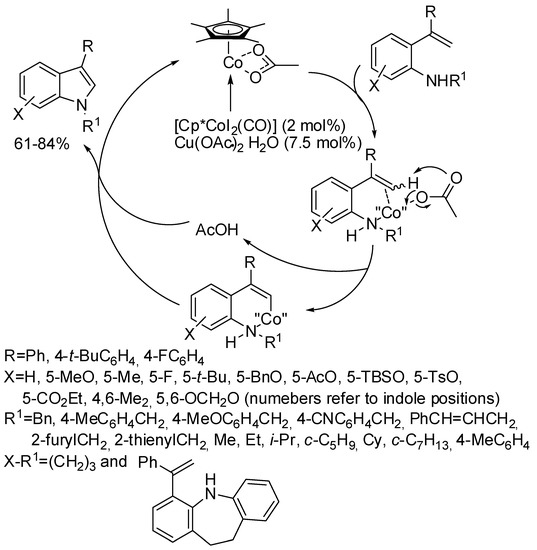
Cobalt is an earth-abundant, low-cost, nontoxic metal, the low electronegativity of which renders the covalently bound C atom more nucleophilic than its heavier congener. Thus, the C–N bond formation can occur faster than other competing reactions. Actually, high valent cobalt was proven efficient in many C–H activation reactions, thus it was tested also in the de novo construction of indole nucleus. Cobaltocene are generally used, because the small ionic radius of cobalt makes nearer the substrate and the Cp*, increasing steric repulsions and thus favoring to distinguish between the two different ortho-positions in meta-substituted aryl substrates, conversely from [Cp*RhIII] which gave inseparable mixtures of regioisomers [18]. Another common feature was the chance of scaling up the reactions without significant yield modification.
Cobalt(III) catalysis often needs an oxidative directing group, but also a redox-neutral directing group has been found effective in the reaction.
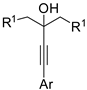
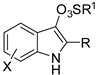
Among oxidative directing groups, Ackermann reported the reaction of nitrones and alkynes (Scheme 2) [19]. This reaction allowed the annulation of unsymmetrically substituted alkynes in contrast to a similar rhodium-catalyzed indole synthesis, which was non-regioselective with diarylalkynes and low-yielding with alkylarylalkynes [20]. However, it should be noted that dialkyl-substituted alkynes delivered a 3,3-disubstituted indoline. This behavior is intermediate between two rhodium(III)-catalyzed syntheses one leading to indolines [21], the other to 2,3-diaryl-substituted indoles with one of the aryl substituents arising from the nitrone and the other from the alkyne substrate [22]. The authors carried out some experiments, which allowed proposing the mechanism depicted in the scheme.
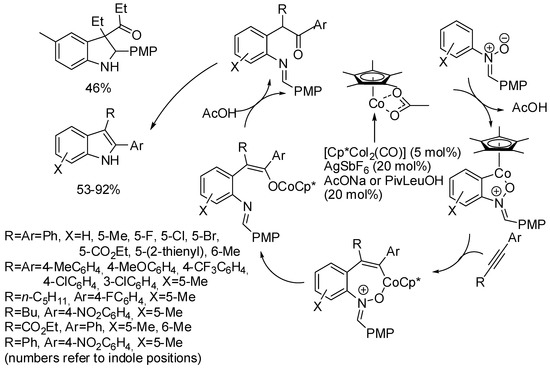
Scheme 2.
Cobalt(III)-catalyzed indolization with nitrones.
Cp*Co(III) catalyst can address the cyclization of ureas and alkynes both to quinolines and indoles. In particular, Glorius found the conditions of the selective cyclization processes (Scheme 3) [23]. The first step is the alkyne insertion to give an eight-membered organometallic intermediate, which, depending on the relative reaction rates of a dehydrative cyclization or a C−N reductive elimination, lead to quinoline (not reported in the scheme) or to indoles. Thus the Lewis acid accelerates the dehydrative cyclization, and improves the electrophilicity of the carbonyl group, improving the quinoline over the indole and this hypothesis was supported by computational calculations. For this reason, N-arylureas allowed the exclusive formation of indoles (Scheme 3, Equation (1)). At the same time, the group of Shi reached the same findings (Scheme 3, Equation (2)) [24]. Both reactions gave only the 6-substituted indole when meta-substituted N-arylureas were used. For unsymmetrical aryl-alkyl substituted alkynes, Glorius [23] found an 8:1 mixture of 2-phenyl-3-ethyl vs. 2-ethyl-3-phenylindole and the exclusive formation of 3-phenyl-2-(phenylethynyl)indole, while Shi [24] always recovered only the isomer with the aryl group in the 2-position. Moreover, Shi [24] performed a reaction with N-pyrrolyl urea with diphenylacetylene recovering 74% yield of indole, while Glorius [23] performed the same reaction with N-piperidylurea in 66% yield. Glorius successfully deprotected the carbamoyl group (76% yields) [23]. Shi showed that terminal alkynes were unreactive [24].
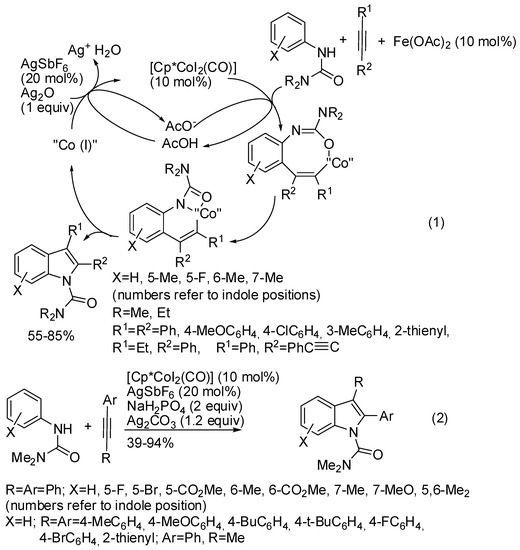
Scheme 3.
Cobalt(III)-catalyzed indolization from ureas and alkynes.
The reaction of N-nitrosoanilines with alkynes is depicted in Scheme 4 [25]. In unsymmetrical alkyl aryl alkynes, the aryl group was mainly found at the 3-position differently from [Cp*Rh(III)] [18] and the previous reaction. In this reaction, regioselectivity ranged from 2:1 to 4:1, while in the reaction of nitrones only a regioisomer was recovered. The envisaged reaction mechanism starts, as in the previous reaction, from insertion of the alkyne. Then an intramolecular substitution occurs to form the pyrrole ring releasing the second nitrogen atom.
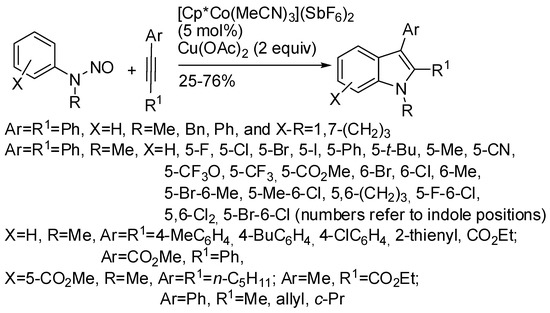
Scheme 4.
Cobalt(III) catalyzed indolization with N-nitrosoanilines.
Cobalt(III) catalysis was also employed for an efficient redox-neutral synthesis starting from Boc-arylhydrazines (Scheme 5) [26]. It is worth of note that ortho-substituted aryl groups afforded the expected indoles in good yields, whereas N-nitrosoanilines were unreactive with these substrates [25]. Unsymmetrical alkyl-aryl and alkyl-ester alkynes gave only one regioisomer. Since other acylhydrazines were unreactive, the authors envisaged stabilization by the Boc group during the reaction pathway, which always contemplate the formation of the seven-membered cobaltacycle followed by a reductive elimination to form the indole nucleus and an oxidative N–N bond cleavage. Alternatively, the seven-membered cobaltacycle could afford the product by a concerted fragmentation.
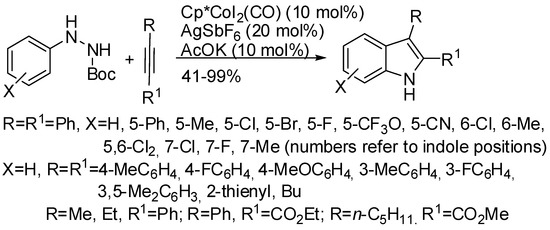
Scheme 5.
Cobalt(III) catalyzed indolization with Boc-arylhydrazines.
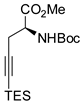
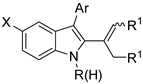
Also N-alkyl-N-arylhydrazines reacted with alkynes in the presence of a Co(III) catalytic system [27]. It is noteworthy that this reaction worked also with terminal alkynes, if a more cationic Co(III) species such as [Cp*Co(MeCN)3](SbF6)2 was employed. In particular, two distinct reaction pathways were observed: if on the neighboring atom of the C≡C there is a chain branching, the bond position remained unaltered, while without branched chains an isomerization to allene occurred (Scheme 6). When a bulky silyl group is present on the C-2 of the indole, it can easily be removed working as synthetic equivalent of an acetylenic unit, and allowed a formal inverse regioselectivity, because the C-3 can be successfully functionalized in many different ways (so the synthetic importance of the reaction increased). The authors rationalized the reaction by envisaging the constant release of very small amounts of allene, which then preferentially reacted owing to its higher reactivity.
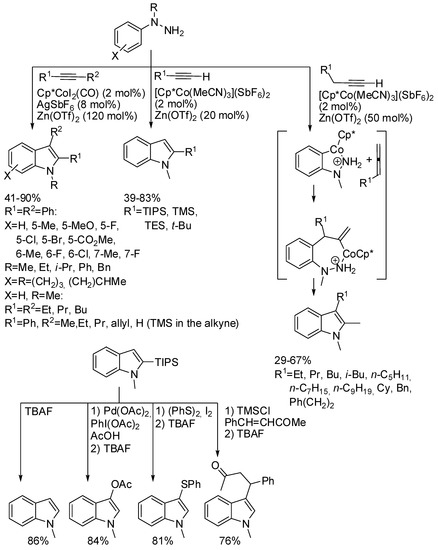
Scheme 6.
Cobalt(III) catalyzed indolization with N-alkyl-N-arylhydrazines.
Transition-metal catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling is an efficient method for the construction of new bonds. Recently, efficient cobalt(III)-catalyzed intramolecular application to ortho-alkenylanilines allowed the synthesis of indoles (Scheme 7) [28]. The authors explained the reaction mechanism as depicted in scheme.
Scheme 7.
Cobalt catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling.
Finally, Wang and Ji developed the synthesis of 3-imine indole derivatives from the Co(II)-catalyzed reaction of isocyanides and sulfonyl azides (Scheme 8) [29]. The reaction conditions made this reaction particularly environmentally friendly, because no oxidants and additives were employed. It should be noted that electron-withdrawing groups (such as halogens or carboxylates) on the isonitrile drastically lowered yields (25–51%). The (E)-isomer was always exclusively recovered. Some experiments were carried out to hypothesize a mechanism. In particular a Co(III)-nitrene intermediate was recognized. Anhydrous conditions were necessary to allow the electrophilic aromatic substitution which led to the indole ring construction. In the presence of water, sulfonylamidyl amide derivatives were recovered.
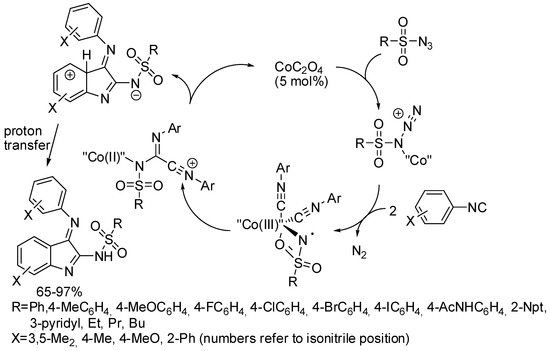
Scheme 8.
Synthesis of 3-imine indole derivatives.
3. Copper
Copper is another earth-abundant, low-cost, and low-toxic metal, thus traces of the catalyst in the isolated product give no problems if used as drugs. Moreover, copper(I) salts can act as a catalyst for a C–N coupling reaction, while copper(II) salts act as the oxidant in the oxidative cyclization of arylalkynes.
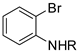
An example of C–N coupling reaction has been described by Bachon and Opatz [30], who allowed reacting 1-(bromomethyl)-2-iodobenzene with α-aminonitriles, easily available from commercially available and cheap aldehydes, amine and hydrogen cyanide by a Strecker reaction (Scheme 9). It should be noted that:
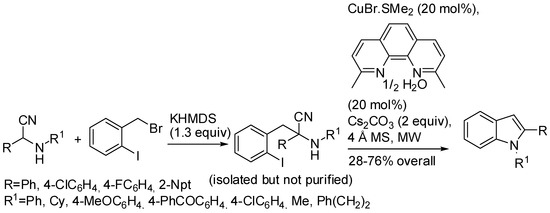
Scheme 9.
Synthesis of indoles from α-aminonitriles and 2-halobenzyl halides.
- in order to ensure the correct and exclusive regiochemistry in the deprotonation step, at least one C=C double bond has to be in conjugation to the α-center of the α-aminonitrile;
- bromoarenes are unsuitable for this reaction, unlike palladium used as catalyst (see later in the text);
- 1,10-phenanthroline and 1,2-diaminocyclohexane are not effective as complexing agents of copper.
Another example is represented by the reaction of easily available 2-(2-bromophenyl)acetonitriles, with aldehydes and aqueous ammonia (Scheme 10) [31]. Authors demonstrated the mechanism depicted in Scheme 10 by performing the reaction step-by-step, and isolating all the surmised intermediates. Since 3-substituted indole 2′-deoxyribonucleosides are important artificial DNA bases, authors setup glycosylation of the obtained 3-cyanoindoles in 67–71% overall yield, by a two-step one-pot procedure starting with tolyl-protected chlorosugar, followed by removal of the tolyl protecting group.
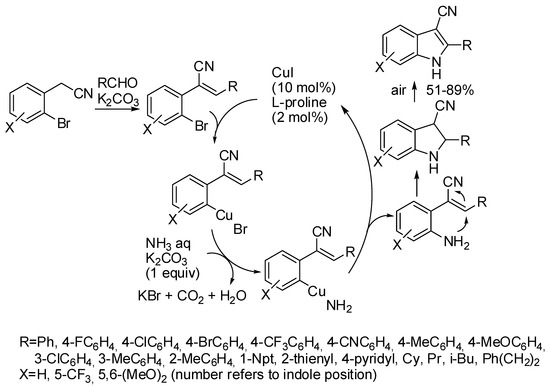
Scheme 10.
Synthesis of 3-cyanoindoles.
Ortho-iodoanilines reacted with a six-fold excess of β-ketoesters or β-diketone to give 2,3-disubstituted indoles (Scheme 11) [32]. The initial condensation to give enaminones seemed to be sensitive to the steric hindrance on the β-ketoester. In fact, ethyl 4,4-dimethyl-3-oxopentanoate was unreactive, and aryloylacetates gave low yields, together with 70%, 38%, and 49% yields of C-alkylated products. After condensation, the reaction is envisaged to proceed with a mechanism very similar to that depicted in the previous example. In addition, ortho-bromoanilines reacted in 66–78% yields, but required prolonged reaction times. Unsymmetrical diketones produced a mixture of regioisomers.
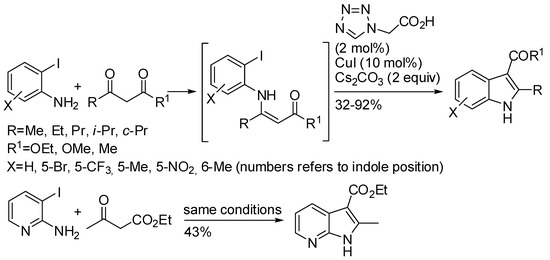
Scheme 11.
Reaction of ortho-iodoanilines and β-ketoesters or β-diketones.
The work of Yu, Chang et al. allowed the synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine and indole derivatives using CuI as catalyst and iodine as oxidant by another cross-dehydrogenative coupling reaction (Scheme 12) [33].
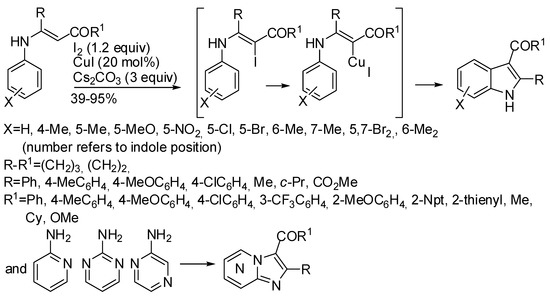
Scheme 12.
Synthesis of indole and imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine by cross-dehydrogenative coupling.
It should be noted that, under these reaction conditions, 2-aminopyridines reacted on the nitrogen atom, while, in the previous example [32], the reaction could be carried out also from anilines and ketones without significant lowering of the overall yields. 3-Iodo-2-aminopyridine closed the ring on the iodine-substituted position. The author explained this feature assuming that iodine produced a β-iodoenamide and not an iodoarene, and then the following steps contemplated the classical oxidative addition of Cu(I) to the iodide and a base-promoted cyclization. This assumption was then supported by DFT calculations using four different functionals, which demonstrated that the base deprotonates the enamino function and the copper favors the carbanion attack at the aryl moiety with respect to re-protonation; hydride transfer to the catalyst then completes the indole synthesis, in a very fast step; finally, the oxidant regenerates the catalyst [34].
Then the same reaction was mediated by NBS/CuCl (Scheme 13) [35]. Some features must be outlined:
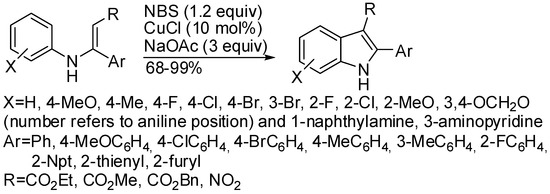
Scheme 13.
Oxidative cyclization of N-arylenamines.
- N-(3-bromophenyl)-β-enamino ester led to a mixture of 6-bromo- and 4-bromoindole in 29% and 61% yield, respectively, but N-(3-pyridinyl) or 3,4-(methylenedioxyphenyl)-β-enamino ester afforded exclusively the 4-aza- and the 5,6-(methylenedioxy)indole;
- 3-(2-furyl)-3-(4-methoxyphenylamino)acrylate gave the expected indole in 96% yield, but 3-(2-furyl)-3-(phenylamino)acrylate was unreactive;
- reduction of 3-nitroindoles with Zn/TMSCl afforded 3-aminoindoles, while reduction with H2/Pd/C in ethanol gave 3-(N,N-diethylamino)indoles in moderate to high yields.
3-Arylsulfonyl-2-trifluoromethyl-1H-indoles could show interesting biological activities, thus Dolbier and co-workers set up a two-step synthesis staring from methyl-phenylsulfones and trifluoroacetimidoyl chlorides. The trifluorometylimino-β-sulfonylaryl intermediates, which predominated over the enamino tautomers, were cyclized using copper(II) acetate (Scheme 14) [36]. In the envisaged mechanism, author claimed equilibrium between Cu(II) and Cu(I) salts and the latter was the true catalytic species.
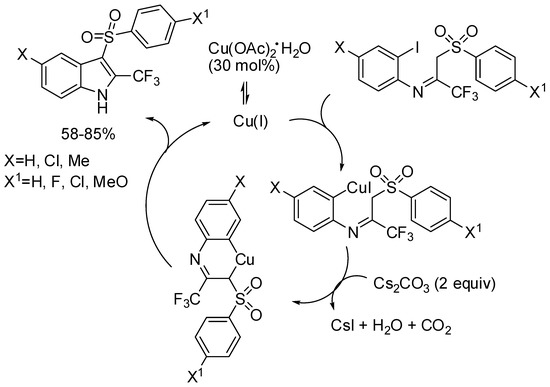
Scheme 14.
Synthesis of 3-arylsulfonyl-2-trifluoromethyl-1H-indoles.
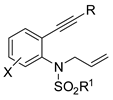
Aryl N-picolinoyl enamides in which the pyridyl group acted as traceless directing group were cyclized in a microwave assisted reaction under Cu(OPiv)2 catalysis and MnO2 as the oxidant (Scheme 15) [37]. When two possible regioisomers are available the less sterically encumbered was always mainly recovered. For instance, in meta-substituted arenes, 5- vs. 7-substituted indole ratio ranged from 49:1 to 10:1, while 2-naphtyl-substituted enamide gave a 5:1 benzo[f] vs. benzo[g] ratio. Under standard conditions thienyl and benzothienyl substrates were unstable, but the corresponding indoles could be recovered in low yields (41 and 19% yield respectively) by using stoichiometric Cu(OPiv)2 with conventional heating method. The reaction was conducted on 1.0 mmol scale with decreased yield (61 vs. 91%). N-picolinoyl was essential for the reaction. In fact, N-benzoyl derivative afforded oxazoles. Authors carried out some experiments to support the mechanism depicted in the scheme.
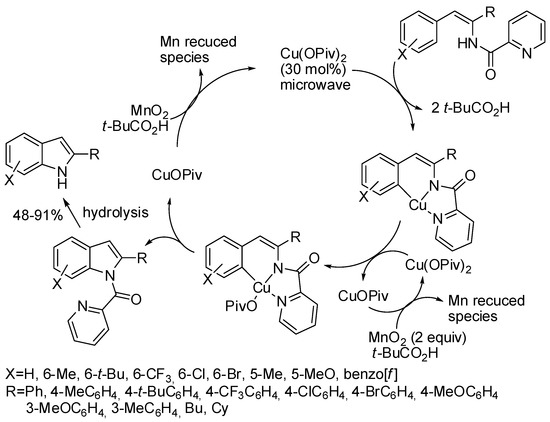
Scheme 15.
Cu-catalyzed intramolecular C–H amination.
The easy available 2-alkenylanilines underwent cyclization to 3-substituted indoles with Cu(OAc)2 in stoichiometric amounts (Scheme 16) [38]. In fact the reaction worked better when copper itself acted as the oxidant, with respect to its use in catalytic amounts in the presence of an external oxidant. The reaction suffered from steric hindrance, in fact, 4-substituted indoles as well as ortho-substituents in the 3-aryl moiety decreased significantly the yields. Moreover, 2-methyl-3-phenylindole was also recovered in the 33% yield. Mechanistic investigation ruled out a radical process, thus envisaging a pathway as described in Scheme 16. Notably, the reaction was scaled up to gram-scale.
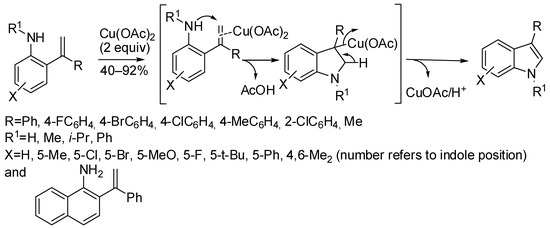
Scheme 16.
Cyclization of 2-alkenylanilines.
The indoloindole (5,10-dihydroindolo[3,2-b]indole) skeleton is a common building block for preparing various high-spin organic and OLED polymers. Several ancient synthetic strategies are known for their preparation, but recently a double cyclization of diarylalkyne sulfonamides has appeared in the literature (Scheme 17, Equation (1)) [39]. The tosyl group was found as the better amino protecting group, phenylsulfonyl, 4-chlorophenylsulfonyl and the mesyl protecting groups gave similar yields (77–83% yield), but the acetyl or Boc protecting groups were unreactive. In the surmised mechanism Cu(OAc)2 coordinates the triple bond, thus favoring the nucleophilic attack of tosylamino nitrogen atom. Then, in the second cyclization step Cu(OAc)2 serves as the oxidant as in the previous reaction (Scheme 16), but, conversely from there, where the reaction course was unaffected by radical scavengers, in this reaction radical scavengers inhibited the cyclization step. The reaction was successfully scaled up to gram scale.
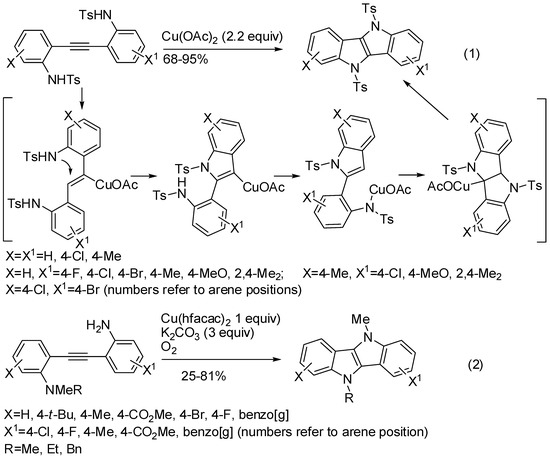
Scheme 17.
Synthesis of indoloindoles.
Very similar was the cyclization of 1-(2-aminophenyl)-2-(N,N-dimethylaminophenyl)acetylene (Scheme 17, Equation (2)) [40]. Conversely from the reaction of Du and co-workers, in which a strong electron withdrawing protecting group is necessary, here an intermolecular N-methyl transfer from the nitrogen atom of N,N-dimethylamine to the primary amine groups was found as the crucial step to give cyclization. Then oxygen provided the oxidation step. It should be noted that only the methyl group rearranged, in fact N,N-diphenylamino derivative was unreactive. Moreover, both 1-(2-aminophenyl)-2-(N-methylaminophenyl)acetylene and bis(N-methylaminophenyl)acetylene did not undergo the second cyclization step leading to 2-aminophenylindoles.
In a paper, in which many indole and indoline derivatives were prepared Yao and co-workers also synthesized 1,2-disubstituted indoles by reaction of N-substituted 2-iodobenzamides and 2-alkynylanilines (Scheme 18) [41]. N-benzyl substituted-2-iodobenzamide is less reactive and stable in the reaction conditions and gave the worse results.
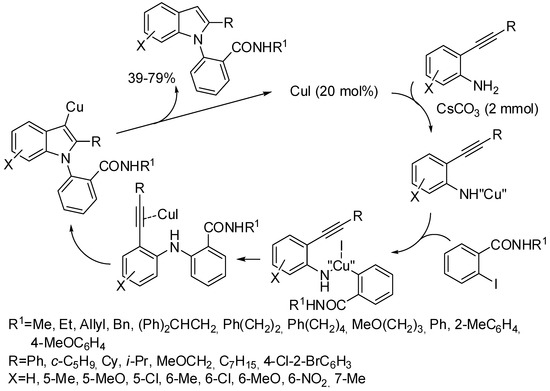
Scheme 18.
1,2-Disubstituted indoles from 2-iodobenzamide derivatives.
Yao and co-workers prepared 3-arylindoles from 2-bromoarylaminoalkanes under Cu(I) catalysis (Scheme 19) [42]. The starting materials were obtained in the same paper by Friedel–Crafts alkylation of bromo-substituted β-nitrostyrenes and arenes. The reaction worked only with electron donating groups on both starting aryl moieties and with chlorine derivatives on the aryl group not involved in the cyclization process. Sometimes air oxygen is not enough to oxidize the indolenine intermediate and therefore MnO2 had to be added. 2-Bromo-4-methoxy-1-(2-nitro-1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl)benzene did not cyclize under copper catalysis but it furnished 3-(2-bromo-4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-indole in 91% yield when refluxed with Fe (5 equiv) in AcOH/EtOH.
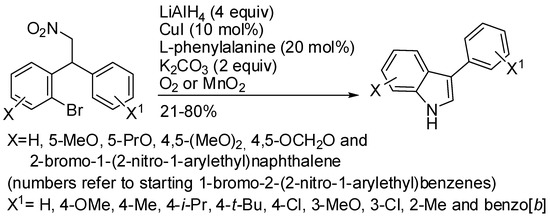
Scheme 19.
3-Arylindoles from nitroalkanes.
Finally, a copper catalyzed aerobic radical cascade reaction which involved benzylamines should be mentioned (Scheme 20) [43]. Benzylamines protected with electron-withdrawing groups were unreactive, while unprotected benzylamine partially decomposed under reaction conditions. Mixtures of isomers were obtained with both unsymmetrical biaryl amines (the isomers were easily separated in 36% and 44% yields) and meta-substituted benzylamines (5,6-Me2 vs. 4,5-Me2 ratio 1.8:1). Benzylamines, with different key motifs in biologically important molecules, were also effective in this indolization reaction, allowing the synthesis of potential drugs. However, a higher catalyst loading was required, because of the competitive copper coordination onto other heteroatoms. Authors performed test experiments to elucidate the mechanism depicted in scheme.
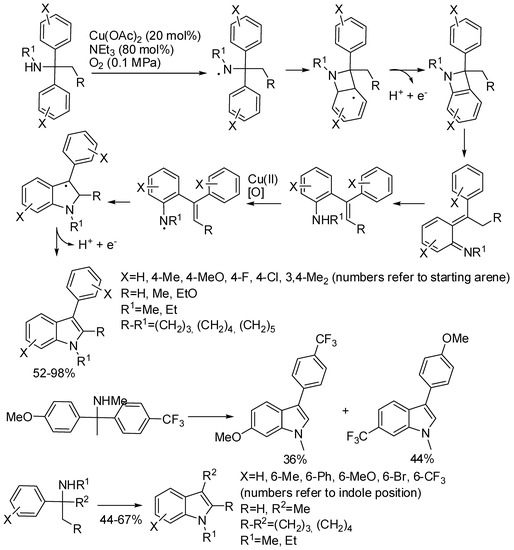
Scheme 20.
Copper-catalyzed aerobic [1,3]-nitrogen shift.
4. Gold
Hydroamination of alkynes is known to be easily performed under gold catalysis [44]. Moreover, the heterogeneous catalysis allows an easy recycling of the catalyst. Thus, commercial gold nanoparticles supported on titanium dioxide were successfully tested for the alkyne hydroamination [45]. In particular, the intramolecular hydroamination led to indoles (Scheme 21) and the gold nanoparticles were recycled five times without loss of efficiency. With aliphatic substituents on the other side of alkyne triple bond, an acid promoter [H3PO4·12WO3 (5 mol %)] was required. The scale-up of the reaction was not attempted for the intramolecular reaction, but only for the intermolecular version.
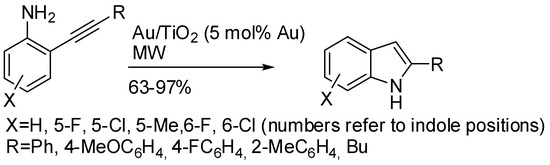
Scheme 21.
2-Arylindoles by gold nanoparticles catalysis.
Dual gold/ruthenium catalysis allowed a synthesis of 2,3-disubstituted indoles, which could be an alternative to the classical Larock indole synthesis, because milder and base-free reaction conditions are requested and the visible light for photoredox catalysis can be produced by a simple household source [46]. The reaction was scaled up to a gram-scale (86% yields). However, some aryldiazonium salts bearing methyl, dimethyl, naphthyl, 3,5-dioxomethylene, and 3-bromo-5-chloro substituents were unsuccessful in this reaction. Some experiments carried out by the authors prompted them to propose the mechanism depicted in Scheme 22.
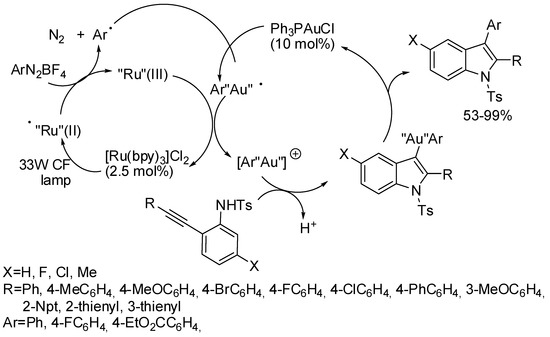
Scheme 22.
Indoles by photoredox/gold catalysis.
Another gold-catalyzed hydroamination involved NHC–gold complexes (Scheme 23) [47]. The reaction was widely applicable, but with two notable exceptions: 8-aminoquinoline and an alkyne substituted with a trimethylsilyl group were unreactive.
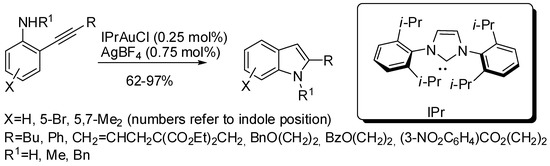
Scheme 23.
Hydroamination reaction catalyzed by NHC–gold complexes.
Gold complexes were tested in the cascade reaction of 2-(phenylethynyl)aniline and cyclohexanone [48]. The hydroamination to afford 2-phenylindole was exclusively obtained (95% yield) with 1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)imidazol-2-ylidene gold(I) triflate (IPrAuOTf). With binuclear catalysts 3-OTf2 and 2-OTf2 (Scheme 24) a mixture of 2-phenylindole and the cascade product was obtained in a 78 and 14% yield and a 25 and 75% yield, respectively.
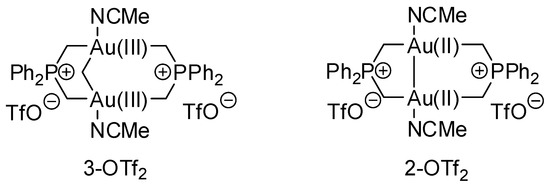
Scheme 24.
Gold catalysts for the cascade reaction of 2-(phenylethynyl)aniline and cyclohexanone.
Zhang had reported the gold-catalyzed tandem reactions of 2-alkynylarylazides with carboxylic acids [49]. Continuing his study in the time range of this review, he and his coworkers attempted the same tandem reaction with methane sulfonic acid in dioxane under t-BuXPhosAuNTf2, catalysis [50]. Surprisingly, they found the incorporation of a molecule of ring-opened solvent, and recovered 2-(2-((2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)oxy)ethoxy)ethyl methanesulfonate. The reaction was then extended to tetrahydropyran with good results (Scheme 25). When R was an alkyl group the yields were lower. With R = cyclopropyl, H and with oxetane, tetrahydrofuran, 2-phenyloxirane, the reaction gave a mixture of unknown side products. Moreover, in the reaction with 4,6-dichloro substituted azide, 5,7-dichloro-2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-ylmethanesulfonate was recovered in a 29% yield as a side product. The mechanism depicted in Scheme 25 was proposed by authors, but without experimental support.
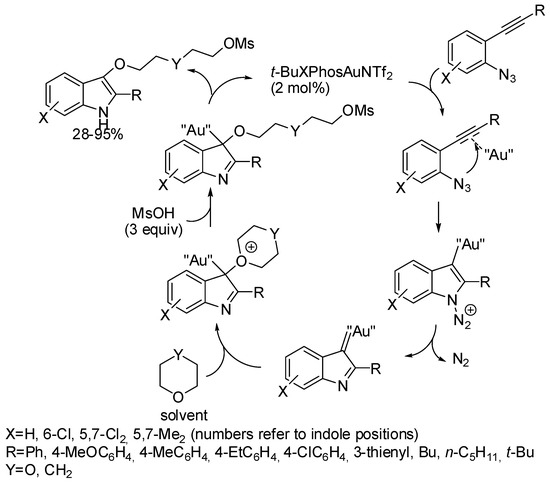
Scheme 25.
Indoles by gold-catalyzed cyclization of 2-alkynylarylazides.
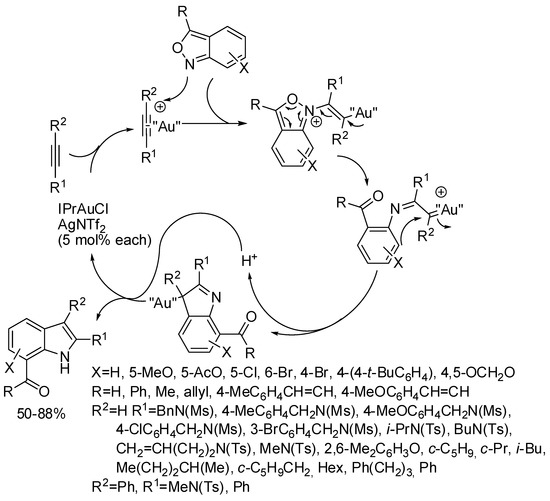
IPrAuCl promoted the synthesis of 2-substituted indoles from o-alkynylnitroarenes (Scheme 26) [51]. It should be noted that if 3-[(2-nitrophenyl)ethynyl]quinoline afforded the corresponding indole, 3-nitro-2-(phenylethynyl)pyridine did not close the pyrrole ring and only amine was recovered in 33% yield. Authors ascribed this different behavior to the strong coordination of pyridine ring and to the weaker coordination of quinoline with the gold atom, which should modify the envisaged reaction mechanism.
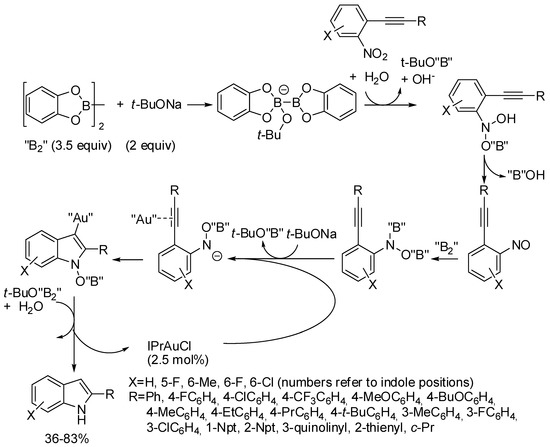
Scheme 26.
Indoles from 2-alkynylnitroarenes with diboron as reductant.
Unprotected 7-acylindoles, valuable biological active molecules and key intermediates in the synthesis of other important drugs, have been prepared by the gold-catalyzed reaction of anthranil derivatives with alkynes (Scheme 27) [52]. The key step of this reaction was envisaged as α-imino gold carbene. The reaction worked well with polarized alkynes such as ynamides and aryl alkynyl ethers, but among non-terminal ynamides, only phenyl-substituted ynamides reacted. The product from aryl alkynyl ether was also successfully converted into 7-formyloxindole, as well as products from ynamides were manipulated at the 7-formyl group, leading to 7-hydroxymethyl and 7-alkynylindoles. Since anthranils with electron-donating groups generally afforded higher yields, authors suggested an electrophilic aromatic substitution mechanism. Non-polarized alkynes needed the addition of 10 mol % MsOH to facilitate the deauration process and an excess of alkyne. 1-Phenyl-1-hexine led only to 2-butyl-3-phenyl-7-formylindole but in a 27% yield, owing to a competing hydride-shift pathway.
Scheme 27.
7-Acylindoles from annulation of anthranils with alkynes.
5. Palladium
Palladium-based methodologies are certainly the most famous transition metal catalyzed reaction for the synthesis of nitrogen heterocycles [5,7,9,11,13]. In the last two years, other methodologies have appeared in the literature. Palladium catalyzed α-arylation of carbonyl derivatives are other examples of the cross-dehydrogenative coupling reactions already encountered in the previous section. The efficiency of this reaction has been found deeply influenced by the steric and electronic properties of the palladium ligand. For instance, NHC/Pd catalyst was proven efficient in this reaction (Scheme 28) [53]. The reaction showed some interesting features:
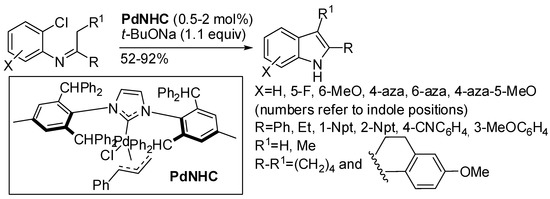
Scheme 28.
Pd-NHC catalyzed α-arylation of imines.
The steric hindrance seemed to have a positive effect on the reaction, because bulkier 1-naphthalene derivative was recovered in higher yield or after shorter times than 2-naphthalene derivative; a 10 mmol scale reaction afforded improved yield; the intermolecular one-pot from anilines and ketones did not afford clean reaction; reaction with chalcones leading to 2,3-diphenyl-indoles or with pyridine imines leading to 5- and 7-azaindole did not work; some products are important as drugs or for the synthesis of organic electronic materials; authors reported a detailed mechanism supported by computational studies and a set of experiments.
Solé and co-workers reported a domino four-step aza-Michael/α-arylation/Michael addition/β-elimination strategy to achieve 3-[2-(phenylsulfonyl)ethyl]indoles (Scheme 29) [54]. From the results of a previous similar synthesis of tetrahydroisoquinolines [55], the authors knew that, conversely from acrylates, the competitive Heck reaction did not interfere with the initial aza-Michael addition and that the sulfone α-arylation was the most important step to be optimized. Then, the authors found that the higher electrophilicity and the higher acidity of phenyl sulfone allowed recovering of higher yields than methyl sulfone. Finally, the mechanism of the α-arylation step was supported by density functional theory (DFT) calculations.
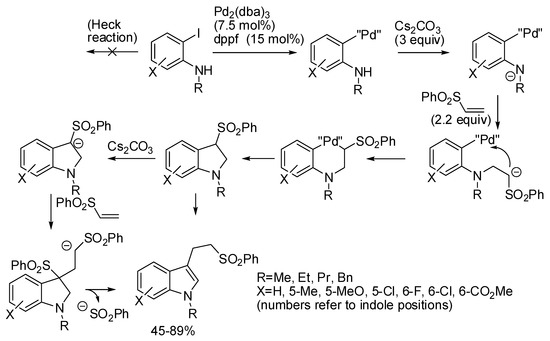
Scheme 29.
Three-component synthesis of 3-[2-(phenylsulfonyl)ethyl]indoles.
Gharpure studied the Heck reaction for the synthesis of benzo[1,4]heterocycles, and found that iodo aza-tethered vinylogous carbonates led to indoles instead of the expected oxazepines (Scheme 30) [56]. They also proposed the mechanism depicted in Scheme 30, after carrying out some test experiments.
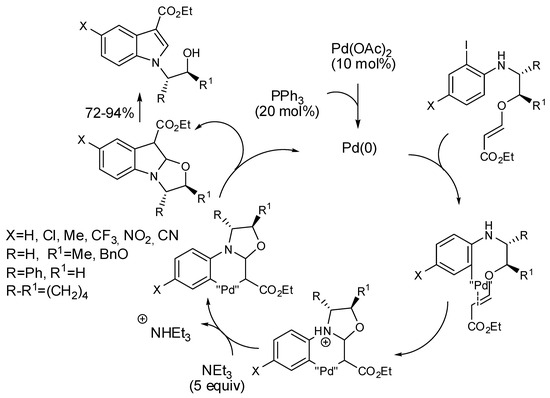
Scheme 30.
Unexpected formation of indoles.
In the previous section (Scheme 9) [30], the synthesis of indoles from α-aminonitriles and 2-halobenzyl halides has been described under copper catalysis. In the same paper, authors performed the reaction also under palladium catalysis; in fact with Pd(dppf)Cl2 (10 mol %) as the catalyst and sodium t-butoxide (3 equiv) as the base products were recovered in 4–94% yield. In particular, palladium catalysis revealed less efficient for N-alkyl substituted indoles and more efficient for electron-withdrawing substituted aryl groups in both R and R1 positions. Moreover, palladium catalysis allowed cyclization also on bromoarenes.
Recently, the synthesis of 1,2,3-trisubstituted indoles from α-diketones and N-substituted anilines has been reported (Scheme 31) [57]. The most relevant feature is the reductive environment, when other reactions involving imines or enamines required an oxidation step. With asymmetric diketones such as 2,3-pentanedione or m-substituted anilines, mixtures of products were recovered, the selectivity depending on the different stability of the enamines in the former case or from the steric hindrance of the 4- with respect to the 6-position of the final indole, in the second one. However, the reaction with substituted anilines (not reported in the scheme) was always incomplete and significant amounts of their α-ketoamine precursors were recovered. A possible explanation could be the electron-withdrawing effect of the substituents. In fact also MeO group was put in the meta-position, where it was unable to exert its donating power by resonance, but it exerts only inductive electron-withdrawing effect. The formation of an enamine in the first stage was demonstrated by the reaction of diphenylethanedione, in which only the reduction of the carbonyl group was observed. Therefore, the proposed mechanism expected the formation of a palladium hydride from the catalyst and the hydrogen atmosphere. On the other hand, ketone and aniline formed an enamine, followed by reduction to ketoamine. Its enolic form underwent palladium hydride addition, acid catalyzed dehydration, and aromatic electrophilic substitution. Finally, palladium hydride elimination led to indole and regenerated the catalyst.
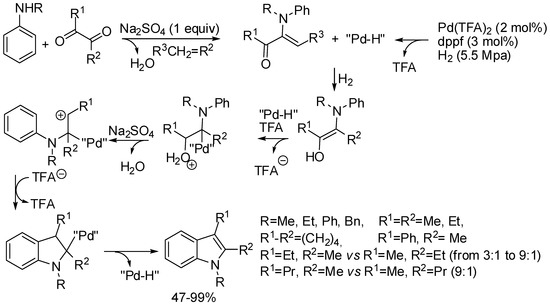
Scheme 31.
Synthesis of 1,2,3-trisubstituted indoles from α-diketones and N-substituted anilines.
The group lead by Chen and Cheng reported the indole formation in water from 2-(2-aminoaryl)acetonitriles with arylboronic acids, which are low-toxic, and air- and moisture-stable, thus important in green chemistry (Scheme 32, Equation (1)) [58]. The lowest yields were found in the reaction of relatively strong electron-withdrawing trifluoromethyl and acetyl groups. The same research group repeated the reaction with potassium aryltrifluoroborates (Scheme 32, Equation (2)) [59]. A reaction with 2-[2-(methylamino)phenyl]acetonitrile led to N-methyl indole in 37% yield. The reaction suffered from steric effects of substituents on the aromatic ring of the fluoroborate, but it can be scaled up to a gram scale (81% yields with longer reaction time). The obtained 2-arylindoles were then successfully submitted to Baeyer–Villiger oxidation, Baeyer–Villiger oxidation/amination and sulfenylation. The surmised mechanism expected the formation of a palladium-aryl species by palladium-boron transmetallation, followed by carbopalladation. The ketimine palladium species should be protonated by p-toluenesulfonic acid to regenerate the catalyst, and then the ketimine condensed under acidic conditions to indole. The acetyl group is cleaved by TsOH during the reaction course in Equation (1). It should be noted that potassium aryltrifluoroborates are more stable when stored, owing to the exceptionally strong boron–fluorine bonds, while arylboronic acids often are difficult to purify and quantify due to their spontaneous dehydration when stored. However, the reaction of boronic acids with 2-(2-aminophenyl)acetonitriles was also attempted and product was recovered in a 43% yield.
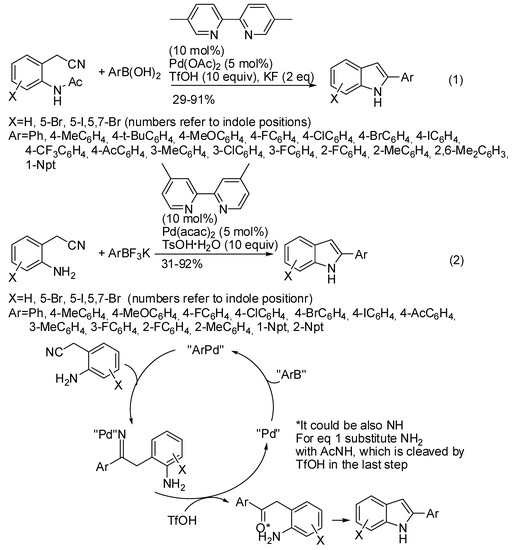
Scheme 32.
Palladium-catalyzed tandem addition/cyclization in aqueous medium.
Another approach to indoles by palladium catalysis is the Sonogashira coupling of 2-haloanilines with alkynes, followed by cyclization. The reactions, appeared in the literature in the time range of this review, are collected in Table 1.

Table 1.
Palladium catalyzed reactions of 2-haloanilines with alkynes to give indoles.
In the reaction reported in Table 1 entry 1 [60], the N-tosyl protecting group was found essential to obtain good results, but no explanation was given. The reaction is highly ortho-selective, in fact, only the ortho-chloro substituent underwent coupling in dichloroanilines, also in the presence of an excess amount of alkyne. This behavior allowed performing further reactions on the remaining chloro substituents. Authors attributed this ortho-selectivity to the formation of a hetero-aggregate and supported their hypothesis with ESI-TOF-MS analysis in the negative ion mode.
The reaction reported in Table 1 entry 2 was then applied to the total synthesis of other derivatives, among them the bisindole natural product (−)-aspergilazine A (Scheme 33) [61].
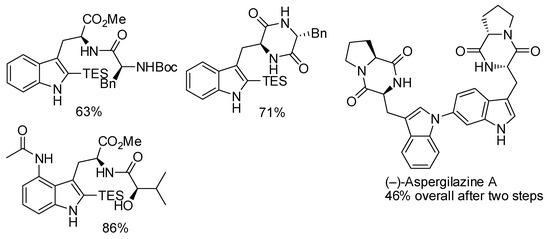
Scheme 33.
Some derivatives prepared with the reaction described in Table 1 entry 2 [50].
In the reaction reported in Table 1 entry 4 [63], the Sonogashira coupling was completely selective toward the iodine. In fact, 5-chloro-2-iodoanilne gave indole in high yields. Other N-protecting groups as well as free aniline did not give the indole and reactions stopped at the Sonogashira stage. Also complex structures such as carbohydrate and steroid derivatives were compatible (90% and 95% yields, respectively).
Some oxidative annulations of aniline derivatives have been also reported. For instance, anilines underwent addition to electron-withdrawing substituted internal alkynes to give enamines. In the presence of a Pd-catalyst these enamines cyclized by double C–H activation and oxygen acted as the oxidant to yield indoles in one pot manner (Scheme 34) [65].
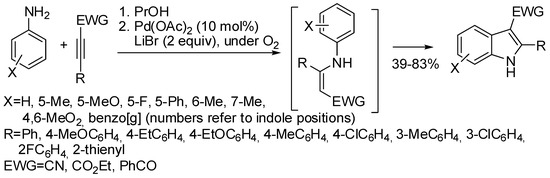
Scheme 34.
One-pot synthesis of indoles from electron-withdrawing substituted alkynes and anilines.
Moreover under palladium catalysis, another oxidative annulation was obtained by reaction of N-Ts-anilines and styrenes (Scheme 35) [66]. Cupric acetate in air worked as the oxidant (the use of an inert gas such as argon led to lower yield). The addition of benzoquinone increased yield but it was demonstrated ineffective as co-oxidant. 3-Arylindoles are the main products, but often some detectable amount of 2-arylindoles was found (3/2 ratios ranging from 100:0 to 91:9). Meta-alkoxy substituted anilines gave exclusively the 6-substituted indole, whereas the reaction of 2-naphthylamine resulted in a 5:1 mixture of benzo[e] and benzo[f]indole (85% overall). N,N′-bistosyl-1,3-diaminobenzene reacted with a large excess of 4-nitrostyrene leading to the corresponding 1,7-dihydropyrrolo[3,2-f]indole in 57% yield as a single regioisomer. Also secondary alkyl-substituted alkenes gave good yields of 3-alkylindoles, while primary alkyl derivatives led to a complicated mixture. Some transformations of the obtained indoles were successfully performed. Moreover, some test experiments to elucidate the mechanism were carried out, in particular authors demonstrated that only 2-(1-phenylethen-1-yl)aniline cyclized under the reaction condition (98%), thus they proposed the mechanism depicted in the scheme.
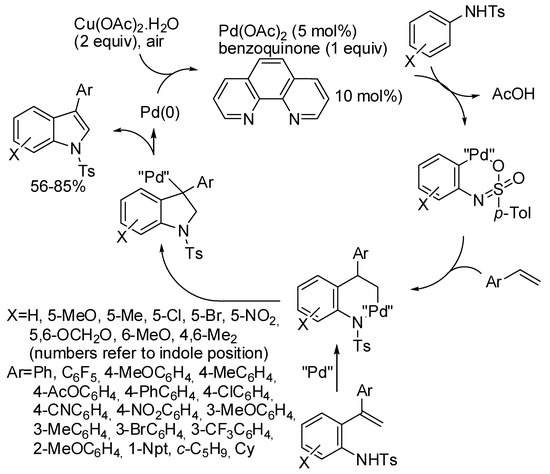
Scheme 35.
Palladium-catalyzed regioselective synthesis of 3-arylindoles.
Palladium catalyzed cyclization of alkynylanilines and derivatives are widely studied in the time range of this review and the reported reactions are collected in Table 2.

Table 2.
Cyclization of alkynylanilines under palladium catalysis.
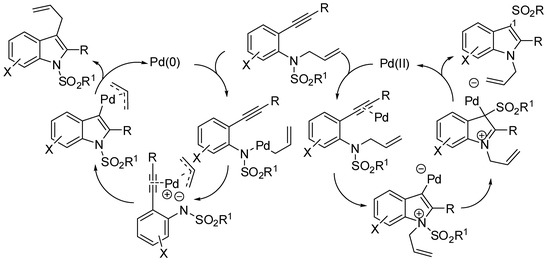
Scheme 36.
Surmised mechanism for the reaction described in Table 2 entry 1 [56].
The synthesis of tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indoles by Chen, Han and Lu (Table 2 entry 4) [69] is a valuable alternative to the classical oxa-Pictet–Spengler reaction generally used to synthesize these compounds. Moreover, it should be noted that anilines bearing either Br or CF3 substituents gave only 50% and 44% yields, respectively, in the non-asymmetric reaction, but 72% and 80% yields, respectively, in the asymmetric reaction. Authors explained this difference as a consequence of a different coordination ability of the asymmetric ligand to palladium. The same reason was claimed to explain the non-reactivity of 2-substituted cyclohexanones in the asymmetric version. Regarding the mechanism, a control experiment demonstrated that the reaction was a tandem process, and not a one-pot, two-step reaction. In fact, 2-substituted indoles did not cyclize under the reported reaction conditions. As a consequence, after formation of the classical 3-palladium indole, the less hindered C=C inserted into the carbon–palladium bond. Then protonation of this intermediate regenerated the catalyst and released the product.
The reaction to pentaleno[2,1-b]indoles is very similar (Table 2, entry 5) [70], but with some significant differences: such as mesyl, protecting group gave similar results as tosyl, benzoyl gave only an unidentified product, acetyl did not react; and the asymmetric reaction gave low enantiomeric excesses.
Finally, the reaction reported in the last entry of Table 3 [73], allowed the synthesis of 1H-indole-3-sulfonates, that the same research group unsuccessfully attempted under gold catalysis (see gold section [39]).

Table 3.
Palladium catalyzed oxidative cyclization of substituted arenes to indoles.
The cross-coupling reaction of 2-alkynylarylazides with aryl bromides allowed the synthesis of indoles (Scheme 37) [74]. It should be noted that, conversely from Cacchi’s aminopalladation/reductive elimination of 2-alkynyltrifluoroacetanilides [75], simple 2-alkynylaniines did not cyclize under these reaction conditions. On the other hand, iminophosphorane formation has been known for a long time to occur when phosphine and azides react together. On these basis, authors proposed two possible decompositions of the cyclized intermediate obtained from attack of arylpalladium(II) activated triple bond by the nitrogen of the phosphinimine moiety: a reductive elimination followed by hydrolysis or the formation of a palladium(II) carbene species, migration of the aryl group, isomerization, protonation and reductive formation of the product and regeneration of the catalyst.
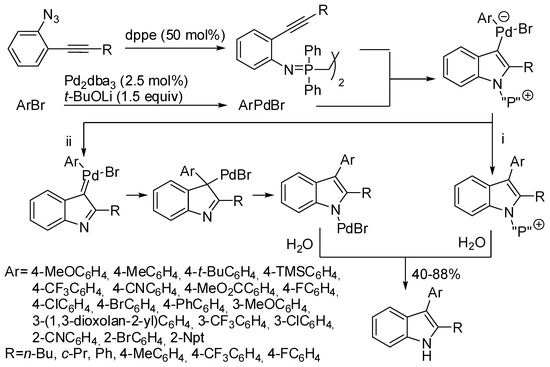
Scheme 37.
Synthesis of indoles from in situ generated phosphinimine.
The Cadogan–Sundberg synthesis, from reductive cyclization of o-vinylnitroarenes is another method of indole synthesis starting from nitrogen-substituted arenes. Classically, the reaction is heated in boiling triethylphosphite, but it was performed also employing carbon monoxide as the reducing agent. Recently, the reaction was conducted in a continuous flow reactor (Scheme 38) [76]. However, if the interfacial areas are much larger in a continuous flow reactor than in a conventional stirred tank, thus increasing reaction rates, the CO reduced palladium(II) to palladium(0) nearly instantly and created a palladium cluster deposit, which stopped the reaction of the less reactive o-vinylnitroarenes at very low conversions. Conversion was increased by adding 1,10-phenantroline and tributylamine to stabilize palladium and mixing CO and o-vinylnitroarenes at a high temperature, before encountering the catalyst. Only the indole was detected in the crude reaction, thus column chromatography is unnecessary. The reaction was scaled up to 12 mmol of substrate, producing 1.3 g/h (84% yields) of product.
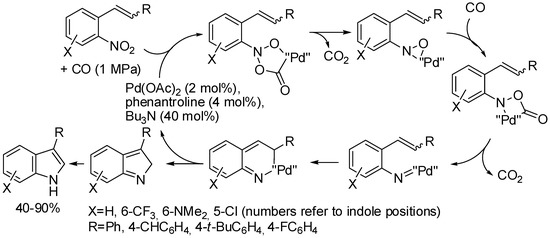
Scheme 38.
Continuous flow synthesis of indoles by reduction of o-vinylnitroarenes.
A series of 1,4-, 1,3-, and 2,3-bis(2-nitroaryl)-1,3-butadienes led to the corresponding 2,2′-, 2,3′-, and 3,3′-biindoles, in another palladium catalyzed, carbon monoxide reduction of nitroarenes (Scheme 39) [77]. The reaction was also carried out with 1,2-bis(2-nitroaryl)ethenes and 1,1-bis(2-nitroaryl)ethenes, but complex reaction mixtures were recovered, in which the cyclized product arising from carbon monoxide insertion was the most abundant.
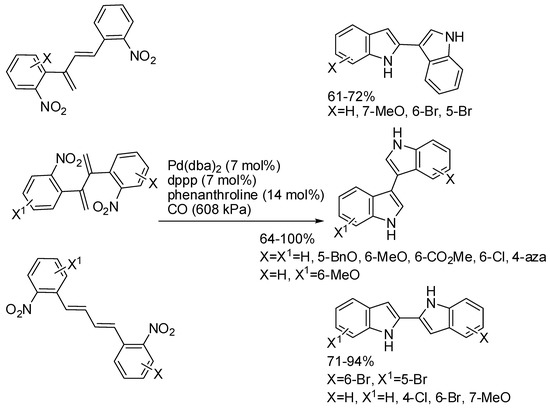
Scheme 39.
Double palladium catalyzed reductive cyclization.
In the first part of this section some two-component oxidative couplings and cyclizations and in the previous sections some oxidative cyclizations of substituted arenes to indoles have been described. In Table 3 are summarized the examples of oxidative cyclization of substituted arenes appeared in the literature in the time range covered by this review.
Choroindole prepared accordingly to the procedure described in Table 3 entry 1 [76] was then successfully submitted to some C–C cross-coupling reactions. About the mechanism, after coordination of palladium to nitrogen, this species can then ortho-metallate the arene. Subsequent C–N reductive palladium elimination led to indole and to a Pd(0) species, which is finally oxidized by O2 to regenerate the catalyst.
After conducting some test experiments, authors proposed the mechanism depicted in Scheme 40 for the divergent synthesis reported in Table 3 entries 4 and 5.
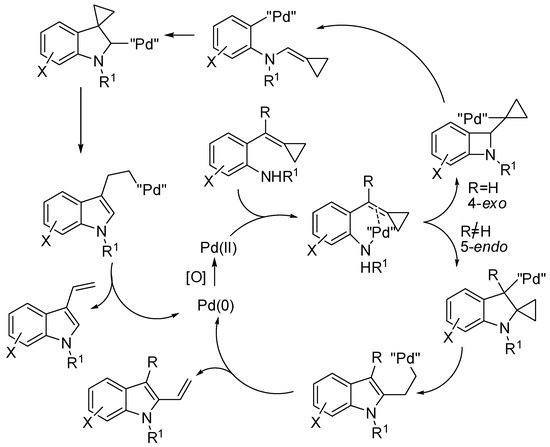
Scheme 40.
Mechanism of the cyclization of aniline-tethered alkylidenecyclopropanes.
Some products, obtained from the reaction reported in Table 3 last entry [81], were prepared in large scale and then used as building blocks for the formal synthesis of drug Alosetron and a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist.
In Table 3 entry 2 [79], the synthesis of indole fused coumarin derivatives has been already reported. However, the reaction needs the preparation of the amino coumarin starting material. Hajra was able to prepare the same derivatives by one-pot procedure starting from commercially available coumarins and anilines [82]. Reaction conditions are very similar (the only exception was the use of oxygen atmosphere, instead of air), and 19 examples were reported with yields ranging from 53 to 81%. 3-Methyl aniline gave 9-methylchromeno[4,3-b]indol-6(11H)-one and 7-methylchromeno[4,3-b]indol-6(11H)-one in 2:1 ratio.
In this review, we encountered many reaction in which the directing group is covalently bound to the substrate, but recently, some reactions, in which transient directing group are used, have appeared in the literature [83]. Moreover, C–H functionalization can be extended to remote positions. An instance of this strategy allowed the synthesis of spiropalladacycle via an intramolecular carbopalladation followed by C–H activation, then quenched by alky halides [84]. The reaction was mainly studied for benzofurans, but some N-substituted indoles were also prepared (Scheme 41).
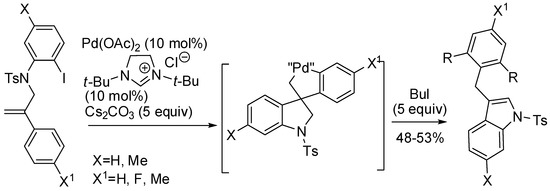
Scheme 41.
Remote C–H alkylation and C–C bond cleavage.
The importance of trifluoromethyl substituted indoles has been already outlined in this review (see Scheme 14) [36]. Another example of their synthesis was reported by Pedroni and Cramer under palladium catalysis [85]. They started from trifluoroacetimidoyl chlorides derived from 2-methylanilines (Scheme 42). The authors found a drastic influence of reagent concentration, especially when they attempted a scale-up of the reaction. They found an optimum concentration at 0.25 M, allowing scaling-up to 2.5 g of starting material and recovering indole in a 77% isolated yield.
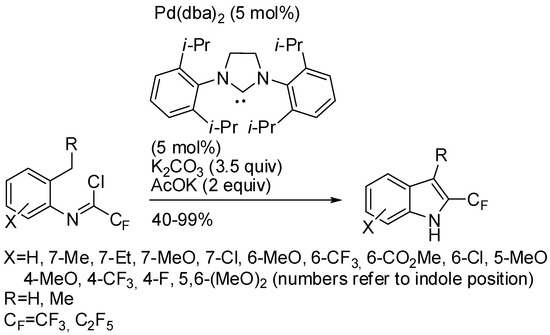
Scheme 42.
2-(Trifluoromethyl)indoles via Pd(0)-catalysis.
The use of gaseous CO2 as inexpensive and non-toxic C1 source allowed the preparation of indole carboxylic acids starting from of N-allenyl-2-iodoanilines (Scheme 43) [86]. Some experiments were carried out before the authors proposed the catalytic cycle depicted in scheme. Moreover, some transformations the reactive exo-olefin allowed the preparation of many 3-substituted indole-2-carboxylates and in particular the key intermediate for the synthesis of strychnocarpine, a biologically active β-carboline alkaloid.
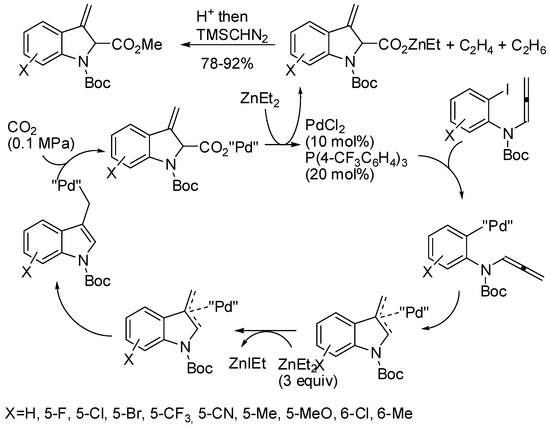
Scheme 43.
Palladium-catalyzed intramolecular arylative carboxylation of allenes.
Attempting the synthesis of an eight-membered ring by reaction of N-tosylhydrazones and bromonitrobenzenes, Hamze and coworkers discovered an unexpected cyclization to indole (Scheme 44) [87]. The reaction mechanism was elucidated by calculating the energy surface by DFT calculation at B3LYP/6-311G(d,p) level. Some compounds were then evaluated as potential chemotherapic agents and 2-[3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-1H-indol-1-yl]aniline displayed potent activity at nanomolar concentrations against human colon carcinoma cell line.
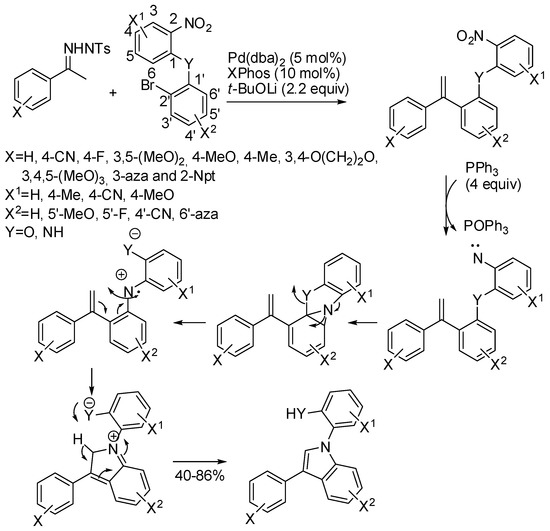
Scheme 44.
Reaction between N-tosylhydrazones and bromonitrobenzenes.
Syntheses of indoles that at the same time assemble both benzene and pyrrole rings are quite rare. One is the intramolecular Diels–Alder cycloaddition of 2-amidofurans recently applied in an eight-step total synthesis of (−)-cycloclavine (the cyclization step was obtained in 48% yield, without any metal catalyst) [88]. A recent modification took instead advantage from the formation of a π-allyl palladium complex (Scheme 45) [89]. The product formation is justified by either a Diels-Alder cycloaddition or a stepwise Friedel-Craft reaction and the authors did not present evidence in favor of one or the other mechanism.
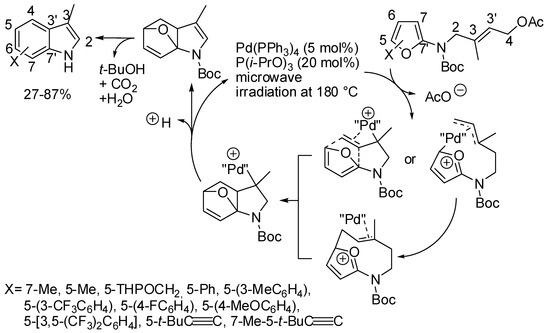
Scheme 45.
Pd(0)-catalyzed cascade formation of indoles from furans.
6. Rhodium
Cyclization of 2-alkynylanilines has been largely considered in the previous sections and will be further described in the next sections of this review as an efficient and versatile method for construction of 2-substituted indoles.
Methods for the one-pot synthesis of 2,3-disubstituted indoles are less common, an instance being that reported in Table 2 entry 6 [71]. Another method has been reported by Inamoto by means of a rhodium catalyzed cyclization of 2-alkynylanilines in the presence of isocyanates (Scheme 46) [90]. Although the authors did not describe a probable mechanism, they suggested a pathway very similar to that proposed by Yanada [71]. However, it should be noted that Inamoto justified his statement by the unreactivity of 2-substituted indoles under his reaction conditions [90], while Yanada exactly by the arylation of 2-substituted indoles under palladium catalysis [71].
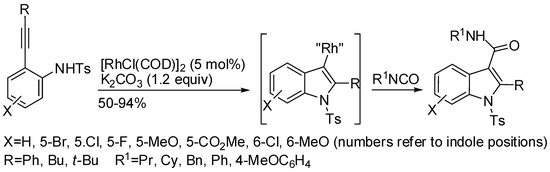
Scheme 46.
Cyclization of 2-alknylanilines in the presence of isocyanates.
Another rhodium(III)-catalyzed synthesis which started from 2-alkynylaniline was the cascade cyclization/electrophilic amidation using N-pivaloyloxylamides as the electrophilic nitrogen (Scheme 47) [91]. The reaction was also useful to prepare valuable compounds because the product can undergo to several transformations.
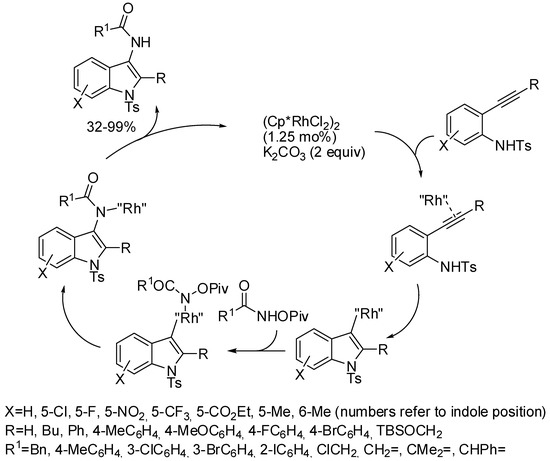
Scheme 47.
Rhodium(III)-catalyzed for the synthesis of 3-amidoindoles.
Recently a mechanochemically induced indole synthesis in ball mills has been reported (Scheme 48) [92]. The reaction did not required any solvent or heating and oxygen was the oxidant thus reducing amounts of copper(II) salt required. Mechanochemical conditions could be employed also to efficiently remove the acetyl protecting group (90% milling with 2.0 equiv of KOH). The only significant drawback was the low yield (9%) with a dialkyl-substituted alkyne.
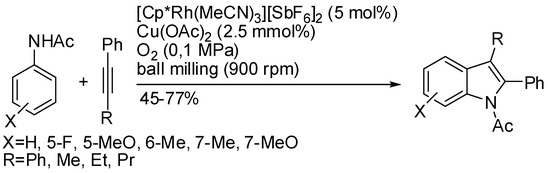
Scheme 48.
Mechanochemical synthesis of indoles.
Under rhodium catalysis, other cyclizations promoted by traceless labile directing groups have been described (see Scheme 1). An example is the rhodium catalyzed annulation of tertiary aniline N-oxides, which simultaneously allowed C–H activation, oxygen-atom transfer, and N-dealkylative cyclization in good yields [93]. The envisaged mechanism is depicted in Scheme 49, but alternative pathways were not ruled out by the authors.
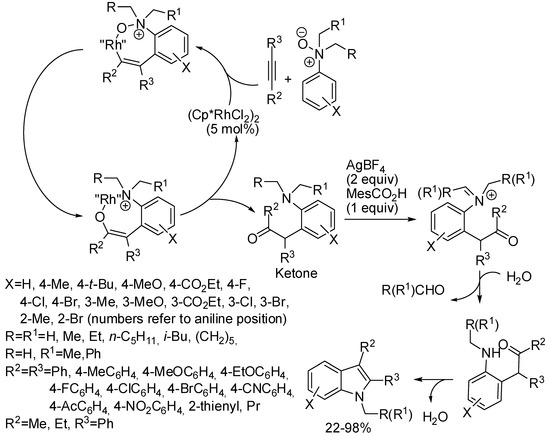
Scheme 49.
Rhodium-catalyzed annulation of tertiary aniline N-oxides.
The reaction showed some interesting features:
- N-oxides with two different alkyl groups were not selectively cleaved (N-ethyl vs. N-methyl 1.6:1 and N-benzyl vs. N-methyl 4.6:1);
- cyclization on meta-substituted aniline N-oxides always occurred at the less hindered position (6-substituted indoles) except for m-OMe derivatives which gave a nearly 1:1 mixture of 4- and 6-isomers;
- ortho-bromoaniline N-oxide gave partial debromination (33% and 5% yields of 7-bromo e 7-unsubstituted indole respectively);
- ortho methylaniline N-oxide gave 49% and 24% yields of indole and uncyclized ketone, respectively;
- from aryl alkyl-disubstituted alkynes the expected isomer with the aryl group in the 2-position was exclusively recovered;
- octyne gave indole with difficulty (22% yield, together with 40% of ketone);
- N-oxides of naphthylamines, strong electron-withdrawing 4-substituted anilines, N-methyldiphenylamine, and 1-ethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline did not react;
- a gram scale reaction was performed recovering 1.28 g of product (85% yields).
A method contemplating a nitrogen traceless directing group, namely hydrazine, was reported by Zhu (Scheme 50) [94]. Mixtures of 6- and 4-substituted indoles were obtained from meta-substituted hydrazines, in particular only 6-methyl indole (79%), and 0.15:1 and 0.08:1 4/6 ratio for fluoro and chloroindoles (76% and 73% overall yield), respectively. The most relevant feature was the easy scale up to a 13.4 g scale (60% yield) at a very low catalyst loading ([Rh] 0.01 mol %/[Ag] 0.1 mol %). Moreover, spectroscopic evidence of the five-membered rhodacycle intermediate generally envisaged in these reactions was obtained.
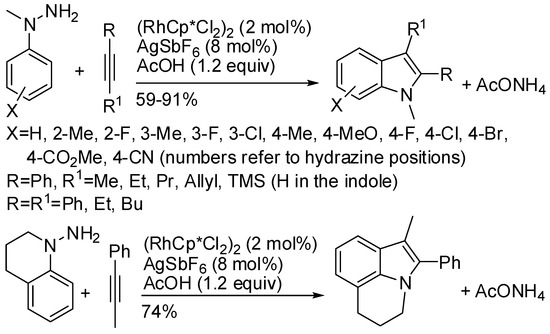
Scheme 50.
Synthesis of indoles with amino traceless directing group.
N-Substituted indole derivatives were also obtained from other hydrazine derivatives such as phenidones via Rh(III)-catalyzed C–H activation in tandem with the N–N bond cleavage (Scheme 51) [95]. Asymmetric acetylenes gave only single regioisomers, very likely by the control of the nucleophilic addition of the Rh–C bond to alkyl–aryl acetylenes. One of the prepared products was then used as key intermediate for an economical route to access a known potent anticancer drug.
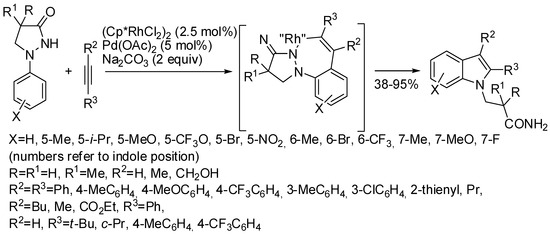
Scheme 51.
Synthesis of N-substituted indole derivatives from phenidones.
Other Rh(III)-catalyzed C–H bond activations were based on carbene migratory insertion, thus employing diazo compound and anilines as starting compounds for the reaction. As for alkynes, reaction involving simple anilines will be described before reaction of traceless directing groups. For instance, Rh(III) catalyzed the cyclization of pyrimidyl-substituted anilines and diazo compounds. Two similar protocols have been reported for the regioselective synthesis of indole-3-carboxylic acid esters (Scheme 52, Equations (1) and (2)) [96,97]. The main features are:
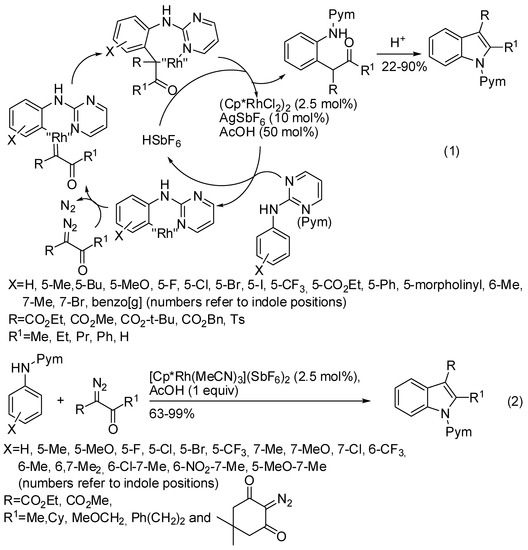
Scheme 52.
Indole derivatives from pyrimidyl-substituted anilines and diazo compounds.
- Both reactions gave only 6-substituted indoles from meta-substituted anilines and Wang [97] showed that 2,5-substituted substrates were unreactive, thus demonstrating that regioselectivity was driven by steric factors.
- Both research groups performed also some experiments to support the mechanism and envisaged the same mechanism as depicted in Scheme 52.
- The pyrimidyl group could be readily removed by treatment with NaOEt in DMSO during 24 h, but at 100 °C Wang recovered ethyl 2-methyl-1H-indole-3-carboxylate in 85% yield [97], while at 120 °C Lin and Yao obtained also the decarboxylation and 2-substituted N-H free indole in 71% yield [96].
- On the other hand, Wang was able to selectively remove the C-3 ester group in 82% yield, and then the pyrimidyl group in 80% (64% overall) [97].
- α-Diazomalonates did not cyclize under both conditions, but Lin and Yao [96] recovered alkylated anilines from dimethyl 2-diazomalonic esters, methyl 2-diazo-2-(phenylsulfonyl)acetate and ethyl 2-diazo-2-(diethoxyphosphoryl)acetate in 30–47% yields.
- It should be noted that Lin and Yao reported that the diazo derivative of Meldrum’s acid was completely unreactive [96], while Wang obtained indole from 2-diazo-5,5-dimethylcyclohexane-1,3-dione in 67% yield [97], thus demonstrating that is the second ester group which prevent the cyclization to indole.
- Lin and Yao [96] obtained 1.16 g (82% yields) by scaling up their reaction.
- Lin and Yao [96] further utilized the pyrimidyl group as directing group for C-7 functionalization and obtained many 7-substituted indoles in 44–87% yields.
- Lin and Yao [96] successfully performed the reaction of α-diazo-β-aldehyde esters.
While methyl 2-diazo-2-(phenylsulfonyl)acetate only alkylated N-pyrimidylanilines, 2-anilinopyridine and sulfonyl diazoesters led to the formation of oxindole derivatives (Scheme 53) [98].
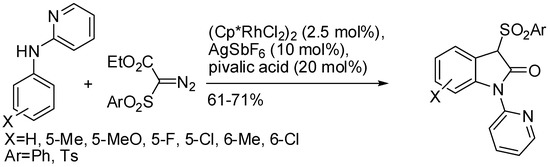
Scheme 53.
Oxindole derivatives from pyridyl-substituted anilines and diazo compounds.
1-Aminoindoles are an important class of indoles in medicinal chemistry. Traditional methods required the synthesis of the indole nucleus and then its amination with unsafe reagents [99,100]. The transition-metal-catalyzed C−H activation represents a valuable and less dangerous alternative to their synthesis.
However, reported syntheses used the harshly removable N-acetyl protecting group on the nitrogen atom not involved in the ring closure [101,102]. Therefore, in the last two years, easily removable protecting groups have been introduced. One instance is represented by the rhodium-catalyzed cascade reaction of aryl hydrazines, diazo compounds and ketones (Scheme 54) [103]. Pre-formed hydrazone gave the product, thus demonstrating its formation in the first reaction step. It should be noted that no Fisher indolization product was recovered, but the second nitrogen atom served as the directing group, in a mechanism, which authors proposed very similar to that depicted in Scheme 52. Among meta-substituted phenylhydrazines, only 3-fluoro gave a mixture of isomers (1:2.8 6- vs. 4-substituted indole ratio in 72% total yield), either for less steric request or for an enhanced acidity of the hydrogen atom near the fluorine, by ortho-directing effect. The reaction worked well with different diazoacetoacetates (methyl, iso-propyl, tert-butyl and benzyl gave products in 52–84% yields), or diazoalkanoates but did not work with diazo benzoylacetate or diazo diketones. Although imine is a well-known labile protecting group, its removal was not attempted.
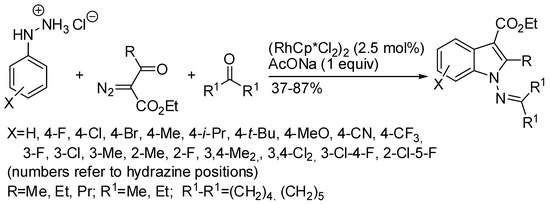
Scheme 54.
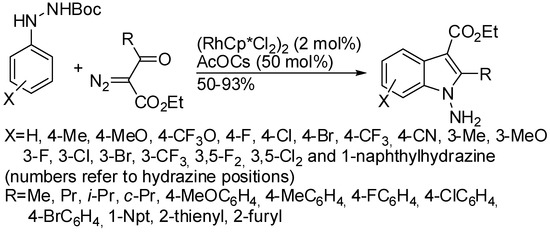
1-Aminoindoles via Rh(III)-catalyzed three-component annulation.
The coupling of Nβ-Boc-Nα-arylhydrazines with diazoketoesters instead afforded free N-amino indoles (Scheme 55) [104]. Authors demonstrated that Boc-deprotection was the last stage of the reaction mechanism. With meta-substituted phenylhydrazines, a mixture of 6- and 4-substittuted indoles in 1:0.03, 1:0.15, 1:0.15 ratios was recovered for methoxy, chloro and bromo derivatives, respectively, while only 6-substituted indoles from methyl, fluoro and trifluoromethyl derivatives.
Scheme 55.
Synthesis of unprotected 1-aminoindoles.
The dimethylamino urea framework was also used as the directing group and the reaction of N-arylureas with α-diazo β-keto or α-diazo β-aldehyde esters allowed the synthesis of 2,3- or 3-substituted indoles (Scheme 56) [105]. Deprotection of the urea to free-NH indoles was successfully performed both with TBAF (91%) and with anhydrous NaOH in EtOH (85%). The plausible mechanism was similar to that depicted in Scheme 3 and was supported with some experimental evidence.
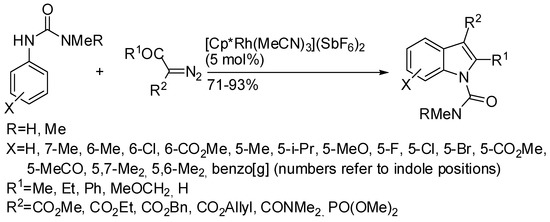
Scheme 56.
Indole derivatives from N-arylureas and α-diazo-β-keto esters.
Reactions, which released the directing group, thus leading to unprotected indoles, are also known, but they are obviously less atom economic. Some of them eliminated the directing group to form the pyrrolic double bond; other used classical traceless directing groups. For instance, imidamide directing group belongs to the first class, releasing acetamide to aromatize the indole skeleton (see mechanism depicted in Scheme 57) [106]. In fact, the same indole was recovered from the reaction of ethyl 2-diazo-3-oxo-butanoate, -pentanoate, and -3-phenylpropanoate. Methyl, benzyl, t-butyl 2-diazo-3-oxobutanoate and α-diazo acetylacetone gave indoles in 51−90% yields. It is worth of note that meta-substituted imidamides exclusively led to 6-substituted indoles except in the 3-fluoro derivative, which exclusively afforded 4-fluoroindole, but the author did not explain why. Two of the prepared indoles were then efficiently converted into an analogue of a known serotonin antagonist and into a known anti-inflammatory and analgesic indole.
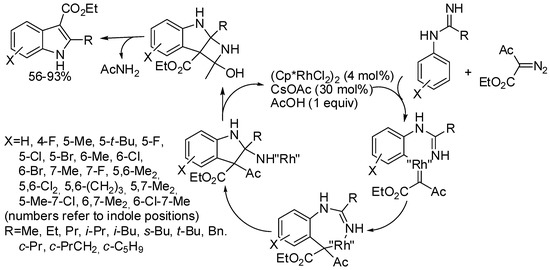
Scheme 57.
Rh(III)-catalyzed indolization of imidamides and diazo ketoesters.
An elimination of acetic acid occurred also in the Rh(III)-catalyzed reaction of nitrones with diazo compounds (Scheme 58) [107]. Authors investigated other diazo-derivatives and found that diazomalonate did not react, while methyl 2-diazo-3-oxo-3-phenylpropanoate eliminated benzoic acid as well as methyl 2-diazo-2-(dialkoxyphosphoryl)acetates dialkoxyphosphoric acid. From literature and some experiments to support a plausible mechanism, authors finally assembled the mechanism depicted in Scheme 58.
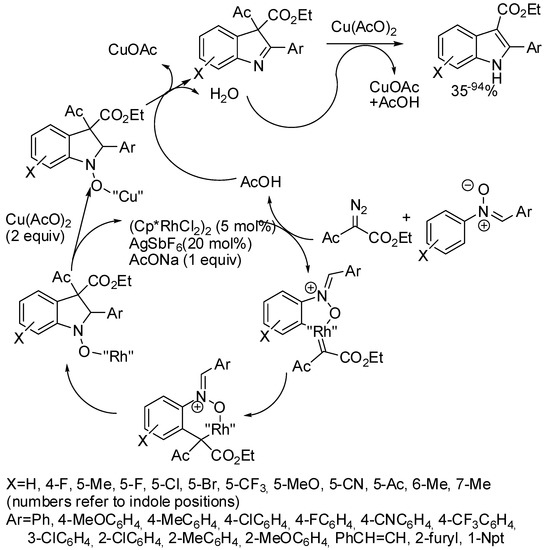
Scheme 58.
Rh(III)-catalyzed synthesis of indoles from nitrones and diazo-acetoacetate.
The reaction of N-nitrosoanilines with alkynes has been described in this review under cobalt (Scheme 4) catalysis. However, Rh(III)-catalyzed also the reaction with α-diazo-β-keto compounds (Scheme 59) [108]. The nitroso group is the only true traceless directing group described in this section. The reaction was sensitive to the bulkiness of the N-substituents and of the arene. For instance N-Et and N-i-Pr derivatives gave products in 84% and 61% yields, respectively, with respect to an 88% yield recovered from the corresponding N-Me derivative. Moreover, ortho-substituted N-nitrosoanilines gave exclusively 6-substituted indoles except for 2-fluoro N-nitrosoaniline, which led to 7-fluoroindole. The reaction of N-nitroso-tetrahydroquinoline afforded the expected product in a 67% yield. The authors performed reactions to obtain information about the mechanism and they proposed a mechanism in agreement with the general mechanism depicted in Scheme 1.
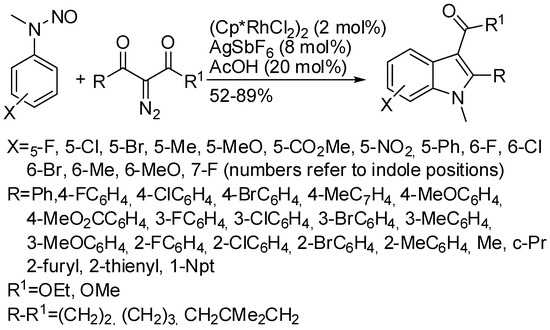
Scheme 59.
Rh(III)-catalyzed synthesis of indoles from N-nitrosoanilines and diazo ketoesters.
Rh(III) complexes catalyzed the reaction of azobenzenes with vinyl ketones or N,N-dimethyl acrylamides to 2-acylindoles (Scheme 60) [109], while vinyl esters led to indazoles. The reaction chemospecifically releases a mole of aniline. In fact, only 4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylaniline is released from 4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-4′-methoxyazobenzene and from 4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl-4′-methoxycarbonylazobenzene. Meta-substituted azobenzenes gave exclusively 6-substitutted indoles. Chalcone did not react and other vinyl ketones leading to 2,3-disubstituted indoles were not tested. A known antimitotic agent was achieved in gram scale using this method. Some mechanistic experiments allowed the surmising of the mechanism depicted in Scheme 60.
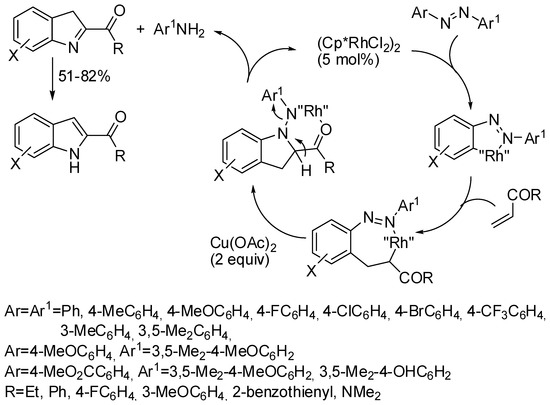
Scheme 60.
Rh(III)-catalyzed reaction of azobenzenes with vinyl ketones or N,N-dimethyl acrylamides.
The reaction was then extended to both (Z) and (E)-olefins either symmetrical or asymmetrical [110]. Addition of AgSbF6 (10 mol %) and Cu(OAc)2 (30 mol %) to the rhodium cyclopentadienyl catalyst was essential to the success of the reaction. Products were recovered in 34–71% yields. Ortho-substituted azobenzenes gave very poor yields (19%). 4-Methylazobenzene gave a mixture of 5-methyl and benzo unsubstituted indole in a 34% and a 19% yield, respectively, while 4-trifluorometylazobenzene gave exclusively the benzo unsubstituted indole in a 47% yield.
Finally, three reactions involving lower-valent rhodium complexes should be mentioned. For instance, Rh(II)-complexes are able to catalyze denitrogenation reactions of N-sulfonyl 1,2,3-triazoles, which are masked diazo compounds, to synthesize 3-indolylimines from N-propargyl anilines [111]. Recently, 2-triazole-N-benzyl anilines were employed instead to afford 2,3-disubstituted indoles (Scheme 61) [112]. The authors outlined that strong electron-donating, as well as ortho-substituents on the N-benzyl group, decreased the yields, very likely for unexpected side reactions in the former case and steric hindrance in the latter one. No experimental evidence or calculations were reported to support the envisaged mechanism.
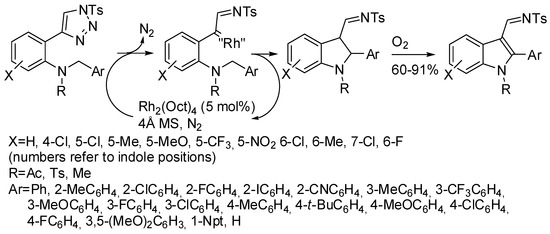
Scheme 61.
Rh(II)-catalyzed synthesis of indoles from 2-tetrazoleanilines.
Synthesis of indoles with de novo construction of the benzene ring is quite rare. At the end of Section 5, we already reported an example. Also Rh(I) allowed the assemble of the benzenoid ring from pyrrole propargylic esters and carbon monoxide as well as other benzo-heterocycles starting from the corresponding propargylic esters [113]. Propargylic esters are easily prepared in high yields from heterocyclic carbaldehydes and alkynyl Grignard reagents followed by in situ esterification. These compounds had been already successfully employed to construct pyrrole and pyridine rings [114,115,116], thus their extension to benzenoid rings is not surprisingly. Only 4-hydroxy-4-(pyrrol-2-yl)-pent-2-ynoate reacted among internal alkynes although in low yields (58%), because the 1,2-acyloxy migration did not generally occur in these substrates. The surmised mechanism was supported by DFT calculations (Scheme 62). Although most reactions were carried out with Ts-protected pyrrole, the reaction worked also with the Boc-protecting group, and it can be easily removed to free indoles. The pivalate and hydroxyl groups derived from the benzannulation can be easily manipulated to give many other substituted indoles.
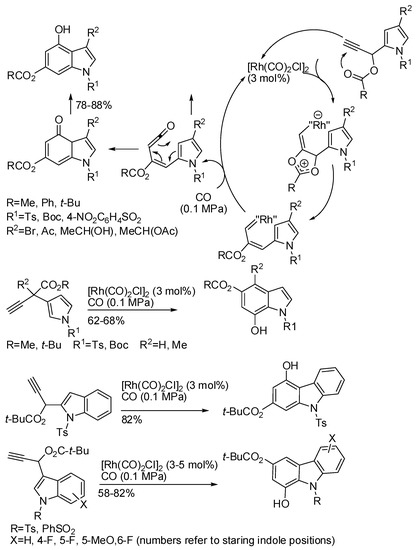
Scheme 62.
Rh(I)-catalyzed annulation of pyrrole propargylic esters.
Finally a cationic rhodium(I)/H8−BINAP complex allowed the cycloisomerization of 2-(2-silylethynyl)anilines via 1,2-silicon migration (Scheme 63) [117]. However, the reaction, which efficiently worked with phenols, showed some drawbacks with anilines. In fact, concentrated conditions led to desilylated products, and 10−30% yields of 2-sylylindoles are always recovered. Authors explained this behavior by the higher nucleophilicity of the amino group than the hydroxy group, which allowed cyclization before the vinylidene intermediate formation. The H8−BINAP catalyst should diminish the electrophilicity of the activated alkyne.
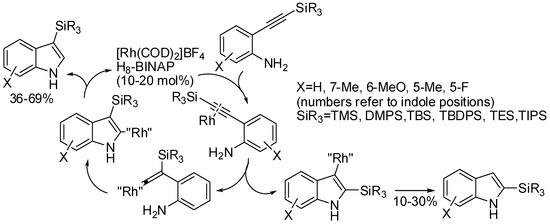
Scheme 63.
Rh(I)/H8−BINAP catalyzed cycloisomerization of 2-(2-silylethynyl)anilines.
7. Ruthenium
Ruthenium complexes, which are less expensive than Rh(III) catalysts, are other widely used catalyst for the synthesis of indoles. However, the C–H functionalization achieved with Rh(III)-based catalysts is not generally expandable to Ru(II) systems. Among the factors determining this not simple generalization, the choice of directing groups is an important one. In the time range covered by this review, the first ruthenium-catalyzed cycloisomerization of alkynylanilides has been reported (Scheme 64) [118]. This reaction often required high temperatures to occur and the presence of an acyl group protecting the nitrogen atom to gain regioselectivity. In fact, free anilines gave mixture of 2- and 3-substituted indoles. Authors ascribed this lack of regioselectivity to the high nucleophilicity of the amino group, which attacked the activated triple bond before formation of the vinylidene complex, which led to 3-substituted indoles.
Scheme 64.
Ruthenium-catalyzed cycloisomerization of 2-alkynylanilides.
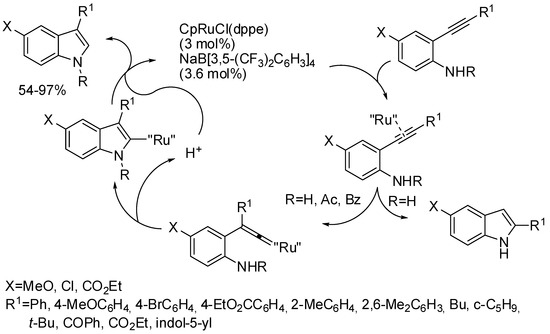
As mentioned above, in Rh(III) and Co(III) catalytic systems, traceless directing groups containing N–O, N–N, and C–N bonds have been widely employed. Before 2016 with Ru(II) catalytic system instead [119,120,121,122], only traceless groups with N–O bond had been employed and only an N–N-bond cleavage was reported: the reactions of alkynes and 1-arylpyrazolidin-3-ones [123]. Nevertheless, the pyrazolidin-3-one group cannot be considered a traceless group, because it was retained in the indole as N-(3-propanamide) moiety. In 2016, Zhu and co-workers described the first Ru(II) catalyzed synthesis of indoles by a true traceless directing group, by using arylhydrazines and alkynes (Scheme 65) [124]. Meta-substituted phenylhydrazines always gave a mixture of regioisomers, in which the 6-substituted prevailed over 4-substituted indoles in 1:0.07 to 1:0.9 ratios. 2-Substitutted indoles were obtained from alkynes containing a Me3Si substituent. The reaction was performed also on a large-scale reaction (2.36 g of recovered indole) but yield drastically dropped to 36% from 91% although only 0.1 mol % of the catalyst was loaded. Authors performed a series of experiments to demonstrate a mechanism very close to that depicted in Scheme 1. The role of Zn(OTf)2 is to generate the more reactive Ru(p-cymene)(OTf)2 and needed in excess to favor the formation of the cationic Ru(II) species. This protocol applied to alkenes led to 2-vinylanilines, but a mixture of [RuI2(p-cymene)]2 (10 mol %), AgBF4 (1 equiv) and Cu(OAc)2 (1.5 equiv) was able to suppress β-hydride elimination in the reaction of N-pyrimidylanilines with electronically biased alkenes, leading to indolines [125].
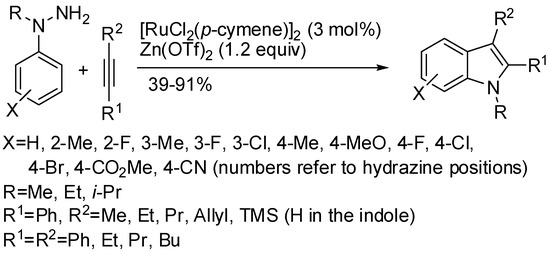
Scheme 65.
Ruthenium-catalyzed synthesis of indole from arylhydrazines.
The C–H activation followed by coupling with diazo compounds has remained underexplored under ruthenium catalysis, although the reactivity of a Ru(II)–C bond towards an electrophile might even exceed that of the Rh(III) counterparts. An instance was the Ru(II)-catalyzed reaction of imidamides with diazo compounds (Scheme 66) [126]. Li had published also the rhodium version of this reaction (Scheme 57) [106] with similar features as following:
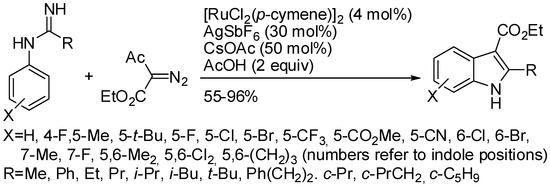
Scheme 66.
Ruthenium-catalyzed synthesis of indoles from imidamides and diazo ketoesters.
- meta-halogeno substituted imidamides exclusively led to 6-substituted indoles except 3-fluoro derivative which exclusively afforded 4-fluoroindole and once more no explanation was given;
- methyl, benzyl, tert-butyl 2-diazo-3-oxobutanoate and α-diazoacetylacetone also gave indoles in 46–83% yields;
- the proposed mechanism was the same. However, under ruthenium catalysis, some benzimidamides were allowed to react and the C–H activation occurred exclusively at the N-aryl ring.
Moreover, also α-diazodiethylmalonate reacted leading to 3,3-disubstituted 3H-indoles in 30–97% yields.
Ru catalytic systems are known to promote the intermolecular coupling of anilines with diols to synthesize indole and quinoline derivatives [127,128,129,130,131,132]. In particular in 2016, Lee and Yi found that also the tetra-nuclear Ru complex [(PCy3)(CO)RuH]4(μ-O)(μ-OH)2 catalyzed this synthesis in the presence of cyclopentane as an oxidant (Scheme 67) [133]. The indole products were regioselectively formed with the carbon carrying the secondary alcohol moiety in the 2-position. Some experiments were carried out by the authors to describe a plausible mechanistic hypothesis as depicted in Scheme 67.
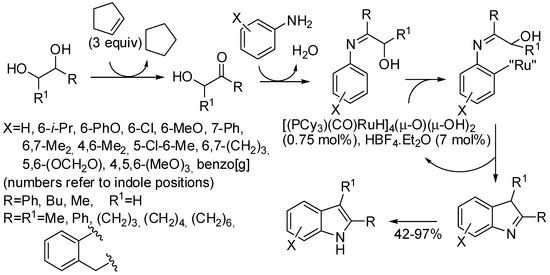
Scheme 67.
Ruthenium-catalyzed dehydrative C−H coupling of arylamines with 1,2-diols.
Another ruthenium catalyzed reaction was the cycloisomerization between enamides and silylalkynes (Scheme 68) [134]. Only a well-defined ruthenium hydride gave the 2,3-disubstitued indole, which was prepared in situ by reaction of a Grubbs II catalyst and trimethylsilylenol. Then camphor sulfuric acid (+)-CSA allowed the aromatization of the indoline. However, the amount of CSA has to be tested in each reaction.
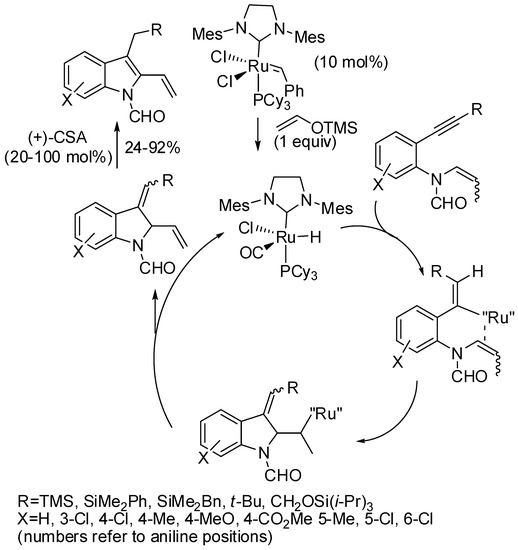
Scheme 68.
Ruthenium-catalyzed 1,6-aromatic enamide−silylalkyne cycloisomerization.
8. Miscellaneous
Other metals can synthesize indoles but are less frequently used, either because of their cost, toxicity, or simply because their widespread use in this chemistry makes hard to find out something new yet. These metals are listed here in alphabetical order.
Indole-based phosphines are particularly interesting both for pharmaceutical properties and for the synthetic development of the phosphine moiety. Methods, in which the indole ring is formed with the concomitant incorporation of a phosphorus moiety, are particularly interesting for their step-economy. After a reaction out-of-range of this review [135], another example was the synthesis of 3-phosphinoylindoles by means of over-stoichiometric silver salts. These phosphinoyl derivatives are interesting as non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (Scheme 69) [136]. The reaction proceeded through a radical cascade cycloaddition-desulfonylation of N-Ts-2-alkynylanilines with phosphine oxides. The radical character of the reaction was demonstrated by authors introducing radical scavengers and finding no indole formation.
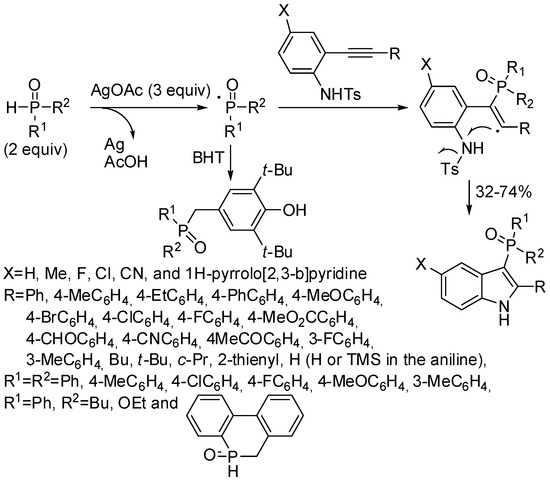
Scheme 69.
Synthesis of 3-phosphinoylindoles.
Urea as a directing group in the C–H activation has been widely encountered in this review. In particular, in Scheme 2 the reaction of ureas and alkynes has been described under Cp*Co(III) catalysis [23]. Lu, Xu and co-workers prepared indolo[1,2-c]quinazolin-6(5H)-ones exploiting the directing ability of the urea framework towards C–H functionalization and placing a triple bond on the second aryl group (Scheme 70) [137].
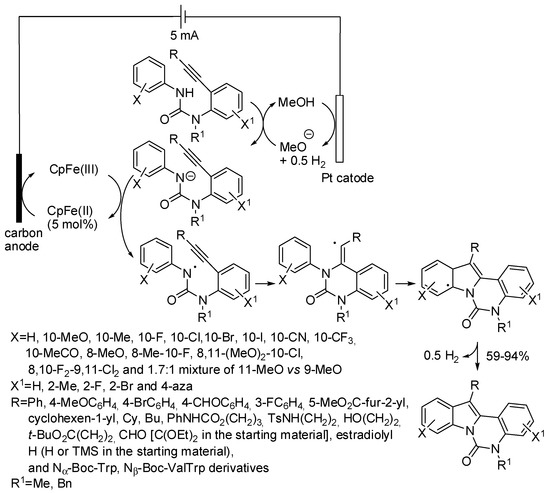
Scheme 70.
Synthesis of indolo[1,2-c]quinazolin-6(5H)-ones.
It should be also noted that the double substitution of one of the nitrogen atoms prevented cyclization on it. This reaction, too, proceeded through a SET mechanism, initiated by electrochemical oxidation of ferrocene. As in the previous reaction 3-unsubstituted indoles could be prepared from either a terminal or a trimethylsilyl-substituted alkyne, but in higher yields. The pyrimido[1,6-a]indol-1(2H)-one nucleus is exclusively formed, in fact, reaction leading to the more strained 1H-imidazo[1,5-a]indol-3(2H)-one were unsuccessful. The meta-substitution of the benzene fused in the indole nucleus led to a mixture of 9 and 11-substituted compounds (11-:9-OMe = 1.7:1). The reaction was successfully scaled up to gram scale and therefore applied to the synthesis of isocryptolepine. Finally, azaindoles were also prepared starting from the corresponding aminopyridines.
In Section 4, we already described a reaction in which a catalyst acted as a photosensitizer (Scheme 22) [46]. Another example has been reported with Ir(ppy)3 and the cobaloxime [Co(dmgH)2(4-CO2Me-pyridine)Cl] as the catalyst (Scheme 71) [138]. The meta-substituted enamines gave mixture of isomeric indoles with prevalence of the 4-substituted one (2.7:1 to 1.2:1) except for the bulky t-butyl group in which the 4 vs. 6 ratio was 0.8:1. It should be noted also a partial debromination of the meta-bromo (about 40% yield) but not of the para-bromo enamine. The authors surmised that the electron densities of indoles at C4, C5, and C6 position are different, thus facilitating elimination of bromine from C4 and C6 positions. Amides instead of ester at C3 reduced the reactivity of the enamine (55% yields). A gram-scale reaction gave indole in 82% yield. Some experiments were then carried out to propose the mechanism depicted in Scheme 71.
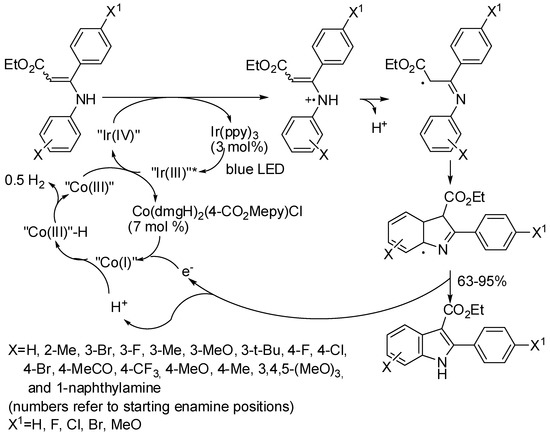
Scheme 71.
Indole synthesis under visible light irradiation.
In Section 6 (Scheme 52 and Scheme 53) [96,97,98] the use of 2-pyrimidyl and 2-pyridyl directing group in the rhodium catalyzed C–H activation was described. In addition, iridium(III) complexes allowed the indolization of 2-pyrimidyl and 2-pyridylanilines and α-diazoesters (Scheme 72, Equation (1)) [139]. An almost complete regioselectivity towards the 6-substituted indole was observed with different meta-substituted anilines. Diazomalonate did not react. The directing group was removed in a 63% overall yield after treatment with MeOTf and then with EtONa. The envisaged mechanism is very similar to that depicted in Scheme 52, Equation (1). Iridium catalyst was also able to perform the reaction with anilides (Scheme 72, Equation (2)) [140]. The steric crowding of ortho-substituted acetanilides considerably decreased the indole yield. Meta-substituted acetanilide gave an inseparable mixture of regioisomers.
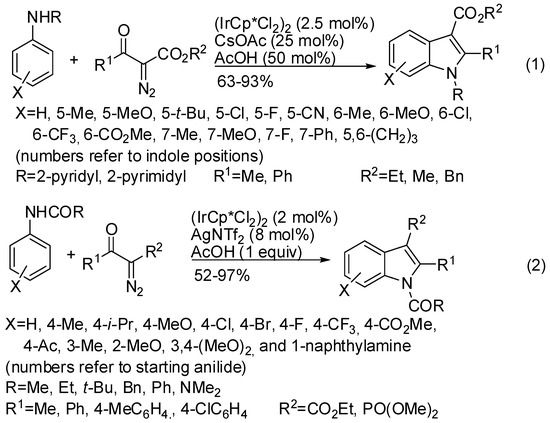
Scheme 72.
Iridium(III)-catalyzed coupling of anilines with α-diazoesters.
An iron catalyst was employed in the cyclization of styrylazides (Scheme 73) [141]. The reaction worked with both (E)- and (Z)-isomers with comparable yield, thus the mixture can be safely used. Moreover, the reaction with biarylazides led to carbazoles. About the mechanism, some kinetic experiments allowed envisaging a mechanism that parallels the rhodium-catalyzed variant [142].
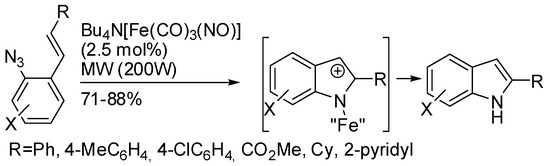
Scheme 73.
Iron catalyzed cyclization of styrylazides.
A quite different approach to indole synthesis has been proposed by Wan and co-workers [143], who set up a radical-carbene coupling reaction (Scheme 74). The reaction of meta-toluidine yielded a 2:1 mixture of 4- and 6-isomers. Kinetic experiments and introduction of radical scavengers allowed hypothesizing the mechanism depicted in Scheme 74.
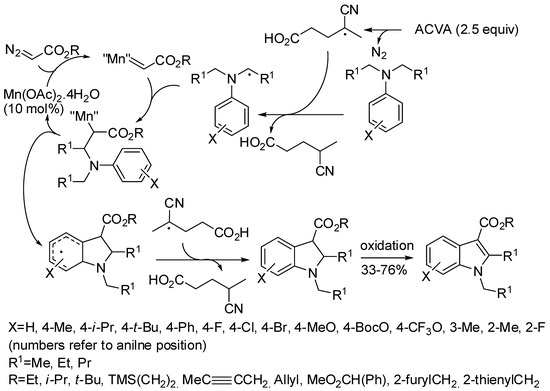
Scheme 74.
Mn-catalyzed synthesis of indoles from aromatic amines and diazo compounds.
The use of metal nanoparticles has been already encountered in this review for gold (Scheme 21) [45] and palladium (Table 1 entries 3 and 4) [62,63], the easy recovery and recycling being the major advantage of these catalysts. Gold nanoparticles worked also in neat conditions, thus avoiding the use of organic solvents often undesirable for environment friendly reasons. In the time range of this review another application of nanoparticles has appeared in the literature: the synthesis of indoles in water by aerobic alcohol oxidation and subsequent cyclization [144]. Polystyrene-stabilized platinum nanoparticles were used as the catalyst under phase transfer conditions by tetrabutylammonium bromide (Scheme 75). The authors found that the catalyst nanoparticles, recovered after the first cycle, were larger (3.6 nm vs. 2.0 nm) and less active (50% vs. 88% yield), but size and activity did not significantly change in the following four cycles.
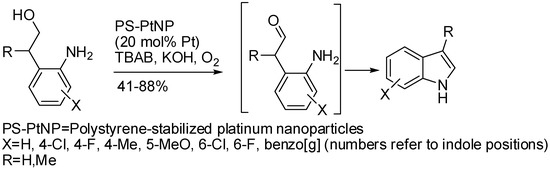
Scheme 75.
Polystyrene-stabilized Pt nanoparticles catalyzed indole synthesis.
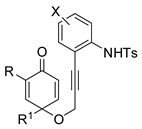
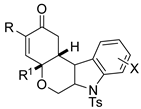
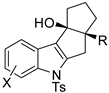
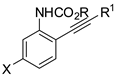
Propargyl ethers undergo nucleophilic attack with ether extrusion by some platinum catalyst. In the presence of a Lewis acid enhancing the platinum reactivity, 4-(2-aminoaryl)propargyl ethers originated indole α,β-unsaturated carbene intermediates, which in turn allowed vinylogous addition of enol nucleophiles (Scheme 76) [145]. The enol nucleophiles was used in large excess (5 equiv), because lower amounts generated indole in lower yield after longer reaction times. N-Acetyl- and N-Ts-protected anilines were less efficient than N-Boc ones. The obtained products were then manipulated to give fused heterocyclic compounds related to mitomycins structure.
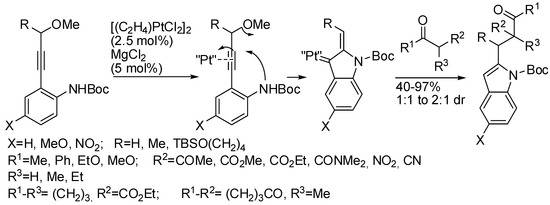
Scheme 76.
Indole synthesis by platinum catalyzed annulation.
Recently a synthesis of 2,3-disubstituted indoles was obtained by cyclization of the dianion of 2-ethynylaniline followed by electrophilic trapping. [146] The authors found that 2,3-zinc dianions of indoles with an easily removable 4-methoxybenzyl protecting group are stable, while lithium ones are stable at −78 °C with a hardly removable N-methyl group but open even at −100 °C with a N-sulfonyl framework. Then coupling with excess allyl bromide in the presence of CuCN·2LiCl or iodine led to 2,3-diallylindole in an 89% yield on a gram scale. Other reactions were carried out on a 0.2–0.4 g scale and all the product distributions included significant amounts of mono-, di- and/or unsubstituted indoles. An excess of iodine (no catalyst), iodobenzene and 2-iodothiophene [Pd2(dba)3·CHCl3 (5 mol %)/PPh3 (20 mol % as the catalyst] mainly afforded 2,3-disubstituted indoles in 67–87% yields. The addition of very slight excess of methyliodide or 4-methoxybenzoyl chloride mainly afforded the 3-substituted indole (73–74% yields), according to the higher reactivity of this position. This selectivity allowed functionalizing the C2 position with a different electrophile (64–76% yields) and recovering of a 5H-indeno[1,2-b]-indol-10-one derivative from the reaction with 2-iodobenzoyl chloride (58% yield). On the other hand, transition metal catalysis afforded the 2-substituted indoles (47–75% yields), but the best catalyst was to be chosen time after time. Interestingly 2,5-diethynyl-1,4-phenylenediamine underwent double cyclization and aqueous quenching of the tetrazinc intermediate led to benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b′]dipyrrole (92% yield), as well as 40% of tetraphenylbenzodipyrrole upon reaction with iodobenzene under palladium catalysis. Finally, the authors also prepared an indole zincate intermediate by addition of only 1 equiv of PhZnBr to the lithium dianion of 2-ethynylaniline. This zincate intermediate was able to add at the C3 position diarylketones in 76–77% yield or chalcone in a Michael manner (83% yield), whereas the dizincioindole did not. The addition of benzophenone can be followed by allylation in the presence of CuCN·2LiCl. Chlorotrimethylstannane gave an almost 1:1 mixture of 2-stannylindole and unsubstituted indole.
9. Conclusions
The importance of indoles as structural elements in pharmaceuticals, natural products, and compounds for other diverse applications means that new synthetic methods are being perpetually developed. During the drafting of this review many papers continued to appearing in the literature. They have been not discussed here but they could be of interest for the reader [147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159]. Recently, the classical syntheses, which are still widely used and improved, have been juxtaposed with many transition metal catalyzed syntheses. Metals such as cobalt, copper, gold, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium, and others allow the cyclization of diverse starting materials such as nitrones, azo esters, hydrazides, nitrosoanilines, enamines, or imines. This review shows how many different indole syntheses are reported in a very short time frame. This fact leaves the road open for other new strategies as well as new applications of known reactions to complex molecule synthesis.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| acac | Acetylacetonate |
| ACVA | cis-4,4′-azobis(4-cyanovaleric acid) |
| BHT | di-tert-Butylhydroxytoluene |
| Bn | Benzyl (phenylmethyl) |
| Boc | tert-Butoxycarbonyl |
| COD | 1,5-Cyclooctadiene |
| Cp | Cyclopentadienyl anion |
| Cp* | Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl anion |
| Cy | Cyclohexyl |
| dba | Dibenzylideneacetone |
| DBU | 1,5-diazabiciclo(5.4.0)undec-7-ene |
| DMPS | Dimethylphenylsilyl |
| dppe | 1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane |
| dppf | 1,1′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene |
| dppp | 1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane |
| dr | Diastereomeric ratio |
| H8-BINAP | 2,2′-Bis(diphenylphospino)-5,5′,6,6′,7,7′,8,8′-octahydro-1,1′-binaphthyl |
| Hex | Hexyl |
| hfacac | Hexafluoroacetylacetonate |
| HMDS | Hexamethyldisylazide |
| JohnPhos | (2-Biphenyl)di-tert-butylphosphine |
| Mes | 2,4,6-Trimethylphenyl (mesityl) |
| Ms | Methanesulfonyl (mesyl) |
| MS | Molecular sieves |
| MW | Microwave |
| NHC | N-heterocyclic carbene |
| Npt | Naphthyl |
| Oct | Octyl |
| Piv | Pivaloyl (2,2-dimethylpropanoyl) |
| PMP | 4-methoxyphenyl |
| ppy | Tris[2-phenylpyridinato-C2,N] |
| PS | Polystyrene nanoparticles |
| SET | Single electron transfer |
| TBAB | Tetrabutylammonium bromide |
| TBDPS | tert-Butyldiphenylsilyl |
| TBS | tert-Butyldimethylsilyl |
| TES | Triethylsilyl |
| Tf | trifluoromethanesulfonyl |
| TIPS | Triisopropylsilyl |
| TMS | Trimethylsilyl |
| Ts | 4-Methylbenzenesulfonyl (tosyl) |
| t-BuXPhos | 2-Di-tert-butylphosphino-2′,4′,6′-triisopropylbiphenyl |
| XPhos | 2-Dicyclohexylphosphino-2′,4′,6′-triisopropylbiphenyl |
References
- Baeyer, A.; Emmerling, A. Synthese des Indols. Chem. Ber. 1869, 2, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, G.W. (Ed.) Heterocyclic Scaffolds II: Reactions and Applications of Indoles. In Topics in Heterocyclic Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 26, ISBN 978-3-642-15733-2. [Google Scholar]
- Gribble, G.W. Indole Ring Synthesis: From Natural Products to Drug Discovery; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-0-470-51218-0. [Google Scholar]
- Leitch, J.A.; Bhonoah, Y.; Frost, C.G. Beyond C2 and C3: Transition-Metal-Catalyzed C–H Functionalization of Indole. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 5618–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agasti, S.; Dey, A.; Maiti, D. Palladium-catalyzed benzofuran and indole synthesis by multiple C–H functionalizations. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 6544–6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Lan, J.; Liu, K.-Y. Progress in the Synthesis of 2,3-Disubstituted Indole by Cyclization. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 2619–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Huang, F.; Yu, L.; Yu, Z. Indole synthesis through transition metal-catalyzed C–H activation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, M.; Moody, C.J. Indole synthesis—Something old, something new. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikai, N.; Wei, Y. Synthesis of Pyrroles, Indoles, and Carbazoles through Transition-Metal-Catalyzed C–H Functionalization. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Glorius, F. Efficient and versatile synthesis of indoles from enamines and imines by cross-dehydrogenative coupling. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9220–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platon, M.; Amardeil, R.; Djakovitch, L.; Hierso, J.-C. Progress in palladium-based catalytic systems for the sustainable synthesis of annulated heterocycles: A focus on indole backbones. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3929–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taber, D.F.; Tirunahari, P.K. Indole synthesis: A review and proposed classification. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 7195–7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacchi, S.; Fabrizi, G. Update 1 of: Synthesis and Functionalization of Indoles through Palladium-Catalyzed Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, PR215–PR283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, S.W.; Ko, T.Y. Metal-Catalyzed Synthesis of Substituted Indoles. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2018, 7, 1467–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Miura, M.; Nomura, M. Palladium-Catalyzed Regioselective Mono- and Diarylation Reactions of 2-Phenylphenols and Naphthols with Aryl Halides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1997, 36, 1740–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palucki, M.; Buchwald, S.L. Palladium-Catalyzed α-Arylation of Ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 11108–11109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, B.C.; Hartwig, J.F. Palladium-Catalyzed Direct α-Arylation of Ketones. Rate Acceleration by Sterically Hindered Chelating Ligands and Reductive Elimination from a Transition Metal Enolate Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 12382–12383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Song, C.; Sun, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, J. Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Indole Synthesis Using N–N Bond as an Internal Oxidant. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16625–16631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Moselage, M.; Gonzàlez, M.J.; Ackermann, L. Selective Synthesis of Indoles by Cobalt(III)-Catalyzed C–H/N–O Functionalization with Nitrones. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2705–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Lu, X. Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Redox-Neutral C–H Annulation of Arylnitrones and Alkynes for the Synthesis of Indole Derivatives. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 2944–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dateer, R.B.; Chang, S. Selective Cyclization of Arylnitrones to Indolines under External Oxidant-Free Conditions: Dual Role of Rh(III) Catalyst in the C–H Activation and Oxygen Atom Transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4908–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Xin, X.; Wang, C.; Wan, B. Rhodium-Catalyzed C–H Annulation of Nitrones with Alkynes: A Regiospecific Route to Unsymmetrical 2,3-Diaryl-Substituted Indole. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10613–10617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Vàsquez-Céspedes, S.; Gensch, T.; Glorius, F. Control over Organometallic Intermediate Enables Cp*Co(III) Catalyzed Switchable Cyclization to Quinolines and Indoles. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2352–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Z.; Liu, B.; Xu, J.-W.; Yan, S.-Y.; Shi, B.-F. Indole Synthesis via Cobalt(III)-Catalyzed Oxidative Coupling of N-Arylureas and Internal Alkynes. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 1776–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Jiao, N. Cationic Cobalt(III) Catalyzed Indole Synthesis: The Regioselective Intermolecular Cyclization of N-Nitrosoanilines and Alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4035–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerchen, A.; Vàsquez-Céspedes, S.; Glorius, F. Cobalt(III)-Catalyzed Redox-Neutral Synthesis of Unprotected Indoles Featuring an N–N Bond Cleavage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3208–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, K.; Song, C.; Zhu, J. Co(III)-Catalyzed, Internal and Terminal Alkyne-Compatible Synthesis of Indoles. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 3806–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorai, J.; Reddy, A.C.S.; Anbarasan, P. Cobalt(III)-Catalyzed Intramolecular Cross-Dehydrogenative C−H/X−H Coupling: Efficient Synthesis of Indoles and Benzofurans. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 16042–16046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.-Y.; Li, J.-H.; Wang, S.-Y.; Ji, S.-J. Cobalt(II)-catalyzed bis-isocyanide insertion reactions with sulfonyl azides via nitrene radicals: Chemoselective synthesis of sulfonylamidyl amide and 3-imine indole derivatives. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 11173–11176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachon, A.-K.; Opatz, T. Synthesis of 1,2-Disubstituted Indoles from α-Aminonitriles and 2-Halobenzyl Halides. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 1858–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Fan, X. Synthesis of 3-Cyano-1H-indoles and Their 2′-Deoxyribonucleoside Derivatives through One-Pot Cascade Reactions. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 9530–9538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-G.; Li, Z.-H.; Xie, J.-W.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Dai, B. Copper-catalyzed synthesis of 2,3-disubstituted indoles from ortho-haloanilines and β-keto esters/β-diketone. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wei, W.; Zhao, T.; Liu, X.Y.; Wu, J.; Yu, W.Q.; Chang, J.B. Iodine/Copper Iodide-Mediated C–H Functionalization: Synthesis of Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines and Indoles from N-Aryl Enamines. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 9326–9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, C.E.P.; Silva, P.J. Computational exploration of the reaction mechanism of the Cu+-catalysed synthesis of indoles from N-aryl enaminones. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 150582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.-Z.; Zhao, S.-H.; Chen, H.; Yu, S.-W.; Xu, X.-Y.; Yuan, W.-C.; Zhang, X.-M. Facile Synthesis of 2,3-Disubstituted Indoles by NBS/CuCl Mediated Oxidative Cyclization of N-Aryl Enamines. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 1409–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, S.E.; Gallagher, R.; Gilliland, R.J.; Ghiviriga, I.; Dolbier, W.R. Jr. Synthesis of 3-phenylsulfonyl-2-trifluoromethyl-1H-indoles: A copper catalyzed cyclization approach. J. Fluor. Chem. 2017, 193, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, C.; Takamatsu, K.; Hirano, K.; Miura, M. A Divergent Approach to Indoles and Oxazoles from Enamides by Directing-Group-Controlled Cu-Catalyzed Intramolecular C−H Amination and Alkoxylation. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 9112–9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Yu, J.-T.; Sun, S.; Zheng, Q.; Cheng, J. Copper-mediated intramolecular aza-Wacker-type cyclization of 2-alkenylanilines toward 3-aryl indoles. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang-Negrerie, D.; Du, Y. Cu(OAc)2-Mediated Cascade Annulation of Diarylalkyne Sulfonamides through Dual C–N Bond Formation: Synthesis of 5,10-Dihydroindolo[3,2-b]indoles. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 3322–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, H.E.; Oniwa, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Jin, T. N-Methyl Transfer Induced Copper-Mediated Oxidative Diamination of Alkynes. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 2487–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villuri, B.K.; Kotipalli, T.; Kavala, V.; Ichake, S.S.; Bandi, V.; Kuo, C.-W.; Yao, C.-F. Synthesis of spiro isoindolinone-indolines and 1,2-disubstituted indoles from 2-iodobenzamide derivatives. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 74845–74858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Kuo, C.-W.; Konala, A.; Yang, T.H.; Lin, L.; Chen, Y.-W.; Kavala, V.; Yao, C.F. Synthesis of 3-arylindole derivatives from nitroalkane precursors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 96049–96056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, T.; Cheng, X.-F.; Zhou, X.; Fei, F.; Wang, X.-S. A Copper-Catalyzed Aerobic [1,3]-Nitrogen Shift through Nitrogen-Radical 4-exo-trig Cyclization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15436–15440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debrouwer, W.; Heugebaert, T.S.A.; Roman, B.I.; Stevens, C.V. Homogeneous Gold-Catalyzed Cyclization Reactions of Alkynes with N- and S-Nucleophiles. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 2975–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Hammond, L.; Xu, B.; Hammond, G.B. Commercial Supported Gold Nanoparticles Catalyzed Alkyne Hydroamination and Indole Synthesis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 3313–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Zhang, S.; Du, H.; Zhu, C. Cascade photoredox/gold catalysis: Access to multisubstituted indoles via aminoarylation of alkynes. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 14400–14403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalska, M.; Grela, K. Simple and Mild Synthesis of Indoles via Hydroamination Reaction Catalysed by NHC-Gold Complexes: Looking for Optimized Condition. Synlett 2016, 27, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, B.R.; Bezpalko, M.W.; Foxman, B.M.; Wade, C.R. Lewis Acid Catalysis with Cationic Dinuclear Gold(II,II) and Gold(III,III) Phosphorus Ylide Complexes. Organometallics 2016, 35, 2830–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, V.; Cui, X.; Ma, M. Gold-Catalyzed Tandem Reactions of 2-Alkynyl Arylazides and Carboxylic Acids for the Synthesis of 1H-Indol-3-yl Esters. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 35, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, X.; Fan, H.; Lyu, C.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Rao, W. Gold-catalyzed formation of indole derivatives from 2-alkynyl arylazides and oxygen-containing heterocycles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56319–56322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Yang, K.; Chen, J.; Song, Q. Gold(I)-catalyzed synthesis of 2-substituted indoles from 2-alkynylnitroarenes with diboron as reductant. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 8354–8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Huang, L.; Xie, J.; Rudolph, M.; Rominger, F.; Hashmi, A.S.K. Gold-Catalyzed C–H Annulation of Anthranils with Alkynes: A Facile, Flexible, and Atom-Economical Synthesis of Unprotected 7-Acylindoles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marelli, E.; Corpet, M.; Minenkov, Y.; Neyyappadath, R.M.; Bismuto, A.; Buccolini, G.; Curcio, M.; Cavallo, L.; Nolan, S.P. Catalytic α-arylation of imines leading to N-unprotected indoles and azaindoles. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé, D.; Pérez-Janer, F.; Zulaica, E.; Guastavino, J.F.; Fernández, I. Pd-Catalyzed α-Arylation of Sulfones in a Three-Component Synthesis of 3-[2-(Phenyl/methylsulfonyl)ethyl]indoles. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, D.; Pérez-Janer, F.; Mancuso, R. Pd0-Catalyzed Intramolecular α-Arylation of Sulfones: Domino Reactions in the Synthesis of Functionalized Tetrahydroisoquinolines. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 4580–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharpure, S.J.; Anuradha, D. Synthesis of Benzo[1,4]heterocycles using Palladium Catalyzed Heck Reaction to Vinylogous Carbonates/Carbamates: Unexpected Formation of Indoles via Carbopalladation Intercepted byNucleopalladation. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 6136–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez-Medina, G.E.; Amézquita-Valencia, M.; Cabrera, A.; Sharma, P. Synthesis of 2,3-Disubstituted Indoles from α-Diketones and N-Substituted Anilines: One-Pot Pd-Catalyzed Reductive Amination. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 1450–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Qi, L.; Hu, K.; Gong, J.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Wu, H. The Development of a Palladium-Catalyzed Tandem Addition/Cyclization for the Construction of Indole Skeletons. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 3631–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Hu, K.; Gong, J.; Qi, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Chen, J. Palladium-catalyzed tandem addition/cyclization in aqueous medium: Synthesis of 2-arylindoles. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 4300–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Akiyama, T.; Sasou, H.; Katsumata, H.; Manabe, K. One-Pot Synthesis of Substituted Benzo[b]furans and Indoles from Dichlorophenols/Dichloroanilines Using a Palladium–Dihydroxyterphenylphosphine Catalyst. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 5450–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, K.V.; Kieffer, M.E.; Reisman, S.E. A Mild and General Larock Indolization Protocol for the Preparation of Unnatural Tryptophans. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 4750–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, C.B.; Bharti, R.; Kumara, S.; Das, P. Supported palladium nanoparticles-catalyzed decarboxylative coupling approaches to aryl alkynes, indoles and pyrrolines synthesis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 71117–71121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, A.; Gustafson, K.P.J.; Yuan, N.; Tai, C.-W.; Persson, I.; Zou, X.; Bäckvall, J.-E. Synthesis of Benzofurans and Indoles from Terminal Alkynes and Iodoaromatics Catalyzed by Recyclable Palladium Nanoparticles Immobilized on Siliceous Mesocellular Foam. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 12886–12891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panyam, P.K.R.; Gandhi, T. Palladium(II)/N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Catalyzed Regioselective Heteroannulation of Tertiary Propargyl Alcohols and o-Haloanilines to form 2-Alkenylindoles. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2017, 359, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Guan, Z.; Yao, X.; Shi, W.; Chen, H. One-Pot Synthesis of Indoles from Alkynes and Anilines through Palladium-Catalyzed Double C–H Activation using O2 as the oxidant. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, S.W.; Ko, T.Y.; Jang, Y.H. Palladium-Catalyzed Regioselective Synthesis of 3-Arylindoles from N-Ts-Anilines and Styrenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6636–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, F.; Du, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, H. Highly selective intramolecular addition of C–N and S-N bonds to alkynes catalyzed by palladium: A practical access to two distinct functional indoles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 70682–70690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, A.; Omote, M.; Kusumoto, K.; Komori, M.; Tarui, A.; Sato, K.; Ando, A. A dramatic enhancing effect of InBr3 towards the oxidative Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction of 2-ethynylanilines. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Han, X.; Lu, X. Enantioselective Synthesis of Tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indoles: Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Aminopalladation/1,4-Addition Sequence. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14698–14701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Han, X.; Lu, X. Atom-Economic Synthesis of Pentaleno[2,1-b]indoles via Tandem Cyclization of Alkynones Initiated by Aminopalladation. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, M.; Kanayama, T.; Tanaka, R.; Okamoto, N.; Sueda, T.; Yanada, R. Regioselective Arylative Ring-Closing Reaction of 2-Alkynylphenyl Derivatives: Formation of Arylated Benzoxazin-2-ones, Benzoxazin-2-amines and 2,3-Disubstituted Indoles. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 5990–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, C.; Ouyang, L.; Li, C.; Wu, W.; Jiang, H. N-Heterocyclic carbene palladium-catalyzed cascade annulation/alkynylation of 2-alkynylanilines with terminal alkynes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 7898–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Lyu, C.; Yong, W.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Rao, W. Synthesis of 1H-indole-3-sulfonates via palladium catalyzed tandem reactions of 2-alkynyl arylazides with sulfonic acid. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 6080–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Palladium-Catalyzed Synthesis of Indoles and Isoquinolines with in situ Generated Phosphinimine. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battistuzzi, G.; Cacchi, S.; Fabrizi, G. The Aminopalladation/Reductive Elimination Domino Reaction in the Construction of Functionalized Indole Rings. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 2671–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glotz, G.; Gutmann, B.; Hanselmann, P.; Kulesza, A.; Roberge, D.; Kappe, C.O. Continuous flow synthesis of indoles by Pd-catalyzed deoxygenation of 2-nitrostilbenes with carbon monoxide. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 10469–10478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, N.H.; Dacko, C.A.; Akhmedov, N.G.; Söderberg, B.C.G. Double Palladium Catalyzed Reductive Cyclizations. Synthesis of 2,2′-, 2,3′-, and 3,3′-Bi-1H-indoles, Indolo[3,2-b]indoles, and Indolo[2,3-b]indoles. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 9337–9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clagg, K.; Hou, H.; Weinstein, A.B.; Russell, D.; Stahl, S.S.; Koenig, S.G. Synthesis of Indole-2-carboxylate Derivatives via Palladium-Catalyzed Aerobic Amination of Aryl C–H Bonds. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 3586–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Chen, W.-W.; Xu, B.; Xu, M.-H. Access to Indole-Fused Polyheterocycles via Pd-Catalyzed Base-Free Intramolecular Cross Dehydrogenative Coupling. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 11501–11507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Simaan, M.; Marek, I.; Wei, Y.; Shi, M. Palladium-catalyzed oxidative cyclization of aniline-tethered alkylidenecyclopropanes with O2: A facile protocol to selectively synthesize 2- and 3-vinylindoles. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Yu, B.; Huang, H. Palladium-Catalyzed Dehydrogenative Difunctionalization of Aminoalkenes with Aminals as Oxidants and Electrophiles. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 4600–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.; Ali, M.A.; Jana, S.; Samanta, S.; Hajra, A. Palladium-catalyzed synthesis of indole fused coumarins via cross-dehydrogenative coupling. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Ca’, N.; Fontana, M.; Motti, E.; Catellani, M. Pd/norbornene: A winning combination for selective aromatic functionalization via C–H bond activation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Shi, Z.; Sperger, T.; Yasukawa, Y.; Kingston, C.; Schoenebeck, F.; Lautens, M. Remote C–H alkylation and C–C bond cleavage enabled by an in situ generated palladacycle. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedroni, J.; Cramer, N. 2-(Trifluoromethyl)indoles via Pd(0)-Catalyzed C(sp3)-H Functionalization of Trifluoroacetimidoyl Chlorides. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 1932–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, Y.; Mita, T.; Sato, Y. Palladium-Catalyzed Intramolecular Arylative Carboxylation of Allenes with CO2 for the Construction of 3-Substituted Indole-2-carboxylic Acids. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 2710–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bzeih, T.; Lamaa, D.; Frison, G.; Hachem, A.; Jaber, N.; Bignon, J.; Retailleau, P.; Alami, M.; Hamze, A. Csp2−Csp2 and Csp2−N Bond Formation in a One-Pot Reaction between N-Tosylhydrazones and Bromonitrobenzenes: An Unexpected Cyclization to Substituted Indole Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 6700–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, S.R.; Wipf, P. Eight-Step Enantioselective Total Synthesis of (−)-Cycloclavine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wipf, P. Indole synthesis by palladium-catalyzed tandem allylic isomerization—Furan Diels–Alder reaction. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 7093–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizukami, A.; Ise, Y.; Kimachi, T.; Inamoto, K. Rhodium-Catalyzed Cyclization of 2-Ethynylanilines in the Presence of Isocyanates: Approach toward Indole-3-carboxamides. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 748–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Tong, X.; Liu, G. Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Cascade Cyclization/Electrophilic Amidation for the Synthesis of 3-Amidoindoles and 3-Amidofurans. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 2058–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, G.N.; Junga, C.L.; Bolm, C. Mechanochemical indole synthesis by rhodium-catalysed oxidative coupling of acetanilides and alkynes under solventless conditions in a ball mill. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 2520–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, B. Rhodium-Catalyzed Annulation of Tertiary Aniline N-Oxides to N-Alkylindoles: Regioselective C–H Activation, Oxygen-Atom Transfer, and N-Dealkylative Cyclization. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 3856–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Song, C.; Zhu, J. A Versatile, Traceless C–H Activation-Based Approach for the Synthesis of Heterocycles. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 2427–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- .Fan, Z.; Lu, H.; Li, W.; Genga, K.; Zhang, A. Rhodium-catalyzed redox-neutral coupling of phenidones with alkynes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 5701–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Gao, S.; Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Lin, A.; Yao, H. Multiple Roles of the Pyrimidyl Group in the Rhodium-Catalyzed Regioselective Synthesis and Functionalization of Indole-3-carboxylic Acid Esters. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Liang, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, B. Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Synthesis of Indole Derivatives From Pyrimidyl-Substituted Anilines and Diazo Compounds. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allu, S.; Ravi, M.; Swamy, K.C.K. Rhodium(III)-Catalysed Carbenoid C(sp2)–H Functionalisation of Aniline Substrates with α-Diazo Esters: Formation of Oxindoles and Characterisation/Utility of an Intermediate-Like Rhodacycle. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 5697–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, U.; Uddin, M.; Wengryniuk, S.E.; McDonald, S.L.; Coltart, D.M. A simple and efficient approach to the N-amination of oxazolidinones using monochloroamine. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 4799–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaga, A.; Peng, X.; Hirao, H.; Chiba, S. Diastereo-Divergent Synthesis of Saturated Azaheterocycles Enabled by t-BuOK-Mediated Hydroamination of Alkenyl Hydrazones. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 19112–19118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chen, H.; Liu, P. Rhodium-Catalyzed Oxidative Annulation of Hydrazines with Alkynes Using a Nitrobenzene Oxidant. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Yu, K.; Li, B.; Xu, S.; Song, H.; Wang, B. Rh(III)-catalyzed synthesis of 1-aminoindole derivatives from 2-acetyl-1-arylhydrazines and diazo compounds in water. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 6130–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Cui, X. Facile synthesis of 1-aminoindoles via Rh(III)-catalysed intramolecular three-component annulation. Org. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 2179–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Wang, L.; Guo, S.; Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J. A C–H Activation-Based Strategy for N-Amino Azaheterocycle Synthesis. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 4359–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Shi, J.; Wu, B.; Guo, Y.; Huang, J.; Yi, W. One-pot synthesis of 2,3-difunctionalized indoles via Rh(III)-catalyzed carbenoid insertion C–H activation/cyclization. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 8054–8058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Yu, S.; Li, X. Rh(III)-Catalyzed Synthesis of N-Unprotected Indoles from Imidamides and Diazo Ketoesters via C–H Activation and C–C/C–N Bond Cleavage. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Qin, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, B. Synthesis of 2,3-Disubstituted NH Indoles via Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed C–H Activation of Arylnitrones and Coupling with Diazo Compounds. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 11505–11511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, K.; Zha, S.; Song, C.; Zhu, J. C–H Activation-Based Traceless Synthesis via Electrophilic Removal of a Directing Group. Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Entry into Indoles from N-Nitroso and α-Diazo-β-keto Compounds. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Lin, S.; Yi, X.; Xi, C. Substrate-Controlled Transformation of Azobenzenes to Indazoles and Indoles via Rh(III)-Catalysis. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.; Han, S.H.; Mishra, N.K.; De, U.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, Y.H.; Kim, I.S. Synthesis and Anticancer Evaluation of 2,3-Disubstituted Indoles Derived from Azobenzenes and Internal Olefins. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 6265–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, B.; Chou, C.H.; Chung, C.C.; Lin, P.C. Synthesis of Substituted 3-Indolylimines and Indole-3-carboxaldehydes by Rhodium(II)-Catalyzed Annulation. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3752–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Fu, J.; Yuan, H.; Gong, J.; Yang, Z. Synthesis of 2,3-Disubstituted Indoles and Benzofurans by the Tandem Reaction of Rhodium(II)-Catalyzed Intramolecular C–H Insertion and Oxygen-Mediated Oxidation. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 10180–10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xie, H.; Fu, X.; Liu, J.-T.; Wang, H.-Y.; Xi, B.-M.; Liu, P.; Xu, X.; Tang, W. Rhodium(I)-Catalyzed Benzannulation of Heteroaryl Propargylic Esters: Synthesis of Indoles and Related Heterocycles. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 10410–10414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriele, B.; Mancuso, R.; Salerno, G.; Lupinacci, E.; Ruffolo, G.; Costa, M. Versatile Synthesis of Quinoline-3-Carboxylic Esters and Indol-2-Acetic Esters by Palladium-Catalyzed Carbonylation of 1-(2-Aminoaryl)-2-Yn-1-Ols. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 4971–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriele, B.; Veltri, L.; Salerno, G.; Mancuso, R.; Costa, M. Multicomponent Cascade Reactions: A Novel and Expedient Approach to Functionalized Indoles by an Unprecedented Nucleophilic Addition-Heterocyclization-Oxidative Alkoxycarbonylation Sequence. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 3355–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, B.; Veltri, L.; Salerno, G.; Mancuso, R.; Costa, M. A General Synthesis of Indole-3-carboxylic Esters by Palladium-Catalyzed Direct Oxidative Carbonylation of 2-Alkynylaniline Derivatives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2549–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, H.; Nakamura, K.; Noguchi, K.; Shibata, Y.; Tanaka, K. Rhodium-Catalyzed Cycloisomerization of 2-Silylethynyl Phenols and Anilines via 1,2-Silicon Migration. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 1654–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Mutoh, Y.; Saito, S. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Cycloisomerization of 2-Alkynylanilides: Synthesis of 3-Substituted Indoles by 1,2-Carbon Migration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7749–7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, L.; Fenner, S. Ruthenium-Catalyzed C–H/N–O Bond Functionalization: Green Isoquinolone Syntheses in Water. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 6548–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ma, J.; Wang, N.; Feng, H.; Xu, S.; Wang, B. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Oxidative C–H Bond Olefination of N-Methoxybenzamides Using an Oxidizing Directing Group. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 736–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Ackermann, L. Dehydrative C–H/N–OH Functionalizations in H2O by Ruthenium(II) Catalysis: Subtle Effect of Carboxylate Ligands and Mechanistic Insight. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 12070–12082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanowatari, S.; Ackermann, L. Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed C–H Functionalizations with Allenes: Versatile Allenylations and Allylations. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 16246–16251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Huang, Y. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Redox-Neutral C–H Activation via N–N Cleavage: Synthesis of N-Substituted Indoles. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5976–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Chen, K.; Zhu, J. Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed Traceless C−H Functionalization Using an N−N Bond as an Internal Oxidant. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 14508–14512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, M.K.; Bhunia, S.K.; Jana, R. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed intermolecular synthesis of 2-arylindolines through C–H activation/oxidative cyclization cascade. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 6906–6909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qi, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Li, X. Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed C–H Activation of Imidamides and Divergent Couplings with Diazo Compounds: Substrate-Controlled Synthesis of Indoles and 3H-Indoles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11877–11881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.S. Ruthenium-catalysed synthesis of indoles from anilines and trialkanolamines in the presence of tin(II) chloride dehydrate. Chem. Commun. 1998, 995–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.S.; Oh, B.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, T.-J.; Shim, S.C. Synthesis of quinolines via ruthenium-catalysed amine exchange reaction between anilines and trialkylamines. Chem. Commun. 2000, 1885–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.S.; Kim, J.S.; Oh, B.H.; Kim, T.-J.; Shim, S.C.; Yoon, N.S. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Synthesis of Quinolines from Anilines and Allylammonium Chlorides in an Aqueous Medium via Amine Exchange Reaction. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 7747–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursky, M.; Lorentz-Petersen, L.L.R.; Olsen, L.B.; Madsen, R. Iridium- and ruthenium-catalysed synthesis of 2,3-disubstituted indoles from anilines and vicinal diols. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 5576–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monrad, R.N.; Madsen, R. Ruthenium-catalysed synthesis of 2- and 3-substituted quinolines from anilines and 1,3-diols. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Xie, F.; Wang, X.T.; Yan, F.; Wang, T.; Chen, M.; Ding, Y. Improved indole syntheses from anilines and vicinal diols by cooperative catalysis of ruthenium complex and acid. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 6022–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yi, C.S. Catalytic Synthesis of Substituted Indoles and Quinolines from the Dehydrative C–H Coupling of Arylamines with 1,2- and 1,3-Diols. Organometallics 2016, 35, 1973–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamoto, K.; Ohno, S.; Hyogo, N.; Fujioka, H.; Arisawa, M. Ruthenium-Catalyzed 1,6-Aromatic Enamide−Silylalkyne Cycloisomerization: Approach to 2,3-Disubstituted Indoles. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 8733–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondoh, A.; Yorimitsu, H.; Oshima, K. Synthesis of 2-Indolylphosphines by Palladium-Catalyzed Annulation of 1-Alkynylphosphine Sulfides with 2-Iodoanilines. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1476–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Lu, G.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Tang, G.; Zhao, Y. A Cascade Phosphinoylation/Cyclization /Desulfonylation Process for the Synthesis of 3-Phosphinoylindoles. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 1242–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.-W.; Mao, Z.-Y.; Zhao, H.-B.; Melcamu, Y.Y.; Lu, X.; Song, J.; Xu, H.-C. Electrochemical C–H/N-H Functionalization for the Synthesis of Highly Functionalized (Aza)indoles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9168–9172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-J.; Meng, Q.-Y.; Lei, T.; Zhong, J.-J.; Liu, W.-Q.; Zhao, L.-M.; Li, Z.-J.; Chen, B.; Tung, C.-H.; Wu, L.-Z. An Oxidant-Free Strategy for Indole Synthesis via Intramolecular C–C Bond Construction under Visible Light Irradiation: Cross-Coupling Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.-D.; Pan, C.-L.; Li, X. Iridium(III)- and rhodium(III)-catalyzed coupling of anilines with α-diazoesters via chelation-assisted C–H activation. Org. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Borah, G. Direct Access to Indoles by IrIII-Catalyzed C–H Functionalization of Acetanilides with Diazo Compounds. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2272–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, I.T.; Plietker, B. Iron-Catalyzed Intramolecular C(sp(2))-H Amination. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 1519–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Leslie, B.E.; Driver, T.G. Dirhodium(II)-catalyzed intramolecular C–H amination of aryl azides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 5056–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, L.; Ma, M.; Jiang, J.; Wan, X. Radical-carbene coupling reaction: Mn-catalyzed synthesis of indoles from aromatic amines and diazo compounds. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5993–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtaka, A.; Kozono, M.; Takahashi, K.; Hamasaka, G.; Uozumi, Y.; Shinagawa, T.; Shimomura, O.; Nomura, R. Linear Polystyrene-stabilized Pt Nanoparticles Catalyzed Indole Synthesis in Water via Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation. Chem. Lett. 2016, 45, 758–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegretti, P.A.; Huynh, K.; Ozumerzifon, T.J.; Ferreira, E.M. Lewis Acid Mediated Vinylogous Additions of Enol Nucleophiles into an α,β-Unsaturated Platinum Carbene. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilies, L.; Isomura, M.; Yamauchi, S.-I.; Nakamura, T.; Nakamura, E. Indole Synthesis via Cyclative Formation of 2,3-Dizincioindoles and Regioselective Electrophilic Trapping. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Zhou, B.; Wu, Z.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of Carbazoles from 2-Iodobiphenyls by Palladium-Catalyzed C–H Activation and Amination with Diaziridinone. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, R.; Singh, K.N. Palladium Catalyzed C–C and C–N Bond Formation via ortho-C–H Activation and Decarboxylative Strategy: A Practical Approach towards N-Acylated Indoles. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, Y.; Armunanto, R.; Pranowo, H.D. Investigation of rubidium(I) ion solvation in liquid ammonia using QMCF-MD simulation and NBO analysis of first solvation shell structure. J. Mol. Model. 2018, 24, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Li, D.; Zeng, F. Palladium-Catalyzed Sequential Vinylic C−H Arylation/Amination of 2-Vinylanilines with Aryl boronic Acids: Access to 2-Arylindoles. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Chen, X.; Mo, B.; Li, X.; Sun, P.; Chen, C. Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Multisubstituted Indoles through Tandem Ullmann-Type C−N Formation and Cross-dehydrogenative Coupling Reactions. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 5288–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zou, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. One-Pot Synthesis of Indole-3-acetic Acid Derivatives through the Cascade Tsuji−Trost Reaction and Heck Coupling. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 6805–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panyam, P.K.R.; Sreedharan, R.; Gandhi, T. Synthesis of topologically constrained naphthalimide appended palladium(II)-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes—Insights into additive controlled product selectivity. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 4357–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, S.; Wang, B.; Li, B. The regioselective synthesis of 2-phosphinoylindoles via Rh(III)-catalyzed C–H activation. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Cheng, B.; Duan, X.; Bao, B.; Li, Y.; Zhai, H. Synthesis of cis-5,5a,6,10b-Tetrahydroindeno[2,1-b]indoles through Palladium-Catalyzed Decarboxylative Coupling of Vinyl Benzoxazinanones with Arynes. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishia, K.; Oikawa, K.; Yano, H.; Suzuki, T.; Obora, Y. N,N-Dimethylformamide-stabilized palladium nanoclusters as a catalyst for Larock indole synthesis. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 11324–11329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcadi, A.; Cacchi, S.; Fabrizi, G.; Ghirga, F.; Goggiamani, A.; Iazzetti, A.; Marinelli, F. Palladium-Catalyzed Cascade Approach to 12-(Aryl)indolo-[1,2-c]quinazolin-6(5H)-ones. Synthesis 2018, 50, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Shen, X.-Q.; Chu, J.-J.; Hu, B.-L.; Zhang, X.-G. Palladium-catalyzed intramolecular aerobic C–H amination of enamines for the synthesis of 2-trifluoromethylindoles. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirujano, F.; Lopez-Maya, E.; Navarro, J.A.R.; De Vos, D.E. Pd(II)–Ni(II) Pyrazolate Framework as Active and Recyclable Catalyst for the Hydroamination of Terminal Alkynes. Top. Catal. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).