Abstract
Novel solid strong base catalysts have attracted considerable attention in fine chemical synthesis owing to their unique advantages. In this work, a magnetic solid strong base catalyst with controlled morphology and porous carbon shell structure was successfully fabricated using low-cost carbon sources combined with Fe3O4 nanoparticles. KOH was used to introduce strong basic sites through ultrasonic-assisted impregnation. The carbon shell acted as a protective barrier to suppress detrimental interactions between basic species and the support while maintaining structural integrity after high-temperature activation without morphology degradation. The obtained K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst exhibits excellent catalytic performance and near-ideal superparamagnetic behavior. In the transesterification reaction for dimethyl carbonate (DMC) synthesis, the K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst provides superior performance than conventional solid base catalysts and maintains stable activity over six consecutive cycles. Notably, efficient solid–liquid separation was achieved successfully via magnetic separation, demonstrating practical applicability for the K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst.
1. Introduction
With the growing emphasis on green chemistry, the development of environmentally friendly catalysts has become a focal point of the research [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Among diverse heterogeneous catalytic systems, solid base catalysts have obtained widespread attention in fine chemical synthesis owing to their distinct advantages, including mild reaction conditions, facile product separation, excellent recyclability, minimized equipment corrosion, and superior environmental compatibility [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. Mesoporous silica is considered as an ideal support for solid base catalysts. However, strong basic species tend to react with siliceous support, leading to structure collapse [17,18,19]. Furthermore, the separation and recovery of solid base catalysts remain challenging, primarily relying on filtration or centrifugation, which are not only costly but also time-consuming, limiting the practical application of solid base catalysts [20,21,22,23,24,25].
Non-silicon-based carbon materials have a wide range of applications and are indispensable in fields such as adsorption, composite materials, fuel cells, and new energy sources, due to unique surface chemical properties and physical structures [17,25]. It has been confirmed that the sol–gel process is able to carbonize resorcinol and formaldehyde polymers (RF) into porous carbon. Subsequently, various methods have been explored to control the structure and morphology of the products for different applications, such as battery anodes, ion exchange resins, gas diffusion electrodes in fuel cells, and electrodes for capacitive deionization in aqueous solutions.
Magnetic carbon materials have consistently been a prominent research focus. Zhang et al. successfully synthesized Fe3O4@C nano-microspheres through hydrothermal/solvothermal carbonization of glucose in the presence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles, improving the electrochemical performance of nanostructured transition metal oxides as superior anode materials for lithium-ion batteries [26]. Lei et al. employed dopamine as both carbon and nitrogen source to fabricate nitrogen-doped core–shell structured magnetic particles [27]. Furthermore, Li et al. developed an innovative approach involving a polystyrene (PS) coating on Fe3O4 particles followed by high-temperature carbonization, resulting in the formation of carbon-coated nano-microspheres [28]. Li et al. reported a new and robust magnetically recoverable catalyst specifically engineered for the green synthesis of benzothiazoles and benzoxazoles [29]. If carbon-based solid base catalysts are endowed with magnetism, separation and regeneration would become highly convenient, significantly reducing operational costs [30,31]. Nevertheless, research on magnetic carbon-based mesoporous solid base materials remains relatively scarce in the literature to date.
This study presents the synthesis of magnetic solid base catalyst with well-defined morphology and porous carbon shell structure, achieved by integrating RF-derived porous carbon with Fe3O4 nanoparticles. The KOH, as a strong alkaline precursor, significantly enhances the basicity of the catalyst, while the incorporation of the carbon shell effectively prevents reactions between the highly basic species and the support. Figure 1 illustrates the preparation process of the K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst, highlighting that the porous structure of the support is initially well maintained. The results further indicate that the developed magnetic solid base catalysts outperform typical solid base catalysts in terms of catalytic activity. Notably, the catalysts exhibit superparamagnetic behavior, facilitating rapid separation via an external magnetic field after the reaction.
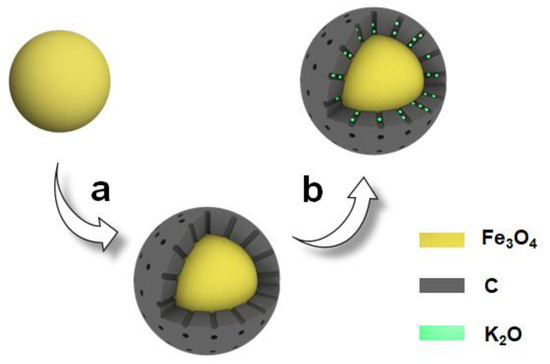
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram for the fabrication of K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres via (a) coating porous carbon on Fe3O4 microspheres and (b) loading K2O on C/Fe3O4 microspheres.
Dimethyl carbonate (DMC) represents a pivotal green chemical building block in modern organic synthesis, acclaimed for its versatile reactivity, favorable physicochemical properties, and low environmental impact. Its exceptional utility stems from its capacity to replace highly toxic reagents (e.g., phosgene, methyl chloroformate) in methylation/carbonylation reactions while also serving as an eco-friendly substitute for halogenated solvents (e.g., trichloroethane) and aromatic hydrocarbons (e.g., benzene, xylene) in coatings applications. Owing to these multifaceted applications, DMC is recognized as a new cornerstone of sustainable chemistry [12]. Although sodium methoxide exhibits high catalytic activity in the transesterification synthesis of DMC from ethylene carbonate and methanol, its homogeneous nature imposes severe limitations: challenging product-catalyst separation, stringent equipment requirements, high energy consumption, and significant environmental contamination. These drawbacks have spurred intensive research into heterogeneous alternatives, including anion-exchange resins, organic/inorganic solid bases, and hybrid catalysts. Against this backdrop, we selected the transesterification reaction as a model system to validate the performance of our designed K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst. This magnetic solid base uniquely integrates a protective carbon shell that stabilizes active sites while enabling rapid magnetic separation—addressing critical gaps in existing catalytic technologies.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Characteristics
Figure 2 displays the TG profile of C/Fe3O4 magnetic spheres under an air atmosphere. Data correspond to the as-synthesized C/Fe3O4 sample before pyrolysis at 600 °C for 3 h under N2 atmosphere. The TG curve exhibits two distinct mass loss stages. The initial mass loss occurring at approximately 100 °C corresponds to the evaporation of physiosorbed water molecules. The subsequent mass reduction, commencing around 320 °C, results from the oxidative decomposition of carbonaceous components into CO2. Visual inspection confirmed the complete transformation of the final product into a reddish hue, demonstrating the exhaustive combustion of carbon constituents and the exclusive formation of Fe2O3 as the product. Quantitative analysis determined the carbon content in the C/Fe3O4 composite to be 47.8 wt%. Table 1 provides the composition of the magnetic mesoporous strong base materials. The content of Fe3O4 in the C/Fe3O4 sample is 51.4 wt%. Further analysis reveals that this result is consistent with the carbon mass fraction of 47.8 wt% calculated from the TG data mentioned earlier, indicating that the porous carbon has been successfully coated onto the Fe3O4 particles. For the K/C/Fe3O4 sample, the content of K2O is 5.5 wt%, which suggests that the basic species have been successfully introduced onto the C/Fe3O4 carrier.
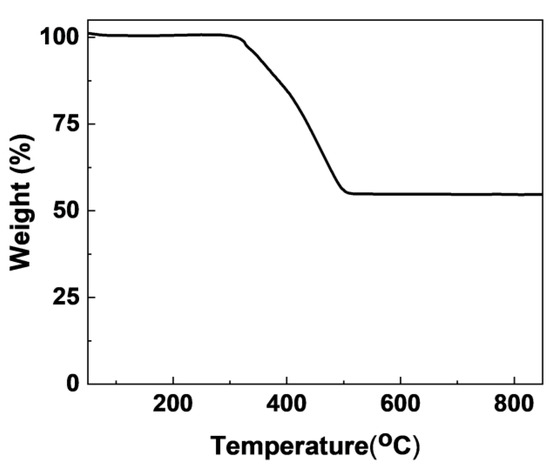
Figure 2.
TG analysis of pristine C/Fe3O4 magnetic spheres under air flow, characterizing the as-synthesized precursor prior to pyrolysis (600 °C, 3 h, N2).

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of different samples.
Figure 3 presents the SEM and TEM images of Fe3O4 particles, C/Fe3O4, and K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres. The SEM (Figure 3a) and TEM (Figure 3b) images of pristine Fe3O4 particles demonstrate well-defined spherical morphology with a textured surface topography. These particles exhibit monodisperse size distribution with an average diameter of approximately 300 nm. Figure 3c further illustrates the irregular surface features of the Fe3O4 particles. The selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of the Fe3O4 particles, depicted in Figure 3d, exhibits multiple concentric diffraction rings, which confirm the polycrystalline nature of the Fe3O4 particles. These diffraction rings correspond to the (220), (311), (400), (422), (511), and (440) crystal planes, which are characteristic of the Fe3O4 structure. Figure 3e,f present the SEM and TEM images of C/Fe3O4 composite particles, revealing a well-developed core–shell architecture. The micrographs confirm the successful formation of a continuous porous carbon shell through the polymerization and subsequent carbonization of resorcinol-formaldehyde precursors on the Fe3O4 core. In contrast to the bare Fe3O4 particles, the carbon-coated spheres display a smooth surface morphology with significantly increased particle dimensions. Quantitative analysis indicates a uniform carbon shell thickness of about 90 nm. The SEM and TEM images of K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres (Figure 3g,h) demonstrate that the introduction of basic species preserves the core–shell configuration and spherical morphology. After the introduction of the basic species, the sample did not aggregate significantly, only showing slight adhesion, thus indicating that the basic species are uniformly dispersed within the carbon shell layer. We have further examined the recovered catalyst by powder SEM. The micrographs (Figure S1) reveal that the micro spherical morphology remains intact after five catalytic cycles; no discernible aggregation, fracture, or surface roughening is observed.
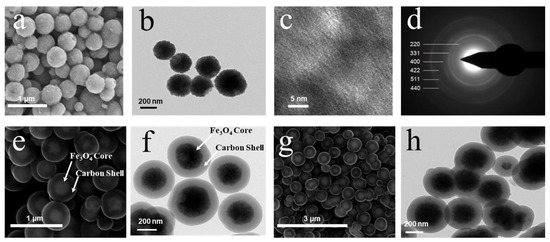
Figure 3.
(a) SEM, (b) TEM, (c) HRTEM and (d) SAED pattern of Fe3O4 particles; (e) SEM and (f) TEM images of the C/Fe3O4 samples; (g) SEM and (h) TEM images of the K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres.
EDX-mapping analysis was conducted to further investigate the surface elemental composition of the K/C/Fe3O4 composite. As illustrated in Figure 4, the K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres are predominantly composed of four distinct elements: Fe, O, C, and K. The elemental distribution of Fe matches the shape of the magnetic nanoparticles, corresponding to the spherical morphology of Fe3O4. The C element demonstrates a characteristic shell-like distribution pattern, with higher density observed at the periphery and lower density in the central region. The K element is uniformly dispersed throughout the entire sample, confirming the homogeneous incorporation of basic species within the carbon shell without any noticeable aggregation. Notably, the O element displays a concentration gradient, with higher intensity in the core region corresponding to the Fe3O4 phase and lower intensity at the edges. The residual O signal detected at the periphery can be attributed to the presence of K2O, providing further evidence for the successful integration of basic oxide species into the carbon shell structure. This comprehensive elemental mapping not only validates the core–shell architecture of the composite but also confirms the effective functionalization of the carbon shell with potassium-based basic sites.
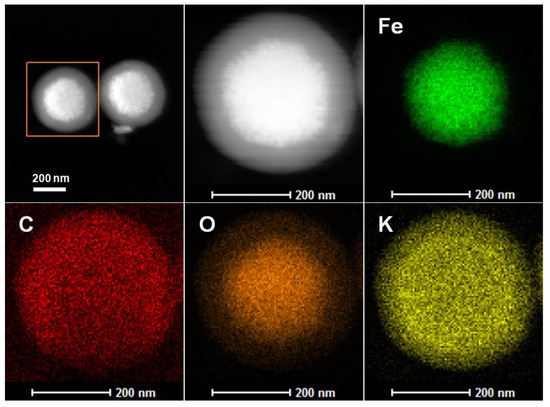
Figure 4.
EDX-mapping of the sample K/C/Fe3O4.
Figure 5 presents the XRD patterns of Fe3O4, C/Fe3O4, and K/C/Fe3O4 microsphere samples, providing detailed insights into their crystalline structures. The Fe3O4 magnetic spheres (JCPDS No. 65-3107) display distinct and well-defined diffraction peaks at 2θ values of 30.2°, 35.7°, 43.3°, 53.5°, 57.2°, and 62.8° [17,23,25]. These peaks are indexed to the (220), (311), (400), (422), (511), and (440) crystal planes of the face-centered cubic (Fd3m space group) structure of magnetite, respectively. The observed diffraction features are in excellent agreement with the selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern analysis of Fe3O4, as previously shown in Figure 3d, thereby confirming the accuracy and consistency of the structural characterization. Upon the deposition of a carbon layer and the incorporation of K, the characteristic diffraction peaks of Fe3O4 remain clearly observable in the XRD patterns of both C/Fe3O4 and K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres. This observation confirms the preservation of the cubic Fe3O4 crystal structure throughout the synthesis process, even with the introduction of additional components. Notably, the diffraction peaks of the C/Fe3O4 and K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres exhibit enhanced intensities and reduced peak widths compared to those of the pristine Fe3O4 particles. This enhancement in peak intensity and narrowing of peak widths can be attributed to the increased particle size of C/Fe3O4 and the carbonization process, which collectively contributes to an improved degree of crystallization of Fe3O4. The carbon layer not only enhances the structural stability of the Fe3O4 particles but also promotes a more ordered arrangement of the Fe3O4 crystallites, thereby resulting in the observed improvements in the XRD patterns.
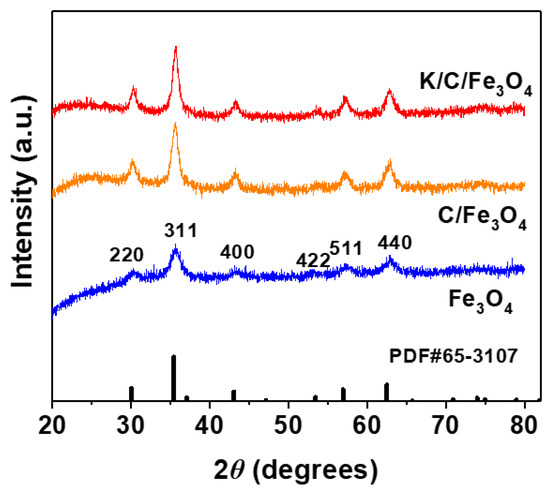
Figure 5.
Wide-angle XRD patterns of Fe3O4, C/Fe3O4 and K/C/Fe3O4 samples as well as standards for Fe3O4 (JCPDS no. 65-3107).
The Scherrer analysis of the Fe3O4 (311) reflection yields a coherent-scattering (crystallite) dimension of about 28 nm. Transmission electron microscopy, on the other hand, reveals spherical entities with an overall diameter of 300 nm. This apparent difference arises because the two techniques probe distinct structural levels. X-ray diffraction is sensitive only to the size of single-crystal domains; the value of 28 nm, therefore, reflects the dimension of the individual magnetite crystallites. Electron microscopy images the secondary particles, which are dense agglomerates composed of many such crystallites. These agglomerates form spontaneously during the hydrothermal synthesis because of oriented attachment and van der Waals interactions, leading to the 300 nm spheres observed in TEM.
The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms and corresponding pore size distributions of Fe3O4, C/Fe3O4, and K/C/Fe3O4 samples are presented in Figure 6, with their structural parameters summarized in Table 1. As depicted in Figure 6a, the Fe3O4 particles exhibit negligible hysteresis and demonstrate a relatively low specific surface area of 59 m2·g−1 along with a pore volume of 0.07 cm3·g−1, which can be attributed to interparticle voids formed during nanoparticle packing. Upon carbon coating, the C/Fe3O4 sample displays a substantial increase in specific surface area to 263 m2·g−1, accompanied by a distinct hysteresis loop, characteristic of a Type I isotherm. The observed hysteresis in the intermediate pressure region confirms the presence of mesoporous structures. Following K functionalization, the K/C/Fe3O4 sample exhibits a slight reduction in both specific surface area and total pore volume, while retaining a diminished yet discernible hysteresis loop, indicating the preservation of mesoporous features. Additionally, the notable adsorption in the low-pressure region for both carbon-containing samples suggests the formation of a well-developed microporous structure after porous carbon coating. From the pore size distribution analysis (Figure 6b, Table 1), it is evident that the C/Fe3O4 sample exhibits predominant pore sizes at 1.2 nm, 2.0 nm, and 3.5 nm. In addition, after K incorporation, an enlargement in pore size is observed (4.8 nm, 7.1 nm), likely due to the high-temperature reaction between K and carbon, which partially etches the carbon framework, thereby modifying the pore structure. While micropores govern surface area, the persistent hysteresis and 2.0–8.0 nm pore modes confirm coexisting mesoporosity critical for mass transport.
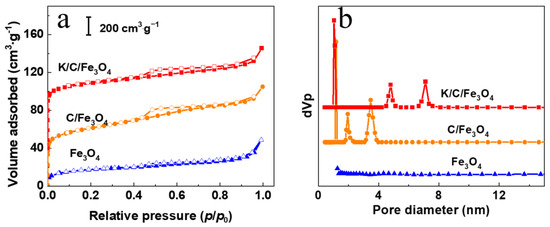
Figure 6.
(a) N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distributions of Fe3O4, C/Fe3O4 and K/C/Fe3O4 samples. Curves are offset for clarity.
Figure 7 presents the infrared spectra of Fe3O4, RF/Fe3O4, C/Fe3O4, and K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres. For Fe3O4 particles, the peaks at 1652 and 1396 cm−1 are attributed to the carboxyl groups, which result from the addition of sodium citrate during synthesis. The broad band spanning 3300–3800 cm−1 corresponds to surface-adsorbed water molecules. For carbonized samples (C/Fe3O4 and K/C/Fe3O4), the attenuation of this broad band suggests the hydrophobic nature of the porous carbon surface. In contrast, the RF/Fe3O4 spectrum exhibits distinct vibrational features: the absorption bands in the 2800–3000 cm−1 arise from −CH2 stretching vibrations of polymeric species, while the broad peak centered at 3380 cm−1 comprises contributions from aromatic −OH groups of resorcinol. The absorption band at 1614 cm−1 is assigned to aromatic ring stretching vibrations, and those at 1222 and 1092 cm−1 correspond to methylene ether linkages in the resorcinol-formaldehyde polymer [32]. The relatively weak intensity of these bands implies that the polymerization form is not predominant. Notably, the carbonization process effectively eliminates all organic functional groups, confirming complete thermal decomposition of the polymer matrix. Furthermore, the introduction of K species does not generate any new absorption features in the FTIR spectrum, indicating that K is not chemically bonded to the carbon framework in any detectable form.
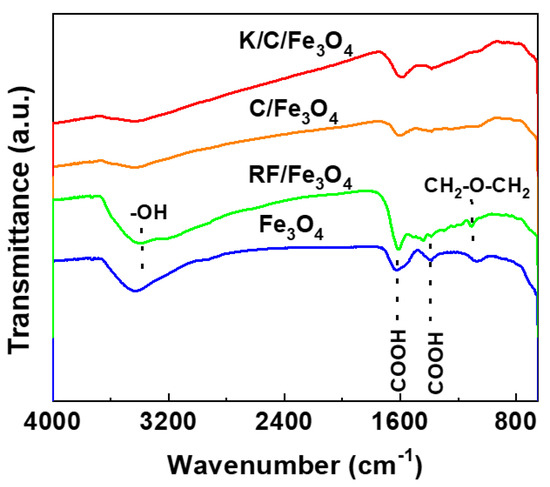
Figure 7.
IR spectra of the Fe3O4, RF/Fe3O4, C/Fe3O4, and K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres.
2.2. Magnetic Properties
The magnetic properties of the synthesized samples were thoroughly characterized using VSM to evaluate their performance in magnetic separation and recovery processes. As shown in Figure 8a, the saturation magnetization (Ms) values of the Fe3O4, C/Fe3O4, and K/C/Fe3O4 samples were determined to be 44.0, 28.6, and 26.7 emu g−1, respectively. These results confirm the excellent superparamagnetic behavior of the synthesized materials, which is crucial for their efficient separation and recovery using an external magnetic field. The introduction of basic species in the K/C/Fe3O4 sample leads to a slight decrease in saturation magnetization compared to the pristine Fe3O4 and C/Fe3O4 materials. However, the K/C/Fe3O4 sample still maintains a sufficiently high level of magnetization (26.7 emu g−1) to ensure its magnetic responsiveness to an external magnetic field. The value remains comfortably above the 5–10 emu g−1 range typically cited as sufficient for conventional magnetic separation devices. Nevertheless, the retained magnetization suggests that magnetic recovery should not become limiting when eventual scale-up is pursued. This balance between basicity and magnetism is essential for the practical application of the catalyst in various chemical processes, where both catalytic activity and ease of separation are required.
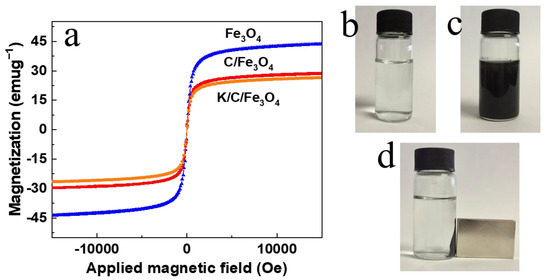
Figure 8.
(a) The magnetic hysteresis loops of the Fe3O4 particles, C/Fe3O4 microspheres and K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres. Digital photos of the (b) reactant solution, (c) K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres in the reactant solution, and (d) K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres in the reactant solution with a magnet.
As depicted in Figure 8c, the K/C/Fe3O4 sample is uniformly dispersed in the reactant solution (Figure 8b). When an external magnetic field is applied, as shown in Figure 8d, the well-dispersed K/C/Fe3O4 particles rapidly migrate and adhere to the vial wall. This migration results in a clear and transparent supernatant solution, which closely resembles the initial reactant solution depicted in Figure 8b. In addition, the K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst exhibits remarkable redispersibility upon the removal of the magnetic field, with gentle agitation facilitating its rapid rehomogenization in the reactant solution. The combination of strong superparamagnetic and excellent redispersibility makes these magnetic solid base catalysts highly suitable for practical applications, particularly in catalyst recovery and reuse, which are essential for economic and environmental sustainability.
2.3. Basicity and Catalytic Performances
The alkaline properties of the prepared magnetic solid-base catalysts were assessed through quantitative analysis of surface basic site, and the results were compiled in Table 1. Titration analysis reveals that the Fe3O4 and C/Fe3O4 samples exhibit minimal basic site contents of 0.03 and 0.07 mmol·g−1, respectively, demonstrating the absence of significant basic species on their surfaces. Following the incorporation of KOH as a basic modifier, the K/C/Fe3O4 sample achieves a substantially enhanced basicity of 1.03 mmol·g−1. This value shows good agreement with the theoretical basicity of 1.17 mmol·g−1 calculated from XRF data, thereby verifying the successful loading of basic species onto C/Fe3O4.
Figure 9 displays the CO2-TPD profiles of C/Fe3O4 and K/C/Fe3O4 samples. The CO2-TPD deconvolution further quantifies basic strength distribution (Table S1). In the case of the C/Fe3O4, no CO2 desorption peak is detected even at elevated temperatures up to 500 °C, which can be attributed to the lack of basic species. In contrast, the K/C/Fe3O4 sample exhibits a prominent desorption peak centered at approximately 300 °C, characteristic of medium-strength basic sites. Furthermore, an additional CO2 desorption peak emerges at 460 °C, demonstrating the formation of strong basic sites in the K/C/Fe3O4 sample compared to the C/Fe3O4 [33]. These findings are in excellent agreement with the previously obtained basicity measurements, thereby providing robust evidence for the successful incorporation of strong basic sites in K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst.
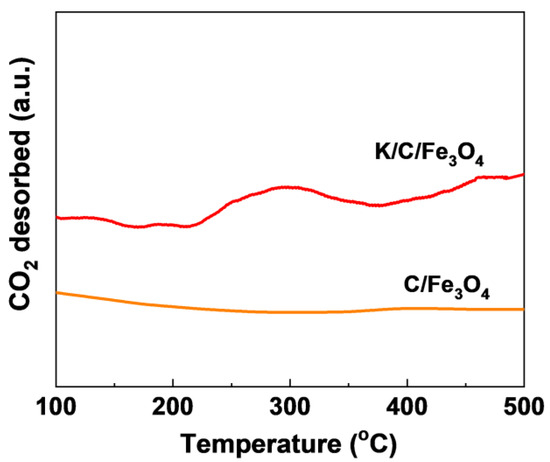
Figure 9.
CO2-TPD profiles of C/Fe3O4 and K/C/Fe3O4 samples.
The catalytic performance of the magnetic solid base catalysts was thoroughly evaluated through the transesterification of ethylene carbonate for the synthesis of DMC, following the established protocols reported in the literature [34,35]. Ethylene carbonate undergoes transesterification with methanol via a nucleophilic substitution pathway, as illustrated in Figure 10, the catalyst’s basic sites first deprotonate CH3OH to generate CH3O−, which is then attacked by the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of vinyl carbonate. This nucleophile then attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of ethylene carbonate, cleaving the C–O bond of the cyclic carbonate and yielding the transient alkoxide intermediate CH3OCOOCH2CH2O− (step I). Rapid proton exchange with a second methanol molecule converts this intermediate into its neutral form CH3OCOOCH2CH2OH while regenerating the active CH3O− nucleophile (step II). A subsequent intramolecular nucleophilic substitution releases dimethyl carbonate (DMC) and deposits ethylene glycolate (CH2OHCH2O−) on the surface (step III). Final proton transfer with methanol restores the catalytic base and liberates ethylene glycol (CH2OHCH2OH), completing the cycle (step IV).
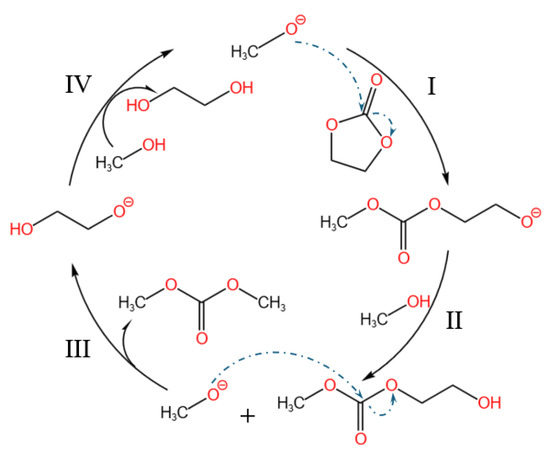
Figure 10.
A possible mechanism for the transesterification of ethylene carbonate and methanol catalyzed by CaO/mSiO2/Fe3O4 (CH3O− generated from basic sites of catalyst). Arrows indicate the direction of nucleophilic attack; Roman numerals (I–IV) mark reaction steps (I Nucleophilic ring-opening, II Methanol-assisted proton exchange, III DMC release & ethylene glycolate formation, IV Ethylene glycol liberation).
We have performed the transesterification in the complete absence of any catalyst at 65 °C for 6 h. Under identical conditions, the DMC yield was only 1.0 mol% (Figure S2a), confirming that the reaction is truly catalytic and that no appreciable background activity exists. When Fe3O4 and C/Fe3O4 are employed as catalysts for 6 h, the DMC yields are relatively low of 3.7 mol% and 4.5 mol%, respectively. The results are presented in Figure 11a. These results indicate the limited presence of active basic sites on the surfaces of these catalysts, which is consistent with the basicity data summarized in Table 1. Notably, the catalytic performance of the K/C/Fe3O4 sample was significantly superior to that of the other catalysts. When K/C/Fe3O4 is utilized as the catalyst, the DMC yield reached a maximum of 30.7 mol% after 6 h reaction. This substantial increased yield highlights the effectiveness of the K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst in promoting the transesterification reaction.
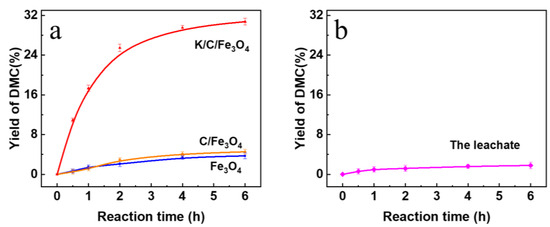
Figure 11.
The yields of DMC with (a) Fe3O4, C/Fe3O4 and K/C/Fe3O4 samples and (b) the leachate.
To further contextualize the performance of the K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst, a comparative analysis was conducted with several conventional solid base catalysts, in the synthesis of DMC, as detailed in Table 2. The catalytic activities of metal oxides such as MgO (7.6%), MgO/NPC (11.4%), CaO/G (13.5%) and Na2O/Al2O3 (28.2%) were found to be significantly lower than that of K/C/Fe3O4. Notably, under identical reaction conditions, our K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst demonstrates markedly superior activity relative to functionalized carbon-based base catalysts (MgO/G, Na2O/G and K2O/C/SBA-15). Even CsX zeolite, which is known for its strong basicity, exhibited a catalytic activity of only 6.0%. To further assess the activity based on active sites, turnover frequency (TOF) values for different catalysts were calculated. The formula and assumptions used for TOF are provided in Supporting Information Note S1. Although KNO3/C and CeO-meso-400 achieved slightly higher DMC yields than K/C/Fe3O4, the latter exhibited a significantly higher TOF value of 57.6 h−1. In contrast, the TOF values for KNO3/C and CeO-meso-400 were only 35.2 h−1 and 16.5 h−1, respectively. This indicates that K/C/Fe3O4 demonstrated superior catalytic activity in terms of reaction rate. These comparative results clearly demonstrate that the magnetic solid base catalysts K/C/Fe3O4 samples developed in this study exhibit superior catalytic performance compared to typical solid base catalysts.

Table 2.
The yield of DMC under the catalysis of different samples.
To investigate the stability of the basic sites within the catalyst, recycling experiments were conducted. The K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst could be rapidly and conveniently recovered after reaction via the application of an external magnetic field. No significant catalyst loss was observed during the recovery process. As shown in Figure 12, the regenerated catalyst largely retained its initial catalytic activity even after six consecutive reaction cycles, exhibiting only a marginal decline in performance. It is noteworthy that powder XRD of the catalyst recovered after six consecutive cycles (Figure S3) exhibits identical reflections to those of the fresh sample, confirming that the spinel Fe3O4 lattice and the carbon scaffold remain structurally intact. Furthermore, leaching experiments were performed. An equivalent mass of the K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst was stirred in methanol for 24 h, and the potassium ion concentration in the liquid phase was subsequently analyzed by ICP-OES. Results (Table 1) indicated that the leached potassium accounted for merely 2.1% of the total potassium loading on the catalyst, demonstrating the effective confinement of basic species by the carbon shell layer. To elucidate the catalytic mechanism, the leachate was employed as a catalyst for the transesterification reaction. The resulting DMC yield was only 1.8% (Figure 11b). In conjunction with the significantly higher yield (30.7%) achieved using the original catalyst system, this finding strongly indicates that the reaction proceeds predominantly via heterogeneous catalysis. Consequently, the K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst synthesized in this study demonstrates exceptional stability for the synthesis of DMC via transesterification.
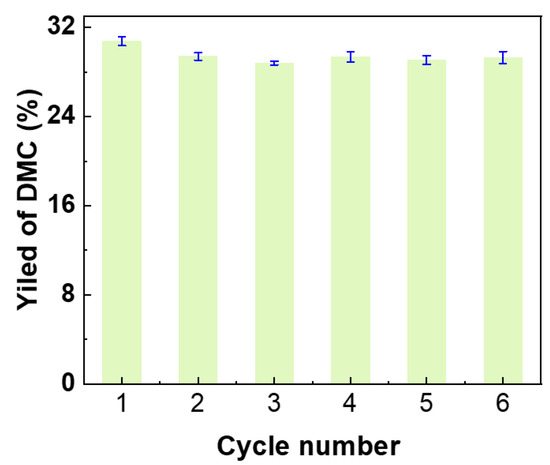
Figure 12.
Reusability of the K/C/Fe3O4 microspheres as the catalyst for the synthesis of DMC.
To isolate the role of the carbon shell, we prepared K/Fe3O4 by simple incipient-wetness impregnation of KOH onto bare Fe3O4. In the first run this material delivered 28.3 mol% DMC yield (Figure S2a), which is close to that of K/C/Fe3O4 (30.7 mol%). However, upon a second catalytic cycle the activity collapsed to 3.5 mol% (Figure S2b), whereas the carbon-shielded K/C/Fe3O4 retained 30.2% after six cycles. The sharp deactivation observed for K/Fe3O4 is attributed to leaching of soluble potassium species. These findings underscore the indispensable function of the porous carbon layer: it stabilizes the alkaline phase and enables robust recycling.
2.4. Mechanism of Stable Basic Site Formation
The formation of catalytically active basic sites was predominantly governed by high-temperature activation. The K/C/Fe3O4 sample was activated by KOH at 700 °C for 2 h. During this process, the carbon shell reacted with KOH, forming highly stable potassium species embedded within the carbon matrix.
Existing studies corroborate that thermal activation under alkaline conditions facilitates the development of stable basic functionalities [42,43,44]. Fundamentally, this activation process primarily involves the reduction in hydroxides and the oxidation of carbon, concurrently accompanied by the development of porosity within the carbon support [44,45]. The selection of the 700 °C activation temperature was informed by systematic optimization within this work and validated against established protocols [44,45,46]. This specific thermal regime enables a pronounced redox interaction between KOH and the carbon support, culminating in the creation of active basic sites. The absence of distinct crystalline potassium phases (e.g., K2O, KOH, or K2CO3) in the XRD patterns (Figure 5), combined with the exceptional catalytic stability (Figure 12), strongly suggests that potassium species exist as isolated atoms anchored via K-C coordination bonds within the carbon matrix. This coordination mechanism aligns with recent reports on single-atom solid superbases, where K–C configurations ensure both atomic dispersion and robust stability [24]. The interaction between potassium species and carbon is exceptionally strong. This process yields thermally resilient potassium centers that serve as highly dispersed basic sites. The stabilization mechanism likely involves electron donation from potassium to the unoccupied orbitals of carbon, forming an electron-rich interfacial complex [47]. Moreover, the engineered C/Fe3O4 support exhibited a substantial specific surface area (264 m2 g−1, Table 1), providing an optimal substrate for the uniform dispersion of potassium species. Collectively, these synergistic effects endow the synthesized K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst with sustained catalytic activity and stable basic site performance.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
The synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles was conducted as follows. It is essential to maintain the reaction system under moisture-free conditions from precursor preparation to final product isolation. Anhydrous FeCl3 (1.30 g) was promptly combined with 40.0 mL of ethylene glycol and dissolved completely. To ensure homogeneity, sodium citrate (0.50 g) and sodium acetate (2.00 g) were successively added to the solution under constant stirring. The mixture was then subjected to mechanical stirring at a rate of 500 rpm for 0.5 h, yielding a uniform dark-yellow colloidal suspension. The precursor colloidal suspension was subsequently subjected to hydrothermal treatment in a Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave maintained at 200 °C for 10 h. Following natural cooling to 25 °C, the resultant magnetite nanoparticles were collected through successive washing with ethanol and deionized water.
3.2. Synthesis of C/Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
The fabrication process of C/Fe3O4 magnetic particles is conducted as described below. A homogeneous mixture consisting of 0.50 g Fe3O4, 280 mL deionized water, 0.4 mL concentrated aqueous ammonia, and 0.8 g resorcinol were introduced into a three-necked flask and subjected to mechanical stirring at 30 °C for 1 h. Subsequently, 1.2 mL formaldehyde was added dropwise to the reaction mixture, followed by continuous stirring for 6 h. Then, the reaction temperature was elevated to 80 °C, and the mixture was maintained under stirring for 5 h. The obtained product, after thorough washing and drying, is denoted as RF/Fe3O4. The RF/Fe3O4 composite was carbonized in a tubular furnace under nitrogen atmosphere at 600 °C for 3 h, yielding the final product designated as C/Fe3O4.
3.3. Synthesis of K/C/Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
The alkaline precursor is introduced via the wet impregnation method. Specifically, KOH (0.01 g) was dissolved in deionized water (10 mL), followed by the addition of C/Fe3O4 (0.1 g). The mixture is then subjected to ultrasonication for 10 min. Subsequently, the mixture is evaporated under continuous mechanical stirring at 80 °C until complete dryness is achieved. The obtained powder is subsequently calcined in a nitrogen atmosphere at 600 °C for 3 h. The final product is designated as K/C/Fe3O4.
3.4. Characterization
3.4.1. Structural and Morphological Analysis
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of the samples was performed utilizing a Bruker D8 Advance diffractometer (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). The instrument was configured with monochromatic Cu Kα radiation, operating at 40 kV and 30 mA. The 2θ scan was conducted over a range of 5° to 80°.
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) imaging was performed using an FEI Talos 200X instrument (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Meanwhile, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) imaging was conducted with a Zeiss Gemini SEM 300 (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).
The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms were recorded with a BSD-660 (BSD, Beijing, China). Surface area quantification employed the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) model, utilizing multipoint adsorption data from the 0.04–0.20 P/P0 pressure region. Total pore volume calculations utilized the maximum adsorbed nitrogen quantity at P/P0 = 0.99. Mesoporous size distribution analysis applied non-local density functional theory (NLDFT) to the adsorption isotherm branch data.
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was performed using a Nicolet iS10 spectrometer (Thermofisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) to obtain spectral data. Thermogravimetric (TG) analysis was conducted using a TGA209F1 instrument (Netzsch, Waldkraiburg, Germany) to assess the thermal stability of the samples. TG analysis utilized air to enable complete carbon combustion for quantitative analysis, contrasting with synthesis under N2 where inert conditions, and the samples were heated from ambient temperature to 1073 K at a constant rate of 10 K·min−1.
3.4.2. Magnetic and Basicity Characterization
The UV-visible (UV-vis) absorption spectra of the samples were recorded using a Shimadzu UV-2401PC spectrophotometer (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan), with barium sulfate (BaSO4) utilized as the reflectance reference standard. Magnetic properties were characterized using a Lakeshore 7407 vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) at 300 K. Elemental composition analysis was conducted by X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy utilizing an ARL ADVANT’XP wavelength-dispersive spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
CO2 temperature-programmed desorption (CO2-TPD) was performed using a BELSORP BEL-CAT-A analyzer (Microtrac BEL Corp., Osaka, Japan). The sample was pretreated under helium atmosphere at 500 °C for 2 h. After cooling to room temperature, CO2 adsorption proceeded for 1 h, followed by helium purging, with subsequent temperature ramping to 500 °C at 8 °C min−1. The CO2 liberation was detected by an OmniStar mass spectrometer.
The total basic site density was determined through acid-base back-titration methodology. Precisely 50 mg of catalyst was dispersed in 10.0 mL of 0.05 M hydrochloric acid solution. Following 24 h of shaking agitation, magnetic phase separation was achieved through application of an external magnetic field to the reaction system, enabling precise isolation of the clarified supernatant. Quantitative analysis of unreacted acid in the supernatant was performed via potentiometric titration using 0.01 M sodium hydroxide solution, with endpoint determination conducted through pH metric verification [45,48].
3.5. Catalytic Performances
The production of DMC was achieved through a catalytic ester group exchange process between methanol and ethylene carbonate (EC). In a representative synthesis, a stoichiometric excess of methanol (0.50 mol, 4:1 molar ratio relative to EC) was combined with EC (0.10 mol) and a magnetically recoverable heterogeneous catalyst (K/C/Fe3O4, 160 mg) in a three-necked round-bottom flask (50 mL capacity). In a standard procedure, methanol (0.50 mol), ethylene carbonate (0.10 mol), and K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst (80 mg) were charged into a 50 mL three-necked round-bottom flask equipped with a water-cooled condenser. The reaction system, equipped with a reflux condenser, was maintained at 65 °C under continuous agitation for a predetermined duration [49]. The K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst was subsequently separated from the reaction mixture using magnetic separation. Quantitative compositional analysis of the reaction products was performed using an Agilent 7890A gas chromatograph equipped with a flame ionization detector.
Gas chromatography analysis: high-purity helium (99.999%) served as the carrier gas at a constant linear velocity of 42.3 cm·s−1. The injector and detector temperatures were maintained at 250 °C and 300 °C, respectively. Samples (0.5 μL) were introduced via a 10:1 split ratio. The temperature program initiated at 40 °C (hold 3 min), ramped to 120 °C at 15 °C·min−1, then to 240 °C at 30 °C·min−1 (final hold 2 min). Compounds were quantified using internal standard calibration with decane, achieving a detection limit of 0.01 ppm. Retention times were calibrated against authentic standards: methanol (1.8 min), DMC (4.2 min), ethylene carbonate (7.5 min), ethylene glycol (5.1 min).
4. Conclusions
This study successfully synthesize a magnetically responsive solid strong base catalyst, K/C/Fe3O4, utilizing Fe3O4 particles as the magnetic core and incorporating strongly basic K2O species. The K/C/Fe3O4 catalyst exhibits a well-defined spherical morphology with a structurally intact carbon shell (90 nm thickness) even after high-temperature activation, providing an optimal platform for the incorporation of basic species. The resulting catalyst demonstrates both strong basic sites and excellent catalytic performance of 30.7 mol% in DMC synthesis, maintaining its catalytic efficacy without significant degradation over six consecutive reaction cycles, surpassing conventional solid strong base materials. Furthermore, the superparamagnetic characteristics enable efficient magnetic separation post-reaction under an external magnetic field.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal15080743/s1. Figure S1. SEM images of recovered catalyst after six catalytic cycles. Figure S2. (a) The yields of DMC with K/Fe3O4 and no catalyst. (b) Reusability of the K/Fe3O4 microspheres as the catalyst for the synthesis of DMC. Figure S3. XRD patterns of the recovered catalyst after six catalytic cycles. Table S1. Basic site distribution of samples from CO2-TPD deconvolution. Note S1: TOF Calculation Simplified.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.X. and Y.Z.; methodology, T.L., X.L., G.S. and Y.G.; software, Q.G., G.K. and X.L.; validation, Q.G. and Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, T.L. and Q.G.; writing—review and editing, D.X. and Y.Z.; funding acquisition, D.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (NO. GYZX240406).
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tao, Y.; Guan, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, S.; Ma, R.; Zheng, H.; Gong, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Liu, S.; Ou, H.; et al. Ruthenium single atomic sites surrounding the support pit with exceptional photocatalytic activity, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202400625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, P.; Song, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhan, S.; Li, Y. Enhanced interfacial electron transfer by asymmetric Cu-Ov-In Sites on In2O3 for efficient peroxymonosulfate activation, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202216403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, X.; Pei, X.; Liu, W.; Leng, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, C.; Hu, L.; Su, Q.; Wu, C.; et al. Room-temperature laser planting of high-loading single-atom catalysts for high-efficiency electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 13788–13795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.S.; Liu, S.; Shao, X.B.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, P.; Yan, J.T.; Sun, L.B. Calcium single atoms stabilized by nitrogen coordination in metal–organic frameworks as efficient solid base catalysts. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 678, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.B.; Song, X.R.; Peng, S.S.; Zheng, X.Q.; Qi, S.C.; Tan, P.; Liu, X.Q.; Sun, L.B. Low-temperature fabrication of potassium single-atom solid base catalysts with high activity in transesterification. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Shao, J.; Pan, B.; Salam, A.; Boutin, E.; Groizard, T.; Wang, S.; Ding, J.; et al. In-situ spectroscopic probe of the intrinsic structure feature of single-atom center in electrochemical CO/CO2 reduction to methanol. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, R.; Pang, J.; Wang, A.; Li, N.; Zhang, T. Production of renewable hydrocarbon biofuels with lignocellulose and its derivatives over heterogeneous catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 2889–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, D. Microenvironment engineering of single/dual-atom catalysts for electrocatalytic application. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, X.Q.; Jiang, H.L.; Sun, L.B. Metal-organic frameworks for heterogeneous basic catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8129–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liang, Z.B.; Zou, R.Q.; Zhao, Y.L. Heterogeneous catalysis in zeolites, mesoporous silica, and metal-organic frameworks. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.B.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhou, H.C. Design and fabrication of mesoporous heterogeneous basic catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5092–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.B.; Liu, S.; Xing, Z.W.; Tang, J.X.; Li, P.; Liu, C.; Chi, R.Z.; Tan, P.; Sun, L.B. Atomically dispersed magnesium with unusual catalytic activity for transesterification reaction. AIChE J. 2024, 70, e18567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Wan, G.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, H.; Yu, S.; Jiang, H. From metal–organic frameworks to single-atom Fe implanted N-doped porous carbons: Efficient oxygen reduction in both alkaline and acidic media. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 130, 8661–8665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Sun, L.B. Direct fabrication of strong basic sites on ordered nanoporous materials: Exploring the possibility of metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 1686–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Varma, R.S. Selectivity enhancement in heterogeneous photocatalytic transformations. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 1445–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Baylon, R.A.; Liu, C.; Mei, D.; Martin, K.J.; Venkitasubramanian, P.; Wang, Y. Key roles of lewis acid-base pairs on ZnxZryOz in direct ethanol/acetone to isobutene conversion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.T.; Shao, M.Q.; Gu, C.; Peng, S.S.; Liu, X.Q.; Sun, L.B. Low-temperature conversion of base precursor KNO3 on core–shell structured Fe3O4@C: Fabrication of magnetically responsive solid strong bases. Catal. Today 2021, 374, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.B.; Yang, J.; Kou, J.H.; Gu, F.N.; Chun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Zou, Z.G. One-pot synthesis of potassium-functionalized mesoporous γ-alumina: A solid superbase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3418–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.W.; Wang, H.Y.; Feng, L.; Zhu, J.Z.; Liu, J.X.; Li, W.X. Crystal-phase engineering in heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2023, 124, 164–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, F.; Mehlmann, P.; Muck-Lichtenfeld, C.; Bergander, K.; Dielmann, F. Reversible carbon dioxide binding by simple lewis base adducts with electron-rich phosphines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1840–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, B.; Acharyya, K.; Howlader, P.; Mukherjee, P.S. Molecular cage impregnated palladium nanoparticles: Efficient, additive-free heterogeneous catalysts for cyanation of aryl halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Jiang, S.; Li, L.; Guan, N. Nitridation of BaO supported on mesoporous materials: Basicity characterization and catalytic properties. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 391, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.B.; Xu, H.C.; Xing, Z.W.; Liu, S.; Song, X.R.; Pen, S.S.; Tan, P.; Sun, L.B. Calcium single atom catalyst with unusual activity and stability for the synthesis of dimethyl carbonate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 691, 137386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.S.; Shao, X.B.; Gu, M.X.; Zhang, G.S.; Gu, C.; Nian, Y.; Jia, Y.M.; Han, Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Sun, L.B. Catalytically Stable Potassium Single-Atom Solid Superbases. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202215157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.T.; Gao, X.J.; Qi, S.C.; Huang, L.; Peng, S.S.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.Q.; Sun, L.B. Potassium- incorporated mesoporous carbons: Strong solid bases with enhanced catalytic activity and stability. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 2794–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.M.; Wu, X.L.; Hu, J.S.; Guo, Y.G.; Wan, L.J. Carbon coated Fe3O4 nanospindles as a superior anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 3941–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Han, F.; Li, D.; Li, W.C.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.Q.; Lu, A.H. Dopamine as the coating agent and carbon precursor for the fabrication of N-doped carbon coated Fe3O4 composites as superior lithium ion anodes. Nanoscale 2013, 3, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, T.T.; Zhang, L.Y.; Su, Z.M.; Wang, C.G.; Wang, R.S. Selected-control synthesis of monodisperse Fe3O4 @C core-shell spheres, chains, and rings as high-performance anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Chem.-Eur. J. 2012, 18, 11417–11422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sead, F.F.; Jain, V.; R, R.; Devi, A.; Kashyap, A.; Sharma, G.C.; Bhakuni, P.N.; Kazemi, M.; Javahershenas, R. New and robust magnetically recoverable catalyst for the green synthesis of benzothiazoles and benzoxazoles. Polyhedron 2025, 276, 117564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.N.; Peng, S.S.; Feng, L.N.; Lu, S.Q.; Ma, L.J.; Yue, M.B. One-pot synthesis of acidic and basic bifunctional catalysts to promote the conversion of ethanol to 1-butanol. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 261, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.S.; Yang, M.H.; Zhang, W.K.; Li, X.N.; Wang, C.; Yue, M.B. Fabrication of ordered mesoporous solid super base with high thermal stability from mesoporous carbons. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 242, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulik, S.; Sotiriou-Leventis, C.; Leventis, N. Time-efficient acid-catalyzed synthesis of resorcinol-formaldehyde aerogels. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 6138–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Huang, W.Y. Synthesis and characterization of potassium- modified alumina superbases. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 2537–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Sun, L.B.; Liu, X.Y.; Sun, Y.H.; Song, X.L.; Liu, X.Q. Isolated lithium sites supported on mesoporous silica: A novel solid strong Base with high catalytic activity. Chem.Commun. 2012, 48, 6423–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Chen, W.; Wu, P.; Zhu, Z.; Li, X. Cu-Mg-Zr/SiO2 catalyst for selective hydrogenation of ethylene carbonate to methanol and ethylene glycol. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 2624–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, W.; Guo, J.; Xu, G.; Jia, F.; Shi, L. Excess soluble alkalis to prepare highly efficient MgO with relative low surface oxygen content applied in DMC synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.B.; Xing, Z.W.; Liu, S.Y.; Miao, K.X.; Qi, S.C.; Peng, S.S.; Liu, X.Q.; Sun, L.B. Atomically Dispersed Calcium as Solid Strong Base Catalyst with High Activity and Stability. Green Energy Environ. 2024, 9, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.S.; Zhang, G.S.; Shao, X.B.; Gu, C.; Liu, X.Q.; Sun, L.B. Generation of Strong Basicity in Metal–Organic Frameworks: How Do Coordination Solvents Matter? ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 8058–8065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Long, K.Z.; Wu, F.; Xue, B.; Li, Y.X.; Cao, Y. Efficient synthesis of dimethyl carbonate via transesterification of ethylene carbonate over a new mesoporous ceria catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 484, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.B.; Nian, Y.; Peng, S.S.; Zhang, G.S.; Gu, M.X.; Han, Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Sun, L.B. Magnesium single-atom catalysts with superbasicity. Sci. China Chem. 2023, 66, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.S.; Shao, X.B.; Gu, C.; Xing, Z.W.; Qi, S.C.; Han, Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Sun, L.B. Graphene-anchored sodium single atoms: A highly active and stable catalyst for transesterification reaction. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 4979–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, R.; Joo, S.H.; Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M. Ordered mesoporous carbons. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.C.; Xue, D.M.; Liu, X.Q.; Shi, Y.Q.; Sun, L.B. N-doped porous carbons for CO2 capture: Rational choice of N-containing polymer with high phenyl density as precursor. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enterría, M.; García, F.S.; Martínez Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.M.D. Synthesis of ordered micro–mesoporous carbons by activation of SBA-15 carbon replicas. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 151, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.Q.; Sun, L.B.; Chun, Y.; Xu, Q.H. Catalytic performance of porous carbons obtained by chemical activation. Carbon 2008, 46, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Gao, Q.M.; Hu, J. High Hydrogen Storage Capacity of Porous Carbons Prepared by Using Activated. Carbon J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7016–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Shen, Z. Formation of graphite-potassium intercalation compounds during activation of MCMB with KOH. Carbon 2003, 41, 1862–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Liu, Y.; Qi, S.C.; Liu, X.Q.; Huang, L.; Sun, L.B. Calcium oxide-modified mesoporous silica loaded onto ferriferrous oxide core: Magnetically responsive mesoporous solid strong base. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 526, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Li, T.T.; Tan, P.; Peng, S.S.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Sun, L.B. Generating Strongly Basic Sites on Magnetic Nano-Stirring Bars: Multifunctional Integrated Catalysts for Transesterification Reaction. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 2721–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).