Abstract
The current work is established with the object of modifying the source of Fenton system and substituting iron source as a catalyst with magnetite/potato peels composite material (POT400-M) to be an innovative solar photocatalyst. The structural and morphological characteristics of the material are assessed through X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The technique is applied to treat oil spills that pollute seawater. The effectiveness of the operating parameters is studied, and numerical optimization is applied to optimize the most influential parameters on the system, including POT400-M catalyst (47 mg/L) and hydrogen peroxide reagent (372 mg/L) at pH 5.0, to maximize oil removal, reaching 93%. Also, the aqueous solution and wastewater temperature on the oxidation reaction is evaluated and the reaction exhibited an exothermic nature. Kinetic modeling is evaluated, and the reaction is found to follow the second-order kinetic model. Thermodynamic examination of the data exhibits negative enthalpy (ΔH′) values, confirming that the reaction is exothermic, and the system is verified to be able to perform at the minimal activation energy barrier (−51.34 kJ/mol).
1. Introduction
Oil pollution is signified as one of the most serious damages to rivers as well as seawater. Oil pollution sources include leaks from municipal sewage systems, industrial facilities, and fishing vessels, as well as crude oil transportation [1,2,3]. Additionally, ships may empty bilge water into the sea [4,5]. Such common routines often routines often lead to pump large-scale oil spill accidents that cause long-term and short-term environmental damage [6,7,8]. Crude oil travels thousands of miles and passes through numerous areas prior to reaching end users [9,10,11]. Oil spills in seas or oceans could come from tanker cargo or occur as a result of any operation or accident occurring in the oil industry [12]. Recently, oil spills and oil refineries have been leading to the formation of complex intermediates in aquatic systems, posing a significant threat to human and aquatic life, as well as the environment [5,13,14,15,16]. Although long-term outcomes are not certain, short-term outcomes include airlessness on the water surface [17]. The key drawbacks of oil pollution in rivers are its noxious effects on aquatic animals, plants, and human health [18,19]. Furthermore, oil spill pollution is categorized by its rapid extension and coverage of the water surface. Spills quickly spread in large quantities, developing air barriers that cause significant environmental deterioration [20]. Oil spills in seawater not only damage large areas of the sea, but also the shores, where the oil is ultimately washed up [21,22].
According to industrial records, over 80% of worldwide trade is transported across the sea by ships [23]. However, the ever-increasing use and transport of crude oil and oil products have led to elevated percentages of spills on various scales [24,25,26,27]. Therefore, an accidental large-scale oil spill may happen. In addition, besides such human-made accidents involving oil leaking into the environment, natural catastrophes may also cause oil to leak into the ecosystem [6,16]. Suggesting novel methodologies [28,29,30,31] to remove and minimize such toxic discharge is an urgent responsibility of the academic community [32]. The goal of academics and researchers is to explore and eliminate harmful and persistent toxic discharge, with the search for environmentally benign materials and effective methodologies still gaining attention. A paradigm shift toward a sustainable environment is needed in waste recovery to convert it into value-added material [33,34,35]. The main target of academic sectors and industrial developers is to innovate industry–ecology symbiosis.
Although some traditional wastewater management technologies are widely applied, they are difficult to implement in rural areas [36,37,38], or they may lack high treatment efficiency [39,40]. Therefore, there is a clear gap in integrated solutions that combine timely detection with sustainable treatments [11,39,41]. Furthermore, some current treatment methods, such as advanced oxidation processes [42], are efficient but expensive, which makes them impractical for field applications [43]. Therefore, ecological treatment is a more viable solution [44]. Among the introduced chemical and photochemical oxidation systems, the Fenton reaction is proficient and highlighted for its ease of operation. Fenton is demonstrated to be an effective technique for the mineralization of various pollutants in wastewater [45,46]. This procedure is a homogeneous system based on the use of hydrogen peroxide-augmented iron catalysts in certain pH environments to produce highly reactive species, specifically hydroxyl (·OH) radicals, which are the main sources for in situ treatment [47,48,49,50,51,52]. ·OH radicals are recognized as non-selective intermediates and can oxidize numerous types of contaminants in liquid discharge [3,53]. Additionally, the efficacy of the procedure is supported under mild temperature and pressure environments [48]. Furthermore, the system requires only a short oxidation reaction time for broad mineralization of pollutants [54,55,56]. However, the working pH of the aqueous medium under acidic conditions, about 3.0, is categorized as low pH. This acidic pH presents an obstacle to the system’s application, requiring excess treatment prior to the final discharge [13,57]. Furthermore, chemical precursors play a key role in industrial applications due to their economic significance [22].
With increasing modernization, the vast amount of agro-industrial waste materials produced poses a threat to the ecosystem. With the rise of public awareness and regulations preventing toxic effluents and solid waste from being released into the environment, researchers are developing innovative technologies to urgently remediate such toxic discharge. All over the world, millions of tons of potato are grown. This results in a yield of 6–10% potato peels, which are categorized as a solid waste material. However, they could be classified as a biodegradable resource [16]. To address solid waste and water challenges, impaired wastewater must be treated using nontraditional resources in order to generate usable water and reduce waste in the environment through an industrial ecology system. Furthermore, this approach sets the foundation for scalable, sustainable technologies with applications that extend beyond the Middle East to other water-stressed regions, ensuring a significant global impact [58,59]. According to the authors’ knowledge and referring to accessible previously cited work, there is still a lack of published data on modulating augmented magnetite/potato peel composites as a precursor for modified Fenton oxidation reactions.
In this study, treated potato peels were converted into bio-char augmented with environmentally benign magnetite to be investigated as a solar photocatalyst. To date, the modified form of magnetized nanoparticles have not been applied to treat oily wastewater streams in a recyclable way for successive use.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphological and Structural Characterization of POT400-M
2.1.1. XRD
The XRD diffractogram pattern of the potato peel waste ash augmented with magnetite nanoparticles is depicted in Figure 1. The diffractograms exhibit two different phases: amorphous and crystalline cellulose. The main crystalline cellulose diffraction peak appears at 2θ of 20°, corresponding to the crystallographic plane (002). Also, a low-intensity peak of the amorphous region at 2θ, corresponding to 18.0°, is recognized. The potato ash mainly exhibited phases of potassium hydrogen disilicate (KHSi2O5), with peaks at 2θ of 29.0 and 32.0) and potassium chloride (KCl), with peaks at 2θ of 42.0, 52.0, 58.0, and 65.0. Furthermore, CaCO3 was identified at 2θ of 33. Additionally, the typical XRD pattern of POT400-M signifies that the peaks at 2θ values of 30.0° (220), 35.3° (311), 43.0° (400), 56.9° (511), and 62.8° (440) are consistent with the reference (JCPDS No. 89-4319) standard XRD pattern for the pure cubic spinel crystal structure of magnetite.
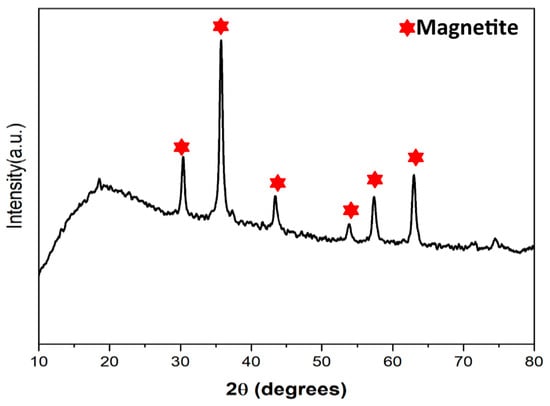
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of the POT400-M composite.
2.1.2. SEM Morphology and Particle Size Distribution
The morphology of the POT400-M powder sample was examined via scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and the attained image is observable in Figure 2a. The morphology of the SEM image shows mixed features, including small semi-spherical particles of magnetite. Scattered grains appeared on the surface, which exhibited a rough texture. The particle size distribution was calculated, and the average particle size was 22.23 nm (Figure 2b). The discrete nanoparticles were very small in size and appeared to be connected to each other. The separate morphology of each nanoparticle presented a clear spherical shape.
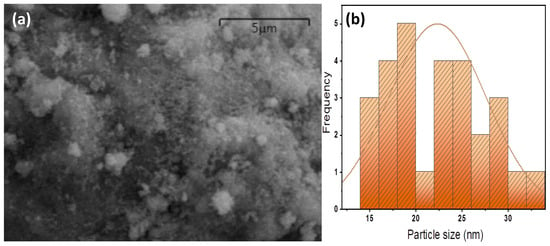
Figure 2.
SEM image (a) and particle size distribution (b) of POT400-M composite.
2.1.3. EDX Analysis
The energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) elemental analysis spectrum is displayed in Figure 3. The composition of the POT400-M material was also investigated and is displayed in the inset table. The results show that the POT400-M composite mostly comprised Fe, C, and O components, together with Ti and Al and minimal levels of Ca, K, and Cl. The existence of iron indicates the presence of mixed magnetite in the POT400-M composite material. Additionally, the sample showed a high amount of Fe, which signifies the existence of magnetite in the hybrid material. Overall, the POT400-M composite comprises both magnetite and potato ash components.
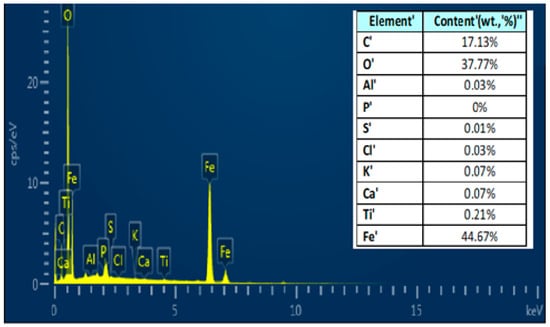
Figure 3.
Chemical composition of the POT400-M composite inferred by EDX, with the element amounts in the inset table.
2.2. Oil Spill Oxidation
2.2.1. Effect of Oxidation Time on Different Oxidation Systems
Initially, a set of experiments was carried out to evaluate the individual effects of magnetite, hydrogen peroxide, and solar radiation on oil spill wastewater oxidation. The results were compared with the introduced dual solar-modified Fenton (POT400-M composite/H2O2) oxidation system. Figure 4 shows both the influence of the abovementioned various oxidation systems and the effect of oxidation time. The data displayed in Figure 4 indicate that even though solar oxidation and the individually applied systems exhibited oil oxidation, as evaluated by chemical oxygen demand (COD) reduction, the rate of oxidation was lower when the dual oxidation system (POT400-M composite/H2O2) was applied under solar radiation. According to the experimental data, the modified Fenton-based system demonstrated relatively higher oxidation efficiency, reaching 89% compared to the other studied systems. Furthermore, it is essential to mention that such results were achieved using 40 mg/L of the POT400-M composite Fenton-based catalyst and 400 mg/L of H2O2 at pH 6.0.
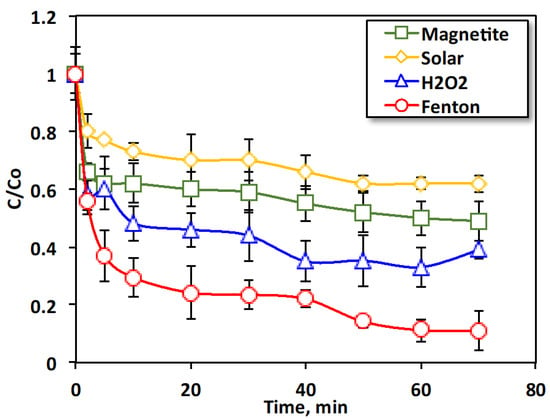
Figure 4.
Effects of reaction time on different oxidation systems.
It is noteworthy that oxidation rates of only 38, 51, and 61% were acquired when the systems of solar radiation, magnetite, and H2O2, respectively, were individually applied. This may be associated with the insufficient OH radicals produced in such systems. However, confirming the effectiveness of the solar/POT400-M composite/H2O2 system, the experimental data demonstrated higher removal rates. This verifies that the presence of the hybrid POT400-M composite augmented with H2O2 in the modified Fenton reaction increased the OH radicals, enhancing the efficiency of the oxidation reaction.
Generally, advanced oxidation technologies based on integrated solar energy systems require milder conditions compared to those based on thermal technologies. Hence, photocatalytic Fenton reaction can be considered as a faster and effective reaction compared to the thermal reactions. The collectors required for solar catalytic oxidation are similar to conventional solar thermal collectors, with some main differences. For example, the aqueous solution must be exposed to the ultraviolet irradiation from solar energy. Such data was previously reported in the literature for the treatment of oily effluent using Fenton-like oxidation systems [6].
2.2.2. Effectiveness of Modified Fenton-like System’s Multiple Parameters (POT400-M Catalyst, Hydrogen Peroxide, and pH Value)
It is essential in keeping Fenton-like’s multiple reagents either hydrogen peroxide or catalyst concentrations are minimal since the high doses might both reduces the oxidation effectiveness and increasing the process cost. In this regard, to assess the influence of such reagents, i.e., H2O2 and POT400-M catalyst, on the modified Fenton-like oxidation of oil spill effluent, their addition to the system was studied at different concentrations. The decomposition of H2O2 peroxide reagent in the presence of the dual POT400-augmented magnetite composite catalyst, acting as a Fenton-like system for producing ·OH radicals, was studied at various concentrations. The results displayed in Figure 5a indicate that there were increases in the oil mineralization and removal efficiency from 53 to 90% with increases in the reagent. However, beyond a certain optimal limit, further increases in the concentration of hydrogen peroxide reagent resulted in a continuing gradual reduction in the oxidation reaction rate, resulting in only 37% removal. Also, it is important to note that when H2O2 is present in excess of the optimal amount, this peroxide reagent acts as an ·OH radical scavenger rather than a producer. This leads to decreased efficiency in oil removal [22].
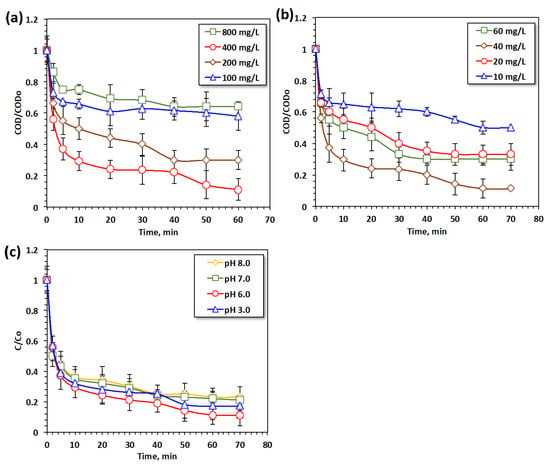
Figure 5.
Effects of POT400-M oxidation system on oil aqueous effluent, demonstrating the influence of POT400-M-based Fenton-like system operational parameters: (a) catalyst; (b) H2O2, (c) pH.
Experimental tests were conducted to determine the effect of the POT400-M reagent concentration on the photochemical oxidation reaction system, and the data are presented in Figure 5b. To assess the effectiveness of this reagent, its dose was varied, and the optimum dose was found to be 40 mg/L, which corresponds to a removal efficiency of 90%. This may be due to the presence of Al3+ and Fe2+/3+ ions in the reaction medium, which are responsible for creating photoactive hydroxo complexes. These complexes can capture photons from UV illumination, thereby producing OH hydroxyl radicals, which are considered to be the most reactive oxidizing species. The metal ions also react with hydrogen peroxide reagent to produce additional oxidative hydroxyl radicals, creating a cyclic reaction that attacks and hydroxylates the pollutant. However, further increases in the POT400-M catalyst concentration result in a decline in the oxidation efficacy, which reaches only 70%. This is due to the overdosing of the catalyst, which blocks UV illumination, thereby reducing oil oxidation efficiency [18,56].
Generally, established Fenton-like oxidation reactions are highly sensitive to the operating pH, with limitations at acidic pH levels. This acidic pH limitation is an obstacle for practical applications of the system. Therefore, a reaction was conducted at various pH levels to check the influence of pH, ranging from the original wastewater value (6.0) to acidic (3.0), neutral (7.0) and alkaline (8.0) conditions. The experimental results displayed in Figure 5c indicate that high oil removal efficiency was achieved at the natural pH of the wastewater without any extra adjustment, revealing 90% oil oxidation. Nevertheless, it is essential to note that wastewater oxidation occurred across the entire studied pH range, indicating that the reaction can proceed over a wide pH range. These pH results may overcome the drawbacks of the pH value limitation in the Fenton oxidation system. Generally, iron-based Fenton systems work within an acidic pH range. This restriction in the conventional Fenton technique requires a pre-acidification step prior to final discharge for pH correction [19]. Interestingly, the novel system not only demonstrates sustainability, but it also exhibits fast cost-effective oxidation for oil-spill wastewater effluent, confirming its application for wide pH range.
2.2.3. Effect of Temperature on Oxidation Kinetics and Thermodynamics
To reach to a real practical life application, it is vital to examine the temperature influence meanwhile the circumstances in the real field could be spilled at various temperatures. Therefore, the impact of temperature on solar oxidation was determined over a wide temperature range, from 32 °C to 60 °C. The data presented in Figure 6 reveal that the reaction occurred at various temperatures, however, the maximal yield occurred at room temperature. This result may be because, at high temperatures, the hydrogen peroxide reagent decomposed into oxygen molecule and water. Therefore, the reaction oxidation efficiency was limited to only 53%. This decrease in oil removal with increasing temperatures may be associated with catalyst deactivation at higher temperatures. Furthermore, reaction intermediates formed at higher temperatures, unlike at room temperature, which is unwanted in catalytic reactions. Increasing the temperature of the reaction may also cause desorption, where oil that was already adsorbed onto the catalyst is desorbed from the catalyst pores and surface. This may simultaneously occur with catalytic oxidation, thus, decreasing the overall reaction rate [60,61,62,63,64].
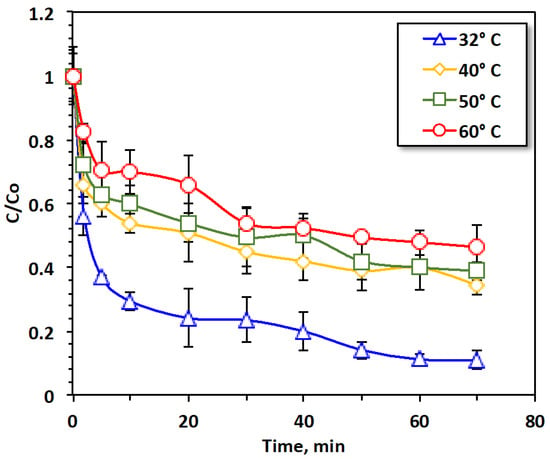
Figure 6.
Effects of POT400-M oxidation system on oil aqueous effluent, demonstrating the influence of temperature on the oxidation system.
To examine the oxidation of oil spills through the modified Fenton system, kinetic modeling was applied to assess the reaction rate constants. At different initial temperatures, the empirical and theoretical values of different (zero-, first-, and second-order) kinetic models were evaluated and compared for the modified Fenton system based on POT400-M. Subsequently, a comparison of the correlation coefficient values (R2) was carried out to assess these models and select the most appropriate one. A higher correlation coefficient, R2, indicates better suitability of the model to express the empirical and theoretical data. Therefore, the zero-order model was rejected due to its low correlation coefficient values (R2), which ranged from 0.55 to 0.73. Although the first- and second-order kinetic models had high correlation coefficient values, the second order model had the highest, since the correlation values ranged from 0.92 to 0.99. Therefore, the second-order kinetic model accurately describes the experimental data, as shown in Table 1. Fitting the data to the second-order kinetic model indicates the reaction is dependent on the amount of oil oxidized on the material surface. It is estimated from the data displayed in Table 1 that the half-life time (t1/2) increases with the temperature.

Table 1.
Photocatalytic kinetic models and statistical analysis of oil spill oxidation via POT400-M *.
To accurately assess the temperature effect on oil oxidation by the proposed system, the thermodynamic activation variables were evaluated. The data was estimated based on the second-order kinetic model equation using the Arrhenius equation (, where A is the pre-exponential factor constant; Ea is the energy of activation (kJ/mol); R is the gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K); and T is temperature (K)). The energy (Ea) can be estimated from the slope of the linear plot of ln k2 versus 1/T (Figure 7), providing a value of (−Ea/R). Furthermore, the Eyring equation (, where kB and h are Boltzmann and Planck’s constants, respectively) was applied to attain the Gibbs free energy data [50]. According to the Eyring equation, the value Gibbs free energy value was calculated as Then, the values of activation enthalpy (ΔH′) and entropy (ΔS′) can be calculated using the equations and , respectively [54].
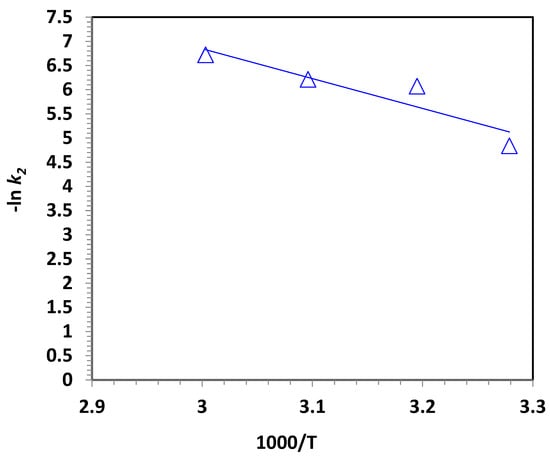
Figure 7.
Arrhenius plot of ln k2 versus 1000/T for modified POT400-M Fenton oxidation (solid lines signify least-squares fitting).
The results of the abovementioned equations and calculations are presented in Table 2. According to the data displayed in the table, the negative enthalpy of activation (ΔH′) values indicate the exothermic nature of the reaction and confirm the data displayed in Figure 7. Additionally, the negative values of entropy (ΔS′) confirm the spontaneity of the oxidation system. Furthermore, the positive values of Gibbs free energy of activation (ΔG′ > 0) indicate the spontaneous nature of the reaction and that the reaction is conducted with a low energy barrier. This data indicates that the reaction occurs with a decrease in the degree of freedom of the contaminants in the wastewater. It also suggests that the contact between the hydroxyl radicals (·OH) and oil molecules is efficient for the reaction. The reaction requires a low energy barrier to proceed, as confirmed by the value of −51.34 kJ/mol. It is important to note that the negative values of activation energy indicate that the oxidation rate decreases as the reaction temperature increases, which is in accordance with the abovementioned negative dependence on temperature elevation. This data is supported by previously published results in the literature on treating various types of wastewater with similar reagents [50].

Table 2.
Thermodynamic parameters of oily wastewater oxidation Fenton-based POT400-M system.
2.2.4. Recyclability and Stability
The 3Rs approach, “Recover, Recycle, and Reuse”, was applied to assess the stability and recyclability of the agro-waste-based magnetic catalyst, aiming to satisfy the sustainability criteria. Using this concept, the heterogeneous magnetite-based carbon catalyst POT400-M was collected after each experiment and recovered to evaluate its stability in order to deduce the cost of the Fenton reaction. First, after the reaction was complete, the catalyst was collected and washed with distilled water multiple times. Then, it was subjected to drying at 105 °C in an electric oven. Subsequently, the dried material was prepared for reuse. The experimental data for multiple uses of the material for oily water oxidation was evaluated and displayed in Figure 8.
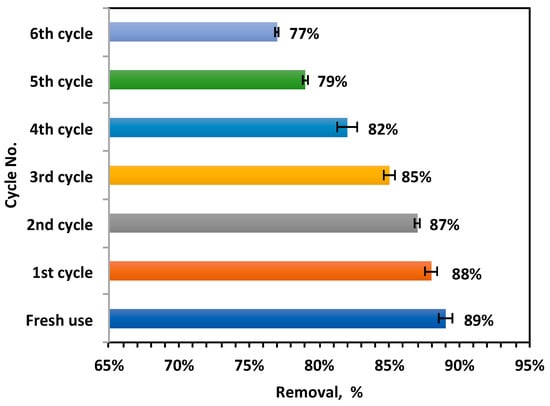
Figure 8.
Reuse routine of the POT400-M composite material.
The experimental results from successive uses of the material indicate that it maintained catalytic activity, even after multiple uses. Even after six cyclic oxidation cycles, the material showed only a 12% reduction in removal efficiency. A reasonable stability of The material demonstrated reasonable stability after repeated use, decreasing to only 77% by the sixth cycle compared to 89% with its initial use. Therefore, the POT400-M material demonstrated promising sustainability characteristics. However, it is worth mentioning that there the efficiency of the material treatment decreased in comparison to its initial use. This could be associated with the occupation of active sites on the material by organic intermediate molecules. This leads to the blockage of active sites on the material, thereby preventing them from attacking the organic pollutants. Such intermediates thus hinder catalytic activity [28,65]. Therefore, the overall reaction rate decreased. However, further work is essential at this stage to improve the material’s activity.
2.2.5. Numerical Optimization and Experimental Design
The Box–Behnken design, based on response surface methodology (RSM), was selected as an effective tool to optimize the selected variables: POT400-M concentration (Γ1), hydrogen peroxide concentration (Γ2), and pH (Γ3). These variables were chosen because they are the most influential parameters on the oxidation system, with COD removal as the response variable. Based on the preliminary data, the parameters were evaluated at three coded levels as −1, 0, or 1 (Table 3). A total of 15 experiments were conducted, and the full experimental design is presented in Table 4. The three independent parameters (Γ1, Γ2, and Γ3) and their mathematical correlation with the response (Y) are expressed by the polynomial quadratic correlation in Equation (1) [25], where (Y) represents the predicted response, and (βo, βi, β2 and βii) are the set of independent parameters influencing the Y response, corresponding to the intercept, linear, quadratic, and interaction terms respectively.

Table 3.
Natural and coded levels of the experimental domain boundaries and their spacing for the POT400-M modified Fenton system.

Table 4.
Box–Behnken design matrix showing coded and natural variables for the POT400-M/H2O2 system.
The optimum values of the coded independent parameters were determined (Mathematica software, version V 5.2). Additionally, analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to test the statistical accordance and evaluate the fitness of the quadratic model [26]. Additionally, graphical analysis was further performed to better illustrate the interactions between the proposed independent variables at their coded levels in the model (MATLAB R2017a software). This design involved analyzing the experimental data via response surface and contour schemes.
The results of the NOVA test tabulated in Table 5 demonstrate the Fisher variance ratio (F-test), indicating that the data variation around the mean is adequate, and the effects of the predicted parameters are statistically significant. The regression model is considered to be well-correlated and efficient at a minimal level of probability (p-value > F-value = 0.0001) [33]. As presented in Table 5, the probabilities (p-values) of all coefficients are less than 0.05; therefore, the quadratic regression model displayed in Equation (2) is significant and sufficient to describe the experimental data.

Table 5.
ANOVA test results and data of the quadratic model for the POT400-M-based Fenton system.
The influence of the interaction between the POT400-M and hydrogen peroxide is graphically illustrated in 3D surface and 2D contour plots. The graphical plots are displayed in Figure 9, illustrating the COD removal response and the interactions between each pair of variables. As exhibited in Figure 9a, there was a clear effect of the interaction between the POT400-M catalyst (Γ1) and H2O2 reagent concentrations (Γ2) on COD removal (%). The COD reduction decreased when very low or very high concentrations of both reagents (POT400-M catalyst (Γ1) and H2O2 reagent (Γ2)) were used. This verifies the vital action of the optimal doses of the POT400-M catalyst and hydrogen peroxide on the generation of hydroxyl (·OH) radicals, which are mainly responsible for the oxidation reaction in the system. As plotted in the Figure 9b, the highest oxidized oil, indicated by COD removal, was achieved at a near acidic pH level. There was an interaction between the POT400-M catalyst (Γ1) concentration and the pH (Γ3) value. Therefore, the maximum COD removal rates correspond to the optimal values of POT400-M and pH. This may be related to the fact that the maximum production of hydroxyl (·OH) radicals is linked to the acidic pH conditions. Thus, this may enhance the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by POT400-M, thereby oxidizing more oil [13].
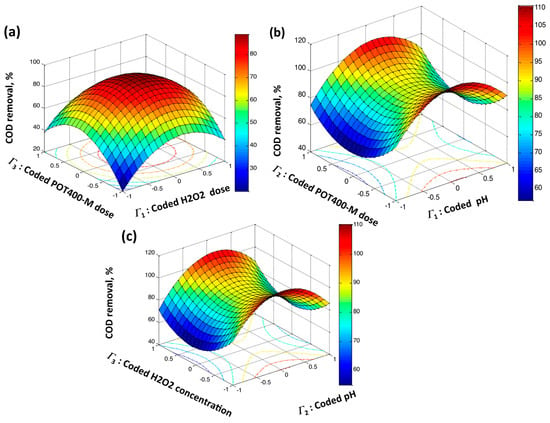
Figure 9.
Graphical representation of numerical design response surface for COD oxidation, including (a) 3D surface and 2D contour plots of coded POT400-M and H2O2 concentrations, (b) 3D surface and 2D contour plots of coded POT400-M concentrations and pH, and (c) 3D surface and 2D contour plots of coded H2O2 dose and pH.
The interaction between the hydrogen peroxide (Γ2) and pH (Γ3) is presented in Figure 9c, which shows that the ideal removal efficacy occurred at an acidic pH level and the optimal POT400-M concentration. However, POT400-M doses other than the optimal value affected the COD oxidation rate, thereby reducing the process efficiency. Consequently, overdosing POT400-M limits the total oxidation rate of the system.
Numerical optimization using Mathematica software (V 5.2) was carried out to optimize the process variables that could maximize the COD removal response. The optimal values were found to be 47 mg/L POT400-M, 372 mg/L hydrogen peroxide, and a pH of 5.0, resulting in a maximum COD reduction of 96%. Finally, to validate the model’s adequacy, three additional runs were carried out using the optimal values. The measured average response value of 93% was compared with the predicted one of 96%, confirming the model’s significance.
2.2.6. Comparative Analysis
Table 6 presents the Fenton oxidation results using the current win–win material as a benign sustainable solar photocatalyst compared with the previously studied materials in the literature for oil separation applications. For various oil types contaminating water, there are numerous treatment techniques, including filtration, adsorption, biological treatment; however, there is lack of reports in the literature on oxidation methods. Table 6 also lists various examples of combined techniques, such as physical separation by adsorption or filtration and biological treatment. The oil/water separation mechanism is based on oil demulsification and separation techniques.

Table 6.
Removal of different oil types from wastewater through various techniques *.
It is worth noting that the composite based on magnetite particles introduced in the current work is a superior catalyst since it is an easy recoverable substance that presents an opportunity for reuse. Therefore, this work offers the merits of applying a recyclable material, thereby minimizing the cost of treatment. Furthermore, using potato peel as a waste-derived component in the composite turns the catalytic oxidation process into a win–win technology. The application of this waste-based catalyst material is not only environmentally friendly, but also significantly reduces the cost of the waste remediation technique.
Table 6 presents a comparison showing that, with the exception of references [35,37,43], removal efficiencies reported in the literature for oily wastewaters ranged from almost 70% to complete removal, with the current work achieving 93% [39,40,60]. The range of the removal efficiencies is attributable to the variety of hydrocarbon compounds and their nature in wastewaters. However, some techniques have shown poor removal efficiencies [35,37,43]. It is important to note that the current study is based on waste stream valorization, using a recyclable substance that can help reduce the cost of treatment.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Field Sampling and Tested Oil
The study area is located in the Red Sea near the shore at a longitude and latitude of 33°48′ E and 27°15′ N, respectively. The oil spilled at this location is due to marine activities near the shore. The samples were collected throughout the summer of the year of 2024. Oily water samples were collected near the seashore, where the temperature was about 32 °C. Then, the samples were taken to the laboratory for analysis and further subjected to treatment. After collection, the oil spill water samples were subjected for analysis and kept for further use according to the standard methods [25], in plastic containers at 4 °C. The main characteristics of the oily water samples were investigated and recorded as follows: pH 7.5, 52,700 S/m conductivity, and 27,520 mg/L total dissolved solids (TDS). Furthermore, the oil content in the wastewater samples was 203 mg/L, and the chemical oxygen demand (COD) was 7133 mg/L.
3.2. Magnetic Bio-Char Preparation
First, potato peel agro-waste samples were collected from a potato-processing plant and transported to the laboratory for treatment and conversion into bio-char. After collection, the potato peel waste was subjected to ordinary washing to remove impurities prior to treatment. The peels were successively rinsed with distilled water to remove all the dust particles. Then, they exposed to sunlight for drying for a week, and then subjected to drying in an electric oven at 80 °C for three days to remove any excess water content at the time of use. The resultant dried peels were ground into a fine powder with a pestle and mortar, and then sieved to obtain particle sizes of about 0.5 mm. Additionally, the peels were thermally activated by heating at 400 °C in an electrical furnace for 2 h at a heating rate of 10 °C/min under atmospheric air. The resultant material was designated as POT400.
Secondly, magnetite nanoparticles were prepared via simple co-precipitation routine. The method is conducted by using the aqueous solutions of the stoichiometric ratios of (2:1) from the precursors of Fe2(SO4)3:Fe(SO4), respectively, followed by precipitation at 11.0 pH value. Also, the pH value was adjusted using a digital pH meter (Model AD1030, Adwa instrument, Szeged, Hungary). Afterwards, the attained precipitate mixture was subjected to continuous stirring at 80 °C to produce nanoparticles, which were then consecutively washed with distilled water to reach pH 7.0. The material was then placed in an electrical oven to dry at a moderate temperature (60 °C), producing a fine magnetite powder. Then, mixing the biomass with magnetite, as an environmentally friendly substance, was prepared by integrating the bio-char with the prepared magnetite nanoparticles and designated as POT400-M. Subsequently, the powder was stored in hermetic plastic bags until use.
3.3. Characterization of the Material
The prepared material was subjected to characterization prior to its application as a photocatalytic oxidation system for oily water treatment. Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) was conducted through the use of a Bruker-Nonius Kappa CCD diffractometer (Baton Rouge, LA, USA). This diffractometer was equipped with a CuKα X-ray source with a wavelength of 1.5405. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was conducted with the use of a FE-SEM, Quanta FEG 250 (Hefei, Anhui, China), equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) detector.
3.4. Solar Photochemical Reactor Configuration
The pilot-scale experimental setup is designed to concentrate solar energy through a parabolic trough collector, and the photochemical design is designed to operate and use the solar energy efficiently. The photochemical system consists of a parabolic collector with a tubular silica glass tube mounted on its focal line. Once the parabola is pointed towards the sun, parallel sunrays occurring on the reflector are reflected onto the basin tube. The tubular reactor is connected to a feed/discharge basin, creating a closed circlet.
The parabolic trough collectors needed for this solar catalytic Fenton oxidation system are similar to those used for conventional solar thermal collectors but without the need for high energy. Therefore, the system is not thermally insulated. The aqueous solution must be exposed to UV irradiation from solar energy. Furthermore, a transparent tubular reactor is applied to allow the ultraviolet radiation to penetrate since the most effective photons for the solar-driven oxidation reaction are within the ultraviolet wavelength range. Additionally, temperature does not play a significant role in the process. Therefore, there is no need for the thermal insulation. In this reactor, the aqueous oily water flows through a tubular reactor mounted on the focal line of the parabola to utilize the solar energy efficiently. The tubular reactor is made of a silica glass tube. The reflector collects sun radiation parallel to the axis of the parabola and directs it towards the focal line where the tubular reactor is installed, to ensure the total transmission of UV radiation.
3.5. Methodology and Photocatalytic Determination
Oily contaminated wastewater was collected near the seashore and then transported to the laboratory to check its characterization. The oily water samples were kept following the standard methods for water and wastewater treatment until use in the experiments (at 4 °C). Next, 1000 mL of the oily water was poured into a glass vessel to assess the oil concentration on its catalytic oxidation efficacy. The initial aqueous mixture pH was adjusted, if required, to the desired values by using drops of diluted solutions of sulphuric acid or sodium hydroxide. Subsequently, the POT400-M substance was added to the aliquot effluent, and the Fenton oxidation reaction was initiated by the addition of hydrogen peroxide reagent. Furthermore, to study the temperature effect on the oxidation reaction, a temperature is varied from 32 °C to 60 °C through the reaction and such temperatures are controlled through a controlled water bath.
The samples were then analyzed based on the standard methods of examination of wastewater, and the Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is monitored in three replicates and compared to the initial Chemical Oxygen Demand (CODo).
Additionally, for the object of comparison, synthetic material (RP 18) supplied by Oil Pollution Environmental Control Ltd (OPE) that is commonly used as hydrophobic material for oil removal is applied. RP 18 consists mainly of polypropylene and polyester yarn fibers covered with cationic emulsifiers. Schematic overview of the process description set-up and steps is explored in Figure 10.
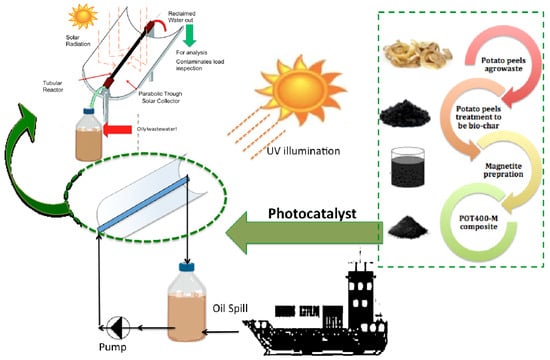
Figure 10.
Schematic illustration of the experimental steps.
4. Conclusions
This work introduces the 3Rs (Recover, Recycle, and Reuse) criteria. The investigation focuses on the novel use of potato peel agro-waste, thermally treated at 400 °C and augmented with environmentally friendly magnetite nanoparticles. The hybrid magnetic bio-char nanoparticles (POT400-M) were then used as a as a recyclable heterogeneous oxidation catalyst for the solar-driven Fenton reaction, serving as an effective oxidation system. The reaction is sustainable since it uses renewable solar energy for activating the oxidation through the use of a solar collector and photochemical reactor, maximizing the capture of solar radiation. The process is used to treat oil spill wastewater as a win–win ecological system. The optimal oxidation variables determined using the Box–Behnken design model were 372 mg/L hydrogen peroxide and 47 mg/L POT400-M, at pH 5.0, with a good correlation coefficient value (R2 0.96). Also, the kinetic model was investigated and the experimental results fit well with the second-order kinetic model. Moreover, the thermodynamic variables verified that the reaction is exothermic and can be conducted at a low energy barrier. From a profitable and marketable perspective, the use of UV irradiance sourced from renewable and low-cost solar energy is a very favorable and attractive technique.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.N., H.A.N. and M.A.T.; Methodology, M.A.T.; Software, M.M.N.; Writing—original draft, M.M.N. and M.A.T.; Writing—review and editing, M.M.N., H.A.N. and M.A.T.; Visualization, H.A.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University for funding this research work through project number (PSAU/2025/01/33266).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ifelebuegu, A.O.; Lale, E.E.; Mbanaso, F.U.; Theophilus, S.C. Facile Fabrication of Recyclable, Superhydrophobic, and Oleophilic Sorbent from Waste Cigarette Filters for the Sequestration of Oil Pollutants from an Aqueous Environment. Processes 2018, 6, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, M.A.; Nabwey, H.A. Recent advances in solar still technology for solar water desalination. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.G.; Richardot, W.H.; Li, S.; Buruaem, L.; Wei, H.-H.; Dodder, N.G.; Schick, S.F.; Novotny, T.; Schlenk, D.; Gersberg, R.M.; et al. Assessing Toxicity and in Vitro Bioactivity of Smoked Cigarette Leachate Using Cell-Based Assays and Chemical Analysis. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, M.; Li, Y.; Cheng, F.; Liu, Y.; Gao, M.; Liu, G.; Hu, L.; Liang, Y. Effectiveness of discarded cigarette butts derived carbonaceous adsorbent for heavy metals removal from water. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, R.; Pang, S.K.; Yung, K.C.; Yin, L.K. Comprehensive study of used cigarette filters-derived porous activated carbon for Supercapacitors: From biomass waste to sustainable energy source. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 925, 116915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almojjly, A.; Johnson, D.; Oatley-Radcliffe, D.; Hilal, N. Removal of oil from oil-water emulsion by hybrid coagulation/sand filter as pre-treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 26, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Dan, Z.; Duan, N.; Chen, G.; Gao, W.; Zhao, W. Zn (II), Pb (II), and Cd (II) adsorption from aqueous solution by magnetic silica gel: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30938–30948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut-Jadhav, S.; Pinjari, D.V.; Saini, D.R.; Sonawane, S.H.; Pandit, A.B. Intensification of degradation of methomyl (carbamate group pesticide) by using the combination of ultrasonic cavitation and process intensifying additives. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Nan, Z. Formation of octahedron-shaped ZnFe2O4/SiO2 with yolk–shell structure. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2020, 141, 109410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourali, P.; Behzad, M.; Arfaeinia, H.; Ahmadfazeli, A.; Afshin, S.; Poureshgh, Y.; Rashtbari, Y. Removal of acid blue 113 from aqueous solutions using low-cost adsorbent: Adsorption isotherms, thermodynamics, kinetics and regeneration studies. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3079–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.N.; Nikoloski, A.N.; Bahri, P.A.; Li, D. Facile fabrication of perovskite-incorporated hierarchically mesoporous/macroporous silica for efficient photoassisted-Fenton degradation of dye. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 491, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Huynh, K.A.; Padungthon, S.; Pranudta, A.; Amonpattaratkit, P.; Tran, L.B.; Phan, P.T.; Nguyen, N.H. Synthesis of natural flowerlike iron-alum oxide with special interaction of Fe-Si-Al oxides as an effective catalyst for heterogeneous Fenton process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Shen, S.; Zhong, W.; Cao, S. Advances in designing heterojunction photocatalytic materials. Chin. J. Catal. 2021, 42, 710–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.; Jiang, C.; Cheng, B.; Wageh, S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Yu, J. A Review of Direct Z-Scheme Photocatalysts. Small Methods 2017, 1, 1700080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, J.; Yang, L.; Deng, F.; Arramel; Li, X. A review of updated S-scheme heterojunction photocatalysts. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 177, 142–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, F.A.; Al-Zaqri, N.; EI marghany, A.; Alghamdi, A.A.; Alorabi, A.Q.; Baghdadi, N.; AL-Shehri, H.S.; Wahab, R.; Ahmad, N. Synthesis of nanocauliflower ZnO photocatalyst by potato waste and its photocatalytic efficiency against dye. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 11538–11547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Xu, R.; Jia, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Lu, T. Recent advances in the photocatalytic oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-diformylfuran. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 14, 26707–26724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xue, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, N.; Chang, S.; Wang, H.; Pang, H.; Chen, H. Treatment of real benzene dye intermediates wastewater by the Fenton method: Characteristics and multi-response optimization. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolobajev, J.; Katte, E.; Viisimaa, M.; Go, A.; Trapido, M.; Tenno, T.; Dulova, N. Reuse of ferric sludge as an iron source for the Fenton-based process in wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintor, A.M.; Vilar, V.J.; Boaventura, R.A. Decontamination of cork wastewaters by solar-photo-Fenton process using cork bleaching wastewater as H2O2 source. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnago, R.F.; Berselli, D.; Medeiros, P. Treatment of wastewater from car wash by fenton and photo-fenton oxidative processes. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 13, 838–850. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Cloud, R.M. Natural Sorbents in Oil Spill Cleanup. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.A.; El-Samni, T.M. Physical and Chemical Properties of Rice Straw Ash and Its Effect on the Cement Paste produced from different cement types materials and methods. J. King Saud. Univ. Eng. Sci. 2006, 19, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeb, A.M.; Farouq, R.; Mohamed, O.; Tony, M.A. Oil spill clean-up using combined sorbents: A comparative investigation and design aspects. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 100, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; Port City Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Primo, O.; Rueda, A.; Rivero, M.J.; Ortiz, I. An Integrated Process, Fenton Reaction−Ultrafiltration, for the Treatment of Landfill Leachate: Pilot Plant Operation and Analysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, H.A.; Alatabe, M.J.A. Treatment oilfield produced water using coagulation/flocculation process (case study: Alahdab Oilfield). Pollution 2021, 7, 787–797. [Google Scholar]
- Mico, M.M.; Chourdaki, S.J.; Bacardit, J.; Sans, C. Degradation of p-nitrophenol using CuO/Al2O3 as a Fenton-like catalyst under microwave irradiation. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2010, 32, 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Mirshahghassemi, S.; Aminzadeh, B.; Torabian, A. Optimizing electrocoagulation and electro-Fenton process for treating car wash wastewater. Environ. Health Eng. Manag. J. 2017, 4, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorsargol, M.; Razmara, Z.; Amiri, M.M. The role of hydroxyl and carboxyl functional groups in adsorption of copper by carbon nanotube and hybrid graphene–carbon nanotube: Insights from molecular dynamic simulation. Adsorption 2020, 26, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, P.; Men, Y.-L.; Pan, Y.-X. Boosting the adsorption and removal of dye from water by COOH-functionalized carbon nanotubes. Green Chem. Eng. 2023, 4, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.W.; Choi, D.J.; Kim, S.K.; Her, N.; Zoh, K.D. Adsorption characteristics of selected hydrophilic and hydrophobic micropollutants in water using activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 270, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Ying, D.; Liang, X.; Zhu, M.; Lin, X.; Xu, Q.; Cai, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L. A novel cationic polyelectrolyte microsphere for ultrafast and ultra-efficient removal of heavy metal ions and dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, J.; Tan, J.; Jiang, M.; Fu, S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X. In situ synthesis of novel peroxo-functionalized Ti3C2Tx adsorbent for aqueous pollutants removal: Role of oxygen-containing terminal groups. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Bai, R. Development of chitosan-based granular adsorbents for enhanced and selective adsorption performance in heavy metal removal. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, A.M.; Kamal, M.M.; Kenawy, N.; El Manakhly, H. Role of interior structure of agro and non-agro materials for industrial wastewater treatment. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2009, 5, 978–985. [Google Scholar]
- Luna, J.M.; Rufino, R.D.; Jara, A.M.A.T.; Brasileiro, P.P.F.; Sarubbo, L.A. Environmental applications of the biosurfactant produced by Candida sphaerica cultivated in low-cost substrates. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 480, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ge, L.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Li, F. Layered double hydroxide functionalized textile for effective oil/water separation and selective oil adsorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Dai, L.; Wei, B.; Chang, Q. Increasing the hydrophobicity of filter medium particles for oily water treatment using coupling agents. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Gawad, H.S. Oil and Grease Removal from Industrial Wastewater Using New Utility Approach. Adv. Environ. Chem. 2014, 2014, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udonne, J.D. Chemical treatment of emulsion problem in crude oil production. J. Pet. Gas Eng. 2012, 7, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, F.A.; Zamora, J.; Ferrer, I.M.; Kinyuac, M.; Velázqueza, J.M. Adsorption of Crude Oil from Crude Oil-Water Emulsion by Mesoporous Hafnium Oxide Ceramics. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Chang, Q. Filtration of oil from oily wastewater via hydrophobic modified quartz sand filter medium. J. Water Reuse Desalinat. 2018, 8, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushenas, P.; Yusop, Z.; Majidnia, Z.; Nasrollahpour, R. Photocatalytic degradation of spilled oil in sea water using maghemite nanoparticles. Desalinat. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 5837–5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadikina, A.N.; Mohd nawawia, M.G.; Othmana, N.; Rasit Alib, R.; Umi, A.A. Removal of Oily Wastewater Using Chitosan-filled Filter Media. J. Teknol. 2015, 74, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nour, M.M.; Tony, M.A.; Nabwey, H.A.; Shaaban, S.M. Experimental Design and Numerical Optimization of Photochemical Oxidation Removal of Tetracycline from Water Using Fe3O4-Supported Fruit Waste Activated Carbon. Catalysts 2025, 15, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Guo, J.; Chen, T.; Liu, H. Superhydrophobic Polypyrrole-Coated Cigarette Filters for Effective Oil/Water Separation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabwey, H.A.; Tony, M.A. Dewatered Sludge Decorated with Nanoparticles for Alum Sludge Conditioning towards the Concept of “End-of-Waste”. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thabet, R.H.; Fouad, M.K.; El Sherbiny, S.A.; Tony, M.A. Zero-waste approach: Assessment of aluminum-based waste as a photocatalyst for industrial wastewater treatment ecology. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2022, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyan, A.; Leong, C.L.; Bilad, M.R.; Kurnia, K.A.; Susilawati, S.; Prayogi, S.; Narkkun, T.; Faungnawakij, K. Cigarette Butt Waste as Material for Phase Inverted Membrane Fabrication Used for Oil/Water Emulsion Separation. Polymers 2021, 13, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Wan, B.; Wang, F.; Xue, M.; Wu, H.; Li, W. Superhydrophobic fibers from cigarette filters for oil spill cleanup. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 44469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, M.A. Recent frontiers in solar energy storage via nanoparticles enhanced phase change materials: Succinct review on basics, applications and their environmental aspects. Energy Storage 2021, 3, e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, M.A.; Eltabey, M.M. End-of-life waste criteria: Synthesis and utilization of Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles as a super paramagnetic photocatalyst for synergistic wastewater remediation. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, T.A.; Dutra, F.V.A.; Pires, B.C.; Tarley, C.R.T.; Manoa, V.; Borges, K.B. Preparation and characterization of a composite based on polyaniline, polypyrrole and cigarette filters: Adsorption studies and kinetics of phenylbutazone in aqueous media. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 64450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, C.; Shi, J.; Chen, J.; Han, H. Novel and multifunctional adsorbent fabricated by Zeolitic imidazolate framworks-8 and waste cigarette filters for wastewater treatment: Effective adsorption and photocatalysis. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 299, 122190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabwey, H.A.; Tony, M.A. Distinct pathway of multiferroic silver-decorated zinc ferrite nanocatalyst performance for Acinate insecticide oxidation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jia, C.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, S. Utilization of cigarette butt waste as functional carbon precursor for supercapacitors and adsorbents. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Danso, E.; Bagheri, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Facile functionalization of cellulose from discarded cigarette butts for the removal of diclofenac from water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 219, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabwey, H.A.; Abdelkreem, M.; Tony, M.A.; Al Hoseny, N.F. Smart win-win waste management: Superhydrophobic filter using valorized cellulose acetate from discarded cigarette butts for cleaning-up marine oil spill at Hurghada Red Sea shore in Egypt. Frontiers 2024, 11, 1270026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.A.; Tony, M.A.; Nabwey, H.A.; Awad, M.M. Potential of the Biomass Waste Originating from Saccharum officinarum as a Fenton Precursor for the Efficient Oxidation of Azo Dye from an Aqueous Stream. Processes 2023, 11, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamaralalage, D.; Sawai, O.; Nunoura, T. Reusing the generated sludge as Fe source in Fenton process for treating crepe rubber wastewater. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 21, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Lei, J. Study on adsorption of methylene blue by a novel composite material of TiO2 and alum sludge. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 32799–32807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulinari, J.; da Silva Júnior, A.H.; de Oliveira, C.R.S.; Júnior, F.W.R. Valorization and treatment of oily wastewaters from agro-industries using lipases: An overview. In Science, Technology and Innovation: From the Field to the Meal; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.R.; Huang, C.; Lin, S. Reuse of fresh water sludge in cement making. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).