The Catalytic Performance of Metal-Oxide-Based Catalysts in the Synthesis of Glycerol Carbonate: Toward the Green Valorization of Glycerol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Catalyst Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussions
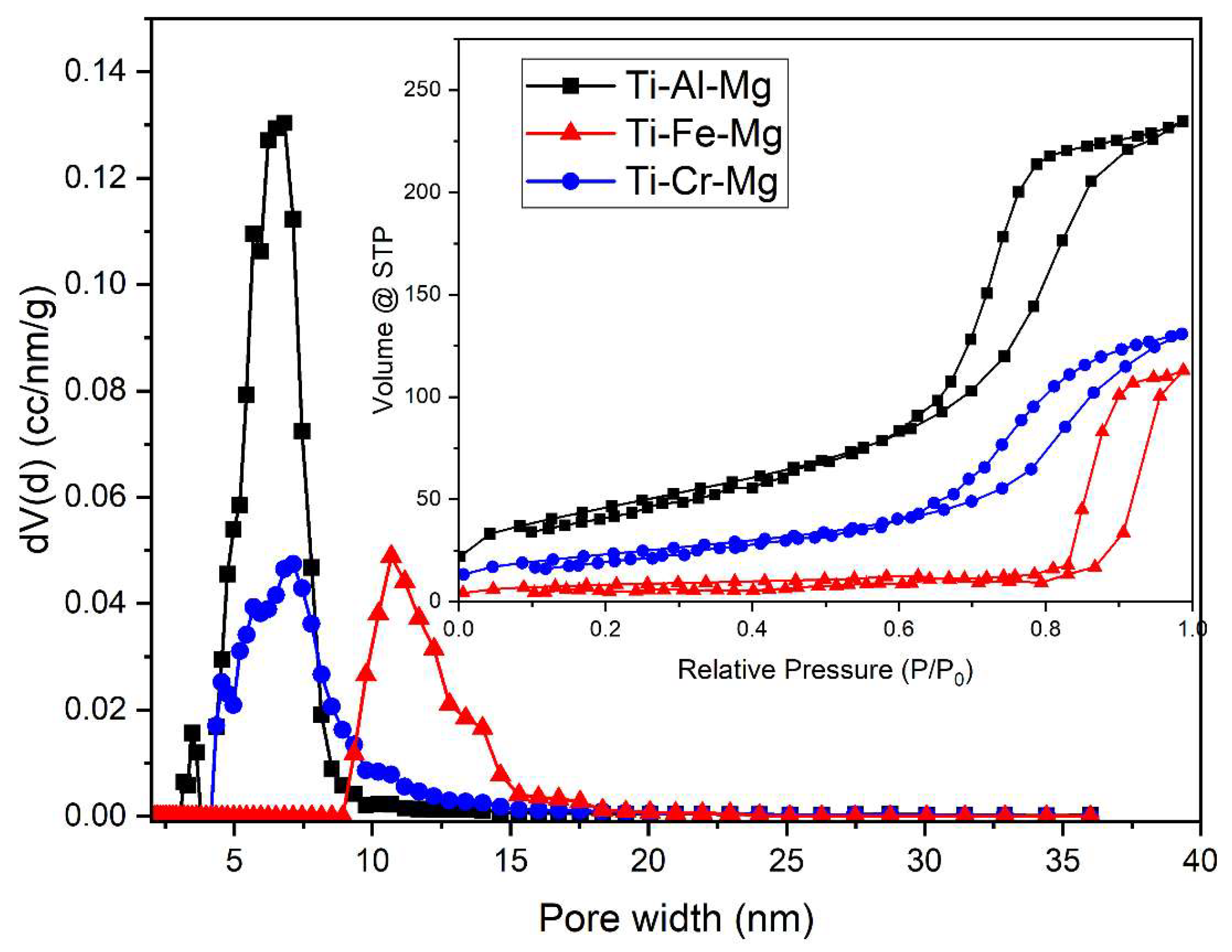
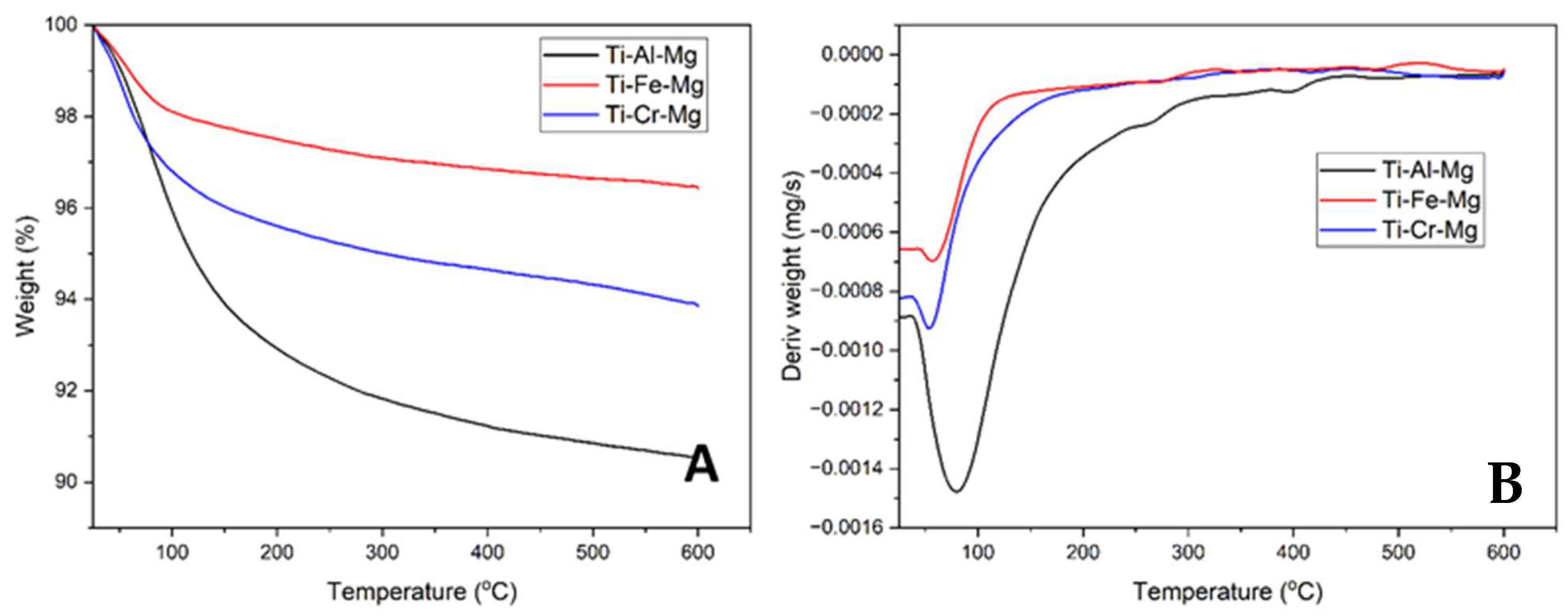
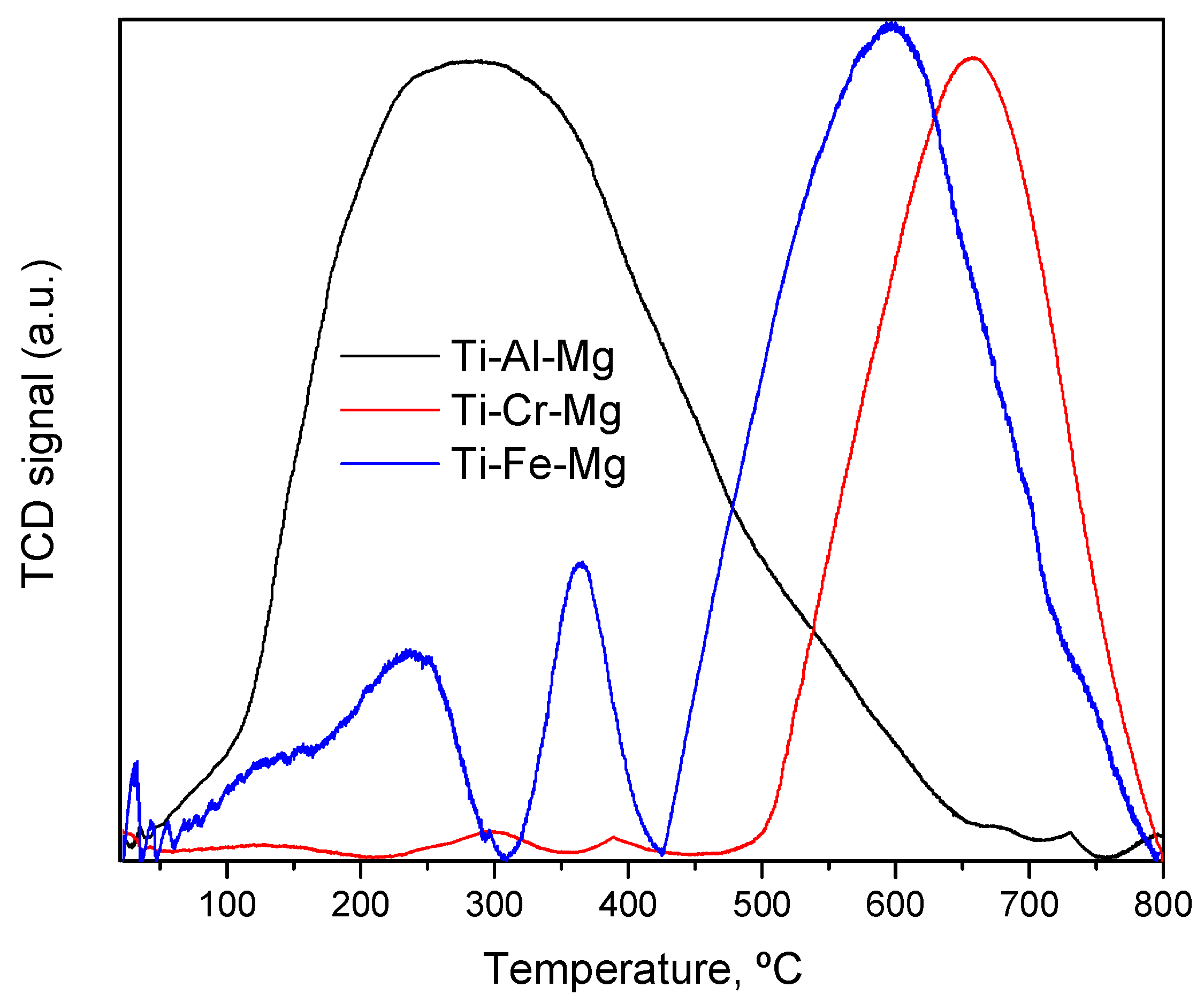
3.1. Catalyst Characterization
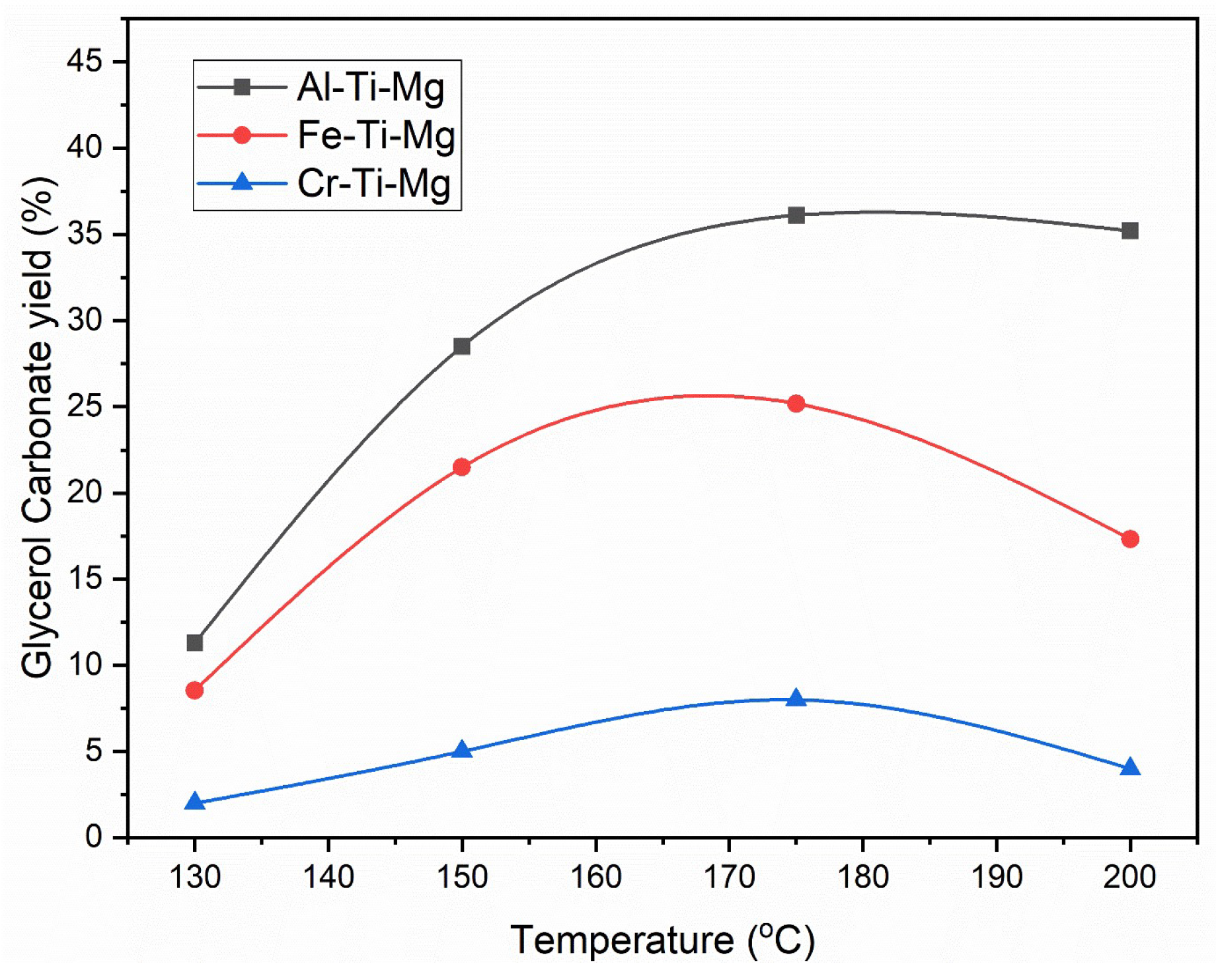
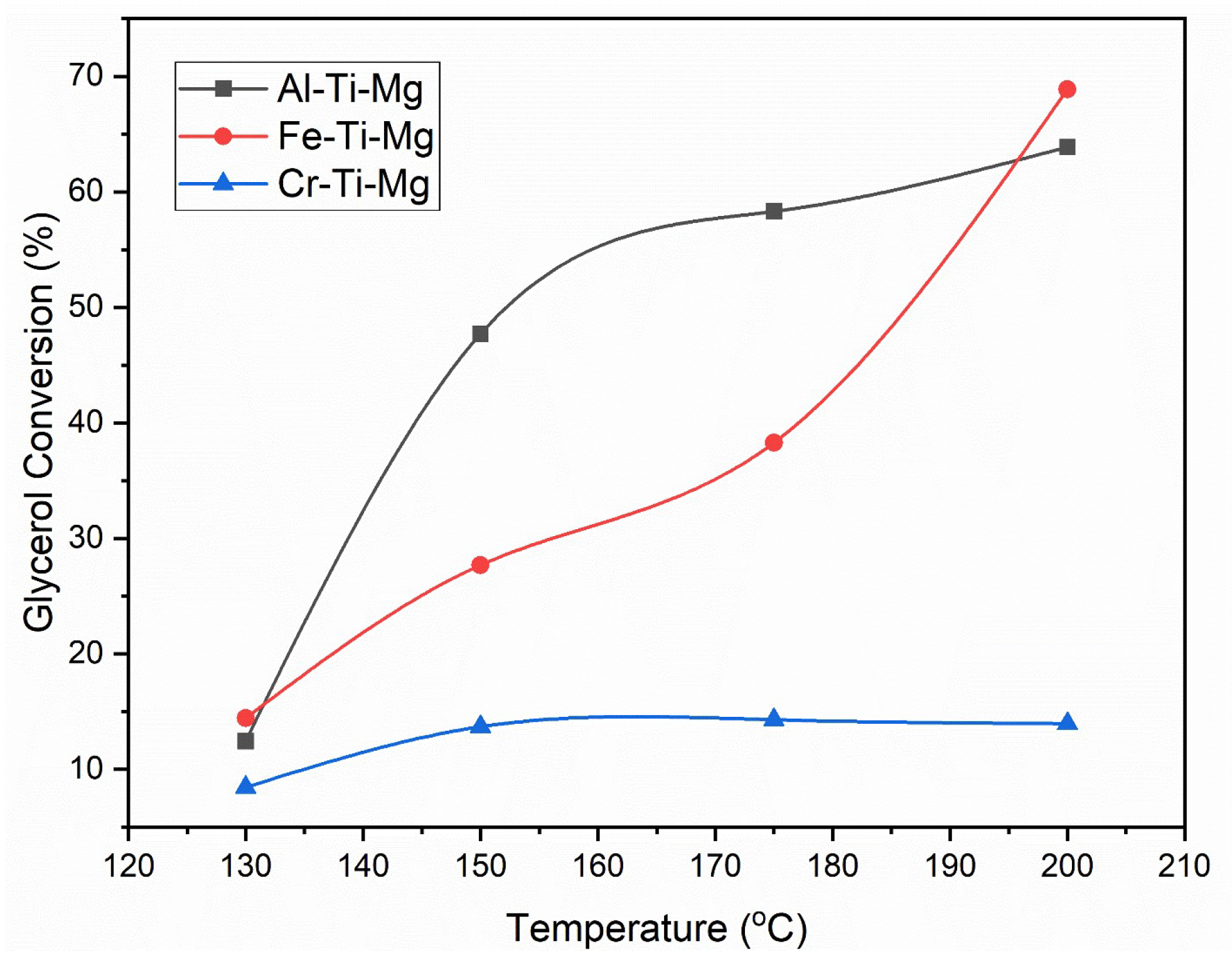
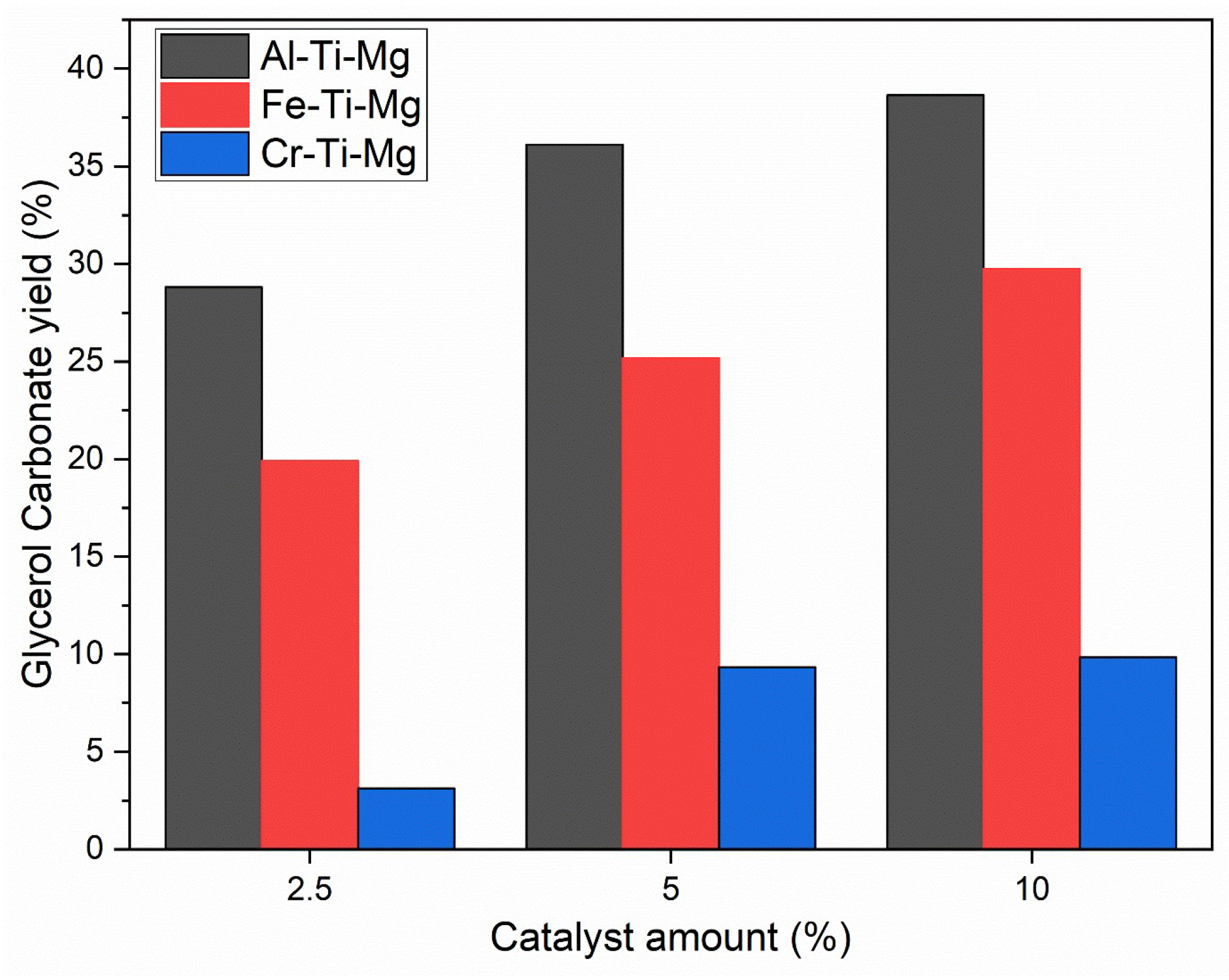
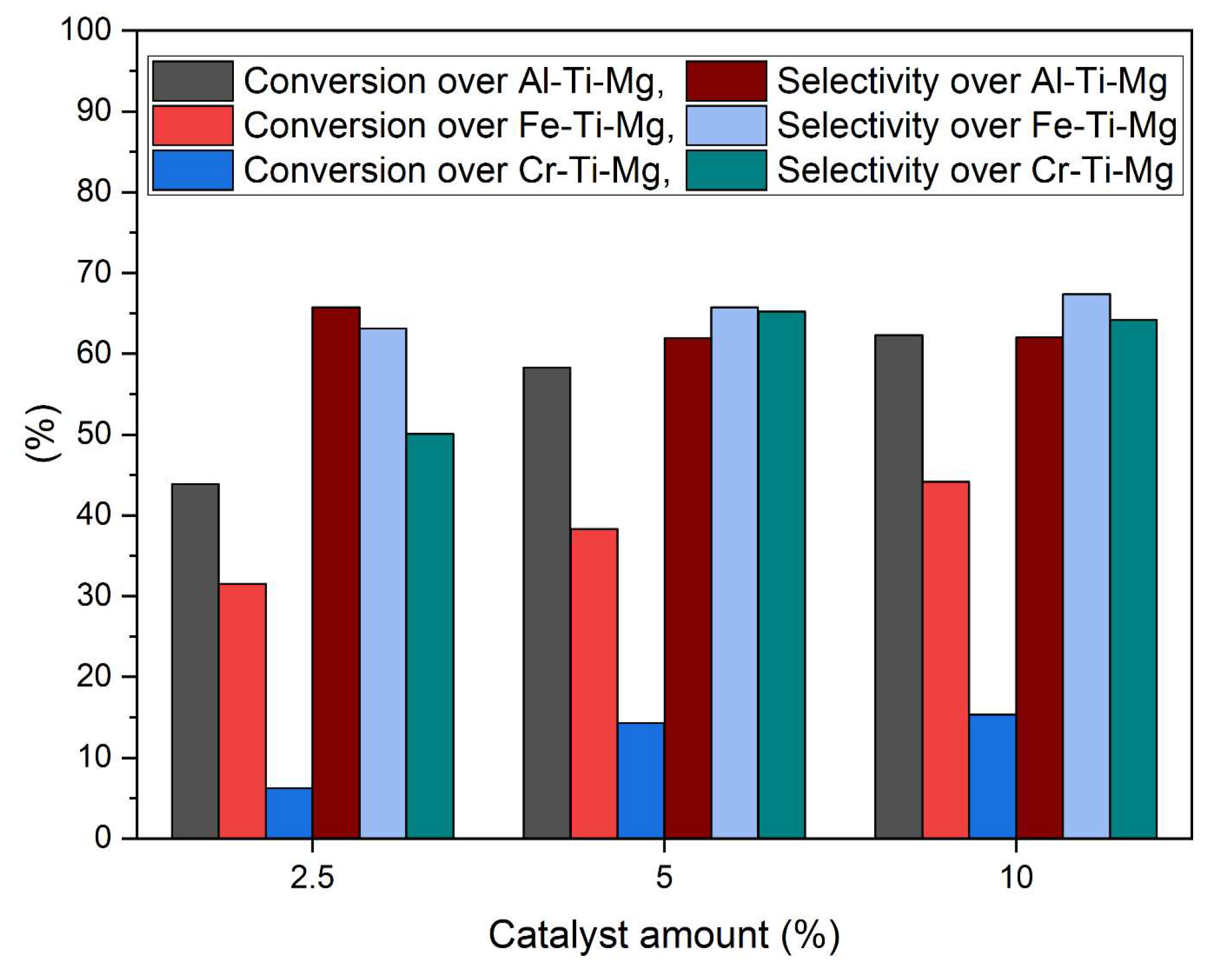
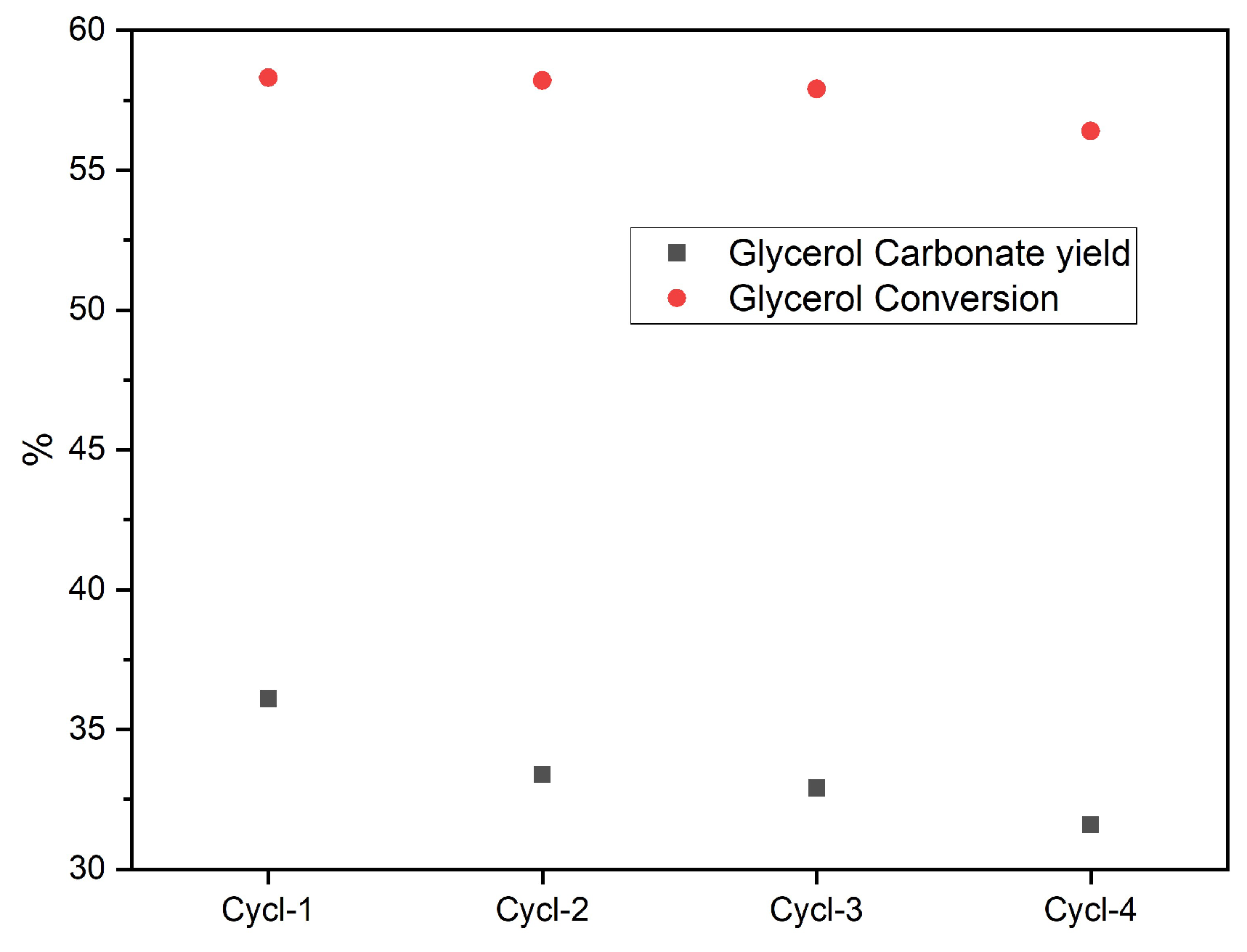
3.2. Catalysts’ Effect on Glycerol Carbonate Synthesis
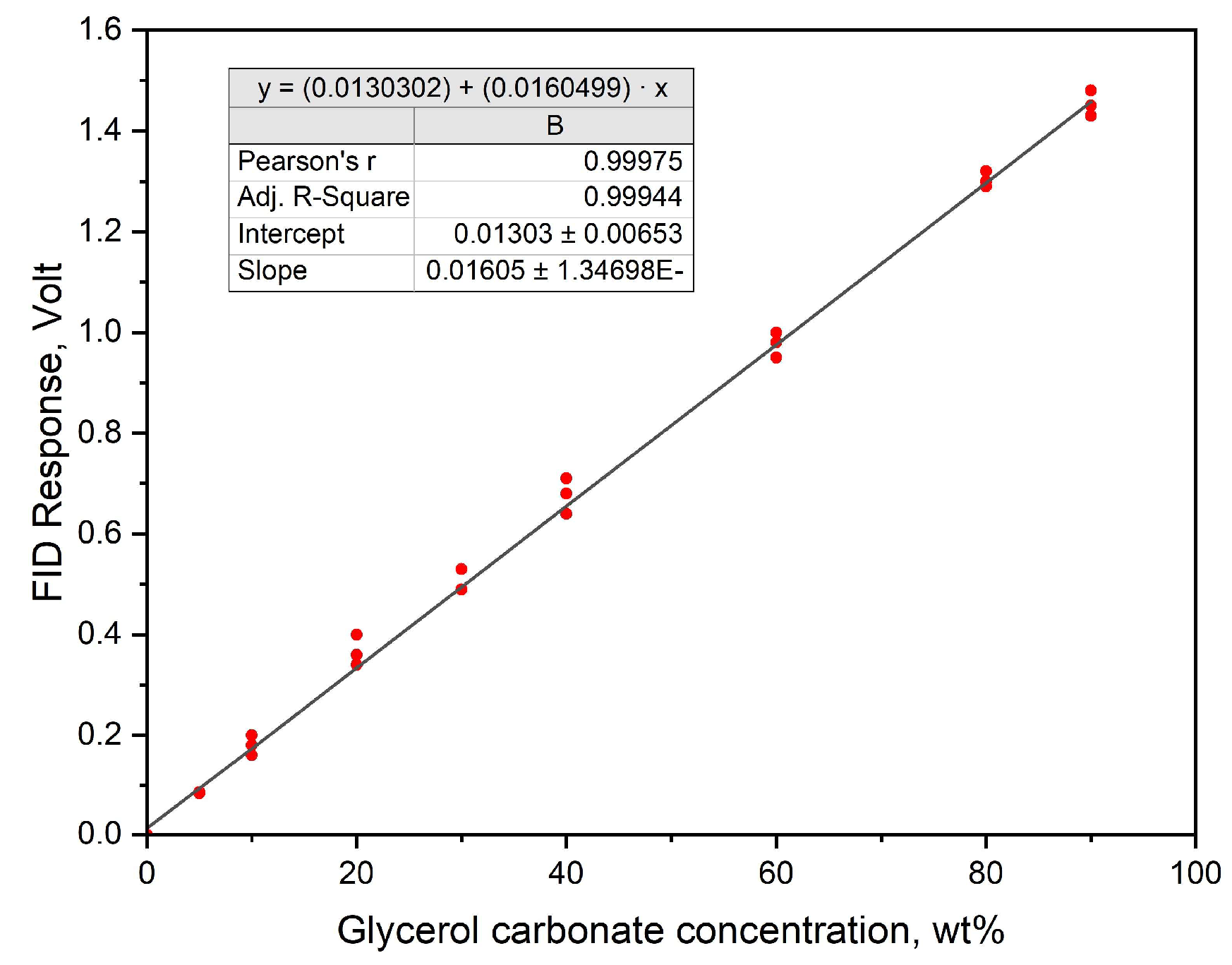
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Catalysts Synthesis
4.3. Experimental Setup and Procedure for Catalyst Testing in Glycerol Carbonate Synthesis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Global Energy Review; IEA: Paris, France, 2025; Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-2025 (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Vasquez, W.V.; Hernández, D.M.; del Hierro, J.N.; Martin, D.; Cano, M.P.; Fornari, T. Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction of Oil and Minor Lipid Compounds of Cake Byproduct from Brazil Nut (Bertholletia excelsa) Beverage Production. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2021, 171, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. Putting CO2 to Use; IEA: Paris, France, 2019; p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Lukato, S.; Kasozi, G.N.; Naziriwo, B.; Tebandeke, E. Glycerol Carbonylation with CO2 to Form Glycerol Carbonate: A Review of Recent Developments and Challenges. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Xiang, M.; He, M.; Zhou, W.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Wu, Z.; Su, Y. Transformation of CO2 with Glycerol to Glycerol Carbonate over ETS-10 Zeolite-Based Catalyst. Molecules 2023, 28, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inrirai, P.; Keogh, J.; Centeno-Pedrazo, A.; Artioli, N.; Manyar, H. Recent Advances in Processes and Catalysts for Glycerol Carbonate Production via Direct and Indirect Use of CO2. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 80, 102693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdhani, X. Thermodynamic and Chemical Equilibrium in the Carbonylation the Glycerol with Carbon Dioxide to Produce Glycerol Carbonate by Using Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Catalyst. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2018, 7, 420–427. [Google Scholar]
- Procopio, D.; Di Gioia, M.L. An Overview of the Latest Advances in the Catalytic Synthesis of Glycerol Carbonate. Catalysts 2022, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.H.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Yuan, H. Production of Glycerol Carbonate by Coupling Glycerol and CO2 over Various Metal Oxide Catalyst. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 83, 102813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kurdhani, J.M.H.; Wang, H. The Synthesis of Glycerol Carbonate from Glycerol and Carbon Dioxide over Supported CuO-Based Nanoparticle Catalyst. Molecules 2023, 28, 4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozorio, L.P.; Mota, C.J.A. Direct Carbonation of Glycerol with CO2 Catalyzed by Metal Oxides. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 3260–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, D.; Gao, P.; Wang, F.; Zhao, N.; Xiao, F.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y. The Synthesis of Glycerol Carbonate from Glycerol and CO2 over La2O2CO3-ZnO Catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 2801–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, L.; Liu, J.; He, D. Transforming glycerol and CO2 into glycerol carbonate over La2O2CO3–ZnO catalyst—A case study of the photo-thermal synergism. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; He, D. Transformation of CO2 and Glycerol to Glycerol Carbonate over CeO2–ZrO2 Solid Solution —— Effect of Zr Doping. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 118, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiao, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, N.; Xiao, F.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, B. Synthesis of Glycerol Carbonate by Direct Carbonylation of Glycerol with CO2 over Solid Catalysts Derived from Zn/Al/La and Zn/Al/La/M (M = Li, Mg and Zr) Hydrotalcites. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 989–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, P.; Chakraborty, R. E-Waste Derived Silica-Alumina for Eco-Friendly and Inexpensive Mg-Al-Ti Photocatalyst towards Glycerol Carbonate (Electrolyte) Synthesis: Process Optimization and LCA. Waste Manag. 2022, 140, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados-Reyes, J.; Salagre, P.; Cesteros, Y. CaAl-Layered Double Hydroxides as Active Catalysts for the Transesterification of Glycerol to Glycerol Carbonate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 132–133, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Xing, Z.; Fang, L. Control of Chloride Ion Corrosion by MgAlOx/MgAlFeOx in the Process of Chloride Deicing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 9269–9281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvamani, T.; Anandan, S.; Asiri, A.M.; Maruthamuthu, P.; Ashokkumar, M. Preparation of MgTi2O5 Nanoparticles for Sonophotocatalytic Degradation of Triphenylmethane Dyes. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 75, 105585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, M.A.; Naeem, R.; McKee, V.; Hakeem, A.S.; Mazhar, M. MgTi2O5 Thin Films from Single Molecular Precursor for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 161, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpelli, F.; Mastropietro, T.F.; Poerio, T.; Godbert, N. Mesoporous TiO2 Thin Films: State of the Art. Titan. Dioxide-Mater. A Sustain. Environ. 2018, 508, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiko, V.P.; Karlagina, Y.Y.; Samokhvalov, A.A.; Polyakov, D.S.; Manokhin, S.S.; Radaev, M.M.; Odintsova, G.V.; Gornushkin, I.B. Surface Structuring and Reverse Deposition of Nanoporous Titanium Oxides by Laser Ablation of Titanium in Air. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2022, 42, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Shi, Q.; Wang, M.; Lv, X.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, W. Synthesis of Nanoscale Lambda-Ti3O5 via a PEG Assisted Sol-Gel Method. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 848, 156585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Harraz, F.A.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Almas, T.; Kumar, R.; Al-Assiri, M.S.; Baskoutas, S. Iron-Doped Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles as Potential Scaffold for Hydrazine Chemical Sensor Applications. Coatings 2020, 10, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.; Chahal, S.; Chauhan, A.S.; Kumar, P.; Shukla, R.; Singh, S.K. X-Ray Analysis of MgO Nanoparticles by Modified Scherer’s Williamson-Hall and Size-Strain Method. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 12, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hadeethi, Y.; Sayyed, M.I. Effect of Gd2O3 on the Radiation Shielding Characteristics Of Sb2O3–PbO–B2O3–Gd2O3 glass system. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 13768–13773. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.; Shen, X.; Niu, Q.; Duan, H.; Tang, C.; Tao, B.; Chen, S.; Shangguan, Q.; Feng, B.; Yu, H.; et al. Thermally and Chemically Stable Fe/Mg-Layered Double Oxides-Biochar for Enhanced Polystyrene Nanoplastic Adsorption and Sustainable Recycling. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 160918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zang, P.; Liu, X.; Mi, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. A Novel Highly Active Catalyst Form CuFeMg Layered Double Oxides for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO by CO. Fuel 2022, 317, 123469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainuri, M. Hematite from Natural Iron Stones as Microwave Absorbing Material on X-Band Frequency Ranges. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 196, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibot, P. Centimetric-Sized Chromium (III) Oxide Object Synthesized by Means of the Carbon Template Replication. Ceramics 2020, 3, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallesham, B.; Rangaswamy, A.; Rao, B.G.; Rao, T.V.; Reddy, B.M. Solvent-Free Production of Glycerol Carbonate from Bioglycerol with Urea Over Nanostructured Promoted SnO2 Catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2020, 150, 3626–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloprogge, J.T. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Study of Layered Double Hydroxides with Different Exchangeable Anions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Song, Y.; Shan, D.; Han, E.H. In Situ Growth of Mg-Al Hydrotalcite Conversion Film on AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3281–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Shinoda, Y. Magnesium Dititanate (MgTi2O5) with Pseudobrookite Structure: A Review. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2011, 12, 034301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayanthi, S.; Kutty, T.R.N. Microwave Dielectric Properties of Mg4Al2Ti9O25 Ceramics. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaogi, M.; Ishii, T.; Yamaura, K. Post-Spinel-Type AB2O4 High-Pressure Phases in Geochemistry and Materials Science. Commun. Chem. 2024, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilania, G.; Kocevski, V.; Valdez, J.A.; Kreller, C.R.; Uberuaga, B.P. Prediction of Structure and Cation Ordering in an Ordered Normal-Inverse Double Spinel. Commun. Mater. 2020, 1, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Conradie, J.; Erasmus, E. Comparison of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Multiplet Splitting of Cr 2p Peaks from Chromium Tris(β-Diketonates) with Chemical Effects. J. Electron Spectros. Relat. Phenom. 2016, 206, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yang, Q.; Hu, L.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Shao, Z.; Lu, C. Insights over Titanium Modified FeMgO x Catalysts for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO x with NH 3. Catalysts 2019, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Aytuna, Z.T.; Bhardwaj, A.; Wilhelm, M.; Khan, L.; May, B.; Mueller, D.N.; Mathur, S. Controlling Degree of Inversion in MgFe2O4 Spinel Films Grown in External Magnetic Fields. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Miyajima, N.; Sinmyo, R.; Kojitani, H.; Mori, D.; Inaguma, Y.; Akaogi, M. Discovery of New-Structured Post-Spinel MgFe2O4: Crystal Structure and High-Pressure Phase Relations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, Y.; Fu, Z.; Su, B.L. Hierarchically Structured Porous Materials: Synthesis Strategies and Applications in Energy Storage. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1667–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perego, C.; Millinib, R. Porous Materials in Catalysis: Challenges for Mesoporous Materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3956–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Liang, X. Model Construction of Micro-Pores in Shale: A Case Study of Silurian Longmaxi Formation Shale in Dianqianbei Area, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.D.; Chandan, P.A. A Green Process for Glycerol Valorization to Glycerol Carbonateover Heterogeneous Hydrotalcite Catalyst. Catal. Today 2014, 237, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, R.; Ichikawa, K.; Kase, M. New Reactions of Organic Isocyanates. I. Reaction with Alkylene Carbonates. J. Org. Chem. 1960, 25, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadima, A.; Muraza, O. Sustainable Production of Glycerol Carbonate from By-Product in Biodiesel Plant. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, J.; Rousseau, C.; Lynikaite, B.; Šačkus, A.; de Leon, C.; Rollin, P.; Tatibouët, A. Tosylated Glycerol Carbonate, a Versatile Bis-Electrophile to Access New Functionalized Glycidol Derivatives. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 8571–8581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosallanejad, S.; Dlugogorski, B.Z.; Kennedy, E.M.; Stockenhuber, M. On the Chemistry of Iron Oxide Supported on γ-Alumina and Silica Catalysts. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5362–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, M.; Brissonnet, Y.; Guélou, E.; De-Oliveira-Vigier, K.; Barrault, J.; Jérôme, F. Acid-Catalyzed Dehydration of Fructose and Inulin with Glycerol or Glycerol Carbonate as Renewably Sourced Co-Solvent. ChemSusChem 2010, 3, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursin, C.; Hansen, C.M.; Van Dyk, J.W.; Jensen, P.O.; Christensen, I.J.; Ebbehoej, J. Permeability of Commercial Solvents Through Living Human Skin. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1995, 56, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudorache, M.; Protesescu, L.; Coman, S.; Parvulescu, V.I. Efficient Bio-Conversion of Glycerol to Glycerol Carbonate Catalyzed by Lipase Extracted from Aspergillus Niger. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, D. Surface Properties of Cu/La2O3 and Its Catalytic Performance in the Synthesis of Glycerol Carbonate and Monoacetin from Glycerol and Carbon Dioxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 419, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, W.K.; Ngoh, G.C.; Yusoff, R.; Aroua, M.K. A Review on the Performance of Glycerol Carbonate Production via Catalytic Transesterification: Effects of Influencing Parameters. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 88, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
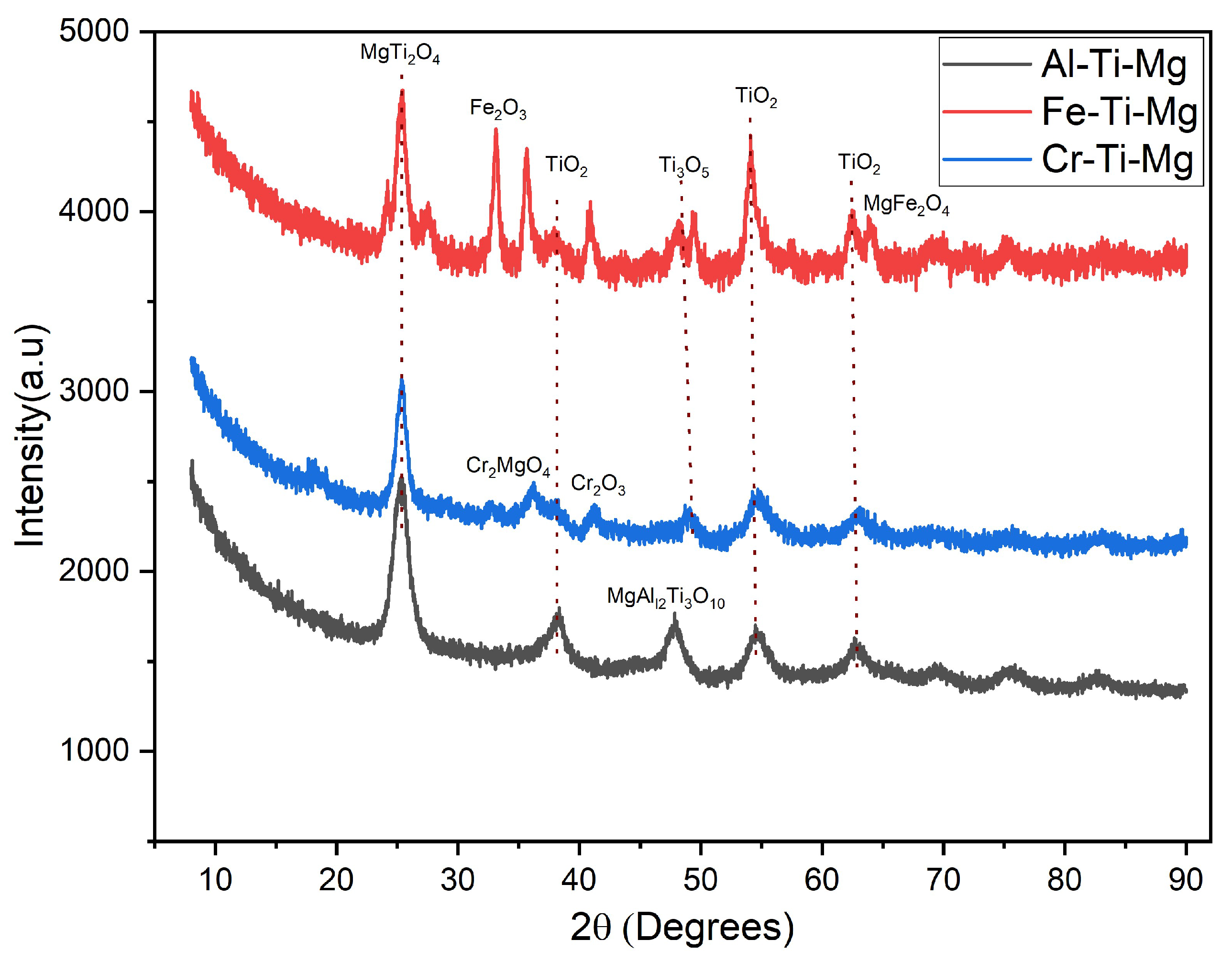
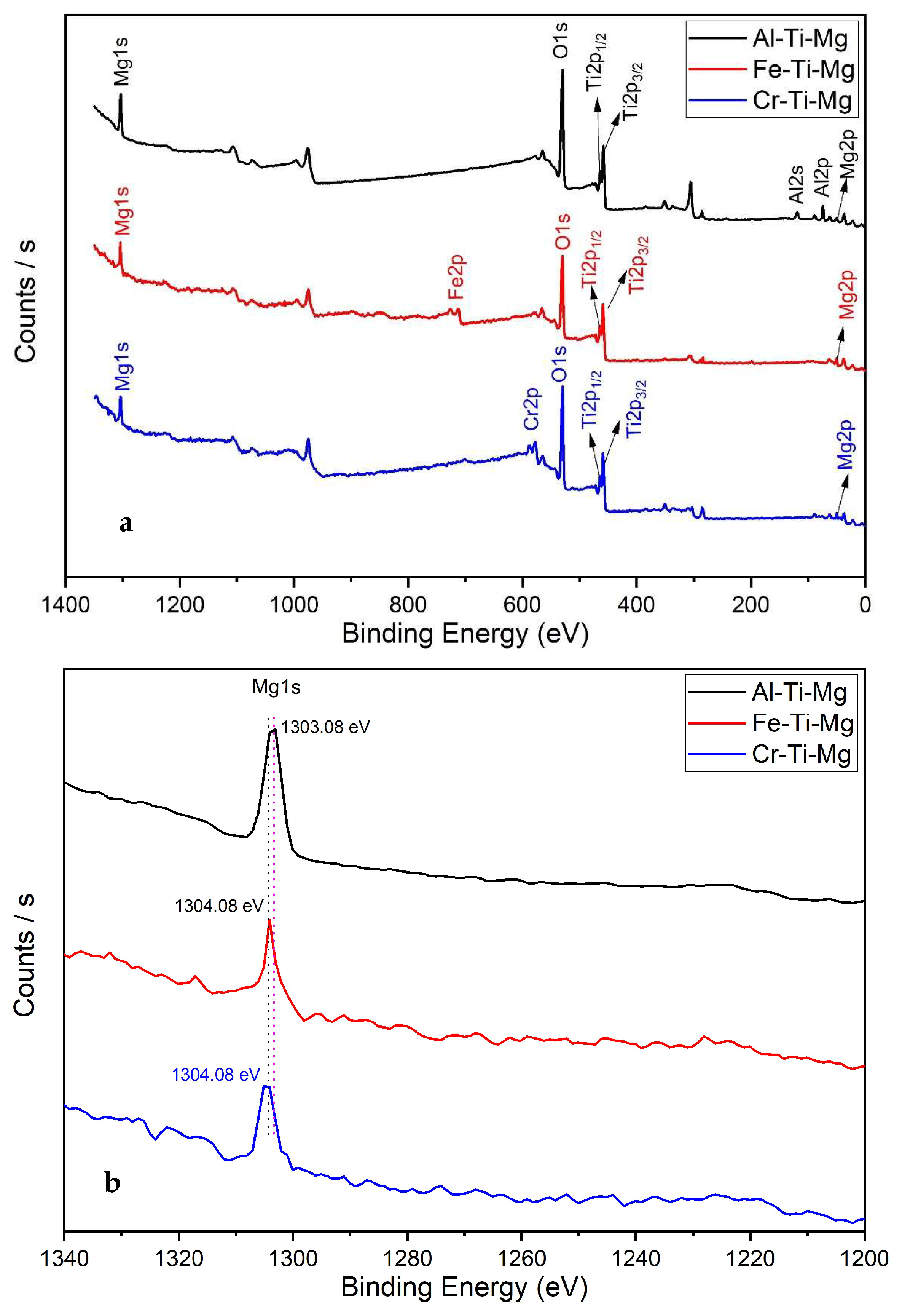
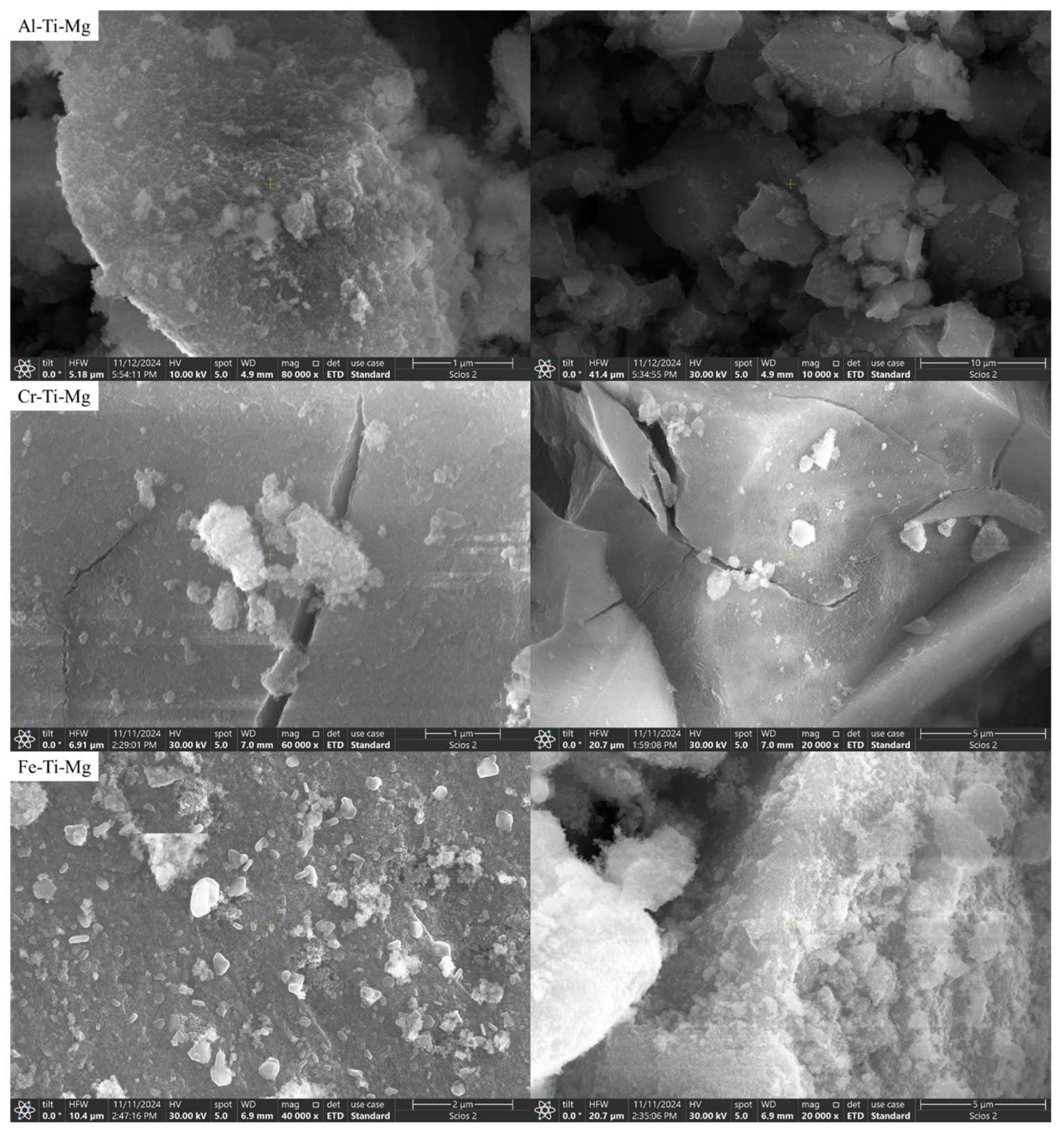
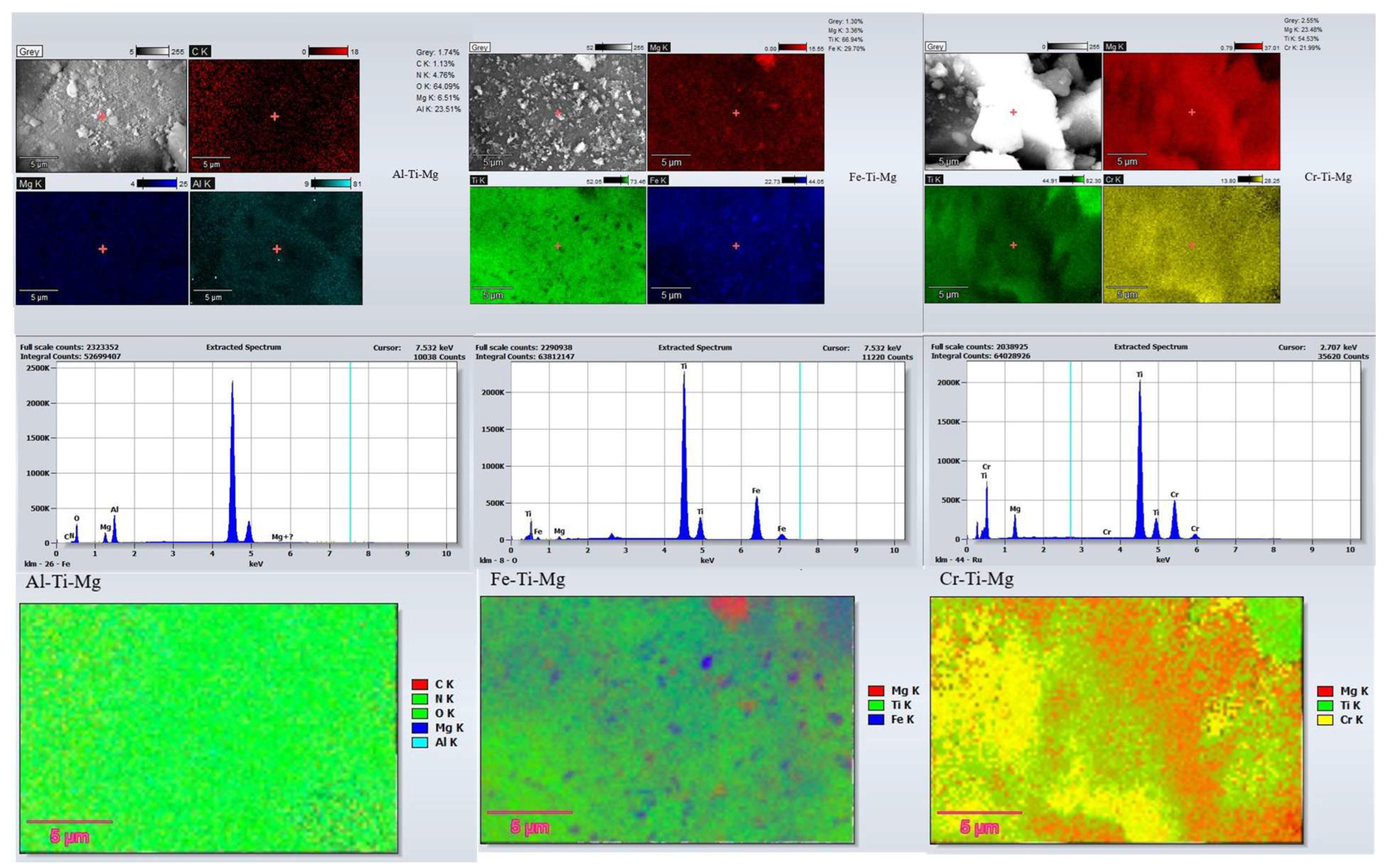
| 2θ | Ti-Al-Mg | Ti-Fe-Mg | Ti-Cr-Mg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxide Type | Crystallite Size (nm) | Oxide Type | Crystallite Size (nm) | Oxide Type | Crystallite Size (nm) | |
| 25.37 | MgTi2O4 | 0.087 | MgTi2O4 | 0.143 | MgTi2O4 | 0.116 |
| 33.27 | - | - | Fe2O3 | 0.249 | - | - |
| 36.17 | - | - | - | - | Cr2MgO4 | 0.092 |
| 38.25 | TiO2 | 0.062 | TiO2 | 0.276 | TiO2 | 0.074 |
| 41.23 | - | - | - | - | Cr2O3 | 0.135 |
| 47.45 | MgAl2Ti3O10 | 0.108 | - | - | - | - |
| 48.80 | - | - | Ti3O5 | 0.268 | Ti3O5 | 0.149 |
| 54.65 | TiO2 | 0.088 | TiO2 | 0.224 | TiO2 | 0.086 |
| 62.75 | MgO | 0.090 | MgO | 0.172 | MgO | 0.106 |
| 64.10 | - | - | MgFe2O4 | 0.237 | - | - |
| Catalysts | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Width (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-Al-Mg | 119.43 | 0.345 | 6.81 |
| Ti-Cr-Mg | 54.47 | 0.193 | 7.12 |
| Ti-Fe-Mg | 28.20 | 0.166 | 10.68 |
| Catalyst | Parameters | Glycerol Conversion (%) | GC Yield (%) | Selectivity (%) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20%La2O2CO3-ZnO | Temperature: 150 °C; PCO2: 55 bar; Time: 6 h; | 6.9 | 6.1 | 88.40 | [13] |
| Ce0.98Zr0·02O2 | Temperature: 150 °C; PCO2: 40 bar; Time: 5 h; | 40.9 | 36.3 | 88.75 | [14] |
| La2O2CO3/ZnO (La/Zn = 1:4) | Temperature: 170 °C; PCO2: 30 bar; Time: 7 h; | 30.3 | 14.3 | 47.20 | [12] |
| Cu/Mg-Al-Zr | Temperature: 150 °C; PCO2: 40 bar; Time: 12 h; | 11.5 | 2.4 | 20.9 | [54] |
| 30%,CuO/Al2O3 | Temperature: 150 °C; PCO2: 40 bar; Time: 5 h; | 37.8 | 15.0 | 39.8 | [10] |
| Co-ETS-10 | Temperature: 170 °C; PCO2: 40 bar; Time: 6 h; | 35.0 | 12.7 | 36.3 | [5] |
| Zn-ETS-10 | Temperature: 170 °C; PCO2: 40 bar; Time: 6 h; | 32.7 | 11.7 | 35.6 | [5] |
| Ti-Al-Mg | Temperature: 175 °C; PCO2: 10 bar; Time: 4 h; | 58.3 | 36.1 | 61.9 | Present work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Charif, M.L.; Doukeh, R.; Ciuparu, D.M. The Catalytic Performance of Metal-Oxide-Based Catalysts in the Synthesis of Glycerol Carbonate: Toward the Green Valorization of Glycerol. Catalysts 2025, 15, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060534
Charif ML, Doukeh R, Ciuparu DM. The Catalytic Performance of Metal-Oxide-Based Catalysts in the Synthesis of Glycerol Carbonate: Toward the Green Valorization of Glycerol. Catalysts. 2025; 15(6):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060534
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharif, Mirna Lea, Rami Doukeh, and Dragos Mihael Ciuparu. 2025. "The Catalytic Performance of Metal-Oxide-Based Catalysts in the Synthesis of Glycerol Carbonate: Toward the Green Valorization of Glycerol" Catalysts 15, no. 6: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060534
APA StyleCharif, M. L., Doukeh, R., & Ciuparu, D. M. (2025). The Catalytic Performance of Metal-Oxide-Based Catalysts in the Synthesis of Glycerol Carbonate: Toward the Green Valorization of Glycerol. Catalysts, 15(6), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060534








