Sulfonate Ionic Liquid as a Stable and Active Catalyst for Levoglucosenone Production from Saccharides via Catalytic Pyrolysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
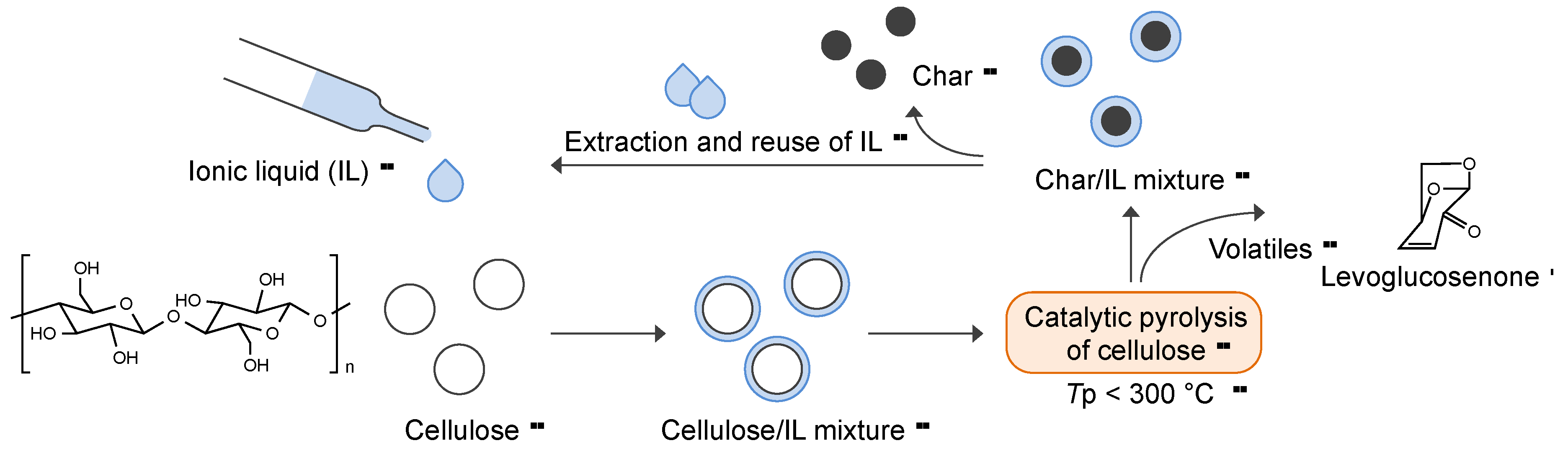
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Cellulose/IL Mixtures
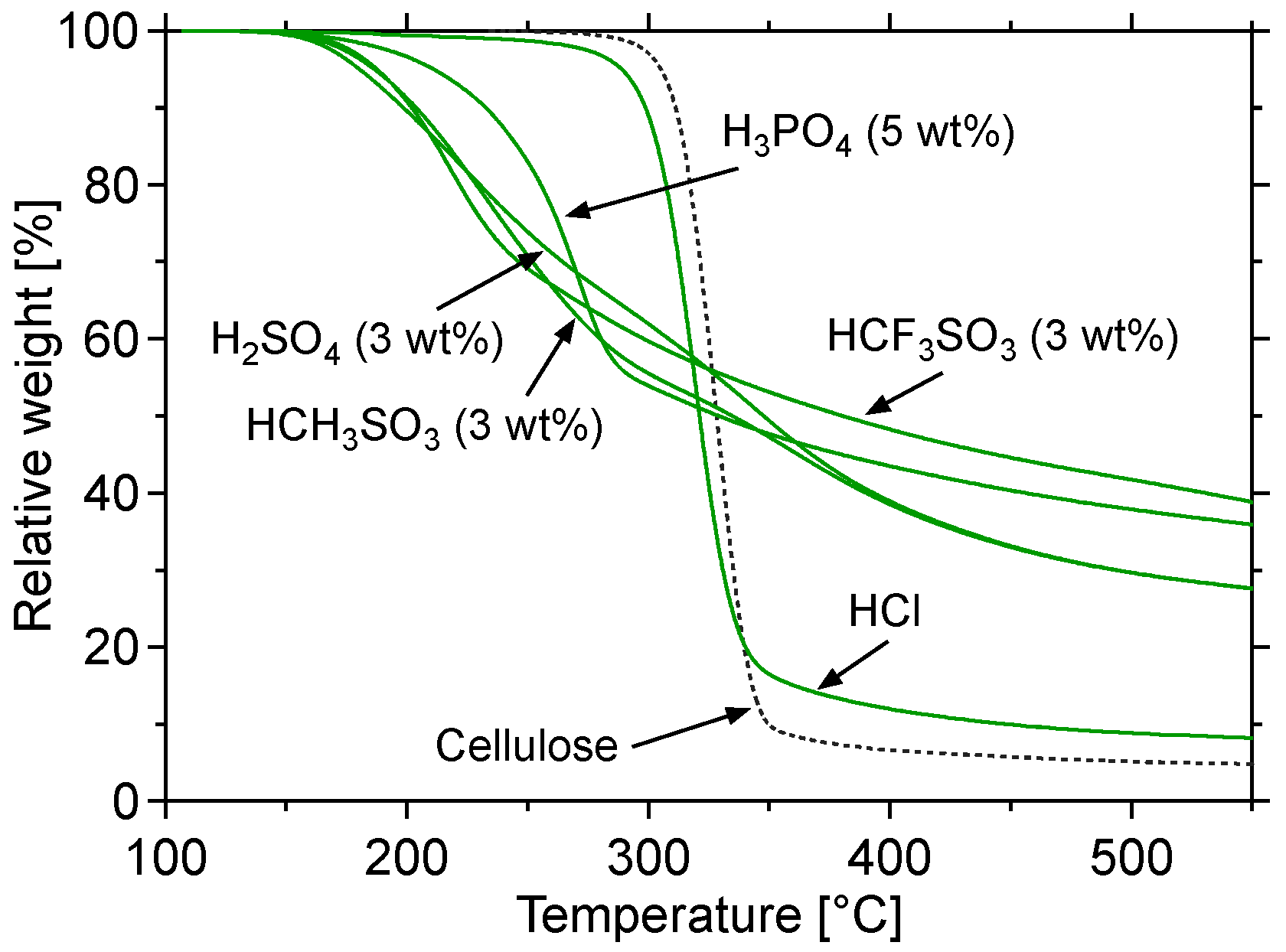
2.1.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis
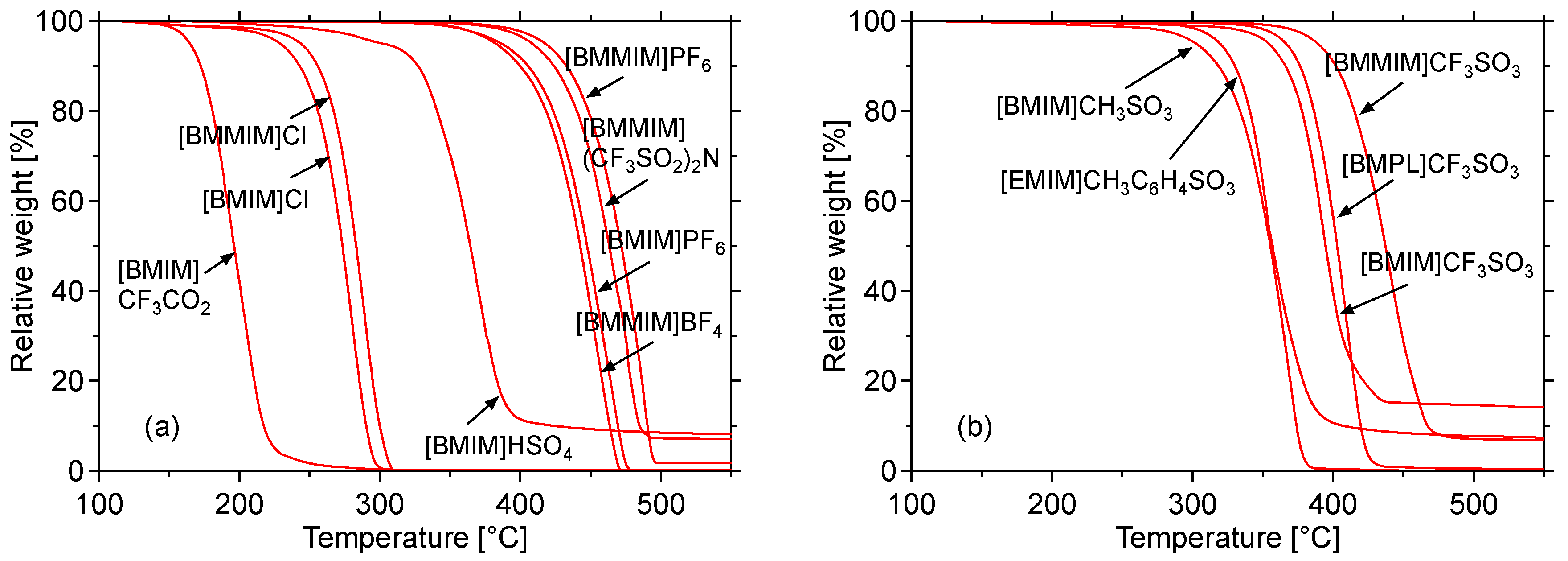
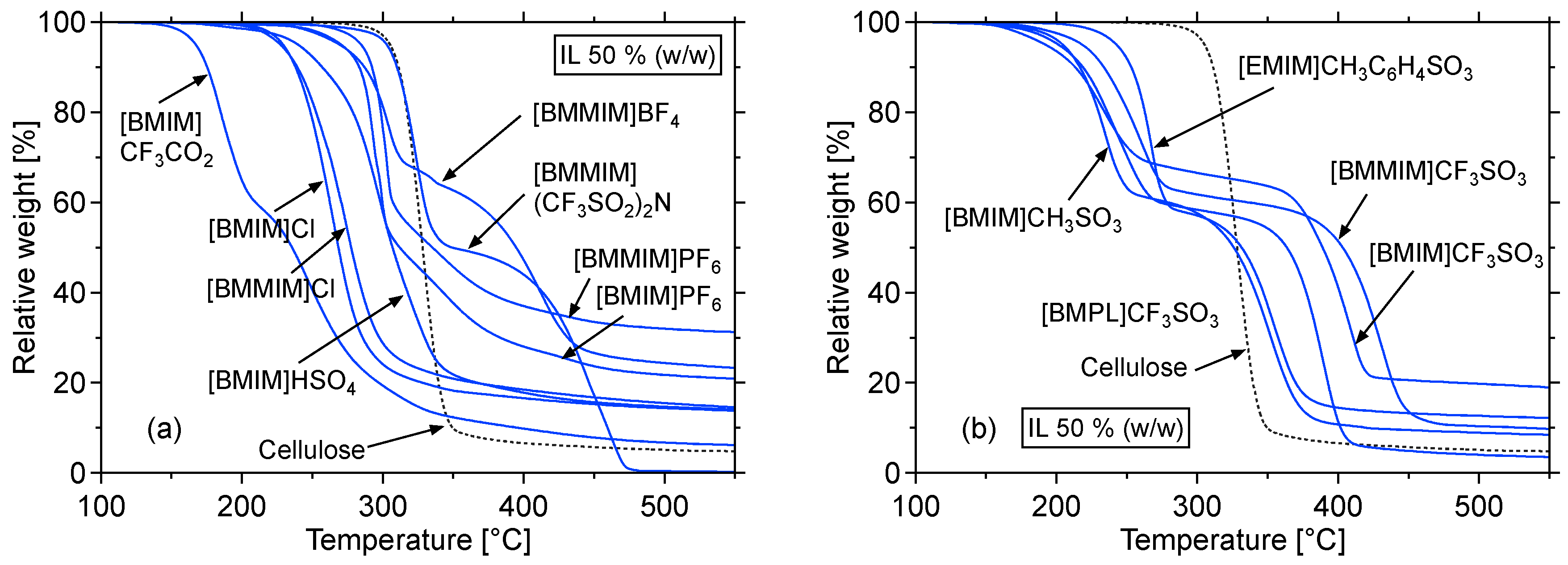
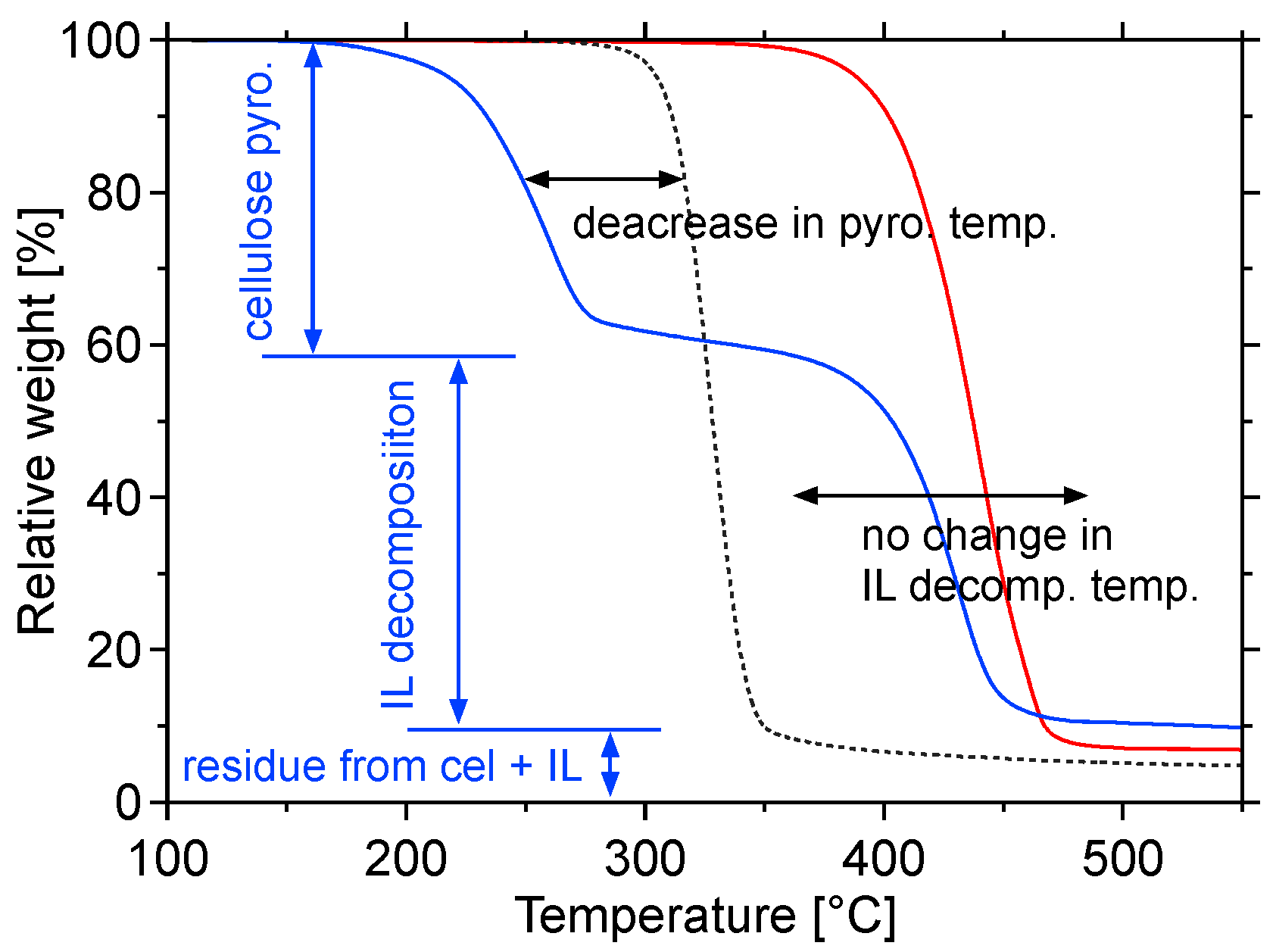
| IL | Cellulose pyrolysis | IL decomposition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tstart,cel [°C] | Tonset,cel [°C] | Tstart,IL [°C] | Tonset,IL [°C] | Tstart,IL – Tonset,cel [°C] | |
| None | 292 | 310 | – | – | – |
| [BMMIM]BF4 | 243 | 282 | 356 | 416 | 74 |
| [BMMIM](CF3SO2)2N | 279 | 307 | 381 | 433 | 74 |
| [BMIM]CH3SO3 | 181 | 210 | 262 | 332 | 52 |
| [EMIM]CH3C6H4SO3 | 223 | 251 | 299 | 333 | 48 |
| [BMPL]CF3SO3 | 175 | 208 | 346 | 383 | 138 |
| [BMIM]CF3SO3 | 166 | 198 | 322 | 370 | 124 |
| [BMMIM]CF3SO3 | 189 | 224 | 365 | 407 | 141 |
2.1.2. Pyrolysis Products
| Entry | IL | Tp a [°C] | Yields [wt% on a cellulose mass basis] | IL recovery [%] | Total mass balance [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO/CO2 | Condensable matter b (water) | Char b | Levoglucosenone (in mol c) | |||||
| 1 | None d | 350 | 0.8/2.8 | 57.3 (22.2) | 24.6 | 2.4 (3.1) | – | 85.5 |
| 2 | [BMIM]Cl | 300 | 0.91/8.5 | 51.4 (34.4) | 51.4 | 3.0 (3.9) | 7.3 | 71.1 |
| 3 | [BMMIM]BF4 d | 300 | 0.9/4.8 | 69.9 (20.8) | 63.3 | n.d. (–) | 78.6 | 98.4 |
| 4 | [BMIM]HSO4 | 300 | 2.7/17.4 | 67.9 (39.0) | 67.6 | 1.9 (2.4) | 15.5 | 85.6 |
| 5 | [BMMIM](CF3SO2)2N | 350 | 1.2/3.8 | 64.4 (31.1) | 23.3 | 1.9 (2.5) | 101.1 | 96.6 |
| 6 | [BMIM]CH3SO3 | 300 | 0.7/3.8 | 81.3 (40.2) | 27.6 | 20.7 (26.7) | 85.3 | 99.4 |
| 7 | [EMIM]CH3C6H4SO3 | 300 | 0.8/3.8 | 77.8 (37.7) | 31.1 | 29.7 (38.2) | 81.6 | 97.6 |
| 8 | [BMPL]CF3SO3 | 300 | 0.2/2.2 | 52.6 (30.0) | 32.1 | 25.0 (32.1) | 96.9 | 91.9 |
| 9 | [BMIM]CF3SO3 | 300 | 1.1/3.0 | 59.0 (37.8) | 44.8 | 18.1 (23.3) | 94.7 | 101.3 |
| 10 | [BMMIM]CF3SO3 d | 300 | 0.8/2.2 | 62.0 (32.0) | 32.7 | 21.4 (27.6) | 99.4 | 98.6 |
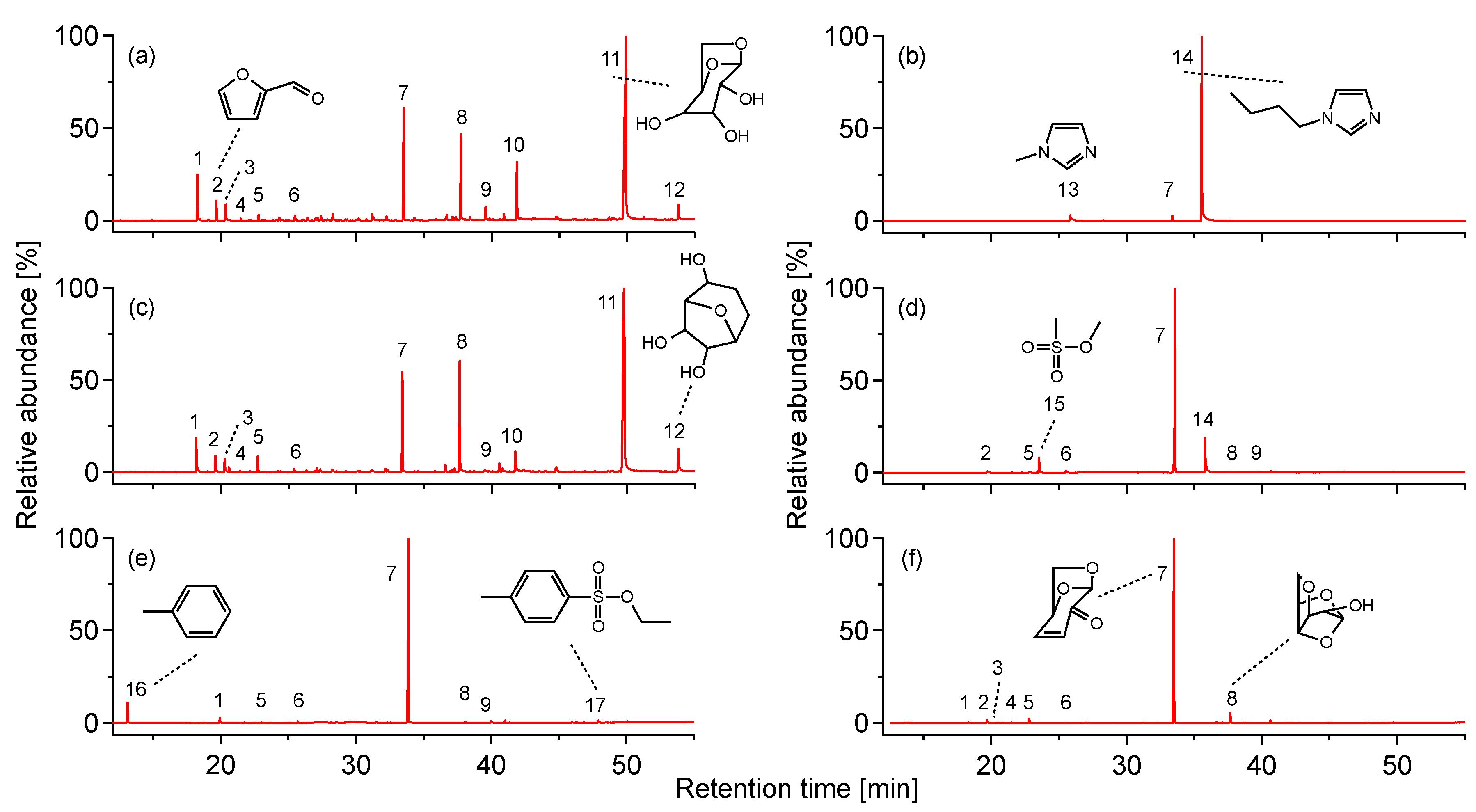
2.1.3. Discussion on Catalysis of Sulfonate ILs
| Entry | Acid | Tp [°C] | Yields [wt% on a cellulose mass basis] | Total mass balance [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO/CO2 | Condensable matter (water) | Char | Levoglucosenone (in mol) | ||||
| 11 | H3PO4 (3 wt%) a | 300 | 1.1/2.7 | 42.8 (32.9) | 57.3 | 8.9 (11.5) | 97.4 |
| 12 | HCl (3 wt%) | 300 | 0.2/1.0 | 21.9 (13.0) | 71.6 | 1.6 (2.0) | 94.9 |
| 13 | H2SO4 (3 wt%) | 300 | 1.4/3.2 | 39.4 (25.0) | 56.6 | 8.4 (10.8) | 100.7 |
| 14 | CH3SO3H (3 wt%) | 300 | 1.3/3.5 | 41.7 (34.5) | 53.2 | 1.9 (2.5) | 99.7 |
| 15 | CF3SO3H (3 wt%) | 300 | 2.3/4.7 | 34.9 (24.1) | 57.5 | 3.3 (4.2) | 99.4 |
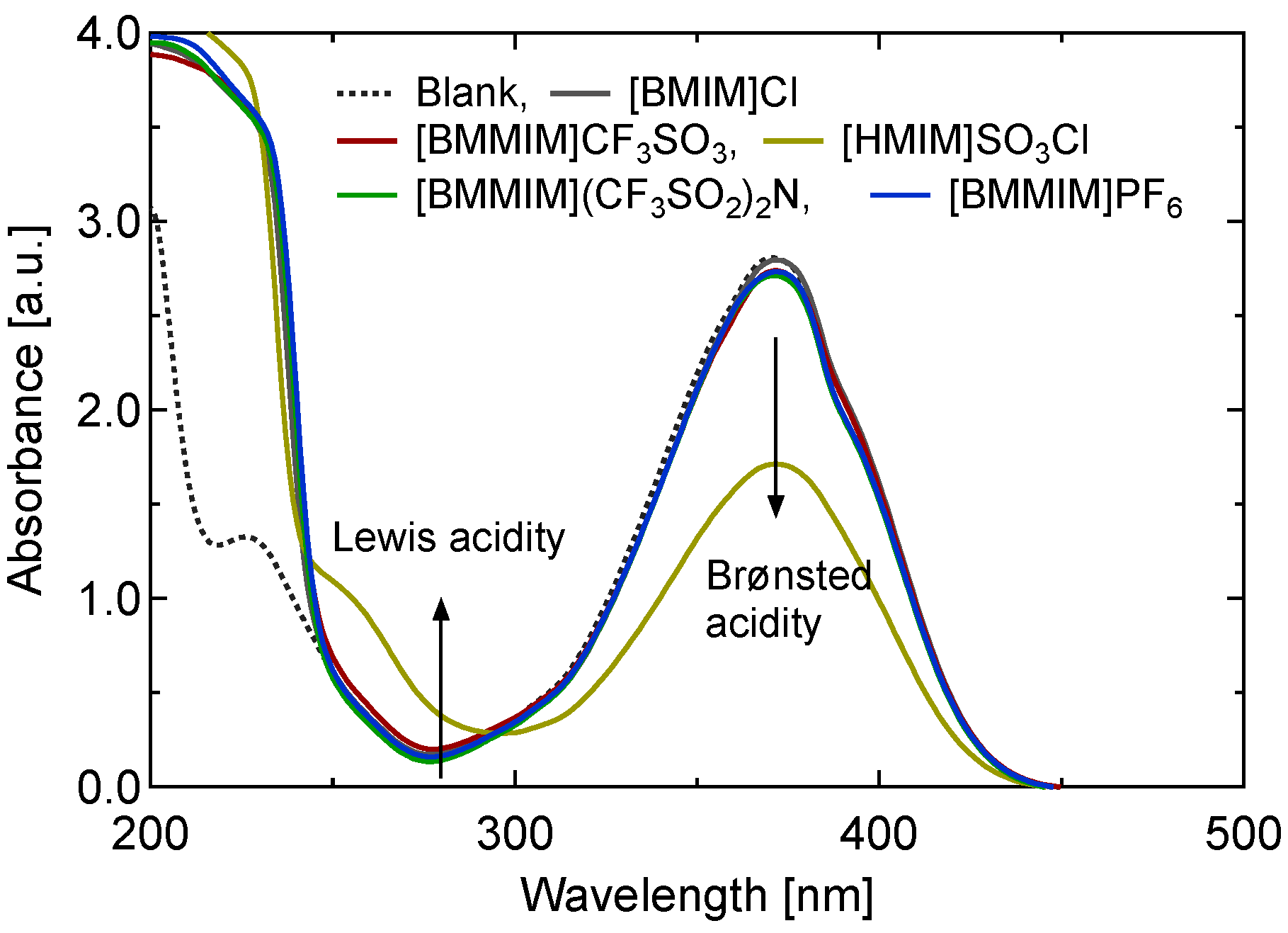
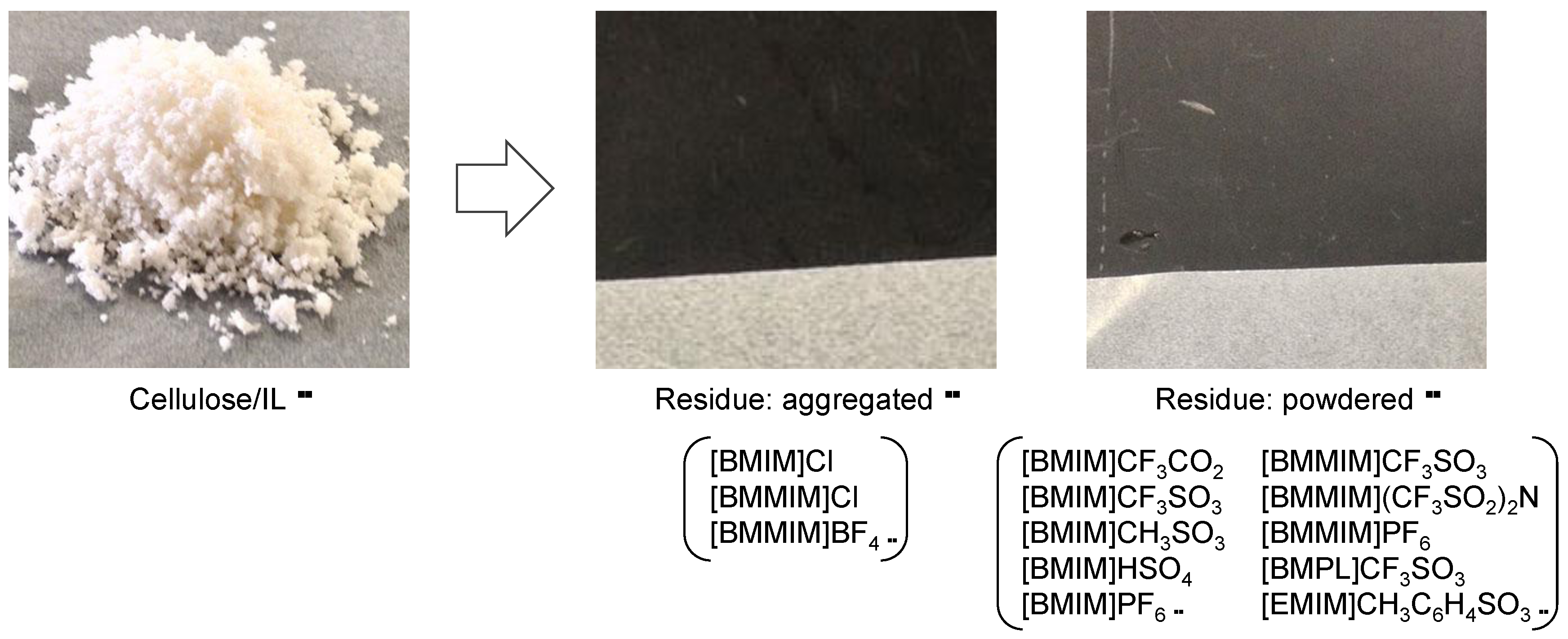
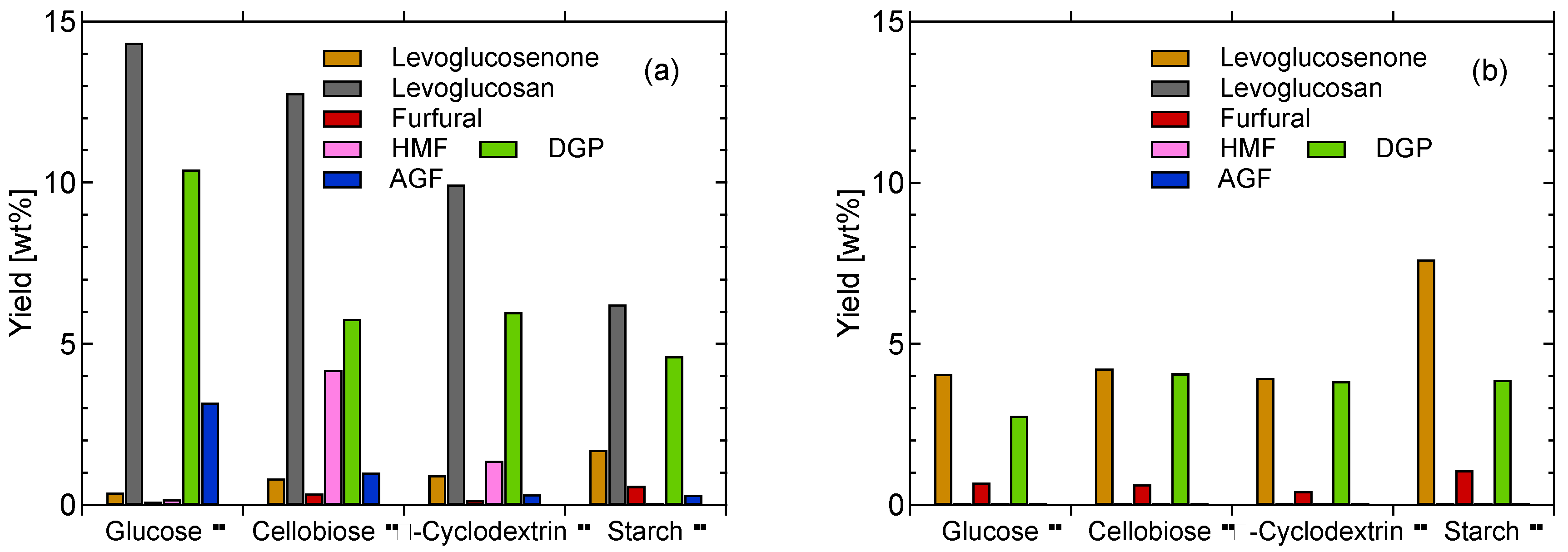
2.2. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Saccharides Other than Cellulose by ILs
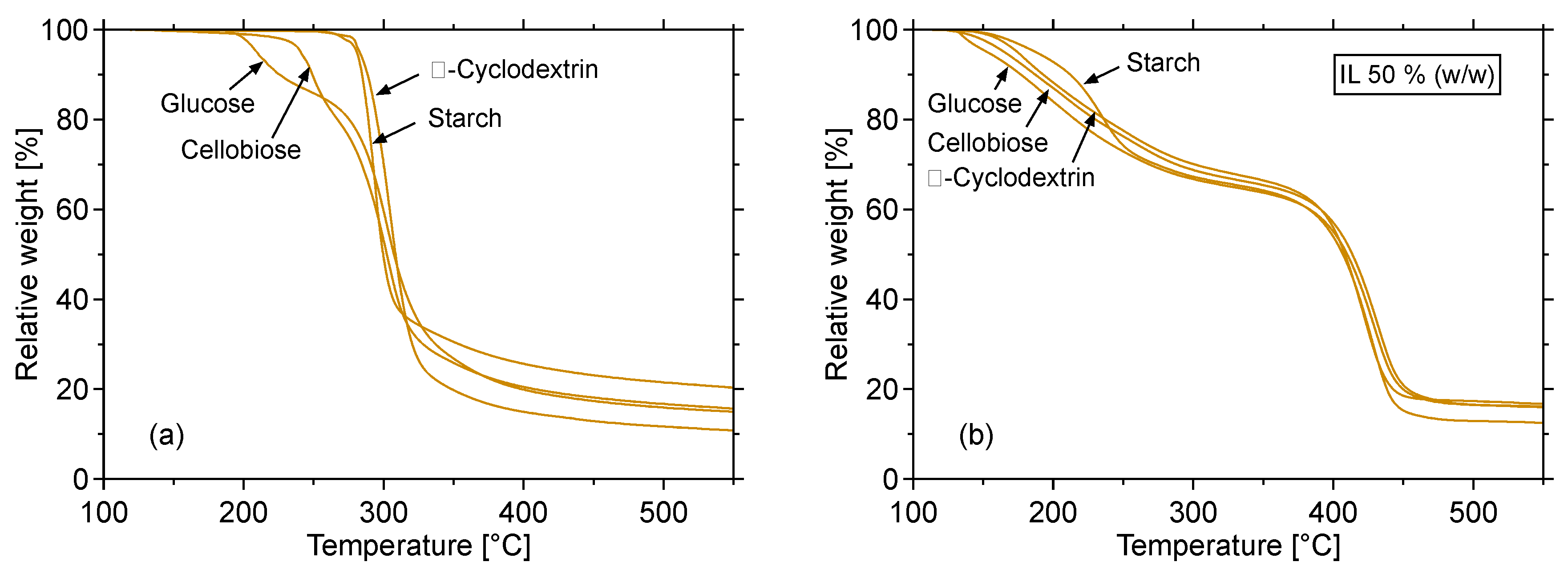
| Entry | Sample a | Tp [°C] | Yields [wt% on a cellulose mass basis] | IL recovery [%] | Total mass balance [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO/CO2 | Condensable matter (water) | Char | Levoglucosenone | |||||
| 16 | Glucose | 350 | 2.27 | 54.7 (36.0) | 33.1 | 0.4 | – | 97.2 |
| 17 | Cellobiose | 350 | 1.92 | 51.0 (29.4) | 34.3 | 0.8 | – | 94.0 |
| 18 | α-Cyclodextrin | 350 | 2.52 | 51.3 (31.2) | 32.5 | 0.9 | – | 93.2 |
| 19 | Starch | 350 | 1.83 | 54.6 (36.9) | 31.3 | 1.7 | – | 93.9 |
| 20 | Glucose/IL | 300 | 1.08 | 55.4 (38.0) | 44.1 | 4.1 | 95.8 | 100.7 |
| 21 | Cellobiose/IL | 300 | 1.08 | 55.5 (33.0) | 42.8 | 4.2 | 96.5 | 100.1 |
| 22 | α-Cyclodextrin/IL | 300 | 1.12 | 54.6 (35.8) | 44.8 | 3.9 | 94.4 | 99.6 |
| 23 | Starch/IL | 300 | 1.13 | 56.6 (34.1) | 41.0 | 7.6 | 95.9 | 99.5 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Pyrolysis and the Product Analysis
3.3. Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olivier-Bourbigou, H.; Magna, L.; Morvan, D. Ionic liquids and catalysis: Recent progress from knowledge to applications. Appl. Catal. A 2010, 373, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution of Cellose with Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Chen, Z.-L. Research progress on dissolution and functional modification of cellulose in ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2008, 142, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansalot-Matras, C.; Moreau, C. Dehydration of fructose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in the presence of ionic liquids. Catal. Commun. 2003, 4, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, J.B.; Raines, R.T. Simple Chemical Transformation of Lignocellulosic Biomass into Furans for Fuels and Chemicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Song, H.; Chou, L. Catalytic conversion of cellulose to chemicals in ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadi, A.; Schall, C.; Varanasi, S. Mitigation of cellulose recalcitrance to enzymatic hydrolysis by ionic liquid pretreatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2007, 137–140, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Ragauskas, A.J. Ionic Liquid as a Green Solvent for Lignin. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2007, 27, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Doherty, T.V.; Linhardt, R.J.; Dordick, J.S. Ionic liquid-mediated selective extraction of lignin from wood leading to enhanced enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 102, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, B.J.; Ekerdt, J.G. Depolymerization of oak wood lignin under mild conditions using the acidic ionic liquid 1-H-3-methylimidazolium chloride as both solvent and catalyst. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Zhu, Q.; Ma, D.; Liu, X.; Han, X. Direct conversion and NMR observation of cellulose to glucose and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) catalyzed by the acidic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Catal. A 2011, 334, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Qiao, K.; Tomida, D.; Yokoyama, C. Preparation of 5-hydroymethylfurfural by dehydration of fructose in the presence of acidic ionic liquid. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Simanjuntaka, F.S.H.; Oh, J.Y.; Lee, K.I.; Lee, S.D.; Cheong, M.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, H. Ionic-liquid-catalyzed decarboxylation of glycerol carbonate to glycidol. J. Catal. 2013, 297, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, L.; Demange, R.; Zhu, Y.H.; Vogel, P. The use of levoglucosenone and isolevoglucosenone as templates for the construction of C-linked disaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 1235–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samet, A.V.; Lutov, D.N.; Firgang, S.I.; Lyssenko, K.A.; Semenov, V.V. A concise approach to chiral chromenes based on levoglucosenone. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 3026–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, S.; Zhou, Z.; Norinaga, K.; Hayashi, J.-i. Efficient levoglucosenone production by catalytic pyrolysis of cellulose mixed with ionic liquid. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 3306–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlake, C.P.; Crosthwaite, J.M.; Hert, D.G.; Aki, S.N.V.K.; Brennecke, J.F. Thermophysical Properties of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2004, 49, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, P.A. Why Does a Reduction in Hydrogen Bonding Lead to an Increase in Viscosity for the 1-Butyl-2,3-dimethyl-imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids? J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4844–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Peng, J.; Hu, S.; Li, J.; Zhai, M. Thermal decomposition of allyl-imidazolium-based ionic liquid studied by TGA–MS analysis and DFT calculations. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 501, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemantle, M. Chapter 1 Introduction. In An Introduction to Ionic Liquids; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dobele, G.; Rossinskaja, G.; Telysheva, G.; Meier, D.; Faix, O. Cellulose dehydration and depolymerization reactions during pyrolysis in the presence of phosphoric acid. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1999, 49, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobele, G.; Dizhbite, T.; Rossinskaja, G.; Telysheva, G.; Meier, D.; Radtke, S.; Faix, O. Pre-treatment of biomass with phosphoric acid prior to fast pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2003, 68–69, 197–211. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, X.W.; Wang, Z.; Liao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Q.X. Preparation of levoglucosenone through sulfuric acid promoted pyrolysis of bagasse at low temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids: Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Qiao, K.; Tomida, D.; Yokoyama, C. 1-Methylimidazolium Chlorosulfate ([HMIm]SO3Cl): A Novel Ionic Liquid with Dual Brønsted–Lewis Acidity. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 728–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowhurst, L.; Mawdsley, P.R.; Perez-Arlandis, J.M.; Salter, P.A.; Welton, T. Solvent–solute interactions in ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 2790–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulati, N.; Sobkowiak, M.; Mathews, J.P.; Painter, P. Low-Temperature Treatment of Illinois No. 6 Coal in Ionic Liquids. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 3548–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, E.B.; Goldsmith, A.I.; Seeman, J.I. A model that distinguishes the pyrolysis of d-glucose, D-fructose, and sucrose from that of cellulose. Application to the understanding of cigarette smoke formation. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2003, 66, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kudo, S.; Zhou, Z.; Yamasaki, K.; Norinaga, K.; Hayashi, J.-i. Sulfonate Ionic Liquid as a Stable and Active Catalyst for Levoglucosenone Production from Saccharides via Catalytic Pyrolysis. Catalysts 2013, 3, 757-773. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3040757
Kudo S, Zhou Z, Yamasaki K, Norinaga K, Hayashi J-i. Sulfonate Ionic Liquid as a Stable and Active Catalyst for Levoglucosenone Production from Saccharides via Catalytic Pyrolysis. Catalysts. 2013; 3(4):757-773. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3040757
Chicago/Turabian StyleKudo, Shinji, Zhenwei Zhou, Kento Yamasaki, Koyo Norinaga, and Jun-ichiro Hayashi. 2013. "Sulfonate Ionic Liquid as a Stable and Active Catalyst for Levoglucosenone Production from Saccharides via Catalytic Pyrolysis" Catalysts 3, no. 4: 757-773. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3040757
APA StyleKudo, S., Zhou, Z., Yamasaki, K., Norinaga, K., & Hayashi, J.-i. (2013). Sulfonate Ionic Liquid as a Stable and Active Catalyst for Levoglucosenone Production from Saccharides via Catalytic Pyrolysis. Catalysts, 3(4), 757-773. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3040757




