Physicochemical Characterization and Formation Pathway of Hydrochar from Brewer’s Spent Grain via Hydrothermal Carbonization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
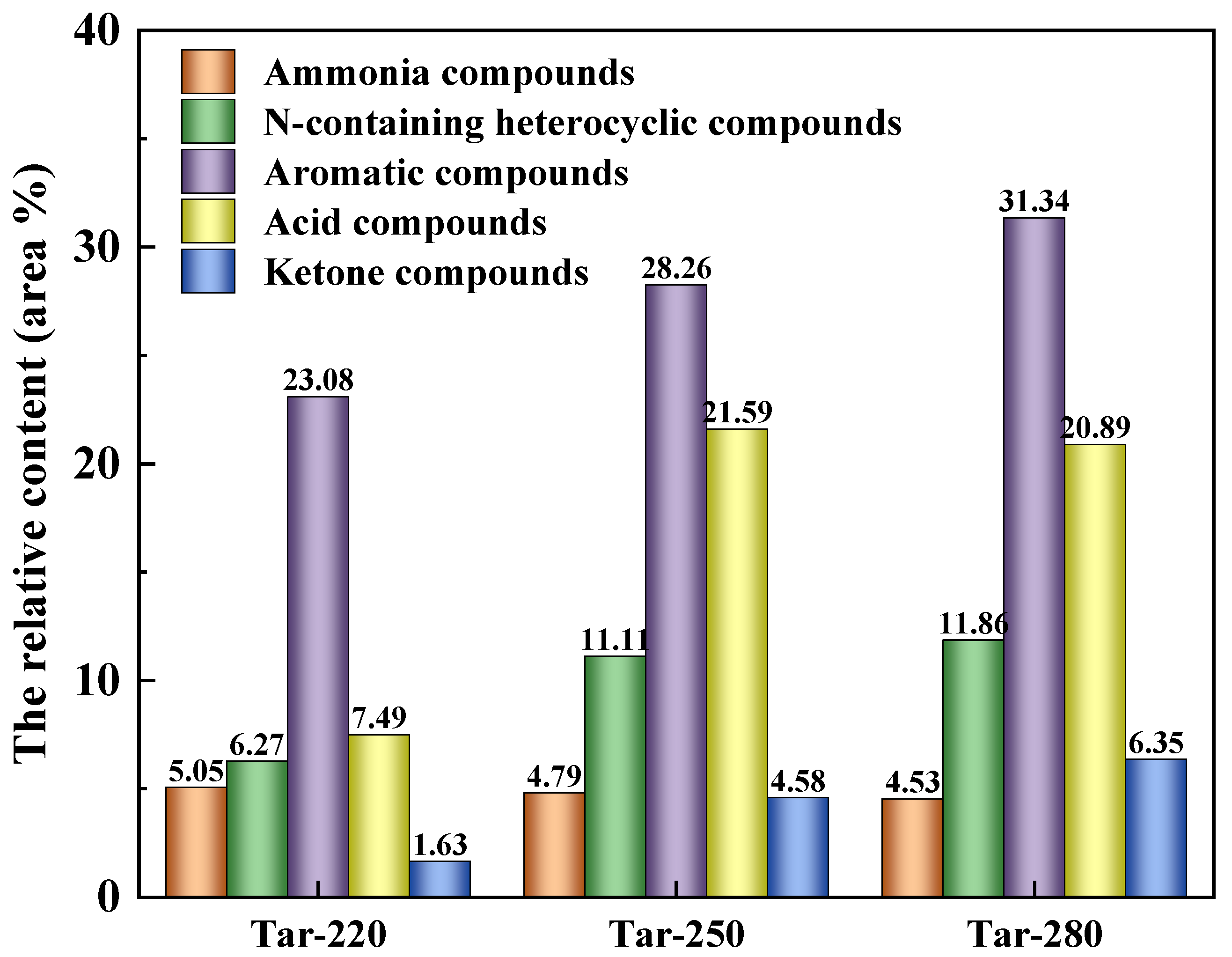
2.1. The Composition Analysis of Tar
2.2. Proximate and Ultimate Analysis of BSG and Hydrochars
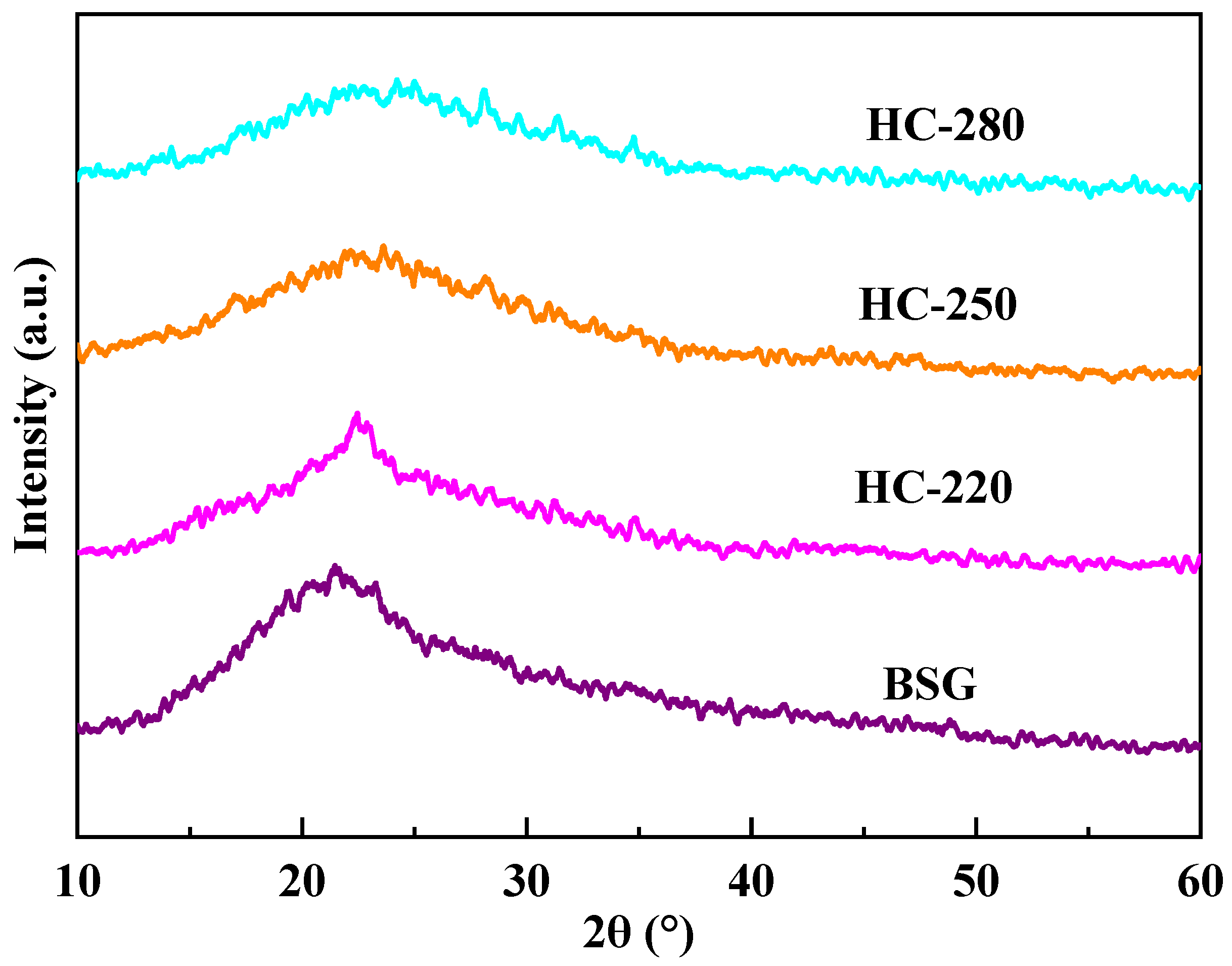
2.3. Microcrystalline Structure Analysis of BSG and Hydrochar
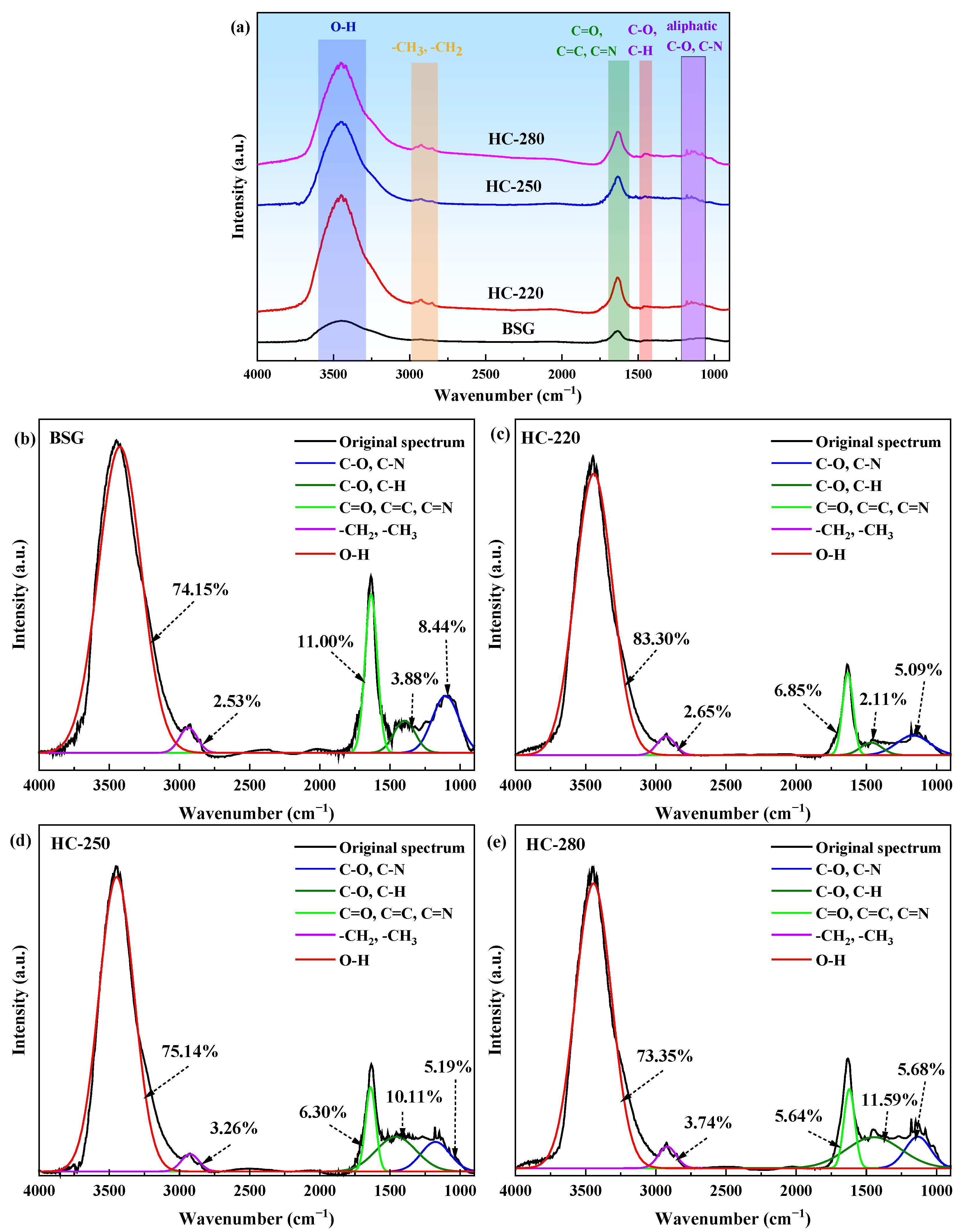
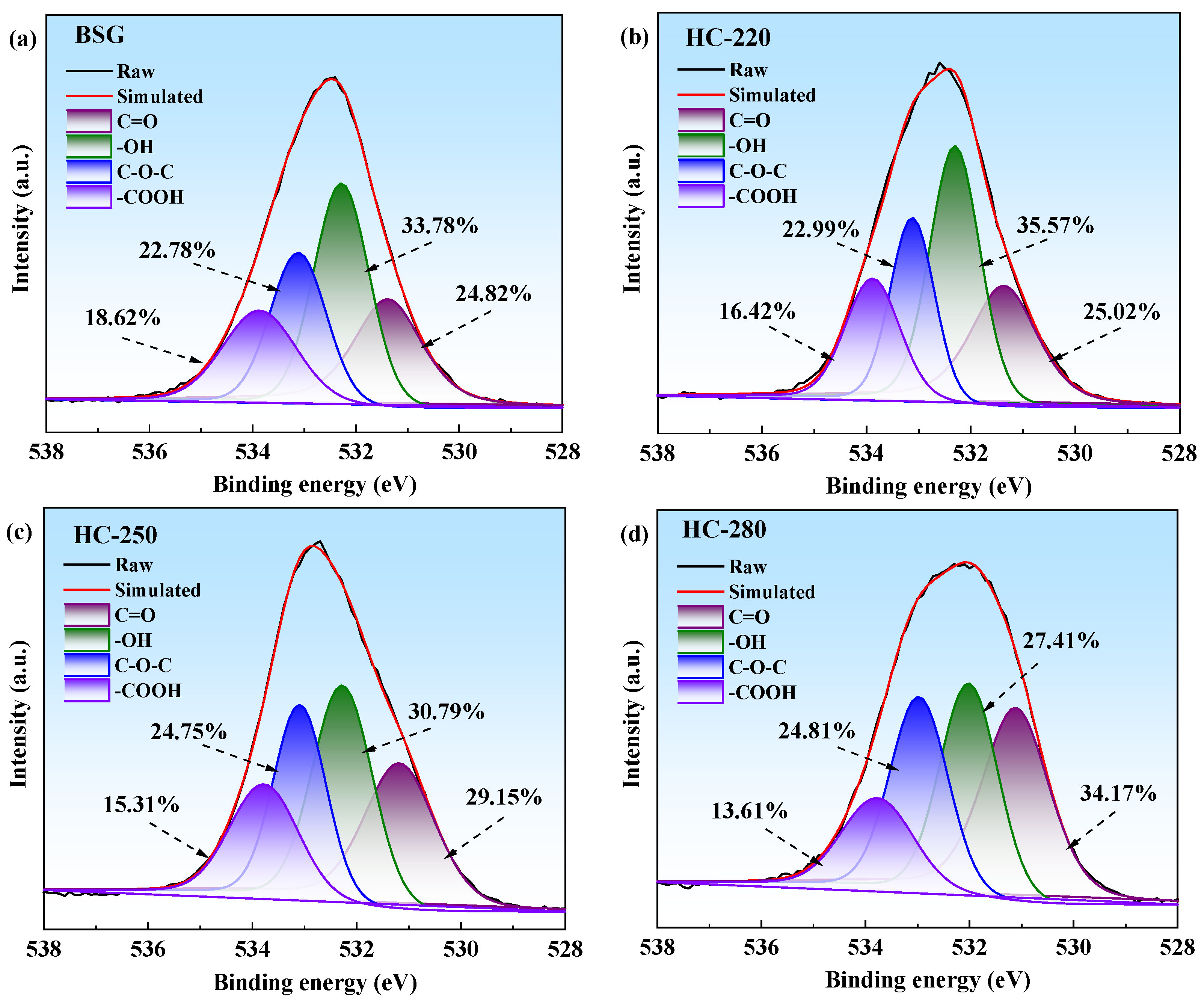
2.4. Surface Chemical Properties Analysis of BSG and Hydrochar
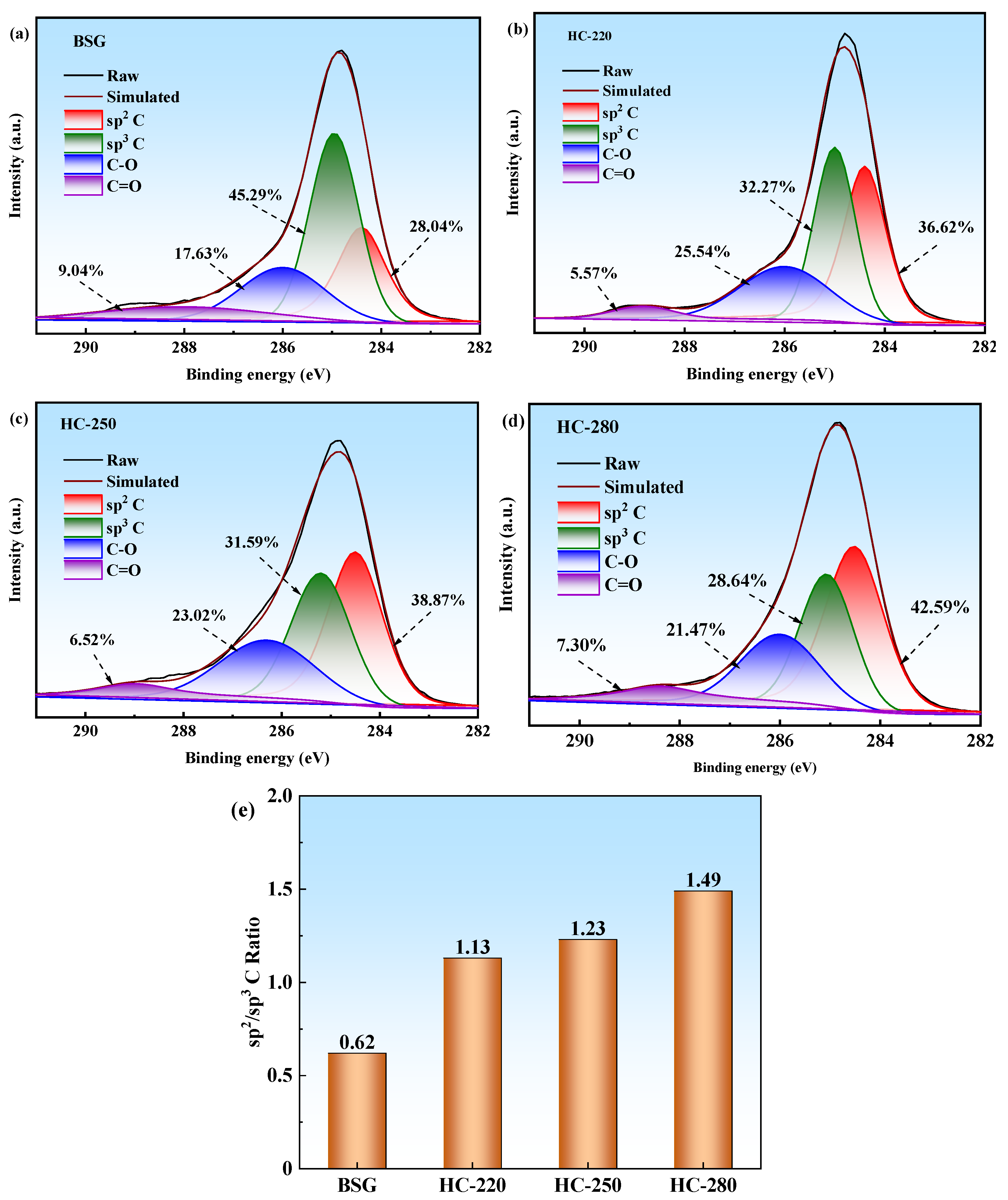
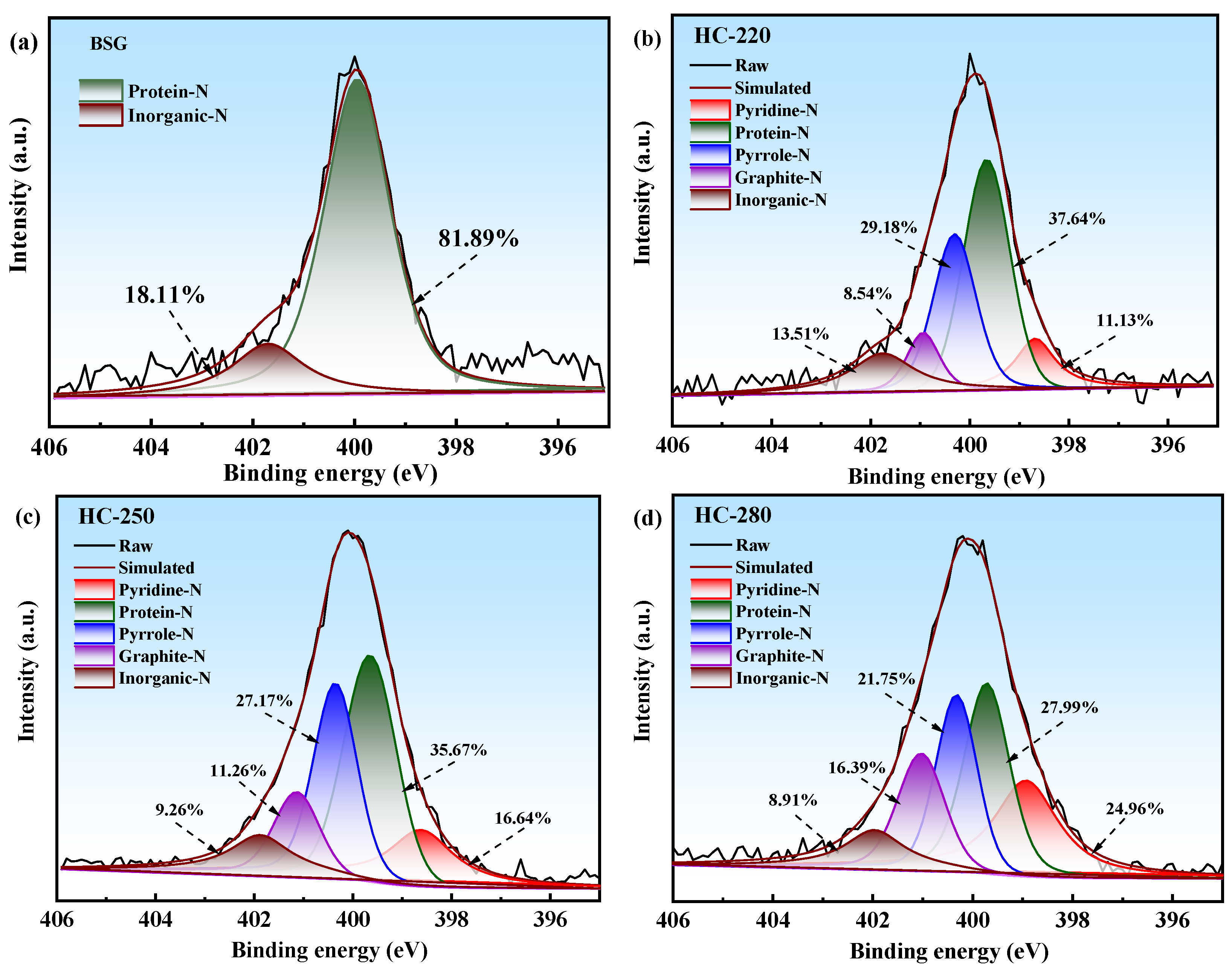
2.5. XPS Analysis of BSG and Hydrochars
2.6. SEM Analysis of BSG and Hydrochar
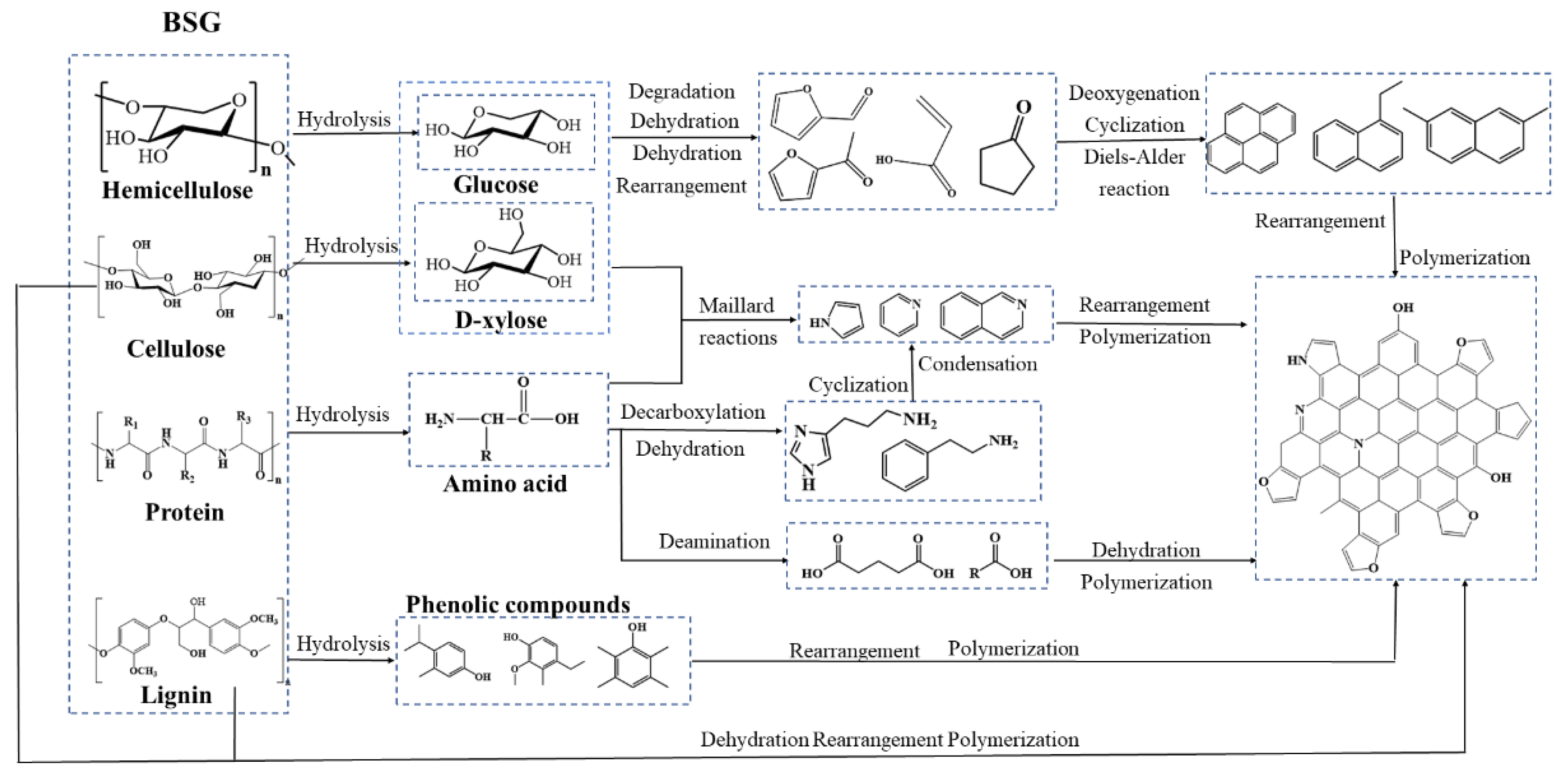
2.7. The Formation Pathways of Hydrochar
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
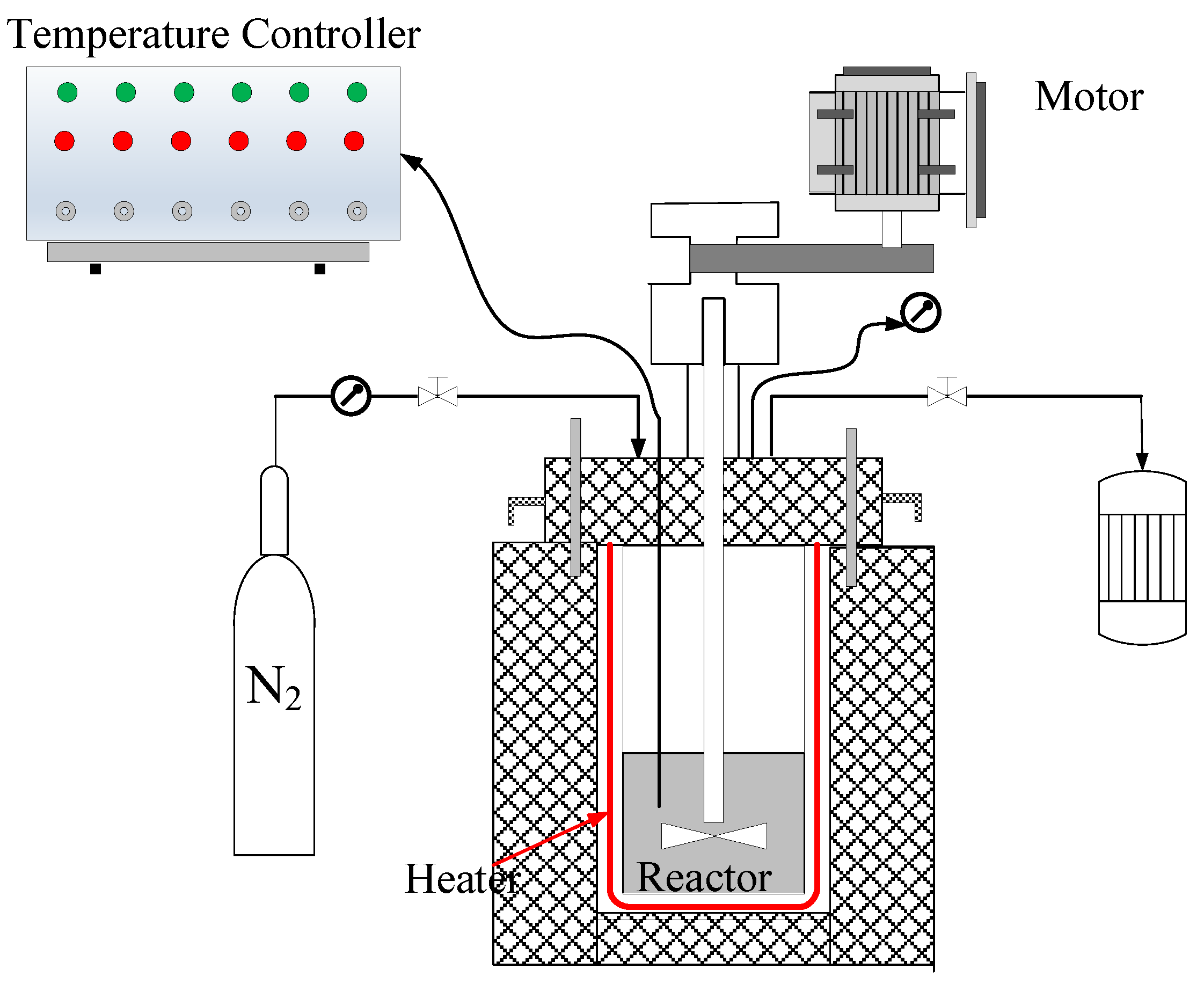
3.2. Hydrothermal Carbonization Experiments
3.3. Characterization
3.3.1. Tar Analysis
3.3.2. Hydrochar Analysis
4. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashokkumar, V.; Venkatkarthick, R.; Jayashree, S.; Chuetor, S.; Dharmaraj, S.; Kumar, G.; Chen, W.-H.; Ngamcharussrivichai, C. Recent advances in lignocellulosic biomass for biofuels and value-added bioproducts—A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Mun, T.-Y.; Yang, W.; Lee, U.; Hwang, J.; Jang, E.; Choi, C. Effects of hydrothermal treatment of sewage sludge on pyrolysis and steam gasification. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 103, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H. Generalized two-dimensional correlation infrared spectroscopy to reveal the mechanisms of lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 3013–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Guo, Q.; Ding, L.; Gong, Y.; Yu, G. Insights into pyrolysis process of coconut shell waste hydrochar: In-situ structural evolution and reaction kinetics. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 448, 141701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Cheng, A.-S.; Xie, W.-L.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.-B.; Zhu, L.-J.; Zhang, B.; Li, M.-X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, T.-P.; et al. The oxalic acid-assisted fast pyrolysis of biomass for the sustainable production of furfural. Fuel 2022, 322, 124279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, T.P.; Quesada, H.B.; Bergamasco, R.; Vareschini, D.T.; de Barros, M.A.S.D. Activated hydrochar produced from brewer’s spent grain and its application in the removal of acetaminophen. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.S.; Orive, M.; Iñarra, B.; Castelo, J.; Estévez, A.; Nazzaro, J.; Iloro, I.; Elortza, F.; Zufía, J. Brewers’ Spent Yeast and Grain Protein Hydrolysates as Second-Generation Feedstuff for Aquaculture Feed. Waste Biomass- Valorization 2020, 11, 5307–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, L.D.M.S.; Lira, T.S.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Ataíde, C.H.; Barrozo, M.A.S. Pyrolysis of brewer’s spent grain: Kinetic study and products identification. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 121, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Yang, W.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liang, C.; Liu, S.; Ling, C.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Z. Comprehensive Research on the Influence of Nonlignocellulosic Components on the Pyrolysis Behavior of Chinese Distiller’s Grain. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 3103–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abifarin, J.; Obada, D.; Dauda, E.; Dodoo-Arhin, D. Experimental data on the characterization of hydroxyapatite synthesized from biowastes. Data Brief. 2019, 26, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zheng, C.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J. Co-hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge and banana stalk: Fuel properties of hydrochar and environmental risks of heavy metals. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadullah, M. Barriers of commercial power generation using biomass gasification gas: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poerschmann, J.; Weiner, B.; Wedwitschka, H.; Baskyr, I.; Koehler, R.; Kopinke, F.-D. Characterization of biocoals and dissolved organic matter phases obtained upon hydrothermal carbonization of brewer’s spent grain. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 164, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasner, C.; Deerberg, G.; Lyko, H. Hydrothermal Carbonization: A Review. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2011, 83, 1932–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Dai, X.; Yao, J. Characteristics of hydrothermal treatment for the disintegration of oxytetracycline fermentation residue and inactivation of residual antibiotics. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 126011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abifarin, J.K.; Abifarin, F.B.; Ofodu, J.C. Lignin-hydrothermal fabrication of 3D hierarchical porous carbon for energy storage application. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2024, 26, 101883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arauzo, P.; Du, L.; Olszewski, M.; Zavala, M.M.; Alhnidi, M.; Kruse, A. Effect of protein during hydrothermal carbonization of brewer’s spent grain. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, B.; Wang, T.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. Production of char from sewage sludge employing hydrothermal carbonization: Char properties, combustion behavior and thermal characteristics. Fuel 2016, 176, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhong, Z.; Ding, K.; Song, Z. Production of aromatic hydrocarbons from catalytic co-pyrolysis of biomass and high density polyethylene: Analytical Py–GC/MS study. Fuel 2015, 139, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, S.S.; Rosendahl, L.; Rudolf, A. Hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass: A review of subcritical water technologies. Energy 2011, 36, 2328–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, D.; Wang, L.; Xu, G. Hydrothermal pretreatment for biogas production from anaerobic digestion of antibiotic mycelial residue. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. A review of the hydrothermal carbonization of biomass waste for hydrochar formation: Process conditions, fundamentals, and physicochemical properties. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso-Boateng, E.; Shama, G.; Wheatley, A.; Martin, S.; Holdich, R. Hydrothermal carbonisation of sewage sludge: Effect of process conditions on product characteristics and methane production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, C.; Xu, B.; Wang, T.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. Influence of temperature on nitrogen fate during hydrothermal carbonization of food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauline, A.L.; Joseph, K. Hydrothermal carbonization of organic wastes to carbonaceous solid fuel—A review of mechanisms and process parameters. Fuel 2020, 279, 118472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Mei, J.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, M.; Ma, T.; Ma, Z. Combined pretreatment with torrefaction and washing using torrefaction liquid products to yield upgraded biomass and pyrolysis products. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 228, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Gentili, F.G.; Söderlind, U.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H. Hydrothermal carbonization of natural microalgae containing a high ash content. Fuel 2019, 249, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Zou, B.; Ma, X.; Qu, Y.; Rong, C.; Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z. Preparation of carbon black from rice husk by hydrolysis, carbonization and pyrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8220–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Ma, Z.; Jin, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, Y. Hydrothermal carbonization of kitchen wastes: Physicochemical properties and combustion performance of hydrochars. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2025, 17, 033105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Shen, Y.; Ge, X.; Chen, M. Micro-mesoporous carbons from original and pelletized rice husk via one-step catalytic pyrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A. The production of carbon materials by hydrothermal carbonization of cellulose. Carbon 2009, 47, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, G.; An, Q.; Lin, L.; Shang, Y.; Wan, C. From wasted sludge to valuable biochar by low temperature hydrothermal carbonization treatment: Insight into the surface characteristics. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, P.; Huang, S.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Wu, S. Hydrothermal carbonization characteristics and mechanism of penicillin mycelial residues and CO2 gasification performance of hydrochars. Biomass-Bioenergy 2024, 183, 107130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yu, S.; Hao, N.; Wells, T.; Meng, X.; Li, M.; Pu, Y.; Liu, S.; Ragauskas, A.J. Characterization of products from hydrothermal carbonization of pine. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, T. Ethanol production from pulp & paper sludge and monosodium glutamate waste liquor by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation in batch condition. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 191, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, P.; Areeprasert, C.; Shen, Y.; Yoshikawa, K.; Xu, G. Hydrothermal treatment of antibiotic mycelial dreg: More understanding from fuel characteristics. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, J.; Wu, S. Fuel properties and combustion kinetics of hydrochar prepared by hydrothermal carbonization of bamboo. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 205, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhou, K.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Z.; Tong, Z.; Zhao, Z. Hydrophobic N-doped porous biocarbon from dopamine for high selective adsorption of p-Xylene under humid conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Yang, L. Adsorption of Volatile Organic Compounds at Medium-High Temperature Conditions by Activated Carbons. Energy Fuels 2019, 34, 3679–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Xia, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, H. Transformation of Nitrogen and Evolution of N-Containing Species during Algae Pyrolysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6570–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, A.; Koch, F.; Stelzl, K.; Wüst, D.; Zeller, M. Fate of Nitrogen during Hydrothermal Carbonization. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 8037–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Balasubramanian, R.; Srinivasan, M. Hydrothermal conversion of biomass waste to activated carbon with high porosity: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, P. Hydrothermal Degradation of Amino Acids. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 4947–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, C.; Liu, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Qiu, R. Synergistic effect of hydrothermal co-carbonization of sewage sludge with fruit and agricultural wastes on hydrochar fuel quality and combustion behavior. Waste Manag. 2019, 100, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, S.; Cui, D.; Pan, S.; Xu, F.; Xu, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, G. Co-hydrothermal carbonization of corn stover and food waste: Characterization of hydrochar, synergistic effects, and combustion characteristic analysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | Proximate Analysis (wt.%, Dry Basis) | Ultimate Analysis (wt.%, Dry Basis) | Atomic Ratio | Yield (%) | HHV b (MJ/kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ash | Fixed Carbon | Volatile | C | H | O a | N | S | H/C | O/C | |||
| BSG | 3.89 ± 0.06 | 14.05 ± 0.15 | 82.06 ± 0.25 | 50.17 | 7.67 | 34.39 | 3.67 | 0.21 | 1.83 | 0.51 | - | 32.74 |
| HC-220 | 2.28 ± 0.11 | 23.14 ± 0.24 | 74.58 ± 0.19 | 61.32 | 7.35 | 26.52 | 2.39 | 0.14 | 1.44 | 0.32 | 77.51 | 34.70 |
| HC-250 | 1.85 ± 0.09 | 25.82 ± 0.17 | 72.33 ± 0.20 | 64.25 | 7.12 | 24.44 | 2.25 | 0.09 | 1.33 | 0.29 | 72.14 | 35.03 |
| HC-280 | 1.72 ± 0.10 | 27.07 ± 0.12 | 71.21 ± 0.14 | 66.91 | 6.97 | 22.32 | 2.03 | 0.05 | 1.25 | 0.25 | 65.33 | 35.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Huang, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, X.; Wu, S. Physicochemical Characterization and Formation Pathway of Hydrochar from Brewer’s Spent Grain via Hydrothermal Carbonization. Catalysts 2025, 15, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090847
Liu P, Huang S, Wu Y, Li X, Wei X, Wu S. Physicochemical Characterization and Formation Pathway of Hydrochar from Brewer’s Spent Grain via Hydrothermal Carbonization. Catalysts. 2025; 15(9):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090847
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Pengbo, Sheng Huang, Youqing Wu, Xueqin Li, Xiao Wei, and Shiyong Wu. 2025. "Physicochemical Characterization and Formation Pathway of Hydrochar from Brewer’s Spent Grain via Hydrothermal Carbonization" Catalysts 15, no. 9: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090847
APA StyleLiu, P., Huang, S., Wu, Y., Li, X., Wei, X., & Wu, S. (2025). Physicochemical Characterization and Formation Pathway of Hydrochar from Brewer’s Spent Grain via Hydrothermal Carbonization. Catalysts, 15(9), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090847







